CLINICAL UTILITY OF POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION FOR IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
|
|
|
- Jewel Madison Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article CLINICAL UTILITY OF POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION FOR IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN Monica Chaudhary 1, C.P. Baveja 1, V.K. Sharma 1 and G.R. Sethi 2 (Original received on Revised version received on Accepted on ) Summary Background: Conventional bacteriological methods rarely detect M. tuberculosis in clinical samples from children and, hence are of limited use in the diagnosis of active tuberculosis in them. There is need for an alternative detection method which is rapid, specific and sensitive. Aim: The efficacy of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) was evaluated in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in children. Methods: Sixty two (62) hospitalized children were included in the study. Thirty-one were suffering from active tuberculosis, 11 children had tuberculous infection but no active disease and 20 children had other unrelated diagnosis. Early morning gastric aspirates and sputum samples were processed using conventional techniques of mycobacterial isolation and PCR for M. tuberculosis complex specific MPB64 gene. Favorable response to anti- tubercular treatment (ATT) was taken as the gold standard. Results: In the active tuberculosis group 12 out 31 children were positive by PCR while microscopy and culture were positive in 3 and 6 children respectively. All samples positive by microscopy and culture were positive by PCR giving a sensitivity of 100% for culture confirmed cases. Conclusion: Benefit of rapid and reliable results with PCR offers an appreciable advantage over traditional techniques when used in conjunction with clinical profile and epidemiological factors such as age, socio-economic and nutritional status, contact history and any other intercurrent illness. [Indian J Tuberc 2006: 53: ] Key Words: PCR, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Tuberculosis, Children, Diagnosis. INTRODUCTION In India, the overall prevalence of infection (as judged by the standard tuberculin test) is about 30% in contrast to 2-3 % in developed countries. About 20% of children become tuberculin positive by the age of 5 years and 55% by 20 years 1. As much as 43% of children under the age of 1 year, 24% of children 1-5 years of age and 15% of adolescents develop active tuberculosis sometime after primary infection. The diagnosis of active tuberculosis in children is usually epidemiological and indirect which include exposure tracing, adequate history, tuberculin skin test, chest roentgenogram and physical examination 2. Conventional diagnostic tests such as acid fast stain are frequently negative in children with active tuberculosis disease and multiple cultures give positive results in no more than 20% of samples 3. A delay in diagnosis has been directly related to poor prognosis and severe disease. With PCR becoming widely available, it is important to know how to interpret its results in children. We have tried to evaluate the role of PCR for detection of M. tuberculosis in clinical samples from children with and without tuberculosis. MATERIAL AND METHODS Sixty-two (62) hospitalized children were taken from the Pediatrics ward, Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi. Thirty-one (31) cases had clinical diagnosis of tuberculosis which was made in the presence of following criteria: (1) Abnormal chest X-ray suggestive of tuberculosis like para tracheal gland, hilar lymphadenopathy, segmental lesion, miliary lesion, unresolving pneumonia, chronic cavitary lesion. With (2) a) positive tuberculin test which is taken 1. Department of Microbiology, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi. 2. Department of Pediatrics, Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi. Correspondence: Dr. Monica Chaudhary, 33/20, Rajpur Road, Civil Lines, Delhi jaglanbs@hotmail.com
2 MONICA CHAUDHARY ET AL 213 as10-mm or more induration at hrs following 1TU of PPD intradermally Or b) an adult source case identified with contagious M.tuberculosis disease. All the children with clinical diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis were given anti-tubercular treatment (ATT) and were observed regularly for a minimum period of three months for clinical improvement. Eleven (11) children had a positive tuberculin skin test but on diagnostic and radiological evaluation had no evidence of active tuberculosis disease. These children were identified during contact investigations and presented with vague symptoms like fever/ cough/ anorexia/weight loss. All these children received preventive therapy. Twenty (20) children had bacterial or viral broncho-pulmonary infections with negative tuberculin skin test and who completely recovered after appropriate nontubercular treatment (Table 1). Early morning gastric aspirates and sputum specimens (from older children) were collected 4 from all the children before the institution of any treatment. All the specimens were decontaminated and concentrated by using conventional techniques 5. Each sample was examined by Ziehl-Neelsen (ZN) stain and cultured on Lowenstien-Jensen (LJ) medium 5. PCR was performed in three different areas physically separated from each other. The reaction mix was made in a sterile laminar flow hood. DNA extraction and PCR were carried out according to the protocol published by Dar L et al 6. A 240 bp region ( ) from the gene encoding MPB 64 protein was selected for amplification using the following primers: 1. [ ] TCCGCTGCCAGTCGTCTTCC-3 2. [ ] GTCCTCGCGAGTCTAGGCCA-3 Amplification of the gene was done in 50µl of reaction mixture containing 10µl of genomic DNA, 10mM Tris HCl (ph-8.3), 1.5 mm MgCl 2, 50mM NaCl, 200µl of each dntp (Boehringer Mannheim, Germany),0.4µM of each primer and 1.25 U of Taq DNA Polymerase (Amplitaq, Perkin Elmer). The reaction mixture was overlaid with 50µl of light mineral oil to prevent evaporation. Amplification was carried out for 40 cycles in a DNA Thermal cycler( Perkin Elmer, Cetus, USA). Each cycle comprised of 3 steps: denaturation (94 C for 2 minutes); annealing (55 C for 2 minutes); extension (72 C for 2 minutes). Table 1: Demographic profile of the study groups Clinically active Infection without No Tuberculosis Total disease disease No. of children Mean age (years) Sex ratio 1:0.82 1:0.90 1:0.53 1:0.75 (male : female) No. of children vaccinated with BCG
3 214 DIAGNOSIS OF PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS BY PCR Table 2: Bacteriological and PCR results in the three study groups Tuberculosis status Children with a positive result Smear Culture PCR Active disease 5(9.67%) 6(19.35%) 12(38.7%) (n=31) Infection without disease 0 0 2(18.1%) (n=11) No Tuberculosis (n=20) The final extension step was for 5 minutes at 72 o C. Each test included a positive control consisting of DNA extracted from M. tuberculosis 37 Ra, and a minimum of three interspersed negative controls containing distilled water in the place of sample. Detection and Identification of the Amplified Product: The amplified product was electrophoresed into 2% agarose gels. The gels were stained with ethidium bromide and visualized in an ultraviolet transilluminator. The presence of a 240 bp fragment indicated a positive PCR result. Hae III digest of FX174 DNA was used as molecular size marker. RESULTS The results are shown in Table 2. PCR was positive in all 6 culture positive samples showing 100% correlation with culture results. However PCR was positive in 6 culture negative specimens also, thus detecting 19.3% more cases when compared to culture results and 29.03% more cases when compared to microscopy results. All the 11 children who had tuberculosis infection but no disease were negative by microscopy and culture but 2(18.1%) were positive by PCR. Twenty (20) children with other unrelated broncho-pulmonary infections were negative by microscopy, culture and PCR DISCUSSION Tuberculosis is difficult to diagnose in children because of poor yield on standard diagnostic laboratory tests and the lack of characteristic symptoms in majority of the children. A presumptive diagnosis is usually established on the basis of clinical criteria and the results of tuberculin skin test. In countries where BCG is commonly used, the decision is further complicated by difficulties in interpretation of skin test results 3. The problem is compounded by the fact that conventional epidemiological tools used for assessment are difficult to apply in this category because of the absence of an objective method or a gold standard for the diagnosis of tuberculosis 7. Our study confirmed the difficulty in obtaining bacterial proof of tuberculosis in children. Only 9.67% (3/31) of children with active disease had positive smears and 19.3% (6/31) had positive cultures which is comparable with other studies from 2, 3,7,8,9. India and abroad DNA amplification by PCR identified M.tuberculosis in 38.7 %( 12/ 31) of children with active tuberculosis. In microscopy negative
4 MONICA CHAUDHARY ET AL 215 specimens and culture negative specimens PCR was able to detect 29.03% and 19.3% more positive cases respectively. It was unlikely that these were false positive samples because all the positive patients by PCR showed improvement on institution of ATT. Most of the American and European studies 7, 8, 10 have shown PCR positivity on specimens from children with pulmonary tuberculosis to be between 24% and 83%. There were 19 cases of active tuberculosis in whom PCR was negative. Of these, 11 children had hilar shadows but no pulmonary infilterates on chest X-ray which is consistent with the common observation that positive results are obtained more often in specimens from children with pulmonary infiltrates than with hilar adenopathy alone 3. Other negatives could have resulted from various reasons. Because samples were collected in the course of routine diagnostic evaluation, determined by the child s primary physician, we had limited control over the number of specimens collected from each child. Although it is possible that a higher number of specimens may have increased the yield of PCR 3,8,our study is representative of clinical practice. Moreover, our hospital is a referral centre and rarely receives patients who have not received some treatment (including ATT) prior to admission. The previous treatment status often proves difficult to establish, as many of our patients are illiterate. M.tuberculosis was also detected in 2 children (18.1%) with tuberculosis infection without disease. It was unlikely that this was a false positive reaction because a rigorous protocol was followed to prevent carry over contamination and negative controls yielded consistently negative results. Both these children had a recent history of exposure to active pulmonary tuberculosis. Our results signify that M.tuberculosis was present in sufficient density to be detected in samples by PCR and also highlight the artificial character of the clinical distinction between infection and disease. Recognition of infected patients without symptoms is difficult in pediatric practice. In children, the development of tuberculosis disease is usually a continuum from infection to lympho-hematogenous spread to pulmonary disease. It can be difficult to determine clinically at what point tuberculosis infection progresses to disease 10. More than half of these children have enlarged lymphnodes as assessed on CT scan but with no detectable disease on chest radiograph. Positive PCR results have been reported in children with tuberculosis infection but no apparent disease 3,8,10. American Thoracic Society 11 gives guidelines for treatment of infected children based on clinical and radiographic criteria and recommends a one-drug regimen with isoniazid. Thus according to these established criteria, PCR is not a good test to distinguish between tuberculous infection from disease in children who have been infected recently. We therefore, consider it unjustified to collect gastric aspirates or sputum samples for PCR routinely in children with suspected tuberculosis infection and rather it should be reserved for clinically suspected cases of tuberculosis disease with abnormal pulmonary findings. We conclude that though, the sensitivity of PCR is certainly higher than that of culture for detecting M. tuberculosis in children, PCR alone is insufficient as a single diagnostic test. Technical considerations, including the use of suitable controls and the retesting of doubtful positive samples considerably influence the sensitivity and specificity. But a well standardized PCR when taken in conjunction with epidemiological and clinical factors, offers the benefit of rapid and reliable results within 48 hrs thereby removing a significant amount of clinical diagnostic uncertainty and influences the decision regarding ATT. Specific early diagnosis will lead to evidence based management of children with tuberculosis in comparison to empirical therapy adopted in most cases. REFERENCES 1. Ghai O P. Tuberculosis in childhood. In: Essential Paediatrics, 3rd edition. Interprint, 1993: Starke J R. Modern approach to the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis in children.paediatr Clin Nor Am 1988; 35(3):
5 216 DIAGNOSIS OF PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS BY PCR 3. Pierre C,Oliver C, Lecossier D, Boussougant Y, Patrick Y, Hance AJ. Diagnosis of primary tuberculosis in children by amplification and detection of mycobacterial DNA. Am Rev Respir Dis 1993; 147: Mycobacteria.In: Bailey and Scotts Diagnostic Microbiology, 10th edition. Betty AF, Sahm DF, Wiessfield AS (eds) pp: Roberts CD, Koneman EW, Kim YK. Mycobacteria. In: Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 5th edition. Blaus A, Hausler WJ, Herrman KL, Isenberg HD, Shadomy HJ (eds),1995. pp: Dar L, Sharma SK, Bhanu NV, Broor S, Chakraborty M, Seth P. Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis by polymerase chain reaction for MPB64 gene: An evaluation in a blind study. Ind J Chest Dis Allied Sci 1998; 40: Jatana SK, Nair MNG, Lahiri KK, Sarin NP.Polymerase Chain Reaction in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Indian Pediatrics 2000; 37: Delacourt C, Poveda JD, Chureau C et al. Use of polymerase chain reaction for improved diagnosis of tuberculosis in children. J Paediatr 1994; 126(5): Singh M, Moosa NVA, Kumar L, Sham M. Role of gastric lavage and broncho-alveolar lavage in bacteriological diagnosis of childhood pulmonary tuberculosis. Indian Paediatrics 2000; 37: Smith KC, Starke JR, Eisenach K, Ong LT, Denby M. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical specimens from children using polymerase chain reaction. Paediatrics 1996; 97(2): American Thoracic Society. Treatment of tuberculosis and tuberculosis infection in adults and children. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994; 149: th TB SEAL CAMPAIGN His Excellency Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam, President of India, who is also the Patron of the Association, inaugurated the 57 th TB Seal Campaign Gandhi Jayanti Day - at a solemn function held at Rashtrapati Bhawan on 2nd October, 2006, when TB Seals on Cultural Heritage were presented to Rashtrapatiji by Dr. Anbumani Ramadoss, Minister for Health and Family Welfare. The special souvenir brought out on the occasion was presented by Smt. P. Lakshmi, Minister of State for Health & Family Welfare, to Rashtrapatiji.
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS USING CONVENTIONAL TOOLS AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION*
 Original Article A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS USING CONVENTIONAL TOOLS AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION* Kavita Modi Parekh 1, Vikas Inamdar 2, Anagha Jog 3 and Anita Kar
Original Article A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE DIAGNOSIS OF PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS USING CONVENTIONAL TOOLS AND POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION* Kavita Modi Parekh 1, Vikas Inamdar 2, Anagha Jog 3 and Anita Kar
Diagnostic Value of Elisa Serological Tests in Childhood Tuberculosis
 Diagnostic Value of Elisa Serological Tests in Childhood Tuberculosis by R. Dayal, a G. Sirohi, a M. K. Singh, a P. P. Mathur, a B. M. Agarwal, a V. M. Katoch, b B. Joshi, b P. Singh, b and H. B. Singh
Diagnostic Value of Elisa Serological Tests in Childhood Tuberculosis by R. Dayal, a G. Sirohi, a M. K. Singh, a P. P. Mathur, a B. M. Agarwal, a V. M. Katoch, b B. Joshi, b P. Singh, b and H. B. Singh
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011
 TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
Application of enzyme amplified mycobacterial DNA detection in the diagnosis of pulmonary & extra-pulmonary tuberculosis
 Indian J Med Res 118, December 2003, pp 224-228 Application of enzyme amplified mycobacterial DNA detection in the diagnosis of pulmonary & extra-pulmonary tuberculosis Vandana Tiwari, Amita Jain & R.
Indian J Med Res 118, December 2003, pp 224-228 Application of enzyme amplified mycobacterial DNA detection in the diagnosis of pulmonary & extra-pulmonary tuberculosis Vandana Tiwari, Amita Jain & R.
TB Intensive Houston, Texas. Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith. November 12, 2009
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
Objective: To determine the sensitivity of bacteriologic studies in pediatric pulmonary tuberculosis.
 Microbiology of Pediatric Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis* José M. Merino, MD; Teresa Alvarez, MD; Manuel Marrero, MD; Sara Ansó, MD; Ana Elvira, MD; Gemma Iglesias, MD; and José B. González, MD Objective:
Microbiology of Pediatric Primary Pulmonary Tuberculosis* José M. Merino, MD; Teresa Alvarez, MD; Manuel Marrero, MD; Sara Ansó, MD; Ana Elvira, MD; Gemma Iglesias, MD; and José B. González, MD Objective:
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Laboratory Evaluation of a New Rapid Slide Culture (RSC) Technique for Diagnosis of Extra-
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Laboratory Evaluation of a New Rapid Slide Culture (RSC) Technique for Diagnosis of Extra-
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children
 Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital (TCH) Estimated TB incidence
Diagnosis of tuberculosis in children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, and Tygerberg Children s Hospital (TCH) Estimated TB incidence
TB: A Supplement to GP CLINICS
 TB: A Supplement to GP CLINICS Chapter 10: Childhood Tuberculosis: Q&A For Primary Care Physicians Author: Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor What is Childhood TB and who is at risk? India
TB: A Supplement to GP CLINICS Chapter 10: Childhood Tuberculosis: Q&A For Primary Care Physicians Author: Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor What is Childhood TB and who is at risk? India
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Smith, MD, MPH July 19, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Smith, MD, MPH July 19, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
The Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis*
 The Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis* jose Manuel Querol, MD, PhD; Maria Amparo Farga, PhD; Damiana Granda, MD, PhD; Concepcion Gimeno, MD, PhD; and
The Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis* jose Manuel Querol, MD, PhD; Maria Amparo Farga, PhD; Damiana Granda, MD, PhD; Concepcion Gimeno, MD, PhD; and
T uberculosis is one of the leading causes of mortality and
 624 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence and risk factors for transmission of infection among children in household contact with adults having pulmonary tuberculosis M Singh, M L Mynak, L Kumar, J L Mathew, S K
624 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence and risk factors for transmission of infection among children in household contact with adults having pulmonary tuberculosis M Singh, M L Mynak, L Kumar, J L Mathew, S K
Biology and Medicine
 eissn: 09748369 Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis by smear microscopy and culture in a tertiary health care facility Biology and Medicine SI Khatib, MT Williamson, R Singh, JM Joshi Accepted: 28 th Feb
eissn: 09748369 Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis by smear microscopy and culture in a tertiary health care facility Biology and Medicine SI Khatib, MT Williamson, R Singh, JM Joshi Accepted: 28 th Feb
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
SMEAR MICROSCOPY AS SURROGATE FOR CULTURE DURING FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY MDR-TB PATIENTS ON DOTS PLUS TREATMENT
 Original Article SMEAR MICROSCOPY AS SURROGATE FOR CULTURE DURING FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY MDR-TB PATIENTS ON DOTS PLUS TREATMENT R. Sarin 1, R. Singla 2, P. Visalakshi 3, A. Jaiswal 4, M.M. Puri 4, Khalid
Original Article SMEAR MICROSCOPY AS SURROGATE FOR CULTURE DURING FOLLOW UP OF PULMONARY MDR-TB PATIENTS ON DOTS PLUS TREATMENT R. Sarin 1, R. Singla 2, P. Visalakshi 3, A. Jaiswal 4, M.M. Puri 4, Khalid
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH April 6, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH April 6, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques. Hugo Donaldson Consultant Microbiologist Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust
 Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques Hugo Donaldson Consultant Microbiologist Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust Learning Objectives 1) When to consider a diagnosis of TB 2) When to consider a referral
Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques Hugo Donaldson Consultant Microbiologist Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust Learning Objectives 1) When to consider a diagnosis of TB 2) When to consider a referral
Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017
 Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures
Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012
 TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
(a) Infection control program. The facility must establish an infection control program under which it--
 420-5-10-.17 Infection Control. (1) The facility must establish and maintain an infection control program designed to provide a safe, sanitary, and comfortable environment and to help prevent the development
420-5-10-.17 Infection Control. (1) The facility must establish and maintain an infection control program designed to provide a safe, sanitary, and comfortable environment and to help prevent the development
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, Pediatric TB Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH March 8, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH March 8, 2012 Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH March 8, 2012 Kim Connelly Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Biochemical and molecular characterization of cerebrospinal fluid for the early and accurate diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2015; 26 (3): 426-430 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Biochemical and molecular characterization of cerebrospinal fluid for the early and accurate diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Biomedical Research 2015; 26 (3): 426-430 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Biochemical and molecular characterization of cerebrospinal fluid for the early and accurate diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
SHORT COURSE CHEMOTHERAPY FOR PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
 SHORT COURSE CHEMOTHERAPY FOR PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN Padma Ramachandran, A.S. Kripasankar and M. Duraipandian* chest radiograph suggestive of tuberculosis. There are a number of reports on
SHORT COURSE CHEMOTHERAPY FOR PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN Padma Ramachandran, A.S. Kripasankar and M. Duraipandian* chest radiograph suggestive of tuberculosis. There are a number of reports on
TUBERCULOSIS. By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi
 TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
TUBERCULOSIS By Dr. Najaf Masood Assistant Prof Pediatrics Benazir Bhutto Hospital Rawalpindi Tuberculosis Infectious, Systemic, Chronic granulomatous disease caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis DEFINITION
Correlation Of Immunological And Pathological Parameters In Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 3 Ver. IV (Mar. 2016), PP 14-25 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation Of Immunological And Pathological
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 3 Ver. IV (Mar. 2016), PP 14-25 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation Of Immunological And Pathological
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
EQUIVALENCE OF ACID ALONE OR ACID-ALCOHOL AS DECOLOURIZING AGENT IN ZIEHL - NEELSEN METHOD
 Original Article 219 EQUIVALENCE OF ACID ALONE OR ACID-ALCOHOL AS DECOLOURIZING AGENT IN ZIEHL - NEELSEN METHOD M. Gomathi Sekar, Fathima Rehman, Vanaja Kumar and N. Selvakumar (Received on 12.4.2012;
Original Article 219 EQUIVALENCE OF ACID ALONE OR ACID-ALCOHOL AS DECOLOURIZING AGENT IN ZIEHL - NEELSEN METHOD M. Gomathi Sekar, Fathima Rehman, Vanaja Kumar and N. Selvakumar (Received on 12.4.2012;
Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 28 4, 373 377, December 2016 Case Report Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review Makoto HAYASHI 1, Satoshi MATSUKURA 1,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 28 4, 373 377, December 2016 Case Report Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review Makoto HAYASHI 1, Satoshi MATSUKURA 1,
EVALUATION OF POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION FOR RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS
 Original Article Ind. J Tub., 2002,49, 133 EVALUATION OF POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION FOR RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS Joy Sarojini Michael 1, M.K. Lalitha 1,Thomas Cherian 2, Kurien Thomas 3,
Original Article Ind. J Tub., 2002,49, 133 EVALUATION OF POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION FOR RAPID DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOUS MENINGITIS Joy Sarojini Michael 1, M.K. Lalitha 1,Thomas Cherian 2, Kurien Thomas 3,
using this recommended dose of 1 TU PPD, should
 Archives of Disease in Childkood, 1980, 55, 795-799 Unreliability of the Mantoux test using 1 TU PPD in excluding childhood tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea KATHLEEN MURTAGH Department of Clinical Sciences,
Archives of Disease in Childkood, 1980, 55, 795-799 Unreliability of the Mantoux test using 1 TU PPD in excluding childhood tuberculosis in Papua New Guinea KATHLEEN MURTAGH Department of Clinical Sciences,
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS. Objectives. Children are not just small adults. Pediatric Tuberculosis 1
 PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS
 PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
PEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS Ann M. Loeffler, M.D. Faculty Consultant Curry International Tuberculosis Center Objectives At the end of this session, participants will be able to describe: how pediatric patients
ANNEXURE A: EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE DMR 164 REPORTING ON HIV AND TB FORM
 ANNEXURE A: EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE DMR 164 REPORTING ON HIV AND TB FORM The form and content of the explanatory note is to: Inform those responsible for completing the DMR 164 Reporting Form - as to
ANNEXURE A: EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE DMR 164 REPORTING ON HIV AND TB FORM The form and content of the explanatory note is to: Inform those responsible for completing the DMR 164 Reporting Form - as to
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives l Recognize that tuberculosis as a chronic disease mainly affecting
Mycobacteria & Tuberculosis PROF.HANAN HABIB & PROF ALI SOMILY DEPRTMENT OF PATHOLOGY, MICROBIOLOGY UNIT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives l Recognize that tuberculosis as a chronic disease mainly affecting
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Rapid differentiation of mycobacterium tuberculosis and mycobacterium leprae from sputum by polymerase chain reaction
 Original Article Nepal Medical College Journal 27; 9(1): Rapid differentiation of mycobacterium tuberculosis and mycobacterium leprae from sputum by polymerase chain reaction Bishwa Raj Sapkota, Chaman
Original Article Nepal Medical College Journal 27; 9(1): Rapid differentiation of mycobacterium tuberculosis and mycobacterium leprae from sputum by polymerase chain reaction Bishwa Raj Sapkota, Chaman
Prospective evaluation of World Health Organization criteria to assist diagnosis of tuberculosis in children
 Eur Respir J 99; : DOI:./99.9. Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 99 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 9-9 Prospective evaluation of World Health Organization criteria to assist
Eur Respir J 99; : DOI:./99.9. Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 99 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 9-9 Prospective evaluation of World Health Organization criteria to assist
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Sponsored document from The Journal of Infection
 Sponsored document from The Journal of Infection Impact of a T cell-based blood test for tuberculosis infection on clinical decision-making in routine practice Sarah Gooding a,e, Oni Chowdhury a,e, Tim
Sponsored document from The Journal of Infection Impact of a T cell-based blood test for tuberculosis infection on clinical decision-making in routine practice Sarah Gooding a,e, Oni Chowdhury a,e, Tim
Standard Diagnostic Procedure for Tuberculosis: A Review
 ISSN: 2249 8656 www.stmjournals.com Standard Diagnostic Procedure for Tuberculosis: A Review Suresh Jaiswal*, Jay Prakash Sah, Bhoopendra Sharma Department of Medical Lab Science, School of Health and
ISSN: 2249 8656 www.stmjournals.com Standard Diagnostic Procedure for Tuberculosis: A Review Suresh Jaiswal*, Jay Prakash Sah, Bhoopendra Sharma Department of Medical Lab Science, School of Health and
Search for a low-cost screening test for female genital tuberculosis: A study in a tertiary care level hospital of West Bengal
 Original article Search for a low-cost screening test for female genital tuberculosis: A study in a tertiary care level hospital of West Bengal 1 Dr. Amitava Chakraborty, 2 Dr. Nasima Khondker, 3 Dr. Aditya
Original article Search for a low-cost screening test for female genital tuberculosis: A study in a tertiary care level hospital of West Bengal 1 Dr. Amitava Chakraborty, 2 Dr. Nasima Khondker, 3 Dr. Aditya
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
1 1* 1. B. V. Peerapur, Abdul Kaleem Bahadur, Manasa Divakar
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sodium Hypochlorite Sedimentation Technique: A Simple Way to Enhance Sensitivity of Ziehl-Neelsen Stain in Diagnosis of Smear Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis 1 1* 1 B. V.
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sodium Hypochlorite Sedimentation Technique: A Simple Way to Enhance Sensitivity of Ziehl-Neelsen Stain in Diagnosis of Smear Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis 1 1* 1 B. V.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): Its comparison with conventional techniques for diagnosis of extra-pulmonary tubercular diseases
 2003 Indian Journal of Surgery www.indianjsurg.com Original Article Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): Its comparison with conventional techniques for diagnosis of extra-pulmonary tubercular diseases R.
2003 Indian Journal of Surgery www.indianjsurg.com Original Article Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): Its comparison with conventional techniques for diagnosis of extra-pulmonary tubercular diseases R.
* MILIARY MOTTLING --
 * MILIARY MOTTLING -- RARE CAUSE DR ARATHI SRINIVASAN FELLOW IN PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY DR A ANDAL DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS DR JULIUS XAVIER SCOTT DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY KANCHI KAMAKOTI
* MILIARY MOTTLING -- RARE CAUSE DR ARATHI SRINIVASAN FELLOW IN PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY DR A ANDAL DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS DR JULIUS XAVIER SCOTT DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY KANCHI KAMAKOTI
TB IN EMERGENCIES. Disease Control in Humanitarian Emergencies (DCE)
 TB IN EMERGENCIES Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR) Health Security and Environment Cluster (HSE) (Acknowledgements WHO Stop TB Programme WHO/STB) 1 Why TB? >33% of the global
TB IN EMERGENCIES Department of Epidemic and Pandemic Alert and Response (EPR) Health Security and Environment Cluster (HSE) (Acknowledgements WHO Stop TB Programme WHO/STB) 1 Why TB? >33% of the global
Akansha Arora*, Anil Jain, B. S. Karnawat, Rakesh Kumawat
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Arora A et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Jul;5(4):1609-1613 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Arora A et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Jul;5(4):1609-1613 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY FOR DETECTION OF MYCOBACTERIA BY DIRECT AFB SMEAR EXAMINATION, CULTURE BY LOWENSTEIN JENSEN MEDIA, FLUORESCENT SENSOR TECHNOLOGY BASED BACTEC TM MICRO MGIT TM SYSTEM & PCR Pratibha
A COMPARATIVE STUDY FOR DETECTION OF MYCOBACTERIA BY DIRECT AFB SMEAR EXAMINATION, CULTURE BY LOWENSTEIN JENSEN MEDIA, FLUORESCENT SENSOR TECHNOLOGY BASED BACTEC TM MICRO MGIT TM SYSTEM & PCR Pratibha
Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!!
 Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!! DECLARATION No relevant conflicts of interest to declare OVERVIEW Burden of disease & epidemiology Pathogenesis (not
Gary Reubenson 16 October 2012 PAEDIATRIC TUBERCULOSIS: AN OVERVIEW IN 40 MINUTES!! DECLARATION No relevant conflicts of interest to declare OVERVIEW Burden of disease & epidemiology Pathogenesis (not
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis
 Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Mycobacterial Infections: What the Primary Provider Should Know about Tuberculosis Henry F. Chambers, M.D Professor of Medicine, UCSF Topics for Discussion Epidemiology Diagnosis of active TB Screening
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
Rapid PCR TB Testing Results in 68.5% Reduction in Unnecessary Isolation Days in Smear Positive Patients.
 Rapid PCR TB Testing Results in 68.5% Reduction in Unnecessary Isolation Days in Smear Positive Patients. Item Type Thesis Authors Patel, Ravikumar Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright
Rapid PCR TB Testing Results in 68.5% Reduction in Unnecessary Isolation Days in Smear Positive Patients. Item Type Thesis Authors Patel, Ravikumar Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright
Chapter 4 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease
 Chapter 4 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 75 Introduction.... 77 Medical Evaluation.......................................................... 78 Chapter Summary...
Chapter 4 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 75 Introduction.... 77 Medical Evaluation.......................................................... 78 Chapter Summary...
Bilateral multiple choroidal granulomas and systemic vasculitis as presenting features of tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
 Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Childhood Tuberculosis Some Basic Issues. Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Baylor College of Medicine
 Childhood Tuberculosis Some Basic Issues Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Baylor College of Medicine TUBERCULOSIS IS A SOCIAL DISEASE WITH MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS THE GREAT PARADOX OF TUBERCULOSIS A CAUTIONARY TALE
Childhood Tuberculosis Some Basic Issues Jeffrey R. Starke, M.D. Baylor College of Medicine TUBERCULOSIS IS A SOCIAL DISEASE WITH MEDICAL IMPLICATIONS THE GREAT PARADOX OF TUBERCULOSIS A CAUTIONARY TALE
Statement. Consensus Statement of IAP Working Group: Status Report on Diagnosis of Childhood Tuberculosis
 Statement Consensus Statement of IAP Working Group: Status Report on Diagnosis of Childhood Tuberculosis In consonance with the decision of the Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) to standardize protocols
Statement Consensus Statement of IAP Working Group: Status Report on Diagnosis of Childhood Tuberculosis In consonance with the decision of the Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) to standardize protocols
IMPACT OF IMPROVED TREATMENT SUCCESS ON THE PREVALENCE OF TB IN A RURAL COMMUNITY BASED ON ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE
 Original Article IMPACT OF IMPROVED TREATMENT SUCCESS ON THE PREVALENCE OF TB IN A RURAL COMMUNITY BASED ON ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE P. G. Gopi, R. Subramani, V. Chandrasekaran, T. Santha and P. R. Narayanan
Original Article IMPACT OF IMPROVED TREATMENT SUCCESS ON THE PREVALENCE OF TB IN A RURAL COMMUNITY BASED ON ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE P. G. Gopi, R. Subramani, V. Chandrasekaran, T. Santha and P. R. Narayanan
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Impact of a T cell-based blood test for tuberculosis infection on clinical decision-making in routine practice
 Journal of Infection (2007) 54, e169ee174 www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/jinf CASE REPORT Impact of a T cell-based blood test for tuberculosis infection on clinical decision-making in routine practice
Journal of Infection (2007) 54, e169ee174 www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/jinf CASE REPORT Impact of a T cell-based blood test for tuberculosis infection on clinical decision-making in routine practice
Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of. Latent Tuberculosis. Infection and Tuberculosis Disease
 Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Collar stud abscess an interesting case report
 Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor Camilla Rodrigues, MD co-author Abstract Most individuals who get exposed
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor Camilla Rodrigues, MD co-author Abstract Most individuals who get exposed
INTENSIFIED TB CASE FINDING
 INTENSIFIED TB CASE FINDING My friends call me Intensified Case Finding (ICF) I undertake regularly screening all people with, or at high risk of HIV, for symptoms of TB in health care facilities, communities
INTENSIFIED TB CASE FINDING My friends call me Intensified Case Finding (ICF) I undertake regularly screening all people with, or at high risk of HIV, for symptoms of TB in health care facilities, communities
Assessment of Adenosine Deaminase Level and the Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction in Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion
 Assessment of Adenosine Deaminase Level and the Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction in Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion Nagila A 1*, Khanal S 2, Dhakal N 3, Bhatta M 4, Tamrakar BK 5 1 Associate
Assessment of Adenosine Deaminase Level and the Utility of Polymerase Chain Reaction in Diagnosis of Tuberculous Pleural Effusion Nagila A 1*, Khanal S 2, Dhakal N 3, Bhatta M 4, Tamrakar BK 5 1 Associate
Use of the BacT/ALERT MB Mycobacteria Blood Culture System for Detecting ACCEPTED
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on December 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:.11/jcm.011-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on December 00 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:.11/jcm.011-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Dr Francis Ogaro MTRH ELDORET
 Dr Francis Ogaro MTRH ELDORET TB in children often severe, disseminated and can progress rapidly and with poor outcome TB diagnosis in children has relied on clinical, imaging, microscopy and TST findings.
Dr Francis Ogaro MTRH ELDORET TB in children often severe, disseminated and can progress rapidly and with poor outcome TB diagnosis in children has relied on clinical, imaging, microscopy and TST findings.
The Diagnosis of Active TB. Deborah McMahan, MD TB Intensive September 28, 2017
 The Diagnosis of Active TB Deborah McMahan, MD TB Intensive September 28, 2017 Agenda Epidemiology Big picture Conditions that Should Make You Suspicious Which test? Eeenie meenie miny mo Radiographic
The Diagnosis of Active TB Deborah McMahan, MD TB Intensive September 28, 2017 Agenda Epidemiology Big picture Conditions that Should Make You Suspicious Which test? Eeenie meenie miny mo Radiographic
Nucleic Acid Amplification Test for Tuberculosis. Heidi Behm, RN, MPH Acting TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Oregon, Department of Health Services
 Nucleic Acid Amplification Test for Tuberculosis Heidi Behm, RN, MPH Acting TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Oregon, Department of Health Services What is this test? Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT)
Nucleic Acid Amplification Test for Tuberculosis Heidi Behm, RN, MPH Acting TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Oregon, Department of Health Services What is this test? Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT)
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Pulmonary TB aspects
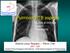 Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 4: Tuberculosis
 Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
2 ND YEAR RESEARCH ELECTIVE RESIDENT S JOURNAL Volume X, Ellie R. Carmody. A. Background and Study Rationale.
 Operating characteristics and effectiveness of a screening algorithm for the detection of active tuberculosis in adult outpatients with HIV infection in Mozambique Ellie R. Carmody A. Background and Study
Operating characteristics and effectiveness of a screening algorithm for the detection of active tuberculosis in adult outpatients with HIV infection in Mozambique Ellie R. Carmody A. Background and Study
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses
 Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
Tuberculosis (TB) Fundamentals for School Nurses June 9, 2015 Kristin Gall, RN, MSN/Pat Infield, RN-TB Program Manager Marsha Carlson, RN, BSN Two Rivers Public Health Department Nebraska Department of
P. Dandapat. Eastern Regional Station ICAR-Indian Veterinary Research Institute 37 Belgachia Road, Kolkata
 Evaluation of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Gamma Interferon Assay, Single Intradermal Tuberculin and Comparative Intradermal Tuberculin Tests in Naturally Infected Cattle Herds P. Dandapat Eastern
Evaluation of the Sensitivity and Specificity of Gamma Interferon Assay, Single Intradermal Tuberculin and Comparative Intradermal Tuberculin Tests in Naturally Infected Cattle Herds P. Dandapat Eastern
TB in Children. Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012
 TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
The diagnostic value of gyrb RFLP PCR. Mycobacteria in patients with clinical. in Mazandaran
 Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences The diagnostic value of gyrb RFLP PCR test t in differentiation between pathogenic Mycobacteria in patients with clinical suspicions spicions of tuberculosis in
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences The diagnostic value of gyrb RFLP PCR test t in differentiation between pathogenic Mycobacteria in patients with clinical suspicions spicions of tuberculosis in
Mandakini Patel, Komal Patel, Sonal Italiya, Kumarbhargav Kaptan Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Surat, Gujarat, India
 IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOSIS IN LYMPH NODE CYTOLOGY BY BLEACH METHOD FOR DETECTION OF ACID FAST BACILLI IN COMPARISON TO CONVENTIONAL ZIEHL NEELSEN STAINING METHOD Mandakini Patel, Komal Patel, Sonal
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOSIS IN LYMPH NODE CYTOLOGY BY BLEACH METHOD FOR DETECTION OF ACID FAST BACILLI IN COMPARISON TO CONVENTIONAL ZIEHL NEELSEN STAINING METHOD Mandakini Patel, Komal Patel, Sonal
Application of Smear Microscopy, Culture and Polymerase Chain Reaction for Diagnosis of Tuberculous Meningitis in Puducherry
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences Volume 5, Issue 4, Page No: 1-5 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Application of Smear
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences Volume 5, Issue 4, Page No: 1-5 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Application of Smear
Northwestern Polytechnic University
 Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
Clinical Tuberculosis Assessment by Health Care Provider Clinicians should review and verify the information in the Tuberculosis (TB) Screening Questionnaire (attached). Persons answering YES to any questions
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
At the end of this session, participants will be able to:
 Advanced Concepts in Pediatric Tuberculosis: Infection Control, Source Case and Contact Investigation Ana M. Alvarez, M.D. Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University
Advanced Concepts in Pediatric Tuberculosis: Infection Control, Source Case and Contact Investigation Ana M. Alvarez, M.D. Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X Assessment for Performance of Middlebrook 7H9 with Oleic-Albumin-Dextrose-Catalase Culture Media for Isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X Assessment for Performance of Middlebrook 7H9 with Oleic-Albumin-Dextrose-Catalase Culture Media for Isolation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Pediatric tuberculosis (i.e., Tuberculosis
 G U I D E L I N E S Updated National Guidelines for Pediatric Tuberculosis in India, 2012 ASHOK KUMAR, DEVESH GUPTA, SHARATH BURUGINA NAGARAJA, *VARINDER SINGH, # GR SETHI AND JAGADISH PRASAD From Central
G U I D E L I N E S Updated National Guidelines for Pediatric Tuberculosis in India, 2012 ASHOK KUMAR, DEVESH GUPTA, SHARATH BURUGINA NAGARAJA, *VARINDER SINGH, # GR SETHI AND JAGADISH PRASAD From Central
TOG The Way Forward
 TOG 2016- The Way Forward Main Changes in Diagnostic algorithm Definition (Type, Classification, Outcome) Registration at the time of Diagnosis (PHI level Notification Register) Long term follow up (till
TOG 2016- The Way Forward Main Changes in Diagnostic algorithm Definition (Type, Classification, Outcome) Registration at the time of Diagnosis (PHI level Notification Register) Long term follow up (till
Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers
 Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers Who Should Be Screened for Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI)?... 2 What tests are used to screen for LTBI?... 2 How
Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI) Questions and Answers for Health Care Providers Who Should Be Screened for Latent Tuberculosis Infection (LTBI)?... 2 What tests are used to screen for LTBI?... 2 How
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012 An Introduction to Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH August 10, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012 An Introduction to Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Smith, MD, MPH August 10, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
11/3/2009 SECOND EDITION Madhukar Pai McGill University. ISTC Training Modules Introduction
 SECOND EDITION 2009 Madhukar Pai McGill University Introduction 1 Purpose of ISTC ISTC Version 2: Key Points 21 Standards Differ from existing guidelines: standards present what should be done, whereas,
SECOND EDITION 2009 Madhukar Pai McGill University Introduction 1 Purpose of ISTC ISTC Version 2: Key Points 21 Standards Differ from existing guidelines: standards present what should be done, whereas,
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 2-5, 2011 Pediatric TB Jeffrey Starke, MD August 5, 2011 Jeffrey Starke, MD has the following disclosures to make: Is on a data safety monitoring board for Hoffman
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 2-5, 2011 Pediatric TB Jeffrey Starke, MD August 5, 2011 Jeffrey Starke, MD has the following disclosures to make: Is on a data safety monitoring board for Hoffman
CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT]
![CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT]](/thumbs/89/99628771.jpg) CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] QUESTION: : Which children in the United States should get a tuberculin skin test? Do questionnaires really work? Jeffrey
CHILDHOOD TUBERCULOSIS: NEW WRINKLES IN AN OLD DISEASE [FOR THE NON-TB EXPERT] QUESTION: : Which children in the United States should get a tuberculin skin test? Do questionnaires really work? Jeffrey
A Profile of Bacteriologically Confirmed Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children
 RESEARCH PAPERS A Profile of Bacteriologically Confirmed Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children SOUMYA SWAMINATHAN, MANJULA DATTA, MP RADHAMANI, SARA MATHEW, AM REETHA, SARALA RAJAJEE, REMA MATHEW, A RADHAKRISHNAN,
RESEARCH PAPERS A Profile of Bacteriologically Confirmed Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Children SOUMYA SWAMINATHAN, MANJULA DATTA, MP RADHAMANI, SARA MATHEW, AM REETHA, SARALA RAJAJEE, REMA MATHEW, A RADHAKRISHNAN,
Improved diagnostic value of PCR in the diagnosis of female genital tuberculosis leading to infertility
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2005), 54, 927 931 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45943-0 Improved diagnostic value of PCR in the diagnosis of female genital tuberculosis leading to infertility N. Vijaya Bhanu, 1,3
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2005), 54, 927 931 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45943-0 Improved diagnostic value of PCR in the diagnosis of female genital tuberculosis leading to infertility N. Vijaya Bhanu, 1,3
CDPH - CTCA Joint Guidelines Guideline for Micobacteriology Services In California
 CDPH - CTCA Joint Guidelines Guideline for Micobacteriology Services In California These guidelines are intended to be used as an educational aid to help clinicians make informed decisions about patient
CDPH - CTCA Joint Guidelines Guideline for Micobacteriology Services In California These guidelines are intended to be used as an educational aid to help clinicians make informed decisions about patient
Key Words: Pulmonary Tuberculosis; Smear and Culture Findings; India METHODS
 Original Article EVALUATION OF BACTERIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF SMEAR POSITIVE PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS UNDER PROGRAMME CONDITIONS IN THREE DISTRICTS IN THE CONTEXT OF DOTS IMPLEMENTATION IN INDIA C.N. Paramasivan
Original Article EVALUATION OF BACTERIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF SMEAR POSITIVE PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS UNDER PROGRAMME CONDITIONS IN THREE DISTRICTS IN THE CONTEXT OF DOTS IMPLEMENTATION IN INDIA C.N. Paramasivan
Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Philippine General Hospital
 Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Albert B. Albay Jr., MD Jemylyn Garcia, MD Joel Santiaguel, MD UP- TB in the Philippines 6 th leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Albert B. Albay Jr., MD Jemylyn Garcia, MD Joel Santiaguel, MD UP- TB in the Philippines 6 th leading cause of morbidity and mortality
