Supplemental Table 1. List of cell lines used
|
|
|
- Nelson Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Table 1. List of cell lines used Common species name Latin species name Source Common Marmoset Southern Lesser Bushbaby Callithrix jacchus In-house (1 line) Coriell number (if applicable) MLS (yrs) Age Passage Number Sup Fig. 1A SupFig. 1B X X X X X X X X X Galago moholi Coriell PR X X X X X X Coquerel's Mouse Lemur Mizra coquereli Coriell PR X X X X X Pygmy Marmoset Callithrix pygmaea Coriell PR X X X X X X X X Pygmy Marmoset Callithrix pygmaea Coriell PR X X Red-bellied Lemur Eulemur rubriventer Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X Red Tamarin Saguinus midas Coriell PR X X X X X X X X Noisy Douroucouli Aotus vociferans Coriell PR X X X X X X X X L'Hoest's Monkey Cercopithecus lhoesti Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X X Red Titi Callicebus cupreus Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X Olive Baboon Papio anubis Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X Patas Monkey Erythrocebus patas Coriell AG X Squirrel Monkey Saimiri sciureus Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X White (Verreaux's) Sifaka Vervet Propithecus verreauxi Chlorocebus aethiops Coriell PR X X X In-house (3 lines) Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Sup Fig. 3 Fig. 3A, B Fig. 3C Fig. 3F Fig. 4A, B Fig. 4C Fig. S8 X X X X X X X X X X X X Common Woolly Monkey Lagothrix lagotricha Coriell AG X X X X X X X X X Colobus Monkey Colobus guereza Coriell PR X Guianan Saki Pithecia pithecia Coriell PR X X X X X Ring-tailed Lemur Lemur catta Coriell PR X Hamadryas Baboon Cynomolgus Rhesus Macaque Papio hamadryas Macaca fascicularis Macaca mulatta In-house (2 lines) In-house (2 lines) In-house (3 lines) X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Mandrill Mandrillus sphinx Coriell PR X X X X X X Red-capped Mangabey Cercocebus torquatus Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X Bonobo Pan paniscus Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X X Bonobo Pan paniscus Coriell PR X X X Gorilla Gorilla gorilla Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X Gorilla Gorilla gorilla Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X X X White-handed Gibbon Hylobatus lar Coriell PR X X X X X X X X Orangutan Pongo pygmaeus Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X X X Chimpanzee Pan troglodytes Coriell PR X X X X X X X X X X X Chimpanzee Pan troglodytes Coriell PR X X X X X X Human Homo sapiens Coriell GM X X X X X X X Human Homo sapiens Coriell GM X X X X Human Homo sapiens Coriell GM X X X Fig. 5A-C
2 Two-Way ANOVA Least Significant Difference Post-Hoc Test Supplemental Table 2. Two way ANOVA and post-hoc analyses for mouse liver tissue
3 A B Supplemental Figure 1. Proteolytic activity in fibroblast lysates increases with lifespan among species of primates. (A) Scatterplot of Suc-LLVY-AMC degradation during incubation with cell lysate from different primate species in the absence of ATP. (B) Scatterplot of Suc-LLVY-AMC degradation in lysates supplemented with 0.25mM ATP. Error bars if present represent the SEM of two cell lines derived from independent animals. MLS = Maximum Species Lifespan in years. Response from one cell-line of human fibroblasts is shown with an H, but is not included in statistical analysis.
4 A B C D E F Supplemental Figure 2. Fibroblasts from longer lived species of primates have greater 20S proteasome activity (A-D) Scatterplots of 4 independent experiments using different independent sets of primate species. Proteasome activity measured in a Native polyacrylamide gel using an in-gel overlay by Suc-LLVY-AMC. (E) Combined data from the 4 scatterplots. (F) Re-plot of Figure 1B in which three outliers (shown with arrows in panel E) were removed. Removal of these datapoints does not change any of the conclusions drawn from this data. Results for human cell-lines are shown with an H but are not included in statistical analysis.
5 Pigmy Marmoset-1 Pigmy Marmoset-2 Red Tamarin Noisy Douroucouli L'Hoest's Monkey Red Titi Olive Baboon Squirrel Monkey Vervet-1 Vervet-2 Woolly Monkey Hamadryas Baboon Cynomolgas Rhesus Macaque Mandrill Red-capped Mangabey Bonobo Gorilla-1 Gorilla-2 Gibbon Orangutan Chimpanzee Human A B C PSMB8 PSMB5 PSMB4 Total Protein D E MLS ( yr) Supplemental Figure 3. Fibroblasts from longer lived species of primates have a significant elevation in PSMB8 levels but no significant lifespan association in levels of PSMB5. (A) Representative immunoblot. Samples were run on a SDS polyacrylamide gel, and then developed using antibodies against PSMB5 (standard proteasome specific subunit), PSMB8 (immunoproteasome specific subunit) or PSMB4 as a measure of total proteasome. (B) Scatterplot of PSMB5 level adjusted to total protein. (C) Scatterplot of PSMB5 level adjusted to PSMB4. (D) Scatterplot of PSMB8 level adjusted to total protein. (E) Scatterplot of PSMB8 level adjusted to PSMB4. Error bars if present represent the SEM of 2 cell lines derived from independent animals. MLS = Maximum lifespan in years. The Red-capped Mangabey (indicated with an arrow) was considered an outlier in panels A & B. Removal of this datepoint did not change the conclusions of these panels. With the removal of the Red-capped Mangabey no significant correlation was observed between PSMB5 and lifespan in either panel A (R 2 = 0.01 p = 0.74) or panel B (R 2 = 0.01 p = 0.69).
6 A B Supplemental Figure 4. (A) Antibody binding epitope based on NCBI sequence data. (B) Custom peptide sequences were produced by thermo scientific. Peptides were subjected to a direct ELISA assay and screened by an antibody to PSMB8. Binding was quantified using a TMB substrate
7 PSMB8 partial mrna sequence PSMB5 partial mrna sequence Supplemental Figure 5. PSMB8 and PSMB5 primer sequences. Sequence homology was determined through comparisons of primate sequences available on NCBI. These included: Humans (Homo sapiens), Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), Chimpanzee (Pan trogloytes), Bonobo (Pan paniscus), Orangutan (Pongo abelii), Gibbon (Hylobatus leucogenys), Rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta), Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis), Baboon (Papio anubis), Squirrel monkey (Saimiri boliviensis), Vervet (Chlorocebus sabaeus), Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) and Galago (Otolemur garnettii). The set of species for which mrna data was available was not consistent between genes. The Tarsier (Tarsius syrichta) sequence was not included as none of the primate species assayed in this paper were found on that branch of the primate phylogeny. The * symbol was used to represent nucleotides that are completely conserved between the species assayed.
8 Control + IFN-γ Supplemental Figure 6. Scatterplot of H 2 O 2 dose required to reduce cell viability to 50% ± IFN-γ
9 A B Supplemental Figure 7. (A) Antibody binding epitope based on NCBI sequence data. (B) Custom peptide sequences were produced by Thermo Scientific. Antibody binding affinity for New World monkeys and Galagos (not shown) was very different from that of Old World monkeys, Baboons and Great Apes as a result these groups were not used in measurements of IFNGR2. Peptides were subjected to a direct ELISA assay and screened by an antibody to IFNGR2. Binding was quantified using a TMB substrate.
10 IFNGR2 partial sequence Supplemental Figure 8. IFNGR2 primer sequence. Sequence homology was determined through comparisons of primate sequences available on NCBI. These included: Humans (Homo sapiens), Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), Chimpanzee (Pan trogloytes), Bonobo (Pan paniscus), Orangutan (Pongo abelii), Gibbon (Hylobatus leucogenys), Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta), Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis), Baboon (Papio anubis), Squirrel Monkey (Saimiri boliviensis), Vervet (Chlorocebus sabaeus), Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) and Galago (Otolemur garnettii). The set of species for which mrna data was available was not consistent between genes. The Tarsier (Tarsius syrichta) sequence was not included as none of the primate species assayed in this paper were found on that branch of the primate phylogeny. The * symbol was used to represent nucleotides that are completely conserved between the species assayed.
11 A B C Supplemental Figure 9. Fibroblasts from longer lived species of primates have increased mrna expression of STAT1 but no significant association to lifespan in mrna expression for IFNGR1 or JAK1. (A) Scatterplot of relative STAT1 mrna levels. (B) Scatterplot of relative IFNGR1 mrna levels. (C) Scatterplot of relative JAK1 mrna levels. Error bars if present represent the SEM of 2 cell lines derived from independent animals.
12 TAP1 partial mrna sequence TAP2 partial mrna sequence Supplemental Figure 10. TAP1 and TAP2 primer sequences. Sequence homology was determined through comparisons of primate sequences available on NCBI. These included: Humans (Homo sapiens), Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), Chimpanzee (Pan trogloytes), Bonobo (Pan paniscus), Orangutan (Pongo abelii), Gibbon (Hylobatus leucogenys), Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta), Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis), Baboon (Papio anubis), Squirrel monkey (Saimiri boliviensis), Vervet(Chlorocebus sabaeus), Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) and Galago (Otolemur garnettii). The set of species for which mrna data was available was not consistent between genes. The Tarsier (Tarsius syrichta) sequence was not included as none of the primate species assayed in this paper were found on that branch of the primate phylogeny. The * symbol was used to represent nucleotides that are completely conserved between the species assayed.
13 β-2 microglobulin partial mrna sequence Supplemental Figure 11. β-2 microglobulin primer sequences. Sequence homology was determined through comparisons of primate sequences available on NCBI. These included: Humans (Homo sapiens), Gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), Orangutan (Pongo abelii), Chimpanzee (Pan trogloytes),, Gibbon (Nomascus leucogenys), Marmoset (Callithrix jacchus), Tamerin (Saguinus midas), Squirrel monkey (Saimiri boliviensis), Rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta), Baboon (Papio anubis), Cynomolgus (Macaca fascicularis), Green monkey (Chlorocebus sabaeus), and Galago (Otolemur garnettii). The set of species for which mrna data was available was not consistent between genes. The Tarsier (Tarsius syrichta) sequence was not included as none of the primate species assayed in this paper were found on that branch of the primate phylogeny. The * symbol was used to represent nucleotides that are completely conserved between the species assayed.
14 A B C D Supplemental Figure 12. Scatterplot showing standardized contrast analysis for (A) ATP-independent proteolytic activity. (B) PSMB8 mrna. (C) INFGR2 mrna. (D) IFN-γ induced change in LD50. Values are calculated as described in Garland et al., 1994 and are based on the phylogeny in Pickering et al., 2014 (Note N = N - 1 of original results due to the pairwise comparisons involved in the phylogenetic contrast) Garland T, Adolph SC. Why Not to Do 2-Species Comparative-Studies - Limitations on Inferring Adaptation. Physiol Zool Jul-Aug;67(4): Pickering, A. M., Lehr, M., Kohler, W. J., Han, M. L. & Miller, R. A. (2014) Fibroblasts From Longer-Lived Species of Primates, Rodents, Bats, Carnivores, and Birds Resist Protein Damage. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, doi: /gerona/glu115.
15 A B C D Supplemental Figure 13. Scatterplot of mass-adjusted changes in (A) ATP-independent proteolytic activity. (B) PSMB8 mrna. (C) Log 10 INFGR2 mrna. (D) IFN-γ induced change in LD50. Values represent the residual from either maximum lifespan, or the variable of interest, plotted against log 10 (mass) (g).
16 A B Supplemental Figure 14. (A) Scatterplot of cell passage number against maximum lifespan. Error bars if present show the highest and lowest passage number used for this cell line. (B) Scatterplot of donor animal age against maximum lifespan. (C) Scatterplot of donor animal age (as a fraction of maximum lifespan) against maximum lifespan. Error bars if present show the highest and lowest age of donor animals used. Each data point represents an independent species. Humans are shown with an H but are excluded from analyses.
17 Supplemental Figure 15. Assessment of cellular endpoints after removal of data from Mouse Lemur, Noisy Douroucouli, Patas Monkey and Woolly Monkey, the four species for which donor age exceeded 50% of species maximum lifespan. The association of MLS with these endpoints is replicated in this truncated set of species, although in one case the association no longer reaches the standard criterion for statistical significance (PSMB8 mrna, p = 0.07).
18 A B C D Supplemental Figure 16. PSMB5 levels in liver samples of mice subjected to a variety of life-extending interventions. (A) Rapamycin. (B) NDGA. (C) 17-α-Estradiol. (D) Snell dwarf. Data are presented as bar graphs of PSMB5 levels adjusted to β-actin. Data are plotted as a percent of control males. Error bars represent SEM where N = 4 (except for Snell dwarfs where N = 6). For rapamycin, NDGA, and 17-α-estradiol, controls were littermates that received mouse chow with no drugs. For the Snell dwarf study, controls were littermates.
First generation microarray-system for identification of primate species subject to bushmeat trade
 The following supplement accompanies the article First generation microarray-system for identification of primate species subject to bushmeat trade A.-C. Rönn 1, O. Andrés 2, F. López-Giráldez 2, 3, C.
The following supplement accompanies the article First generation microarray-system for identification of primate species subject to bushmeat trade A.-C. Rönn 1, O. Andrés 2, F. López-Giráldez 2, 3, C.
Mirror self-recognition in nonhuman primates: A phylogenetic approach 1
 Japanese Psychological Research 1997, Volume 39, No. 3, 266 275 Special Issue: Cognition and behavior of chimpanzees Short Report Mirror self-recognition in nonhuman primates: A phylogenetic approach 1
Japanese Psychological Research 1997, Volume 39, No. 3, 266 275 Special Issue: Cognition and behavior of chimpanzees Short Report Mirror self-recognition in nonhuman primates: A phylogenetic approach 1
Index 297. Vervet monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops) , See also Monkey; Old World monkey Virunga National Park 159
 Index Africa ix-x, 62, 64, 67, 75, 95-100, 152, 159, 161, 217, 237-238, 245-248, 253-255, 276, 279, 288 See also entries for individual countries Aging xiii, 2, 95, 191-193, 195, 197-199, 201, 205, 207-208,
Index Africa ix-x, 62, 64, 67, 75, 95-100, 152, 159, 161, 217, 237-238, 245-248, 253-255, 276, 279, 288 See also entries for individual countries Aging xiii, 2, 95, 191-193, 195, 197-199, 201, 205, 207-208,
Ateles fusciceps Nelson et al., 2015 Evaluating handedness measures in spider monkeys zoo 1 5
 Alouatta caraya da Cunha et al., 2006 Alouatta pigra Briseno-Jamarillo et al., 2015 Alouatta pigra Kitchen et al., 2004 Alouatta pigra Kitchen, 2004 Alouatta pigra Kitchen, 2006 Aotus nigriceps Bicca-Marques
Alouatta caraya da Cunha et al., 2006 Alouatta pigra Briseno-Jamarillo et al., 2015 Alouatta pigra Kitchen et al., 2004 Alouatta pigra Kitchen, 2004 Alouatta pigra Kitchen, 2006 Aotus nigriceps Bicca-Marques
Nonhuman Primate Models of Human Ontogeny
 Nonhuman Primate Models of Human Ontogeny Steven R. Leigh Department of Anthropology University of Illinois Urbana, IL USA 61801 Running head: Models of human growth and development 28 pages of text, including
Nonhuman Primate Models of Human Ontogeny Steven R. Leigh Department of Anthropology University of Illinois Urbana, IL USA 61801 Running head: Models of human growth and development 28 pages of text, including
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Testing the accuracy of ancestral state reconstruction The accuracy of the ancestral state reconstruction with maximum likelihood methods can depend on the underlying model used in the reconstruction.
Testing the accuracy of ancestral state reconstruction The accuracy of the ancestral state reconstruction with maximum likelihood methods can depend on the underlying model used in the reconstruction.
Research done and Report prepared by Campaigns Against the Cruelty to Animals
 Research done and Report prepared by Campaigns Against the Cruelty to Animals P.O. Box 16021, 617 Belmont St. New Westminster, British Columbia V3M-6W6 Canada ericka@catcahelpanimals.org iwccites@hotmail.com
Research done and Report prepared by Campaigns Against the Cruelty to Animals P.O. Box 16021, 617 Belmont St. New Westminster, British Columbia V3M-6W6 Canada ericka@catcahelpanimals.org iwccites@hotmail.com
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix Data The sample sizes and distribution of traits used in the analyses are summarised in Table S1. Primate trait data were extracted from the literature and from primary sources (Dataset
Supplementary Appendix Data The sample sizes and distribution of traits used in the analyses are summarised in Table S1. Primate trait data were extracted from the literature and from primary sources (Dataset
SPACE, TIME AND NUMBER IN THE BRAIN SEARCHING FOR THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL THOUGHT
 SPACE, TIME AND NUMBER IN THE BRAIN SEARCHING FOR THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL THOUGHT SPACE, TIME AND NUMBER IN THE BRAIN SEARCHING FOR THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL THOUGHT AN ATTENTION AND PERFORMANCE
SPACE, TIME AND NUMBER IN THE BRAIN SEARCHING FOR THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL THOUGHT SPACE, TIME AND NUMBER IN THE BRAIN SEARCHING FOR THE FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICAL THOUGHT AN ATTENTION AND PERFORMANCE
Artificial Mutations and Natural Variations in the CD46 Molecules from Human and Monkey Cells Define Regions Important for Measles Virus Binding
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 1997, p. 6144 6154 Vol. 71, No. 8 0022-538X/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Artificial Mutations and Natural Variations in the CD46 Molecules from
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 1997, p. 6144 6154 Vol. 71, No. 8 0022-538X/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Artificial Mutations and Natural Variations in the CD46 Molecules from
Evolution of Human Nature Exercise Workbook
 Evolution of Human Nature Exercise Workbook Alan R. Rogers 1 and Elizabeth A. Cashdan All rights reserved. February 4, 2014 1 Department of Anthropology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Contents
Evolution of Human Nature Exercise Workbook Alan R. Rogers 1 and Elizabeth A. Cashdan All rights reserved. February 4, 2014 1 Department of Anthropology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Contents
What Do Primates Hear? A Meta-analysis of All Known Nonhuman Primate Behavioral Audiograms
 Int J Primatol (2009) 30:55 91 DOI 10.1007/s10764-008-9330-1 What Do Primates Hear? A Meta-analysis of All Known Nonhuman Primate Behavioral Audiograms Mark N. Coleman Received: 1 May 2008 / Accepted:
Int J Primatol (2009) 30:55 91 DOI 10.1007/s10764-008-9330-1 What Do Primates Hear? A Meta-analysis of All Known Nonhuman Primate Behavioral Audiograms Mark N. Coleman Received: 1 May 2008 / Accepted:
The World of Primates
 The World of Primates From mouse lemurs to gorillas, the Primates are an extremely diverse and successful Order of mammals. There is no single feature that makes an animal a primate, but rather a suite
The World of Primates From mouse lemurs to gorillas, the Primates are an extremely diverse and successful Order of mammals. There is no single feature that makes an animal a primate, but rather a suite
The Evolution of Inequity Aversion: Nonhuman Primate Responses to Unequal Reward Distributions
 Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Theses Theses and Dissertations 5-1-2016 The Evolution of Inequity Aversion: Nonhuman Primate Responses to Unequal Reward Distributions Jessica Feller Southern
Southern Illinois University Carbondale OpenSIUC Theses Theses and Dissertations 5-1-2016 The Evolution of Inequity Aversion: Nonhuman Primate Responses to Unequal Reward Distributions Jessica Feller Southern
Supplementary Table 1. Relationships between physiological measures and proxies of nutritional status across primate taxa
 Supplementary Table 1. Relationships between physiological s and proxies of nutritional status across primate taxa Primates Species Setting Nutritional status proxy Prosimians Lemur catta wild Fruit intake
Supplementary Table 1. Relationships between physiological s and proxies of nutritional status across primate taxa Primates Species Setting Nutritional status proxy Prosimians Lemur catta wild Fruit intake
Phylogenetic Analyses of Dimorphism in Primates: Evidence for Stronger Selection on Canine Size Than on Body Size
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 130:50 59 (2006) Phylogenetic Analyses of Dimorphism in Primates: Evidence for Stronger Selection on Canine Size Than on Body Size Sandra Thorén, 1 Patrik Lindenfors,
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL ANTHROPOLOGY 130:50 59 (2006) Phylogenetic Analyses of Dimorphism in Primates: Evidence for Stronger Selection on Canine Size Than on Body Size Sandra Thorén, 1 Patrik Lindenfors,
Originally published as:
 Originally published as: Ehlers, B., Spieß, K., Leendertz, F., Peeters, M., Boesch, C., Gatherer, D., McGeoch, D.J. Lymphocryptovirus phylogeny and the origins of Epstein-Barr virus (2010) Journal of General
Originally published as: Ehlers, B., Spieß, K., Leendertz, F., Peeters, M., Boesch, C., Gatherer, D., McGeoch, D.J. Lymphocryptovirus phylogeny and the origins of Epstein-Barr virus (2010) Journal of General
Lymphocryptovirus phylogeny and the origins of Epstein Barr virus
 Journal of General Virology (2010), 91, 630 642 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.017251-0 Lymphocryptovirus phylogeny and the origins of Epstein Barr virus Bernhard Ehlers, 1 Katja Spieß, 1 Fabian Leendertz, 2 Martine
Journal of General Virology (2010), 91, 630 642 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.017251-0 Lymphocryptovirus phylogeny and the origins of Epstein Barr virus Bernhard Ehlers, 1 Katja Spieß, 1 Fabian Leendertz, 2 Martine
Role of the single deaminase domain APOBEC3A in virus restriction, retrotransposition, DNA damage and cancer
 Journal of General Virology (2016), 97, 1 17 DOI 10.1099/jgv.0.000320 Review Correspondence Edward B. Stephens estephen@kumc.edu Role of the single deaminase domain APOBEC3A in virus restriction, retrotransposition,
Journal of General Virology (2016), 97, 1 17 DOI 10.1099/jgv.0.000320 Review Correspondence Edward B. Stephens estephen@kumc.edu Role of the single deaminase domain APOBEC3A in virus restriction, retrotransposition,
Subject Index* macaque 112f
 Subject Index* A-B-O red cell polymorphism 209 a-tocopherol-responsive hemolytic anemia 226 abetalipoproteinemia 231 acanthocephaliasis 65 acariasis, cutaneous 23 acid fast bacilli, leprosy llf Actinobacillus,
Subject Index* A-B-O red cell polymorphism 209 a-tocopherol-responsive hemolytic anemia 226 abetalipoproteinemia 231 acanthocephaliasis 65 acariasis, cutaneous 23 acid fast bacilli, leprosy llf Actinobacillus,
Characteristics of the ocular fundus in primates
 J. Anat. (1967), 101, 4, pp. 693-699 693 With 16 figures Printed in Great Britain Characteristics of the ocular fundus in primates LEE R. WOLIN AND L. C. MASSOPUST, JR. Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Cleveland
J. Anat. (1967), 101, 4, pp. 693-699 693 With 16 figures Printed in Great Britain Characteristics of the ocular fundus in primates LEE R. WOLIN AND L. C. MASSOPUST, JR. Laboratory of Neurophysiology, Cleveland
Monkeys and Prosimians: Social Learning
 Monkeys and Prosimians: Social Learning D. M. Fragaszy and J. Crast, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA ã 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Introduction In this chapter, we highlight examples
Monkeys and Prosimians: Social Learning D. M. Fragaszy and J. Crast, University of Georgia, Athens, GA, USA ã 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Introduction In this chapter, we highlight examples
Mangabeys (Cercocebus torquatus lunulatus) solve the reverse contingency task without a modiwed procedure
 Anim Cogn (2007) 10:387 396 DOI 10.1007/s10071-007-0076-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Mangabeys (Cercocebus torquatus lunulatus) solve the reverse contingency task without a modiwed procedure Anna Albiach-Serrano Federico
Anim Cogn (2007) 10:387 396 DOI 10.1007/s10071-007-0076-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Mangabeys (Cercocebus torquatus lunulatus) solve the reverse contingency task without a modiwed procedure Anna Albiach-Serrano Federico
Suborder Haplorrhini
 Suborder Haplorrhini Suborders split ~63 MYA Differences: Strepsirrhini Name means curved nose Retain enzyme that manufacture vitamin C Don t have a post-orbital plate Have a rhinarium, the wet & naked
Suborder Haplorrhini Suborders split ~63 MYA Differences: Strepsirrhini Name means curved nose Retain enzyme that manufacture vitamin C Don t have a post-orbital plate Have a rhinarium, the wet & naked
Supplementary Figure 1. CFTR protein structure and domain architecture.
 A Plasma Membrane NH ₂ COOH Supplementary Figure. CFT protein structure and domain architecture. (A) Open state CFT homology model, ribbon representation from Serohijos et al. 8 PNAS 5:356. CFT domains
A Plasma Membrane NH ₂ COOH Supplementary Figure. CFT protein structure and domain architecture. (A) Open state CFT homology model, ribbon representation from Serohijos et al. 8 PNAS 5:356. CFT domains
Do male "long-distance calls" function in mate defense? A comparative study of long distance calls in primates
 Chapter 4 Do male "long-distance calls" function in mate defense? A comparative study of long distance calls in primates With Nunn, C. L. (Behavioural Ecology and Sociobiology, in press) Chapter 4 45 46
Chapter 4 Do male "long-distance calls" function in mate defense? A comparative study of long distance calls in primates With Nunn, C. L. (Behavioural Ecology and Sociobiology, in press) Chapter 4 45 46
Habituating primates: processes, techniques, variables and ethics
 C:/ITOOLS/WMS/CUP/2155700/WORKINGFOLDER/SETC/9780521194099C02.3D 33 [33 50] 8.9.2010 6:14PM 2 elizabeth a. williamson and anna t. c. feistner Habituating primates: processes, techniques, variables and
C:/ITOOLS/WMS/CUP/2155700/WORKINGFOLDER/SETC/9780521194099C02.3D 33 [33 50] 8.9.2010 6:14PM 2 elizabeth a. williamson and anna t. c. feistner Habituating primates: processes, techniques, variables and
The number of males in primate social groups: a comparative test of the socioecological model
 Behav Ecol Sociobiol (1999) 46: 1±13 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 REVIEW Charles L. Nunn The number of males in primate social groups: a comparative test of the socioecological model Received: 24 July 1998 /
Behav Ecol Sociobiol (1999) 46: 1±13 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 REVIEW Charles L. Nunn The number of males in primate social groups: a comparative test of the socioecological model Received: 24 July 1998 /
Circadian rhythm Size in Evolutionary Perspective Forest and Savanna
 ConTenTs Introduction x Chapter 1: the general features of primates 1 Size Range and Adaptive Diversity Brachiation Distribution and Abundance Natural History of Primates Reproduction and Life Cycle Growth
ConTenTs Introduction x Chapter 1: the general features of primates 1 Size Range and Adaptive Diversity Brachiation Distribution and Abundance Natural History of Primates Reproduction and Life Cycle Growth
Evolution of Human Nature Exercise Workbook
 Evolution of Human Nature Exercise Workbook Alan R. Rogers 1 and Elizabeth A. Cashdan All rights reserved. September 30, 2006 1 Department of Anthropology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112
Evolution of Human Nature Exercise Workbook Alan R. Rogers 1 and Elizabeth A. Cashdan All rights reserved. September 30, 2006 1 Department of Anthropology, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112
Peaceful Primates: The History and Function of Reconciliation in Non-Human Primate Societies
 UNDERGRADUATE ESSAY EvoS Journal: The Journal of the Evolutionary Studies Consortium Peaceful Primates: The History and Function of Reconciliation in Non-Human Primate Societies Benjamin M. Seitz Department
UNDERGRADUATE ESSAY EvoS Journal: The Journal of the Evolutionary Studies Consortium Peaceful Primates: The History and Function of Reconciliation in Non-Human Primate Societies Benjamin M. Seitz Department
Although it is widely assumed that human brain evolution
 Human frontal lobes are not relatively large Robert A. Barton a,1 and Chris Venditti b a Evolutionary Anthropology Research Group, Department of Anthropology, Durham University, Durham DH1 3LE, United
Human frontal lobes are not relatively large Robert A. Barton a,1 and Chris Venditti b a Evolutionary Anthropology Research Group, Department of Anthropology, Durham University, Durham DH1 3LE, United
Primate Behavioral Ecology Anthro 381. Nicole Hess, PhD
 Primate Behavioral Ecology Anthro 381 Nicole Hess, PhD Day 1! Syllabus! Perry short film on Abby s group:!http://www.prehensileproductions.com/! Start next series of intro slides ( Why study? ) Why study
Primate Behavioral Ecology Anthro 381 Nicole Hess, PhD Day 1! Syllabus! Perry short film on Abby s group:!http://www.prehensileproductions.com/! Start next series of intro slides ( Why study? ) Why study
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3073 LATS2 Binding ability to SIAH2 Degradation by SIAH2 1-160 161-402 403-480 -/ 481-666 1-666 - - 667-1088 -/ 1-0 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic drawing of LATS2 deletion mutants and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3073 LATS2 Binding ability to SIAH2 Degradation by SIAH2 1-160 161-402 403-480 -/ 481-666 1-666 - - 667-1088 -/ 1-0 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic drawing of LATS2 deletion mutants and
CURRICULUM VITAE TANYA M. MUELLER
 CURRICULUM VITAE TANYA M. MUELLER Department of Anthropology MSC01 1040 909 Washington St. NE University of New Mexico Albuquerque NM 87110 Albuquerque NM 87131 505-259-1905 505-277-4524 swbaboon@gmail.com
CURRICULUM VITAE TANYA M. MUELLER Department of Anthropology MSC01 1040 909 Washington St. NE University of New Mexico Albuquerque NM 87110 Albuquerque NM 87131 505-259-1905 505-277-4524 swbaboon@gmail.com
Effects of Food Dispersion on Dominance Related Behaviors in Garnett's Bushbaby (Otolemur garnettii)?
 The University of Southern Mississippi The Aquila Digital Community Dissertations Spring 5-2013 Effects of Food Dispersion on Dominance Related Behaviors in Garnett's Bushbaby (Otolemur garnettii)? Kyle
The University of Southern Mississippi The Aquila Digital Community Dissertations Spring 5-2013 Effects of Food Dispersion on Dominance Related Behaviors in Garnett's Bushbaby (Otolemur garnettii)? Kyle
Analysis of FY Promoter and Hepatocystis Load in South African Vervet Monkeys (Chlorocebus Aethiops)
 Central Washington University ScholarWorks@CWU All Electronic Theses Electronic Theses Winter 2016 Analysis of FY Promoter and Hepatocystis Load in South African Vervet Monkeys (Chlorocebus Aethiops) Benjamin
Central Washington University ScholarWorks@CWU All Electronic Theses Electronic Theses Winter 2016 Analysis of FY Promoter and Hepatocystis Load in South African Vervet Monkeys (Chlorocebus Aethiops) Benjamin
The B30.2(SPRY) Domain of the Retroviral Restriction Factor TRIM5 Exhibits Lineage-Specific Length and Sequence Variation in Primates
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2005, p. 6111 6121 Vol. 79, No. 10 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.10.6111 6121.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The B30.2(SPRY)
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2005, p. 6111 6121 Vol. 79, No. 10 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.10.6111 6121.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The B30.2(SPRY)
Pigeons learn virtual patterned-string problems in a computerized touch screen environment
 Anim Cogn (2013) 16:737 753 DOI 10.1007/s10071-013-0608-0 ORIGINAL PAPER Pigeons learn virtual patterned-string problems in a computerized touch screen environment Edward A. Wasserman Yasuo Nagasaka Leyre
Anim Cogn (2013) 16:737 753 DOI 10.1007/s10071-013-0608-0 ORIGINAL PAPER Pigeons learn virtual patterned-string problems in a computerized touch screen environment Edward A. Wasserman Yasuo Nagasaka Leyre
General and Comparative Endocrinology
 General and Comparative Endocrinology 174 (2011) 150 155 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect General and Comparative Endocrinology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygcen Hair cortisol
General and Comparative Endocrinology 174 (2011) 150 155 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect General and Comparative Endocrinology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygcen Hair cortisol
Gustatory responsiveness of West African Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) to seven substances tasting sweet to humans
 Linköping University Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology Master Thesis, 60 hp Educational Program: Applied Ethology and Animal Biology Spring 2016 to spring 2017 LITH-IFM-x-EX 17/3362--SE Gustatory
Linköping University Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology Master Thesis, 60 hp Educational Program: Applied Ethology and Animal Biology Spring 2016 to spring 2017 LITH-IFM-x-EX 17/3362--SE Gustatory
Mouse Clec9a ORF sequence
 Mouse Clec9a gene LOCUS NC_72 13843 bp DNA linear CON 1-JUL-27 DEFINITION Mus musculus chromosome 6, reference assembly (C57BL/6J). ACCESSION NC_72 REGION: 129358881-129372723 Mouse Clec9a ORF sequence
Mouse Clec9a gene LOCUS NC_72 13843 bp DNA linear CON 1-JUL-27 DEFINITION Mus musculus chromosome 6, reference assembly (C57BL/6J). ACCESSION NC_72 REGION: 129358881-129372723 Mouse Clec9a ORF sequence
How to choose a pelleted product: Manufacturer por4olios, feeding instruc8ons, product promo8on and nutri8onal knowledge
 How to choose a pelleted product: Manufacturer por4olios, feeding instruc8ons, product promo8on and nutri8onal knowledge Marcus Clauss Clinic for Zoo Animals, Exo2c Pets and Wildlife, Vetsuisse Faculty,
How to choose a pelleted product: Manufacturer por4olios, feeding instruc8ons, product promo8on and nutri8onal knowledge Marcus Clauss Clinic for Zoo Animals, Exo2c Pets and Wildlife, Vetsuisse Faculty,
Identification of Postentry Restrictions to Mason-Pfizer Monkey Virus Infection in New World Monkey Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2008, p. 11140 11151 Vol. 82, No. 22 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00269-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification of Postentry
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2008, p. 11140 11151 Vol. 82, No. 22 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00269-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification of Postentry
An Analysis of Primate Behavioral Responses to Environmental Change: An Anthropological and Neurobiological Approach
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Fall 2013 An Analysis of Primate Behavioral Responses to Environmental Change: An Anthropological and Neurobiological
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Fall 2013 An Analysis of Primate Behavioral Responses to Environmental Change: An Anthropological and Neurobiological
Visitors' Effects on the Welfare of Animals in the Zoo: A Review
 This article was downloaded by: [Dr Kenneth Shapiro] On: 09 June 2015, At: 07:09 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Dr Kenneth Shapiro] On: 09 June 2015, At: 07:09 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
recombination events in the primate genome
 Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on September 12, 2005 as 10.1534/genetics.105.043976 HERV-mediated recombination 1 Human endogenous retroviral elements as indicators of ectopic recombination
Genetics: Published Articles Ahead of Print, published on September 12, 2005 as 10.1534/genetics.105.043976 HERV-mediated recombination 1 Human endogenous retroviral elements as indicators of ectopic recombination
Lecture 9: Primate Behavior - Ecology
 Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution Lecture 9: Primate Behavior - Ecology Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier feldmekj@lavc.edu Homework 2 Why do primates live in groups? Benefits of group life Costs of group life
Anthro 101: Human Biological Evolution Lecture 9: Primate Behavior - Ecology Prof. Kenneth Feldmeier feldmekj@lavc.edu Homework 2 Why do primates live in groups? Benefits of group life Costs of group life
Petra H. J. M. Vlamings, Jana Uher, and Josep Call. Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes 2006, Vol. 32, No. 1, 60 70 Copyright 2006 by the American Psychological Association 0097-7403/06/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0097-7403.32.1.60 How
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes 2006, Vol. 32, No. 1, 60 70 Copyright 2006 by the American Psychological Association 0097-7403/06/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0097-7403.32.1.60 How
Prefrontal white matter volume is disproportionately larger in humans than in other primates
 Prefrontal white matter volume is disproportionately larger in humans than in other primates P Thomas Schoenemann, Michael J Sheehan & L Daniel Glotzer Determining how the human brain differs from nonhuman
Prefrontal white matter volume is disproportionately larger in humans than in other primates P Thomas Schoenemann, Michael J Sheehan & L Daniel Glotzer Determining how the human brain differs from nonhuman
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 15 Primate sociality: Predators and living in groups Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Most haplorrine, and
 Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 15 Primate sociality: Predators and living in groups Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Most haplorrine, and many strepsirrhine, primates are social: they live in
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 15 Primate sociality: Predators and living in groups Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Most haplorrine, and many strepsirrhine, primates are social: they live in
Female Coordination of Group Travel in Wild Propithecus and Eulemur
 International Journal of Primatology, Vol. 20, No. 6, 1999 Female Coordination of Group Travel in Wild Propithecus and Eulemur Elizabeth M. Erhart 1 and Deborah J. Overdorff' 1,2 Received November 11,
International Journal of Primatology, Vol. 20, No. 6, 1999 Female Coordination of Group Travel in Wild Propithecus and Eulemur Elizabeth M. Erhart 1 and Deborah J. Overdorff' 1,2 Received November 11,
Genetic polymorphism and zoonotic potential of Enterocytozoon bieneusi
 AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 10 January 2014 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.03845-13 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 Genetic
AEM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 10 January 2014 Appl. Environ. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/aem.03845-13 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 Genetic
PUBLICATIONS Leslie Ann Knapp January 2008
 PUBLICATIONS Leslie Ann Knapp January 2008 Papers in refereed journals: Leigh, S.R., J.M. Setchell, L.A. Knapp and E.J. Wickings (in press). Growing long in the tooth: Canine tooth size and fitness in
PUBLICATIONS Leslie Ann Knapp January 2008 Papers in refereed journals: Leigh, S.R., J.M. Setchell, L.A. Knapp and E.J. Wickings (in press). Growing long in the tooth: Canine tooth size and fitness in
Martin Clunes s Wild Life: The Lemurs of Madagascar, 2012 Rating = 4
 LEMURS, LORISES, AND TARSIERS Island of Lemurs: Madagascar, 2014 Instructor Rating, Mean = 3.88 (SD = 0.86; n = 17) Runtime: 41 minutes Narrator: Morgan Freeman Species featured: Prolemur simus (Greater
LEMURS, LORISES, AND TARSIERS Island of Lemurs: Madagascar, 2014 Instructor Rating, Mean = 3.88 (SD = 0.86; n = 17) Runtime: 41 minutes Narrator: Morgan Freeman Species featured: Prolemur simus (Greater
VALGUS DEVIATION OF THE DISTAL PHALANX
 J. Anat., Lond. (192), 9, 2, pp. 171-177 171 With text-figures Printed in Great Britain VALGUS DEVIATION OF THE DISTAL PHALANX OF THE GREAT TOE C. H. BARNETT Department of Anatomy, St Thomas's Hospital
J. Anat., Lond. (192), 9, 2, pp. 171-177 171 With text-figures Printed in Great Britain VALGUS DEVIATION OF THE DISTAL PHALANX OF THE GREAT TOE C. H. BARNETT Department of Anatomy, St Thomas's Hospital
ENDOGENOUS retroviruses arise from retroviral
 Copyright Ó 2005 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.043976 Human Endogenous Retroviral Elements as Indicators of Ectopic Recombination Events in the Primate Genome Jennifer F.
Copyright Ó 2005 by the Genetics Society of America DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.043976 Human Endogenous Retroviral Elements as Indicators of Ectopic Recombination Events in the Primate Genome Jennifer F.
A Survey of Pancreatic Lesions in Nonhuman Primates
 Vet. Pathol. IY(Supp. 7): 193-209, 1982 A Survey of Pancreatic Lesions in Nonhuman Primates H. M. MCCLURE and F. W. CHANDLER Yerkes Regional Primate Research Center, Emory University, Atlanta, Ga. and
Vet. Pathol. IY(Supp. 7): 193-209, 1982 A Survey of Pancreatic Lesions in Nonhuman Primates H. M. MCCLURE and F. W. CHANDLER Yerkes Regional Primate Research Center, Emory University, Atlanta, Ga. and
The Use of Human and Conspecific Gestures By Capuchin Monkeys to Solve an Object-Choice Task
 Bucknell University Bucknell Digital Commons Honors Theses Student Theses 2014 The Use of Human and Conspecific Gestures By Capuchin Monkeys to Solve an Object-Choice Task Lindsay Paige Schwartz Bucknell
Bucknell University Bucknell Digital Commons Honors Theses Student Theses 2014 The Use of Human and Conspecific Gestures By Capuchin Monkeys to Solve an Object-Choice Task Lindsay Paige Schwartz Bucknell
ALL ABOUT PRIMATES! Gorilla World and Jungle Trails
 ALL ABOUT PRIMATES! Gorilla World and Jungle Trails WHAT IS A PRIMATE? Primates are a taxonomical Order of related species that fall under the Class Mammalia Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia
ALL ABOUT PRIMATES! Gorilla World and Jungle Trails WHAT IS A PRIMATE? Primates are a taxonomical Order of related species that fall under the Class Mammalia Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia
A n t h r o p o l o g y
 A n t h r o p o l o g y Appreciating Human Diversity Fifteenth Edition Conrad Phillip Kottak University of Michigan McGraw-Hill 2013 McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights Reserved. C H A P T E R THE PRIMATES
A n t h r o p o l o g y Appreciating Human Diversity Fifteenth Edition Conrad Phillip Kottak University of Michigan McGraw-Hill 2013 McGraw-Hill Companies. All Rights Reserved. C H A P T E R THE PRIMATES
Animal Behaviour 84 (2012) 1085e1093. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Animal Behaviour
 Animal Behaviour 84 (2012) 1085e1093 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Animal Behaviour journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/anbehav Review Prosocial behaviour in animals: the influence
Animal Behaviour 84 (2012) 1085e1093 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Animal Behaviour journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/anbehav Review Prosocial behaviour in animals: the influence
Vocal repertoire of sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus torquatus atys) in the Taï National Park
 1 3 4 6 7 8 9 11 1 13 14 1 16 Vocal repertoire of sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus torquatus atys) in the Taï National Park Friederike Range 1 & Julia Fischer 1 Department of Psychology, University of Pennsylvania,
1 3 4 6 7 8 9 11 1 13 14 1 16 Vocal repertoire of sooty mangabeys (Cercocebus torquatus atys) in the Taï National Park Friederike Range 1 & Julia Fischer 1 Department of Psychology, University of Pennsylvania,
Social Interaction Effects on Reward and Cognitive Abilities in Monkeys
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, Department of Psychology Psychology, Department of 2009 Social Interaction Effects on Reward and Cognitive
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, Department of Psychology Psychology, Department of 2009 Social Interaction Effects on Reward and Cognitive
The 40th Meeting of the American Society of Primatologists Scientific Program
 The 40th Meeting of the American Society of Primatologists Scientific Program Friday, August 25, 2017 : Day 1 01:00 PM-02:00 PM: PROGRAM COMMITTEE MEETING (Foyer) [71] 01:00 PM-03:00 PM: PRIMATE CARE COMMITTEE
The 40th Meeting of the American Society of Primatologists Scientific Program Friday, August 25, 2017 : Day 1 01:00 PM-02:00 PM: PROGRAM COMMITTEE MEETING (Foyer) [71] 01:00 PM-03:00 PM: PRIMATE CARE COMMITTEE
instruction at your institution, sending it to specific colleagues who you know, and providing a copy to your institution s administrator.
 This article was originally published in the Encyclopedia of Neuroscience published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author's benefit and for the benefit of the author's
This article was originally published in the Encyclopedia of Neuroscience published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author's benefit and for the benefit of the author's
Laura Garzel, DVM, MS
 Nonhuman Primates Laura Garzel, DVM, MS New World vs Old World Primates Old World Asia and Africa Ischial callosities and cheek pouches Infraorder Catarrhini Narrow nose, nostrils angled down, elongated
Nonhuman Primates Laura Garzel, DVM, MS New World vs Old World Primates Old World Asia and Africa Ischial callosities and cheek pouches Infraorder Catarrhini Narrow nose, nostrils angled down, elongated
Orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus abelii) Spatial Memory and Behavior in a Foraging Task
 Journal of Comparative Psychology 1999, Vol. 113, No. 2, 213-217 Copyright 1999 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0735-7036/99/S3.00 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus abelii)
Journal of Comparative Psychology 1999, Vol. 113, No. 2, 213-217 Copyright 1999 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0735-7036/99/S3.00 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus abelii)
Gustatory responsiveness to food-associated sugars and acids in pigtail macaques, Macaca nemestrina
 Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 495±504 Gustatory responsiveness to food-associated sugars and acids in pigtail macaques, Macaca nemestrina Matthias Laska* Department of Medical Psychology, University
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 495±504 Gustatory responsiveness to food-associated sugars and acids in pigtail macaques, Macaca nemestrina Matthias Laska* Department of Medical Psychology, University
A Comparison of Positive Reinforcement Training Techniques in Owl and Squirrel Monkeys: Time Required to Train to Reliability
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ANIMAL WELFARE SCIENCE, 16:211 220, 2013 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 1088-8705 print/1532-7604 online DOI: 10.1080/10888705.2013.798223 A Comparison of Positive Reinforcement
JOURNAL OF APPLIED ANIMAL WELFARE SCIENCE, 16:211 220, 2013 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 1088-8705 print/1532-7604 online DOI: 10.1080/10888705.2013.798223 A Comparison of Positive Reinforcement
ALL ABOUT PRIMATES! Gorilla World and Jungle Trails
 ALL ABOUT PRIMATES! Gorilla World and Jungle Trails PRIMATE EVOLUTION The ancestors of primates show up in the fossil record around 85 to 65 million years ago. The first true primates fossil was discovered
ALL ABOUT PRIMATES! Gorilla World and Jungle Trails PRIMATE EVOLUTION The ancestors of primates show up in the fossil record around 85 to 65 million years ago. The first true primates fossil was discovered
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/430/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The 4E-BP eif4e axis promotes rapamycinsensitive growth and proliferation in lymphocytes Lomon So, Jongdae Lee, Miguel
Social inhibitory control in five lemur species
 DOI 10.1007/s10329-015-0467-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Social inhibitory control in five lemur species Rachna B. Reddy 1,2 Evan L. MacLean 1 Aaron A. Sandel 2 Brian Hare 1,3 Received: 27 November 2014 / Accepted:
DOI 10.1007/s10329-015-0467-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Social inhibitory control in five lemur species Rachna B. Reddy 1,2 Evan L. MacLean 1 Aaron A. Sandel 2 Brian Hare 1,3 Received: 27 November 2014 / Accepted:
Patricia L. Whitten, Ph.D.
 Curriculum vitae Patricia L. Whitten, Ph.D. Personal Data Current Appointment: Professor of Anthropology, Emory University Affiliations Core Faculty, Neuroscience and Behavioral Biology Program Affiliated
Curriculum vitae Patricia L. Whitten, Ph.D. Personal Data Current Appointment: Professor of Anthropology, Emory University Affiliations Core Faculty, Neuroscience and Behavioral Biology Program Affiliated
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna
 Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Representational format determines numerical competence in monkeys
 Received 10 Nov 2010 Accepted 2 Mar 2011 Published 29 Mar 2011 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1262 Representational format determines numerical competence in monkeys Vanessa Schmitt 1,2 & Julia Fischer 1,2 A range
Received 10 Nov 2010 Accepted 2 Mar 2011 Published 29 Mar 2011 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1262 Representational format determines numerical competence in monkeys Vanessa Schmitt 1,2 & Julia Fischer 1,2 A range
Unit 4 continued Primates and primate behavior
 Unit 4 continued Primates and primate behavior 1 Primates Traits found across the primate order *Tendency towards erect posture *Highly prehensile hands and feet *Generalized dentition *Reliance on complex
Unit 4 continued Primates and primate behavior 1 Primates Traits found across the primate order *Tendency towards erect posture *Highly prehensile hands and feet *Generalized dentition *Reliance on complex
SPONTANEOUS DIABETES IN MONKEYS
 Laboratory Animals (1974) 8, 161-166. 161 SPONTANEOUS DIABETES IN MONKEYS by S. M. JONES Department of Dental Science, Royal College of Surgeons of England, Downe, Orpington, Kent SUMMARY The clinical
Laboratory Animals (1974) 8, 161-166. 161 SPONTANEOUS DIABETES IN MONKEYS by S. M. JONES Department of Dental Science, Royal College of Surgeons of England, Downe, Orpington, Kent SUMMARY The clinical
DC-SIGN from African Green Monkeys Is Expressed in Lymph Nodes and Mediates Infection in trans of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIVagm
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2004, p. 798 810 Vol. 78, No. 2 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.2.798 810.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. DC-SIGN from African
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2004, p. 798 810 Vol. 78, No. 2 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.2.798 810.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. DC-SIGN from African
Quantity matching by an orangutan (Pongo abelii)
 DOI 10.1007/s10071-013-0662-7 ORIGINAL PAPER Quantity matching by an orangutan (Pongo abelii) Jennifer Vonk Received: 11 June 2013 / Revised: 8 July 2013 / Accepted: 10 July 2013 Ó Springer-Verlag Berlin
DOI 10.1007/s10071-013-0662-7 ORIGINAL PAPER Quantity matching by an orangutan (Pongo abelii) Jennifer Vonk Received: 11 June 2013 / Revised: 8 July 2013 / Accepted: 10 July 2013 Ó Springer-Verlag Berlin
Key words: anatomy; Cebus libidinosus; chimpanzees; forearm extensor muscles; modern humans; manipulatory behavior; monkeys; primates
 THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 293:2056 2070 (2010) Comparative Anatomical Study of the Forearm Extensor Muscles of Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al., 2000; Primates, Cebidae), Modern Humans, and Other Primates,
THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 293:2056 2070 (2010) Comparative Anatomical Study of the Forearm Extensor Muscles of Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al., 2000; Primates, Cebidae), Modern Humans, and Other Primates,
INDEX. California State University, Fullerton, v-vi, 263, 280 Cannibalism, 47 Celebes black macaque (Macaca nigra), see primates,
 INDEX Action Plan for Asian Primate Conservation, 23, 24; see also International Union for the Conservation of Nature, species survival commission Africa, 45, 252 African apes, see primates, Agenda Twenty
INDEX Action Plan for Asian Primate Conservation, 23, 24; see also International Union for the Conservation of Nature, species survival commission Africa, 45, 252 African apes, see primates, Agenda Twenty
30 Years with AIDS: Where it Came From and Why It s Still With Us. Kevin McCarthy Ben Morris Jamie Schafer
 30 Years with AIDS: Where it Came From and Why It s Still With Us Kevin McCarthy Ben Morris Jamie Schafer 30 Years with AIDS: Where it Came From and Why It s Still With Us Kevin McCarthy Part I: The Origins
30 Years with AIDS: Where it Came From and Why It s Still With Us Kevin McCarthy Ben Morris Jamie Schafer 30 Years with AIDS: Where it Came From and Why It s Still With Us Kevin McCarthy Part I: The Origins
SEQUENCE EVOLUTION OF THE SPERM LIGAND ZONADHESIN CORRELATES NEGATIVELY WITH BODY WEIGHT DIMORPHISM IN PRIMATES
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00035.x SEQUENCE EVOLUTION OF THE SPERM LIGAND ZONADHESIN CORRELATES NEGATIVELY WITH BODY WEIGHT DIMORPHISM IN PRIMATES Holger Herlyn 1,2 and Hans Zischler
ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00035.x SEQUENCE EVOLUTION OF THE SPERM LIGAND ZONADHESIN CORRELATES NEGATIVELY WITH BODY WEIGHT DIMORPHISM IN PRIMATES Holger Herlyn 1,2 and Hans Zischler
Primate Sleep in Phylogenetic Perspective
 Primate Sleep in Phylogenetic Perspective The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link Terms
Primate Sleep in Phylogenetic Perspective The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link Terms
Rapid Evolution of PARP Genes Suggests a Broad Role for ADP-Ribosylation in Host-Virus Conflicts
 Rapid Evolution of PARP Genes Suggests a Broad Role for ADP-Ribosylation in Host-Virus Conflicts Matthew D. Daugherty 1, Janet M. Young 1, Julie A. Kerns 1,2, Harmit S. Malik 1,3 * 1 Division of Basic
Rapid Evolution of PARP Genes Suggests a Broad Role for ADP-Ribosylation in Host-Virus Conflicts Matthew D. Daugherty 1, Janet M. Young 1, Julie A. Kerns 1,2, Harmit S. Malik 1,3 * 1 Division of Basic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12005 a S Ψ ΨΨ ΨΨ ΨΨ Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ ΨΨ Ψ Ψ ΨΨΨΨΨΨ S1 (a.a. 1 751) S2 (a.a. 752 1353) S1 Fc S1 (a.a. 1-747) Fc b HCoV-EMC-S1-Fc SARS-CoV-S1-Fc HCoV-EMC-S1-Fc SARS-CoV-S1-Fc kda - 170 - - 130
doi:10.1038/nature12005 a S Ψ ΨΨ ΨΨ ΨΨ Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ Ψ ΨΨ Ψ Ψ ΨΨΨΨΨΨ S1 (a.a. 1 751) S2 (a.a. 752 1353) S1 Fc S1 (a.a. 1-747) Fc b HCoV-EMC-S1-Fc SARS-CoV-S1-Fc HCoV-EMC-S1-Fc SARS-CoV-S1-Fc kda - 170 - - 130
Jurmain et al. Chapter 7. Primate Behavior
 Jurmain et al. Chapter 7 Primate Behavior Primate Studies Primate studies often use an ecological approach to explain variation in primate behavior between different species and within a single species.
Jurmain et al. Chapter 7 Primate Behavior Primate Studies Primate studies often use an ecological approach to explain variation in primate behavior between different species and within a single species.
Boucher et al NCOMMS B
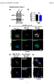 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (linked to Figure 1). mvegfr1 constitutively internalizes in endothelial cells. (a) Immunoblot of mflt1 from undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells with indicated genotypes;
1 Supplementary Figure 1 (linked to Figure 1). mvegfr1 constitutively internalizes in endothelial cells. (a) Immunoblot of mflt1 from undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells with indicated genotypes;
Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-gal antibody
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 84, pp. 1369-1373, March 1987 Immunology Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-gal antibody and the Galal->3Gal epitope in primates* URI GALILItt, MARGARET
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 84, pp. 1369-1373, March 1987 Immunology Evolutionary relationship between the natural anti-gal antibody and the Galal->3Gal epitope in primates* URI GALILItt, MARGARET
Andrea W. Clay a b, Mollie A. Bloomsmith a b, M. Jackson Marr b & Terry L. Maple b a Yerkes National Primate Research Center, Emory
 This article was downloaded by: [Dr Kenneth Shapiro] On: 09 June 2015, At: 08:19 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
This article was downloaded by: [Dr Kenneth Shapiro] On: 09 June 2015, At: 08:19 Publisher: Routledge Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered Number: 1072954 Registered office: Mortimer
Behavioural Brain Research
 Behavioural Brain Research 18 (011) 1 7 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Behavioural Brain Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbr Research report A new tool for measuring hand
Behavioural Brain Research 18 (011) 1 7 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Behavioural Brain Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbr Research report A new tool for measuring hand
The Challenge Hypothesis: Fecal Cortisol Levels in Male Red-Bellied Lemurs During the Reproductive Season
 The Challenge Hypothesis: Fecal Cortisol Levels in Male Red-Bellied Lemurs During the Reproductive Season Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Stolar, Lillian Anna Publisher The University of Arizona.
The Challenge Hypothesis: Fecal Cortisol Levels in Male Red-Bellied Lemurs During the Reproductive Season Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Stolar, Lillian Anna Publisher The University of Arizona.
Received 19 December 2002/Accepted 12 August 2003
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2003, p. 12310 12318 Vol. 77, No. 22 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.22.12310 12318.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Structure
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2003, p. 12310 12318 Vol. 77, No. 22 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.22.12310 12318.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Structure
Non-invasive monitoring of endocrine status Engineering in laboratory primates: methods, guidelines. and applications
 Open Sciences doi:10.5194/asr-5-1-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Science & Research Open Access Proceedings Drinking Water Non-invasive monitoring of endocrine status Engineering
Open Sciences doi:10.5194/asr-5-1-2010 Author(s) 2010. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Science & Research Open Access Proceedings Drinking Water Non-invasive monitoring of endocrine status Engineering
1. Place the families from the third unit of lecture onto the cladogram below in their appropriate places.
 BIOL 325 Plant Systematics Dr. Hardy Some Practice problems for Exam 3 material Revised (problem # 44 added) (keep in mind that 1/3 of the final exam will be on material from the first two exams). 1. Place
BIOL 325 Plant Systematics Dr. Hardy Some Practice problems for Exam 3 material Revised (problem # 44 added) (keep in mind that 1/3 of the final exam will be on material from the first two exams). 1. Place
EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF CEREBRAL MALARIA
 EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF HASTINGS OZWARA, PhD MALARIA PROGRAMME INSTITUTE OF PRIMATE RESEARCH P. O BOX 24481, KAREN - 00502 NAIROBI TEL 254 20 882571/4 FAX 254 20 882546 E-MAIL: OZWARA@IPR.OR.KE INTRODUCTION
EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF HASTINGS OZWARA, PhD MALARIA PROGRAMME INSTITUTE OF PRIMATE RESEARCH P. O BOX 24481, KAREN - 00502 NAIROBI TEL 254 20 882571/4 FAX 254 20 882546 E-MAIL: OZWARA@IPR.OR.KE INTRODUCTION
Novel Adenoviruses in Wild Primates: a High Level of Genetic Diversity and Evidence of Zoonotic Transmissions
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2011, p. 10774 10784 Vol. 85, No. 20 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00810-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Novel Adenoviruses in
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2011, p. 10774 10784 Vol. 85, No. 20 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.00810-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Novel Adenoviruses in
Left Nipple Preferences in Infant Pan paniscus and P. troglodytes
 International Journal of Primatology, Vol. 27, No. 6, December 2006 ( C 2006) DOI: 10.1007/s10764-006-9086-4 Left Nipple Preferences in Infant Pan paniscus and P. troglodytes William D. Hopkins 1,2,5 and
International Journal of Primatology, Vol. 27, No. 6, December 2006 ( C 2006) DOI: 10.1007/s10764-006-9086-4 Left Nipple Preferences in Infant Pan paniscus and P. troglodytes William D. Hopkins 1,2,5 and
TWO MAJOR GROUPS: PROSIMIANS NOT MANY SPECIES, LESS ADVANCED ANTHROPOIDS A TON OF SPECIES, MORE ADVANCED
 PRIMATES TWO MAJOR GROUPS: PROSIMIANS NOT MANY SPECIES, LESS ADVANCED ANTHROPOIDS A TON OF SPECIES, MORE ADVANCED PROSIMIANS: RESEMBLE OTHER MAMMALS MORE THAN ANTHROPOID PRIMATES MORE SMELL DEPENDENT FOR
PRIMATES TWO MAJOR GROUPS: PROSIMIANS NOT MANY SPECIES, LESS ADVANCED ANTHROPOIDS A TON OF SPECIES, MORE ADVANCED PROSIMIANS: RESEMBLE OTHER MAMMALS MORE THAN ANTHROPOID PRIMATES MORE SMELL DEPENDENT FOR
