Hepatitis B Control. Table of Contents
|
|
|
- Loreen Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION GOALS DEFINITIONS CASE MANAGEMENT HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS... 5 TABLE 2: HEPATITIS B IMMUNE GLOBULIN... 6 HEPATITIS B IMMUNE GLOBULIN (HBIG) HEALTH TEACHING TO PREVENT TRANSMISSION OF HBV VACCINE ELIGIBILITY SEROLOGIC TESTING FOR HEPATITIS B IN SPECIFIC GROUPS BOOSTER DOSES AND RE-IMMUNIZATION INTERPRETATION OF TESTING RESULTS ISOLATED HEPATITIS B CORE ANTIBODY POSITIVE TEST RESULT AUTHORITY REFERENCES... 12
2 Page INTRODUCTION virus (HBV) infection is transmitted through exposure to infectious blood and body fluids. It is most commonly acquired through sexual contact, injection drug use, and perinatal exposure from mother to infant. 2.0 GOALS To reduce the annual incidence of hepatitis B virus infection reported in British Columbia by offering: A universal infant hepatitis B immunization program Immunization of all susceptible Grade 6 students Immunization of all individuals who are at high risk of becoming infected with HBV Immunization of close, non-immune contacts of persons who are acutely or chronically infected with HBV Universal screening of all pregnant women for, and screening for hepatitis Be antigen for women who are positive Assessment of the risk of infection for persons potentially exposed to HBV, and provision of post-exposure immunoprophylaxis as indicated Counselling for infected persons and their contacts 3.0 DEFINITIONS 3.1 Acute hepatitis B infection: Confirmed case: Presence of surface antigen and IgM class antibody to core antigen ( positive and anti-hbc IgM positive) OR Loss of over a period of 6 months in the context of a compatible clinical history or probable exposure OR Acute clinical illness 1 and positive (and anti-hav and anti-hcv ) when the test for IgM antibody to anti-hbc is not available 1 Acute clinical illness is characterized by a discrete onset of symptoms and jaundice or elevated serum aminotransferase levels.
3 Page 2 Probable case: Acute clinical illness in a client who is linked to a confirmed case 3.2 Chronic hepatitis B infection: Confirmed case: Persistence of positivity for more than 6 months. OR Presence of and anti-hbc IgG positive and anti-hbc-igm. 3.3 infection of undetermined status: Presence of with no other clinical or laboratory markers. 3.4 Contact: An individual who has had exposure to potentially infectious blood or body fluids of an HBV infected person Infective potential of blood or body fluids: blood contains the highest HBV titre of all bodily fluids and is the most important vehicle for transmission of infection. Semen and vaginal fluids have been implicated in sexual transmission. The following are considered potentially infectious: cerebrospinal, synovial, pleural, peritoneal, pericardial and amniotic fluids, and saliva. Feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine and vomitus are not considered potentially infectious, unless they contain blood. The risk of transmission from these fluids/materials is extremely low 3.5 Percutaneous exposure: Contact through the skin with blood of an HBV infected person, for example, through needlestick or other sharps injury, tattooing, body piercing, electrolysis, or acupuncture. Non-intact skin exposure: blood or body fluid comes into contact with a wound < 3 days old, or with skin having compromised integrity (e.g. dermatitis, abrasions, fresh cutaneous scratches, burns or other lesions). For human bites, the clinical evaluation of risk must include the possibility that the person bitten and the person who inflicted the bite were exposed to bloodborne pathogens (i.e. there is blood in the mouth of the biter or in the wound of the person bitten). 3.6 Mucosal exposure: Contact of the mucous membrane lining body cavities of eyes, nose, mouth, vagina, rectum or urethra with blood or body fluid of an HBV infected person.
4 Page Perinatal exposure: Infection of an infant at birth from an HBV infected mother. The likelihood of transmission of infection to the infant increases when the positive mother is also hepatitis Be antigen positive. 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT Confirm the diagnosis with the attending physician before contacting the client. For clients with a clinical presentation in the absence of available laboratory confirmation, discuss follow up with the Medical Health Officer (MHO) or delegate. Initiate a report in the Communicable Disease Surveillance System (CDSS) module of iphis. For an acute infection, obtain a history of risk factors/potential exposure for the six month period preceding serological diagnosis. Complete the Enhanced Surveillance Report and submit to BCCDC Hepatitis Services. If risk factors indicate the possibility of a transfusion transmissible infection, (where client has been donor or recipient) follow the reporting process in the Transfusion Transmissible Infections chapter of the Communicable Disease Control Manual. Identify case contacts in the 6 months prior to onset of infection. Initiate appropriate immunoprophylaxis of contacts. Ascertain hepatitis B vaccination status and/or whether anti-hbs level has been previously determined. Refer to Table 1: Post-Exposure Prophylaxis and Table 2: Immune Globulin Co-ordinate provision of hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG as required to all contacts Counsel case and contacts about minimizing further transmission of hepatitis B virus. Refer to section 6.0 entitled Health Teaching to Prevent Transmission of HBV. Arrange that a person with acute infection be retested at six months, to determine if they have become a chronic carrier. Report in iphis as chronic hepatitis B if this occurs, while maintaining the previous report of the acute infection.
5 Page HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT Distribution of HBIG is the responsibility of Canadian Blood Services. There may also be a designated depot for HBIG within a health region. If an individual or a physician informs the health unit of percutaneous or mucosal exposure and needs to obtain HBIG and/or hepatitis B vaccine, the following steps are recommended: Obtain details of exposure Determine testing requirements (see Table 1) and eligibility for HBIG and hepatitis B vaccine. Ask exposed person s physician to arrange testing of exposed person s/source s blood as indicated. Refer to the guidelines for Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Management and use the Hlth 2339 and Hlth 2340 forms for testing and follow-up. When HBIG is indicated, contact Canadian Blood Services or designated depot for health region. Arrange with the physician and the exposed person for the provision and administration of HBIG and/or hepatitis B vaccine.
6 Page 5 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Note: this table does not apply to immunocompromised persons; this group requires consultation with a physician specializing in infectious diseases. Vaccination history of exposed person Documented anti- HBs level ( 10 IU/L) on prior testing Unvaccinated or Known nonresponder to one course of Hep B vaccine Received 1 dose of Hep B vaccine, anti-hbs status unknown Received 2 doses of a 3 dose series of Hep B vaccine, anti-hbs status unknown Complete Hep B vaccination (2 or 3 dose series) and anti-hbs status unknown Known nonresponder after two courses of Hep B vaccine Test exposed person for:, anti-hbc & anti-hbs. Test for all three markers for medical-legal purposes Test for all 3 markers Test for all 3 markers Test for all 3 markers Test for all 3 markers. If anti-hbs is <10 IU/L, then Test for all 3 markers. If anti-hbs is 10 IU/L, then Test for all 3 markers. If anti-hbs is <10 IU/L, then Test for & anti-hbc. Do not test for anti-hbs. If source is positive or tests positive within 48 hrs of exposure If source is unknown/not tested/tests within 48 hours of exposure Post-exposure re-testing No action required. No action required. No action required. Give Immune Globulin (HBIG) and vaccine series Give HBIG & complete Hep B vaccine series. Give HBIG & 3rd dose of Hep B vaccine. Repeat 3 rd dose if given too early in series. Do not give HBIG. Complete Hep B vaccine series. Give HBIG and 1 dose of vaccine. Give HBIG only & give another dose of HBIG in 1 mo. Give Hep B vaccine series Give 2 nd Hep B vaccine series Complete Hep B vaccine series. Give 1 dose of Hep B vaccine & retest for anti-hbs in 4 wks; if <10 IU/L repeat series. Do not give HBIG. Complete Hep B vaccine series. 1 dose Hep B vaccine & retest for anti-hbs in 4wks; if <10 IU/L complete second series. No action required. Re-test for at 3 months & for all 3 markers at 6 & 12 months Re-test for at 3 months & for all 3 markers at 6 & 12 months Re-test for at 3 months & for all 3 markers at 6 & 12 months No re-testing required. Re-test for at 3 months & for all 3 markers at 6 & 12 months Re-test for at 3 months & for & anti-hbc at 6 & 12 months. Consensual adult sex with known STW or IDU is not an indication for HBIG, nor is a community acquired needlestick injury: the risk of transmission is low and the number needed to treat to prevent infection is extremely high. HBIG is indicated in the case of sexual assault. HBIG dose for all clients 8.3kg is 0.06ml/kg. Give HBIG as soon as possible, and no later than 14 days following an exposure. If the client presents >14 days following an exposure, give vaccine only. vaccine schedule is 0, 1 and 6 months for post-exposure prophylaxis. A non-responder to a series of vaccine is someone who demonstrates an anti-hbs level of < 10 UI/L, when measured 1 to 6 months post-vaccination. A second series of vaccine is offered to non-responders when there has been percutaneous or mucosal exposure
7 Page 6 TABLE 2: HEPATITIS B IMMUNE GLOBULIN HEPATITIS B IMMUNE GLOBULIN (HBIG) TRADE NAME: BAYHEP B (BAYER) INDICATIONS 1. Infant born to known positive woman 2. Infant born to woman at high risk for hepatitis B infection (i.e. intravenous drug use, sex trade work) whose infectious status is unknown or (possible window period) 3. Household contact or primary caregiver of infant < 12 months of age has acute hepatitis B infection 4. Percutaneous or mucosal exposure to positive source. 5. Sexual partner(s) of person with known acute or chronic hepatitis B infection REINFORCEMENTS: An at-risk known nonresponder to two series of vaccine requires 2 doses of HBIG one month apart DOSAGE 1. Give HBIG 0.5 ml IM immediately after birth, along with first dose of hepatitis B vaccine series 2. Give HBIG 0.5 ml IM immediately after birth, along with first dose of hepatitis B vaccine series 3. Give HBIG and hepatitis B vaccine 0.06 ml/kg of body weight as required, considering the immune status of the infant and history of hepatitis B immunization. 4. Give HBIG 0.06 ml/kg of body weight and hepatitis B vaccine as required, considering the client s immune status and history of hepatitis B immunization. 5. Give HBIG 0.06 ml/kg of body weight as soon as possible following most recent sexual exposure, along with hepatitis B vaccine series CONTRAINDICATIONS: None There is no upper limit to the volume of HBIG that can be administered. There is no outer time limit for administering HBIG in infants <12 month s of age, when the infant s exposure to the known risk factor(s) is ongoing. For infants < 8.3 kg, give 0.5 ml HBIG. When HBIG is required, give as soon as possible following exposure and no later than 14 days after exposure. If client is identified > 14 days after exposure, give hepatitis B vaccine only. Refer to Post- Exposure Prophylaxis table. For steady, long term sexual partners of chronic hepatitis B carriers, test for, anti-hbc and anti-hbs to determine if client is susceptible and requires HBIG, or has been infected previously.
8 Page HEALTH TEACHING TO PREVENT TRANSMISSION OF HBV Advise those infected with HBV to reduce transmission of infection to others by: Not donating blood, semen, breastmilk, body organs or tissues; Not sharing toothbrushes, dental floss, razors, earrings or manicure equipment (articles that might have traces of blood); Keeping all open cuts and sores bandaged until healed; Discussing with sexual partner(s) the fact that you are infected with HBV. Inform sexual partners of the availability of hepatitis B vaccine. Protection from infection cannot be ensured until the vaccine series has been completed and a protective anti-hbs level demonstrated through testing. Use of latex condoms will reduce the risk of HBV transmission; Putting articles with blood on them (e.g. tampons, pads, Kleenex, dental floss and bandages) in a separate plastic bag before disposing into household garbage; Disposing of bloody sharp items (razor blades, needles etc) into a hard container, taped shut; Using bleach to clean up blood spills. Wet surfaces with 1 part bleach to 9 parts water and leave sitting for 10 minutes before wiping off; Not sharing drug snorting or smoking equipment such as straws or pipes, or injection equipment such as cookers, cotton, filters, water, syringes and needles; Avoiding pregnancy until or identified as a chronic carrier; Advising your doctor, dentist, and anyone who might come into contact with your blood (such as those who do electrolysis, acupuncture, body piercing, and tattooing) that you are infected with HBV. 7.0 VACCINE ELIGIBILITY Refer to the Immunization Manual, Section VII, Biological Products, for the pre- and post- exposure indications for individuals eligible for publicly-funded vaccine. 8.0 SEROLOGIC TESTING FOR HEPATITIS B IN SPECIFIC GROUPS 8.1 Pregnancy: All pregnant women should be routinely tested for at the first prenatal visit. HBeAg testing, as a measure of infectivity, is done when the test result is positive. If testing has not been done during pregnancy, it should be done at the time of delivery. Repeat testing prior to delivery may be considered for women with ongoing high-risk behaviour. See Section X, Appendices, in the Immunization Program Manual for additional information.
9 Page Adopted Children at High Risk: Children adopted from countries, geographic regions or family situations in which there is a high prevalence of HBV infection should be screened for. If the results are positive, the household contacts should be immunized, preferably before the adoption. 8.3 Pre-vaccination Testing: Testing for, anti-hbc and anti-hbs is recommended for persons at high risk of having been infected (i.e. IDU, STW, and persons born in a country of high hepatitis B prevalence). Testing will assist in the medical management and contact follow-up of those individuals found to be infected, and prevent the mistaken belief that no risk is posed to others. Testing is indicated when students entering health care professions have been previously vaccinated, but their response to initial vaccination is unknown. 8.4 Post-vaccination testing: post-vaccination testing, when indicated, is done 1 month after (and no longer than 6 months after) completion of the vaccine series. Post vaccination testing is indicated for: Infants born to known positive mother Infants with a mother, father, or primary caregiver at high risk for hepatitis B infection (e.g. intravenous drug use, sex trade worker) Sexual partners of persons with acute or chronic hepatitis B infection Household contacts of persons with acute or chronic hepatitis B infection Individuals who have had a percutaneous or mucosal exposure to hepatitis B Immunocompromised individuals who may be expected to have a lower seroconversion rate (e.g. end-stage renal disease clients, HIV, HSCT and solid organ transplant recipients) Students in health care professions Health care workers Accountability mechanisms should be in place to ensure that every infant born to a hepatitis B infected mother receive HBIG and a full course of vaccine, as well as testing for serologic response to vaccine. It is the responsibility of the employer (through Occupation Health program) to implement testing and vaccination programs for health care workers. Those who fail to respond to a first series of hepatitis B vaccine should be offered a second series. Determination of inadequate antibody response after a second complete vaccine series will identify those who will need passive protection (i.e. HBIG) after potential exposure to hepatitis B. Health care workers are encouraged to keep a record of immunization and testing results.
10 Page BOOSTER DOSES AND RE-IMMUNIZATION. Routine booster doses in immunocompetent people are not needed, since protection has been shown to last for at least 15 years. While antibody wanes over time, immune memory persists. The absence of detectable anti-hbs in a person who previously demonstrated an adequate level of anti-hbs does not mean lack of protection. Non-responders to 1 course of hepatitis B vaccine (i.e. anti-hbs is < 10 IU/L): An additional three dose series will produce a protective antibody response in 50% to 70% of otherwise healthy people who fail to show a response after the first series. Individuals who fail to respond to the 2 nd three-dose vaccination series are unlikely to benefit from further immunization. A second series of vaccine is provided free ONLY to the following: Infants born to positive mothers Infants born to mothers at high risk of hepatitis B infection Clients with immunosuppressive disorders Dialysis/pre-dialysis clients (see Vaccine Program for End Stage Renal Disease Clients, Immunization Program Manual, Section VII) Health care students Individuals who have had an exposure to hepatitis B virus and require immunoprophylaxis.
11 Page INTERPRETATION OF TESTING RESULTS Factor to be tested Term Use surface antigen Detection of acutely or chronically infected person Anti-HBs Anti-HBc Anti-HBc IgM HBeAg Anti-HBe anti-hbc anti-hbs anti-hbc anti-hbs anti-hbc anti-hbs anti-hbc IgM anti-hbs anti-hbc anti-hbs anti-hbc anti-hbs Antibody to Antibody to core antigen (HBcAg) IgM class antibody to HBcAg e Antigen Antibody to HBeAg positive ( 10 IU/L) positive positive ( 10 IU/L) positive positive positive positive positive Identification of resolved infection with HBV; determination of immunity after hepatitis B vaccination Identification of individuals with prior infection with HBV (not present after immunization). Indicates acute or recent infection with HBV; detectable for 4-6 months after infection. Identification of infected individuals at increased risk of transmitting HBV. Identification of infected individuals at lower risk for transmitting HBV. susceptible immune due to vaccination immune due to natural infection acute infection chronic infection isolated anti-core positive four interpretations possible (see below)
12 Page ISOLATED HEPATITIS B CORE ANTIBODY POSITIVE TEST RESULT (, anti-hbc positive, anti-hbs ) There are four possible interpretations of this result: The client is in the window phase of an acute infection, between the disappearance of and the appearance of anti-hbs. Assess re: clinical symptoms and risk factors for hepatitis B. To determine if this is an acute case, test for anti-hbc IgM if available, or repeat test after several weeks. Consider as infectious to others and counsel accordingly. Provide HBIG and hepatitis B vaccine to contacts as needed. Results may represent chronic infection with that is escaping detection. Consider the client to have a low level of infectivity, and provide hepatitis B vaccine to household and sexual contacts. Provide hepatitis B vaccine to the client to confirm chronic status, as indicated by undetectable anti-hbs at series completion. Results may represent a remote resolved infection with the decline of anti-hbs to levels that are undetectable. Individuals with resolved infections and sub-detectable anti-hbs would be expected to exhibit an anamnestic response to hepatitis B vaccine, with protective levels of antibody developing after a single dose of vaccine. This may be a false positive test result and the client is susceptible to hepatitis B and is not infectious to others. False positive individuals would be expected to develop detectable anti-hbs on the completion of a three dose series of hepatitis B vaccine.
13 Page AUTHORITY Health Act REFERENCES 1. Advisory Committee on Epidemiology and the Division of Disease Surveillance, Bureau of Infectious Diseases, Laboratory Centre for Disease Control, Health Protection Branch, Health Canada. (2000). Case Definitions for Diseases under National Surveillance. Canada Communicable Disease Report, Vol. 26S3. 2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2002). Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases. (7 th ed.) Atlanta, Georgia: Public Health Foundation. 3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2001). Recommendations for preventing transmission of infections among chronic hemodialysis patients. MMWR 50 (No. RR- 5), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2001). Updated U.S. Public Health Service Guidelines for the Management of Occupational Exposure to HBV, HCV and HIV and Recommendations for Post-exposure Prophylaxis. MMWR 50(No. RR-11), Chin, J. (2000). Control of Communicable Diseases Manual (17 th ed.) Washington, DC: American Public Health Association. 6. Committee on Infectious Diseases, American Academy of Pediatrics. (2003). Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. (26 th ed.). Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics. 7. LCDC. (1997). An integrated protocol to manage health care workers exposed to bloodborne pathogens. CCDR 23S2, Moyer, L. and Margolis, H.S. (1999). Needle Tips and the Coalition News. Atlanta, Georgia: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 9. National Advisory Committee on Immunization. (2002) Canadian Immunization Guide. (6 th ed.) Ottawa, ON: Canadian Medical Association.
TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION Goals... 2
 (Adapted with permission from: BCCDC Communicable Disease Control Hepatitis B Guideline September 2009) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 1.1 Goals... 2 2.0 CLINICAL DESCRIPTION... 2 3.0 EPIDEMIOLOGY...
(Adapted with permission from: BCCDC Communicable Disease Control Hepatitis B Guideline September 2009) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 2 1.1 Goals... 2 2.0 CLINICAL DESCRIPTION... 2 3.0 EPIDEMIOLOGY...
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Prince Edward Island Guidelines for the Management and Control of Hepatitis B. December 2017
 Prince Edward Island Guidelines for the Management and Control of Hepatitis B December 2017 Table of Contents Case Definition... 2 Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... 3 Clinical Presentation... 4
Prince Edward Island Guidelines for the Management and Control of Hepatitis B December 2017 Table of Contents Case Definition... 2 Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... 3 Clinical Presentation... 4
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments
 Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Greater Glasgow and Clyde. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts
 Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Hepatitis STARS Program. Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003
 Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis B at a Glance
 Return completed form, preferably within 30 days of U.S. date of arrival, to address on reverse side of this form. Review overseas medical exam if available and document immunization dates. Indicate if
Return completed form, preferably within 30 days of U.S. date of arrival, to address on reverse side of this form. Review overseas medical exam if available and document immunization dates. Indicate if
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Chapter 5 Serology Testing
 Chapter 5 Serology Testing 49 50 This page intentionally left blank. Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Diagnosis of HBV infection (acute vs. chronic) is based on clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic
Chapter 5 Serology Testing 49 50 This page intentionally left blank. Diagnostic Tests for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Diagnosis of HBV infection (acute vs. chronic) is based on clinical, laboratory, and epidemiologic
BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B. Acute HBV Questionnaire
 BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B Informed Consent: Please read to individual and answer any questions There are about 60,000 people with hepatitis B in BC. We want to find
BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B Informed Consent: Please read to individual and answer any questions There are about 60,000 people with hepatitis B in BC. We want to find
Blood Borne Pathogens. Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N.
 Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations. Viral Hepatitis Language. Types of Viral Hepatitis 7/1/2013
 Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
Hepatitis B and C Overview, Outbreaks, and Recommendations Elizabeth Lawlor, MS Healthy Kansans living in safe and sustainable environments. Viral Hepatitis Language Acute infection is when the infection
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Hepatitis B Vaccine Biological Page
 Hepatitis B Vaccine Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.234 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide Immunization
Hepatitis B Vaccine Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.234 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide Immunization
HCSP TRAINING MANUAL
 HCSP TRAINING MANUAL SECTION IV: HCV TRANSMISSION AND PREVENTION Alan Franciscus, Editor-in-Chief The information in this guide is designed to help you understand and manage HCV and is not intended as
HCSP TRAINING MANUAL SECTION IV: HCV TRANSMISSION AND PREVENTION Alan Franciscus, Editor-in-Chief The information in this guide is designed to help you understand and manage HCV and is not intended as
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Transmission/Prevention
 Transmission/Prevention Section Three Transmission/Prevention Hepatitis C is transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. Any break in the skin may allow HCV to enter the body, even if no blood is visible. The
Transmission/Prevention Section Three Transmission/Prevention Hepatitis C is transmitted by blood-to-blood contact. Any break in the skin may allow HCV to enter the body, even if no blood is visible. The
How does HBV affect the liver?
 Hepatitis B Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It s the largest solid organ in the body and is located under your rib cage on the upper right
Hepatitis B Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It s the largest solid organ in the body and is located under your rib cage on the upper right
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page
 Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.233 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide
Hepatitis B Immune Globulin Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.233 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide
Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another?
 Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another? HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or "pre-cum"),
Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another? HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or "pre-cum"),
Hepadnaviridae family (DNA) Numerous antigenic components Humans are only known host May retain infectivity for more than 7 days at room temperature
 Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Hepatitis B Epidemic jaundice described by Hippocrates in 5th century BC Jaundice reported among recipients of human serum and yellow fever vaccines in 1930s and 1940s Australia antigen described in 1965
Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women. Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School
 Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School Obstetric Complications and HIV Obstetric complications are not increased in
Obstetric Complications in HIV-Infected Women Jeanne S. Sheffield, MD Maternal-Fetal Medicine UT Southwestern Medical School Obstetric Complications and HIV Obstetric complications are not increased in
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE HEPATITIS B
 DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training.
 You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
Bloodborne Pathogens. By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Bloodborne Pathogens By Deborah Massarella RN, MSN 2010, 2014 Objectives At conclusion of in-service learners will: 1. Identify two types of personal protective equipment. 2. Identify two prevention measures
Sandi Mitchell Nurse Educator Clinical Prevention Services BCCDC
 Sandi Mitchell Nurse Educator Clinical Prevention Services BCCDC sandi.mitchell@bccdc.ca Hepatitis A, B and C Testing Transmission Treatment What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
Sandi Mitchell Nurse Educator Clinical Prevention Services BCCDC sandi.mitchell@bccdc.ca Hepatitis A, B and C Testing Transmission Treatment What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
You WILL survive Blood Borne Pathogens. Joanne Hathorn RN IL/NCSN Sheri Boress RN IL/NCSN Health Services WPS 60
 You WILL survive Blood Borne Pathogens Joanne Hathorn RN IL/NCSN Sheri Boress RN IL/NCSN Health Services WPS 60 At first you may be afraid of children getting sick, bleeding knees and bloody noses in your
You WILL survive Blood Borne Pathogens Joanne Hathorn RN IL/NCSN Sheri Boress RN IL/NCSN Health Services WPS 60 At first you may be afraid of children getting sick, bleeding knees and bloody noses in your
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases
 Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
Bloodborne Infectious Diseases Dr. Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Bloodborne Pathogens Bloodborne pathogens Pathogenic organisms present
INTERPRETING HEPATITIS B SEROLOGY
 INTERPRETING HEPATITIS B SEROLOGY RECOMMENDED WORDING FOR NATIONAL LABORATORIES TO REPORT HEPATITIS B DIAGNOSTIC TEST RESULTS THIS DOCUMENT HAS BEEN ENDORSED BY: Australasian Society for HIV Medicine,
INTERPRETING HEPATITIS B SEROLOGY RECOMMENDED WORDING FOR NATIONAL LABORATORIES TO REPORT HEPATITIS B DIAGNOSTIC TEST RESULTS THIS DOCUMENT HAS BEEN ENDORSED BY: Australasian Society for HIV Medicine,
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Lifetime risk of infection >60% Early childhood infections common
 Hepatitis Community Medicine HBV Public health sig HBV is 100 times more infectious than HIV. >350 million chronically infected worldwide. >1 million people die annually of HBV- related chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis Community Medicine HBV Public health sig HBV is 100 times more infectious than HIV. >350 million chronically infected worldwide. >1 million people die annually of HBV- related chronic liver disease.
Infection/Disease Control HEPATITIS CONTROL PROGRAM
 OPERATING PROCEDURE NO. 153-29 Florida State Hospital Chattahoochee, Florida July 8, 2009 Infection/Disease Control HEPATITIS CONTROL PROGRAM 1. Purpose: To establish consistent surveillance, reporting,
OPERATING PROCEDURE NO. 153-29 Florida State Hospital Chattahoochee, Florida July 8, 2009 Infection/Disease Control HEPATITIS CONTROL PROGRAM 1. Purpose: To establish consistent surveillance, reporting,
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Training Objectives. Provide a basic understanding of:
 Training Objectives Provide a basic understanding of: 1. Bloodborne pathogens (BBP) 2. Common modes of transmission of BBP 3. Methods to prevent transmission of BBP 4. Information to help school staff
Training Objectives Provide a basic understanding of: 1. Bloodborne pathogens (BBP) 2. Common modes of transmission of BBP 3. Methods to prevent transmission of BBP 4. Information to help school staff
HEPATITIS C, ACUTE CRUDE DATA. Number of Cases 5 Annual Incidence a LA County 0.05 California b 0.10 United States b 0.68 Age at Diagnosis Mean 38
 2016 Annual Morbidity Report HEPATITIS C, ACUTE a Rates calculated based on less than 19 cases or events are considered unreliable b Calculated from: CDC. Notice to Readers: Final 2016 Reports of Nationally
2016 Annual Morbidity Report HEPATITIS C, ACUTE a Rates calculated based on less than 19 cases or events are considered unreliable b Calculated from: CDC. Notice to Readers: Final 2016 Reports of Nationally
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification
 SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
SUBJECT: Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Counseling/Education, Testing, Referral, and Partner Notification Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States.
Hepatitis Case Investigation
 * indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
* indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
HIV and PEP. LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED
 HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV, STI AND OTHER BLOOD- BORNE DISEASES. Kolářová M., EPI Autumn 2015
 HIV, STI AND OTHER BLOOD- BORNE DISEASES Kolářová M., EPI Autumn 2015 Chlamydia infection Genital warts Gonorrhoea Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV infection and AIDS Human papillomavirus infection Sexually
HIV, STI AND OTHER BLOOD- BORNE DISEASES Kolářová M., EPI Autumn 2015 Chlamydia infection Genital warts Gonorrhoea Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV infection and AIDS Human papillomavirus infection Sexually
Detection of Hepatitis B and C in Primary Care
 Detection of Hepatitis B and C in Primary Care Presentation 2 January 2016 Quality Quality Education Education for for aa Healthier Healthier Scotland Scotland 1 1 Learning Outcomes Participants will be
Detection of Hepatitis B and C in Primary Care Presentation 2 January 2016 Quality Quality Education Education for for aa Healthier Healthier Scotland Scotland 1 1 Learning Outcomes Participants will be
Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff Insert Nurse Name, Credentials Here Insert Organization Here This presentation was adapted from the Ohio Department of Health, School and Adolescent Health
Bloodborne Pathogens Training for School Staff Insert Nurse Name, Credentials Here Insert Organization Here This presentation was adapted from the Ohio Department of Health, School and Adolescent Health
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Safety Tips from the WorkSafe People
 Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Immunization of Adults in High Risk Populations. Carol A. Kurbis MD, CCFP, FRCPC WRHA Medical Officer of Health
 Immunization of Adults in High Risk Populations Carol A. Kurbis MD, CCFP, FRCPC WRHA Medical Officer of Health OBJECTIVES To review recommendations for immunization in adult populations, with a focus on
Immunization of Adults in High Risk Populations Carol A. Kurbis MD, CCFP, FRCPC WRHA Medical Officer of Health OBJECTIVES To review recommendations for immunization in adult populations, with a focus on
Summary of Key Points. WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Information for Health Care Workers
 Information for Health Care Workers This Bulletin highlights precautions to be taken by health care workers who may be exposed to blood and body fluids. In general, workers should minimize direct contact
Information for Health Care Workers This Bulletin highlights precautions to be taken by health care workers who may be exposed to blood and body fluids. In general, workers should minimize direct contact
Hepatitis B Vaccine: ENGERIX -B
 Hepatitis B Vaccine: ENGERIX -B Revision Date: August 25, 2016 Rationale for Policy Update: Incorporated updated CIG and ACIP recommendations for immune compromised individuals and those with renal disease.
Hepatitis B Vaccine: ENGERIX -B Revision Date: August 25, 2016 Rationale for Policy Update: Incorporated updated CIG and ACIP recommendations for immune compromised individuals and those with renal disease.
Hepatitis B. Data from the Travel Health Surveillance Section of the Health Protection Agency Communicable Disease Surveillance Centre
 Hepatitis B Introduction Hepatitis B virus is one of the most prevalent viruses worldwide and is a major cause of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is a hepadnavirus, consisting of
Hepatitis B Introduction Hepatitis B virus is one of the most prevalent viruses worldwide and is a major cause of chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. It is a hepadnavirus, consisting of
Hepatitis B. What is hepatitis B? How is HBV spread?
 2015 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a liver condition caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV can be chronic, in which case it can lead to liver failure, liver cancer, or
2015 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a liver condition caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV can be chronic, in which case it can lead to liver failure, liver cancer, or
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
Bloodborne Pathogens Training. IEA, Inc.
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
Bloodborne Pathogens Training IEA, Inc. Review the potential hazard of exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (OPIMs). Review safe work practices to prevent occupational exposure
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update. Primary Causes of Chronic Liver Disease in the U.S. Hepatitis Definition. Hepatitis Viruses.
 Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Learning Objectives: Hepatitis Update ASCLS-Michigan March 31, 2016 Dr. Kathleen Hoag Upon attendance of this seminar and review of material provided, the attendees will be able to: 1. List hepatitis viruses
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens
 Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Introduction to Blood Borne Pathogens What are blood pathogens? Any infectious microorganism in the human blood that can cause disease is a Blood borne pathogen. Three of these pathogens include hepatitis
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc.
 Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Training for Employees of Taylor Special Care Services, Inc. TSCS Taylor Special Care Services housing staffing counseling on-going support Simon Pop, MBA Chief Operating Officer 2015 2016 Guidelines:
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
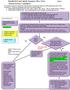 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Hepatitis C. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Hepatitis C Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn: More about Hepatitis C. The importance of the liver. Risk factors and prevention. Signs and symptoms. Hepatitis C Virus: Is a virus that
Hepatitis C Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn: More about Hepatitis C. The importance of the liver. Risk factors and prevention. Signs and symptoms. Hepatitis C Virus: Is a virus that
Acute Hepatitis B Fact Sheet
 What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a virus that enters the bloodstream and then infects the liver. Each year, thousands of people all ages get hepatitis B and 5,000 die of chronic (long-term) liver problems
What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a virus that enters the bloodstream and then infects the liver. Each year, thousands of people all ages get hepatitis B and 5,000 die of chronic (long-term) liver problems
Blood Borne Pathogens
 Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
What is hepatitis? What is hepatitis A? How is it spread? What are the symptoms? How soon do symptoms appear? How is hepatitis A diagnosed?
 Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Universal Precautions
 Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
The Alphabet Soup of Viral Hepatitis Testing
 The Alphabet Soup of Viral Hepatitis Testing August 18, 2011 Patricia Slev, PhD, DABCC Medical Director, Serologic Hepatitis and Retrovirus Laboratory, ARUP Laboratories Assistant Professor of Pathology,
The Alphabet Soup of Viral Hepatitis Testing August 18, 2011 Patricia Slev, PhD, DABCC Medical Director, Serologic Hepatitis and Retrovirus Laboratory, ARUP Laboratories Assistant Professor of Pathology,
Hepatitis B. What Is Hepatitis? What Are The Two Stages Of Hepatitis? Published on: 5 Oct 2010
 Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
iphis Case ID #: Reported Date: Reporting Source: Diagnosing Health Unit: Branch Office: Outbreak Number:
 Case Investigation Form: Hepatitis C Legend iphis system mandatory Required Case Information (add dates as YYYY-MM-DD) Case s Last Name: Case s First Name: Middle Name: Birth Date: Male Gender: Female
Case Investigation Form: Hepatitis C Legend iphis system mandatory Required Case Information (add dates as YYYY-MM-DD) Case s Last Name: Case s First Name: Middle Name: Birth Date: Male Gender: Female
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training
 Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing. Origins of Liver Science
 Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Uses and Misuses of Viral Hepatitis Testing Richard S Lang, MD, MPH, FACP Chairman, Preventive Medicine Vice-Chair, Wellness Institute Raul J Seballos, MD, FACP Vice-Chair, Preventive Medicine Wellness
Carrier state and chronic infection state. At-risk populations
 John T. Stutts, MD, MPH University of Louisville School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Carrier state and chronic infection state -
John T. Stutts, MD, MPH University of Louisville School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Carrier state and chronic infection state -
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
2017 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens and the role of Greenwood School District 50 and OSHA.
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: F:
 University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
The facts you need to know
 Hepatitis B The facts you need to know Patient information booklet Know it. Test it. Treat it. Table of contents About this booklet 3 What is hepatitis? 3 What is chronic hepatitis B? 3 Can someone be
Hepatitis B The facts you need to know Patient information booklet Know it. Test it. Treat it. Table of contents About this booklet 3 What is hepatitis? 3 What is chronic hepatitis B? 3 Can someone be
Orion ISO Universal Precautions Employee Training Module
 Orion ISO Universal Precautions Employee Training Module Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms. Bloodborne pathogens are viruses or bacteria present in human blood and body fluids which can infect
Orion ISO Universal Precautions Employee Training Module Pathogens are disease-causing microorganisms. Bloodborne pathogens are viruses or bacteria present in human blood and body fluids which can infect
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C
 S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
S401- Updates in the Treatments of Hepatitis B & C Ruben Gonzalez-Vallina, MD Director of Gastroenterology Outpatient Initiatives Miami Children s Hospital Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
Epidemiology of Acute Hepatitis C Infection in Canada Results from the Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance System (EHSSS)
 Epidemiology of Acute Hepatitis C Infection in Canada Results from the Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance System (EHSSS) At a Glance Reported rates of acute HCV declined from.5 per, population in to.
Epidemiology of Acute Hepatitis C Infection in Canada Results from the Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance System (EHSSS) At a Glance Reported rates of acute HCV declined from.5 per, population in to.
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE
 CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
CITY & HACKNEY ELIC EAST LONDON INTEGRATED CARE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B IN PRIMARY CARE Chronic Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is an important public health problem globally and a leading cause of liver
EWSLETTER CONTROL DISEASE. Viral Hepatitis Compendium
 MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH DISEASE CONTROL N EWSLETTER Volume 30, Number 7 (pages 45-56) November/December 2002 Viral Hepatitis Compendium Included under the broad umbrella of viral hepatitis are several
MINNESOTA DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH DISEASE CONTROL N EWSLETTER Volume 30, Number 7 (pages 45-56) November/December 2002 Viral Hepatitis Compendium Included under the broad umbrella of viral hepatitis are several
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS
 Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Greenwood School District 50 OSHA UPDATE 2012 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS TOPICS OSHA TERMS UPDATES HEPATITIS B HEPATITIS C HIV REPORTING AN EXPOSURE OBJECTIVES To have a basic understanding of bloodborne pathogens
Hepatitis B and Hepatitis B Vaccine
 Hepatitis B and Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine- Preventable Diseases Note to presenters: Images of vaccine-preventable diseases are available from the Immunization Action Coalition website at http://www.vaccineinformation.org/photos/index.asp
Hepatitis B and Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine- Preventable Diseases Note to presenters: Images of vaccine-preventable diseases are available from the Immunization Action Coalition website at http://www.vaccineinformation.org/photos/index.asp
A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses. HIV and AIDS Hepatitis B Hepatitis C
 A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses HIV and AIDS Hepatitis B Hepatitis C A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses This question and answer tool kit has been designed by the Children in Care Team (Integrated
A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses HIV and AIDS Hepatitis B Hepatitis C A Pocket Guide to Blood-borne Viruses This question and answer tool kit has been designed by the Children in Care Team (Integrated
A. Background for Trainer: B. What OSHA Requires: Bloodborne Pathogens. Lesson Plan 6080a
 Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV
 Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties An exposure that might place health
Guidelines for Post- Exposure Prophylaxis for HAV, HBV, HCV & HIV By Dr. Sinan Butrus F.I.C.M.S Clinical Standards & Guidelines Kurdistan Board For Medical Specialties An exposure that might place health
Bloodborne Pathogen Module. Chelmsford Public Schools September, 2016
 Bloodborne Pathogen Module Chelmsford Public Schools September, 2016 Why is this important? v OSHA BB Pathogen Standard anyone whose job requires exposure to BB pathogens is required to complete training
Bloodborne Pathogen Module Chelmsford Public Schools September, 2016 Why is this important? v OSHA BB Pathogen Standard anyone whose job requires exposure to BB pathogens is required to complete training
OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program
 OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Dear Colleague, This letter is to introduce myself and explain the role I play with the Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis B Program. Alaska
OB Provider Guide to Alaska s Perinatal Hepatitis B Prevention Program Dear Colleague, This letter is to introduce myself and explain the role I play with the Alaska Perinatal Hepatitis B Program. Alaska
Standard Precautions Protecting Yourself From Risk. Compiled by Florida State University Institute for Family Violence Studies
 Standard Precautions Protecting Yourself From Risk Compiled by Florida State University Institute for Family Violence Studies Case Scenario 1 And keep others safe around you? Case Scenario 1 Commonly called
Standard Precautions Protecting Yourself From Risk Compiled by Florida State University Institute for Family Violence Studies Case Scenario 1 And keep others safe around you? Case Scenario 1 Commonly called
