Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
|
|
|
- Silvia Peters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 3: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research
2 Introduction to Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) Historical Background TLRs as the link between innate and adaptive immunity What kind of Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns do TLRs recognize What s known about TLR structure and activity The detailed signaling pathways which TLRs
3 Introduction to Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) The discovery of the Toll-like receptors 1985: Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard identified Toll genes (Toll = cool, weird in German) in Drosophila melanogaster as gene important in embryogenesis in establishing the dorsal-ventral axis. 1989: Janeway predicts that our immune system uses PAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) as tools to identify molecules that would always be associated with infection. The concept that immune systems decide when to initiate a response based on the microbial nature of the molecules encountered became known as the pattern recognition hypothesis 1994: Nomura et al. described the first reported human Toll-like receptor 1996: Jules Hoffmann et al. find that Toll has a role in the fly's immunity to fungal infection 1997: Janeway and Medzhitov discovered a human protein with structural similarity to drosophila Toll that could activate immune response genes in human cells (TLR4). 1998: Beutler discovered that a mouse strain with an altered response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (called LPS or endotoxin) was due to a mutation in the TLR4 gene. There are 11 TLR family members in human and 12 in mice. Each responds to a distinct set of microbial products. Because the specificity of Toll-like receptors (and other innate immune receptors) cannot easily be changed in the course of evolution, these receptors recognize molecules that are constantly associated with threats (i.e. pathogen or cell stress), that are not subject to mutation, and are highly specific to these threats (i.e. cannot be mistaken for self molecules).
4 Overview Article 1: A46R Inhibits multiple IL-1 induced signals Interacts with MyD88 and antagonizes MyD88-dependent signaling Targets the TIR domain-rich TLR4 signaling Antagonizes TRIF-dependent pathways (TLR3 signaling) Is expressed early during infection and contributes to VV virulence A46R and A52R are not functionally redundant (but cooperate in interfering with TLR3 signaling) Article 2: Imidazoquinoline-induced response is MyD88-dependent TLR7 -/- cells respond to CpG DNA = the TLR signaling is not compromised TLR7 -/- cells do not respond to imidazoquinoline (but TLR signaling is OK) Imidazoquinoline-induced signaling is TLR7-dependent In vivo Imidazoquinolines do not trigger an immune response in TLR7 -/- mice
5 Paper 1 Vaccinia virus protein A46R targets multiple Toll-like interleukin-1 receptor adaptors and contributes to virulence Journal of Experimental Medicine 201, pp (2005) March 21, 2005 Julianne Stack, Ismar R. Haga,Martina Schröder,Nathan W. Bartlett,Geraldine Maloney,Patrick C. Reading,Katherine A. Fitzgerald,Geoffrey L. Smith,and Andrew G. Bowie
6 Questions A. In Figure 2e in the paper, the authors change from HEK 293 cells to RAW cells. What might have motivated their choice? B. Why is studying TLR4 signaling using the chimeric protein CD4-TLR4 such a good / simple model system? C. If the authors already show by IP that TLR4, MAL and TRAM pull down A46R (Fig. 3b-d), why do they do an GST-pulldown in Fig. 3e? D. Do you consider the action of the A46R protein from Vaccina Virus to be a good example of immune evasion? (Which TIR-domain containing proteins does A46R interact with?)
7 Paper 2 Small anti-viral compounds activate immune cells via the TLR7 MyD88 dependent signaling pathway Nature Immunology 3, pp (2002) Published online: 22 January 2002; doi: /ni758 Hiroaki Hemmi, Tsuneyasu Kaisho, Osamu Takeuchi, Shintaro Sato, Hideki Sanjo, Katsuaki Hoshino, Takao Horiuchi, Hideyuki Tomizawa, Kiyoshi Takeda & Shizuo Akira
8 Questions A. What might have motivated the authors to study the pathways by which drugs like Imiquimod stimulate the immune system? (do they perhaps have unique tools?) B. Have the authors properly motivated their choice to make an TLR7 -/- mouse? C. Why might the authors have chosen to perform three different types of assays in Figure 3a,b and c and what does it tell you about the cell-types that they study? D. What is the function of the CpG control? Has the control been consistently used throughout the manuscript?
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
1. TLR. TLR Toll-like receptors. Toll Toll-like receptor, TLR TLR TLR TLR. type I TLR TLR. Toll
 54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Under the Radar Screen:
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Preparation: Details 2 papers per week, distributed the week
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Preparation: Details 2 papers per week, distributed the week
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Bruce A. Beutler and Jules A. Hoffmann. Ralph M. Steinman
 PRESS RELEASE 20-0-03 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided that The 20 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine shall be divided, with one half jointly to Bruce A. Beutler and Jules
PRESS RELEASE 20-0-03 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet has today decided that The 20 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine shall be divided, with one half jointly to Bruce A. Beutler and Jules
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
DOWNLOAD OR READ : LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE ENDOTOXIN INDUCES IL 18 VIA CD14 IN HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD MONONUCLEAR CELLS IN VITRO PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE ENDOTOXIN INDUCES IL 18 VIA CD14 IN HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD MONONUCLEAR CELLS IN VITRO PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 lipopolysaccharide endotoxin induces il 18
DOWNLOAD OR READ : LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE ENDOTOXIN INDUCES IL 18 VIA CD14 IN HUMAN PERIPHERAL BLOOD MONONUCLEAR CELLS IN VITRO PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 lipopolysaccharide endotoxin induces il 18
Innate Immunity Depends on Toll-Like Receptors
 Innate Immunity Depends on Toll-Like Receptors From flies to mammals, these proteins provide a first-line defense and are implicated in infectious and autoimmune diseases William Check omething about the
Innate Immunity Depends on Toll-Like Receptors From flies to mammals, these proteins provide a first-line defense and are implicated in infectious and autoimmune diseases William Check omething about the
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
 The Poxvirus Protein A52R Targets Toll-like Receptor Signaling Complexes to Suppress Host Defense Mary T. Harte, 1 Ismar R. Haga, 3 Geraldine Maloney, 2 Pearl Gray, 1 Patrick C. Reading, 3 Nathan W. Bartlett,
The Poxvirus Protein A52R Targets Toll-like Receptor Signaling Complexes to Suppress Host Defense Mary T. Harte, 1 Ismar R. Haga, 3 Geraldine Maloney, 2 Pearl Gray, 1 Patrick C. Reading, 3 Nathan W. Bartlett,
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Review Articles. Advances in Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 Review Articles Advances in Immunology I AN MACKAY, M.D., AND FRED S. ROSEN, M.D., Editors INNATE IMMUNITY RUSLAN MEDZHITOV, PH.D., AND CHARLES JANEWAY, JR., M.D. THE immune system has traditionally been
Review Articles Advances in Immunology I AN MACKAY, M.D., AND FRED S. ROSEN, M.D., Editors INNATE IMMUNITY RUSLAN MEDZHITOV, PH.D., AND CHARLES JANEWAY, JR., M.D. THE immune system has traditionally been
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Immune receptors Y Y. Multiple immune responses CLR TLR NLR ITAM RLR. C-type lectin. ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif
 C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Inflammatory pathways in acute kidney injury and exploring novel therapies. Vecihi Batuman, MD FASN Huberwald Professor of Medicine
 Inflammatory pathways in acute kidney injury and exploring novel therapies Vecihi Batuman, MD FASN Huberwald Professor of Medicine SoutheastLouisiana Veterans Health Care System OBJECTIVES 1. Review the
Inflammatory pathways in acute kidney injury and exploring novel therapies Vecihi Batuman, MD FASN Huberwald Professor of Medicine SoutheastLouisiana Veterans Health Care System OBJECTIVES 1. Review the
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Basic immunology. Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Review Toll-like receptor downstream signaling Taro Kawai 1 and Shizuo Akira 1,2
 Arthritis Research & Therapy Vol 7 No 1 Kawai and Akira Review Toll-like receptor downstream signaling Taro Kawai 1 and Shizuo Akira 1,2 1 ERATO, Japan Science and Technology Agency, Osaka, Japan 2 Department
Arthritis Research & Therapy Vol 7 No 1 Kawai and Akira Review Toll-like receptor downstream signaling Taro Kawai 1 and Shizuo Akira 1,2 1 ERATO, Japan Science and Technology Agency, Osaka, Japan 2 Department
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Roles of Toll-like receptors in innate immune responses
 REVIEW Roles of Toll-like receptors in innate immune responses Kiyoshi Takeda and Shizuo Akira* Department of Host Defense, Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, Osaka University, and Japan Science
REVIEW Roles of Toll-like receptors in innate immune responses Kiyoshi Takeda and Shizuo Akira* Department of Host Defense, Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, Osaka University, and Japan Science
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 8: Apoptosis Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Myxoma virus Poxvirus Infects rabbits
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 8: Apoptosis Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Myxoma virus Poxvirus Infects rabbits
Toll-like Receptor Signaling During Infection and Inflammation Prof. Luke O Neill
 Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid
Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid
Ch 12. Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses
 Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
LETTERS. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses
 doi:10.1038/nature04734 Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses Hiroki Kato 1,3 *, Osamu Takeuchi 1,3 *, Shintaro Sato 3, Mitsutoshi Yoneyama 4, Masahiro Yamamoto
doi:10.1038/nature04734 Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses Hiroki Kato 1,3 *, Osamu Takeuchi 1,3 *, Shintaro Sato 3, Mitsutoshi Yoneyama 4, Masahiro Yamamoto
Clinical Significance of Toll-Like Receptor and Toll-Like Receptor Blocker
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.14777/uti.2016.11.1.1 Urogenit Tract Infect 2016;11(1):1-6 Clinical Significance of Toll-Like Receptor and Toll-Like Receptor
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.14777/uti.2016.11.1.1 Urogenit Tract Infect 2016;11(1):1-6 Clinical Significance of Toll-Like Receptor and Toll-Like Receptor
This information is current as of January 11, Sharon L. McCoy, Stephen E. Kurtz, Carol J. MacArthur, Dennis R. Trune and Steven H.
 This information is current as of January 11, 2019. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Identification of a Peptide Derived from Vaccinia Virus A52R Protein That Inhibits Cytokine Secretion
This information is current as of January 11, 2019. References Subscription Permissions Email Alerts Identification of a Peptide Derived from Vaccinia Virus A52R Protein That Inhibits Cytokine Secretion
311 Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology
 311 Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology Editors R.W. Compans, Atlanta/Georgia M.D. Cooper, Birmingham/Alabama T. Honjo, Kyoto H. Koprowski, Philadelphia/Pennsylvania F. Melchers, Basel M.B.A.
311 Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology Editors R.W. Compans, Atlanta/Georgia M.D. Cooper, Birmingham/Alabama T. Honjo, Kyoto H. Koprowski, Philadelphia/Pennsylvania F. Melchers, Basel M.B.A.
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
 Differential Requirement for TANK-binding Kinase-1 in Type I Interferon Responses to Toll-like Receptor Activation and Viral Infection Andrea K. Perry, 1 Edward K. Chow, 2 Julia B. Goodnough, 1 Wen-Chen
Differential Requirement for TANK-binding Kinase-1 in Type I Interferon Responses to Toll-like Receptor Activation and Viral Infection Andrea K. Perry, 1 Edward K. Chow, 2 Julia B. Goodnough, 1 Wen-Chen
PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of TLR-4. By Christina, Ania and Xiaofu
 PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of TLR-4 By Christina, Ania and Xiaofu Introduction Macrophage PAMP Bacteria LPS Gram -ve LTA Gram +ve activation Clearance Macrophage PAMP Bacteria
PKR is required for macrophage apoptosis after activation of TLR-4 By Christina, Ania and Xiaofu Introduction Macrophage PAMP Bacteria LPS Gram -ve LTA Gram +ve activation Clearance Macrophage PAMP Bacteria
Heterogeneity of TLR-induced responses in dendritic cells: from innate to adaptive immunity
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Immunobiology 209 (2004) 191 198 www.elsevier.de/imbio REVIEW Heterogeneity of TLR-induced responses in dendritic cells: from innate to adaptive immunity Fabio Re a, *, Jack L. Strominger
ARTICLE IN PRESS Immunobiology 209 (2004) 191 198 www.elsevier.de/imbio REVIEW Heterogeneity of TLR-induced responses in dendritic cells: from innate to adaptive immunity Fabio Re a, *, Jack L. Strominger
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Where are we heading?
 Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 5: Where are we heading? Unit 5: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Section Lectures: Immunology/Virology Time: 9:00 am 10:00 am LRC 105 A & B
 Section Director: Cliff Bellone, Ph.D. Office: Doisy Hall - R 405 Phone: 577-8449 E-Mail: bellonec@slu.edu Lecturers: James Swierkosz, Ph.D. Office: Medical School Rm. 412 Phone: 577-8430 E-Mail: swierkoszje@slu.edu
Section Director: Cliff Bellone, Ph.D. Office: Doisy Hall - R 405 Phone: 577-8449 E-Mail: bellonec@slu.edu Lecturers: James Swierkosz, Ph.D. Office: Medical School Rm. 412 Phone: 577-8430 E-Mail: swierkoszje@slu.edu
PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether each of the following statements are true or false.
 MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
1. The barriers of the innate immune system to infection
 Section 3.qxd 16/06/05 2:11 PM Page 12 12 SECTION THREE: Fleshed out 1. The barriers of the innate immune system to infection Questions What are the three characteristics of the innate immune system? What
Section 3.qxd 16/06/05 2:11 PM Page 12 12 SECTION THREE: Fleshed out 1. The barriers of the innate immune system to infection Questions What are the three characteristics of the innate immune system? What
Scavenger Receptors and Innate Immunity to Fungal Pathogens
 Scavenger Receptors and Innate Immunity to Fungal Pathogens Terry K. Means Ph.D. Assistant Professor in Medicine Center for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard
Scavenger Receptors and Innate Immunity to Fungal Pathogens Terry K. Means Ph.D. Assistant Professor in Medicine Center for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard
Tissue-Specific mrna Expression Profiles of Human Toll-Like Receptors and Related Genes
 886 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(5) 886 892 (2005) Vol. 28, No. 5 Tissue-Specific mrna Expression Profiles of Human Toll-Like Receptors and Related Genes Masuhiro NISHIMURA* and Shinsaku NAITO Division of Pharmacology,
886 Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(5) 886 892 (2005) Vol. 28, No. 5 Tissue-Specific mrna Expression Profiles of Human Toll-Like Receptors and Related Genes Masuhiro NISHIMURA* and Shinsaku NAITO Division of Pharmacology,
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Toll-like receptors in innate immunity
 International Immunology, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 1 14 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxh186 ª 2005 The Japanese Society for Immunology Review Article Toll-like receptors in innate immunity Kiyoshi Takeda 1 and Shizuo
International Immunology, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 1 14 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxh186 ª 2005 The Japanese Society for Immunology Review Article Toll-like receptors in innate immunity Kiyoshi Takeda 1 and Shizuo
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Review Article Current Views of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 240365, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2010/240365 Review Article Current Views of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways Masahiro Yamamoto and Kiyoshi
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 240365, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2010/240365 Review Article Current Views of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling Pathways Masahiro Yamamoto and Kiyoshi
Overview: The immune responses of animals can be divided into innate immunity and acquired immunity.
 GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
GUIDED READING - Ch. 43 - THE IMMUNE SYSTEM NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted.
The recognition of microbial products by the host innate
 IL-10 Released by Concomitant TLR2 Stimulation Blocks the Induction of a Subset of Th1 Cytokines That Are Specifically Induced by TLR4 or TLR3 in Human Dendritic Cells 1 Fabio Re 2 * and Jack L. Strominger*
IL-10 Released by Concomitant TLR2 Stimulation Blocks the Induction of a Subset of Th1 Cytokines That Are Specifically Induced by TLR4 or TLR3 in Human Dendritic Cells 1 Fabio Re 2 * and Jack L. Strominger*
Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors
 Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors Min-Fu Tsan*,,1 and Baochong Gao*, *Research Service, VA Medical Center, Washington, DC; Department of Medicine, Georgetown University, Washington, DC; and Department
Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors Min-Fu Tsan*,,1 and Baochong Gao*, *Research Service, VA Medical Center, Washington, DC; Department of Medicine, Georgetown University, Washington, DC; and Department
Table S1. Primers used to quantitatively amplify the human mirnas precursors and indicated genes
 Table S1. Primers used to quantitatively amplify the human mirnas precursors and indicated genes Forward primer (5 3 ) Rervese primer (5 3 ) U6 CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT 5S TACGGCCATACCACCCTGAA
Table S1. Primers used to quantitatively amplify the human mirnas precursors and indicated genes Forward primer (5 3 ) Rervese primer (5 3 ) U6 CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT 5S TACGGCCATACCACCCTGAA
Writing Effective Grant Proposals
 WritingEffectiveGrantProposals SUPPLEMENTALHANDOUT EXERCISES (toaccompanypowerpointslidepresentation) PamelaDerish ScientificPublicationsManager DepartmentofSurgery,UCSF tel415.885 7686 Pamela.Derish@ucsfmedctr.org
WritingEffectiveGrantProposals SUPPLEMENTALHANDOUT EXERCISES (toaccompanypowerpointslidepresentation) PamelaDerish ScientificPublicationsManager DepartmentofSurgery,UCSF tel415.885 7686 Pamela.Derish@ucsfmedctr.org
Lecture 17: Attack by Complement and Counterattack by Microbes
 Lecture 17: Attack by Complement and Counterattack by Microbes 2 Review Concepts of Complement Complement was addressed in Lecture 3 Major first line of defense (innate immunity) Major functions: Opsonization
Lecture 17: Attack by Complement and Counterattack by Microbes 2 Review Concepts of Complement Complement was addressed in Lecture 3 Major first line of defense (innate immunity) Major functions: Opsonization
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
A Slfn2 mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence
 Supplementary Information A Slfn mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence Michael Berger, Philippe Kres, Karine Crozat, Xiaohong Li, Ben A. Croker, Owen
Supplementary Information A Slfn mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence Michael Berger, Philippe Kres, Karine Crozat, Xiaohong Li, Ben A. Croker, Owen
Review Article Toll-Like Receptors Dysregulation after Influenza Virus Infection: Insights into Pathogenesis of Subsequent Bacterial Pneumonia
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pulmonology Volume 2011, Article ID 142518, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/142518 Review Article Toll-Like Receptors Dysregulation after Influenza Virus Infection:
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Pulmonology Volume 2011, Article ID 142518, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/142518 Review Article Toll-Like Receptors Dysregulation after Influenza Virus Infection:
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Relative sizes of infectious agents
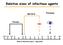 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Lessons from the Field: Parasite DNA Drives the Innate Immune Response to Malaria (it's not just the caiparinhas)
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms UMass Center for Clinical and Translational Science Research Retreat 2011 UMass Center for Clinical and Translational Science Research Retreat
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms UMass Center for Clinical and Translational Science Research Retreat 2011 UMass Center for Clinical and Translational Science Research Retreat
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Cytokine expression in Danio rerio (zebrafish) in response to TLR-7 agonist - Imiquimod. by Kevin Alan Paternostro A THESIS.
 Cytokine expression in Danio rerio (zebrafish) in response to TLR-7 agonist - Imiquimod by Kevin Alan Paternostro A THESIS submitted to Oregon State University University Honors College in partial fulfillment
Cytokine expression in Danio rerio (zebrafish) in response to TLR-7 agonist - Imiquimod by Kevin Alan Paternostro A THESIS submitted to Oregon State University University Honors College in partial fulfillment
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
IFNg. IFNg IL-5 IL-13 IL-17 IL-22. LTi NCR+ ILC3. IL-17 IL-22 IFNg
 Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
On the Discovery of the Dendritic Cell and Its Role in Adaptive Immunity
 Jake Noveck Queens College, Biology Senior Ralph M. Steinman, MD (January 14, 1943 September 30, 2011) On the Discovery of the Dendritic Cell and Its Role in Adaptive Immunity Every time that we breathe,
Jake Noveck Queens College, Biology Senior Ralph M. Steinman, MD (January 14, 1943 September 30, 2011) On the Discovery of the Dendritic Cell and Its Role in Adaptive Immunity Every time that we breathe,
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity
 Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
In other words. how to prevent David from killing Goliath. Tammy Rickabaugh, Ph.D. January 14, 2014
 In other words. how to prevent David from killing Goliath Tammy Rickabaugh, Ph.D. January 14, 2014 2011 Nobel Prize in Medicine IMMUNOLOGISTS!!!!!!! Bruce A. Beutler Jules A. Hoffman Ralph M. Steinman
In other words. how to prevent David from killing Goliath Tammy Rickabaugh, Ph.D. January 14, 2014 2011 Nobel Prize in Medicine IMMUNOLOGISTS!!!!!!! Bruce A. Beutler Jules A. Hoffman Ralph M. Steinman
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Viral Activation of Macrophages through TLR-Dependent and -Independent Pathways
 This information is current as of October 6, 2018. Viral Activation of Macrophages through TLR-Dependent and -Independent Pathways Lene Malmgaard, Jesper Melchjorsen, Andrew G. Bowie, Søren C. Mogensen
This information is current as of October 6, 2018. Viral Activation of Macrophages through TLR-Dependent and -Independent Pathways Lene Malmgaard, Jesper Melchjorsen, Andrew G. Bowie, Søren C. Mogensen
The Troll in Toll: Mal and Tram as bridges for TLR2 and TLR4 signaling
 The Troll in Toll: Mal and Tram as bridges for TLR2 and TLR4 signaling Frederick J. Sheedy 1 and Luke A. J. O Neill School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland Abstract: Signaling
The Troll in Toll: Mal and Tram as bridges for TLR2 and TLR4 signaling Frederick J. Sheedy 1 and Luke A. J. O Neill School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College, Dublin, Ireland Abstract: Signaling
Activation of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase by Gram-Negative Flagellin
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2001, p. 4424 4429 Vol. 69, No. 7 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4424 4429.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activation
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2001, p. 4424 4429 Vol. 69, No. 7 0019-9567/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.7.4424 4429.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Activation
APPLICATIONS. Updated: July 2015
 APPLICATIONS Updated: July 2015 1 Contents APPLICATIONS... 3 Principles of immunomodulation and immune stimulation in animals... 3 What is immune stimulation?... 3 Rationale for targeting the innate immune
APPLICATIONS Updated: July 2015 1 Contents APPLICATIONS... 3 Principles of immunomodulation and immune stimulation in animals... 3 What is immune stimulation?... 3 Rationale for targeting the innate immune
Role of Toll-Like Receptors in Pathogen Recognition
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2003, p. 637 646 Vol. 16, No. 4 0893-8512/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.4.637 646.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Role
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2003, p. 637 646 Vol. 16, No. 4 0893-8512/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.4.637 646.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Role
The Host Response: Toll Like Receptor Expression in Periprosthetic Tissues as a Biomarker for Deep Joint Infection
 The Host Response: Toll Like Receptor Expression in Periprosthetic Tissues as a Biomarker for Deep Joint Infection Cara Cipriano, MD, Aparna Maiti, PhD, Gregory Hale, MD, William A. Jiranek, MD. VCU Health
The Host Response: Toll Like Receptor Expression in Periprosthetic Tissues as a Biomarker for Deep Joint Infection Cara Cipriano, MD, Aparna Maiti, PhD, Gregory Hale, MD, William A. Jiranek, MD. VCU Health
HMGB1-TLR4 Interactions: Mediators of Kidney Lung Crosstalk?
 HMGB1-TLR4 Interactions: Mediators of Kidney Lung Crosstalk? Dept of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine The University of Tokyo Kent Doi, MD. PhD Organ crosstalk in AKI Grams ME, Rabb H. Kidney Int.
HMGB1-TLR4 Interactions: Mediators of Kidney Lung Crosstalk? Dept of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine The University of Tokyo Kent Doi, MD. PhD Organ crosstalk in AKI Grams ME, Rabb H. Kidney Int.
Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology
 Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology PJL:2011 Bacterial Overview: Morphology, Structure, Jargon General Features Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria Spirochaetes Firmicutes Actinobacteria No nuclear membrane
Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology PJL:2011 Bacterial Overview: Morphology, Structure, Jargon General Features Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria Spirochaetes Firmicutes Actinobacteria No nuclear membrane
Lung Reperfusion Injury
 Lung Reperfusion Injury Michael S. Mulligan, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Section of Thoracic Surgery Director, Lung Transplant Program University of Washington Medical Center Guiding Principles in
Lung Reperfusion Injury Michael S. Mulligan, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Section of Thoracic Surgery Director, Lung Transplant Program University of Washington Medical Center Guiding Principles in
