Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 18 The Urinary System. Multiple-Choice Questions
|
|
|
- Francine Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 5e (Martini/Nath) Chapter 18 The Urinary System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The urinary system A) regulates plasma concentrations of electrolytes. B) regulates blood volume by removing RBCs from circulation. C) contributes to stabilizing blood ph. D) A and C only E) all of the above Learning Outcome: ) Organs of the urinary system that are involved with urine transport are the A) urethra and ureters. B) kidneys and bladder. C) ureters and kidneys. D) urethra and bladder. E) kidneys and urethra. Answer: A Learning Outcome: ) Using anatomical terminology, identify the correct order of words that make this a true statement: The kidney extends slightly more than the kidney. A) right; superiorly; left B) right; inferiorly; left C) left; superiorly; right D) left; inferiorly; right E) right; anteriorly; left Answer: C Learning Outcome: 18.1 Page 1 of 27
2 4) Urine is stored by the A) liver. B) urinary bladder. C) kidney. D) ureter. E) urethra. Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following is correct about the location of the kidney? A) There is one kidney deep to the liver. B) The kidneys are bilateral and retroperitoneal. C) The left kidney is lower than the right. D) The kidneys are in the anterior abdominal wall. E) all of the above Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following carries urine from the kidney to the bladder? A) small intestine B) prostate C) liver D) ureter E) urethra Learning Outcome: ) The kidneys are A) located in a position that is retroperitoneal. B) surrounded by a renal capsule. C) protected by the lower ribs of the rib cage. D) A and B only E) all of the above Learning Outcome: 18.1 Page 2 of 27
3 8) A pyelogram, an X-ray of the urinary system in which radio-opaque dye is injected into the urinary pathways, can be used to detect A) kidney stones. B) structural abnormalities of the kidney. C) obstruction of the ureters. D) tumors or growths in the urinary bladder. E) all of the above Answer: E Learning Outcome: 18.1 Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications 9) A renal corpuscle includes the A) glomerulus and glomerular capsule. B) glomerulus and renal tubule. C) glomerular capsule and renal tubule. D) renal tubule and collecting tubule. E) pyramid and glomerulus. Answer: A 10) The renal pyramid is A) the innermost layer of kidney tissue. B) a conical-shaped structure that is located in the renal medulla. C) an internal cavity lined by the fibrous capsule and located in the area of the hilus. D) a large branch of the renal pelvis. E) a knot of capillaries that lies within the renal corpuscle. 11) The innermost layer of kidney tissue is the A) renal cortex. B) renal medulla. C) major calyx. D) minor calyx. E) renal pelvis. Page 3 of 27
4 12) Cortical tissue located between renal pyramids is called A) medulla. B) renal columns. C) renal pelvises. D) nephrons. E) calyces. 13) Renal columns are A) internal cavities of the fibrous capsule located in the area of the hilus. B) the expanded ends of the ureters. C) the basic functional units of the kidney. D) located adjacent to interlobar vessels. E) conical-shaped structures that are located in the renal medulla. 14) Major calyces are A) large branches of the renal pelvis. B) expanded ends of nephrons. C) basic functional layers of the kidney. D) conical-shaped structures that are located in the renal medulla. E) the expanded ends of renal pyramids. Answer: A 15) The glomerular capsule and glomerulus make up the A) renal pyramid. B) loop of Henle. C) renal corpuscle. D) renal tubule system. E) collecting system. Answer: C Page 4 of 27
5 16) The expanded end of a nephron is the A) glomerulus. B) glomerular capsule. C) proximal convoluted tubule. D) distal convoluted tubule. E) loop of Henle. 17) A DCT is A) the expanded end of a nephron. B) a knot of capillaries that lies within the renal corpuscle. C) the portion of the nephron closest to the renal corpuscle. D) the portion of the nephron that attaches to the collecting duct. E) the horseshoe-shaped segment of the nephron. 18) The portion of the nephron that attaches to the collecting duct is the A) proximal convoluted tubule. B) loop of Henle. C) distal convoluted tubule. D) collecting duct. E) minor calyx. Answer: C 19) The portion of the nephron between the glomerular capsule and the nephron loop is the A) proximal convoluted tubule. B) renal corpuscle. C) distal convoluted tubule. D) collecting duct. E) minor calyx. Answer: A Page 5 of 27
6 20) The visceral epithelium of the glomerular capsule is the A) capillary endothelium. B) lamina densa. C) podocytes. D) basement membrane of the capillaries. E) capsular space. Answer: C 21) The renal tubule contains cells adapted for absorption by having A) cilia. B) microvilli. C) villi. D) flagella. E) all of the above 22) The following is a list of the blood vessels that carry blood to the kidney: 1. afferent arteriole 2. arcuate artery 3. interlobar artery 4. renal artery 5. glomerulus 6. interlobular artery 7. efferent arteriole 8. peritubular capillary The proper order in which blood passes through these vessels is A) 4, 6, 2, 3, 1, 5, 7, 8. B) 4, 3, 2, 6, 1, 5, 7, 8. C) 4, 3, 2, 6, 7, 5, 1, 8. D) 4, 6, 2, 3, 7, 5, 1, 8 E) 4, 3, 6, 2, 1, 5, 7, 8. Diff: 2 Page 6 of 27
7 23) Which of the following are too large to be filtered? A) amino acids. B) glucose. C) lipids. D) proteins. E) none of the above Skill Level: 2 Reviewing Concepts 24) The countercurrent mechanism functions in the A) nephron. B) renal corpuscle. C) glomerulus. D) loop of Henle. E) filtration unit. Learning Outcome: ) Reabsorption of glucose occurs mostly in the A) renal sinus. B) proximal convoluted tubule. C) distal convoluted tubule. D) nephron loop. E) renal corpuscle. Learning Outcome: ) Most hydrogen ions are secreted into the A) glomerular capsule. B) PCT. C) loop of Henle. D) DCT. E) collecting duct. Learning Outcome: 18.3 Page 7 of 27
8 27) The primary function of the proximal convoluted tubule is A) filtration. B) absorption of ions, organic molecules, vitamins, and water. C) secretion of acids and ammonia. D) secretion of drugs. E) adjustment of urine volume. Learning Outcome: ) The ability to form a concentrated urine depends on the regulation of the A) proximal convoluted tubule. B) collecting duct. C) distal convoluted tubule. D) loop of Henle. E) Bowman's capsule. Learning Outcome: ) The cells of the proximal convoluted tubule normally reabsorb A) approximately 60 percent of the volume of the filtrate produced in the renal corpuscle. B) virtually all of the glucose and other nutrients under normal conditions. C) cations such as sodium, calcium, and magnesium. D) anions such as bicarbonate, chloride, sulfate, and phosphate. E) all of the above Answer: E Learning Outcome: ) General characteristics of normal urine include A) specific gravity. B) bacteria. C) ph. D) A and B only E) A and C only Answer: E Learning Outcome: 18.3 Page 8 of 27
9 31) Which of the following is the lesser amount? A) the concentration of solute in the filtrate at the beginning of the loop of Henle B) the concentration of solute in the filtrate at the bottom of the descending limb of the nephron loop Learning Outcome: 18.3 Skill Level: 2 Reviewing Concepts 32) ADH promotes water reabsorption mainly through the wall of the A) loop of Henle. B) proximal convoluted tubule. C) distal convoluted tubule. D) collecting duct. E) minor calyx. 33) Which of the following is aldosterone able to affect? A) regulation of body fluid concentration B) regulation of body fluid volume C) removal of wastes D) ph regulation E) formation of plasma proteins Answer: A 34) When the level of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) increases, A) more urine is produced. B) less urine is produced. C) less water is reabsorbed by the nephron and collecting duct. D) the specific gravity of the urine decreases. E) more salt is secreted by the nephron. Page 9 of 27
10 35) In response to decreased levels of aldosterone, the kidneys could produce A) a larger volume of urine. B) urine with a higher concentration of sodium ions. C) urine with a lower concentration of potassium ions. D) urine with a lower specific gravity. E) urine with less urea. 36) The juxtaglomerular apparatus regulates the filtration rate by A) vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole. B) vasodilation of the afferent arteriole. C) vasoconstriction of the peritubular capillaries. D) vasodilation of the efferent arteriole. 37) The hormone ADH A) is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland in response to changes in blood osmolarity. B) stimulates the kidneys to retain sodium ions. C) stimulates water conservation at the kidneys. D) causes the kidneys to produce a large volume of urine. E) all of the above Answer: C 38) The amount of potassium secreted by the kidneys is regulated by A) ADH. B) aldosterone. C) parathormone. D) atrial natriuretic peptide. E) cortisol. Page 10 of 27
11 39) If the afferent arteriole becomes constricted, A) blood flow into the efferent arteriole will increase. B) GFR will decrease. C) GFR will increase. D) hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus will increase. E) the protein concentration in the filtrate will increase. Skill Level: 2 Reviewing Concepts 40) Factors that increase the secretion of ADH include A) increased concentration of sodium ions in the ECF. B) water deprivation. C) increased osmolarity of the ECF. D) decreased renal blood flow. E) all of the above Answer: E Skill Level: 2 Reviewing Concepts 41) If, through injury, the blood flow to the kidneys decreases, which of the following will occur? A) The renin-angiotensin system will be activated. B) Sodium reabsorption will be inhibited. C) There will be systemic vasodilation. D) Obligatory water reabsorption will decrease. E) The amount of ADH in the blood will decrease. Answer: A Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications 42) Management of renal failure involves restriction of water and salt intake and reducing caloric intake to a minimum; dietary proteins are also limited. This combination lessens the strain on the urinary system by A) minimizing volume of urine produced. B) altering the pigments produced. C) preventing the generation of large quantities of nitrogenous waste products. D) A and C only E) all of the above Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications Page 11 of 27
12 43) The micturition reflex center is located in the A) hypothalamus. B) medulla oblongata. C) pons. D) lumbar spinal cord. E) sacral spinal cord. Answer: E Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following is the most distal part of the male urethra? A) prostatic urethra B) membranous urethra C) penile urethra D) glandular urethra E) glans urethra Answer: C Learning Outcome: ) The ureters and urinary bladder are lined by A) stratified squamous epithelium. B) pseudostratified columnar epithelium. C) simple cuboidal epithelium. D) transitional epithelium. E) simple columnar epithelium. Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following is greater? A) the length of the urethra in males B) the length of the urethra in females Answer: A Learning Outcome: 18.5 Page 12 of 27
13 47) The term incontinence refers to the A) inability to void (expel) urine. B) inability to control urination. C) inability to control kidney function. D) process of urinating. E) process of urine production. Learning Outcome: ) The detrusor muscle A) moves urine through the ureters. B) compresses the urinary bladder and expels urine through the urethra. C) functions as the internal urinary sphincter. D) functions as the external urinary sphincter. E) is located in the renal pelvis. Learning Outcome: ) The intracellular fluid (ICF) is found in A) blood vessels. B) lymph. C) the cells of the body. D) the interstitial spaces. E) the cerebrospinal fluid. Answer: C Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following is considered transcellular fluid? A) interstitial fluid B) plasma C) cerebrospinal fluid D) intercellular fluid E) lymph Answer: C Learning Outcome: 18.6 Page 13 of 27
14 51) Movement of water between compartments is by A) diffusion. B) osmosis. C) active transport. D) pinocytosis. E) facilitated diffusion. Learning Outcome: ) Which compartment is the largest? A) lymph B) plasma C) interstitial fluid D) transcellular fluid E) cerebrospinal fluid Answer: C Learning Outcome: ) The most abundant cation in the ECF is A) chloride. B) potassium. C) sodium. D) bicarbonate. Answer: C 54) The principal cation in the ICF is A) sodium. B) potassium. C) calcium. D) magnesium. E) chloride. Page 14 of 27
15 55) When water is lost but electrolytes are retained, A) the osmolarity of the ECF falls. B) osmosis moves water from the ICF to the ECF. C) both the ECF and the ICF become more dilute. D) there is an increase in the volume of the ICF. E) all of the above 56) Hypoproteinemia could lead to A) a drastic increase in the osmolarity of the blood. B) a temporary increase in blood volume. C) decreased thirst. D) hypotension. E) activation of the renin-angiotensin mechanism. 57) Intracellular fluid contains high concentrations of A) chloride and potassium. B) potassium and phosphate. C) sodium and phosphate. D) potassium and sulfate. E) magnesium and bicarbonate. 58) When the level of sodium ions in the ECF increases, A) osmoreceptors swell. B) a person experiences an increased thirst. C) less ADH is released. D) there is an increase in the level of aldosterone. E) there is an decrease in the level of atrial natriuretic peptide. Page 15 of 27
16 59) When the amount of sodium ions in the ECF increases, A) osmoreceptors are stimulated. B) there is decreased thirst. C) ADH secretion decreases. D) aldosterone secretion increases. E) there is an increase in the volume of urine produced. Answer: A 60) Calcium homeostasis primarily reflects A) a balance between absorption in the gut and excretion at the kidneys. B) careful regulation of blood calcium levels by the kidneys. C) an interplay between parathormone and aldosterone. D) an interplay between reserves in the bone, the rate of absorption, and the rate of excretion. E) hormonal control of calcium reserves in the bones. 61) The thirst center is located in the A) thalamus. B) hypothalamus. C) midbrain. D) pons. E) medulla oblongata. 62) Dehydration would cause A) fluid to shift from the ECF to the ICF. B) decreased secretion of ADH. C) increased thirst. D) decreased levels of aldosterone. E) all of the above Answer: C Page 16 of 27
17 63) If excessive amounts of water are taken into the body, A) the release of ADH increases. B) osmoreceptors in the brain begin to swell. C) more water is reabsorbed from the renal tubule. D) the collecting duct becomes more permeable to water. E) none of the above 64) The primary stimulus in the blood for the secretion of aldosterone is A) rising potassium levels. B) falling potassium levels. C) rising sodium levels. D) falling sodium levels. E) none of the above 65) Ions normally found in urine and plasma include which of the following? A) chloride B) bicarbonate C) potassium D) sodium E) all of the above Answer: E 66) Dan has been lost in the desert for two days with very little water. As a result of this exposure, one would expect to observe A) elevated ADH levels. B) decreased blood concentration. C) normal urine production. D) increased blood volume. E) cells enlarged with fluid. Answer: A Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications Page 17 of 27
18 67) The most important factor affecting the ph of body fluids is the concentration of A) lactic acid. B) ketone bodies. C) organic acids. D) carbon dioxide. E) hydrochloric acid. 68) The most abundant intracellular mechanism for regulating ph is A) protein buffers. B) the carbonic acid-bicarbonate buffer system. C) the phosphate buffer system. D) changes in the rate and depth of breathing. E) all of the above Answer: A 69) Hypoventilation would cause A) respiratory acidosis. B) respiratory alkalosis. C) metabolic acidosis. D) metabolic alkalosis. E) none of the above Answer: A 70) In response to respiratory alkalosis, A) the respiratory rate increases. B) the tidal volume increases. C) the kidneys conserve bicarbonate. D) the kidneys secrete more hydrogen ions. E) the body retains more carbon dioxide. Answer: E Page 18 of 27
19 71) A person who suffers from emphysema can exhibit signs of A) respiratory acidosis. B) respiratory alkalosis. C) metabolic acidosis. D) metabolic alkalosis. E) none of the above Answer: A 72) A person who suffers from chronic diabetes can exhibit signs of A) respiratory acidosis. B) respiratory alkalosis. C) metabolic acidosis. D) metabolic alkalosis. E) none of the above Answer: C 73) A person who chronically consumes large amounts of antacids to settle an upset stomach may risk A) respiratory acidosis. B) respiratory alkalosis. C) metabolic acidosis. D) metabolic alkalosis. E) none of the above 74) Which of the following is an example of a physiologic buffer? A) bicarbonate ions B) phosphate ions C) proteins D) renal mechanisms E) none of the above Page 19 of 27
20 75) Acid-base buffer systems minimize ph changes by A) converting weak acids to strong acids. B) converting strong acids to weak acids. C) causing breathing rate to increase. D) excreting hydrogen ions in the urine. E) a decrease in the net glomerular filtration pressure. 76) Ingestion of sodium bicarbonate to relieve indigestion may lead to A) metabolic acidosis. B) metabolic alkalosis. C) respiratory acidosis. D) respiratory alkalosis. Skill Level: 2 Reviewing Concepts Matching Questions 1) Match the region of the nephron in the first column with its primary function in the second column. 1. renal corpuscle A. conduction of urine to minor calyx 2. distal convoluted tubule B. reabsorption of ions, vitamins, water, and organics 3. papillary duct C. reabsorption of sodium ions and secretion of acids 4. collecting duct D. reabsorption of water and sodium ions 5. proximal convoluted E. filtration of plasma to initiate urine formation tubule Answer: 1-E, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D, 5-B Page 20 of 27
21 2) Match the acid-base disorder in the first column with its characteristic treatment in the second column. 1. metabolic acidosis A. improve ventilation 2. metabolic alkalosis B. administer bicarbonate 3. respiratory acidosis C. reduce respiratory rate, allow rise in PCO2 4. respiratory alkalosis D. no treatment below ph 7.55; above ph 7.55, administer ammonium chloride Answer: 1-B, 2-D, 3-A, 4-C Fill in the Blank Questions 1) Movement of fluid from the peritubular capillaries to the renal tubule is called. Answer: secretion 2) Water reabsorption occurs by the process of. Answer: osmosis Learning Outcome: ) ADH is produced by cells in the. Answer: hypothalamus 4) The osmoreceptors of the nephron are located in the. Answer: macula densa 5) Substances that combine with hydrogen ions in solution are called. Answer: bases Page 21 of 27
22 6) The most abundant source of hydrogen ions are those from. Answer: metabolism Essay Questions 1) David's grandfather suffers from hypertension. His doctor tells him that part of his problem stems from renal arteriosclerosis. Why would this cause hypertension? Answer: Renal hypertension would restrict blood flow to the kidneys and produce renal ischemia. Decreased blood flow and ischemia would trigger the juxtaglomerular apparatus to produce more renin, which would lead to elevated levels of angiotensin II and aldosterone. Angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction, increased peripheral resistance, and thus increased blood pressure. Aldosterone will promote sodium retention. This would lead to more water retained by the body and an increase in blood volume. This too would contribute to a higher blood pressure. Another factor to consider would be the release of more erythropoietin in response to tissue hypoxia. The erythropoietin would stimulate the formation of red blood cells, which would lead to increased blood viscosity and again contribute to the hypertension. Diff: 2 Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications 2) Sylvia is suffering from severe edema in her arms and legs. Her physician prescribes a diuretic (a substance that will increase the volume of urine produced). Why might this help to alleviate Sylvia's problem? Answer: Increasing the volume of urine produced would decrease the total blood volume of the body. This in turn would lead to a decreased blood hydrostatic pressure. Edema is frequently the result of hydrostatic pressure of the blood exceeding the opposing forces at the capillaries in the affected area. Depending on the actual cause of the edema, decreasing the blood hydrostatic pressure would decrease edema formation and possibly cause some of the fluid to move from the interstitial space back to the blood. Diff: 2 Learning Outcome: 18.6 Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications 3) Fred suffers from chronic emphysema. Blood tests show that his blood ph is normal but his bicarbonate levels are elevated significantly. How can this be? Answer: As long as the ratio of bicarbonate ion to carbonic acid is 20:1, the ph of body fluids will remain normal. Since Fred's condition is chronic (long term), his body has compensated for the excess carbonic acid (the result of hypercapnia due to poor ventilation) by increasing the amount of bicarbonate to match the elevated level of acid. This process involves the kidneys, where some of the excess carbon dioxide is converted into carbonic acid and the carbonic acid is allowed to dissociate. The hydrogen ions are secreted, and the newly formed bicarbonate is conserved to maintain a proper buffering capacity. Diff: 2 Skill Level: 3 Critical Thinking & Clinical Applications Page 22 of 27
23 Labeling Exercises Using the figure above, identify the labeled part. 1) Label A: Answer: Cortex 2) Label B: Answer: Medulla 3) Label C: Answer: Renal sinus Page 23 of 27
24 4) Label D: Answer: Renal pelvis 5) Label E: Answer: Hilus 6) Label F: Answer: Renal papilla 7) Label G: Answer: Ureter 8) Label H: Answer: Renal capsule 9) Label I: Answer: Renal columns 10) Label J: Answer: Minor calyx 11) Label K: Answer: Major calyx Page 24 of 27
25 12) Label L: Answer: Renal pyramids 13) Label M: Answer: Nephron loop 14) Label N: Answer: Renal corpuscle 15) Label O: Answer: Proximal convoluted tubule 16) Label P: istal convoluted tubule 17) Label Q: Answer: Collecting duct 18) Label R: Answer: Superior margin of hilus 19) Label S: Answer: Inferior margin of hilus Page 25 of 27
26 20) Label T: Answer: Ureter 21) Label U: Answer: Renal papilla 22) Label V: Answer: Renal capsule 23) Label W: Answer: Renal columns 24) Label X: Answer: Minor calyx 25) Label Y: Answer: Major calyx 26) Label Z: Answer: Renal pelvis 27) Label AA: Answer: Renal sinus Page 26 of 27
27 28) Label BB: Answer: Renal pyramids 29) Label CC: Answer: Cortex 30) Label DD: Answer: Medulla Page 27 of 27
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 25: Urinary System
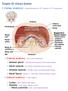 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #10: Chs. 26-28 DUE: (see course schedule) Assignments not turned in at the beginning of class will be accepted. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #10: Chs. 26-28 DUE: (see course schedule) Assignments not turned in at the beginning of class will be accepted. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Chapter 26 The Urinary System
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Unit 15 - The Urinary System 1
 Unit 15 - The Urinary System 1 I. Unit 15: The Urinary System A. Functions of the Urinary System 1. Elimination of waste products a) Nitrogenous wastes b) Toxins c) Drugs 2. Regulate aspects of homeostasis
Unit 15 - The Urinary System 1 I. Unit 15: The Urinary System A. Functions of the Urinary System 1. Elimination of waste products a) Nitrogenous wastes b) Toxins c) Drugs 2. Regulate aspects of homeostasis
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Unit 15: The Urinary System
 Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
Unit 15: The Urinary System I. Functions of the Urinary System A. Elimination of waste products 1. Nitrogenous wastes 2. Toxins 3. Drugs B. Regulate aspects of homeostasis 1. Water balance 2. Electrolytes
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a.
 I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
I. Anatomy of the Urinary System A. Kidneys 1. Right lower than Left* 2. Retroperitoneal 3. Layers that secure kidneys in the abdominal cavity a. Renal fascia b. Perinephric fat (Adipose) capsule c. Fibrous
Urinary System Multiple Choice Practice Test. c. Kidneys have three protective layers d. The adrenal gland is located deep within the kidney
 Urinary System Multiple Choice Practice Test 1. Which of the following is a function of the urinary system? a. Regulates water b. Regulates balance of acids, bases, and electrolytes c. Filters waste from
Urinary System Multiple Choice Practice Test 1. Which of the following is a function of the urinary system? a. Regulates water b. Regulates balance of acids, bases, and electrolytes c. Filters waste from
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Histology / First stage The Urinary System: Introduction. Kidneys
 The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
The Urinary System: Introduction The urinary system consists of the paired kidneys and ureters, the bladder, and the urethra. This system helps maintain homeostasis by a complex combination of processes
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Concentration
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Chapter 24: The Urinary System
 Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Chapter 24: The Urinary System Overview of kidney functions n Regulation of blood ionic composition n Regulation of blood ph n Regulation of blood volume n Regulation of blood pressure n Maintenance of
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Waste. Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8. Urinary System. Urinary System. Nitrogenous Wastes. Nitrogenous Wastes 4/22/2016
 Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Waste Urinary System Anatomy Urinary Section pages 5-8 Metabolism produces waste products What is the primary waste product of cellular respiration? How does the body dispose of it? Urinary System Urinary
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
Excretion and Waste Management. Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski
 Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Waste Products & Kidney Function
 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
