Biology December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY
|
|
|
- Jerome Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your name and ID number. You will have 4 points deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!! WRITE YOUR TEST FORM LETTER above your name on the answer sheet. WRITE YOUR LAB SECTION DAY & TIME AND TA'S NAME on the upper margin of your answer sheet. Your exam should have 39 questions and a page of figures. Please check to make sure it is complete. For each of the following questions, please indicate the most correct answer by blackening the corresponding letter on the accompanying answer sheet. Each correct answer is worth 2 points. Partial credit of ½ point may be available for questions that have answers such as all the above, both a and b are true, etc. 1. Indicate the proper sequence of events during inspiration: 1. Inspiratory muscles contract 7. No pressure gradient 2. Inspiratory muscles relax 8. Pressure gradient from lungs to environment 3. Thoracic cavity enlarges 9. Pressure gradient from environment to lungs 4. Thoracic cavity decreases 10. No air flow between lungs and environment 5. Lungs expand 11. Air flow from lungs to environment 6. Lungs decrease 12. Air flow from environment to lungs a) 1, 3, 5, 9, 12 b) 2, 3, 5, 9, 12 c) 1, 3, 5, 8, 12 d) 1, 4, 6, 9, 12 e) 2, 4, 6, 9, Which of the following respiratory airways are composed of smooth muscle and so may have their radii regulated in response to the autonomic nervous system? a) trachea b) bronchi c) pharynx d) bronchioles e) all the above 3. The regulatory response to the situation in which blood flow to your lungs is too high while the flow of air in your lungs is too low is a) vasodilation and bronchoconstriction b) vasodilation and bronchodilation c) vasoconstriction and bronchodilation d) vasoconstriction and bronchoconstriction e) no response your body can not regulate this situation 1
2 4. Three people are breathing in the following ways: Tidal Volume (ml/breath) Respiratory Rate (breaths/min) Dead Space Volume (ml) Person Person Person Which of the following statements is true? a) person 2 has the highest alveolar ventilation, but pulmonary ventilation does not differ among the 3 people b) person 2 has the highest alveolar ventilation and the highest pulmonary ventilation c) person 1 has the highest alveolar ventilation and person 2 has the highest pulmonary ventilation d) person 3 has an alveolar ventilation of 0 e) both a and d are true 5. A patient comes into the emergency room where you work with a spinal injury in his neck. Which of the following are most likely to occur? a) His heart will stop beating b) He will be unable to have any kind of basic breathing rhythm c) He will be unable to regulate the magnitude of ventilation d) All the above e) Only b and c are likely to occur 6. The location of gas exchange with the blood a) Alveoli b) Bronchioles c) Bronchi d) All the above e) Both a and c 7. On the Wookiee planet of Kashyyyk the atmosphere has a higher pressure and a higher O 2 content than on earth such that a Wookiee has a P O2 of 200 mm Hg in his alveoli, a P O2 of 100 mm Hg in his deoxygenated blood as it reaches his pulmonary capillaries, and a hemoglobin-oxygen binding curve as shown in Figure 1. Assuming that a Wookiee s respiratory physiology is similar to a human s, what is the P O2 of blood leaving his pulmonary capillaries? a) 0 mm Hg b) 50 mm Hg c) 100 mm Hg d) 150 mm Hg e) 200 mm Hg 8. Approximately what is the percent oxygen saturation of the hemoglobin leaving a Wookiee s pulmonary capillaries under normal conditions (see Figure 1)? a) 0% b) 20% c) 40% d) 80% e) 95% 2
3 9. A right-shift of a Wookiee s Hb-O 2 saturation curve during exercise would cause (Figure 1) a) normal unloading in the systemic capillaries and substantially reduced oxygen loading in the alveolar capillaries b) normal unloading in the systemic capillaries and substantially increased oxygen loading in the alveolar capillaries c) increased unloading in the systemic capillaries and substantially reduced oxygen loading in the alveolar capillaries d) increased unloading in the systemic capillaries and normal oxygen loading in the alveolar capillaries e) decreased unloading in the systemic capillaries and substantially increased oxygen loading in the alveolar capillaries 10. On Kashyyyk, 50% of the air is oxygen and the atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1000 mm Hg. What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere? a) 5000 mm Hg b) 1000 mm Hg c) 750 mm Hg d) 500 mm Hg e) 200 mm Hg 11. The primary regulator of the magnitude of ventilation in normal circumstances is a) the H + concentration of the brain extracellular fluid monitored by the central chemoreceptors b) the P O2 of the arterial blood monitored by central chemoreceptors c) the P O2 of the arterial blood monitored by peripheral chemoreceptors d) the P CO2 of arterial blood monitored by central chemoreceptors e) the P CO2 of arterial blood monitored by peripheral chemoreceptors 12. Deoxygenated hemoglobin helps transport CO 2 by a) binding about 30% of the CO 2 in the blood b) binding H + ions produced by the conversion of CO 2 to H + and HCO 3 - c) binding HCO 3 - produced by the conversion of CO 2 to H + and HCO 3 - d) both a and b e) both a and c 13. If the P O2 of your blood falls by 20% your body responds by a) Peripheral chemoreceptors increasing ventilation rate b) Central chemoreceptors increasing ventilation rate c) The respiratory center in the medulla increasing the rhythm of inspiration d) Doing nothing e) All the above are true except d 14. Of the Na + filtered into the tubular system, about is recovered through the process of. a) 75%; tubular reabsorption b) 90%; tubular reabsorption c) 75%; tubular secretion d) 99.5%; tubular reabsorption e) 99.5%; tubular secretion 3
4 15. The functional unit of the kidney is the a) glomerulus b) proximal tubule c) collecting ducts d) nephron e) loop of Henle 16. Blood enters the glomerulus from. a) The peritubular capillary b) The efferent arteriole c) The afferent arteriole d) Bowman s capsule e) The vasa recta 17. Which of the following best describe glomerular filtrate? a) It is identical to blood b) It is identical to plasma c) It is very similar to plasma except it contains no proteins or red blood cells d) It is very similar to plasma except it contains no proteins, red blood cells or glucose e) It is very similar to plasma except it contains no proteins, red blood cells, glucose or Na Which of the following statements about regulation of glomerular filtration rate is true? a) During exercise blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate increase and more urine is produced b) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasoconstriction of the affarent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production c) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasodilation of the affarent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production d) During exercise the kidney can detect an increase in blood pressure and vasoconstrict affarent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production e) Both b and d are true 19. The tubular structure involved in filtration in the kidney is a) The glomerulus b) Bowman s capsule c) The proximal tubule d) The distal tubule e) The peritubular capillary 20. The descending loop of Henle is, whereas the ascending loop of Henle is. a) permeable to water but not permeable to Na + ; not permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out b) permeable to water and permeable to Na + ; permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out c) not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + ; not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + d) not permeable to water but permeable to Na + ; permeable to water but not permeable to Na + e) permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out; permeable to water but not permeable to Na + 4
5 21. The countercurrent system set up by the Loop of Henle creates an osmotic gradient that a) in the absence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. b) in the absence of vasopressin prevents water from leaving the collecting tubule and so produce a concentrated urine. c) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. d) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via active transport and so produce a concentrated urine. e) does none of the above 22. On planet Tatooine the Hutts evolved a urinary system very similar to humans. Fig 2 shows the collecting duct passing through the gradient set up by the Loop of Henle. What is the most concentrated urine the Hutts can produce? The most dilute urine they can produce? a) 1000; 100 b) 1400; 300 c) 1800; 100 d) 1800; 300 e) 2000; Which of the following statements about K + is true? a) secretion of H + causes secretion of K + b) it is regulated during reabsorption c) increases in plasma K + causes decreases in aldosterone production d) conservation of Na + can cause secretion of K + e) all the above are true except for b 24. Reabsoprtion of water in the proximal tubules a) Is a Na + dependent passive process b) Is a Na + dependent active process c) Osmotically follows Na + from the tubule to the interstitial fluid d) Both a and c are true e) Both b and c are true 25. If a person becomes overhydrated, the ICF will become a) hypertonic b) hypotonic c) isotonic 26. because a) Na + b) K + c) Ca ++ d) Cl - e) water 27. moves from the. a) ECF to the ICF b) ICF to the ECF c) Plasma to the interstitial fluid d) Interstitial fluid to the plasma 5
6 28. Which of the following statements about urea reabsorption in the proximal tubules is (are) true? a) Only 50% of the urea filtered is excreted b) Urea is actively reabsorbed following Na + c) Urea is actively reabsorbed following water d) Urea is passively reabsorbed following Na + e) None of the above are true 29. If blood pressure falls below normal, is released by the juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidney, which converts Angiotensinogen to Angiotensin I; a) renin b) aldosterone c) vasopressin d) atrial natriuretic peptide e) corticosterone 30. then angiotensin converting enzyme converts Angiotensin I to Angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to secrete a) renin b) aldosterone c) vasopressin d) atrial natriuretic peptide e) corticosterone 31. which the reabsorption of in the distal and collecting tubules of nephrons. a) increases; Na + b) decreases; Na + c) increases; water d) decreases water 32. An increase in ventilation rate results in a) More CO 2 than usual being expired b) An increase in plasma H + c) The reaction CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H + + HCO3 - being driven to the left d) All the above e) Both a and c 33. When a person has diabetes mellitus, they may suffer from a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis 34. The result of an excessive loss of HCO 3 - while CO 2 stays the same a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis 35. The most effective response to bring the body back to complete acid-base balance is by a) Lungs b) Buffers c) Kidneys 6
7 36. Vomiting can lead to a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis 37. The result of a buildup of CO 2 while HCO 3 - stays the same a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis 38. Which of the following can cause hypertension? a) Renal disease b) Atherosclerosis c) Adrenal tumors d) Abnormalities in the Na + -K + -ATPase pump e) All the above 39. The only fluid that can have its composition and volume directly regulated is the a) ICF b) ECF c) plasma d) interstitial fluid e) lymph 7
8 Figure 2 Figure
9 Biology December 2010 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your name and ID number. You will have 4 points deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!! WRITE YOUR TEST FORM LETTER above your name on the answer sheet. WRITE YOUR LAB SECTION DAY & TIME AND TA'S NAME on the upper margin of your answer sheet. Your exam should have 39 questions. Please check to make sure it is complete. For each of the following questions, please indicate the most correct answer by blackening the corresponding letter on the accompanying answer sheet. Each correct answer is worth 2 points. Partial credit of ½ point may be available for questions that have answers such as all the above, both a and b are true, etc. 1. A tidal volume of 1200 ml/breath, a respiratory rate of 5 breaths per minute and a dead space volume of 200 ml gives a pulmonary ventilation rate of and an alveolar ventilation rate of. a) 6000; 5000 b) 6000; 6000 c) 5000; 5000 d) 5000; 6000 e) 500; Hypoventilation causes a) Respiratory acidosis b) Excessive loss of CO 2 c) Increase in HCO 3 - d) Both a and b e) Both a and c 3. Which of the following statements about urea reabsorption in the proximal tubules is (are) true? a) Only 50% of the urea filtered is excreted b) Urea is actively reabsorbed following Na + c) Urea is actively reabsorbed following water d) Urea is passively reabsorbed following Na + e) None of the above are true 4. The kidneys receive what percent of resting cardiac output? a) 1% b) 5% c) 15% d) 20% e) 50% 1
10 5. Increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system can increase blood pressure by a) Increasing heart rate b) Increasing stroke volume c) Decreasing the radius of blood vessels d) All the above are true e) Both a and b are true 6. What does contraction of the diaphragm cause? a) decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore a decrease in atmospheric pressure b) decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure c) increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure d) decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore an increase in intra-alveolar pressure e) increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore an increase in intra-alveolar pressure 7. Which of the following statements about reabsorption of glucose is (are) true? a) Glucose is actively transported across the apical membrane b) For glucose to be reabsorbed Na + must be actively transported across the basolateral membrane c) Glucose is actively transported across the basolateral membrane d) Both a and b are true e) Both b and c are true 8. The ratio of HCO 3 - to CO 2 falling less than 20 to 1 can cause a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both a and c 9. What is the primary mechanism of carbon dioxide transport in blood? a) dissolved in the plasma b) dissolved in the red blood cells c) bound to hemoglobin d) as bicarbonate dissolved in the plasma e) as bicarbonate dissolved in the red blood cells 10. Which of the following is NOT a function of the kidneys? a) regulation of plasma ionic concentration b) regulation of plasma osmolarity c) regulation of plasma temperature d) regulation of plasma volume e) regulation of plasma hydrogen concentration 11. As the lungs expand, intra-alveolar pressure and air moves the lungs. a) increases : out of b) increases : into c) decreases : out of d) decreases : into e) does not change : neither into nor out of 2
11 12. The descending loop of Henle is a) permeable to water but not permeable to Na + b) permeable to water and permeable to Na + c) not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + d) not permeable to water but permeable to Na whereas the ascending loop of Henle is a) permeable to water but not permeable to Na + b) permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out c) not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + d) not permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out 14. This countercurrent system sets up an osmotic gradient that a) in the absence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. b) in the absence of vasopressin prevents water from leaving the collecting tubule and so produce a concentrated urine. c) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. d) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via active transport and so produce a concentrated urine. 15. Which of the following statements about regulation of glomerular filtration rate is true? a) During exercise blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate increase and more urine is produced b) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production c) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasodilatation of the afferent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production d) During exercise the kidney can detect an increase in blood pressure and vasoconstrict afferent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production e) Both b and d are true 16. After fluid passes through the entire proximal tubule, the fluid will enter the. a) loop of Henle b) distal tubule c) connecting tubule d) collecting duct e) Bowman's capsule 17. Which of the following does NOT contribute to the rapid movement of gases into and out of the blood within the lungs? a) rapid blood flow b) thin membrane c) large surface area d) concentration gradient e) permeability of the membrane 3
12 18. Reabsoprtion of water in the proximal tubules a) Is a Na + dependent passive process b) Is a Na + dependent active process c) Occurs because water osmotically follows Na + from the tubule to the interstitial fluid d) Both a and c are true e) Both b and c are true 19. Anakin Skywalker, from the planet Tatooine, has a P O2 of 200 mm Hg in his alveoli and a P O2 of 80 mm Hg in his tissues. Assuming that Anakin s respiratory physiology functions similar to yours, what is the P O2 of blood leaving his lung capillaries? a) 0 mm Hg b) 80 mm Hg c) 100 mm Hg d) 160 mm Hg e) 200 mm Hg 20. Which of the following statement(s) about metabolic acidosis is (are) true? a) CO 2 levels increase b) HCO 3 - levels increase c) Ventilation increases to blow off excess CO 2 in response to metabolic acidosis d) Kidneys eliminate HCO 3 - in response to metabolic acidosis e) Both a and c are true 21. Equilibration of pressure between the intrapleural space and the alveoli will lead to a) air moving out of the lungs b) air moving into the lungs c) a pneumothorax (the lung will collapse) d) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease e) restrictive pulmonary disease 22. Which of the following cause release of aldosterone? a) Low levels of Na + in the plasma b) High levels of Na + in the plasma c) Low levels of K + in the plasma d) Both a and c e) Both b and c 23. Movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveoli and blood occurs by what process? a) simple diffusion b) facilitated diffusion c) osmosis d) primary active transport e) secondary active transport 24. Buffers in the body will release H + ions in response to a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both b and d 4
13 25. On Tatooine, 50% of the air is oxygen and the atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1000 mm Hg. What is the partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere? a) 5000 mm Hg b) 1000 mm Hg c) 750 mm Hg d) 500 mm Hg e) 200 mm Hg 26. Which of the following occurs when intra-alveolar pressure exceeds atmospheric pressure? a) air moves into the lung b) air moves out of the lung c) the lung collapses d) the lung must be expanding e) intrapleural pressure is greater than intra-alveolar pressure 27. Once produced, urine travels through the until it reaches the bladder, from which it is released into the external environment through the. a) ureter : urethra b) urethra : ureter c) collecting duct : ureter d) collecting duct : urethra e) renal hilus : ureter 28. The renal process(es) that is (are) non-selective a) Glomerular filtration b) Tubular reabsorption c) Tubular secretion d) Both a and b e) Both a and c 29. A reduction in HCO 3 - while CO 2 stays the same can be caused by a) Strenuous exercise b) Vomiting c) High altitude d) Lung disease e) Both c and d 30. If the amount of hemoglobin in your body drops by 20% your body responds by a) Peripheral chemoreceptors upregulating hemoglobin production b) Central chemoreceptors upregulating hemoglobin production c) The respiratory center in the medulla upregulation hemoglobin production d) Doing nothing e) All the above are true except d 31. Which of the following are considered to be primary causes of high blood pressure? a) Salt management problems by the kidney b) Adrenal tumors c) Brain tumors d) Atherosclerosis e) Both a and d 5
14 32. Diffusion of gases in the lungs is facilitated by a) Length of bronchi b) Thinness of walls of alveoli c) Large surface area of alveoli d) Both a and b are true e) Both b and c are true 33. If a person becomes overhydrated, the ICF will become because moves from ; this will cause the cells to. a) Hypotonic; water; ECF to ICF; expand b) Hypotonic, Na + ; ECF to ICF; expand c) Hypotonic, Na + ; ICF to ECF; shrink d) Hypertonic; water; ICF to ECF; shrink e) Hypertonic; Na + ; ICF to ECF; shrink Questions 34 to 39 refer to the following paragraph: When Na + levels decline, ECF volume and blood pressure decrease, and the juxtaglomerular apparatus secretes the hormone (34) d, which ultimately causes production of the hormone Angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce (35) c, which increases Na + reabsorption in the distal and collecting tubules of the kidneys by adding more (36) d to the membranes there. This results in an increase in ECF volume and hence blood pressure. In addition Angiotensin II stimulates (37) e and stimulates the production of the hormone (38) a which causes the kidneys to retain (39) a. Questions 34, 35, 38: a) vasopressin, b) epinephrine, c) aldosterone, d) renin e) acetylcholine Question 36: a) phospholipids, b) Na + channels, c) K + channels, d) Na + -K + -ATPase pumps, e) Ca ++ channels Question 37: a) thirst, b) vasodilation, c) vasoconstriction, d) urine production e) both a and c Question 39: a) water, b) H +, c) K +, d) Ca ++, e) glucose 6
15 Biology December 2011 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your name and ID number. You will have 10 points deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!! WRITE YOUR TEST FORM LETTER above your name on the answer sheet. WRITE YOUR LAB SECTION DAY & TIME AND TA'S NAME on the upper margin of your answer sheet. Your exam should have 39 questions. Please check to make sure it is complete. For each of the following questions, please indicate the most correct answer by blackening the corresponding letter on the accompanying answer sheet. Each correct answer is worth 2 points. Partial credit of ½ point may be available for questions that have answers such as all the above, both a and b are true, etc. 1. Three people are breathing in the following ways: Tidal Volume (ml/breath) Respiratory Rate (breaths/min) Dead Space Volume (ml) Person Person Person Which of the following statements is true? a) person 2 has the highest alveolar ventilation, but pulmonary ventilation does not differ among the 3 people b) person 2 has the highest pulmonary ventilation but alveolar ventilation does not differ among the 3 people c) person 1 has the highest alveolar ventilation and person 2 has the highest pulmonary ventilation d) person 3 has a pulmonary ventilation of 0 e) both a and d are true 2. Kangaroo rats, which live in the deserts of the US southwest and can survive consuming very low levels of water, have very long loops of Henle. Such long loops of Henle would result in which of the following? a) a higher osmolarity in the deeper regions of the renal medulla and the ability to produce a more concentrated urine b) a lower osmolarity in the deeper regions of the renal medulla and the ability to produce a more concentrated urine c) a higher osmolarity in the deeper regions of the renal medulla and the ability to produce a more dilute urine d) a lower osmolarity in the deeper regions of the renal medulla and the ability to produce a more dilute urine e) a higher osmolarity in the renal cortex and the ability to produce a more dilute urine 1
16 3. In TV sitcoms, characters suffering from anxiety are often told to breath in paper bags. This is because anxious people frequently hyperventilate which leads to, causing an excessive loss of. Breathing into a paper bag alleviates the situation by causing a buildup of. a) Respriatory acidosis; CO 2 ; CO 2 b) Respiratory alkalosis; CO 2 ; CO 2 c) Respiratory alkalosis; HCO 3 - ; CO 2 d) Respiratory acidosis; HCO 3 - ; CO 2 e) Respiratory alkalosis; HCO 3 - ; HCO 3-4. The step in glucose reabsorption on which all other steps critically depend is the a) active transport of Na + from inside the epithelial cell into the ECF across the basolateral membrane b) active transport of Na + from tubular lumen into the ECF across the basolateral membrane c) active transport of Na + from inside the epithelial cell into the ECF across the apical membrane d) active transport of Na + from the tubular lumen into the epithelial cell across the apical membrane e) passive transport of glucose from the tubular lumen into the ECF across the apical membrane 5. Oxygenated blood is found in which of the following? a) right atrium only b) pulmonary artery only c) pulmonary vein only d) both the right atrium and pulmonary artery e) both the right atrium and pulmonary vein 6. Your lungs are smaller than your thoracic (chest) cavity, yet occupy most of it. What two factors make this possible? a) Intrapleural fluid and large surface area of alveoli b) Transmural pressure gradient and intrapleural fluid c) Large surface area of alveoli and transmural pressure gradient d) Pressure gradient from lungs to environment and intrapleural fluid e) Transmural pressure gradient and pressure gradient from lungs to environment 7. The process regulated by the kidneys to maintain proper amounts of K + is (are) a) Filtration b) Reabsoprtion c) Secretion d) Both a and c e) Both b and c 8. Which of the following are considered to be primary causes of high blood pressure? a) Salt management problems by the kidney b) Adrenal tumors c) Brain tumos d) Atherosclerosis e) Both a and d 2
17 9. Systemic venous P O2 entering the lungs is alveolar P O2, therefore the pressure gradient is a) greater then, from lungs to blood b) greater than, from blood to lungs c) less than, from lungs to blood d) less than, from blood to lungs e) equal to, from blood to lungs 10. If nothing else is removed from the filtrate once it reaches the late distal tubules, the urine excreted would have which of the following properties? a) devoid of ions and large volume b) high osmolarity and low volume c) low osmolarity and low volume d) low osmolarity and large volume e) high osmolarity and large volume 11. Blood enters the glomerulus from. a) The peritubular capillary b) The efferent arteriole c) The afferent arteriole d) Bowman s capsule e) The vasa recta 12. Which of the following specifically describes the movement of air into and out of the lungs? a) Secondary ventilation b) Pulmonary ventilation c) Internal respiration d) Respiration e) Expiration 13. An increase in ventilation rate results in a) More CO 2 than usual being expired b) An increase in plasma H + c) The reaction CO 2 + H 2 O H 2 CO 3 H + + HCO 3 - being driven to the left d) All the above e) Both a and c 14. If the P O2 of your blood falls by 20% your body responds by a) Peripheral chemoreceptors increasing ventilation rate b) Central chemoreceptors increasing ventilation rate c) The respiratory center in the medulla increasing the rhythm of inspiration d) Doing nothing e) All the above are true except d 15. Despite being less than 1% of body weight, the kidneys receive what percent of resting cardiac output? a) 1% b) 5% c) 15% d) 20% e) 50% 3
18 16. The ratio of HCO 3 - to CO 2 increasing to greater than 20 to 1 is caused by a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both b and d 17. After fluid passes through the entire proximal tubule, the fluid will enter the. a) loop of Henle b) distal tubule c) connecting tubule d) collecting duct e) Bowman's capsule 18. Solute S is excreted in the urine at a rate that is lower than the amount filtered into the tubular system. On the basis of this information, which of the following is the most precise conclusion that can justifiably be drawn regarding the kidney's processing of solute S? a) S is neither reabsorbed nor secreted b) S is definitely reabsorbed and may be secreted c) S is definitely secreted and may be reabsorbed d) S is definitely both reabsorbed and secreted 19. Of the Na + filtered into the tubular system, about is recovered through the process of. a) 75%; tubular reabsorption b) 90%; tubular reabsorption c) 75%; tubular secretion d) 99.5%; tubular reabsorption e) 99.5%; tubular secretion 20. Which of the following processes is NOT a part of external respiration? a) the movement of air into and out of the lungs by bulk flow b) the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and blood by diffusion c) the transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and body tissues by the blood d) the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood and tissues by diffusion e) the use of oxygen and generation of carbon dioxide by the mitochondria during energy metabolism 21. During intense exercise, the metabolic activity of muscle causes a in the partial pressure of oxygen in the muscle, the movement of oxygen into the muscle. a) decrease : reducing b) decrease : facilitating c) increase : reducing d) increase : facilitating e) does not change : facilitating 4
19 22. The descending loop of Henle is, whereas the ascending loop of Henle is. a) permeable to water but not permeable to Na + ; not permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out b) permeable to water and permeable to Na + ; permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out c) not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + ; not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + d) not permeable to water but permeable to Na + ; permeable to water but not permeable to Na + e) permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out; permeable to water but not permeable to Na Which of the following is a source of water input? a) gastrointestinal tract only b) renal tubules only c) metabolism only d) both gastrointestinal tract and metabolism e) both the gastrointestinal tract and renal tubules 24. The most effective response to bring the body back to complete acid-base balance is by the a) Lungs b) Buffers c) Kidneys d) Liver e) Heart 25. Which of the following is NOT a function of the respiratory system? a) vocalization b) ion balance of blood c) acid-base balance of blood d) enhancing venous return e) heat loss 26. The functional unit of the kidney is the a) glomerulus b) proximal tubule c) collecting ducts d) nephron e) loop of Henle 27. Increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system can increase blood pressure by a) Increasing heart rate b) Increasing stroke volume c) Decreasing the radius of blood vessels d) All the above are true e) Both a and b are true 5
20 28. The normal fasting plasma concentration of solute X is 100 mg/dl, and the renal threshold (maximum reabsorption rate) of solute X is 375 mg/dl. If the plasma concentration of solute X doubles to 200 mg/dl, then a) the rate at which solute X is reabsorbed will double b) the amount of solute X filtered into the tubular system will be halved c) the amount of solute X in the excreted urine will increase d) the amount of water in the excreted urine will increase e) both c and d will occur 29. When Na + levels decline, ECF volume and blood pressure, and the juxtaglomerular apparatus secretes the hormone. a) increases, increases, aldosterone b) decreases, decreases, renin c) increases, decreases, renin d) decreases, decreases, angiotensinongen e) decreases, decreases, aldosterone 30. What is the partial pressure of oxygen in a gas mixture that is 40% oxygen, 40% argon, and 20% helium, when the total pressure of the gas is 1,000 mm Hg? a) 100 mm Hg b) 200 mm Hg c) 333 mm Hg d) 400 mm Hg e) 600 mm Hg 31. Which of the following statements about regulation of glomerular filtration rate is true? a) During exercise blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate increase and more urine is produced b) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasoconstriction of the affarent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production c) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasodilation of the affarent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production d) During exercise the kidney can detect an increase in blood pressure and vasoconstrict affarent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production e) Both b and d are true 32. When air is no longer moving through the respiratory tract and the airway is open to the environment, the pressure within the lung is equal to. a) systolic blood pressure b) transpulmonary pressure c) intrapleural pressure d) atmospheric pressure e) end-diastolic pressure 33. Which of the following statements is FALSE of a rightward shift in the hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve? a) Affinity for oxygen is increased. b) It can occur in active tissue. c) Hemoglobin unloading of oxygen is increased. d) Oxygen loading onto hemoglobin is decreased. e) It can occur as a result of an increase in temperature or acidity in the tissue. 6
21 34. If a person becomes overhydrated, the ICF will become because moves from the. a) hypertonic; Na + ; ICF to the ECF b) hypotonic; Na + ; ECF to the ICF c) hypertonic; water; ECF to the ICF d) hypotonic; water; ECF to the ICF e) hypotonic; K + ; ICF to the ECF 35. Buffers in the body will absorb H + ions in response to a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both a and c 36. The countercurrent system set up by the Loop of Henle creates an osmotic gradient that a) in the absence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. b) in the absence of vasopressin prevents water from leaving the collecting tubule and so produce a concentrated urine. c) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. d) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via active transport and so produce a concentrated urine. e) does none of the above 37. When a person has diabetes mellitus, they may suffer from a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both a and c 38. If a person is normallly hydrated but then consumes a large quantity of a hyperosmotic solution, it will. a) have no effect on cell osmolarity and thereby cell size b) cause cells to shrink due to an increase in the osmolarity of extracellular fluid c) cause cells to swell due to an increase in the osmolarity of extracellular fluid d) cause cells to swell due to a decrease in the osmolarity of extracellular fluid e) cause cells to shrink due to a decrease in the osmolarity of extracellular fluid 39. Which of the following is NOT one of the functions of angiotensin II? a) vasoconstriction b) stimulate aldosterone secretion c) stimulate antidiuretic hormone (ADH or vasopressin) secretion d) increased thirst e) stimulate renin secretion 7
22 Biology November 2012 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your name and ID number. You will have 4 points deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!! WRITE YOUR TEST FORM LETTER above your name on the answer sheet. WRITE YOUR LAB SECTION DAY & TIME AND TA'S NAME on the upper margin of your answer sheet. Your exam should have 39 questions. Please check to make sure it is complete. For each of the following questions, please indicate the most correct answer by blackening the corresponding letter on the accompanying answer sheet. Each correct answer is worth 2 points. Partial credit of ½ point may be available for questions that have answers such as all the above, both a and b are true, etc. 1. Solute S is excreted in the urine at a rate that is higher than the amount filtered into the tubular system. On the basis of this information, which of the following is the most precise conclusion that can justifiably be drawn regarding the kidney's processing of solute S? a) S is neither reabsorbed nor secreted b) S is definitely reabsorbed and may be secreted c) S is definitely secreted and may be reabsorbed d) S is definitely both reabsorbed and secreted 2. Which of the following increases oxygen unloading from hemoglobin? a) increased carbon dioxide in the tissue b) increased oxygen levels in the tissue c) increased blood ph d) decreased metabolism e) decreased temperature 3. A reduction in HCO 3 - while CO 2 stays the same can be caused by a) Strenuous exercise b) Vomiting c) High altitude d) Lung disease e) Both c and d 4. Despite being less than 1% of body weight, the kidneys receive what percent of resting cardiac output? a) 1% b) 5% c) 15% d) 20% e) 50% 1
23 5. Movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between alveoli and blood occurs by what process? a) simple diffusion b) facilitated diffusion c) osmosis d) primary active transport e) secondary active transport 6. The renal process(es) that is(are) non-selective a) Glomerular filtration b) Tubular reabsorption c) Tubular secretion d) Both a and b e) Both a and c 7. Which of the following statements about reabsorption of glucose is (are) true? a) Glucose is actively transported across the apical membrane b) For glucose to be reabsorbed Na + must be actively transported across the basolateral membrane c) For glucose to be reabsorbed Na + must be actively transported across the apical membrane d) Both a and b are true e) Both b and c are true 8. The most effective response to bring the body back to complete acid-base balance is by the a) Lungs b) Buffers c) Kidneys d) Liver e) Heart 9. What does contraction of the diaphragm cause? a) decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore a decrease in atmospheric pressure b) decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure c) increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure d) decrease in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore an increase in intra-alveolar pressure e) increase in the volume of the thoracic cavity and therefore an increase in intra-alveolar pressure 10. Approximately of Americans have high blood pressure; the cause of this high blood pressure has been identified for approximately of these people. a) 10%; 90% b) 25%; 10% c) 50%; 100% d) 10%; 10% e) 25%; 50% 11. Buffers in the body will release H + ions in response to a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both b and d 2
24 12. If you have a tidal volume of 200 ml/breath, a respiratory rate of 20 breaths per minute and a dead space volume of 200 ml, your pulmonary ventilation rate is and your alveolar ventilation rate is. a) 4000; 0 b) 4000; 4000 c) 3800; 0 d) 4000; 3800 e) 3800; Diffusion of gases from the lungs into the blood is facilitated by a) Length of bronchi b) Thinness of walls of alveoli c) Large surface area of alveoli d) Both a and b are true e) Both b and c are true 14. Which of the following is NOT a function of the kidneys? a) regulation of plasma ionic concentration b) regulation of plasma osmolarity c) regulation of plasma temperature d) regulation of plasma volume e) regulation of plasma hydrogen concentration 15. Which of the following does NOT contribute to the rapid movement of gases into and out of the blood within the lungs? a) rapid blood flow b) thin membrane c) large surface area d) concentration gradient e) permeability of the membrane 16. The descending loop of Henle is a) permeable to water but not permeable to Na + b) permeable to water and permeable to Na + c) not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + d) not permeable to water but permeable to Na whereas the ascending loop of Henle is a) permeable to water but not permeable to Na + b) permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out c) not permeable to water and not permeable to Na + d) not permeable to water and Na + is actively transported out 18. This countercurrent system sets up an osmotic gradient that a) in the absence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. b) in the absence of vasopressin prevents water from leaving the collecting tubule and so produce a concentrated urine. c) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via osmosis and so produce a concentrated urine. d) in the presence of vasopressin allows water to leave the collecting tubule via active transport and so produce a concentrated urine. 3
25 19. Once produced, urine travels through the until it reaches the bladder, from which it is released into the external environment through the. a) ureter : urethra b) urethra : ureter c) collecting duct : ureter d) collecting duct : urethra e) renal hilus : ureter 20. Increased activity of the sympathetic nervous system can increase blood pressure by a) Increasing heart rate b) Decreasing stroke volume c) Increasing the radius of blood vessels d) All the above are true e) Both a and b are true 21. The structure of the tubular system involved in filtration in the kidney is a) The glomerulus b) Bowman s capsule c) The proximal tubule d) The distal tubule e) The peritubular capillary 22. Which of the following statement(s) about metabolic acidosis is (are) true? a) CO 2 levels increase b) HCO 3 - levels increase c) Ventilation increases to blow off excess CO 2 in response to metabolic acidosis d) Kidneys eliminate HCO 3 - in response to metabolic acidosis e) Both a and c are true 23. What is the primary mechanism of carbon dioxide transport in blood? a) dissolved in the plasma b) dissolved in the red blood cells c) bound to hemoglobin d) as bicarbonate dissolved in the plasma e) as bicarbonate dissolved in the red blood cells 24. A patient comes into the emergency room where you work with a spinal injury in his neck. Which of the following are most likely to occur? a) His heart will stop beating b) He will be unable to have any kind of basic breathing rhythm c) He will be unable to regulate the magnitude of ventilation d) All the above e) Only b and c are likely to occur 25. The ratio of HCO 3 - to CO 2 falling less than 20 to 1 can cause a) metabolic acidosis b) metabolic alkalosis c) respiratory acidosis d) respiratory alkalosis e) both a and c 4
26 26. Which of the following respiratory airways are composed of smooth muscle and so may have their radii regulated in response to the autonomic nervous system? a) trachea b) bronchi c) pharynx d) bronchioles e) all the above 27. The normal plasma concentration of solute X is 100 mg/dl, and the renal threshold (maximum reabsorption rate) of solute X is 100 mg/dl. If the plasma concentration of solute X doubles to 200 mg/dl, then a) the rate at which solute X is reabsorbed will double b) the amount of solute X filtered into the tubular system will be halved c) the amount of solute X in the excreted urine will increase d) the amount of solute X secreted will double e) both c and d will occur 28. Which of the following statements about regulation of glomerular filtration rate is true? a) During exercise blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate increase and more urine is produced b) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production c) During exercise the parasympathetic causes vasodilation of the afferent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production d) During exercise the kidney can detect an increase in blood pressure and vasoconstrict afferent arterioles to reduce glomerular filtration rate and therefore reduce urine production e) Both b and d are true 29. Hypoventilation causes a) Respiratory acidosis b) Excessive loss of CO 2 c) Increase in HCO 3 - d) Both a and b e) Both a and c 30. The location of gas exchange with the blood a) Alveoli b) Bronchioles c) Bronchi d) All the above e) Both a and c 31. An increase in venous return can increase blood pressure by increasing a) heart rate b) stroke volume c) vasoconstriction d) blood viscosity e) all of the above 5
27 32. Anakin Skywalker, from the planet Tatooine, has a P O2 of 200 mm Hg in his alveoli and a P O2 of 80 mm Hg in his tissues and a hemoglobin-oxygen dissociation curve shown in Fig. 1. Assuming that Anakin s respiratory physiology functions similar to yours, what is the P O2 of blood leaving his lung capillaries? a) 0 mm Hg b) 80 mm Hg c) 100 mm Hg d) 160 mm Hg e) 200 mm Hg 33. Approximately what is the percent oxygen saturation of the hemoglobin leaving Anakin s systemic capillaries (Figure 1)? a) 0% b) 20% c) 40% d) 75% e) 95% Questions 34 to 39 refer to the following paragraph: When Na + levels decline, ECF volume and blood pressure decrease, and the juxtaglomerular apparatus secretes the hormone (34) d, which ultimately causes production of the hormone Angiotensin II. Angiotensin II stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce (35) c, which increases Na + reabsorption in the distal and collecting tubules of the kidneys by adding more (36) d to the membranes there. This results in an increase in ECF volume and hence blood pressure. In addition Angiotensin II stimulates (37) e and stimulates the production of the hormone (38) a which causes the kidneys to retain (39) a. Questions 34, 35, 38: a) vasopressin, b) epinephrine, c) aldosterone, d) renin e) acetylcholine Question 36: a) phospholipids, b) Na + channels, c) K + channels, d) Na + -K + -ATPase pumps, e) Ca ++ channels Question 37: a) thirst, b) vasodilation, c) vasoconstriction, d) urine production e) both a and c Question 39: a) water, b) H +, c) K +, d) Ca ++, e) glucose 6
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys
 Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment
 Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Hill et al. 2004, Fig. 27.6
 Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Excretion and Waste Management. Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski
 Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
Chapter 25: Urinary System
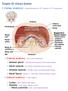 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/80/80449526.jpg) 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
Reminder: Today: Exam I Thursday. A. Urinary System. B. Respiratory System. Urinary System Physiology: Urine Formation:
 Exam I Reminder: Today: A. Urinary System Exam II Exam I Thursday B. Respiratory System Mariners Baseball: Travel Day... Next: Tampa Bay Devil Rays Glomerular Filtration: 1) Blood pressure = driving force
Exam I Reminder: Today: A. Urinary System Exam II Exam I Thursday B. Respiratory System Mariners Baseball: Travel Day... Next: Tampa Bay Devil Rays Glomerular Filtration: 1) Blood pressure = driving force
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
AP Biology. Homeostasis. Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. Homeostasis
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Functions of Proximal Convoluted Tubules
 1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology
 Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Question 1: Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the
Class XI Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Biology Question 1: Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) Glomerular filtration rate is the amount of glomerular filtrate formed in all the
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 18 The Urinary System. Multiple-Choice Questions
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 18 The Urinary System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The urinary system A) regulates plasma concentrations of electrolytes. B) regulates blood
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 18 The Urinary System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The urinary system A) regulates plasma concentrations of electrolytes. B) regulates blood
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
