Dtiring the first year of life, diffuse
|
|
|
- Bruce Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 February 1971 Volume 10, Number 2 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Electron microscopic study of hereditary corneal edema Atsushi Kanai, Stephen Waltman, Frank M. Polack, and Herbert E. Kaufman Hereditary corneal edema is a previously undescribed corneal dystrophy thought to be transmitted as a dominant trait. This study presents five members of a family with hereditary corneal edema and describes the uniqueness of their condition from other corneal dystrophies. Emphasis is placed on electron microscopic studies of a corneal button from one member who had penetrating keratoplasty. Keywords: heredity, corneal dystrophy, corneal edema, collagen fibrils, Descemet's membrane, corneal endothelium, histopathology, light microscopy, electron microscopy. Dtiring the first year of life, diffuse corneal clouding is usually caused by infantile glaucoma or infections and inflammatory processes. Although several of the mucopolysaccharidases may also cause corneal clouding, other signs and symptoms predominate. Maumenee* described a congenital, hereditary corneal dystrophy characterized by diffuse corneal edema during the first year of life. His report is the only one which even partially resembles the heredi- From the Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, University of Florida and the Veterans Administration Hospital, Gainesville, Fla. This study was supported in part by United States Public Health Service Grants EY-00033, EY-00446, and EY from the National Eye Institute. Manuscript submitted Oct. 19, 1970; revised manuscript accepted Dec. 28, Reprint requests: Dr. Herbert E. Kaufman, Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, Fla tary corneal edema we observed in five members of one family. A general discussion of the particular characteristics of this condition and electron microscopic studies of a corneal button from one member who had penetrating keratoplasty comprise our report. Case histories This corneal disease first appeared in Patient I (Caucasian woman) and her twin (presumed monozygotic) sister (Patient II). Their parents have normal-appearing corneas with normal corneal thicknesses, and there is no history of corneal disease in either kinship. Patient I developed corneal clouding and photophobia at the age of three. Her poor vision necessitated several surgical procedures, and at present she has a clear graft in her right eye. Patient II has a mild asymptomatic case and has not required surgical treatment. Her best corrected vision is 20/25 Oxford unit (O.U.); corneal endothelial changes with overlying stromal edema are most marked in the periphery. However, all of Patient II's children (Patients III, IV, and V) have profound corneal disease. Patient II's husband has normal corneas with normal corneal thicknesses. Patient III (boy) developed corneal clouding between three and six months of age. By one
2 90 Kanai et al. Investigative Ophthalmology F<-Hn«wj, Examined 1 Affected f Propositus 0 0 O Examined Normal Not Examined Reported Normal Fig. 1. Pedigree of family with hereditary corneal edema. 1L and 11s Are twins. Fig. 2. Vascularized, edematous cornea of left eye of K, T, The vascularization developed in four months and prompted keratoplasty. year of age, his corneas were opaque (Corneal diameter normal). Surgery was deferred because of his age, and his corneas have slowly cleared. When last examined (age five years), his visual acuity was 10/30 O.U.; his corneas were thickened and edematous mainly peripherally. Patient IV (girl) was asymptomatic when first examined at six months of age. However, peripheral corneal edema and thickening were easily distinguished with a hand light (central corneas were clear). Her ocular findings have remained stable for the past sis months. Patient V (girl) was noted to have bilateral diffuse corneal edema when she was 18 months old (Fig. 1). Four months later she developed photophobia and slight circumcorneal injection in both eyes. Examination revealed a roughened epithelium (pigskin appearance) and stromal edema (more marked peripherally). The anterior chambers were deep. Her left eye worsened and developed marked comeal vascularization inferiorly. The vessels were superficial and midstromal (Fig. 2). On July 1, 1969, she underwent a 7.5 mm. penetrating keratoplasty in her left eye. The anterior chamber, ins, and lens appeared normal at the time of the operation. Three weeks postoperatively her graft was clear, and photophobia had disappeared in this eye. At present she can see well enough to grasp small objects. Materials and methods The corneal button was obtained at the time of Patient V's surgery (7/1/69). It was fixed in two per cent osmium tetroxide with phosphate buffer at 4 C, for two hours. Then it was sectioned into smaller pieces, dehydrated through a series of ethyl alcohol solutions, and embedded in epon. Thick (lfi) sections were stained with toluidine blue and studied simultaneously with the light
3 Volume 10 Number 2 Hereditary corneal edema 91 microscope for orientation in electron microscopy. The embedded tissue was cut with a Porter- Blum microtome and stained with uranyl acetate and lead acetate. Uranyl acetate combined with phosphotungstic acid was used for the study of collagen fibrils. Electron micrographs were taken with an Hitachi 11-C microscope. Results Low-power electron microscopic examination of thick sections revealed a corneal epithelium with six to seven layers of cells (Fig. 3). The specimen showed distention of intercellular spaces, particularly at the level of the middle or basal cell layer. High-power examination of the corneal epithelium revealed desmosomes of normal appearance. Dense granular material and cell projections were seen within the intercellular spaces (Fig. 4). In the basal cells some mitochondria were swollen, and there was a decreased density of the matrix with distension of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Free ribosome particles were detached from their membranes, and there were moderate numbers of vesicles adjacent to the cell membrane. Basal cells with low density cytoplasm showed more advanced alterations of organelles. Both the basal cell membrane and the basement membrane appeared undulated with occasional small gaps between them. However, basal cells were well attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes (Fig. 5). Bowman's membrane was about 10 to 12 H in thickness, but was absent in some areas and replaced by disorganized collagen fibrils. Extensive abnormalities were present in the corneal stroma, as well as the Descemet's membrane and the endothelium. The anterior stroma showed irregular alignment of lamellae with vascularization and altered keratocytes (Fig. 6). A cross section of these collagen fibrils ranged between 250 and 350A in diameter. The middle and posterior portion of the stroma was swollen. It possessed an irregular arrangement of collagen fibrils within the lamellae and disorganization of lamellae Fig. 3. Intercellular edema of epithelial cell (Ep) with absence of Bowman's membrane (arrow). Disorganized stromal lamellae (St) with vascularization (V). (BM), Bowman's membrane. (Light microscope section. Toluidine blue. xloo.) with the formation of several stromal "lakes" (Fig. 9). An interesting observation was the two different types of fibrils found in the middle and posterior stroma. The diameter of the smaller fibrils ranged from 100 to 130A. These were found between the cell membrane and adjacent lamellae or between larger fibrils. Larger fibrils ranged between 250 and 350A in diameter (Figs. 7 and 8) with a periodicity of 650 to 700A. Most keratocytes had swollen mitochondria, distended rough endoplasmic reticulum, and intracellular vacuoles with retracted cytoplasmic processes (Fig. 10). Descemet's membrane was irregularly undulated and thinned (Fig. 11). In some areas it was a nonbanded homogeneous structure and in others it showed a nonuniform banded pattern. Between Descemet's membrane and the posterior layer there were numerous nonimiform collagen fibrils; fibrillar material approximately SO to 100A in diameter (Fig. 13); and several keratocytes (Fig. 12). This posterior fibrous layer was covered by two to three cell layers which replaced the endothelium. Many microvilli were seen on the posterior
4 92 Kanai et al. Investigative Ophthalmology February 1971 Fig. 4. Distended intercellular spaces and many cytoplasmic projections. Fine dense granules (arrows) show in distended intercellular spaces. (x37,500,) BM Fig. 5. Flattened basal cell with distended endoplasmic reticulum. Low density cytoplasm of basal cell appear with swollen mitochondria (M). Basement membrane (BM) is present. (St) Stroma; (N) nucleus. (x25,000.)..
5 Volume 10 Number 2 Hereditary corneal edema 93 \ Fig. 6. Low power of anterior stroma (Si) shows irregular wavy lamellae with altered keratocytes. (Ep) Epithelium, (x4,200.) cell surface with gentle undulations. The intercellular spaces were narrow at all levels of the posterior layers and desmosomes attached to the plasma membrane (Fig. 14). Hemidesmosome-like figures (Fig. 13) were seen, on the plasma membrane which faced the stroma. The posterior layer cells contained nucleus, mitochondria, rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, several vacuoles, and numerous tonofilaments. These tonofilaments formed bundles and were concentrated near the cell membrane (Fig. 14). Discussion There have been several electron microscopic studies of various types of corneal dystrophy. 2 " 0 Although hereditary comeal edema (HCE) is similar in many respects to the congenital hereditary corneal dystrophy (CHCD) studied by Maumenee and Kenyon, 1 ' 2 it seems different in important ways. The presenting signs and symptoms in our patients were variable as they were in CHCD, but in all cases, some degree of corneal edema was present. Patient V had
6 ; > *. 94 Kanai et al. Investigative Ophthalmology February Fig. 7. Middle stroma of hereditary corneal edema. Two different diameters o fibrils show in cross section. Smaller fibrils range from 100 to 130A (arrows), large fibrils between 250 and 350A. (x70,000.) Fig. 8. Posterior stroma of hereditary corneal edema. High dense amorphous substance is shown between the disoriented collagen fibrils. Smaller fibrils (arrow) can be seen between larger fibrils. (x70,000.) more corneal edema, especially in the periphery, then described in CHCD. Although she is much younger then Maumenee's patient, the histologic differences are significant, and it is not known whether a patient's age would alter findings this much. Ultrastructural examination showed abnormalities in all corneal layers, particularly the posterior. Outstanding morphologic
7 Volume 10 Number 2 Hereditary corneal edenia 95 Fig. 9. Low power posterior stroma shows lammellar disorganization and formation of "lakes" (L). (x28,000.) Fig, 10. Keratocyte contains distended cndoplasmic reticulum (ER) and swollen mitochondria (M). (Q) Golgi complex. (x27,000.)
8 96 Kanai et at. Investigative Ophthalmology February 1971 Figs. 11 to 13. For legends see opposite page.
9 \ # Fig. 14. Note the thin Descemet's membrane (DM) at the upper portion. Many microvilli are seen on the posterior cell surface. The intercellular spaces are narrow with desmosomes (d). The numerous tonofilaments form bundles and are concentrated near cell membrane. (AC) Anterior chamber; (M) mitochondria; (N) nucleus; (TB) terminal bar. (Original magnification xl8,000.) Fig. 11. Thick section of posterior portion shows irregularly undulated, thinned Descemet's membrane (DM) and posterior cell layers (PL). (St) Stroma; (AC) anterior chamber. (Light microscope section. Toluidine blue. x250.) Fig. 12. Low-power electron microphotograph of posterior portion shows thin descemet's membrane (DM) and two posterior cell layers (PL). (St) Stroma. (x4,400.) Fig. 13. Fine fibrillar material (80 to 100A in diameter, [arrows]) can be seen between Collagen fibrils and the posterior cell (PL). Hemidesmosome-like figures appear on the posterior cellular membrane (SD), (st) Stroma. (Original magnification x56,000.).
10 98 Kanai et al. Investigative Ophthalmology February 1971 changes of the epithelium were enlargement of intercellular spaces, swollen mitochondria, and distension of the endoplasmic reticulum. In the chronically swollen epithelium, distended intercellular spaces indicate cell separation. However, desmosomes were present in our case and were morphologically similar to those found in normal corneas. 7 Dense granules, which are observed in the intercellular spaces of swollen corneas, also appeared in the intercellular spaces of our specimens. Absence of the basement membrane can often be observed in eyes with chronic epithelial edema, 7 or corneal dystrophy. 2 According to Goldman and Kuwabara s this alteration is secondary to basal cell pathology and the result of long-standing separation from the underlying tissue. Deficiency or thinning of Bowman's membrane was a rare finding in our case, and most of the specimens showed normal Bowman's membrane with a thickness of 10 to 12 [x. In Kenyon and Maumenee's case, 2 Bowman's membrane varied in thickness and there were subepithelial bullae. As their patient was nine years old at the time of the operation, these changes could be due to the presence of edema for several years. In our case, the middle or posterior stroma was swollen. It showed large fibrilfree areas or "lakes" (probably occupied by intercellular fluid), and irregularity of the interfibrillary spacing. According to Jakus, 9 normal collagen fibrils measure from 200 to 260A in diameter. Our specimen showed various diameter of collagen fibrils; smaller fibrils with Vz the normal diameter and larger fibrils with almost Wz times the normal diameter. However, the periodicity was within the normal 650 to 700A. Kenyon and Maumenee's 1 ' 2 specimens showed fibrils up to 720A in diameter. In order to explain the increased diameter of these collagen fibrils, they suggested either that collagen fibrils of initially normal size swelled (becoming excessively hydrated) or that enlarged fibrils were caused by a defect in fibrillogenesis. In general, it is believed that hydration of corneal stroma is due to water imbibition by the polysaccharide matrix of interfibrillar space, with no increase in diameter of collagen fibrils. 10 However, delicate filaments (90 to 100A in diameter), which appear in lattice dystrophy, may result from fibril breakdown (fibrillary degeneration 6 ). It seems most likely that the varied diameter of collagen fibrils in our case resulted from altered collagen fibrillogenesis during fetal development. In stromal swelling following endothelial damage, keratocytes show contracted processes with rounding of the cell and its nucleus. However, there are little changes in the intracellular organelles even four days after endothelial damage. 11 Although stromal cells in CHCD were normal, CHE cells had retracted processes, showed swollen mitochondria, distended endoplasmic reticulum, and vacuoles. Long periods of persistant stromal swelling (beginning in the embryonic stage) may have been responsible for these changes. The marked difference between HCE and CHCD was in Descemet's membrane and the endothelium. In CHCD, Descemet's membrane was thinned and lacked the nonbanded homogeneous layer. In HCE, the nonbanded homogeneous material demonstrated undulation, thinning, and small areas showed banded material having no periodicity. Descemet's membrane (on the posterior layer) was invaded by numerous homogeneous processes. The area between Descemet's membrane and the posterior layer was filled with nonparallel-packed collagen fibers, fibril materials, and numbers of keratocytes. In contrast to HCE, Descemet's membrane in Fuch's dystrophy is thicker (caused by increased periodicity 3 ) and the endothelium is thinner than normal. The endothelium was absent in Kenyon and Maumenee's case 1 ' 2 and may have been lost in operative or postoperative handling of the specimen rather than by endothelial degeneration. These authors
11 Volume 10 Number 2 Hereditary corneal edema 99 felt that a true endothelium was present during some period of embryonic development and may have been functionally defective. 2 According to Barber, 12 Descemet's membrane and endothelium begin to form soon after the anterior chamber appears and is fully formed by the 30 mm. stage. They increase in thickness and can be recognized at the 65 to 70 mm. stage. After the fifth month, except for an increase in size, very little change occurs in the cornea until after birth. The HCE specimen suggests that the endothelium was damaged during the formation of Descemet's membrane; its posterior layer being secondarily replaced by fibroblastlike cells or new, altered endothelial cells with a different function. This abnormal posterior layer presumably resulted in edema. Mr. John Valenti provided expert technical assistance. REFERENCES 1. Maumenee, A. E.: Congenital hereditary corneal dystrophy, Amer. J. Ophthal. 50: 1114, Kenyon, K. R., and Maumenee, A. E.: The histological and ultrastructural pathology of congential hereditary corneal dystrophy. Case report, INVEST. OPHTHAL. 7: 475, Kayes, J., and Holmberg, A.: The fine structure of the cornea in Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy, INVEST. OPHTHAL. 3: 47, Teng, C. C: Granular dystrophy of the cornea. A histochemical and electron microscopic study, Amer. J. Ophthal. 63: 1659, Sornson, E. T.: Granular dystrophy of the cornea. An electron microscopic study, Amer. J. Ophthal. 59: 1001, McTigue, J. W., and Fine, B. S.: The stromal lesion in lattice dystrophy of the cornea. A light and electron microscopic study, INVEST. OPHTHAL. 3: 355, Goldman, J. N., Benedek, G. B., Dohlman, C. H., and Kravit, B.: Structural alterations affecting transparency in swollen human corneas, INVEST. OPHTHAL. 7: 501, Goldman, J. N., and Kuwabara, T.: Histopathology of corneal edema, in Dohlman, C. H., editor: Corneal edema, Boston, 1968, Little, Brown & Company, p Jakus, M. A.: The fine structure of the human cornea, in Smelser, G. K., editor: The structure of the eye, New York, 1961, Academic Press, Inc., p Francois, J., Rabaey, M., and Vandermeerssche, G.: L'ultrastructure des tissus oculaires au microscope electronique. II. Etude de la cornee et de la sclerotique, Ophthalmologica (Basel) 127: 74, Yukioka, Y.: Electron microscopic study on the stromal cells of normal and swollen corneas, Acta Soc. Ophthal. Jap., 72: 894, Barber, A. N.: Embryology of the human eye, St. Louis, 1955, The C. V. Mosby Company, p. 81.
T, -he corneal dystrophies have been defined
 Hereditary corneal dystrophy in the Manx cat: a preliminary report Stephen I. Bistner, Gustavo Aguirre, and James N. Shively A progressive, apparently inherited corneal dystrophy is described in an inbred
Hereditary corneal dystrophy in the Manx cat: a preliminary report Stephen I. Bistner, Gustavo Aguirre, and James N. Shively A progressive, apparently inherited corneal dystrophy is described in an inbred
A high percentage of corneal transplants
 The fine structural changes in the corneal endothelium during graft rejection Hajime Inomata* George K. Smelser, and Frank M. Polack Fully penetrating corneal grafts were made between unrelated albino
The fine structural changes in the corneal endothelium during graft rejection Hajime Inomata* George K. Smelser, and Frank M. Polack Fully penetrating corneal grafts were made between unrelated albino
R,'etrocorneal fibrous membrane (RCFM)
 Retrocorneal fibrous membrane Ronald G. Michels, Kenneth R. Kenyon, and A. Edward Maunienee Retrocorneal fibrous membranes were produced experimentally in rabbits by inducing endothelial cell damage with
Retrocorneal fibrous membrane Ronald G. Michels, Kenneth R. Kenyon, and A. Edward Maunienee Retrocorneal fibrous membranes were produced experimentally in rabbits by inducing endothelial cell damage with
n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Composed of stratified squamous epith. n 5% of total corneal thickness (50-90micro m thick)
 Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
Cornea overview Dr. Sarita Tuladhar MD, Ophthalmology Gandaki Medical College Embryology CORNEA: n Corneal epithelium is derived from surface ectoderm n Corneal stroma, descement memb, bowman s layer,
Electron microscopic study of epithelial downgrowth
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1981, 65, 374-382 Electron microscopic study of epithelial downgrowth after penetrating keratoplasty TATSUO YAMAGUCHI, FRANK M. POLACK, AND JOHN VALENTI From the Department
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1981, 65, 374-382 Electron microscopic study of epithelial downgrowth after penetrating keratoplasty TATSUO YAMAGUCHI, FRANK M. POLACK, AND JOHN VALENTI From the Department
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY
 January 1972 Volume 11, Number 1 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Scanning electron microscopy of corneal graft rejection: Epithelial rejection, endothelial rejection, and formation of posterior graft membranes
January 1972 Volume 11, Number 1 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Scanning electron microscopy of corneal graft rejection: Epithelial rejection, endothelial rejection, and formation of posterior graft membranes
Fine structure of rat corneal vessels in advanced stages of wound healing
 Fine structure of rat corneal vessels in advanced stages of wound healing Jeanne Szalay and G. D. Pappas The present work is an examination of the fine structure of corneal vessels in advanced stages of
Fine structure of rat corneal vessels in advanced stages of wound healing Jeanne Szalay and G. D. Pappas The present work is an examination of the fine structure of corneal vessels in advanced stages of
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY. Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia
 August 1969 Volume 8, Number 4 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia 7?. M. H. Pinkerton and David M. Robertson A case of dysproteinemia with corneal and conjunctival
August 1969 Volume 8, Number 4 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Corneal and conjunctival changes in dysproteinemia 7?. M. H. Pinkerton and David M. Robertson A case of dysproteinemia with corneal and conjunctival
Fleck. Pre-Descemet Dystrophies (generally good vision and comfort) Primary Pre-Descemet Dystrophy
 Fleck Etiology: bilateral, sometimes asymmetric, autosomal dominant opacities located in all levels of stroma as early as 1 st decade Slit lamp: well demarcated, small round gray-white doughnut-like, wreath-like
Fleck Etiology: bilateral, sometimes asymmetric, autosomal dominant opacities located in all levels of stroma as early as 1 st decade Slit lamp: well demarcated, small round gray-white doughnut-like, wreath-like
April 1962 Volume 1, Number 2 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY. Symposium on the cornea. Introduction: Factors influencing corneal hydration
 April 1962 Volume 1, Number 2 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Symposium on the cornea Introduction: Factors influencing corneal hydration John E. Harris The swelling of the corneal buttons in aqueous solution
April 1962 Volume 1, Number 2 INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY Symposium on the cornea Introduction: Factors influencing corneal hydration John E. Harris The swelling of the corneal buttons in aqueous solution
Corneal blood staining after hyphaema
 Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Journal of Ophthalmic Medical Technology. Fuchs Dystrophy Amy Hischier
 Journal of Ophthalmic Medical Technology Volume 8, Number 1 October 2013 www.jomtonline.com Fuchs Dystrophy Amy Hischier Patient History: A 55 year old female complained that both of her eyes were red,
Journal of Ophthalmic Medical Technology Volume 8, Number 1 October 2013 www.jomtonline.com Fuchs Dystrophy Amy Hischier Patient History: A 55 year old female complained that both of her eyes were red,
Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells. Special Reference to the Well-Developed Agranular Endoplasmic Reticulum
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 58(4-6) : 583-594, March 1982 Some Observations on the Fine Structure of the Goblet Cells in the Nasal Respiratory Epithelium of the Rat, with Special Reference to the Well-Developed
FUCH S DYSTROPHY & CATARACT SURGERY TREATMENT ALGORITHM
 FUCH S DYSTROPHY & CATARACT SURGERY TREATMENT ALGORITHM ΙΟΑΝΝΙS Α. MALLIAS, MD, PHD Director of the Dept. of Ophthalmology, Mediterraneo Hospital, Glyfada, Athens, Greece Clinical Fellow in Cornea and
FUCH S DYSTROPHY & CATARACT SURGERY TREATMENT ALGORITHM ΙΟΑΝΝΙS Α. MALLIAS, MD, PHD Director of the Dept. of Ophthalmology, Mediterraneo Hospital, Glyfada, Athens, Greece Clinical Fellow in Cornea and
Dystrophies. Molecular Causes. Anterior Membrane Dystrophies (epithelium, basement membrane and Bowman s layer)
 Dystrophies Characteristics of corneal dystrophies About half the members of appropriate age to have the dystrophy( usually autosomal dominant): inherited Usually seen in the first or second decade of
Dystrophies Characteristics of corneal dystrophies About half the members of appropriate age to have the dystrophy( usually autosomal dominant): inherited Usually seen in the first or second decade of
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA. Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962),
 Title ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA Author(s) OKADA, Yoshio; SAGAWA, Yanosuke; IS DAIDO, Shigeo Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962), Issue Date 1962-03-30 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/51710
Title ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATION OF CHRONIC PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA Author(s) OKADA, Yoshio; SAGAWA, Yanosuke; IS DAIDO, Shigeo Citation Acta tuberculosea Japonica (1962), Issue Date 1962-03-30 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/51710
Eye Care for Animals Micki Armour VMD DACVO THE CORNEA
 Eye Care for Animals Micki Armour VMD DACVO THE CORNEA ANATOMY 0.5-0.6mm thick 4 primary layers Epithelium (5-7 cell layers) Stroma (90% total thickness) Descemet s membrane Endothelium (1 layer) ANATOMY-
Eye Care for Animals Micki Armour VMD DACVO THE CORNEA ANATOMY 0.5-0.6mm thick 4 primary layers Epithelium (5-7 cell layers) Stroma (90% total thickness) Descemet s membrane Endothelium (1 layer) ANATOMY-
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey*
 Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
Fine Structure of the Normal Trigeminal Ganglion in the Cat and Monkey* DAVID S. MAXWELL, PH.D. Principal Contributor and Leader of Discussion HE inclusion of animal material m a y be justified as a means
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS*
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
S,Ipecular microscopy has added a new
 Functional and structural changes in the corneal endothelium during in vitro perfusion Bernard E. McCarey,* Henry F. Edelhauser, and Diane L. Van Horn The endothelium of isolated rabbit corneas was perfused
Functional and structural changes in the corneal endothelium during in vitro perfusion Bernard E. McCarey,* Henry F. Edelhauser, and Diane L. Van Horn The endothelium of isolated rabbit corneas was perfused
R,;habdomyosarcoma, the most common
 Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
The synthesis of basement membrane by the corneal epithelium in bullous keratopathy
 The synthesis of basement membrane by the corneal epithelium in bullous keratopathy Kenneth R. Kenyon* With the aid of the electron microscope, the ultrastructural changes associated with bullous keratopathy
The synthesis of basement membrane by the corneal epithelium in bullous keratopathy Kenneth R. Kenyon* With the aid of the electron microscope, the ultrastructural changes associated with bullous keratopathy
Meet Libby. Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies Definitions. Dr. Victor Malinovsky
 Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
Meet Libby Corneal Dysgenesis, Degeneration, and Dystrophies 2006 Dr. Victor Malinovsky Definitions Dysgenesis: (congenital anomalies) A development disorder that results in a congenital malformation of
The Genetic Mysteries of the Corneal Dystrophies
 1 The Genetic Mysteries of the Corneal Dystrophies Sherry J. Bass, OD, FAAO SUNY State College of Optometry New York, N.Y. Sherry Bass has no Financial Interests to Disclose. Detection: Biomicroscopic
1 The Genetic Mysteries of the Corneal Dystrophies Sherry J. Bass, OD, FAAO SUNY State College of Optometry New York, N.Y. Sherry Bass has no Financial Interests to Disclose. Detection: Biomicroscopic
Title. Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1-2): 1- Issue Date DOI. Doc URL. Type.
 Title MYOID CELLS IN THE CALF'S THYMUS Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1-2): 1- Issue Date 1972-06 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.20.1-2.1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/1986
Title MYOID CELLS IN THE CALF'S THYMUS Author(s)SUGIMURA, Makoto CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 20(1-2): 1- Issue Date 1972-06 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.20.1-2.1 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/1986
CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME
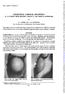 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
Degenerations. Conditions with cloudy cornea at birth or in infancy
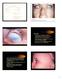 Dermoids The lesions are choristomas, which are congenital masses of tissue that have been dislocated from their normal position Limbal dermoids--overlapping the cornea and sclera, often inferotemporally
Dermoids The lesions are choristomas, which are congenital masses of tissue that have been dislocated from their normal position Limbal dermoids--overlapping the cornea and sclera, often inferotemporally
Effect of phenylephrine on normal and regenerated endothelial cells in cat cornea
 Effect of phenylephrine on normal and regenerated endothelial cells in cat cornea Kenneth L. Cohen, Diane L. Van Horn, Henry F. Edelhauser, and Richard O. Schultz Topical commercial phenylephrine HCl (Neo-Synephrine
Effect of phenylephrine on normal and regenerated endothelial cells in cat cornea Kenneth L. Cohen, Diane L. Van Horn, Henry F. Edelhauser, and Richard O. Schultz Topical commercial phenylephrine HCl (Neo-Synephrine
ANNEX II: Atlas of histopathological lesions of Isolated Chicken Eyes
 ANNEX II: Atlas of histopathological lesions of Isolated Chicken Eyes (from Triskelion, Zeist, The Netherlands) 1. Introduction... 1 2. Semi-quantitative microscopic evaluation of the cornea... 1 3. Histopathology
ANNEX II: Atlas of histopathological lesions of Isolated Chicken Eyes (from Triskelion, Zeist, The Netherlands) 1. Introduction... 1 2. Semi-quantitative microscopic evaluation of the cornea... 1 3. Histopathology
Intercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida
 JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
JouRNAL OF BAcTEROLOGY, Sept. 1975, p. 1139-1143 Vol. 123, No. 3 Copyright 0 1975 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. ntercellular Matrix in Colonies of Candida K. R. JOSH, J. B. GAVN,*
:1c.c :& Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* structure with rounded ends and a striated lamella
 THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1566 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 7, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Preliminary and Short Report GRANULE FORMATION IN THE LANGERHANS CELL* ALVIN S. ZELICKSON,
EVect of trephination technique on the ultrastructure of corneal transplants: guided trephine system v posterior punch technique
 1172 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Vienna, Medical School, Vienna, Austria W Radner Ch Skorpik C Mudrich G Radner Institute of Histology and Embryology II, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
1172 Department of Ophthalmology, University of Vienna, Medical School, Vienna, Austria W Radner Ch Skorpik C Mudrich G Radner Institute of Histology and Embryology II, University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis
 J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 19 New aspect of hepatic nuclear glycogenosis in diabetes1 F. CARAMIA, F. G. GHERGO, C. BRANCIARI, AND G. MENGHINI From the Institute of General Pathology, University of Rome,
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR BLUE NEVUS*
 THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
THE JOURNAL 05' INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkinl Co. Vol. 62, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF MELANIN-PHAGOCYTOSIS BY CUTANEOUS VESSELS IN CELLULAR
PATIENT INFORMATION ON CORNEAL GRAFT
 PATIENT INFORMATION ON CORNEAL GRAFT (TRANSPLANT) SURGERY M ANANDAN What is the cornea? The clear window of the eye approximately 0.5mm thick and 12mm across. It lies in front of the fluid filled anterior
PATIENT INFORMATION ON CORNEAL GRAFT (TRANSPLANT) SURGERY M ANANDAN What is the cornea? The clear window of the eye approximately 0.5mm thick and 12mm across. It lies in front of the fluid filled anterior
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Cogan-Guerry Microcystic Corneal Epithelial
 Cogan-Guerry Microcystic Corneal Epithelial Dystrophy: A Clinical and Electron Microscopic Study ROBERT G. KING, JR., M.D. Associate Professor of Ophthalmology, Medical College of Virginia, Health Sciences
Cogan-Guerry Microcystic Corneal Epithelial Dystrophy: A Clinical and Electron Microscopic Study ROBERT G. KING, JR., M.D. Associate Professor of Ophthalmology, Medical College of Virginia, Health Sciences
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
arthritis "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid (opposite). Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 Peterborough District Hospital
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid arthritis A. J. LYNE Peterborough District Hospital It has been noted that patients suffering from long-standing rheumatoid arthritis
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I970) 54, 410 "Contact lens" cornea in rheumatoid arthritis A. J. LYNE Peterborough District Hospital It has been noted that patients suffering from long-standing rheumatoid arthritis
CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
 THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
PRE-DESCEMET S ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (PDEK) DR ASHVIN AGARWAL
 PRE-DESCEMET S ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (PDEK) DR ASHVIN AGARWAL Endothelial keratoplasty (EK) has evolved at a brisk pace and the volume of data accumulated over the past 10 years has demonstrated that
PRE-DESCEMET S ENDOTHELIAL KERATOPLASTY (PDEK) DR ASHVIN AGARWAL Endothelial keratoplasty (EK) has evolved at a brisk pace and the volume of data accumulated over the past 10 years has demonstrated that
22-24 Febbraio 2018, FIRENZE. ROSSELLA COLABELLI GISOLDI Azienda Ospedaliera S. Giovanni Addolorata Roma
 22-24 Febbraio 2018, FIRENZE ROSSELLA COLABELLI GISOLDI Azienda Ospedaliera S. Giovanni Addolorata Roma In recent years the surgical trends in keratoplasty have greatly changed: the needings of the prepared
22-24 Febbraio 2018, FIRENZE ROSSELLA COLABELLI GISOLDI Azienda Ospedaliera S. Giovanni Addolorata Roma In recent years the surgical trends in keratoplasty have greatly changed: the needings of the prepared
Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich)
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 36 : 285-290 (2002) Ultrastructure of Connective Tissue Cells of Giant African Snails Achatina fulica (Bowdich) Viyada Seehabutr ABSTRACT The connective tissue sheath of cerebral
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Cornea with Peters Anomaly: Perturbed Differentiation of Corneal Cells and Abnormal Extracellular Matrix in the Corneal Stroma
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Cornea with Peters Anomaly: Perturbed Differentiation of Corneal Cells and Abnormal Extracellular Matrix in the Corneal Stroma Kiyomi Ohkawa*, Shizuya Saika*, Yuko Hayashi*, Akihiko
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Cornea with Peters Anomaly: Perturbed Differentiation of Corneal Cells and Abnormal Extracellular Matrix in the Corneal Stroma Kiyomi Ohkawa*, Shizuya Saika*, Yuko Hayashi*, Akihiko
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: endothelial_keratoplasty 9/2009 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Endothelial keratoplasty
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: endothelial_keratoplasty 9/2009 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Endothelial keratoplasty
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION*
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
OPACIFICATION IN PERFORATING CORNEAL GRAFTS*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1954) 38, 10. OPACIFICATION IN PERFORATING CORNEAL GRAFTS*t BY A. G. LEIGH From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London As the success ofa grafting operation ultimately depends upon the
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1954) 38, 10. OPACIFICATION IN PERFORATING CORNEAL GRAFTS*t BY A. G. LEIGH From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London As the success ofa grafting operation ultimately depends upon the
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE
 TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
TRANSFER OF PREMELANOSOMES INTO THE KERATINIZING CELLS OF ALBINO HAIR FOLLICLE PAUL F. PARAKKAL. From the Department of Dermatology, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts 02118 INTRODUCTION
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes
 Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
The normal and abnormal human corneal epithelial surface: a scanning electron microscope study. Roswell R. Pfister and Neal L.
 The normal and abnormal human corneal epithelial surface: a scanning electron microscope study Roswell R. Pfister and Neal L. Burstein* The surface morphology of 108 corneal buttons obtained at keratoplasty
The normal and abnormal human corneal epithelial surface: a scanning electron microscope study Roswell R. Pfister and Neal L. Burstein* The surface morphology of 108 corneal buttons obtained at keratoplasty
Response of the Mouse Lens to Varying Sizes of Injured Area
 Response of the Mouse Lens to Varying Sizes of Injured Area Akino Wakasugi,* Shigekazu Uga,* Yasuhiro Sakai, Miho Matsumoto, Saori Hirayama and Kimiya Shimizu Departments of *Ophthalmic Anatomy and Physiology;
Response of the Mouse Lens to Varying Sizes of Injured Area Akino Wakasugi,* Shigekazu Uga,* Yasuhiro Sakai, Miho Matsumoto, Saori Hirayama and Kimiya Shimizu Departments of *Ophthalmic Anatomy and Physiology;
STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.8, August 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t C. NORIEGA, M.D., AND C. OBERTI, M.D.
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright @ 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.8, August 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES OF THE HUMAN UNFERTILIZED TUBAL OVUM*t C. NORIEGA, M.D., AND C. OBERTI, M.D.
Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus)
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus) T.A.Kannan 1*,
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 6 (2015) pp. 63-68 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Histological and Ultrastructural studies of Caecal tonsil in Chicken (Gallus domesticus) T.A.Kannan 1*,
Elastofibroma dorsi. CASE 1 M.J., a white female clerk, age 61, presented. with a mass below the right scapula which she had noticed
 Elastofibroma dorsi J. R. TIGHE, A. E. CLARK, AND D. J. TURVEY J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 463-469 From the Department ofpathology, St. Thomas' Hospital and Medical School, London SYNOPSIS Two cases of
Elastofibroma dorsi J. R. TIGHE, A. E. CLARK, AND D. J. TURVEY J. clin. Path. (1968), 21, 463-469 From the Department ofpathology, St. Thomas' Hospital and Medical School, London SYNOPSIS Two cases of
Senile: flattening of vertical meridian, thinning of periphery, lack of luster
 Pterygia Etiology: triangular, fibrovascular, connective tissue overgrowths of bulbar conjunctiva onto cornea; distribution of ultraviolet energy- heat, wind, dust, dry atmosphere,higher prevalence nearer
Pterygia Etiology: triangular, fibrovascular, connective tissue overgrowths of bulbar conjunctiva onto cornea; distribution of ultraviolet energy- heat, wind, dust, dry atmosphere,higher prevalence nearer
Chapter 2 Cell. Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology
 Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Chapter 2 Cell Zhou Li Prof. Dept. of Histology and Embryology The inner life of the cell Ⅰ. Plasma membrane (Plasmalemma) 1.1 The structure Unit membrane: inner layer 3-layered structure outer layer mediat
Microfilaments. myosin. In muscle cells. Microfilaments. Microfilaments. Video: Cytoplasmic Streaming. amoeboid movement. Pseudopodia.
 Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
What are some common conditions that affect the cornea?
 What are some common conditions that affect the cornea? Injuries After minor injuries or scratches, the cornea usually heals on its own. Deeper injuries can cause corneal scarring, resulting in a haze
What are some common conditions that affect the cornea? Injuries After minor injuries or scratches, the cornea usually heals on its own. Deeper injuries can cause corneal scarring, resulting in a haze
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Techniques
 Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Techniques SHERAZ DAYA MD FACP FACS FRCS(Ed) FRCOphth Financial Disclosure Company Code 1. Abbott Medical Optics Inc. S 2. Bausch + Lomb C,L 3. Carl Zeiss Meditec
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Techniques SHERAZ DAYA MD FACP FACS FRCS(Ed) FRCOphth Financial Disclosure Company Code 1. Abbott Medical Optics Inc. S 2. Bausch + Lomb C,L 3. Carl Zeiss Meditec
Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials are separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. Complex structure Also
 Dr. Gugale Pritesh Ramanlal M.Sc., Ph.D., B.Ed., D.M.L.T. Email id - pritesh.gugale09@gmail.com Contact numbernumber- 8446475310 Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials
Dr. Gugale Pritesh Ramanlal M.Sc., Ph.D., B.Ed., D.M.L.T. Email id - pritesh.gugale09@gmail.com Contact numbernumber- 8446475310 Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials
ON THE THICKNESS OF THE UNIT MEMBRANE
 Published Online: 1 May, 1963 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.17.2.413 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 1, 2018 ON THE THICKNESS OF THE UNIT MEMBRANE TOSHIYUKI YAMAMOTO, M.D. From the
Published Online: 1 May, 1963 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.17.2.413 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 1, 2018 ON THE THICKNESS OF THE UNIT MEMBRANE TOSHIYUKI YAMAMOTO, M.D. From the
Corneal Transplants. Corneal transplants. What causes cornea problems? Full thickness corneal transplant
 Corneal transplants The cornea is the clear, front window of the eye. It helps focus light into the eye so that you can see. The cornea is made of layers of cells. These layers work together to protect
Corneal transplants The cornea is the clear, front window of the eye. It helps focus light into the eye so that you can see. The cornea is made of layers of cells. These layers work together to protect
AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA
 J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
J. Cell Sci. 4, 211-221 (1969) 211 Printed in Great Britain AN ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE STARCH-CONTAINING PLASTIDS IN THE FERN TODEA BARBARA H. M. SMITH* AND D. S. SMITHf Department of Biology,
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Introduction. Donor tissue preparation for Descemet Membrane Endothelial ASCRS Aim of dissection. DMEK graft preparation
 Introduction Donor tissue preparation for Descemet Membrane Endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) ASCRS - 2015 Endothelial Keratoplasty DSAEK / DSEK DMEK Donor lamellae stroma + DM + endothelium DM + endothelium
Introduction Donor tissue preparation for Descemet Membrane Endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) ASCRS - 2015 Endothelial Keratoplasty DSAEK / DSEK DMEK Donor lamellae stroma + DM + endothelium DM + endothelium
INTRA-CORNEAL LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 629. INTRA-CORNEAL LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY* BY TADEUSZ KRWAWICZ Ophthalmological Clinic, Medical Academy, Lublin, Poland THE operative technique of lamellar keratoplasty is still
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 629. INTRA-CORNEAL LAMELLAR KERATOPLASTY* BY TADEUSZ KRWAWICZ Ophthalmological Clinic, Medical Academy, Lublin, Poland THE operative technique of lamellar keratoplasty is still
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Growth and repair: Cartilage is a vascular tissues that receives nutrients by diffusion through its matrix, cartilage grow by 2 mechanisms:
 Skeletal connective tissues: (cartilage and bone): Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues both adapted to serve as skeletal framework in most vertebrates the presence of solid inter cellular
Skeletal connective tissues: (cartilage and bone): Cartilage and bone are specialized connective tissues both adapted to serve as skeletal framework in most vertebrates the presence of solid inter cellular
QUALIT ATIVE CHARACTERIZATION OF SOME PA THOLOGIC CORNEAL DISEASES USING CONTACT SPECULAR MICROSCOPY
 QUALIT ATIVE CHARACTERIZATION OF SOME PA THOLOGIC CORNEAL DISEASES USING CONTACT SPECULAR MICROSCOPY JOSE DAVID F. MARIN, JR. EVANGELINE MARION A. ABENDANIO ROSSINA LYDIA ALEJO-RAMIREZ SAL V AOOR R. SALCEDA
QUALIT ATIVE CHARACTERIZATION OF SOME PA THOLOGIC CORNEAL DISEASES USING CONTACT SPECULAR MICROSCOPY JOSE DAVID F. MARIN, JR. EVANGELINE MARION A. ABENDANIO ROSSINA LYDIA ALEJO-RAMIREZ SAL V AOOR R. SALCEDA
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Corneal specimens that influence clinical decisions
 Corneal specimens that influence clinical decisions Refractive surgery Corneal dystrophies Microbial infections J. Douglas Cameron, MD Chief, Ophthalmic Pathology Division Neuropathology Department Armed
Corneal specimens that influence clinical decisions Refractive surgery Corneal dystrophies Microbial infections J. Douglas Cameron, MD Chief, Ophthalmic Pathology Division Neuropathology Department Armed
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies
 Arch. histol. jap., Vol. 45, No. 4 (1982) p. 347-354 Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies Kazumasa MIURA, Tohru IZUMI, Junichi FUKUDA, Masaru
Arch. histol. jap., Vol. 45, No. 4 (1982) p. 347-354 Glycogen Aggregates in Cardiac Muscle Cell: A Cytopathological Study on Endomyocardial Biopsies Kazumasa MIURA, Tohru IZUMI, Junichi FUKUDA, Masaru
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
HYALINE RIDGES ON THE POSTERIOR CORNEA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 257 HYALINE RIDGES ON THE POSTERIOR CORNEA*t BY J. C. McGRAND Royal Eye Hospital, London HYALINE or glassy ridge formation on the posterior corneal surface appears to be a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 257 HYALINE RIDGES ON THE POSTERIOR CORNEA*t BY J. C. McGRAND Royal Eye Hospital, London HYALINE or glassy ridge formation on the posterior corneal surface appears to be a
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Biochemical evaluation of the corneal endothelium
 Isolation of the plasma membrane from corneal endothelial cells Z. Suzanne Zam, James Cerda,* and Frank M. Polack The plasma membranes of normal rabbit endothelail cells were isolated by the use of an
Isolation of the plasma membrane from corneal endothelial cells Z. Suzanne Zam, James Cerda,* and Frank M. Polack The plasma membranes of normal rabbit endothelail cells were isolated by the use of an
Distinction layer by layer. HRT II Rostock Cornea Module
 Distinction layer by layer HRT II Rostock Cornea Module Homogenously illuminated, undistorted images Movie capture Manual Pachymetry Epithelial and intra-corneal pachymetry Full corneal thickness Post-LASIK
Distinction layer by layer HRT II Rostock Cornea Module Homogenously illuminated, undistorted images Movie capture Manual Pachymetry Epithelial and intra-corneal pachymetry Full corneal thickness Post-LASIK
Graefe's Archive. Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Retinal vascular patterns
 Retinal vascular patterns VII. Acellular change Toichiro Kuwabara and David G. Cogan The trypsin digestion technique has revealed a preferential loss of endothelial cells (in conditions other than diabetes)
Retinal vascular patterns VII. Acellular change Toichiro Kuwabara and David G. Cogan The trypsin digestion technique has revealed a preferential loss of endothelial cells (in conditions other than diabetes)
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Non-Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty for Bullous Keratopathy in Buphthalmic Eye
 DOI: 10.1159/000446103 Published online: June 2, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
DOI: 10.1159/000446103 Published online: June 2, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International
Descemet s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) surgery
 Patient information Descemet s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) surgery This information leaflet tells you what to expect if you have DMEK surgery an operation on the cornea of the eye along with
Patient information Descemet s membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) surgery This information leaflet tells you what to expect if you have DMEK surgery an operation on the cornea of the eye along with
