SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Jerome Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies used riterion tht dopminergi neurons should hve wide spikes. We found signifint diversity in spike wveforms from identified dopminergi neurons (Fig. S4). There ws no signifint differene ross neuron types in spike durtion (ANOVA F 2,89 = 0.15, P > 0.7). We found tht Type I neurons (nd identified dopminergi neurons, when onsidered seprtely) hd lower seline firing rtes thn Types II or III neurons (Type II Type I men ± 95% CI, 6.73 ± 6.72 spikes/s, Tukey HSD test, P < 0.05; Type III Type I, ± 8.84 spikes/s, P < 0.01), lthough mny Types II nd III neurons hd low firing rtes (<10 spikes/s). Thus, mny identified dopminergi neurons in the present study would hve een missed using previous riteri. Supplementry note 2 Models of RPE typilly ssume two exittory inputs, those from rewrdprediting ues (CS) nd those from rewrd (US), in ddition to inhiitory inputs refleting rewrd expettion disussed ove (Fig. S12). Where do these exittory inputs ome from? Tht some dopminergi neurons respond preferentilly to rewrd (nd wekly to CS) rises the possiility tht these USpreferring neurons my provide other CSpreferring dopminergi neurons with the rewrd signls. If this is the se, these neurons should meet the following preditions. First, exittion of these neurons should use phsi exittion of other dopminergi neurons (the ones lulting RPE). Seond, these neurons should not reeive inhiitory inputs enoding rewrd expettion. First, we oserved tht the exittion of dopminergi neurons (using ChR2 stimultion in DATCre mie) did not use synpti exittion of dopminergi neurons (Fig. S6d). This result does not support the view tht lss of "rewrdoding" dopminergi neurons exites other "RPEoding" dopminergi neurons. Seond, the mgnitude of inhiition during rewrd omission ws s lrge in USpreferring dopminergi 1
2 neurons s in CSpreferring dopminergi neurons (Figs. 4, S8, S9). This does not support the view tht there is lss of dopminergi neurons tht purely enodes rewrd signls. These results suggest tht rewrdenoding neurons, s proposed in the models, re loted outside the. Similrly, lthough CSpreferring dopminergi neurons n, in priniple, provide exittory inputs to other dopminergi neurons, our results do not support this view, suggesting tht exittory inputs for CS lso ome from outside the. Supplementry note 3 Our experiments llow us to mp neuron's funtion onto the trnsmitter it releses. The perentge of Type I neurons (49/95, or 52%) is lose to the estimte of the perentge of dopminergi neurons in rt (5565%) 68. Furthermore, the unidentified Type I neurons showed similr tskrelted tivity to identified dopminergi neurons (Fig. S11,). Together with the oservtion tht Type I neurons, ut not Types II nd III neurons, responded to light stimultion in DATCre mie, this suggests tht unidentified Type I neurons were lso dopminergi (lthough we nnot rule out the possiility tht some Type I neurons were nondopminergi). The seond experiment showed tht identified GABAergi neurons were of Type II. The identity of Type III neurons remins to e determined. They my relese different neurotrnsmitter, suh s glutmte 14, ut we nnot rule out the possiility tht Type III neurons re GABAergi or dopminergi (lthough the ltter seems unlikely, given the high effiieny of ChR2 expression in dopminergi neurons throughout, regrdless of projetion trget; see Figs. S2, S3). 2
3 doi: /nture10754 r 1 r 2 Density Firing rte (spikes/s) r 1 d r 2 Firing rte (spikes/s) Density Firing rte (spikes/s) P(r 1 > riteri) uroc = 0.88 Time odour (s) uroc = P(seline > riteri) e uroc P(r 2 > riteri) P(seline > riteri) Time odour (s) uroc (vs. seline) 1 (Inrese) 0 (Derese) Figure S1. ROC nlysis., Rster plot from 15 trils of 149 igrewrd trils from dopminergi neuron. r 1 nd r 2 orrespond to two exmple 100ms ins., Averge firing rte of this neuron., Are under the reeiver operting hrteristi urve (uroc) for r 1, in whih the neuron inresed its firing rte reltive to seline. We ompred the histogrm of spike ounts during the seline period (dshed line) to tht during given in (solid line) y moving riterion from zero to the mximum firing rte (in this exmple, 68 spikes/s). We then plotted the proility tht the tivity during r 1 ws greter thn the riteri ginst the proility tht the seline tivity ws greter thn the riteri. The re under this urve quntifies the degree of overlp etween the two spike ount distriutions (i.e., the disriminility of the two). The histogrm in the top pnel is trunted t n ordinte vlue of 0.2 for disply purposes. d, Similr to (), ut for r 2, whih orresponds to n uroc vlue lose to 0.5 (i.e., tivity lose to seline). e, uroc response profile for the full durtion of the tsk, with r 1 nd r 2 indited y rrows. Shown elow re the het mp vlues, s depited in Fig
4 doi: /nture10754 DATCre DAPI TH ChR2EYFP VgtCre DAPI TH ChR2EYFP GAD65/67 ChR2EYFP TH % neurons 100 d 0 % ChR2EYFP mong TH neurons 50 µm ChR2EYFP GAD65/67 TH Figure S2. Effiient nd speifi expression of ChR2EYFP in dopminergi nd GABAergi neurons., Blue: DAPI (nuler mrker). Red: immunostining for TH (dopminergi neurons). Green: ChR2EYFP. Sle r is 50 μm., Colors s in ; White: immunostining for GAD65/67. Slies re from DATCre () or VgtCre () mie injeted with raav5chr2eyfp., Perentge of neurons leled for EYFPChR2 nd TH (n = 666 neurons in 2 mie). d, Perentge of neurons leled for EYFPChR2, TH nd GAD65/67 (n = 433 neurons in 2 mie). 4
5 doi: /nture10754 stritum d Distne from midline (mm) 40 P > BLA Fluoresene intensity 50 BLA Stritum 0 Trer TH ChR2EYFP mpfc 0 % ChR2EYFP mong tred DA neurons % ChR2EYFP mong TH mpfc 0 Tred Lterl Figure S3. ChR2 expression is uniform ross dopminergi neurons with different projetion trgets. A reent study found lower levels of DAT in dopminergi neurons projeting to prefrontl ortex, nuleus umens ore, nd solterl mygdl versus those projeting to lterl nuleus umens shell nd dorsolterl stritum16. Beuse Cre expression in the DATCre mouse is under the ontrol of the DAT gene promoter, this ould hve ised ChR2 expression towrd ells with high DAT promoter tivity. To onfirm tht our reordings were not ised towrd dopminergi neurons with prtiulr projetion trget, we injeted fluorogold, retrogrde trer, into the prefrontl ortex, stritum, or solterl mygdl in AAVFLEXChR2injeted DATCre mie, nd ounted the proportion of THexpressing neurons tht lso expressed fluorogold nd ChR2., Fluorogold tring from medil prefrontl ortex (mpfc, left), stritum (middle), nd solterl mygdl (BLA, right) with stins for ell nulei (ToPro3, lue), TH (red), ChR2EYFP (green), fluorogold (white), nd their overly. Sle rs: 1 mm (left) nd 50 μm (right)., The infetion effiieny of dopminergi neurons with identified projetion to mpfc, stritum nd BLA ws similr to the overll infetion effiieny mesured throughout (Fig. S2). The perentge of neurons tripleleled y trer, TH, nd ChR2EYFP ws similr ross projetion trget sites, suggesting tht virusmedited ChR2 expression did not preferentilly trget supopultion of dopminergi neurons (mpfc, n = 67, stritum, n = 145, BLA, n = 35)., Dopminergi neurons with high DAT expression re minly found in the lterl extent of 21, while low DAT expressing neurons re distriuted throughout the medil to lterl extent of. Consistent with the finding in (), the virl infetion effiieny ws similr long the medillterl xis of (n = 39). d, To evlute possile differenes in ellulr ChR2 expression levels, we mesured the reltive ChR2EYFP fluoresene intensity over kground in dopminergi neurons projeting to mpfc, BLA or stritum nd dopminergi neurons in the lterl (prrhil pigmented nuleus). ChR2EYFP expression ws similr in ll nlysed dopminergi neurons (n = 25 for eh ondition). 5
6 Pek mplitude wire 3 (mv) d 0 10 g Unit Men (ms) Pek mplitude wire 2 (mv) Spike Lteny P(spike) SD (ms) Frequeny (Hz) e P(spike) Spikes Frequeny (Hz) f Spike lteny (ms) Lteny (ms) Frequeny (Hz) k Spikes/s m GABAergi exmple 1 PC PC1 o PC3 l n Bseline spikes/s uroc (vs. seline) 1 (Inrese) 0 (Derese) Type I Type II Type III Spike durtion (ms) Time (ms) h Spike Lteny Men (ms) SD (ms) i P(spike) Frequeny (Hz) Time (ms) j Lteny (ms) Frequeny (Hz) Dopminergi GABAergi 0.2 mv 1 ms Figure S4. Identifition of lightresponsive neurons., Isoltion of the neuron in Fig. 3. Binned stterplot shows pek mplitude of spike wveforms from two wires of the tetrode. Isolted unit is the upper luster. The lower luster is noise., Proility of spike (for the seond through tenth pulses in eh trin) s funtion of stimultion frequeny for this neuron., Spike lteny reltive to light onset for this neuron. d, Histogrm of men (left) nd SD (right) spike lteny to light stimultion for 26 identified dopminergi neurons. e, Proility of spike s funtion of stimultion frequeny for eh dopminergi neuron (grey) nd the men ross dopminergi neurons (yn). f, Men ± SEM spike lteny s funtion of stimultion frequeny. g, Response from GABAergi neuron to 5 repetitions of 10 Hz (left) or 20 Hz (right) light stimultion (yn rs). Tiks represent spikes. h, Histogrm of men (left) nd SD (right) spike lteny to light stimultion for 17 identified GABAergi neurons. i, Proility of spike s funtion of stimultion frequeny for eh GABAergi neuron (grey) nd the men ross GABAergi neurons (yn). j, Men ± SEM spike lteny s funtion of stimultion frequeny. k, Response pttern of n exmple identified GABAergi neuron. l, Temporl response profiles of identified GABAergi neurons. Conventions re s in Fig. 2. m, The first three prinipl omponents of the uroc urves of ll neurons from Fig. 2 (smll points) nd from identified GABAergi neurons (lrge points), using the model fit from Fig. 2. Eh GABAergi neuron fell within 95% onfidene intervls of the Type II luster defined in DAT Cre mie. n, Bseline firing rte vs. spike durtion for neurons of eh type with density histogrms in the mrgins. Spike durtion ws lulted s the time t whih the voltge ws signifintly different from seline (1 ms of prespike voltge). o, Men spontneous (lk) nd lightevoked (yn) spike wveforms from 26 identified dopminergi neurons nd 17 identified GABAergi neurons. 6
7 Liks/s Liks/s Dy Figure S5., Liking ehviour from representtive experimentl session from VgtCre mouse. Blk rs indite CS nd US delivery. Shded regions round lik tres denote SEM., men ± SEM liks during the dely etween CS nd US s funtion of dys of the experiment ross VgtCre nimls. 7
8 d % hnge fter irpuff Firing rte (spikes/s) Type I % hnge fter light % hnge fter rewrd omission Big rewrd Smll rewrd Nothing Punishment % hnge fter light 4 Time (s) CS US index % hnge fter light Type I Type II Type III DATCre P< VgtCre % hnge fter light % hnge fter light % hnge fter light Figure S6. Puttive synpti effets of ChR2 stimultion., Firing rtes from Type I neuron in VgtCre mouse., Response of the neuron to 12 trils of 10 Hz light pulses (yn rs). The neuron ws inhiited y GABAergi stimultion., Stter plots of % hnge (mximl mgnitude of hnge in the 520 ms following light pulses) in firing rte fter irpuff, rewrd omission, nd CSUS index vs. % hnge (mximl mgnitude of hnge) in firing rte fter light stimultion in 28 Type I neurons from VgtCre mie. The 11 neurons for whih light stimultion hd signifint effet re shown in lk (Wiloxon rnk sum test, P < 0.05). There ws signifint orreltion etween % hnge in firing rte fter irpuff nd % hnge in firing rte fter light stimultion ross the popultion (r = 0.59, P < 0.001) nd for the 11 neurons with signifint response to light stimultion (r = 0.86, P < 0.001). d, % firing rte hnges from seline in the 520 ms following ll light pulses in DATCre (top row) nd VgtCre (ottom row) mie for eh neuron type. 8
9 CS firing rte (spikes/s) Dely firing rte (spikes/s) US firing rte (spikes/s) GABAergi Dopminergi uroc (rewrded vs. omitted) Type III Punishment CS US index Nothing Smll rewrd Big rewrd uroc (seline vs. omitted) Punishment Nothing Smll rewrd CS US index Big rewrd d uroc (irpuff vs. seline) Punishment Rewrd omission Nothing Smll rewrd Big rewrd CS US index e uroc (rewrded vs. omitted) uroc (irpuff vs. seline) Figure S7., Men firing rtes for identified dopminergi (top row), GABAergi (middle row), nd Type III (ottom row) neurons during CS (left olumn), dely etween CS nd US (middle olumn), nd 500 ms fter US onset (right olumn). Eh neuron is plotted in grey with the men nd SEM overlid. Individul dopminergi neurons re plotted s funtion of their CSUS index, with red inditing lrge CSUS index (i.e., higher firing rte for CS vs. US), lue inditing smll CSUS index., uroc vlues for rewrd present ompred to rewrd sent versus CSUS index. There ws signifint negtive orreltion (r = 0.51, P < 0.05) tht disppered with leverge nlysis, inditing tht the orreltion ws driven mostly y one or two neurons., uroc vlues for seline ompred to rewrd sent versus CSUS index. There ws no signifint orreltion. d, uroc vlues for rewrd present ompred to rewrd sent versus uroc vlues for irpuff ompred to seline. There ws no signifint orreltion. e, uroc vlues for irpuff ompred to seline versus CSUS index. There ws no signifint orreltion. 9
10 Dopmine Type II Type III Rewrded uroc (vs. seline) 1.0 X X X 0.5 Omitted 0.0 Dopminergi neurons P< uroc (omitted vs. seline) Firing rte (spikes/s) Type III Dopmine Type II Type III uroc (rewrded vs. omitted) uroc (Rewrded vs. omitted) GABA 0.0 Figure S8. Response profiles of ll neurons during rewrdomitted trils., Firing ptterns during igrewrd trils in whih rewrd ws delivered (top) nd omitted (ottom). Firing rte hnges from seline were quntified using the uroc urve. Vlues were omputed etween eh neuron's tivity ross time nd its seline tivity. Yellow: inrese from seline, yn: derese from seline., Histogrm of uroc vlues during the rewrd omission period reltive to seline for dopminergi neurons (left) nd exmple Type III neuron nd histogrm of uroc vlues for rewrded versus omitted trils., Differene etween rewrded nd rewrdomitted trils for igrewrd trils for identified dopminergi neurons, unidentified DATCre Types II nd III neurons, nd identified GABAergi neurons. uroc vlues were omputed etween rewrdpresent nd rewrdsent trils. Eh row represents one neuron. Yellow: rewrded > omitted, yn: rewrded < omitted. 10
11 Type I Type II uroc (vs. seline) 1.0 Type III Figure S9. Response profiles of ll neurons during irpuff trils. uroc urves for punishment trils reltive to seline tivity. 11
12 d Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s) Type I: dopminergi Type I: unidentified Type II r CS r US r CS r US Big rewrd Smll rewrd Nothing Punishment f g h CS firing rte (spikes/s) CS slope Rewrd size (µl) Dopminergi P<0.05 CS slope US firing rte (spikes/s) Rewrd size (µl) Dopminergi US slope Spikes/s e Spikes/s Dopminergi GABAergi Spikes/s i US slope Dopminergi Dely slope GABAergi Dely slope Time of hlf mximum firing rte (s odour) Figure S10. Firing ptterns of more exmple neurons nd CS nd US responses in dopminergi neurons., Exmples of firing rtes from identified nd unidentified Type I neurons., Averge firing rtes from 26 identified dopminergi neurons nd 23 unidentified Type I neurons., Exmples of firing rtes from Type II neurons. d, Averge firing rtes from the lowest, middle, nd upper third of the CSUS index histogrm in Fig. 4 (reprodued here). e, The time of hlfmximum firing rte during igrewrd trils from odour onset to rewrd onset. Identified GABAergi neuron firing rtes slowly rose to pek, while identified dopminergi neuron firing rtes peked during the CS. f, Firing rtes for dopminergi neurons during CS nd US. g, Regression slopes of the firing rtes versus rewrd size during CS nd US for dopminergi neurons during CS nd. h, Slope vlues for eh dopminergi neuron during CS nd US. i, Slope vlues during the dely etween CS nd US. While the dely tivity of GABAergi neurons ws prmetrilly modulted y the vlue of rewrd, none of identified dopminergi neurons showed suh modultion. Unidentified Type II neurons showed similr modultion y rewrd vlue s GABAergi neurons (43/47 unidentified Type II neurons showed signifint delyperiod slope vlues nd 40/47 showed signifint differenes etween no, smll nd igrewrd trils, P < 0.001). 12
13 Dopminergi output CS Synpti inputs Cue Exittory Atul rewrd Rewrd expettion Exittory Inhiitory Expettion Inhiition Exittion PFC Ctx Str Amy Hipp RPE Expettion version Aversion LH Expettion DAergi GABAergi Expettion Str Type III PPN Figure S11. Proposed RPE model nd iruit digrm., A synpti model of RPE lultion (fter Houk et l., 1995). Dopminergi spikes re result of exittory inputs out rewrdprediting ues nd tul rewrd, nd inhiitory inputs out rewrd expettion., Shemti intertion of dopminergi (DAergi) nd GABAergi neurons. reeives rewrdexpettion input from prefrontl ortex (PFC, inluding oritofrontl ortex), stritum (str) nd pedunulopontine nuleus (PPN). reeives inputs out versive stimuli from lterl henul (LH). GABAergi neurons integrte informtion out rewrd expettion nd versive stimuli nd dopminergi neurons projet RPE signls to ortex (tx), stritum, mygdl (my), hippompus (hipp), nd elsewhere. Exmple firing rtes from eh type of neuron we reorded re shown. We hve omitted mny other res known to e importnt in this iruit (e.g., rostromedil tegmentl nuleus). See text for detils. 13
14 DAT RN SN SNr RN SN SNr RN SN SNr Vgt RN SN SNr RN SN SNr RN SN SNr Bregm: 3.00 mm Bregm: 3.50 mm Bregm: 3.60 mm 1 mm Figure S12. Histologil reonstrution of reording sites (red irles). Leled strutures: red nuleus (RN), sustnti nigr prs ompt (SN), sustnti nigr prs retiult (SNr),. 14
15 P(spike t 50 Hz light stimultion) ms Isoltion qulity (L rtio) 0.3 mv Figure S13. Dopminergi neurons follow highfrequeny light stimultion., Five onseutive trils of 50 Hz light stimultion from dopminergi neuron., Proility of following 50 Hz stimultion s funtion of isoltion qulity, mesured using the Lrtio. Smller vlues indite etter isoltion. The Lrtio for the exmple neuron is
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture72 Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Kepecs A., Uchid N., Zriwl H. nd Minen Z.F. Confidence estimtes in integrtor models of decision-mking Computing decision
doi:.38/nture72 Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Kepecs A., Uchid N., Zriwl H. nd Minen Z.F. Confidence estimtes in integrtor models of decision-mking Computing decision
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Opponent appetitive-aversive neural processes underlie predictive learning of pain relief
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
Adaptive echolocation behavior in bats for the analysis of auditory scenes
 9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
A role for inhibition in shaping the temporal flow of information in prefrontal cortex 2002 Nature Publishing Group
 A role for inhiition in shping the temporl flow of informtion in prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Grhm V. Willims nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Deprtment of Neuroiology, Yle University School of Medicine,
A role for inhiition in shping the temporl flow of informtion in prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Grhm V. Willims nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Deprtment of Neuroiology, Yle University School of Medicine,
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH
 r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
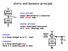 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
2. Hubs and authorities, a more detailed evaluation of the importance of Web pages using a variant of
 5 Web Serch Outline: 1. Pge rnk, for discovering the most ëimportnt" pges on the Web, s used in Google. 2. Hubs nd uthorities, more detiled evlution of the importnce of Web pges using vrint of the eigenvector
5 Web Serch Outline: 1. Pge rnk, for discovering the most ëimportnt" pges on the Web, s used in Google. 2. Hubs nd uthorities, more detiled evlution of the importnce of Web pges using vrint of the eigenvector
Orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala encode expected outcomes during learning
 Oritofrontl cortex nd solterl mygdl encode expected outcomes during lerning Geoffrey Schoenum 1, Andre A. Chi 2 nd Michel Gllgher 1 1 Deprtment of Psychology, Johns Hopkins University, 3400 North Chrles
Oritofrontl cortex nd solterl mygdl encode expected outcomes during lerning Geoffrey Schoenum 1, Andre A. Chi 2 nd Michel Gllgher 1 1 Deprtment of Psychology, Johns Hopkins University, 3400 North Chrles
VTA CRF neurons mediate the aversive effects of nicotine withdrawal and promote intake escalation
 CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
B 1995 Stockton Press All rights reserved /95 $12.00 S. cells (Kelland et al., 1990). These findings indicate that 5-HT
 Bridsh Jouml of Phmology (I995) 116, 1923 1931 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7-1188/95 $12. S Differentil effets of ute nd hroni fluoxetine dministrtion on the spontneous tivity of dopminergi
Bridsh Jouml of Phmology (I995) 116, 1923 1931 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7-1188/95 $12. S Differentil effets of ute nd hroni fluoxetine dministrtion on the spontneous tivity of dopminergi
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 49 11 June 29 doi:1.138/nture828 LETTERS Two types of dopmine neuron distinctly convey positive nd negtive motivtionl signls Msyuki Mtsumoto 1 & Okihide Hikosk 1 Midbrin dopmine neurons re ctivted
Vol 49 11 June 29 doi:1.138/nture828 LETTERS Two types of dopmine neuron distinctly convey positive nd negtive motivtionl signls Msyuki Mtsumoto 1 & Okihide Hikosk 1 Midbrin dopmine neurons re ctivted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
LETTERS. Neural correlates, computation and behavioural impact of decision confidence
 doi:.38/nture72 LETTERS Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Adm Kepecs, Noshige Uchid,2, Htim Zriwl,3 & Zchry F. Minen,4 Humns nd other nimls must often mke decisions on
doi:.38/nture72 LETTERS Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Adm Kepecs, Noshige Uchid,2, Htim Zriwl,3 & Zchry F. Minen,4 Humns nd other nimls must often mke decisions on
Differential neural coding of acoustic flutter within primate auditory cortex
 Differentil neurl coding of coustic flutter within primte uditory cortex Dniel Bendor & Xioqin Wng A sequence of coustic events is perceived either s one continuous sound or s strem of temporlly discrete
Differentil neurl coding of coustic flutter within primte uditory cortex Dniel Bendor & Xioqin Wng A sequence of coustic events is perceived either s one continuous sound or s strem of temporlly discrete
A CLASSIFICATION OF OPIATE RECEPTORS THAT MEDIATE
 Br. J. Phrm. (198), 69, 53-512 A CLASSIFICATION OF OPIATE RECEPTORS THAT MEDIATE ANTINOCICEPTION IN ANIMALS M.B. TYERS1 Phrmology Dept., Glxo Group Reserh Ltd., Wre, Hertfordshire 1 To investigte the opite
Br. J. Phrm. (198), 69, 53-512 A CLASSIFICATION OF OPIATE RECEPTORS THAT MEDIATE ANTINOCICEPTION IN ANIMALS M.B. TYERS1 Phrmology Dept., Glxo Group Reserh Ltd., Wre, Hertfordshire 1 To investigte the opite
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
Canceling actions involves a race between basal ganglia pathways
 Cnceling ctions involves rce etween sl gngli pthwys Roert Schmidt 1, Dniel K Leventhl, Nicols Mllet 1,3, Fujun Chen 1 & Joshu D Berke 1 npg 13 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Slient cues cn prompt
Cnceling ctions involves rce etween sl gngli pthwys Roert Schmidt 1, Dniel K Leventhl, Nicols Mllet 1,3, Fujun Chen 1 & Joshu D Berke 1 npg 13 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Slient cues cn prompt
Medial prefrontal cortical activity reflects dynamic re-evaluation during voluntary persistence
 Medil prefrontl corticl ctivity reflects dynmic re-evlution during voluntry persistence Joseph T McGuire & Joseph W Kle 215 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Deciding how long to keep witing for
Medil prefrontl corticl ctivity reflects dynmic re-evlution during voluntry persistence Joseph T McGuire & Joseph W Kle 215 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Deciding how long to keep witing for
Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABA A conductance in hippocampal interneurons
 Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Non-redundant odor coding by sister mitral cells revealed by light addressable glomeruli in the mouse
 Non-reunnt oor oing y sister mitrl ells revele y light ressle glomeruli in the mouse Ashesh K Dhwle,2, Akri Hgiwr 3, Upiner S Bhll 2, Venktesh N Murthy 3 & Dinu F Alenu 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve.
Non-reunnt oor oing y sister mitrl ells revele y light ressle glomeruli in the mouse Ashesh K Dhwle,2, Akri Hgiwr 3, Upiner S Bhll 2, Venktesh N Murthy 3 & Dinu F Alenu 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserve.
single smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig and rabbit jejunum
 BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
The sensory nature of mnemonic representation in the primate prefrontal cortex
 rticles The sensory nture of mnemonic representtion in the primte prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Mtthew N. Frnowicz nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Section of Neuroiology, Yle School of Medicine, New
rticles The sensory nture of mnemonic representtion in the primte prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Mtthew N. Frnowicz nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Section of Neuroiology, Yle School of Medicine, New
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Fast ensemble representations for abstract visual impressions
 Received Oct 2 Accepted Sep 2 Pulished Nov 2 Fst ensemle representtions for strct visul impressions Allison Ymnshi Lei, Ann Kosovichev 2 & Dvid Whitney DOI:./ncomms OPEN Much of the richness of perception
Received Oct 2 Accepted Sep 2 Pulished Nov 2 Fst ensemle representtions for strct visul impressions Allison Ymnshi Lei, Ann Kosovichev 2 & Dvid Whitney DOI:./ncomms OPEN Much of the richness of perception
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
The auditory cortex mediates the perceptual effects of acoustic temporal expectation
 A r t i c l e s co m p u tt i o n n d s y st e m s The uditory cortex medites the perceptul effects of coustic temporl expecttion Sntigo Jrmillo & Anthony M Zdor 211 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved.
A r t i c l e s co m p u tt i o n n d s y st e m s The uditory cortex medites the perceptul effects of coustic temporl expecttion Sntigo Jrmillo & Anthony M Zdor 211 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supplementary information to accompany the manuscript entitled:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementry informtion to ompny the mnusript entitled: A mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementry informtion to ompny the mnusript entitled: A mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity
