Liver X receptor agonist prevents the evolution of collagen-induced arthritis in mice
|
|
|
- Cecil Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49: doi: /rheumatology/keq007 Advance Access publication 16 February 2010 BASIC SCIENCE Original article Liver X receptor agonist prevents the evolution of collagen-induced arthritis in mice Min-Chan Park 1, Yong-Jin Kwon 1, Soo-Jin Chung 1, Yong-Beom Park 1 and Soo-Kon Lee 1 Abstract Objective. Liver X receptors (LXRs) have been characterized as regulators of macrophage inflammatory pathways. Synthetic LXR agonists inhibit the macrophage response to bacterial pathogens and antagonize the induction of a number of pro-inflammatory genes. The aim of this study was to investigate the preventive effects of synthetic LXR agonist, GW3965, treatment on the evolution of arthritis and inflammatory response in a murine CIA model. Methods. Intradermal injection of bovine type II CIA in DBA/1 mice. Along with the induction of CIA, mice were treated with oral GW3965 (0.1, 0.3 or 1.0 mg/kg/day) or vehicle from Day 1 to Day 40. Clinical assessment for arthritis scores and histopathological assessment of joint sections were performed. The expression of inflammatory mediators was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining. Serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels were determined using ELISA. Results. The CIA incidence was 100% on Day 27 and the severity progressed until Day 35 with histological features of cartilage erosion in vehicle-treated mice. GW3965 treatment significantly reduced the arthritis incidence and attenuated the clinical and histological severity, compared with vehicle-treated mice. GW3965 treatment also significantly reduced inflammatory mediator production in joint sections and serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in a dose-dependent manner. Conclusions. These results indicate that activation of LXRs suppresses the onset of CIA and reduces inflammation and joint destruction in CIA mice. The data could suggest that LXR treatment is an effective prophylactic approach to suppress the evolution of synovitis and resultant joint destruction observed in RA. Key words: Rheumatoid arthritis, Liver X receptors, GW3965, Collagen-induced arthritis. Introduction RA is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation and cartilage and bone destruction in the joints. The inflammation of RA results from the production of prostaglandins, pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide. In particular, in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid synovitis and synovial tissue, macrophages produce a number of inflammatory mediators and interact with 1 Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Yonsei University, College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea. Submitted 23 July 2009; revised version accepted 6 January Correspondence to: Min-Chan Park, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, 712 Eonjuro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul , South Korea. mcpark@yuhs.ac other cells or extracellular matrix macromolecules. In addition, macrophages are involved in the oxidative and nitrosative damage of the joints and their products mediate synovial angiogenesis. Macrophage-derived cytokines, such as TNF-a and IL-1b, which are abundant in synovial tissues and fluid from RA patients, are mitogens for synovial fibroblasts and osteoclasts. These cytokines, acting in both autocrine and paracrine fashions within the joint space, mediate long-term cartilage degradation and bone erosion [1 6]. Macrophages play essential roles in immunity and lipid homoeostasis. They function to scavenge pathogens and apoptotic cells, and it is generally considered that sustained activation of these responses may precipitate pathological states. Macrophages use the nuclear-receptor superfamily, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated! The Author Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
2 GW3965 suppresses CIA receptors and liver X receptors (LXRs). The nuclear receptor superfamily has diverse and important roles in regulating reproductive, homeostatic, inflammatory, immune and metabolic processes [7 10]. Previous studies have outlined the importance of LXRs (LXR-a, encoded by the gene Nr1h3, and LXR-b, encoded by the gene Nr1h2)in the macrophage cholesterol efflux pathway. LXRs are cholesterol sensors that regulate the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism in response to specific oxysterol ligands [11]. In macrophages, oxysterols may be derived from internalized oxidatively modified low density lipoproteins (oxldl) or generated intracellularly from modified cholesterol [12, 13]. LXR activation in macrophages induces expression of several genes involved in lipid metabolism and reverse cholesterol transport, exerting an atheroprotective effect. In addition, LXRs have more recently been characterized as macrophage inflammatory pathway regulators. Mice lacking LXRs show an exaggerated response to lipopolysaccharide. Synthetic LXR agonists inhibit the macrophage-response to bacterial pathogens and down-regulate a number of pro-inflammatory genes. These include IL-1b, IL-6, MMP-9, inducible nitric oxide synthase (inos), cyclo-oxygenase 2 (COX2), adhesion molecules and chemokines [14 16]. Some of these genes are preferentially sensitive to LXRs, indicating LXR-specific effects on inflammatory responses. LXR ligands repressed inflammatory gene expression in macrophages derived from wildtype, Lxra / and Lxrb / mice, but could not do so in cells from Lxrab / mice, indicating that both LXR isoforms possess anti-inflammatory properties [17, 18]. The precise molecular mechanisms responsible for inhibiting inflammatory response genes by LXRs remain to be established, but are at least in part linked to nuclear factor-kb (NF-kB) inhibition [16, 17, 19]. Inflammatory rheumatic diseases, including RA, are significant risk factors in atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease [20, 21]. Furthermore, patients with active RA show altered lipid metabolism, which can be reversed by intensive anti-rheumatic treatment [22], and some of the shared inflammatory mechanisms responsible for rheumatoid synovitis are thought to be directly involved in producing atherosclerotic lesions [23, 24]. These observations suggest a strong integration between metabolism and inflammation. Because LXRs act as a cross-talk between lipid metabolism and inflammation, they may be beneficial in treating arthritis. The purpose of the present study is to investigate the prophylactic and disease-modifying effect of LXRs in a murine CIA, a model that mimics human RA clinically and histologically. We investigated whether a synthetic LXR agonist, GW3965, could prevent the evolution of murine CIA and suppress bone and cartilage destruction in CIA mice. Materials and methods CIA induction and treatment All animals were housed according to the Animal Care Committee of Yonsei University College of Medicine guidelines. All experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Care Committee. Male DBA/1J mice at 8 10 weeks of age (SLC, Shizoka, Japan) were used for CIA induction. Bovine type II collagen (CII; Sigma Chemical, St Louis, MO, USA) was dissolved in 0.01 M acetic acid at 2 mg/ml by stirring overnight at 4 C. Freund s complete adjuvant was prepared by adding Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37 RA (Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) at 5 mg/ml. Mice were injected intradermally at the base of the tail with 100 ml of emulsion (containing 100 g of CII) on Days 1 and 21 as described previously [25]. All mice were fed with GW3965, a synthetic LXR agonist, or vehicle, beginning from Day 1 to Day 40. The synthetic LXR agonist, GW3965, was provided by Jon L. Collins (GlaxoSmithKline R&D, USA) and GW3965 treatment was performed in a manner similar to that in the previous studies [26, 27]. Briefly, mice were fed a western diet (Research diets, Central Lab. Animal Inc., Seoul, Korea; 21% fat, 1.5% cholesterol) supplemented with GW3965 at a dose of 0.1, 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day or vehicle control (0.5% methylcellulose, 2% Tween-80) from Day 1 to Day 40. Sham-treated mice were treated on Days 1 and 21 with 100 ml of 0.01 M acetic acid. Sham-treated mice were also fed with GW3965 or vehicle (10% DMSO) from Day 1 to Day 40. Ten mice were assigned to each group. Clinical and histological assessment of CIA An investigator blinded to the treatment regimen performed all clinical examinations as previously described [28], using the following system: Grade 0, no swelling; Grade 1, slight swelling and erythema; Grade 2, moderate swelling and oedema; Grade 3, extreme swelling and pronounced oedema; and Grade 4, joint rigidity. Mice were evaluated for arthritis on a daily basis. Each limb was graded and limb scores added, giving a maximum possible score of 16 per animal. For histological analysis, mice were anaesthetized and sacrificed 40 days after primary immunization. Paws were randomly collected and fixed in 4% buffered formaldehyde, decalcified, paraffinembedded, sectioned and stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Histopathological changes were scored in a blinded manner based on cell infiltration, cartilage destruction and bone erosion parameters, as previously described [29]. Minor differences between observers were resolved by mutual agreement. Immunohistochemical localization of inflammatory mediators Mice were anaesthetized and sacrificed on Day 40, and paws and knee joints were removed for histopathological examination, which was performed after fixation, decalcification and paraffin embedding of tissue sections. Tissue sections were prepared and stained with H&E. Sections were sequentially incubated with specific antibodies directed against murine TNF-a, IL-1b, inos or COX-2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) followed by the appropriate secondary antibodies (ISU Abxis, Seoul, Korea). All tissue samples were counterstained with haematoxylin. After immunohistochemical 883
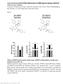
3 Min-Chan Park et al. staining, expression of different markers in the joint synovial tissue was scored semi-quantitatively on a four-point scale, independently and blindly by two investigators, and the averages were calculated. A score of 0 represented minimal expression, 1 represented mild expression, 2 represented moderated expression, whereas 3 represented abundant marker expression [30]. Measurement of pro-inflammatory cytokine levels The TNF-a, IL-1b and IL-6 levels in serum from CIA mice were determined by specific ELISA (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) according to the manufacturer s protocol. Both intra- and interassay coefficients of variation were <8% for all assays. Assessments for GW3965 toxicity We used 15 CIA mice for investigation of the toxicity of GW3965: controls and CIA mice treated with 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg of GW3965. We obtained blood from the controls and the mice treated with GW3965 (0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg) after sacrifice, and examined white blood cell count, haemoglobin, platelet count and levels of aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, blood urea nitrogen and creatinine for liver and kidney toxicity. Statistics The results are shown as the mean (S.E.M.). In experiments involving histology or immunohistochemistry, the results are representative of at least three experiments performed on different days. Data were examined by one-way analysis of variance followed by a Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple comparisons. A Mann Whitney U-test was used to compare the arthritis index medians. P < 0.05 was considered significant. Results FIG. 1Effects of GW3965 on arthritis onset and severity in CIA mice. Effect of GW3965 treatment on CIA evolution CIA developed rapidly in mice immunized with CII. Clinical signs of the disease, including periarticular erythema and oedema, first appeared in the hind paws between 23 and 24 days after CII immunization, with a 100% CIA incidence by Day 32 (Fig. 1A). Erythema and swelling in the hind paws increased in frequency and severity in a (A) The percentage of arthritic mice (arthritis scores >1) is significantly different between vehicle and GW3965 treatment. Treatment with 0.1 mg/kg/day GW3965 slightly suppressed arthritis onset, whereas 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day GW3965 significantly reduced arthritis incidence. (B) Median arthritis scores also indicate a significant difference between vehicle and GW3965 treatment. Doses of 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day of GW3965 significantly reduced arthritis incidence *P <
4 GW3965 suppresses CIA time-dependent manner, reaching maximum arthritis indices between 32 and 34 days after CII immunization in the vehicle-treated mice (Fig. 1B). GW3965 treatment suppressed the evolution of CIA in a dosedependent manner, demonstrated by lower incidence and reduced arthritis severity as shown in Fig. 1. A 0.1 mg/kg/day dose of GW3965 also decreased arthritis severity significantly, but did not remarkably suppress arthritis onset, compared with 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day doses. There was no macroscopic evidence of either hind paw erythema or oedema in the sham-treated mice (data not shown). On Day 40, histological evaluation of paws from CIIimmunized mice revealed signs of severe arthritis and bone erosion. A comparison of the histological damage scores is presented in Fig. 2. GW3965 treatment reduced inflammatory cell infiltration and bone destruction in CIA mice (Fig. 2A). A 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day GW3965 treatment significantly reduced the histological damage scores in the joint sections, compared with vehicletreated mice. However, no significant reduction in arthritis was observed in the mice treated with 0.1 mg/kg of GW3965. There was no evidence of disease in the sham-treated mice from either treatment group (Fig. 2B). FIG. 2Effects of GW3965 on histological changes. Effect of GW3965 treatment on TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2 production Figure 3 shows results from immunohistochemical analysis of joint sections representative of at least two experiments performed on different days. Joints obtained from vehicle-treated mice showed positive staining for TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2, localized primarily to inflamed cells around the joints. GW3965- treated mice with CIA showed significantly reduced staining (Fig. 3A). Semi-quantitative analysis demonstrated a significant dose-dependent decrease in TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2 stain positivity in GW3965- treated mice, compared with vehicle-treated mice. There was no TNF-a, IL-1b, inos or COX-2 staining around joints obtained from sham-treated mice (Fig. 3B). Effect of GW3965 treatment on pro-inflammatory cytokine levels The pro-inflammatory cytokine expression pattern, as assessed by ELISA, is shown in Fig. 4. Compared with vehicle-treated mice, GW3965-treated mice had lower serum TNF-a, IL-1b and IL-6 levels. Serum TNF-a levels in vehicle-treated and 0.1 mg/kg/day GW3964-treated mice were not significantly different, (A) Joint sections from paws of vehicle-treated mice show inflammatory cell infiltration and bone erosion, but remarkably reduced inflammatory cell infiltration in GW3965-treated mice (original magnification 100). (B) Treatment with 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day of GW3965 significantly reduced the histological damage scores in CIA mice. Values are mean (S.E.M.) of 10 mice per group. *P < 0.01 vs sham-treated control; **P < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated CIA mice
5 Min-Chan Park et al. FIG. 3Effects of GW3965 treatment on immunohistochemical staining for TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2. (A) Vehicle-treated mice showed positive staining for TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2, which was localized primarily to inflamed cells around the joints. Staining was significantly reduced in GW3965-treated CIA mice. There was no specific staining in joints from sham-treated mice (original magnification 100). (B) Treatment with 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day of GW3965 significantly reduced TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2 expression. *P < 0.01 vs sham-treated control; **P < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated mice with CIA. but they were significantly greater than in 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg/day GW3965-treated mice. IL-1b and IL-6 serum levels in vehicle-treated mice were significantly higher than those in all GW3965-treated mice, but the differences between GW3965 doses were not statistically significant. There were no significant increases in serum levels of any of the three cytokines in sham-treated mice
6 GW3965 suppresses CIA FIG. 4Effects of GW3965 treatment on pro-inflammatory cytokine production. GW3965 treatment significantly reduced TNF-a (A), IL-1b (B) and IL-6 (C) serum levels in CIA mice compared with vehicle-treated mice. *P < 0.01 vs sham-treated control; **P < 0.01 vs vehicle-treated mice with CIA. ND: not detected. Toxicity of GW3965 in CIA mice Table 1 shows the results of laboratory tests performed to investigate the toxicity of GW3965. There were no differences in white blood cell counts, haemoglobin levels and platelet counts between the controls and the mice treated with GW3965 (0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg). Liver and kidney toxicities were not observed in the mice treated with 0.3 and 1.0 mg/kg of GW3965. Discussion The present study investigated the potential usefulness of a synthetic LXR agonist, GW3965, as an anti-inflammatory agent to suppress arthritis in CIA mice, and found that GW3965 suppresses CIA incidence and severity. Higher GW3965 doses ( mg/kg/day) reduced CIA incidence up to 50% compared with vehicle-treated mice. Although a 0.1 mg/kg/day GW3965 treatment also significantly decreased CIA incidence, the effect was observed at a relatively late time point, and disappeared with time in comparison with higher GW3965 doses. In addition to suppressing CIA onset, GW3965 treatment significantly reduced CIA severity. GW3965 treatment significantly reduced the median arthritis indices and histological joint damage, compared with vehicle-treated mice. Both effects were more prominent at higher GW3965 doses. The regulatory action of LXRs in inflammatory responses is well understood. In addition to the originally identified atheroprotective effects [31, 32], LXRs have recently been identified as macrophage inflammatory pathway regulators. Synthetic LXR agonists, such as GW3965 and T , antagonise the expression of pro-inflammatrory genes, such as inos, COX2, IL-6, IL-1b, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), MCP-3 and MMP9 [17 19]. The precise mechanisms by which LXRs exert these anti-inflammatory effects remain to be established, but a body of evidence implicates inhibition of the NF-kB pathway. Cytokine or bacterial component recognition by the corresponding receptor initiates pro-inflammatory gene expression, and tolllike receptor 3/4 activation by these signals blocks LXR-dependent gene transcription. Moreover, ligand activation of LXR inhibits inflammatory responses to cytokines via a blockade of NF-kB signalling [15, 17, 19, 33]. In the rheumatoid synovium, activation of the NF-kB pathway induces various genes that contribute to the inflammatory response, such as TNF-a, IL-1b, COX-2, MMPs and chemokines that recruit immune cells to the inflamed pannus [34 36]. The present study demonstrated that GW3865 treatment significantly reduced TNF-a, IL-1b, inos and COX-2 expression in the joint tissue and serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in CIA mice. Thus, the suppressed CIA incidence and severity by GW3965 treatment might result, at least in part, from NF-kB pathway inhibition. Furthermore, GW3965 may serve as a negative regulator of articular inflammation in CIA mice. LXR-a is highly expressed in liver, adipose tissue and macrophages, whereas LXR-b is expressed ubiquitously. Recently, Chintalacharuvu et al. [37] showed both LXR-a and LXR-b overexpression in synovium from RA patients, but not in normal synovium. Although the therapeutic effect of LXR agonists in established arthritis has not been reported in the literature, the recent work by Chintalacharuvu et al. [37] documented the regulatory effect of a synthetic LXR agonist, T , on pro-inflammatory cytokine production and resultant joint damage in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice [37]. These results support the proposal that LXR agonists might 887
7 Min-Chan Park et al. TABLE 1 Laboratory findings in control and GW3965-treated mice Parameters Control GW mg/kg GW mg/kg White blood cell, per ml (1003.2) (975.1) (716.5) Haemoglobin, g/dl 13.8 (0.5) 13.6 (0.5) 13.3 (0.5) Platelet, 1000/ml (51.0) (77.5) (80.2) Blood urea nitrogen, mg/dl 24.5 (3.2) 27.1 (3.0) 26.6 (2.5) Creatinine, mg/dl 0.5 (0.1) 0.5 (0.1) 0.5 (0.1) Aspartate transaminase, IU/l (34.0) (31.0) (22.3) Alanine transaminase, IU/l 68.9 (17.0) 78.8 (14.4) 79.1 (11.6) All results are expressed as mean (S.D.). prove clinically useful in suppressing autoimmune diseases, in particular RA. The present study used CIA mice, which has proved to be a useful RA model, since it possesses many cellular and humoral immunity characteristics found in human RA [38, 39]. Similar to previous observations, GW3865 treatment, in the present study, significantly reduced the degree of joint damage in CIA mice by decreasing the expression of inflammatory mediators in a dose-dependent manner. The most interesting finding was that higher LXR agonist doses significantly suppress the evolution of arthritis in CIA mice, which indicates a prophylactic effect of LXR agonist against arthritis onset. Although the function of LXRs to induce macrophage cholesterol efflux and inhibit inflammatory gene expression could generate widespread interest in these proteins as potential targets for atherosclerosis and autoimmune disease treatment, synthetic LXR agonists can increase triglyceride levels. LXR-a is the predominant LXR expressed in liver, and the ability of LXR agonists to stimulate hepatic lipogenesis likely results primarily from LXR-a activation [40 42]. In this regard, the present study has some potential limitations: (i) we evaluated the prophylactic effect of a non-selective, not isotype-selective, synthetic LXR agonist on the evolution of CIA in mice and (ii) we demonstrated only the prophylactic action of GW3965 on the development of CIA and its therapeutic effects on established disease was not evaluated. The demonstration of prophylactic effect alone could not be sufficient for the clinical significance of LXR agonist for the treatment of RA. Thus, the present study mandates future investigations to define the roles of tissue- or isotype-selective LXR agonists in the RA inflammatory response and to investigate the therapeutic effect of synthetic LXR agonists on established disease. In conclusion, treatment with a synthetic LXR agonist significantly suppressed arthritis incidence and attenuated its severity in CIA mice. This LXR agonist reduced the degree of joint damage by inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators. The data obtained in the present study support the conclusion that LXR activation exerts a beneficial effect in RA, given its anti-inflammatory properties, and could serve as a novel prophylactic modality for RA. Rheumatology key messages. GW3965 prophylaxis significantly reduced arthritis incidence and attenuated the clinical and histological severity in CIA mice.. GW3965 prophylaxis significantly reduced inflammatory mediator production in joint sections and serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in a dose-dependent manner. Acknowledgements We are thankful to J. M. Sung, PhD, and K. H. Han, MS, Department of Research Affairs, Yonsei University College of Medicine, for their statistical consultation and Mr D. S. Jang, Department of Research Affairs, Yonsei University College of Medicine, for his help with figure preparations. We would like to also thank J. L. Collins, PhD, GlaxoSmithKline R&D, USA, for providing GW3965. GlaxoSmithKline had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation or manuscript preparation. Funding: This work was supported by the Yonsei University Research Fund ( ) and the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund) (KRF E00097). Disclosure statement: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest. References 1 Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: Harris ED Jr. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med 1990;322:
8 GW3965 suppresses CIA 3 Badolato R, Oppenheim JJ. Role of cytokines, acute-phase proteins, and chemokines in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1996;26: Koch AE. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2005;52: Huang Q, Ma Y, Adebayo A, Pope RM. Increased macrophage activation mediated through toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56: Szekanecz Z, Gaspar L, Koch AE. Angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci 2005;10: Hansson GK. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 2005;352: Valledor AF, Ricote M. Nuclear receptor signaling in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol 2004;67: Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2006;116: Chung SW, Kang BY, Kim SH et al. Oxidized low density lipoprotein inhibits interleukin-12 production in lipopolysaccharide-activated mouse macrophages via direct interactions between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and nuclear factor-kappa B. J Biol Chem 2000;275: Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ. The role of orphan nuclear receptors in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2000;16: Xie B, Zhao J, Kitagawa M et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol is an endogenous ligand for liver X receptor in cholesterol-loaded cells. J Biol Chem 2001;276: Laffitte BA, Tontonoz P. Orphan nuclear receptors find a home in the arterial wall. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2002;4: Glass CK, Ogawa S. Combinatorial roles of nuclear receptors in inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2006;6: Terasaka N, Hiroshima A, Ariga A et al. Liver X receptor agonists inhibit tissue factor expression in macrophages. FEBS J 2005;272: Ogawa S, Lozach J, Benner C et al. Molecular determinants of crosstalk between nuclear receptors and toll-like receptors. Cell 2005;122: Joseph SB, Castrillo A, Laffitte BA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Tontonoz P. Reciprocal regulation of inflammation and lipid metabolism by liver X receptors. Nat Med 2003;9: Castrillo A, Joseph SB, Marathe C, Mangelsdorf DJ, Tontonoz P. Liver X receptor-dependent repression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in macrophages. J Biol Chem 2003;278: Zelcer N, Tontonoz P. Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: Aviña-Zubieta JA, Choi HK, Sadatsafavi M, Etminan M, Esdaile JM, Lacaille D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum 2008;59: Park YB, Ahn CW, Choi HK et al. Atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis: morphologic evidence obtained by carotid ultrasound. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46: Park YB, Choi HK, Kim MY et al. Effects of antirheumatic therapy on serum lipid levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Am J Med 2002;113: Reiss AB, Carsons SE, Anwar K et al. Atheroprotective effects of methotrexate on reverse cholesterol transport proteins and foam cell transformation in human THP-1 monocyte/macrophages. Arthritis Rheum 2008;58: Liuzzo G, Goronzy JJ, Yang H et al. Monoclonal T-cell proliferation and plaque instability in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2000;101: Campbell IK, Hamilton JA, Wicks IP. Collagen-induced arthritis in C57BL/6 (H-2b) mice: new insights into an important disease model of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol 2000;30: Joseph SB, McKilligin E, Pei L et al. Synthetic LXR ligand inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002;99: Naik SU, Wang X, Da Silva JS et al. Pharmacological activation of liver X receptors promotes reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. Circulation 2006;113: Delgado M, Abad C, Martinez C, Receta J, Gomariz RP. Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease. Nat Med 2001;7: Kasama T, Strieter RM, Lukacs NW, Lincoln PM, Burdick MD, Kunkel SL. Interleukin-10 and chemokine regulation during the evolution of murine type-ii collagen-induced arthritis. J Clin Invest 1995;95: Lee SW, Kim JH, Park MC, Park YB, Lee SK. Adiponectin mitigates the severity of arthritis in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 2008;37: Venkateswaran A, Laffitte BA, Joseph SB et al. Control of cellular cholesterol efflux by the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97: Tangirala RK, Bischoff ED, Joseph SB et al. Identification of macrophage liver X receptors as inhibitors of atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002;99: Pascual G, Fong AL, Ogawa S et al. A SUMOylationdependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-gamma. Nature 2005;437: Aya K, Alhawagri M, Hagen-Stapleton A, Kitaura H, Kanagawa O, Novack DV. NF-(kappa)B-inducing kinase controls lymphocyte and osteoclast activities in inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest 2005;115: Bondeson J, Foxwell B, Brennan F, Feldmann M. Defining therapeutic targets by using adenovirus: blocking NF-kappa B inhibits both inflammatory and destructive mechanisms in rheumatoid synovium but spares anti-inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999;96: Makarov SS. NF-kappa B in rheumatoid arthritis: a pivotal regulator of inflammation, hyperplasia, and tissue destruction. Arthritis Res 2001;3: Chintalacharuvu SR, Sandusky GE, Burris TP, Burmer GC, Nagpal S. Liver X receptor is a therapeutic target in 889
9 Min-Chan Park et al. collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2007;56: Stuart JM, Townes AS, Kang AH. Collagen autoimmune arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol 1984;2: Holmdahl R, Andersson M, Goldschmidt TJ, Gustafsson K, Jansson L, Mo JA. Type II collagen autoimmunity in animals and provocations leading to arthritis. Immunol Rev 1990;118: Joseph SB, Laffitte BA, Patel PH et al. Direct and indirect mechanisms for regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression by liver X receptors. J Biol Chem 2002;277: Repa JJ, Liang G, Ou J et al. Regulation of mouse sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c gene (SREBP-1c) by oxysterol receptors, LXRalpha and LXRbeta. Genes Dev 2000;14: Yoshikawa T, Shimano H, Amemiya-Kudo M et al. Identification of liver X receptor-retinoid X receptor as an activator of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol 2001;21:
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis?
 Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
Rheumatology 2005;44(Suppl. 2):ii3 ii7 B cells: a fundamental role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis? doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh616 The role of T cells in the pathogenesis of RA is well established,
NBQX, An AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist, Alleviates Joint Disease In Models Of Inflammatory- And Osteo- Arthritis.
 NBQX, An AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist, Alleviates Joint Disease In Models Of Inflammatory- And Osteo- Arthritis. Cleo S. Bonnet, PhD 1, Anwen S. Williams, PhD 1, Sophie J. Gilbert, PhD 1,
NBQX, An AMPA/Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist, Alleviates Joint Disease In Models Of Inflammatory- And Osteo- Arthritis. Cleo S. Bonnet, PhD 1, Anwen S. Williams, PhD 1, Sophie J. Gilbert, PhD 1,
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
 MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunology and Inflammatory Disease. In pursuit of your success. Autoimmune Arthritis Animal Models Available:
 Immunology and Inflammatory Disease Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic debilitating autoimmune disorder characterized by synovitis that leads to cartilage and bone erosion by invading fibrovascular
Immunology and Inflammatory Disease Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic debilitating autoimmune disorder characterized by synovitis that leads to cartilage and bone erosion by invading fibrovascular
G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi and B. Staels, UR 545 INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille and Université de Lille 2, Lille, France
 LIVER X RECEPTORS (LXRS): TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATORS OF MACROPHAGE CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi and B. Staels, UR 545 INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille and Université de Lille 2, Lille,
LIVER X RECEPTORS (LXRS): TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATORS OF MACROPHAGE CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi and B. Staels, UR 545 INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille and Université de Lille 2, Lille,
Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling
 Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling Noam Zelcer and Peter Tontonoz Review series Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, UCLA,
Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling Noam Zelcer and Peter Tontonoz Review series Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, UCLA,
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
The possible mode of action of Tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor
 129 Mini Review The possible mode of action of Tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor Satoshi Kubo 1), Kunihiro Yamaoka 1), Keisuke Maeshima 2) and Yoshiya Tanaka 1, ) 1) The First Department of Internal Medicine,
129 Mini Review The possible mode of action of Tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor Satoshi Kubo 1), Kunihiro Yamaoka 1), Keisuke Maeshima 2) and Yoshiya Tanaka 1, ) 1) The First Department of Internal Medicine,
Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
 Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2a Is an Essential Catabolic Regulator of Inflammatory Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2a Is an Essential Catabolic Regulator of Inflammatory Rheumatoid Arthritis Je-Hwang Ryu 1,2., Chang-Suk Chae 1., Ji-Sun Kwak 1, Hwanhee Oh 1, Youngnim Shin 1, Yun Hyun Huh 1,
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2a Is an Essential Catabolic Regulator of Inflammatory Rheumatoid Arthritis Je-Hwang Ryu 1,2., Chang-Suk Chae 1., Ji-Sun Kwak 1, Hwanhee Oh 1, Youngnim Shin 1, Yun Hyun Huh 1,
Wei-Tso Chia a,b, Li-Tzu Yeh b, Yuan-Wu Chen b, Herng-Sheng Lee b, Deh-Ming Chang b and Huey-Kang Sytwu b, 1. Introduction
 Disease Markers 26 (2009) 1 7 1 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0593 IOS Press IL-1β in irrigation fluid and mrna expression in synovial tissue of the knee joint as therapeutic markers of inflammation in collagen
Disease Markers 26 (2009) 1 7 1 DOI 10.3233/DMA-2009-0593 IOS Press IL-1β in irrigation fluid and mrna expression in synovial tissue of the knee joint as therapeutic markers of inflammation in collagen
collagen-induced arthritis
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 9784-9788, October 1992 Immunology Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis RICHARD 0. WILLIAMS*, MARC FELDMANN,
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 9784-9788, October 1992 Immunology Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis RICHARD 0. WILLIAMS*, MARC FELDMANN,
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Division of Rheumatology Department of Internal Medicine College of Medicine Seoul National University Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Yun Jong Lee Rheumatoid
Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis
 Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis Charlene Barroga, Ph.D., Yong Hu, Ph.D., Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D., and John Hood,
Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis Charlene Barroga, Ph.D., Yong Hu, Ph.D., Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D., and John Hood,
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
New therapeutic targets for T2DM
 New therapeutic targets for T2DM Targeting inflammation: NF- B, salsalate Gwanpyo Koh Department of Internal Medicine Jeju National University School of Medicine Introduction Obesity is occurring at epidemic
New therapeutic targets for T2DM Targeting inflammation: NF- B, salsalate Gwanpyo Koh Department of Internal Medicine Jeju National University School of Medicine Introduction Obesity is occurring at epidemic
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity. Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China
 Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
silent epidemic,. (WHO),
 Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Protocol for the Successful Induction of Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) in Mice
 Protocol for the Successful Induction of Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) in Mice Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) (1-3) shares both immunological and pathological features with human rheumatoid arthritis
Protocol for the Successful Induction of Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) in Mice Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) (1-3) shares both immunological and pathological features with human rheumatoid arthritis
Activation of Liver X Receptor Alleviates Ocular Inflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
 Immunology and Microbiology Activation of Liver X Receptor Alleviates Ocular Inflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis Hongxia Yang, 1 Shijie Zheng, 1 Yiguo Qiu, 1 Yan Yang, 1 Chaokui Wang, 1 Peizeng
Immunology and Microbiology Activation of Liver X Receptor Alleviates Ocular Inflammation in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis Hongxia Yang, 1 Shijie Zheng, 1 Yiguo Qiu, 1 Yan Yang, 1 Chaokui Wang, 1 Peizeng
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Wnt7a Inhibits Cartilage Matrix Degradation in a Mouse In Vivo Osteoarthritis Model
 Wnt7a Inhibits Cartilage Matrix Degradation in a Mouse In Vivo Osteoarthritis Model Averi Leahy, Andrea Foote, Tomoya Uchimura, Li Zeng, PhD. Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA. Disclosures: A. Leahy: None.
Wnt7a Inhibits Cartilage Matrix Degradation in a Mouse In Vivo Osteoarthritis Model Averi Leahy, Andrea Foote, Tomoya Uchimura, Li Zeng, PhD. Tufts University, Boston, MA, USA. Disclosures: A. Leahy: None.
Apolipoprotein E Deficient Mice Are Resistant to the Development of Collagen-Induced Arthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 2, February 2010, pp 472 477 DOI 10.1002/art.27205 2010, American College of Rheumatology Apolipoprotein E Deficient Mice Are Resistant to the Development of Collagen-Induced
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 62, No. 2, February 2010, pp 472 477 DOI 10.1002/art.27205 2010, American College of Rheumatology Apolipoprotein E Deficient Mice Are Resistant to the Development of Collagen-Induced
Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease
 ARTICLES Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease MARIO DELGADO, CATALINA ABAD, CARMEN MARTINEZ, JAVIER
ARTICLES Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease MARIO DELGADO, CATALINA ABAD, CARMEN MARTINEZ, JAVIER
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, and *National University, Seoul, Korea
 http://arthritis-research.com/content/2/4/293 Primary research Gene therapy for established murine collagen-induced arthritis by local and systemic adenovirus-mediated delivery of interleukin-4 Seon Hee
http://arthritis-research.com/content/2/4/293 Primary research Gene therapy for established murine collagen-induced arthritis by local and systemic adenovirus-mediated delivery of interleukin-4 Seon Hee
 Targeting Adipose Tissue in Rheumatoid Arthritis TARA study HOFFA L SCAPTIPL 0.1013606 0.270906 0.3759505 0.3373511 0.4050987 0.404667 11.6 DISCUSSIONS The study targeted the serum levels of adipokines
Targeting Adipose Tissue in Rheumatoid Arthritis TARA study HOFFA L SCAPTIPL 0.1013606 0.270906 0.3759505 0.3373511 0.4050987 0.404667 11.6 DISCUSSIONS The study targeted the serum levels of adipokines
Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM04690) as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis
 Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM469) as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D., Charlene Barroga, Ph.D., Yong Hu, Ph.D., John
Discovery of a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Wnt Pathway (SM469) as a Potential Disease Modifying Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis Vishal Deshmukh, Ph.D., Charlene Barroga, Ph.D., Yong Hu, Ph.D., John
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 277 281 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/02/040277+05 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0509, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2002) 10, 277 281 2002 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/02/040277+05 $22.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0509, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
1.0 Abstract. Title. Keywords. Rationale and Background
 1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
1.0 Abstract Title A Prospective, Multi-Center Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients on Adalimumab to Evaluate its Effect on Synovitis Using Ultrasonography in an Egyptian Population Keywords Synovitis
Human TNFα Transgenic Mouse Model of Spontaneous Arthritis
 Human TNFα Transgenic Mouse Model of Spontaneous Arthritis HEIDELBERG PHARMA AT A GLANCE CRO situated in Ladenburg, near Heidelberg, Germany 45 employees, 2000 m 2 of lab space Core competence: pre-clinical
Human TNFα Transgenic Mouse Model of Spontaneous Arthritis HEIDELBERG PHARMA AT A GLANCE CRO situated in Ladenburg, near Heidelberg, Germany 45 employees, 2000 m 2 of lab space Core competence: pre-clinical
Tofacitinib ( Xeljanz) Marshall Porter & Lauren Ysais
 Tofacitinib ( Xeljanz) Marshall Porter & Lauren Ysais Learning Objectives to Take with You A small molecule Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor treatment for moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) reduces
Tofacitinib ( Xeljanz) Marshall Porter & Lauren Ysais Learning Objectives to Take with You A small molecule Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor treatment for moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) reduces
Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
 HRB IMDA Oct HRB 2010 IMDA Seminar 28 th Oct 2010 Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) Dr. Orina Belton, School of Biomolecular and Biomedical Science,
HRB IMDA Oct HRB 2010 IMDA Seminar 28 th Oct 2010 Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) Dr. Orina Belton, School of Biomolecular and Biomedical Science,
Title proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Proteomic studies in Collagen Induced Arthritis (CIA) rats
 V{tÑàxÜ@H Proteomic studies in Collagen Induced Arthritis (CIA) rats 5.1. Introduction Over the last few decades, both naturally occurring and genetically engineered animal models of human diseases have
V{tÑàxÜ@H Proteomic studies in Collagen Induced Arthritis (CIA) rats 5.1. Introduction Over the last few decades, both naturally occurring and genetically engineered animal models of human diseases have
LOX-1-deficient mice are resistant to zymosan-induced arthritis: A mini review
 Hashimoto K, Oda Y, Yamagishi K, Tsukamoto I, Akagi M. J Immunological Sci. Mini Review Open Access LOX-1-deficient mice are resistant to zymosan-induced arthritis: A mini review Kazuhiko Hashimoto 1 *,
Hashimoto K, Oda Y, Yamagishi K, Tsukamoto I, Akagi M. J Immunological Sci. Mini Review Open Access LOX-1-deficient mice are resistant to zymosan-induced arthritis: A mini review Kazuhiko Hashimoto 1 *,
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE WIPAWEE WONGCHANA
 IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 22-02-2017 WIPAWEE WONGCHANA WHAT DO YOU SEE? Allergy Ref: http://carrington.edu/blog/medical/vaccines/smallpox-andsmallpox-vaccine/
IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 22-02-2017 WIPAWEE WONGCHANA WHAT DO YOU SEE? Allergy Ref: http://carrington.edu/blog/medical/vaccines/smallpox-andsmallpox-vaccine/
B-cell. Astrocyte SCI SCI. T-cell
 RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
Inflammation in the clinic
 Inflammation in the clinic Stephen T. Holgate MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology ILSI Europe Workshop, Seville, May 14-15 2012 The immune system acts in four general ways to ensure host defence
Inflammation in the clinic Stephen T. Holgate MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology ILSI Europe Workshop, Seville, May 14-15 2012 The immune system acts in four general ways to ensure host defence
Monoclonal Antibodies in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Prof. John D. Isaacs
 John D Isaacs Professor of Clinical Rheumatology Director, Wilson Horne Immunotherapy Centre Newcastle University, UK 1 Rheumatoid arthritis Targeting T-cells Targeting B-cells Costimulation blockade Novel
John D Isaacs Professor of Clinical Rheumatology Director, Wilson Horne Immunotherapy Centre Newcastle University, UK 1 Rheumatoid arthritis Targeting T-cells Targeting B-cells Costimulation blockade Novel
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An update for non rheumatologists
 Rheumatoid Arthritis: An update for non rheumatologists Dimitrios Pappas, M.D., M.P.H. Assistant Professor of Medicine Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Director of Rheumatology Athens
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An update for non rheumatologists Dimitrios Pappas, M.D., M.P.H. Assistant Professor of Medicine Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Director of Rheumatology Athens
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2008)
 ANTI-ARTHRITIC PROPERTY OF THE PLANT RUBIA CORDIFOLIA LIN. Jaijesh P 1, Srinivasan KK 2, Bhagath Kumar P 3, Sreejith G 4, Ciraj AM 4 1- Department of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College, Manipal, Karnataka,
ANTI-ARTHRITIC PROPERTY OF THE PLANT RUBIA CORDIFOLIA LIN. Jaijesh P 1, Srinivasan KK 2, Bhagath Kumar P 3, Sreejith G 4, Ciraj AM 4 1- Department of Anatomy, Melaka Manipal Medical College, Manipal, Karnataka,
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Mitigate Obesity-induced Osteoarthritis And Accelerate Wound Repair
 Omega-3 Fatty Acids Mitigate Obesity-induced Osteoarthritis And Accelerate Wound Repair Chia-Lung Wu, MS, Deeptee Jain, MD, Jenna McNeill, BS, Dianne Little, BVSc, PhD, John Anderson, MD, Janet Huebner,
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Mitigate Obesity-induced Osteoarthritis And Accelerate Wound Repair Chia-Lung Wu, MS, Deeptee Jain, MD, Jenna McNeill, BS, Dianne Little, BVSc, PhD, John Anderson, MD, Janet Huebner,
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS
 LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
LIPOPROTEIN-ASSOCIATED PHOSPHOLIPASE A 2 : EFFECTS OF LOW DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN APHERESIS Patrick M. Moriarty, M.D., FACP, Director, Atherosclerosis and LDL-Apheresis Center, University of Kansas Medical
Regulation of Metabolism by Nuclear Hormone Receptors
 Regulation of Metabolism by Nuclear Hormone Receptors Huey Jing Huang* and Ira G. Schulman { *Department of Biology, Exelixis Inc., 4757 Nexus Centre Drive, San Diego, California 92121 { Center for Molecular
Regulation of Metabolism by Nuclear Hormone Receptors Huey Jing Huang* and Ira G. Schulman { *Department of Biology, Exelixis Inc., 4757 Nexus Centre Drive, San Diego, California 92121 { Center for Molecular
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU. PhD THESIS Summary
 ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
and Restenosis Yangsoo Jang, MD, PhD. Yonsei University College of Medicine
 PPAR- Agonist and In-Stent Restenosis Yangsoo Jang, MD, PhD. Yonsei University College of Medicine Peroxisome Proliferator- activated Receptors (PPAR) Lipid-activated transcription factors : => regulating
PPAR- Agonist and In-Stent Restenosis Yangsoo Jang, MD, PhD. Yonsei University College of Medicine Peroxisome Proliferator- activated Receptors (PPAR) Lipid-activated transcription factors : => regulating
Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction
 혈관연구회창립심포지움, 3 월 3 일, 2005 Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon Medical School Incheon, Korea Atherosclerosis: A progressive process PHASE I: Initiation
혈관연구회창립심포지움, 3 월 3 일, 2005 Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon Medical School Incheon, Korea Atherosclerosis: A progressive process PHASE I: Initiation
T Cell Vaccination as a Tool in the Treatment of Collagen Induced Arthritis in Albino Rats
 T Cell Vaccination as a Tool in the Treatment of Collagen Induced Arthritis in Albino Rats Shahnaz Rafiei 1, Forouzan Karimi 1,2*, Fatemeh Roohollah 3, Ali Rafinejad 1 1 Department of Immunology, School
T Cell Vaccination as a Tool in the Treatment of Collagen Induced Arthritis in Albino Rats Shahnaz Rafiei 1, Forouzan Karimi 1,2*, Fatemeh Roohollah 3, Ali Rafinejad 1 1 Department of Immunology, School
Discussion & Conclusion
 Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Discussion & Conclusion 7. Discussion DPP-4 inhibitors augment the effects of incretin hormones by prolonging their half-life and represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 RHEUMATOID THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eman Sh.Al-Obeidy*, Shatha F. Abdullah** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
RHEUMATOID THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE ARTHRITIS MEDICAL JOURNAL The Role of IL-1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis Eman Sh.Al-Obeidy*, Shatha F. Abdullah** ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND:
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ
 Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
A comparison of statistical methods for adjusting the treatment effects in genetic association studies of quantitative traits
 34 1 Journal of the Korean Society of Health Information and Health Statistics Volume 34, Number 1, 2009, pp. 53 62 53 한경화 1), 임길섭 2), 박성하 3), 장양수 4), 송기준 2) 1), 2), 3), 4) A comparison of statistical
34 1 Journal of the Korean Society of Health Information and Health Statistics Volume 34, Number 1, 2009, pp. 53 62 53 한경화 1), 임길섭 2), 박성하 3), 장양수 4), 송기준 2) 1), 2), 3), 4) A comparison of statistical
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity
 Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for.
 Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
Biologic agents in Internal Medicine-2018: Targeted therapies for. Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the skin Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting the gut Chronic inflammatory diseases affecting
Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases
 54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
Diosgenin, antagonism of LXRs 36 DNA microarray, sesame seed lignan regulation of liver fatty acid metabolism gene expression 12 18, 22, 23
 Subject Index ACC, see Acyl-CoA carboxylase 1 -Acetoxychavicol acetate, inducible nitric oxide synthase suppression in cancer chemoprevention 199, 200 Acetylene carotenoids, anti-inflammatory activity
Subject Index ACC, see Acyl-CoA carboxylase 1 -Acetoxychavicol acetate, inducible nitric oxide synthase suppression in cancer chemoprevention 199, 200 Acetylene carotenoids, anti-inflammatory activity
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Arthritis in mice induced by a single immunisation
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1996; 55: 535-539 535 Medicinal Research Laboratory, Central Research Institute, Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Japan F Kato M Nomura K Nakamura Correspondence to: Dr Fuminori
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1996; 55: 535-539 535 Medicinal Research Laboratory, Central Research Institute, Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha, Japan F Kato M Nomura K Nakamura Correspondence to: Dr Fuminori
E. Larsson, H. Erlandsson Harris, J. C. Lorentzen, A. Larsson 1, B. Månsson 2, L. Klareskog and T. Saxne 2
 Rheumatology 2002;41:996 1000 Serum concentrations of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, fibrinogen and hyaluronan distinguish inflammation and cartilage destruction in experimental arthritis in rats
Rheumatology 2002;41:996 1000 Serum concentrations of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, fibrinogen and hyaluronan distinguish inflammation and cartilage destruction in experimental arthritis in rats
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University
 Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Topical nanocrystalline silver cream inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in animal models of allergic contact dermatitis.
 Topical nanocrystalline silver cream inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in animal models of allergic contact dermatitis. K C Bhol, P J Schechter NUCRYST Pharmaceuticals Inc, Wakefield, MA
Topical nanocrystalline silver cream inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in animal models of allergic contact dermatitis. K C Bhol, P J Schechter NUCRYST Pharmaceuticals Inc, Wakefield, MA
Disease-Modifying Activity in a Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis with an Orally Available Inhibitor of Methionine Aminopeptidase Type-2,
 Disease-Modifying Activity in a Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis with an rally Available Inhibitor of Methionine Aminopeptidase Type-2, PPI-2458 William Westlin, Ph.D. Praecis Pharmaceuticals Waltham, Massachusetts
Disease-Modifying Activity in a Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis with an rally Available Inhibitor of Methionine Aminopeptidase Type-2, PPI-2458 William Westlin, Ph.D. Praecis Pharmaceuticals Waltham, Massachusetts
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Annals of Biological Research, 2010, 1 (1) : 36-40 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) Effect of Chlorophytum
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Annals of Biological Research, 2010, 1 (1) : 36-40 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) Effect of Chlorophytum
CD4-positive lymphocytes play a critical role in early
 LXR Activation Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human CD4-Positive Lymphocytes Daniel Walcher, Andreas Kümmel, Bettina Kehrle, Helga Bach, Miriam Grüb, Renate Durst, Vinzenz Hombach, Nikolaus
LXR Activation Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human CD4-Positive Lymphocytes Daniel Walcher, Andreas Kümmel, Bettina Kehrle, Helga Bach, Miriam Grüb, Renate Durst, Vinzenz Hombach, Nikolaus
Product Datasheet. Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB Unit Size: 0.05 mg. Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23
 Product Datasheet Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB600-1387 Unit Size: 0.05 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at:
Product Datasheet Ly-6G6C Antibody (NIMP-R14) NB600-1387 Unit Size: 0.05 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 23 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at:
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
The Skinny of the Immune System
 The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis
 193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
Down-Regulation of Th1-Mediated Pathology in Experimental Arthritis by Stimulation of the Th2 Arm of the Immune Response
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 3, March 2003, pp 839 845 DOI 10.1002/art.10832 2003, American College of Rheumatology Down-Regulation of Th1-Mediated Pathology in Experimental Arthritis by Stimulation
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 48, No. 3, March 2003, pp 839 845 DOI 10.1002/art.10832 2003, American College of Rheumatology Down-Regulation of Th1-Mediated Pathology in Experimental Arthritis by Stimulation
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Inflammation in OA. Osteoarthritis. Crystals found in synovial fluid. Calcium-containing crystals in OA 10/28/2013. I have no disclosures
 Dublin Academic Medical Centre Dublin Academic Medical Centre How Do Calcium Crystals Induce Inflammation and Contribute to Osteoarthritis I have no disclosures Geraldine McCarthy MD, FRCPI Clinical Professor
Dublin Academic Medical Centre Dublin Academic Medical Centre How Do Calcium Crystals Induce Inflammation and Contribute to Osteoarthritis I have no disclosures Geraldine McCarthy MD, FRCPI Clinical Professor
Patients with knee OA and with joint pain, stiffness and/or functional impairment interfering
 Supplementary Material to Alunno et al. Platelets Contribute to the Accumulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase Type 2 in Synovial Fluid in Osteoarthritis (https://doi.org/10.1160/th17-06-0379) Supplemental
Supplementary Material to Alunno et al. Platelets Contribute to the Accumulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase Type 2 in Synovial Fluid in Osteoarthritis (https://doi.org/10.1160/th17-06-0379) Supplemental
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
The Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in RA FULL VERSION
 The Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in RA FULL VERSION 1 Key Learning Objectives Understand the role of osteoclasts in normal bone remodeling Comprehend the key processes in pathologic osteoclast functions
The Pathogenesis of Bone Erosions in RA FULL VERSION 1 Key Learning Objectives Understand the role of osteoclasts in normal bone remodeling Comprehend the key processes in pathologic osteoclast functions
Lyme Arthritis: Current Concepts and a Change in Paradigm ACCEPTED. Madison, Wisconsin, and Microbiology Research Laboratory and Section of Infectious
 CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 November 2007 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00330-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 14 November 2007 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00330-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Role of HIF-1α in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mini Review
 Role of HIF-1α in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mini Review Abdulkadir Yusif Maigoro 1 *, Haris Jaafar Bello 1,2, Sadeeq Muhammad Shehe 1, Abdullahi Muhammad Labbo 1,3, Anas Muazu 1 1 Department of Bioscience,
Role of HIF-1α in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mini Review Abdulkadir Yusif Maigoro 1 *, Haris Jaafar Bello 1,2, Sadeeq Muhammad Shehe 1, Abdullahi Muhammad Labbo 1,3, Anas Muazu 1 1 Department of Bioscience,
Immunology for the Rheumatologist
 Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
2011 International Conference of Inflammation, Cancer and Metabolic Disorders Program
 Friday, November 4 th, 2011 09:00-09:30 Registration 09:30-09:40 Welcome & Opening Remarks Kenneth K. Wu, M.D., Ph.D. Fu-Tong Liu, M.D., Ph.D. Plenary Lecture I Chair: Kenneth K. Wu, M.D., Ph.D. 09:40-10:40
Friday, November 4 th, 2011 09:00-09:30 Registration 09:30-09:40 Welcome & Opening Remarks Kenneth K. Wu, M.D., Ph.D. Fu-Tong Liu, M.D., Ph.D. Plenary Lecture I Chair: Kenneth K. Wu, M.D., Ph.D. 09:40-10:40
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI
 SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
