JUVENILE-ONSET RECURRENT RESPIratory
|
|
|
- Hubert Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of Dysplasia in Juvenile-Onset Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Javad A. Sajan, MD; Joseph E. Kerschner, MD; Albert L. Merati, MD; Vladimir Osipov, MD; Sara Szabo, MD, PhD; Joel H. Blumin, MD Objectives: To quantify the prevalence of dysplasia and to evaluate the impact of use of cidofovir in recurrent respiratory papilloma biopsy specimens obtained from a pediatric population. Design: Retrospective review of patient medical records and histopathologic test results from January 1, 1998, through December 31, Setting: Children s Hospital of Wisconsin. Patients: Patients with a history of operation treated for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Main Outcome Measures: The presence or absence of dysplasia identified in a papilloma specimen and patient characteristics, such as age of initial presentation, number of operations, tobacco exposure, treatment for reflux, and use of cidofovir, were quantified. Results: Treatment for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis was identified in 21 patients. Age at initial diagnosis ranged from 8 months to 14 years. A total of 123 recurrent respiratory papillomatosis specimens in 20 patients were identified. Dysplasia was seen in less than 1% of samples (1/123), which represents 5% of total patients. Seven patients (35%) received cidofovir treatment and none of them developed dysplasia. These data demonstrate a lack of correlation between cidofovir treatment and dysplasia, with the P value being nonsignificant (Fisher exact test, P=.4). Conclusion: Dysplasia is a rare event in pediatric recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, and there does not appear to be an association between the use of cidofovir and dysplastic changes. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;136(1):7-11 Author Affiliations: Departments of Otolaryngology & Communication Sciences (Drs Sajan, Kerschner, and Blumin) and Pathology (Drs Osipov and Szabo), Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee; and Department of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery, University of Washington, Seattle (Dr Merati). JUVENILE-ONSET RECURRENT RESPIratory papillomatosis (RRP) is generally characterized as an unpredictable, benign, yet debilitative disease of the aerodigestive mucosa caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The papillomata cause dysfunction and obstruction of the larynx (Figure 1) and trachea, which leads to significant morbidity that affects approximately 4.3 per infants and children in the United States. 1,2 In addition to surgical debulking, several adjunctive medicines are used to control juvenileonset RRP. Cidofovir (Vistide; Gilead Sciences, Forest City, California) is an injectable antiviral agent that has gained popularity for use in treatment of juvenileonset RRP. The medication is a cytosine nucleotide analog indicated for the treatment of cytomegalovirus-associated retinitis in patients with AIDS. Cidofovir is also known to have activity against HPV, varicella, herpes simplex, Epstein-Barr, and hepatitis B viruses. 3 Its mechanism of action is believed to involve inhibition of cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase. 4 However, the mechanism of action that contributes to broader antiviral activity of this drug has not been well elucidated. 5 Although the literature shows promise for the use of cidofovir in juvenile-onset RRP, questions remain about its potential carcinogenic adverse effects. 6 In a case report by Wemer et al, 5 progressive dysplasia was seen in a 28-year-old with respiratory papillomatosis treated with cidofovir. Histologic test results from this patient showed no dysplasia when only surgical debulking was performed; however, once the administration of cidofovir began, the patient developed severe disease. As highlighted in this report, the question of dysplastic transformation with the introduction of cidofovir remains relevant. In adults, RRP is believed to become malignant in 2% to 4% of cases 7 ; however, malignant transformation in the pediatric population has not been well characterized. The incidence of dysplasia in juvenile-onset RRP has only been recently described, 8 and therefore the nature of premalignant change remains in question. The purpose of this study is to investigate the prevalence of dysplasia in a group of pediatric patients with RRP and investigate any association with the use 7
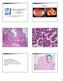
2 25 20 Age at Last Biopsy, y Patient No. Figure 1. Endoscopic view of a pediatric larynx with nearly confluent recurrent respiratory papilloma. of cidofovir. It is hypothesized that dysplastic and neoplastic transformation of juvenile-onset RRP is low with and without cidofovir treatment. METHODS Figure 2. Age at time of last biopsy. The asterisk above the bar represents patients who had more than 10 biopsy specimens taken during the study period. A retrospective review of medical records and histopathologic test results during the 10-year period from January 1, 1998, through December 31, 2008, was performed. This activity was approved by the institutional review boards of the Medical College of Wisconsin and the Children s Hospital of Wisconsin. All patients with a diagnosis of RRP who underwent surgical treatment were identified from a clinical database at the Children s Hospital of Wisconsin. Those who had pathologic specimens available were included in this study. Hospital medical records were reviewed. Demographic and clinical data, such as age at initial presentation, diagnosis, biopsy, and total number of operations, were quantified. Risk factors for dysplasia, such as exposure to tobacco, and symptoms or any treatment for laryngopharyngeal reflux were also recorded. Adjuvant treatment, including the use of cidofovir, was documented. Histopathologic evaluation was performed on hematoxylineosin stained sections with a microscope (BX51; Olympus Imaging Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) in a masked fashion by a board-certified pathologist. A subset of specimens was additionally reviewed by 2 secondary board-certified pathologists (V.O. and S.S.S.) for internal validity. Features evaluated included extent of mitotic activity, level of mitotic figures in relation to epithelial height, (absence of) abnormal mitotic figures, degree and extent of basal cell hyperplasia, disorderly maturation, presence or absence of maturation on surface, nuclear abnormalities (increased nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, hyperchromasia, pleomorphism, and altered polarity), extent of classic koilocytotic cytoatypia, further features associated with HPV effect (extent of binucleation or multinucleation and dyskeratosis), and features of metaplasia (residual respiratory epithelial features in portions of squamous papilloma). Dysplasia was defined as an absence of maturation above the basal cell layer. It is present when the cells above the basal cell layer continue to have a high nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and lack nuclear polarization. The presence of mitoses outside the basal cell epithelium was also considered a feature of dysplasia and ascertained. When these changes are present within the lower one-third of the epithelium, dysplasia was rated as low grade. Moderate-grade dysplasia is present when these changes are present within two-thirds of the epithelium. High-grade dysplasia is defined as the absence of cellular maturation within the entire thickness of the epithelium. Our hypotheses were tested with a 2 or Fisher exact test. P.05 was considered statistically significant to reject the null hypothesis. RESULTS Treatment for RRP was identified in 21 patients. Age at initial diagnosis ranged from 8 months to 14 years. A total of 362 operations were performed in this cohort; however, many of these did not have a pathologic specimen submitted. One patient did not have any pathologic specimens and therefore was left out of further data evaluation. The mean (SD) age at presentation was 3.5(3.6) years. The mean (SD) age at biopsy was 3.6(3.7) years, with a median of 2 and a mode of 1, which demonstrates a sample set skewed toward infancy. A total of 123 specimens from patients with RRP were identified. The mean (SD) number of specimens per child was 6.2(8.8); however, the median was 2 per child because 4 of our patients had 10 or more samples during the study period. The distribution of patient age at the time of the last biopsy and those with more than 10 specimens is displayed in Figure 2. Dysplasia was seen in less than 1% of samples (1/ 123), which represents 5% of the total patients. Figure 3 and Figure 4 are examples of papilloma histopathologic findings. The first masked re-review of specimens showed complete correlation to the original pathology report. The second pathologic review for internal validity showed complete agreement as well. The 1 patient with dysplasia had a total of 10 specimens during the study period. Only 1 of these demonstrated dysplasia, which was graded as focal moderate. The biopsy specimen with dysplasia was identified when the patient was 18 years old. Two subsequent biopsy specimens obtained on this patient within 2 years showed no evidence of significant dysplasia. No specimens showed severe dysplasia or carcinoma in situ. Multiple specimens from 1 patient exhibited features of metaplasia, which included occasional residual goblet cells in squamous epithelium typically in a back- 8
3 A B C D Figure 3. Typical examples of recurrent respiratory papilloma, with a range of human papillomavirus effects, such as basal cell hyperplasia, increased mitoses in the basal half of the epithelium, koilocytotic changes, nucleomegaly, and dyskeratotic cells. A-D, Hematoxylin-eosin stains (original magnification, 100 for A and 400 for B-D). B, An area of squamous metaplasia; the single arrows point to cilia of residual respiratory epithelium; the double arrows point to sheets of plasma cells in the papillary stroma. D, The arrows point to mitoses. ground of reactive epithelial features; only a few additional specimens from other patients showed similar features focally. Five specimens were either small or partly limited by laser cautery artifact, but all showed at least koilocytotic changes. In patients with multiple biopsy specimens, which typically clustered at young ages, the constellation of histologic features tended to remain similar over time, often with initial high mitotic activity, typically restricted to the basal third of the epithelium. Rare mitoses were seen up to half of the epithelial height in 23% of specimens but without associated worrisome features. Although in some patients koilocytotic features were well developed and extensive in early biopsy specimens, in others these became accentuated at later times. Subtle variations in the degree and/or extent of individual evaluated parameters, within the realm expected for HPV effect, were not infrequent in successive biopsy specimens. However, no consistent pattern could be deciphered. Seven patients (35%) received cidofovir treatment during the study. Dosage ranged from 0.2 to 3 ml of cidofovir solution injected permucosally and intralesionally at the time of operative management. The concentration of the solution ranged from 5 to 10 mg/ml, with most patients receiving a solution of 7.5 mg/ml. One patient received 55 injections during the study period. Patients who received cidofovir tended to have greater disease burden (as defined by the volume of papilloma and frequency of return to the operating room) than those who did not. Those who received cidofovir had an operative frequency of approximately 3 to 15 times per year, whereas those who did not receive cidofovir had frequencies of approximately 1 to 5 times per year. No patient who had been treated with cidofovir developed dysplasia. These data demonstrate a lack of correlation between cidofovir treatment and dysplasia, with the P value being nonsignificant (Fisher exact test, P=.4). With respect to other adjuvant therapy, 2 patients (10%) received the mumps vaccine and 1 (5%) received photodynamic therapy. The single dysplastic specimen came from the patient who had undergone photodynamic therapy. Three patients (15%) were treated for laryngopharyngeal reflux with either a histamine 2 -blocker or a proton pump inhibitor. Two patients (10%) had secondhand tobacco exposure and none of these had dysplasia. Neither reflux nor tobacco exposure was associated with dysplasia (χ 2 test, P=.025); however, the power of this statistic is admittedly weak. 9
4 A B Figure 4. Focal moderate dysplasia, with disorderly maturation extending into the upper half of the epithelium and occasional dysplastic nuclei, still with maturation at the surface. A and B, Hematoxylin-eosin stains (original magnification, 400). The double arrows indicate the basal layer, and there are rare mitoses close to the surface. A, The single arrow points to a mitotic figure relatively close to the surface. B, The asterisk indicates nucleomegaly close to the surface. COMMENT Tissue infection with HPV is well known to be associated with epithelial proliferation, atypia, dysplasia, and neoplastic transformation. 9 This has been most classically characterized in dysplastic transformation of the uterine cervix. Both HPV-16 and HPV-18 are the primary high-risk subtypes for malignant transformation, and HPV-6 and HPV- 11 are the low-risk HPV subtypes. Most laryngeal papilloma cases occur because of infection with subtypes 6 and 11, and therefore these cases are typically considered low risk formalignancypotential. 10 Ourstudydemonstratesthatdysplasia in juvenile-onset RRP, a known HPV infection, is rare and confirms data published recently by Lindsay et al. 8 The authors had evaluated 95 specimens from 17 pediatric patients, 7 of whom had received cidofovir adjuvant treatment and showed no dysplasia in their specimens. Our group recently reported 11 a review of adult-onset RRP biopsy specimens. Across 2 institutions, we found dysplasia in 13% of specimens and 22% of patients. We found no correlate to dysplasia and exposure to potential mutagenic agents, including cigarette smoking and cidofovir, in this adult study. InanotherreviewofRRPanddysplasia,Johnsonetal 12 noted a dysplasia rate of 55%. These studies imply that dysplasia is a much more frequent finding in adult patients. Why then is juvenile-onset RRP different? Adult-onset RRP is thought to develop either after reactivation of a latent infection or after a newly acquired infection. Juvenile-onset RRP is considered to occur after HPV exposure at birth, with maternal-to-fetal transmission that occurs from direct contact of the infant to the birth canal in mothers with condylomata. 10 This concept of vertical transmission via direct contact during the birth process, however, has been debated in the literature because there have also been cases of juvenile-onset RRP occurring in those who have been delivered by cesarean section. It has been hypothesized that inoculation alone with HPV may not be enough to cause the clinical disease of RRP. An underlying immunodeficiency has long been postulated. 4 In many children, the disease subsides with maturity, and many adults with the disease have no prior history of childhood illness. 13 Does this gradual maturity of the immune system clear the virus? Unfortunately, no long-term studies of biopsy evaluation have been performed in those in whom clinical disease has cleared, and it remains unknown whether the virus is eradicated or whether some type of immune tolerance develops. A long-term study 14 of patients with juvenile-onset RRP with tissue analysis after clinical resolution could provide answers to these questions, which may be especially important as we enter an era of the quadrivalent HPV vaccine, of which use in the treatment or prevention of RRP is being considered. 10
5 Another difference between pediatric and adult populations is their exposure and longer time of exposure to potential carcinogens known to be associated with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and dysplasia. The patients in this current study had a median age of 2 years, which precludes any prolonged exposures. In addition, only 2 patients in this cohort had any documentation of exposure to secondhand smoke. In the previously reported assessment of adult patients, there existed a higher incidence of tobacco exposure for longer periods; however, this cohort also did not exhibit a correlation between tobacco exposure or advanced age and prevalence of dysplasia. 11 Cidofovir has shown promise in the treatment of juvenile-onset RRP and is part of the arsenal of adjuvant therapy for this disease. 6,15 There has been ongoing concern since the initial use of this medicine with respect to its own carcinogenic potential. Cidofovir was used in approximately one-third of the patients, and none of them developed dysplasia during the study period. There is a potential error in the conclusion of the articles by Wemer et al and others 5,6 that suggests a causative effect between the cidofovir treatments and subsequently observed dysplastic or neoplastic changes. Although this concept is important to highlight to the readership and practicing community, conclusions about cause and effect can be difficult to make on the basis of case reports. Furthermore, data from this and other recent studies show that dysplastic transformation is rare in RRP. A simpler conclusion may be that papilloma followed its natural history over time and developed these changes independently of external factors. Surgically, it remains a challenge to remove 100% of the affected laryngeal tissue, and in many cases, it simply may not even be the goal of the operation (ie, vocal vs airway restoration). If all grossly identified papillomas are removed during direct laryngoscopy, the assumption is that lesions recur at the periphery of the infected but grossly uninvolved mucosa or in grossly flat or nonpapillomatous but affected mucosa. If debulking is incomplete and a portion of the lesion is allowed to mature over years, it may seemingly progress rapidly and become dysplastic. The large number of masked reviewed pathologic specimens is a major strength of this article; however, it suffers from the typical deficiencies afforded to retrospective reviews, such as that of weakened statistical extrapolation toward the sampled population. No consistent data were obtained about HPV subtyping, and therefore any link between HPV subtype and dysplasia in juvenile-onset RRP cannot be made. In our pediatric practice, pathologic specimens are obtained at initial presentation and then sporadically, such as with a change in clinical presentation or papilloma burden. Only approximately 40% of the cases across the study period had any pathologic results to review, which possibly highlights a missed chance to obtain more data. In addition, our study population was skewed toward a young group, with a median age of 2 years. Perhaps if we continue to follow up some of these patients into adulthood, some would develop dysplasia. We anticipate a future study to evaluate these phenomena. The identification of factors associated with premalignant transformation in RRP warrants further investigation. In conclusion, juvenile-onset RRP is rarely associated with laryngeal epithelial dysplasia. Use of cidofovir does not seem to induce dysplastic changes in the HPVinfected laryngeal epithelium. Submitted for Publication: March 31, 2009; final revision received July 19, 2009; accepted September 2, Correspondence: Joel H. Blumin, MD, 9200 W Wisconsin Ave, Milwaukee, WI (jblumin@mcw.edu). Author Contributions: Drs Sajan, Kerschner, Merati, and Blumin had full access to all the data and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: Sajan, Kerschner, Merati, Szabo, and Blumin. Acquisition of data: Sajan, Kerschner, Osipov, Szabo, and Blumin. Analysis and interpretation of data: Sajan, Kerschner, Osipov, Szabo, and Blumin. Drafting of the manuscript: Sajan, Kerschner, and Blumin. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Sajan, Kerschner, Merati, Osipov, Szabo, and Blumin. Statistical analysis: Sajan, Kerschner, and Blumin. Obtained funding: Kerschner and Blumin. Administrative, technical, and material support: Sajan, Kerschner, Szabo, and Blumin. Study supervision: Sajan, Kerschner, Szabo, and Blumin. Financial Disclosure: None reported. Previous Presentation: This study was presented at the American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology Annual Meeting; May 24, 2009; Seattle, Washington. REFERENCES 1. Derkay CS. Task force on recurrent respiratory papillomas: a preliminary report. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1995;121(12): Reeves WC, Ruparelia SS, Swanson KI, Derkay CS, Marcus A, Unger ER. National registry for juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003;129(9): De Clercq E. Therapeutic potential of cidofovir (HPMPC, Vistide) for the treatment of DNA virus (i.e. herpes-, papova-, pox- and adenovirus) infections. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1996;58(1): Stamataki S, Nikolopoulos TP, Korres S, Felekis D, Tzangaroulakis A, Ferekidis E. Juvenile recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: still a mystery disease with difficult management. Head Neck. 2007;29(2): Wemer RD, Lee JH, Hoffman HT, Robinson RA, Smith RJ. Case of progressive dysplasia concomitant with intralesional cidofovir administration for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005;114(11): Snoeck R, Wellens W, Desloovere C, et al. Treatment of severe laryngeal papillomatosis with intralesional injections of cidofovir [(S)-1-(3-hydroxy-2- phosphonylmethoxypropyl)cytosine]. J Med Virol. 1998;54(3): Lee LA, Cheng AJ, Fang TJ, et al. High incidence of malignant transformation of laryngeal papilloma in Taiwan. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(1): Lindsay F, Bloom D, Pransky S, Stabley R, Shick P. Histologic review of cidofovirtreated recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2008; 117(2): Ho GYF, Bierman R, Beardsley L, Chang CJ, Burk RD. Natural history of cervicovaginal papillomavirus infection in young women. N Engl J Med. 1998;338 (7): Derkay CS, Wiatrak B. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a review. Laryngoscope. 2008;118(7): Blumin JH, Handler EB, Simpson CB, Osipov V, Merati AL. Dysplasia in adults with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: incidence and risk factors. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2009;118(7): Johnson JT, Barnes EL, Justice W. Adult onset laryngeal papillomatosis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1981;89(5): Hartley C, Hamilton J, Birzgalis AR, Farrington WT. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: the Manchester experience, J Laryngol Otol. 1994; 108(3): Freed GL, Derkay CS. Prevention of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: role of HPV vaccination. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70(10): Pransky SM, Albright JT, Magit AE. Long-term follow-up of pediatric recurrent respiratory papillomatosis managed with intralesional cidofovir. Laryngoscope. 2003;113(9):
Laryngeal Papillomatosis Associated Dysplasia in the Adult Population: An update on prevalence and HPV subtype
 Laryngeal Papillomatosis Associated Dysplasia in the Adult Population: An update on prevalence and HPV subtype Taryn Davids MD, Susan Muller DMD MS, Justin Wise PhD, Michael M Johns III MD, Adam M Klein
Laryngeal Papillomatosis Associated Dysplasia in the Adult Population: An update on prevalence and HPV subtype Taryn Davids MD, Susan Muller DMD MS, Justin Wise PhD, Michael M Johns III MD, Adam M Klein
Current diagnostic and management trends for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Damon A. Silverman a and Michael J. Pitman b
 Current diagnostic and management trends for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Damon A. Silverman a and Michael J. Pitman b Purpose of review The purpose of this review is to discuss recent literature
Current diagnostic and management trends for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Damon A. Silverman a and Michael J. Pitman b Purpose of review The purpose of this review is to discuss recent literature
British Association of Paediatric Otorhinolaryngology members experience with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
 International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2006) 70, 1183 1187 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl British Association of Paediatric Otorhinolaryngology members experience with recurrent respiratory
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2006) 70, 1183 1187 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl British Association of Paediatric Otorhinolaryngology members experience with recurrent respiratory
Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis
 Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Carla Giannoni, MD Associate Professor Pediatric Otolaryngology Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children s Hospital RRP (JORRP) Page 2 Page 2 xxx00.#####.ppt 7/16/2015
Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Carla Giannoni, MD Associate Professor Pediatric Otolaryngology Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children s Hospital RRP (JORRP) Page 2 Page 2 xxx00.#####.ppt 7/16/2015
OLAF YOU MUST HAVE A TALK AT MT
 OLAF YOU MUST HAVE A TALK AT MT ME.. SEVERE HPV INFECTION - RESPIRATORY PAPILLOMATOSIS. A CONTINUOS DILEMMA. Paula Sánchez-Moreno Pediatric Immunology, Reumatology and Infectious Diseases Unit Hospital
OLAF YOU MUST HAVE A TALK AT MT ME.. SEVERE HPV INFECTION - RESPIRATORY PAPILLOMATOSIS. A CONTINUOS DILEMMA. Paula Sánchez-Moreno Pediatric Immunology, Reumatology and Infectious Diseases Unit Hospital
EVectiveness of cidofovir intralesional treatment in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2011) 268:1305 1311 DOI 10.1007/s00405-011-1599-6 LARYNGOLOGY EVectiveness of cidofovir intralesional treatment in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Maigorzata Wierzbicka
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2011) 268:1305 1311 DOI 10.1007/s00405-011-1599-6 LARYNGOLOGY EVectiveness of cidofovir intralesional treatment in recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Maigorzata Wierzbicka
Human Papilloma Virus RRP. Epidemiology. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Update 11/12/2011
 Human Papilloma Virus Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Update Katherine C. Yung, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Laryngology Dept. of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery DNA virus 7,900 bp long
Human Papilloma Virus Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis Update Katherine C. Yung, MD Assistant Professor, Division of Laryngology Dept. of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery DNA virus 7,900 bp long
Kanazawa et al. SpringerPlus 2013, 2:153 a SpringerOpen Journal
 Kanazawa et al. SpringerPlus 2013, 2:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Rare case of malignant transformation of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis associated with human papillomavirus
Kanazawa et al. SpringerPlus 2013, 2:153 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Rare case of malignant transformation of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis associated with human papillomavirus
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
OTKA azonosító: Típus: K Vezető kutató: Gergely Lajos
 Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), mostly variant B reactivation in renal transplant patients has been published previously, but the pathogenetic role of HHV-6 variant A has not been clarified. During the project
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), mostly variant B reactivation in renal transplant patients has been published previously, but the pathogenetic role of HHV-6 variant A has not been clarified. During the project
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
IN SITUHYBRIDIZATION FOR HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS DNA IN SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS OF THE LARYNX AND
 POL J PATHOL 2010; 1: 32-36 IN SITUHYBRIDIZATION FOR HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS DNA IN SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS OF THE LARYNX AND INVERTED PAPILLOMAS OLGA STASIKOWSKA-KANICKA, MARIAN DANILEWICZ, MAŁGORZATA WĄGROWSKA-DANILEWICZ
POL J PATHOL 2010; 1: 32-36 IN SITUHYBRIDIZATION FOR HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS DNA IN SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMAS OF THE LARYNX AND INVERTED PAPILLOMAS OLGA STASIKOWSKA-KANICKA, MARIAN DANILEWICZ, MAŁGORZATA WĄGROWSKA-DANILEWICZ
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Pegylated interferon for treating severe recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in a child: case report
 DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2017.0031240317 CASE REPORT Pegylated interferon for treating severe recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in a child: case report Rebecca Maunsell I, Maria Angela Bellomo-Brandão
DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2017.0031240317 CASE REPORT Pegylated interferon for treating severe recurrent respiratory papillomatosis in a child: case report Rebecca Maunsell I, Maria Angela Bellomo-Brandão
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Nasal mucosal melanosis may act as a harbinger of melanoma: A case report
 Nasal mucosal melanosis may act as a harbinger of melanoma: A case report The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Nasal mucosal melanosis may act as a harbinger of melanoma: A case report The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Novel human papilloma virus (HPV) genotypes in children with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
 Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:1017 1021 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1174-y ORIGINAL PAPER Novel human papilloma virus (HPV) genotypes in children with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Ioannis N. Mammas & George
Eur J Pediatr (2010) 169:1017 1021 DOI 10.1007/s00431-010-1174-y ORIGINAL PAPER Novel human papilloma virus (HPV) genotypes in children with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Ioannis N. Mammas & George
Human Papillomavirus
 Human Papillomavirus Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of February 18, 2018 9:40 am Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and
Human Papillomavirus Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of February 18, 2018 9:40 am Dawn Palaszewski, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin
 The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin 24.06.15 Norman Barrett Smiles [A brief digression - Chair becoming
The Pathologist s Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Neoplasia in Barrett s Oesophagus Cian Muldoon, St. James s Hospital, Dublin 24.06.15 Norman Barrett Smiles [A brief digression - Chair becoming
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology
 New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Retrospective analysis of laser vs other therapeutic modalities for laryngeal papillomatosis: European multicenter study
 JBUON 2016; 21(5): 1274-1278 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Retrospective analysis of laser vs other therapeutic modalities for
JBUON 2016; 21(5): 1274-1278 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Retrospective analysis of laser vs other therapeutic modalities for
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
 SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
Done by khozama jehad. Neoplasia of the cervix
 Done by khozama jehad Neoplasia of the cervix An overview of cervical neoplasia very import. Most tumors of the cervix are of epithelial origin and are caused by oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus
Done by khozama jehad Neoplasia of the cervix An overview of cervical neoplasia very import. Most tumors of the cervix are of epithelial origin and are caused by oncogenic strains of human papillomavirus
CERVIX. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb.
 CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
Accepted 11 May 2006 Published online 4 October 2006 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: /hed.20491
 CLINICAL REVIEW Mark K. Wax, MD, Section Editor JUVENILE RECURRENT RESPIRATORY PAPILLOMATOSIS: STILL A MYSTERY DISEASE WITH DIFFICULT MANAGEMENT Sofia Stamataki, MD, 1 Thomas P. Nikolopoulos, MD, DM, PhD,
CLINICAL REVIEW Mark K. Wax, MD, Section Editor JUVENILE RECURRENT RESPIRATORY PAPILLOMATOSIS: STILL A MYSTERY DISEASE WITH DIFFICULT MANAGEMENT Sofia Stamataki, MD, 1 Thomas P. Nikolopoulos, MD, DM, PhD,
Recurrent Juvenile Onset Respiratory Papillomatosis
 Recurrent Juvenile Onset Respiratory Papillomatosis Andreas H. Groll, M.D. Infectious Disease Research Program Center for Bone Marrow Transplantation and Department of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology University
Recurrent Juvenile Onset Respiratory Papillomatosis Andreas H. Groll, M.D. Infectious Disease Research Program Center for Bone Marrow Transplantation and Department of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology University
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo. Case Discussions. 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC
 BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
BOSNIAN-TURKISH CYTOPATHOLOGY SCHOOL June 18-19, 2016 Sarajevo Case Discussions Prof Dr Sıtkı Tuzlalı Tuzlalı Pathology Laboratory 60 year old woman Routine gynecologic control LBC 1 2 Endometrial thickening
University of Groningen. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis San Giorgi, Michel
 University of Groningen Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis San Giorgi, Michel IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis San Giorgi, Michel IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Laryngoscopic Characteristics in Vocal Leukoplakia: Inter-rater Reliability and Correlation With Histology Grading
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Laryngoscopic Characteristics in Vocal Leukoplakia: Inter-rater Reliability and Correlation With Histology
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Laryngoscopic Characteristics in Vocal Leukoplakia: Inter-rater Reliability and Correlation With Histology
Effect of Acid and Pepsin on LPR-Sensitive Mucins In Vitro
 Novel Drug Targets for Reflux Disease Role of LPR in Injury and Disease is Controversial Nikki Johnston, Ph.D. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Novel Drug Targets for Reflux Disease Role of LPR in Injury and Disease is Controversial Nikki Johnston, Ph.D. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
HPV vaccination as preventive approach for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis - a 22-year retrospective clinical analysis
 Mauz et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2018) 18:343 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-018-3260-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access HPV vaccination as preventive approach for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
Mauz et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2018) 18:343 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-018-3260-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access HPV vaccination as preventive approach for recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
Human Papilloma Viruses HPV Testing and Treatment of STDs
 Human Papilloma Viruses HPV Testing and Treatment of STDs New York State Collaborative Efforts in Medical Evaluations of Child and Adolescent Sexual Offenses. Child and Adolescent Sexual Offense Post-Assault
Human Papilloma Viruses HPV Testing and Treatment of STDs New York State Collaborative Efforts in Medical Evaluations of Child and Adolescent Sexual Offenses. Child and Adolescent Sexual Offense Post-Assault
Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies. Agenda
 Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
SURGERY FOR PEDIATRIC SUBGLOTTIC STENOSIS: DISEASE-SPECIFIC OUTCOMES
 Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:2001 Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:2001 REPRINTED FROM ANNALS OF OTOLOGY, RHINOLOGY & LARYNGOLOGY December 2001 Volume 110 Number 12 COPYRIGHT 2001, ANNALS PUBLISHING COMPANY
Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:2001 Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110:2001 REPRINTED FROM ANNALS OF OTOLOGY, RHINOLOGY & LARYNGOLOGY December 2001 Volume 110 Number 12 COPYRIGHT 2001, ANNALS PUBLISHING COMPANY
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
University of Groningen. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Tjon-Pian-Gi, Robin Edward Adrianus
 University of Groningen Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Tjon-Pian-Gi, Robin Edward Adrianus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Tjon-Pian-Gi, Robin Edward Adrianus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Laryngeal sequelae of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis surgery in children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Laryngeal sequelae of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis surgery in children JULIANA SATO HERMANN 1, PAULO PONTES 2, LUC LOUIS MAURICE WECKX 3, REGINALDO FUJITA 4, MELISSA AVELINO 5,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Laryngeal sequelae of recurrent respiratory papillomatosis surgery in children JULIANA SATO HERMANN 1, PAULO PONTES 2, LUC LOUIS MAURICE WECKX 3, REGINALDO FUJITA 4, MELISSA AVELINO 5,
Accepted Manuscript. Low grade spindle cell sarcoma of the true vocal folds. Samuel R. Barber, Pavel Kopach, Elizabeth M. Genega, Thomas L.
 Accepted Manuscript Low grade spindle cell sarcoma of the true vocal folds Samuel R. Barber, Pavel Kopach, Elizabeth M. Genega, Thomas L. Carroll PII: S2468-5488(17)30121-2 DOI: 10.1016/j.xocr.2017.11.006
Accepted Manuscript Low grade spindle cell sarcoma of the true vocal folds Samuel R. Barber, Pavel Kopach, Elizabeth M. Genega, Thomas L. Carroll PII: S2468-5488(17)30121-2 DOI: 10.1016/j.xocr.2017.11.006
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals
 PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
Evaluation and Management of Head and Neck Cancer in Patients with Fanconi anemia David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Residency Site Director Weill Cornell Medical Center Associate Professor Division of Head
Laryngeal Papillomatosis: Molecular, Ultrastructural and Clinical Evaluation
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, June: 313-319, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Laryngeal Papillomatosis: Molecular, Ultrastructural and Clinical Evaluation AMR A. EL-BADRY, M.D.*; ISMAIL
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 1, June: 313-319, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Laryngeal Papillomatosis: Molecular, Ultrastructural and Clinical Evaluation AMR A. EL-BADRY, M.D.*; ISMAIL
p16 Cervical HISTOLOGY Histology Compendium & Staining Atlas
 p16 Cervical HISTOLOGY Histology Compendium & Staining Atlas Chapter 1: An Introduction to p16...... 3 Normal Cervical Epithelium and the Cell Cycle....4 HPV Infection and Cervical Disease......................................
p16 Cervical HISTOLOGY Histology Compendium & Staining Atlas Chapter 1: An Introduction to p16...... 3 Normal Cervical Epithelium and the Cell Cycle....4 HPV Infection and Cervical Disease......................................
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Pathology of bladder cancer in Egypt; a current study.
 Pathology of bladder cancer in Egypt; a current study. Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in urology By Mohamed Atef Mohamed Ahmed M.B.B.CH Supervised by Prof.Dr.: Omar Mohamed Abdel-
Pathology of bladder cancer in Egypt; a current study. Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in urology By Mohamed Atef Mohamed Ahmed M.B.B.CH Supervised by Prof.Dr.: Omar Mohamed Abdel-
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S.
 Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Head and Neck Cancer in FA: Risks, Prevention, Screening, & Treatment Options David I. Kutler, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
The surgical plane for lingual tonsillectomy: an anatomic study
 Son et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2016) 45:22 DOI 10.1186/s40463-016-0137-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The surgical plane for lingual tonsillectomy: an anatomic study
Son et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2016) 45:22 DOI 10.1186/s40463-016-0137-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The surgical plane for lingual tonsillectomy: an anatomic study
Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative breast lesions adjacent to malignancy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. IV. (Mar. 2014), PP 84-89 Immunohistochemical studies (ER & Ki-67) in Proliferative
Cancer in the United States, 2004
 Cancer in the United States, 2004 Five-year Cancer Survival Rates (%) US 1974-1998 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1974-1976 1983-1985 1992-1998 Prostate Lung Colon Breast Source: CA Cancer J Clin 2000;50:7-33
Cancer in the United States, 2004 Five-year Cancer Survival Rates (%) US 1974-1998 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1974-1976 1983-1985 1992-1998 Prostate Lung Colon Breast Source: CA Cancer J Clin 2000;50:7-33
Lung Cancer Risks. Cancer in the United States, Cancer Death Rates, US The Scheme: From Nicotine Addiction to Lung Cancer
 Cancer in the United States, 2004 Lung Cancer Risks Cigarette Smoking Environmental Tobacco Smoke Other Carcinogens Asbestos, Arsenic, Radon, Bis(chloromethyl) ether, Chromium, Foundry fumes, nickel, mustard
Cancer in the United States, 2004 Lung Cancer Risks Cigarette Smoking Environmental Tobacco Smoke Other Carcinogens Asbestos, Arsenic, Radon, Bis(chloromethyl) ether, Chromium, Foundry fumes, nickel, mustard
Biliary tract tumors
 Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Short Course 2010 Annual Fall Meeting of the Korean Society for Pathologists Biliary tract tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pathology, Yeungnam Univ. College of Medicine, Daegu,
Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
Index 179. Genital tract contaminants, 17, 20, 22, 150 papilloma virus-infected cells, 47 squamous cells, sources of, 7
 Index Accuracy of urinary cytology, 166 Acute inflammatory cells, 38 catheter sample, 39 herpes simplex infections, 44 carcinomas, 104, 105 non-viral inclusions, 52, 53 voided urine, 17 Adenocarcinoma
Index Accuracy of urinary cytology, 166 Acute inflammatory cells, 38 catheter sample, 39 herpes simplex infections, 44 carcinomas, 104, 105 non-viral inclusions, 52, 53 voided urine, 17 Adenocarcinoma
Ectopic salivary tissue of the tonsil: a case report
 International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2005) 69, 567 571 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl CASE REPORT Ectopic salivary tissue of the tonsil: a case report Jeffrey B. Wise a,b, Kriti Sehgal
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2005) 69, 567 571 www.elsevier.com/locate/ijporl CASE REPORT Ectopic salivary tissue of the tonsil: a case report Jeffrey B. Wise a,b, Kriti Sehgal
Cytyc Corporation - Case Presentation Archive - March 2002
 FirstCyte Ductal Lavage History: 68 Year Old Female Gail Index: Unknown Clinical History: Negative Mammogram in 1995 6 yrs. later presents with bloody nipple discharge Subsequent suspicious mammogram Suspicious
FirstCyte Ductal Lavage History: 68 Year Old Female Gail Index: Unknown Clinical History: Negative Mammogram in 1995 6 yrs. later presents with bloody nipple discharge Subsequent suspicious mammogram Suspicious
chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium
 chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium CHAPTER 1 All squamous cervical cancer (and probably all cervical adenocarcinoma) is associated with oncogenic HPV, and the absence
chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium CHAPTER 1 All squamous cervical cancer (and probably all cervical adenocarcinoma) is associated with oncogenic HPV, and the absence
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva, Report of two Cases with Malignant Transformation
 Journal of Clinical and Anatomic Pathology Case Report Open Access Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva, Report of two Cases with Malignant Transformation Nadereh Ghanee DMD, Selene Saraf
Journal of Clinical and Anatomic Pathology Case Report Open Access Proliferative Verrucous Leukoplakia of the Gingiva, Report of two Cases with Malignant Transformation Nadereh Ghanee DMD, Selene Saraf
HPV Epidemiology and Natural History
 HPV Epidemiology and Natural History Rachel Winer, PhD, MPH Associate Professor Department of Epidemiology University of Washington School of Public Health rlw@uw.edu Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA virus
HPV Epidemiology and Natural History Rachel Winer, PhD, MPH Associate Professor Department of Epidemiology University of Washington School of Public Health rlw@uw.edu Human Papillomavirus (HPV) DNA virus
THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS
 41 THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS T. J. DEELEY AND V. J. DESMET* From the Radiotherapy Department, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London, IF7.12, and the Department of Pathology, Louvain University,
41 THE CLASSIFICATION OF BLADDER TUMOURS T. J. DEELEY AND V. J. DESMET* From the Radiotherapy Department, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London, IF7.12, and the Department of Pathology, Louvain University,
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience
 Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas
 Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
PLEOMORPHIC ADENOMA ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR )
 ( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
( BENIGN MIXED TUMOR ) Grossly, the tumor is freely movable, solid, sometimes lobulated and occasionally cystic. If recurrent, multinodular masses are common. Histologically, within a fibrous capsule,
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2008 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review Craig S. Derkay, MD; Brian Wiatrak,
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2008 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis: A Review Craig S. Derkay, MD; Brian Wiatrak,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
COMPANION MEETING BREAST. Auditorium 11:15 1:00 am. Convenor: A/Professor Gelareh Farshid, SA Pathology, SA
 Australasian Division of the International Academy of Pathology Limited ABN 73 008 593 815 36 TH Annual Scientific Meeting Darling Harbour Convention Centre, Sydney, Australia June 3-5, 2011 COMPANION
Australasian Division of the International Academy of Pathology Limited ABN 73 008 593 815 36 TH Annual Scientific Meeting Darling Harbour Convention Centre, Sydney, Australia June 3-5, 2011 COMPANION
Case 1. Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno
 Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
Case 1 Pathology of gynecological cancer. What do we need to know (Case 1) Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia Locarno SAMO Interdisciplinary Workshop on Gynecological Tumors Lucern, October
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Dysphonia Panel: Benign Lesions. Learner Objectives. Panelists 7/31/2017
 Dysphonia Panel: Benign Lesions Jonathan M. Bock, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Laryngology & Professional Voice Department of Otolaryngology & Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin
Dysphonia Panel: Benign Lesions Jonathan M. Bock, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Laryngology & Professional Voice Department of Otolaryngology & Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions
 Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
Original Research Article A five year study on differential diagnosis of verruciform penile lesions S. Sujatha 1, V. Srinivas Kumar 2*, K. Durga 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Professor
Hiroyuki Hanakawa, Nobuya Monden, Kaori Hashimoto, Aiko Oka, Isao Nozaki, Norihiro Teramoto, Susumu Kawamura
 Accepted Manuscript Radiation-induced laryngeal angiosarcoma: Case report Hiroyuki Hanakawa, Nobuya Monden, Kaori Hashimoto, Aiko Oka, Isao Nozaki, Norihiro Teramoto, Susumu Kawamura PII: S2468-5488(18)30005-5
Accepted Manuscript Radiation-induced laryngeal angiosarcoma: Case report Hiroyuki Hanakawa, Nobuya Monden, Kaori Hashimoto, Aiko Oka, Isao Nozaki, Norihiro Teramoto, Susumu Kawamura PII: S2468-5488(18)30005-5
Statistics and Epidemiology Practice Questions
 1. Which of the following is not considered a measure of central tendency? a. Median b. Range c. Mode d. Average 2. Given the following set of values, what is the median? 4 5 9 3 8 3 7 1 5 3 a. 3 b. 5
1. Which of the following is not considered a measure of central tendency? a. Median b. Range c. Mode d. Average 2. Given the following set of values, what is the median? 4 5 9 3 8 3 7 1 5 3 a. 3 b. 5
Pathologic Characteristics of Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea: Prognostic Factors Based on an Analysis of 59 Cases
 Pathologic Characteristics of Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea: Prognostic Factors Based on an Analysis of 59 Cases The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Pathologic Characteristics of Resected Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Trachea: Prognostic Factors Based on an Analysis of 59 Cases The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Vital staining and Barrett s esophagus
 Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
HPV and PREGNANCY Arsenio Spinillo,, MD
 HPV and PREGNANCY Arsenio Spinillo,, MD University of Pavia, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, IRCCS Fondazione Policlinico San Matteo di Pavia Human Papilloma Virus HPV is a member of the Papovaviridae
HPV and PREGNANCY Arsenio Spinillo,, MD University of Pavia, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, IRCCS Fondazione Policlinico San Matteo di Pavia Human Papilloma Virus HPV is a member of the Papovaviridae
Middle ear squamous papilloma: A report of four cases analyzed by HPV and EBV in situ hybridization
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 7: 41-46, 2014 Middle ear squamous papilloma: A report of four cases analyzed by HPV and EBV in situ hybridization HAN ZHOU 1, ZHIBIN CHEN 1, WEIMING ZHANG 2 and GUANGQIAN XING 1 Departments
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 7: 41-46, 2014 Middle ear squamous papilloma: A report of four cases analyzed by HPV and EBV in situ hybridization HAN ZHOU 1, ZHIBIN CHEN 1, WEIMING ZHANG 2 and GUANGQIAN XING 1 Departments
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients
 HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients Financial Disclosure: None November 8, 2013 Steven J. Wang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
HPV and Head and Neck Cancer: What it means for you and your patients Financial Disclosure: None November 8, 2013 Steven J. Wang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN
 EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Multilevel airway obstruction including rare tongue base mass presenting as severe croup in an infant. Tara Brennan, MD 2,3
 Multilevel airway obstruction including rare tongue base mass presenting as severe croup in an infant Tara Brennan, MD 2,3 Jeffrey C. Rastatter, MD, FAAP 1,2 1 Department of Otolaryngology, Northwestern
Multilevel airway obstruction including rare tongue base mass presenting as severe croup in an infant Tara Brennan, MD 2,3 Jeffrey C. Rastatter, MD, FAAP 1,2 1 Department of Otolaryngology, Northwestern
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
HPV the silent killer, Prevention and diagnosis
 HPV the silent killer, Prevention and diagnosis HPV Human Papilloma Virus is a name given for a silent virus transmitted sexually most of the time, a virus that spreads in the name of love, passion, and
HPV the silent killer, Prevention and diagnosis HPV Human Papilloma Virus is a name given for a silent virus transmitted sexually most of the time, a virus that spreads in the name of love, passion, and
