Tuberculosis of the hip joint region in children
|
|
|
- Erik Randall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
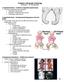
1 Page 38 SA Orthopaedic Journal Autumn 2013 Vol 12 No 1 Tuberculosis of the hip joint region in children MAF Mohideen MBChB(Medunsa) Registrar MN Rasool MBChB(UKZN), FC(Ortho)SA Paediatric Orthopaedics Nelson Mandela School of Medicine, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa Reprints requests: mncwabeh@ukzn.ac.za Abstract Aim: To describe the clinical and radiological manifestations of tuberculosis of the hip joint and the resemblance to common osteoarticular lesions in children. Methods: Thirty-six children (1 to 12 years) were reviewed retrospectively between 1990 and Clinical, laboratory and radiological features were assessed. The hips were classified and the outcome was graded as described by Shanmugasundaram. Results: Common clinical features were a limp, flexion, adduction and internal rotation contractures. Common radiological features were osteopaenia and cystic lesions in the neck and acetabulum. Permeative lesions, focal erosions, pathological fractures and sequestra were less common. Seven children had extra-articular lesions. Of the 29 with osteoarticular involvement, six had purely synovial involvement. Osteoarticular lesions mimicked benign bone and joint conditions. Follow-up was 1 to 6 years, 36% were graded as good, 36% fair and 28% had poor outcome with ankylosis. Other complications included avascular necrosis, coxa vara, coxa magna, growth arrest and flexion-adduction contractures. Conclusion: Tuberculosis of the hip can mimic various benign conditions. Biopsy from a bony lesion is important. The initial radiological appearance predicts the outcome, especially in the normal type of hip. Key words: tuberculosis, hip joint, children Introduction Tuberculosis remains a major cause of skeletal infection in developing countries. In 2008 the WHO report ranked South Africa fourth in terms of absolute number of cases. 1 There were 9.2 million new cases and 0.7 million HIV-positive cases. In 2010, although there were an estimated 8.8 million new cases of TB, South Africa had the third highest incidence compared to the other 21 high burden countries. 2 In the developed world an increase in the number of cases has been reported. This may be attributed to AIDS (acquired immune-deficiency syndrome), immigration and intravenous drug abuse. 3 The increase may be due to immuno-modulation and possibly atypical mycobacteria in some cases. 4 Skeletal tuberculosis accounts for 10 35% of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis and about 2% of all cases of tuberculosis. 5 Most of the literature on tuberculosis of the hip in children is over 40 years old The lesions were mainly destructive. Treatment was by prolonged traction and spica cast. Many surgeons used radical surgery and arthrodesis to control the disease The majority of reports are mixed with adults. 5,12,13 Only two cases involving the hip joint have been reported recently in a series from the United Kingdom. 14 Holland reported one case in The frequency of tuberculosis of the hip joint is next only to that of the spine and constitutes 15% of all cases of osteoarticular tuberculosis. Osteoarticular manifestations may be intra-articular or extra-articular. 5 The variable clinical and radiological presentations may mimic common osseous and articular conditions seen in children and delay the diagnosis of tuberculosis. 16 Tuberculosis of the hip joint has been rarely reported in the recent literature. 17,18
2 SA Orthopaedic Journal Autumn 2013 Vol 12 No 1 Page 39 The aims of this study are to report the clinical and radiological patterns of tuberculosis of the hip joint region in children; highlight the resemblance to various osteoarticular lesions; and correlate the radiological appearance with the outcome of treatment. Materials and methods Thirty-six children were retrospectively reviewed between 1990 and 2011 at a local hospital. The ages ranged between 1 and 12 (average 6) years. There were 21 boys and 15 girls. All the osteoarticular lesions were histologically confirmed for tuberculosis. Clinical and radiological data were collected from case records. Haematological tests done for all patients included a full blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and liver function tests. Radiological tests done included routine hip X-ray, chest X-ray and a bone scan. The Mantoux test was done routinely. Five children had computerised tomography scans to define the bone lesions within the hip. Shanmugasundaram s classification of tuberculosis of the hip joint was used to classify the different radiological patterns of tuberculosis of the hip into seven types 13 (Figure 1). All patients had an open biopsy. Debridement, limited synovectomy and curettage of the osseous cavities and defects were performed when bone lesions were present. Antituberculosis treatment was used for a year. This consisted of isoniazide, rifampicin, pyrazinamide and pyridoxine. Post-operatively the hips were immobilised in a spica cast and physiotherapy was commenced after 3 to 4 weeks. Hospital stay ranged between 3 and 8 weeks. Results Pain around the hip region and a limp were the main clinical features in all children. Fixed flexion contracture of the hip ranging between 10 and 70 was seen in 28 of the patients. Adduction contracture between 10 and 30 was seen in 27 patients. Three children had discharging sinuses and five had a fluctuant abscess. One child presented with a pathological fracture of the proximal femur. The albumen was low in eight patients. The chest X-ray showed evidence of pulmonary tuberculosis in 20% of the cases and the bone scan revealed multiple site involvement in two patients with involvement of the elbow and spine respectively. The patients had an ESR ranging between mm/hr (average 65 mm/hr). Four patients were known to be infected with HIV and were on antiretrovirals for which they were being followed up by the paediatricians. The Mantoux test was negative in six children. All patients had histological features consistent with tuberculosis (granulation, caseous necrosis and giant cells). Localised osteopaenia was a common radiological finding. Twenty-six patients had cystic lesions which were either round or oval in shape in the head, neck or acetabulum. Other lesions seen included the infiltrative (permeative), fusiform, punched-out (erosions) and pathologic fractures. In five patients the growth plate was traversed and four had a sequestrum (Table I). Seven children had extra-capsular tuberculosis and 29 were intra-articular (within the joint capsule) in type. Extra-articular osseous involvement was seen in the proximal femur, Figure 1. Classification of tuberculous infection of the hip by Shanmugasundaram Table I: Radiological characteristics of tuberculous infection of the hip joint region Radiological characteristics Osteopaenia Number ALL Cystic lesions round/oval 26 Infiltrative permeative 4 Fusiform spina ventosa 1 Punched-out erosion 2 Pathological fracture 1 Sequestrum 4 Growth-plate involvement 5 Table II: Classification of tuberculous infection of the hip joint region according to anatomical sites Extra-articular 7 Osteo-articular 29 Greater trochanter 1 Synovial 6 Proximal femur 2 Acetabular 4 Lesser trochanter 1 Epiphyseal 2 Ischium 1 Metaphyseal 11 Body of pubis 1 Epi-metaphyseal 6 Ilium 1 greater and lesser trochanter, ilium, ischium and body of the pubis (Table II). Intra-articular infection involved the synovium, acetabulum, epiphysis, metaphysis or the epi-metaphyseal area (Table II). Using the Shanmugasundaram classification there were eight normal hips (Figures 2, 3, 4 and 5), seven dislocating (Figure 6), two travelling acetabulum (Figure 7), two Perthes, five protrusio acetabuli, two atrophic and three mortar-and-pestle types (Figure 8) (Table III). Six hips required extension-abduction-derotation osteotomies for residual flexion adduction deformities. After completion of antituberculous treatment, outcome was graded as good in 36% of the cases, fair in 36% and poor in 28%. All sinuses healed. The pathological fracture healed with immobilisation by six weeks in a spica cast.
3 Page 40 SA Orthopaedic Journal Autumn 2013 Vol 12 No 1 Figure 2. Radiograph of the right hip showing cystic lesion in the femoral neck of a normal type of hip, which resembles subacute pyogenic osteomyelitis Figure 4a. Radiograph of the left hip showing a cystic lesion in the femoral neck extending into the head; normal type resembling chondroblastoma Figure 3. Radiograph of the right hip ( normal type) shows sequestrum in a nidus resembling osteoid osteoma Figure 4b. Radiograph showing healing of cystic lesion at 9 months The infection can progress through various stages with initial synovitis, effusion and rarefaction, to advanced arthritis with complete destruction. Various radiological appearances are seen, i.e. subluxation, dislocation, erosion, cystic lesions, protrusion and ankylosis. 5 Phemister, in a detailed pathological study, found that primary bone involvement in children was usually metaphyseal due to embolism and infarction in metaphyseal end arteries. 19 Cavities, cystic lesions, erosions and sequestra may occur. The osseous lesions in this study were mainly metaphyseal appearing as cystic, permeative and focal erosions in the cancellous portions of the femoral head, neck and acetabulum. Shanmugasundaram proposed a radiological classification for tuberculosis of the hip joint. 13 He concluded that the radiological appearance of the hip at presentation almost always predicts the final clinical outcome. He described seven morphological types (Figure I) based on the destructive pattern for all ages. In the normal type, the disease mainly involved the synovium. There may be cysts or cavities in the femoral head, neck or acetabulum, with no gross destruction of the subchondral bone and the joint space remains normal. Eight normal hips with a good outcome were seen in this study. In the travelling acetabulum type, the lesion is in the roof. There is narrowing of the joint space, with progressive upward displacement of the femoral head. These are usually associated with a poor prognosis. Two cases were seen in this study with a fair outcome. In the dislocating type, the head dislocates posteriorly, or subluxes due to laxity of ligaments and capsular distension. The prognosis is poor. Seven cases were seen in this study, with poor results in three. Subluxed hips did well following reduction. In the Perthes type, the epiphysis is fragmented, dense and flattened. The femoral neck is widened. It resembles Perthes disease and is probably due to embolic episodes. The prognosis is poor. Fibrous ankylosis was seen in two cases in this study. In the protrusio-acetabuli type, the lesion is mainly in the floor of the acetabulum. With progression, medial displacement of the floor occurs with pressure of the femoral head. The os innominatum gets thinned out in the acetabulum. The prognosis was reported to be good in children. We saw five cases in which the prognosis was fair. Articular cartilage was denuded at surgical exploration. The atrophic hip is characterised by marked narrowing of the joint space. The infection can progress through various stages with initial synovitis, effusion and rarefaction, to advanced arthritis with complete destruction Discussion Tuberculosis of the hip joint in children has a less destructive presentation than was seen in the past. The lesions can present in a synovial or osseous form. The osseous lesions maybe intra-articular, within the joint capsule or extracapsular (extra-articular). 5 The clinical and radiological manifestations can imitate rheumatoid arthritis, transient synovitis, septic arthritis and retroviral disease in the synovial form and various benign or malignant bone lesions seen in children in the osseous type. 3,4,16 The intra-articular form may originate from the acetabular or femoral side, and progresses to involve the joint. Figure 5a. Radiograph of the right hip in the normal type showing a cystic lesion in the acetabulum with a sequestrum image en grelot Figure 5b. CT scan (axial cut) showing the cystic lesion within the acetabulum
4 SA Orthopaedic Journal Autumn 2013 Vol 12 No 1 Page 41 Figure 6. Radiograph showing subluxation of the right hip with a permeative lesion in the femoral neck Figure 7. Radiograph showing a travelling or wandering right hip Figure 8. Radiograph of the right hip showing the mortar-and-pestle type lesion The differentiation from rheumatoid arthritis and idiopathic chondrolysis is difficult. It has a poor prognosis. Two children with poor results were seen in this study; they developed fibrous ankylosis. In the mortar-and-pestle type, the head of the femur becomes ground down progressively, resembling a pestle within a mortar. Patients still retain a good range of movement. We saw three cases with a fair result. In this study, only 36% of patients had a good or excellent result. The majority had a fair or poor result. This is due to late presentation with established radiological changes. These hips were mainly of the poor prognostic types, with erosion of the head or acetabulum, dislocation or joint narrowing. The atrophic type had marked joint line narrowing resembling idiopathic chondrolysis. The clinical features were mainly flexion, adduction and internal rotation contractures with subsequent shortening. Abscesses were seen commonly in the series by Martini. 20 They were rare in this study, and occurred over the anterolateral thigh, posteriorly over the glutei, and medially in the adductor region. Sinuses and lymph nodes were also seen rarely. They were more commonly described in the study by Vohra et al. 16 The characteristic radiological manifestations of tuberculosis of the hip were osteopaenia and cystic bone lesions varying in size, resembling chondroblastoma, eosinophilic granuloma and subacute pyogenic osteomyelitis. Less commonly seen were infiltrative (permeative) lesions resembling chronic osteomyelitis. Pathological fractures and periosteal reaction were rarely seen. Versveld and Solomon emphasised that the cystic lesion in bone reflects the major granulomatous lesion, and biopsy material from this area is more representative of tuberculosis than the surrounding synovium which may exhibit a non-specific inflammatory response. 21 They found a 41% occurrence of hip involvement in children with osteoarticular tuberculosis, and the cystic lesion was predominant. Sequestra are also seen in osteoarticular tuberculosis. A cavity may contain a sequestrum of necrotic spongiosa. Four cases in this study resembled conditions such as osteochondroma and enchondroma. Martini describes these lesions as an image en grelot (little spherical bell) (Figure 5a). 20 Bone grafting of cystic lesions was perfomed by Kumar. 22 Hosalkar used osteoset pellets to fill bone defects. 14 We found that lesions up to 2.5 cm healed spontaneously. The treatment of osteoarticular tuberculosis includes anti-tuberculosis drugs. Many authors suggest that medical treatment alone is enough. Dosages followed the WHO guidelines. Isoniazide (4 6 mg/kg), rifampicin (8 12 mg/kg), pyrazinamide (20 30 mg/kg) and supplemental pyridoxine (5 10 mg/day) were used in this patient group. Other authors believe that surgical debridement and drainage is necessary. Wilkinson and Marmor popularised radical synovectomy, debridement, capsulotomy and curettage. 23,24 Fusion occurred in eleven per cent of hips, and a large number had coxa magna. 23 More recently, Babhulkar and Moon also performed a synovectomy. 5,18 Babhulkar emphasised preservation of the articular cartilage and avoidance of total synovectomy to preserve the blood supply to the head. Dislocation of the head was discouraged. Katayama et al combined joint debridement with interposition of fascia to facilitate hip movement. 25 The results were not encouraging. Vishwakarma interposed a multi-layered cap of amniotic membrane as a biological tissue, in children between the ages of ten and 16 with hip ankylosis. He obtained a stable joint with good function. 26 No inflammatory reaction was recorded. However, long-term follow-up is not available.
5 Page 42 SA Orthopaedic Journal Autumn 2013 Vol 12 No 1 Table III: Types of radiological presentations seen Classification (Shanmugasundaram types) Number of patients Normal 8 Travelling acetabulum 2 Dislocating/subluxing 7 Perthes 2 Protrusion acetabula 5 Atrophic 2 Mortar-and-pestle 3 We used an anterior approach combined with adductor tenotomy and flexor release when contractures were present. Limited synovectomy was performed. Cystic lesions, erosions and infiltrative lesions were routinely curetted and biopsied. Post-operatively the hips were immobilised in abduction of Physiotherapy was commenced after 3 4 weeks. Traction and mobilisation usually yield good results in early cases. However, it is not adequate in an unstable hip. We used a spica cast for unstable hips and applied an above-knee cast with a broomstick in abduction for four to six weeks in stable hips. Shanmugasundaram used skin traction for up to 22 months. 13 Others used skeletal traction. 18 Continuous passive motion (CPM) has also been used. 17 Although fibrous ankylosis was seen in five patients in this series, spontaneous bony fusion did not occur. The outcome of tuberculosis of the hip in children depends on the extent of the disease. Tuberculosis of the femoral head and neck may lead to various deformities. Chronic hyperaemia may lead to enlargement of the femoral head epiphysis and metaphysis (coxa magna). 27 Lesions of the head and neck can cause avascular necrosis after healing, resulting in reduction of the size of the head and neck (coxa brevia). Three cases were seen in this study. Interference with the growth plate can lead to coxa vara. This deformity may also occur with collapse of the femoral neck (Figures 9a and b). Tuberculosis of the hip in children has variable radiological manifestations. The osteoarticular lesions have a variable outcome. Pure osseous lesions with an intact joint outline have a good outcome. As in other studies, 5,17,18 we found that the radiological morphology at presentation generally predicts the final outcome as suggested by Shanmugasundaram. 13 However, the latter study needs to be carried out on a larger scale in relation to several clinical variables. It does not address clinical problems such as flexion, adduction and internal rotation and the role of adductor tenotomy and realignment abduction extension osteotomy. It also does not address lesions in the proximal femur that progress from extra-articular to intra-articular lesions and subsequent complications of coxa vara, avascular necrosis and coxa magna. His patients were immobilised for prolonged periods, some up to 2 years. He did not state whether his patients had biopsies, but stated that surgery provided little benefit. His report combines adults and children. Like Babulkhar, Versveld and Campbell, we advocate open biopsy to provide an accurate diagnosis with limited synovectomy. 5,17,21 Pyogenic osteomyelitis and septic arthritis are common in our environment and can resemble tuberculosis in the chronic phase. We found that prolonged immobilisation was not necessary like other studies. 17,18 Conclusion Tuberculosis of the hip region in children can manifest in various radiological forms. Lack of familiarity may lead to a delay in diagnosis and treatment. No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from any commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article. We used an anterior approach combined with adductor tenotomy and flexor release when contractures were present Post-operatively the hips were immobilised in abduction of Figure 9a. Radiograph showing a cystic permeative lesion within the right femoral neck Figure 9b. Radiograph at 10 months shows healing with coxa vara
6 SA Orthopaedic Journal Autumn 2013 Vol 12 No 1 Page 43 References 1. Dye C, Floyd K, Uplekar M. WHO report Global tuberculosis control: surveillance, planning, financing. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. 2. WHO report Global tuberculosis control: surveillance, planning, financing. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. 3. Yao DC, Sartoris DJ. Musculoskeletal tuberculosis. Radiol Clin N Am 1995;33: Wang MN, Chen WM, Lee KS, et al. Tuberculous osteomyelitis in young children. J Pedr Orthop 1999;19: Babhulkar S, Pande S. Tuberculosis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002;398: Smith LD. Tuberculosis of the hip in children. J Bone Joint Surg 1926;8: Hibbs RA. A preliminary report of twenty cases of hip joint tuberculosis treated by an operation devised to eliminate motion by fusing the joint. J Bone and Joint Surg 1926;8: Wilson JC. Extra-articular fusion of the tuberculous hip joint. California and Western Med 1927;27: McCarroll HR, Heath RD. Tuberculosis of the hip in children. J Bone Joint Surg 1947;29: Gruca A, Warsaw P. Treatment of quiescent tuberculosis of the hip joint by excision and dynamic osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg 1950;32B: Roberts WM, Webster FS. Early surgical treatment of tuberculosis of the hip in children. Surg Gyne Obstet 1951;92: Tuli SM, Mukherjee SK. Excision arthroplasty for tuberculous and pyogenic arthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg 1981;63B: Shanmugasundaram TK (ed). A clinicoradiological classification of tuberculosis of the hip. In: Shanmugasundaram TK. Current concepts in bone and joint tuberculosis. Madras, India: Proceedings of Combined Congress of International Bone and Joint Tuberculosis Club and the Indian Orthop Assoc, 1983, p Hosalkar HS, Agarwal N, Reddy S, et al. Skeletal tuberculosis in children in the western world: 18 new cases with a review of the literature. J Child Orthop 2009;3: Holland TS, Sangster MJ, RW Paton, LP Ormerod. Bone and joint tuberculosis in children in the Blackburn area since 2006: a case series. J Child Orthop 2010;4: Vohra R, Kang HS, Dogra S. Tuberculous osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg 1997;79B: Campbell JA, Hoffman EB. Tuberculosis of the hip in children. J Bone Joint Surg 1995;77: Moon MS, Kim SS, Lee SR, Moon YW, Moon JL, Moon SI. Tuberculosis of the hip in children: A retrospective analysis. Ind J Orthop 2012;46: Phemister DB. Changes in the articular surfaces in tuberculosis arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg 1925;7: Martini M (ed). Tuberculosis of the bones and joints 1988; Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg. 21. Versveld GA, Solomon A. A diagnostic approach to tuberculosis of bones and joints. J Bone Joint Surg 1982;64B: Kumar K, Saxena MB. Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis. Int Orthop 1988;12: Wilkinson MC. Tuberculosis of the hip and knee treated by chemotherapy, synovectomy and debridement: A follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg 1969;51A: Marmor L, Chan KP, Ho KC. Surgical treatment of tuberculosis of the hip in children. Clin Orthop 1969;67: Katayama R, Itami Y. Treatment of hip and knee joint tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg 1962;44A: Vishwakarma GK, Khare AK. Amniotic arthroplasty for tuberculosis of the hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg 1986;68B: Teo EL, Peh WC. Skeletal tuberculosis in children. Paed Radiol 2004;34: SAOJ CRITERIA FOR AUTHORSHIP AND CO-AUTHORSHIP OF ARTICLES The following are internationally acknowledged criteria for authors/co-authors. With the increase in faculty and in research projects, there is a potential for increased confusion and conflict regarding appropriate authorship credit on manuscripts and presentations. The following are some relatively standardised criteria that can be helpful. These may be overstrict when considering clinical studies in which surgeons often do the hands on work that create the study but may not perform major analysis and writing functions. However, all authors should read and contribute editing comments prior to submission. Relman criteria for authorship In particular, to qualify as an author a person should fulfil at least three of the following five requirements: 1. Conception of idea and design of experiment 2. Actual execution of experiment; hands on lab work 3. Analysis and interpretation of data 4. Actual writing of manuscript 5. Be able to present to a learned gathering a lecture on the work; interpret it, defend it and take responsibility for it. These are just guidelines. On the other hand it is probably far worse to leave someone off the list who feels they may have contributed than to include someone who did a bit less. We should all be as inclusive as possible, offer our interested colleagues the opportunity to provide input, analysis and editing of our works to support each other and improve our papers.
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Manage TB Dr. Dina Nair National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai. Lecture 07 Clinical manifestations of TB Session 02
 Manage TB Dr. Dina Nair National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai Lecture 07 Clinical manifestations of TB Session 02 Hello, welcome to the second session on Clinical manifestations of tuberculosis.
Manage TB Dr. Dina Nair National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai Lecture 07 Clinical manifestations of TB Session 02 Hello, welcome to the second session on Clinical manifestations of tuberculosis.
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
The surgical treatment of Perthes disease by
 Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
Modes of Presentation, Diagnostic Pitfalls and Treatment of Non- Spinal Extra-Articular Osseous Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Modes of Presentation, Diagnostic Pitfalls and Treatment of Non- Spinal Extra-Articular Osseous Tuberculosis M.SAEED AKHTAR, KHALID MAHMOOD AWAN, MUHAMMAD AKRAM, ASIF HANIF, ARIF RASHEED
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Modes of Presentation, Diagnostic Pitfalls and Treatment of Non- Spinal Extra-Articular Osseous Tuberculosis M.SAEED AKHTAR, KHALID MAHMOOD AWAN, MUHAMMAD AKRAM, ASIF HANIF, ARIF RASHEED
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A CASE REPORT Babu B. Hundekar 1
 TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion
 Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Bilateral hip pain with right proximal femoral lesion Legg-Calve-Perthes Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head epiphysis during childhood First described by Arthur Thorton Legg in 1909 and published
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
 A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Transient Synovitis of the Hip in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis
 The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
The Limping Child: Differential Diagnosis Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department of Pediatrics
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
 PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August 2015; 2(8) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.672
 CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis in children
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(3):336-40 Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis in children Anil Agarwal, Shariq Azam Khan, Nadeem Akhtar Qureshi Department of Orthopaedics, CNBC, Geeta Colony,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(3):336-40 Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis in children Anil Agarwal, Shariq Azam Khan, Nadeem Akhtar Qureshi Department of Orthopaedics, CNBC, Geeta Colony,
TB or not TB? That should be the question
 TB or not TB? That should be the question SH Liyanage, CM Gupte ( ), A Cobb, MC Beverly Department of Orthopaedics Ealing University Hospital Uxbridge Rd, Southall, Middlesex UB13HW United Kingdom Correspondence:
TB or not TB? That should be the question SH Liyanage, CM Gupte ( ), A Cobb, MC Beverly Department of Orthopaedics Ealing University Hospital Uxbridge Rd, Southall, Middlesex UB13HW United Kingdom Correspondence:
Osteo-articular TB in Children
 Osteo-articular TB in Children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa Questions Spinal TB is the most common
Osteo-articular TB in Children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa Questions Spinal TB is the most common
Treatment of DDH before Walking Age 고려대학안암병원
 Treatment of DDH before Walking Age 이 순혁 고려대학안암병원 Subluxated Hip Always to deg. hip The more, the earlier Even in 2nd Decade Dysplastic Hip Eventually to osteoarthritis but later Etiology of end-stage
Treatment of DDH before Walking Age 이 순혁 고려대학안암병원 Subluxated Hip Always to deg. hip The more, the earlier Even in 2nd Decade Dysplastic Hip Eventually to osteoarthritis but later Etiology of end-stage
TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY
 CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular rim during normal hip range of motion.
 RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
RIM SYNDROME [femoroacetabular impingement] It has been suggested to be a preosteoarthritic mechanism. The condition occurs when the proximal femur repeatedly comes into contact with the native acetabular
Peggers Super Summaries: Paediatric Hip
 EMBRYOLOGY Development o Mesenchymal stem cells cartilage blood supply bone Dates o 6/40 Limb development o 8-11/40 hip development (acetabulum and hip formed from one bone splitting by apoptosis) o 16/40
EMBRYOLOGY Development o Mesenchymal stem cells cartilage blood supply bone Dates o 6/40 Limb development o 8-11/40 hip development (acetabulum and hip formed from one bone splitting by apoptosis) o 16/40
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
 Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) DR MUMTAZ HUSSAIN Senior Registrar DR ABDUL LATIF SAMI (Associate Professor) Head of Department Pediatric Orthopedics Introduction and Definition Epidemiology and
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) DR MUMTAZ HUSSAIN Senior Registrar DR ABDUL LATIF SAMI (Associate Professor) Head of Department Pediatric Orthopedics Introduction and Definition Epidemiology and
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Childhood hip conditions. Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant
 Childhood hip conditions Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Legg-Calve-Perthes disease Slipped Capital femoral epiphysis Limp Arthritis Developmental Dysplasia
Childhood hip conditions Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Legg-Calve-Perthes disease Slipped Capital femoral epiphysis Limp Arthritis Developmental Dysplasia
STUDY OF NON-SPINAL, EXTRA-ARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS, ITS MODES OF PRESENTATION, DIAGNOSTIC PITFALLS AND TREATMENT
 E:/Biomedica Vol. Jul. Dec. 2005/Bio10 (A) STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS, ITS MODES OF PRESENTATION, DIAGNOSTIC PITFALLS AND TREATMENT MURTZA CHEEMA Department of Orthopaedic
E:/Biomedica Vol. Jul. Dec. 2005/Bio10 (A) STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS, ITS MODES OF PRESENTATION, DIAGNOSTIC PITFALLS AND TREATMENT MURTZA CHEEMA Department of Orthopaedic
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies
 Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Bilateral Idiopathic Chondrolysis of the Hip in an Adult: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 CSE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.243 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 ilateral Idiopathic Chondrolysis of the Hip in an dult: Case Report and Review of the Literature Kyoung-Ho
CSE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.4.243 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 ilateral Idiopathic Chondrolysis of the Hip in an dult: Case Report and Review of the Literature Kyoung-Ho
Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:452-457 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.452 Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis Sung Soo Kim, MD, Chan Woo
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:452-457 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.452 Treatment of Late-Onset Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease by Arthrodiastasis Sung Soo Kim, MD, Chan Woo
A Case Report of an Unusual Case of Tuberculous Osteomyelitis Causing Spontaneous Pathological Fracture of Humerus in a Middle Aged Female
 Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2017 Jan Feb: 7(1):41 45 A Case Report of an Unusual Case of Tuberculous Osteomyelitis Causing Spontaneous Pathological Fracture of Humerus in a Middle Aged
Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2017 Jan Feb: 7(1):41 45 A Case Report of an Unusual Case of Tuberculous Osteomyelitis Causing Spontaneous Pathological Fracture of Humerus in a Middle Aged
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Shoulder joint tuberculosis
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2012; 77(4): 55-59 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.07.06 Accepted: 2012.09.04 Shoulder joint tuberculosis Monika Ostrowska 1, Jan Gietka 2, Tomasz Nesteruk 1, Agnieszka Piliszek 1,
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2012; 77(4): 55-59 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.07.06 Accepted: 2012.09.04 Shoulder joint tuberculosis Monika Ostrowska 1, Jan Gietka 2, Tomasz Nesteruk 1, Agnieszka Piliszek 1,
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Idiopathic chondrolysis of the hip: review of the literature
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 268-272 Case report Idiopathic chondrolysis of the hip: review of the literature ANGUS W HUGHES From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham a case report
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1985, 44, 268-272 Case report Idiopathic chondrolysis of the hip: review of the literature ANGUS W HUGHES From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham a case report
Bone and Joint Surgery
 The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume VOLUME 59-A, No. 4 JUNE 1977 Fracture of the Neck and Intertrochanteric Region of the Femur in Children* BY S. TERRY CANALE, M.D.t, AND WILLIAM L.
The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume VOLUME 59-A, No. 4 JUNE 1977 Fracture of the Neck and Intertrochanteric Region of the Femur in Children* BY S. TERRY CANALE, M.D.t, AND WILLIAM L.
Acquired Hip Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Sarah D. Bixby Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Boston, MA
 Acquired Hip Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sarah D. Bixby Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Boston, MA Don t Miss Acquired Hip Disorders SCFE Posterior Hip Dislocation Osteoid
Acquired Hip Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sarah D. Bixby Department of Radiology Boston Children s Hospital Boston, MA Don t Miss Acquired Hip Disorders SCFE Posterior Hip Dislocation Osteoid
Keywords: Tubercular osteomyelitis, Extrapulmonary, Sequestrectomy
 Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. PRIMARY TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS
Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. PRIMARY TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji
 Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
INFANTILE COXA VARA. Case 1 SUMMARY INTRODUCTION CASE HISTORY
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 41 No. 3'September 1986 INFANTILE COXA VARA K. S. OH ILLON SUMMARY Infantile or developmental coxa vara is a relatively infrequent localised dysplasia of unknown etiology which usually
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 41 No. 3'September 1986 INFANTILE COXA VARA K. S. OH ILLON SUMMARY Infantile or developmental coxa vara is a relatively infrequent localised dysplasia of unknown etiology which usually
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
Spina Ventosa in a Young Adult: Report of Two Cases
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(3):444-448 Spina Ventosa in a Young Adult: Report of Two Cases Vishnu Senthil, Anil K Bhat, Ashwath Acharya Department of Orthopaedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal-576104,
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(3):444-448 Spina Ventosa in a Young Adult: Report of Two Cases Vishnu Senthil, Anil K Bhat, Ashwath Acharya Department of Orthopaedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal-576104,
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session. DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips
 Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips Michael A. DiPietro, M.D. John F. Holt Collegiate Professor of Radiology Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable
Society for Pediatric Radiology 2015 Hands on Session DDH: Pitfalls and Practical Tips Michael A. DiPietro, M.D. John F. Holt Collegiate Professor of Radiology Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable
11/4/2018 SUBTLETIES OF LOWER EXTREMITY TRAUMA IMAGING SPEAKER DISCLOSURES
 SUBTLETIES OF LOWER EXTREMITY TRAUMA IMAGING Charles S. Resnik, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Upon completion of this presentation, participants will be better able
SUBTLETIES OF LOWER EXTREMITY TRAUMA IMAGING Charles S. Resnik, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Upon completion of this presentation, participants will be better able
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
L side 65% Torticollis, Plagiocephaly, Metatarsus varus Flat foot.
 DEVELOPMENTAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP [DDH] Older terminology was Congenital dislocation of the hip. DDH means developmental dysplasia of the hip. DDH is better than CDH as dislocation is not always congenital.
DEVELOPMENTAL DISLOCATION OF THE HIP [DDH] Older terminology was Congenital dislocation of the hip. DDH means developmental dysplasia of the hip. DDH is better than CDH as dislocation is not always congenital.
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
Other Hip Disorders: Congenital (Developmental) & Idiopathic 이대목동병원 윤여헌
 Other Hip Disorders: Congenital (Developmental) & Idiopathic 이대목동병원 윤여헌 Children s hip disorders Congenital & developmental disorders Developmental hip dysplasia (dislocation) of the hip Developmental
Other Hip Disorders: Congenital (Developmental) & Idiopathic 이대목동병원 윤여헌 Children s hip disorders Congenital & developmental disorders Developmental hip dysplasia (dislocation) of the hip Developmental
Haemophilia. Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View. Epidemiology of Haemophilic joint disease
 Haemophilia Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View Dr. Alexander Chan Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Prince of Wales Hospital Deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and
Haemophilia Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View Dr. Alexander Chan Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Prince of Wales Hospital Deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
The McHale procedure in the treatment of the painful chronically dislocated hip in adolescents and adults with cerebral palsy
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 181-188 ORIGINAL STUDY The McHale procedure in the treatment of the painful chronically dislocated hip in adolescents and adults with cerebral palsy Anne VAN RIET, Pierre
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 181-188 ORIGINAL STUDY The McHale procedure in the treatment of the painful chronically dislocated hip in adolescents and adults with cerebral palsy Anne VAN RIET, Pierre
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
BNG-345 Orthopaedic Biomechanics. October 30, Name: Solution. This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are 5 sections/questions.
 BNG-345 Orthopaedic Biomechanics Exam 2 October 30, 2015 This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are 5 sections/questions. Grade: #1 / 16 #2 / 24 #3 / 32 #4 / 10 #5 / 18 Final Grade / 100 Page 1
BNG-345 Orthopaedic Biomechanics Exam 2 October 30, 2015 This exam is closed book, closed notes. There are 5 sections/questions. Grade: #1 / 16 #2 / 24 #3 / 32 #4 / 10 #5 / 18 Final Grade / 100 Page 1
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Tuberculosis otitis media
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2013; 9 (5): 329-333 Tuberculosis otitis media Poon Seong LIM, Bee See GOH, Lokman SAIM Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2013; 9 (5): 329-333 Tuberculosis otitis media Poon Seong LIM, Bee See GOH, Lokman SAIM Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti
Sacroiliac joint infection
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2015; 11 (2): 110-114 Sacroiliac joint infection Jon CHUA 1, Kamal JAMIL 1, Kamalnizat IBRAHIM 1, Suraya AZIZ 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Faculty of Medicine,
Ultrasound Scanning of Neonatal Hips
 Ultrasound Scanning of Neonatal Hips Dr. Dickson S F Tsang Associate Consultant Queen Mary Hospital Why? How? What? Outline IAAHS 2nd April, 2011 Outline Why? Why performing hip ultrasound (USG)? Why USG?
Ultrasound Scanning of Neonatal Hips Dr. Dickson S F Tsang Associate Consultant Queen Mary Hospital Why? How? What? Outline IAAHS 2nd April, 2011 Outline Why? Why performing hip ultrasound (USG)? Why USG?
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
1/15/2012. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI. Femoroacetabular impingement. Femoroacetabular impingement
 Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
Femoroacetabular Impingement FAI Previously known as Acetabular rim syndrome Cervicoacetabular impingement Dr. Tudor H Hughes, M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of open reduction of slipped capital femoral epiphysis The capital femoral epiphysis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of open reduction of slipped capital femoral epiphysis The capital femoral epiphysis
A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:319 324 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0600-5 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE A novel method for assessing postoperative femoral head reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip Anthony Cooper
Metha Short Hip Stem System
 Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Simultaneous joint fusion and limb lengthening for knee deformities in children: a one-stage procedure The Kampala experience
 CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2009 / Page 47 C LINICAL A RTICLE Simultaneous joint fusion and limb lengthening for knee deformities in children: a one-stage procedure The Kampala experience
CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2009 / Page 47 C LINICAL A RTICLE Simultaneous joint fusion and limb lengthening for knee deformities in children: a one-stage procedure The Kampala experience
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 Page 78 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Summer 2010 C ASE R EPORT AND R EVIEW OF THE L ITERATURE Traumatic hip dislocation in children: The role of MRI F Sprong MBChB(Pret) Registrar (Ortho) C Snyckers MBChB(Pret),
Page 78 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Summer 2010 C ASE R EPORT AND R EVIEW OF THE L ITERATURE Traumatic hip dislocation in children: The role of MRI F Sprong MBChB(Pret) Registrar (Ortho) C Snyckers MBChB(Pret),
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Outcome of surgical management of late presenting developmental dysplasia of hip with pelvic and femoral osteotomies
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2395-1362.2018.0012 Outcome of surgical management of late presenting developmental dysplasia of hip with pelvic and femoral osteotomies G. Jagadesh 1, Venugopal
Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2395-1362.2018.0012 Outcome of surgical management of late presenting developmental dysplasia of hip with pelvic and femoral osteotomies G. Jagadesh 1, Venugopal
Haemophilia and Orthopaedic Surgery. Brett Halliday Orthopaedic Surgeon Holy Spirit Northside and Royal Brisbane Hospitals
 Haemophilia and Orthopaedic Surgery Brett Halliday Orthopaedic Surgeon Holy Spirit Northside and Royal Brisbane Hospitals Disclaimer Director of Education OTC South Pacific No funds or company support
Haemophilia and Orthopaedic Surgery Brett Halliday Orthopaedic Surgeon Holy Spirit Northside and Royal Brisbane Hospitals Disclaimer Director of Education OTC South Pacific No funds or company support
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
SC FE. Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR
 SC FE Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR Disclosures Lecture specific-nothing to disclose. Dr. Taragin is a member of the medical advisory board of Carestream Health. SAM Goal SCFE = SCIFI PRESENTATION
SC FE Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis SPR Disclosures Lecture specific-nothing to disclose. Dr. Taragin is a member of the medical advisory board of Carestream Health. SAM Goal SCFE = SCIFI PRESENTATION
Subluxation of the hip presenting for the first time
 The treatment of subluxation of the hip in children over the age of four years John A. Fixsen, Patrick L. S. Li From the Hospitals for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London, England Subluxation of
The treatment of subluxation of the hip in children over the age of four years John A. Fixsen, Patrick L. S. Li From the Hospitals for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London, England Subluxation of
Treatment of congenital subluxation and dislocation of the hip by knee splint harness
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1994,18, 34-39 Treatment of congenital subluxation and dislocation of the hip by knee splint harness M. FUKUSHIMA Fukushima Orthopaedic Clinic, Hiroshima City,
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1994,18, 34-39 Treatment of congenital subluxation and dislocation of the hip by knee splint harness M. FUKUSHIMA Fukushima Orthopaedic Clinic, Hiroshima City,
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip
 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Abnormal relationship of femoral head to the acetabulum Formerly known as congenital hip dislocation Believed to be developmental Most dislocations are evident at births
The Pavlik harness is a positioning device commonly
 RESEARCH PAPERS Ultrasound Evaluation of Hip Position in the Pavlik Harness Leslie E. Grissom, MD*, H. Theodore Harcke, MD*, S. Jay Kumar, MOt, George S. Bassett, MOt, G. Dean MacEwen, MOt Fifty infants
RESEARCH PAPERS Ultrasound Evaluation of Hip Position in the Pavlik Harness Leslie E. Grissom, MD*, H. Theodore Harcke, MD*, S. Jay Kumar, MOt, George S. Bassett, MOt, G. Dean MacEwen, MOt Fifty infants
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
7/1/2012. Repetitive valgus stresses cause microfractures in the apophyseal cartilage (weak link) Common in year olds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
 Use of a partial humeral head resurfacing system for management of an osseous mechanic... Page 1 of 12 Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011 Jan-Mar; 5(1): 17 20. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.80465. PMCID: PMC3109768 Copyright
Use of a partial humeral head resurfacing system for management of an osseous mechanic... Page 1 of 12 Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011 Jan-Mar; 5(1): 17 20. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.80465. PMCID: PMC3109768 Copyright
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Surgery for Femoroacetabular Impingement File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: surgery_for_femoroacetabular_impingement 3/2007 6/2018 6/2019 6/2018
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
