England. Clinical Commissioning Policy: Radiosurgery/Radiotherapy for Cavernous Venous Malformations (Cavernomas)
|
|
|
- Tyrone Dwayne Johnson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Radiosurgery/Radiotherapy for Cavernous Venous Malformations (Cavernomas) September 2013 Reference: NHS ENGLAND D05/P/g England 1
2 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations Patients and Information Nursing Policy Commissioning Development Finance Human Resources Publications Gateway Reference: Document Purpose Document Name Author Publication Date Target Audience Guidance Clinical Commissioning Policies and Clinical Commissioning Policy Statements Various, Medical Directorate, Specialised Services 10 September 2013 NHS England Regional Directors, NHS England Area Directors, Directors of Finance Additional Circulation List Clinical Reference Group Chairs Description Production of NHS England's Clinical Commissioning Clinical Commissioning Policies and Clinical Commissioning Policy Statements Cross Reference Superseded Docs (if applicable) Action Required N/A N/A N/A Timing / Deadlines (if applicable) Contact Details for further information Document Status N/A Donna Hakes Medical Directorate, Specialised Services Skipton House London SE1 6LH england.specialisedcommissioning@nhs.net 0 This is a controlled document. Whilst this document may be printed, the electronic version posted on the intranet is the controlled copy. Any printed copies of this document are not controlled. As a controlled document, this document should not be saved onto local or network drives but should always be accessed from the intranet 2
3 NHS England Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic Radiosurgery / Radiotherapy for Cavernous Venous Malformations (Cavernomas) First published: September 2013 Prepared by NHS England Clinical Reference Group for Stereotactic Radiosurgery First published August 2013 Published by the NHS England, in electronic format only. 3
4 Contents Policy Statement... 5 Equality Statement... 5 Plain Language Summary Introduction Definitions Aim and objectives Epidemiology and needs assessment Evidence base Rationale behind the policy statement Criteria for commissioning Patient pathway Governance arrangements Mechanism for funding Audit requirements Documents which have informed this policy Links to other policies Date of review References Version Control Shee 4
5 Policy Statement NHS England will commission in accordance with the criteria outlined in this document. In creating this policy NHS England has reviewed this clinical condition and the options for its treatment. It has considered the place of this treatment in current clinical practice, whether scientific research has shown the treatment to be of benefit to patients, (including how any benefit is balanced against possible risks) and whether its use represents the best use of NHS resources. This policy document outlines the arrangements for funding of this treatment for the population in England. Equality Statement Throughout the production of this document, due regard has been given to eliminate discrimination, harassment and victimisation, to advance equality of opportunity, and to foster good relations between people who share a relevant protected characteristic (as cited in under the Equality Act 2010) and those who do not share it. Plain Language Summary Cavernomas are clusters of abnormal blood vessels mainly found in the brain and spinal cord. They are sometimes known as cavernous angiomas, cavernous hemangiomas or cerebral cavernous malformations. A typical cavernoma looks a bit like a blackberry. It is filled with blood that flows slowly through vessels that are like 'caverns'. Cavernomas vary in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres across. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) destroys abnormal tissues in the brain by the administration of a strong and highly focused dose of radiation. No high level evidence exists for any intervention (either microsurgery or SRS) in patients with cavenomas. In the management of cerebral cavernous malformations where possible without risk of neurological deficit, microsurgery is preferred. SRS is recommended for cavernomas that are in an anatomical situation (brainstem, basal ganglia, thalamus, internal capsule, motor cortex), where microsurgery is deemed to have unacceptably high risk of neurological deficit. It s appropriate for clinicians to consider SRS for a small subset of patients with cavernomas that are in a difficult and unacceptable high risk anatomical situation (brainstem, basal ganglia, thalamus, internal capsule, motor cortex), where there is evidence of effectiveness for SRS, and where conventional surgery is contraindicated or the risk of functional disability would be increased through surgery. 5
6 1. Introduction The basic principle of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for this application is the administration of a strong and highly focused dose of radiation. The procedure allows radiation to be limited to the target area and thus helps spare the surrounding tissues as much as possible. This causes a scarring process in the malformation, reducing the risk of further bleed into the brain. This policy considers the use of SRS for patients with cavernomas and states the criteria to identify which patients should be considered for the intervention. 2. Definitions Cavernomas (also known as cerebral cavernous malformations, cavernous angiomas, or cavernous haemangiomas ) are blood-filled clusters of abnormal vessels. About half of them are symptomatic, and about a quarter of them are in a surgically inaccessible place in the brain. Cavernomas have an estimated prevalence of % i. 76% of the lesions located supratentorially (within reach of surgery), but 8% in the basal ganglia/thalamus and 18% in the brainstem where surgery is high risk. Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Radiotherapy (SRT) The basic principle of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) is the elimination of a functional disorder, or destruction of abnormal tissues, by administration of a strong and highly focused dose of radiation. The procedure allows radiation to be limited to the target area and thus helps spare the surrounding tissues as much as possible. For the purpose of this policy the term SRS is used to mean treatment given as a single dose, and SRT as a hypofractionated treatment of not more than 5 fractions. This policy applies to both of these approaches. Commissioning arrangements for fractionated treatments utilising a larger number of fractions are beyond the remit of this policy but fall win the Radiotherapy CRG policy remit. SRS/SRT is a highly conformal radiotherapy treatment to a precisely delineated target volume, delivered using stereotactic localisation techniques. A multidisciplinary team of neurosurgeons or neuro-oncologists, and neuroradiologists should be involved in SRS case selection, treatment planning and delivery. 3. Aim and objectives The objectives were to establish: If there is sufficiently robust evidence of clinical and cost effectiveness and safety to support the use of SRS for patients with cavernomas? If the evidence is sufficiently robust, what criteria should be used to identify suitable patients to be considered for SRS treatment? 6
7 4. Epidemiology and needs assessment Contemporary population-based prospective studies detected approximately 6 cases/million/year in Scotland, 47-60% of them being asymptomatic ii, 40% of whom becoming symptomatic within 2 years after diagnosis. When patients become symptomatic, typically at the mean age of thirties, 37% present with seizures, 36% with hemorrhage, 23% with headaches, 22% with focal neurological deficits iii. The annual risk of haemorrhage specifically from brainstem and thalamic/basal ganglia cavernous malformations has generally been estimated higher, %/person/year iv,v It is not clear whether deep-seated eloquent malformations are more prone to bleeding, or whether any bleed is more likely to be symptomatic due to higher functional density. After one bleed, further haemorrhage is more likely, the cumulative incidence of rebleed is 56% after 5 years, and 72% after 10 years vi.not only hemorrhage rate, but permanent morbidity and mortality is higher for deep eloquent or infratentorial lesions. A single bleed leads to persisting neurological deficit in up to 40-60% and also carries substantial risk of mortality and each subsequent bleeding episodes cumulatively increase the chance for permanent disability vii,viii Based on the current England population estimate of 53 million, ix we would expect 159 patients to be diagnosed with symptomatic cavernoma each year in England, 40 of these would have the lesion in the brainstem, thalamus and other surgically inaccessible site, where SRS would be considered. 5. Evidence base Evidence can be graded according to the robustness of the study design, giving an indication of the degree to which the evidence should be relied upon when making clinical decisions. The grades of evidence range from level 1 (the most robust) to level 4 (the least robust). The diagram in Appendix 3 outlines the levels of evidence. In the absence of methodologically robust evidence the following statements should remain tentative. No high level evidence exists for any intervention (either microsurgery or SRS) in this cohort. Retrospective studies show that even in the most experienced centres, microsurgery for deep and eloquent cavernomas carry high risk, with over 50% neurological deficit, over a quarter with perioperative complications of tracheostomy, CSF leak etc and over 3% mortality. Surgery does not even fully prevent further haemorrhages: they still occur at a rate of 2% per year x. Radiation induces hyalinization and thickening of the wall of the endothelial-lined vascular channels in arteriovenous malformations and similar radiation-induced vasculopathy is observed in cavernous malformations xi. Though about 50% of lesions reduce in size, the success is measured by the reduced rate of further haemorrhages after treatment. After SRS, re-bleeding rate fell from over 30%/patient/year to 9% within the first two years and to 1 % thereafter 10,xii. After radiosurgery there was only 7% minor morbidity 10. SRS (principally Gamma Knife SRS) compared to surgery appears to provide: shorter hospitalisation a less detrimental impact on quality of life 7
8 better short and long term morbidity avoidance of procedural mortality and lower treatment-related complications The drawback is the lack of radiological endpoint proving success, though this drawback is shared with microsurgery (see postoperative bleed-rate above). Gamma Knife, LINAC and CyberKnife appear to provide similar levels of clinical effectiveness. No evidence was identified on which to base comparisons of the relative safety of Gamma Knife, LINAC and CyberKnife. Cost-effectiveness There is a lack of evidence addressing the cost-effectiveness of SRS compared to other treatment options in a UK setting. However, there is some evidence from other indications that the overall costs, including ancillary treatment and readmission costs are lower for patients treated with SRS than by microsurgery. xiii In 1997 a cost/benefit estimation for conventional fractionated radiotherapy (RT), surgery and radiosurgery (RS) for patients with single brain metastases was undertaken. xiv The cost per life year of median survivorship was $16,250 for RT alone, $13,729 for RS plus RT, and $27,523 for resection plus RT. Hence, according to this study a surgical resection resulted in a 1.8-fold increase in cost, compared to radiosurgery. A similar American comparative cost analysis found that the cost per life year gained for radiosurgery was 30% lower than for surgical resection. xv To-date estimates of the cost-effectiveness of SRS/SRT in comparison with surgery have not been robustly determined from a UK NHS perspective. 6. Rationale behind the policy statement Radiosurgery was introduced as a treatment option for cavernous malformations based on the assumption that the vessels would respond similarly to true arteriovenous malformations that had been proven to be thrombo-obliterated byradiosurgery xvi. Since then increasing worldwide clinical experience together with few documented histopathological cases seem to support the initial intuition, therefore radiosurgery has been recommended as treatment option for cavernous malformations with repeated haemorrhages deemed surgically inaccessible. xvii The evidence base regarding the effectiveness, cost effectiveness and safety of SRS/SRT for treating cavernous venous malformations has been used as a basis for this commissioning policy. SRS/SRT can be used to treat cavernomas where anatomical constraints prevent safe microsurgical removal (brainstem, thalamus, basal ganglia). There is no available robust estimate of the cost effectiveness of SRS/SRT for treatment of cavenoma and ongoing monitoring of numbers and outcomes must be undertaken. 8
9 7. Criteria for commissioning Indications for stereotactic radiosurgery/radiotherapy include newly diagnosed cavernomas, residual cavernomas after microsurgery and recurrent cavernomas. Patients meeting all the following criteria will be routinely funded for SRS/SRT: All patients must have undergone prior assessment by the local neurovascular multi-disciplinary team (MDT). The selection of patients for SRS/SRT must include the consideration of surgical or conservative treatment. In centres where SRS/SRT is delivered, referral may be made directly to the SRS MDT. In centres where there is no local SRS service, referral should be initially to the local neuro-vascular MDT, who can decide on the appropriateness of onward referral to an agreed SRS centre. All patients being considered for SRS /SRT must be discussed by the specialist MDT at the stereotactic treatment centre and must have specialist neurosurgery input. SRS/SRT must not be recommended without the collective agreement of the MDT. It s appropriate for clinicians to consider SRS for a small subset of patients with cavernomas that are in a difficult and unacceptable high risk anatomical situation (brainstem, basal ganglia, thalamus, internal capsule, motor cortex), where there is evidence of effectiveness for SRS, and where conventional surgery is contraindicated or the risk of functional disability would be increased through surgery. Expert opinion suggests that: There is no role for fractionated / hypofractionated treatment (SRT) in the management of cavernomas. 8. Patient pathway The service specification for SRS/SRT describes the detail of the care pathways and describes the key aspects of SRS/SRT services being commissioned and should be referred to in conjunction with this policy. The service will accept referrals from consultant medical staff and appropriate specialist neurovascular MDTs in line with eligibility and referral guidelines. The provider of SRS treatment will discuss all referrals in an SRS MDT prior to accepting the patient for treatment. Treatment options for cavernoma will depend on the anatomical position of the lesion (dictating the perceived risk of alternative intervention with microsurgery), the presentation (incidentally found cavernomas are left untreated), and the estimated lifetime risk of repeated haemorrhages with progressive neurological deterioration if 9
10 untreated (the likelihood of this in a patient over the age of 70 is low). The three management options for patients with cavernous venous malformations are: Surgical removal Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) No intervention 9. Governance arrangements The service specification for SRS/SRT describes the care pathways and key aspects of SRS/SRT services being commissioned and should be referred to in conjunction with this policy. 10. Mechanism for funding From July 2013 NHS England became responsible for commissioning Stereotactic Radiosurgery in line with this policy on behalf of the resident population of England. Funding is transacted as per local contract agreements and terms. 11. Audit requirements Clinical governance guidelines state that all British neurosurgical centres are required to audit their results Audit requirements will require the following data requirements for each patient: 1. Treatment parameters 2. History (rate) of previous haemorrhages 3. Post-radiosurgery haemorrhage events 12. Documents which have informed this policy 2012/13 NHS Standard Contract: Service Specification Contract NSSD 8 Neurosciences (adult0 (subsection 4.1 Neurosurgery) Stereotactic Radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy. 13. Links to other policies This policy follows the principles set out in the ethical framework that govern the commissioning of NHS healthcare and those policies dealing with the approach to experimental treatments and processes for the management of individual funding requests (IFR). 10
11 14. Date of review This policy will be reviewed in April 2016 unless information is received which indicates that the proposed review date should be brought forward or delayed. References Version Control Sheet i Al-Shahi R, Bhattacharya JJ, Currie DG, et al. Prospective, population-based detection of intracranial vascular malformations in adults. The Scottish Intracranial Vascular Malformation Study (SIVMS). Stroke 2003;34: ii Al-Shahi Salman R, Hall JM, Horne MA, et al. Untreated clinical course of cerebral cavernous malformations: a prospective, population-based cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2012;11: iii Gross BA, Lin N, Du R, et al. The natural history of intracranial cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 2011;30:E24 iv Gross BA, Batjer HH, Awad IA, et al. Brainstem cavernous malformations.neurosurgery 2009;64:E v Gross BA, Batjer HH, Awad IA, et al. Cavernous malformations of the basal ganglia and thalamus.neurosurgery 2009;65:7 18. vi Barker II FG, Amin-Hanjani S, Butler WE, et al. Temporal clustering of hemorrhages from untreated cavernous malformations of the central nervous system. Neurosurgery 2001;49: vii Tung H, Giannotta SL, Chandrasoma PT, et al. Recurrent intraparenchymalhemorrhages from angiographically occult vascular malformations. J Neurosurg 1990;73: viii Nagy G, Razak A, Rowe JG, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for deep-seated cavernous malformations: a move toward more active, early intervention. J Neurosurg 2010;113: ix Office for National Statistics.Statistical bulletin: 2011 Census - Population and Household Estimates for England and Wales, March (accessed 16 July 2012). x Abla AA, Lekovic GP, Turner JD, de Oliveira JG, Porter R, Spetzler RF. Advances in the treatment and outcome of brainstem cavernous malformation surgery: a single-center case series of 300 surgically treated patients. Neurosurgery Feb;68(2):403-14; xi Gewirtz RJ, Steinberg GK, Crowly R, et al. Pathological changes in surgically resected angiographically occult vascular malformations after radiation. Neurosurgery 1998;42: xii Lunsford LD, Khan AA, Niranjan A, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for symptomatic solitary cerebral cavernous malformations considered high risk for resection. J Neurosurg 2010;113:23 29 xiii Wellis G, Nagel R, Vollmar C, Steiger HJ. Direct costs of microsurgical management of radiosurgically amenable intracranial pathology in Germany: an analysis of meningiomas, acoustic neuromas, metastases and arteriovenous 11
12 malformations of less than 3 cm in diameter. Acta neurochirurgica 2003;145(4): xiv Mehta M, Noyes W, Craig B, et al. A cost-effectiveness and cost-utility analysis of radiosurgery vs. resection for single-brain metastases. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 1997;39(2): xv Rutigliano MJ, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Strauss MJ, Khanna V, Green M. The cost effectiveness of stereotactic radiosurgery versus surgical resection in the treatment of solitary metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery 1995;37(3): ; discussion xvi Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, et al. Reduction of hemorrhage risk after stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 1995;83: xvii Brown RD Jr, Flemming KD, Meyer FB, et al. Natural history, evaluation, and management of intracranial vascular malformations. Mayo Clinic Proc 2005;80:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations. December Reference : NHSCB/D5/4
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D5/4 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations First published: December
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D5/4 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations First published: December
Specialised Services Policy: CP22. Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Specialised Services Policy: CP22 Document Author: Assistant Director of Planning Executive Lead: Director of Planning ad Performance Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 01 July 2015 Review Date:
Specialised Services Policy: CP22 Document Author: Assistant Director of Planning Executive Lead: Director of Planning ad Performance Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 01 July 2015 Review Date:
Directorate Medical Operations Patients and Information Nursing Policy Commissioning Development. Clinical Reference Group Chairs
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic Radiosurgery/ Radiotherapy for Glomus Tumours (skull base paragangliomas, glomus jugulare tumours) September 2013 Reference: NHS ENGLAND D05/P/f England 1 NHS
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic Radiosurgery/ Radiotherapy for Glomus Tumours (skull base paragangliomas, glomus jugulare tumours) September 2013 Reference: NHS ENGLAND D05/P/f England 1 NHS
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic Radiosurgery / Radiotherapy For Cerebral Metastases. December Reference : NHSCB/D5/1
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic Radiosurgery / Radiotherapy For Cerebral Metastases December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D5/1 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic Radiosurgery / Radiotherapy For Cerebral Metastases December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D5/1 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Stereotactic
Reference: NHS England: 16022/P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) as a treatment option for patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma or Cholangiocarcinoma Reference: NHS England: 16022/P
Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) as a treatment option for patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma or Cholangiocarcinoma Reference: NHS England: 16022/P
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy (all ages) NHS England Reference: P
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1736P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1736P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. September 2013 Reference: E03/PS(HSS)/a.
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome September 2013 Reference: E03/PS(HSS)/a England 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy Statement: Eculizumab for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome September 2013 Reference: E03/PS(HSS)/a England 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Auditory brainstem implant with congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves of cochleae
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Auditory brainstem implant with congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves of cochleae Reference: NHS England: 16062/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Auditory brainstem implant with congenital abnormalities of the auditory nerves of cochleae Reference: NHS England: 16062/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy First published:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy Reference: NHS England xxx/x/x 1 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Deep Brain Stimulation for Refractory Epilepsy First published:
Life after ARUBA: Management of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
 Life after ARUBA: Management of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) Eric L. Zager, MD University of Pennsylvania Department of Neurosurgery No Disclosures Brain AVMs Incidence ~1 in 100,000
Life after ARUBA: Management of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) Eric L. Zager, MD University of Pennsylvania Department of Neurosurgery No Disclosures Brain AVMs Incidence ~1 in 100,000
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for adults with Parkinson's tremor and Familial Essential Tremor Version Number: NHS England B13X06/01 Information Reader Box
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) for adults with Parkinson's tremor and Familial Essential Tremor Version Number: NHS England B13X06/01 Information Reader Box
Stereotactic Radiosurgery/Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannomas)
 Strategic Commissioning Group West Midlands Commissioning Policy (WM/38) Stereotactic Radiosurgery/Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannomas) Version 1 July 2010
Strategic Commissioning Group West Midlands Commissioning Policy (WM/38) Stereotactic Radiosurgery/Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannomas) Version 1 July 2010
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 03/01/2013 Section:
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 03/01/2013 Section:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1711P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Gemcitabine and capecitabine following surgery for pancreatic cancer (all ages) NHS England Reference: 1711P 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2015
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2015
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Skull Base Tumour Treatment NHS Overseas Programme (Adult)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Skull Base Tumour Treatment NHS Overseas Programme (Adult) Reference: NHS England B01/P/d NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Proton Beam Radiotherapy (High Energy) for Skull Base Tumour Treatment NHS Overseas Programme (Adult) Reference: NHS England B01/P/d NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) for haemophilia A (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) for haemophilia A (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16042/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) for haemophilia A (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16042/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Michael K. Morgan, MD, 1 Markus K. Hermann Wiedmann, MD, 1 Marcus A. Stoodley, PhD, 1 and Gillian Z. Heller, PhD 2
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 127:1105 1116, 2017 Microsurgery for Spetzler-Ponce Class A and B arteriovenous malformations utilizing an outcome score adopted from Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a prospective
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 127:1105 1116, 2017 Microsurgery for Spetzler-Ponce Class A and B arteriovenous malformations utilizing an outcome score adopted from Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a prospective
Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in the treatment of oligometastatic disease
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in the treatment of oligometastatic disease Reference: NHS England: 16032/P 2 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) in the treatment of oligometastatic disease Reference: NHS England: 16032/P 2 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 04/01/2014 Section:
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 04/01/2014 Section:
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 11/20/2015
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 11/20/2015
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A tool for treating intracranial conditions. CNSA Annual Congress 2016 Radiation Oncology Pre-congress Workshop
 Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A tool for treating intracranial conditions CNSA Annual Congress 2016 Radiation Oncology Pre-congress Workshop ANGELA McBEAN Gamma Knife CNC State-wide Care Coordinator Gamma Knife
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A tool for treating intracranial conditions CNSA Annual Congress 2016 Radiation Oncology Pre-congress Workshop ANGELA McBEAN Gamma Knife CNC State-wide Care Coordinator Gamma Knife
DOWNLOAD PDF RADIOSURGERY FOR CAVERNOUS MALFORMATIONS IN BASAL GANGLIA, THALAMUS AND BRAINSTEM KIDA, Y
 Chapter 1 : Stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous malformations â Mayo Clinic Most of the lesions were located in the brainstem, followed by the lobar region, cerebellum, thalamus, and basal ganglia
Chapter 1 : Stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous malformations â Mayo Clinic Most of the lesions were located in the brainstem, followed by the lobar region, cerebellum, thalamus, and basal ganglia
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis complex
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis complex Reference: NHS England E09X04/01 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Everolimus for subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA) associated with tuberous sclerosis complex Reference: NHS England E09X04/01 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults Reference: NHS England: 16047/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults Reference: NHS England: 16047/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2017
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 04/01/2017
Reference: NHS England B01X26
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) as a treatment option for patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma or Cholangiocarcinoma Reference: NHS England
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: The use of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) as a treatment option for patients with Hepatocellular carcinoma or Cholangiocarcinoma Reference: NHS England
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Tania Kaprealian, M.D. Assistant Professor UCLA Department of Radiation Oncology August 22, 2015
 Tania Kaprealian, M.D. Assistant Professor UCLA Department of Radiation Oncology August 22, 2015 Most common brain tumor, affecting 8.5-15% of cancer patients. Treatment options: Whole brain radiation
Tania Kaprealian, M.D. Assistant Professor UCLA Department of Radiation Oncology August 22, 2015 Most common brain tumor, affecting 8.5-15% of cancer patients. Treatment options: Whole brain radiation
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR HAEMANGIOBLASTOMA
 1 EVIDENCE SUMMARY REPORT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR HAEMANGIOBLASTOMA QUESTIONS TO BE ADDRESSED: 1. What is the evidence for the clinical effectiveness
1 EVIDENCE SUMMARY REPORT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR HAEMANGIOBLASTOMA QUESTIONS TO BE ADDRESSED: 1. What is the evidence for the clinical effectiveness
Despite recent progress in microsurgical techniques, endovascular
 Application of Single-Stage Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations >10 cm 3 Shunya Hanakita, MD; Tomoyuki Koga, MD, PhD; Masahiro Shin, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Igaki, MD, PhD; Nobuhito
Application of Single-Stage Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations >10 cm 3 Shunya Hanakita, MD; Tomoyuki Koga, MD, PhD; Masahiro Shin, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Igaki, MD, PhD; Nobuhito
Lothian Audit of the Treatment of Cerebral Haemorrhage (LATCH)
 1. INTRODUCTION Stroke physicians, emergency department doctors, and neurologists are often unsure about which patients they should refer for neurosurgical intervention. Early neurosurgical evacuation
1. INTRODUCTION Stroke physicians, emergency department doctors, and neurologists are often unsure about which patients they should refer for neurosurgical intervention. Early neurosurgical evacuation
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dornase alfa inhaled therapy for primary ciliary dyskinesia (all ages)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dornase alfa inhaled therapy for primary ciliary dyskinesia (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16029/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Dornase alfa inhaled therapy for primary ciliary dyskinesia (all ages) Reference: NHS England: 16029/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.7 Hib/MenC vaccination programme NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.7 Hib/MenC vaccination programme NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations Patients and Information
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF BRAIN TUMORS LIGIA TATARANU, MD, Ph D NEUROSURGICAL CLINIC, BAGDASAR ARSENI CLINICAL HOSPITAL BUCHAREST, ROMANIA SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONFIRMING HISTOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS REDUCING TUMOR
Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s NICE quality standard
 March 2017 Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s NICE quality standard Draft for consultation This quality standard covers the assessment and management of non-specific low back pain and sciatica in young
March 2017 Low back pain and sciatica in over 16s NICE quality standard Draft for consultation This quality standard covers the assessment and management of non-specific low back pain and sciatica in young
Specialised Services Policy: CP23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation
 Specialised Services Policy: CP23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation Document Author: Specialist Services Planning Manager for Neurosciences and Complex Conditions Executive Lead: Director of Planning and Performance
Specialised Services Policy: CP23 Vagal Nerve Stimulation Document Author: Specialist Services Planning Manager for Neurosciences and Complex Conditions Executive Lead: Director of Planning and Performance
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.14 Shingles immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.14 Shingles immunisation programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag in the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag in the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Reference: NHS England: 16017/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Selexipag in the treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Reference: NHS England: 16017/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations and Information
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for Adults and Children. January 2013 Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X.
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for Adults and Children January 2013 Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X England 1 NHS England Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for Adults and Children January 2013 Reference: NHS England XXX/X/X England 1 NHS England Clinical Commissioning Policy: Chemotherapy Algorithms for
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No. 31 Meningococcal group B (MenB) programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Commissioning
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR PILOCYTIC ASTROCYTOMA
 1 EVIDENCE SUMMARY REPORT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR PILOCYTIC ASTROCYTOMA QUESTIONS TO BE ADDRESSED: SUMMARY 1. What is the evidence for the clinical
1 EVIDENCE SUMMARY REPORT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR PILOCYTIC ASTROCYTOMA QUESTIONS TO BE ADDRESSED: SUMMARY 1. What is the evidence for the clinical
Insert heading depending line on length; please delete delete. length; please delete other cover options once
 Insert heading depending Insert on Interim Insert heading line length; Clinical please Commissioning depending on line on length; please delete delete other Policy: on line line cover Circumcision length;
Insert heading depending Insert on Interim Insert heading line length; Clinical please Commissioning depending on line on length; please delete delete other Policy: on line line cover Circumcision length;
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR EPENDYMOMA
 1 EVIDENCE SUMMARY REPORT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR EPENDYMOMA QUESTIONS TO BE ADDRESSED: 1. What is the evidence for the clinical effectiveness
1 EVIDENCE SUMMARY REPORT FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEROTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR EPENDYMOMA QUESTIONS TO BE ADDRESSED: 1. What is the evidence for the clinical effectiveness
Department of Anesthesiology. Clinical Base Year Neurosurgery Curriculum. Residency Program Director Department of Neurosurgery
 Clinical Base Year Neurosurgery Curriculum Collaborating Faculty: Julian Bailes, MD Residency Program Director Department of Neurosurgery Educational Purpose: The purpose of this rotation is for residents
Clinical Base Year Neurosurgery Curriculum Collaborating Faculty: Julian Bailes, MD Residency Program Director Department of Neurosurgery Educational Purpose: The purpose of this rotation is for residents
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy. CP29: Bariatric Surgery
 Specialised Services Commissioning Policy CP29: Bariatric Surgery Document Author: Specialist Planner, Cardiothoracic Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 12 June
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy CP29: Bariatric Surgery Document Author: Specialist Planner, Cardiothoracic Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Management Group Issue Date: 12 June
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Otolaryngologist s Perspective of Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Otolaryngologist s Perspective of Stereotactic Radiosurgery Douglas E. Mattox, M.D. 25 th Alexandria International Combined ORL Conference April 18-20, 2007 Acoustic Neuroma Benign tumor of the schwann
Otolaryngologist s Perspective of Stereotactic Radiosurgery Douglas E. Mattox, M.D. 25 th Alexandria International Combined ORL Conference April 18-20, 2007 Acoustic Neuroma Benign tumor of the schwann
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS. Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University
 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University Introduction Brain and spinal cord vascular malformations can be separated into five main categories: 1) Arteriovenous malformation,
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University Introduction Brain and spinal cord vascular malformations can be separated into five main categories: 1) Arteriovenous malformation,
National Breast Cancer Audit next steps. Martin Lee
 National Breast Cancer Audit next steps Martin Lee National Cancer Audits Current Bowel Cancer Head & Neck Cancer Lung cancer Oesophagogastric cancer New Prostate Cancer - undergoing procurement Breast
National Breast Cancer Audit next steps Martin Lee National Cancer Audits Current Bowel Cancer Head & Neck Cancer Lung cancer Oesophagogastric cancer New Prostate Cancer - undergoing procurement Breast
Brain metastases: changing visions
 Brain metastases: changing visions Roberto Spiegelmann, MD Baiona, 2014 Head, Stereotactic Radiosurgery Unit Dept of Neurosurgery, Chaim Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer, Israel The best current estimate
Brain metastases: changing visions Roberto Spiegelmann, MD Baiona, 2014 Head, Stereotactic Radiosurgery Unit Dept of Neurosurgery, Chaim Sheba Medical Center Tel Hashomer, Israel The best current estimate
Specialised Services Policy:
 Specialised Services Policy: CP35 Cochlear Implants Document Author: Specialised Planner for Women & Children s Services Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Executive Board Issue Date: 05
Specialised Services Policy: CP35 Cochlear Implants Document Author: Specialised Planner for Women & Children s Services Executive Lead: Director of Planning Approved by: Executive Board Issue Date: 05
This LCD recognizes these two distinct treatment approaches and is specific to treatment delivery:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY (SRS) AND STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIATION THERAPY (SBRT) CPT4 Codes: 77371, 77372, 77373 LCD ID Number: L33410 J-N FL Responsible
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY (SRS) AND STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIATION THERAPY (SBRT) CPT4 Codes: 77371, 77372, 77373 LCD ID Number: L33410 J-N FL Responsible
DRAFT FOR CONSULTATION. Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Palliative radiotherapy for bone pain
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Palliative radiotherapy for bone pain Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6 pages and over, with Publications Gateway
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Palliative radiotherapy for bone pain Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents of 6 pages and over, with Publications Gateway
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator. Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol
 NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
A06/S(HSS)b Ex-vivo partial nephrectomy service (Adult)
 A06/S(HSS)b 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR EX-VIVO PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY SERVICE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES, A - SERVICE SPECIFICATION Service Specification No. Service Commissioner
A06/S(HSS)b 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR EX-VIVO PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY SERVICE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES, A - SERVICE SPECIFICATION Service Specification No. Service Commissioner
IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOSURGERY USING THE GAMMA KNIFE
 IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOSURGERY USING THE GAMMA KNIFE L. D. LUNSFORD INTRODUCTION Image guided brain surgery became a reality in the mid-1970s after the introduction of the first methods to obtain axial imaging
IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOSURGERY USING THE GAMMA KNIFE L. D. LUNSFORD INTRODUCTION Image guided brain surgery became a reality in the mid-1970s after the introduction of the first methods to obtain axial imaging
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) December Reference : NHSCB/D4/c/7
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D4/c/7 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) First published:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D4/c/7 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) First published:
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus (HPV) programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus (HPV) programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus (HPV) programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.11 Human papillomavirus
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Chemosaturation for liver metastases from ocular melanomas Reference: NHS England A02X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Chemosaturation for liver metastases from ocular melanomas Reference: NHS England A02X05/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover
Cavernoma PSP Survey Responses: Treatments
 Cavernoma PSP Survey Responses: Treatments Grouped questions Item ID Question Comments Should a patient with cerebral or spinal cavernoma have radiosurgery or A1 no treatment/'wait and see'? 1855 27 Why
Cavernoma PSP Survey Responses: Treatments Grouped questions Item ID Question Comments Should a patient with cerebral or spinal cavernoma have radiosurgery or A1 no treatment/'wait and see'? 1855 27 Why
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Dosimetry, see MAGIC; Polymer gel dosimetry. Fiducial tracking, see CyberKnife radiosurgery
 Subject Index Acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2 complications 103, 105 hearing outcomes 103, 105 outcome measures 101 patient selection 105 study design 101 tumor control 101 105 treatment options
Subject Index Acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2 complications 103, 105 hearing outcomes 103, 105 outcome measures 101 patient selection 105 study design 101 tumor control 101 105 treatment options
Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: management and results in 101 cases
 J Neurosurg 88:285 292, 1998 Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: management and results in 101 cases TOMIO SASAKI, M.D., PH.D., HIROKI KURITA, M.D., ISAMU SAITO, M.D., PH.D.,
J Neurosurg 88:285 292, 1998 Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: management and results in 101 cases TOMIO SASAKI, M.D., PH.D., HIROKI KURITA, M.D., ISAMU SAITO, M.D., PH.D.,
CCG data collection for people with severe mental illness receiving a full physical health check and follow-up interventions in primary care
 CCG data collection for people with severe mental illness receiving a full physical health check and follow-up interventions in primary care Technical guidance NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
CCG data collection for people with severe mental illness receiving a full physical health check and follow-up interventions in primary care Technical guidance NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Linear accelerators. Basic technique. Indications of SRS
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Information booklet. Alliance UK. Pregnancy, childbirth and cavernoma. Cavernoma
 Cavernoma Alliance UK Helping the Cavernoma Community Information booklet Pregnancy, childbirth and cavernoma For people interested in pregnancy and birth who are affected by cavernoma www.cavernoma.org.uk
Cavernoma Alliance UK Helping the Cavernoma Community Information booklet Pregnancy, childbirth and cavernoma For people interested in pregnancy and birth who are affected by cavernoma www.cavernoma.org.uk
Rebleeding and Outcome in Patients with Symptomatic Brain Stem Cavernomas
 Original Paper Received: September 5, 2016 Accepted: February 8, 2017 Published online: March 21, 2017 Rebleeding and Outcome in Patients with Symptomatic Brain Stem Cavernomas Antonio Arauz a Hernán M.
Original Paper Received: September 5, 2016 Accepted: February 8, 2017 Published online: March 21, 2017 Rebleeding and Outcome in Patients with Symptomatic Brain Stem Cavernomas Antonio Arauz a Hernán M.
Hemorrhagic vestibular schwannoma: an unusual clinical entity Case report
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (3):Article 9, 1998 Hemorrhagic vestibular schwannoma: an unusual clinical entity Case report Dean Chou, M.D., Prakash Sampath, M.D., and Henry Brem, M.D. Departments of Neurological
Neurosurg Focus 5 (3):Article 9, 1998 Hemorrhagic vestibular schwannoma: an unusual clinical entity Case report Dean Chou, M.D., Prakash Sampath, M.D., and Henry Brem, M.D. Departments of Neurological
STEREOTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR
 STEREOTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR MENINGIOMA PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET STEREOTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR MENINGIOMA You have recently been diagnosed with a meningioma. This leaflet will explain what these are
STEREOTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR MENINGIOMA PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET STEREOTACTIC RADIOTHERAPY FOR MENINGIOMA You have recently been diagnosed with a meningioma. This leaflet will explain what these are
STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY. Monique Blanchard ANUM Radiation Oncology Epworth HealthCare
 STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY Monique Blanchard ANUM Radiation Oncology Epworth HealthCare Overview Stereotactic radiation therapy at Epworth Healthcare What is stereotactic radiation therapy? Delivery
STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY Monique Blanchard ANUM Radiation Oncology Epworth HealthCare Overview Stereotactic radiation therapy at Epworth Healthcare What is stereotactic radiation therapy? Delivery
Specialised Services Policy Position PP104
 Specialised Services Policy Position PP104 Personalised External Aortic Root Support (PEARS) for surgical management of enlarged aortic root (adults) March 2019 Version 1.0 Document information Document
Specialised Services Policy Position PP104 Personalised External Aortic Root Support (PEARS) for surgical management of enlarged aortic root (adults) March 2019 Version 1.0 Document information Document
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1Neonatal hepatitis
NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1 Neonatal hepatitis B immunisation programme NHS public health functions agreement 2017-18 Service specification No.1Neonatal hepatitis
Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars
 IAEA Human Health Campus Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars http://humanhealth.iaea.org The Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Gliomas Luis Souhami, MD Professor Department of Radiation
IAEA Human Health Campus Collection of Recorded Radiotherapy Seminars http://humanhealth.iaea.org The Role of Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Gliomas Luis Souhami, MD Professor Department of Radiation
The Risk of Hemorrhage after Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations
 The new england journal of medicine original article The Risk of Hemorrhage after Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Keisuke Maruyama, M.D., Nobutaka Kawahara, M.D., Ph.D., Masahiro
The new england journal of medicine original article The Risk of Hemorrhage after Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Keisuke Maruyama, M.D., Nobutaka Kawahara, M.D., Ph.D., Masahiro
SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR BY CYBERKNIFE: A CASE REPORT
 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR BY CYBERKNIFE: A CASE REPORT Cheng-Ta Hsieh, 1 Cheng-Fu Chang, 1 Ming-Ying Liu, 1 Li-Ping Chang, 2 Dueng-Yuan Hueng, 3 Steven D. Chang, 4 and Da-Tong Ju 1
SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR BY CYBERKNIFE: A CASE REPORT Cheng-Ta Hsieh, 1 Cheng-Fu Chang, 1 Ming-Ying Liu, 1 Li-Ping Chang, 2 Dueng-Yuan Hueng, 3 Steven D. Chang, 4 and Da-Tong Ju 1
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Pasireotide: An injectable medical therapy for the treatment of Cushing's disease Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for documents
C. Martin Harris, M.D., M.B.A. Holly D. Miller, M.D., M.B.A.
 C. Martin Harris, M.D., M.B.A. Holly D. Miller, M.D., M.B.A. HIMSS 2003 Who We Are C. Martin Harris, M.D., M.B.A. Chief Information Officer Executive Director of e-cleveland Clinic Holly D. Miller, M.D.,
C. Martin Harris, M.D., M.B.A. Holly D. Miller, M.D., M.B.A. HIMSS 2003 Who We Are C. Martin Harris, M.D., M.B.A. Chief Information Officer Executive Director of e-cleveland Clinic Holly D. Miller, M.D.,
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BRAIN METASTASES CNS Site Group Brain Metastases Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM BRAIN METASTASES CNS Site Group Brain Metastases Author: Dr. Norm Laperriere Date: February 20, 2018 1. INTRODUCTION
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis: Changing Treatment Paradigms. Overall Clinical Significance 8/3/13
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis: Changing Treatment Paradigms Jason Sheehan, MD, PhD Departments of Neurosurgery and Radiation Oncology University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA USA Overall
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis: Changing Treatment Paradigms Jason Sheehan, MD, PhD Departments of Neurosurgery and Radiation Oncology University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA USA Overall
Clinical course of untreated cerebral cavernous malformations: an individual patient data meta-analysis
 Statistical Analysis Plan Clinical course of untreated cerebral cavernous malformations: an individual patient data meta-analysis Background The disease A cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is a small
Statistical Analysis Plan Clinical course of untreated cerebral cavernous malformations: an individual patient data meta-analysis Background The disease A cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is a small
PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS. A08/S/d Colorectal: Faecal Incontinence (Adult)
 A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
A08/S/d 2013/14 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR COLORECTAL: FAECAL INCONTINENCE (ADULT) PARTICULARS, SCHEDULE 2- THE SERVICES, A- SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service Commissioner Lead Provider
NHS public health functions agreement Service specification No.5 Rotavirus immunisation programme
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.5 Rotavirus immunisation programme Classification: official 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.5 Rotavirus immunisation programme Classification: official 1 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification
Imaging for suspected glioma
 Imaging for suspected glioma 1.1.1 Offer standard structural MRI (defined as T2 weighted, FLAIR, DWI series and T1 pre- and post-contrast volume) as the initial diagnostic test for suspected glioma, unless
Imaging for suspected glioma 1.1.1 Offer standard structural MRI (defined as T2 weighted, FLAIR, DWI series and T1 pre- and post-contrast volume) as the initial diagnostic test for suspected glioma, unless
Consultation Guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions service specifications
 Consultation Guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions service specifications Consultation guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions
Consultation Guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions service specifications Consultation guide: Specialised gynaecology surgery and complex urogynaecology conditions
Proposed Neurosciences National Structure. Accountability Framework Neurological Alliance (Feedback Loop) National Advisory Group (Neurosciences)
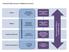 Accountability Framework Neurological Alliance (Feedback Loop) Proposed s National Structure National NHS England National Medical Director National Advisory Group (s) Regional NHS England Sub-Regional
Accountability Framework Neurological Alliance (Feedback Loop) Proposed s National Structure National NHS England National Medical Director National Advisory Group (s) Regional NHS England Sub-Regional
Acoustic Neuroma. Presenting Signs and Symptoms of an Acoustic Neuroma:
 Acoustic Neuroma An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor which arises from the nerves behind the inner ear and which may affect hearing and balance. The incidence of symptomatic acoustic neuroma is estimated
Acoustic Neuroma An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor which arises from the nerves behind the inner ear and which may affect hearing and balance. The incidence of symptomatic acoustic neuroma is estimated
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children
 Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children March 2019 Version 3.0 Document information Document purpose Document name Author Policy Circumcision for Children Welsh Health
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children March 2019 Version 3.0 Document information Document purpose Document name Author Policy Circumcision for Children Welsh Health
International Stereotactic Radiosurgical Society. The 2 nd London Course 28 th & 29 th March 2019 Lord's Cricket Ground
 International Stereotactic Radiosurgical Society The 2 nd London Course 28 th & 29 th March 2019 Lord's Cricket Ground ISRS Radiosurgery Conference Thursday March 28th Speakers and talks include: Day 1
International Stereotactic Radiosurgical Society The 2 nd London Course 28 th & 29 th March 2019 Lord's Cricket Ground ISRS Radiosurgery Conference Thursday March 28th Speakers and talks include: Day 1
Cuts, Closures and Contraception
 Cuts, Closures and Contraception An audit of local contraceptive services in England November 2017 1. Sexual health services are at a tipping point. Local Government Association I SRH provision as a whole
Cuts, Closures and Contraception An audit of local contraceptive services in England November 2017 1. Sexual health services are at a tipping point. Local Government Association I SRH provision as a whole
Chapter 5 Section 3.1
 Radiology Chapter 5 Section 3.1 Issue Date: March 27, 1991 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(b)(2), (b)(2)(x), (c)(2)(viii), and (g)(15) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE CODES 37243, 61793, 61795, 77261-77421, 77427-77799, 0073T
Radiology Chapter 5 Section 3.1 Issue Date: March 27, 1991 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(b)(2), (b)(2)(x), (c)(2)(viii), and (g)(15) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE CODES 37243, 61793, 61795, 77261-77421, 77427-77799, 0073T
Protocol for emergency surgical intervention in patients with a brain tumour v3
 Protocol for emergency surgical intervention in patients with a brain tumour v3 West Midlands Cancer Alliance Coversheet for Cancer Alliance Expert Advisory Group Agreed Documentation This sheet is to
Protocol for emergency surgical intervention in patients with a brain tumour v3 West Midlands Cancer Alliance Coversheet for Cancer Alliance Expert Advisory Group Agreed Documentation This sheet is to
Disclosures. Neurological Manifestations of Von Hippel Lindau Syndrome. Objectives. Overview. None No conflicts of interest
 Neurological Manifestations of Von Hippel Lindau Syndrome ARNOLD B. ETAME MD, PhD NEURO-ONCOLOGY/NEUROSURGERY Moffitt Cancer Center Disclosures None No conflicts of interest VHL Alliance Annual Family
Neurological Manifestations of Von Hippel Lindau Syndrome ARNOLD B. ETAME MD, PhD NEURO-ONCOLOGY/NEUROSURGERY Moffitt Cancer Center Disclosures None No conflicts of interest VHL Alliance Annual Family
Specialised Services Policy CP66: 68-gallium DOTA- peptide scanning for the Management of Neuroendocrine Tumours (NETs)
 Specialised Services Policy CP66: Management of Neuroendocrine Tumours (NETs) Document Author: Assistant Planner for Cancer and Blood Executive Lead: Director of Quality and Nursing Approved by: Management
Specialised Services Policy CP66: Management of Neuroendocrine Tumours (NETs) Document Author: Assistant Planner for Cancer and Blood Executive Lead: Director of Quality and Nursing Approved by: Management
