STUDY OF NON-SPINAL, EXTRA-ARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS, ITS MODES OF PRESENTATION, DIAGNOSTIC PITFALLS AND TREATMENT
|
|
|
- Louise King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 E:/Biomedica Vol. Jul. Dec. 2005/Bio10 (A) STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS, ITS MODES OF PRESENTATION, DIAGNOSTIC PITFALLS AND TREATMENT MURTZA CHEEMA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, King Edward Medical College / Mayo Hospital, Lahore INTRODUCTION The incidence and prevalence of tuberculosis has increased tremendously during present decade and is expected to rise further. It is true for developing as well as developed countries, in fact tuberculosis remains a major international problem despite advances in radiological diagnosis and antituberculous therapy (Vohra et al 1997). Contributing factors are mainly, HIV infection, poor case finding, improper treatment in doses and duration, and poor compliance, which results in multi drug resistance tuberculosis (Narain et al, 1992). Myco bacterium tuberculosis can involve virtually any organ of body (Siddiqui et al 1997) lungs are most frequent site but 1015% of disease is extra pulmonary, 10% of extrapulmonary is Skeletal, in it 50% involve the spine (Popel etal 1953; Abdle Wahab et al, 1988) joints are next in frequncy, tuberculosis of bone without involvement of joint is uncommon disease but its sequalae may be disabling (Tadashi, 1995) and may not be diagnosed early by an orthopaedic surgeon (Vohra et al 1997). Intraosseous tuberculosis is usually caused secondary to a primary focus located in the body else where, which can be located only in 50% of case (Davidson, 1970). Goldblatt and Cremin (1978) showed results upto 31%. Patient with skeletal tuberculosis usually presents with pain, swelling and discharging sinus, begining of the disease is progressive and fistulae are main reason of consultation (Moijtahid, 1995). Presentation may be atypical especially in an immunocompromised patients. In advanced lesions diagnosis is even more difficult because radiological picture may mimic chronic pyogenic osteomyelitis, brodie s abscess, tumours or granulomatous lesions (Vohra et al 1997). To diagnose full history, complete physical examination, skin test, mycodot, haematological examination, culture (pus, urin, sputum), xray of involved area, bone scan and MRI performed. Biopsy is mandatory to confirm the diagnosis. PCR is relatively new technique (Saiki 1988), it is a rapid, sensitive and specific DNA amplification technique for detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis (Noordhock, 1995). To treat the lesion, when indicated surgical intervention is due to promote healing but chemotherapy is mandatory. Indications for surgery may be diagnostic or therapeutic, surgery not only control the disease earlier (Griffith, 1979) but also decreases the length of hospitalization (Nicholisan 1974). For larger symptomatic lesions of weight bearing bones that contain significant sequestra or are in danger of structural collapse, fracture or extention to adjacent joints, particularly in advanced lesions with caseation, fibrosis and destruction of bone and cartilage, the vascularity of such are markedly reduced by extensive scarring. Chemotherapy of disease is divided in two phases initial phase for three months having four drugs and continuous phase of six months having three drugs. MATERIAL AND METHODS A total of patients with osseous tuberculosis were selected, patients of both sex and of all age group were included in study and was conducted in orthopaedic department, unit I, Mayo Hospital, Lahore. On first visit patient s bio data and history was carefully recorded, as mode of presentation, duration of symptoms, other associated illness, history of previous treatment and its effects, and history of contact in close family member. Patients were evaluated clinically for local and systemic examination, any sinus or swelling were noted, bone involved, site and size of lesion, adjacent joints were examined functionally for its, active and passive range of motion. Routine investigations were performed, blood C/E ē ESR, urine C/E, blood sugar, blood urea, LFT s, montous test, biplaner xray of involved area, bone scan. Hb less than 10 gm % were considered anemic. No patient was found to be diabetic or sufferer of hepatic or renal disorder.
2 2 MURTAZA CHEEMA After completing the initial evaluation, the patients were put on list for surgery to confirm the diagnosis on histopathology and PCR. In appropriate anaesthesia (spinal, general or regional block) currettage of the lesion was done. In 10 cases currettage was only diagnostic and in 11 it was therapeutical as well, it was debrided for granulations, pus, debris and sequestrum. Biopsy material was divided in three parts are sent for histopathology / embeded formaline), other for PCR and remaining one third for C/S sent as such all specimen were sent to relavant lab as early as possible ranging from half to two hours. In 13 patients presentation was with sinus, so excision of sinus was also done in two, lesion was more than 10 cm and involving wt bearing area so primary bone grafting was also done (first matatarsal and subchondral area of Tibia). All wounds were closed except patients due to poor skin condition. Chemotherapy was started after confirmation of diagnosis by PCR and histopathology. The regimen used was Rifampicin (10 ml/kg in adults and 10 mg/kg in children). Isoniazid (510 mg/kg in adults and 10 mg/kg in children) Pyrazinamide (2040 mg/kg) Eihambutol 2030 mg/kg body weight. The regimen was 3 HRZE/ hr. FOLLOW UP The patients were discharged on chemotherapy and were advised to visit for follow up for one year, on monthly basis for initial 4 months and than after every two months for remaining eight months on each visit patients were throughly examined for the response of therapy (clinical and radiological), assessment was made clinically for local and general symptoms. Clinical signs of healing included a decrease in pain and swelling, disappearance of sinuses, improvement in gait and in gain in weight biplaner xray of involved area were taken to assess bone healing, decrease in osteoprosis with repair of scalloped lesions and local sclerosis. Fresh Hb, ESR, LFT s and visual acquity to see effectiveness of chemotherapy and to observe the toxic effects of drugs. Out of patients 19 completed their follow up while 2 patients were lost daring follow up. All patients had completed their treatment. RESULTS Young female was found to be most vulnerable to tuberculosis majority was among 10 years 14 (.7%) and female to male ratio was found to be 1.1. Painless sinus was leading mode of presentation 13 (1.90%), followed by pain with swelling in (28.58%) ptients, 2 (9.53%) had soft cystic swelling with fluctuation. Majority of our patients 18 (85.72%) visited after four weeks and 3 (14.28%) presented within a month, no patient presented within a week. Duration of disease was from 1 month to3 month with average duration of.92 months. Most common bone was tibia () fever, ulna (3) fibula, metacarpal, metatarsal cuboid (2) and radius (1). 15 patients (71.42%) had lesions in lower limb and (28.58%) in upper limp. 18 patients (85.72%) has metaphyseal lesions and remaining 3 patients had diaphyseal lesions. Consitutional symptoms were present in nine patients, all of them had fever and seven had associated anorexia. Weight loss was observed in those patients, who had disease of long duration from ( months 3 months). In eleven patient no constitional symptom was observed. Multifocal disease was observed in two patients, are had three lesions, (left proximal fibula, right distal fibula and 5th rib). Her dorsal spine (D 89) was also tender but xrays were normal but bone scan was showing not area. Other patient had two lesions (in subchondral area of left tibia and 5th rib). Ninteen patients had solitary lesion. Primary focus in lungs could be detected only in three patients (14.29%). Four patients had H/o contact in family (2) mother, (1) father (1) Elder brother). Out of 15 lesion in lower limb only three had palpable3 inguinal lymph nodes. Six patients had negative responce 28.57% induration less than 5 mm in martous test. Four had 19.04% borderline induration less than 5 10mm and remaining eleven had positive reaction more than 10mm. Four Patients had ESR less than 20mm. Seven had above 50 mm and eleven had 2050 mm. Hb less than 10 gm % was considered anemic 08 were (38.09%) anemic. 14 patients (.%) had lesion less than 5 cm in size. (28.57%) in between 510 cm and only one (4.7%) had lesion more than 10 cm in size. 12 patients 57.14% had radiological features of osteolytic defect with cortical erosion, followed by cystic expansian of bone (Brodies Abscess) in 7 patient 33.33% and in 2 patient it was closely related to chronic pyogenic osteomyelitis with sequestrum. DISCUSSION Literature on non spinal, extraarticular, osseous tuberculosis is limited but common on tuberculous
3 STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS 3 arthritis and Pott s disease, so comparison with previous studies was found to be a difficult task. Tuberculosis remains a major cause of skeletal infection in many part of the world. Our aim was attention to tuberculous osteomyelitis which is rare when compared with skeletal tuberculosis involving the spine and joint. In about 50% of patients the vertebrae are the site of skeletal involvement (Poppel et al 1953 ; Abdelwahab et al 1988) and isolated bone involvement without spread to a joint often fails to attract attention. Because of the subtle nature of the symptoms, the diagnosis is not made until the process is well advanced. The variable clinical and radiological pictures may mimic chronic pyogenic osteomyelitis, Brodies, abscess, tumors or granulomatous lesions. Tuberculosis has been reported in all bones of the body. In united States the spine is involved in 50% of patients ; the pelvis, in 12% ; the hip and femur, in 10% ; the knee and tibia, in 10% ; the ribs in, 7% ; the ankle and shoulder, in 2% ; elbow and wrist, in 2% ; and multiple sites, in 3% (Hugh G et al 199). In this study young adults in teen age group are found to be common sufferer. Among patients 14 are in 1120 years of age with a percentage of.7%. It is alarming and significant showing high prevelance of tuberculosis in our country. These results are in accordance with Hugh G 199 who stated that when the prevelence of tuberculosis in a community is high, most of the population in that community has been infected by the age of twenty years. These results are also in accordance with the studies in India (Rajeev Vohra et al 1997) and Pakistan (Zarina Niazi 1989), tuberculosis is found to be more common in young age group. Females are predominant in the study having tuberculosis with 1.90%. It is perhaps due to less access to health care and more prone to live with risk factors, low socioeconomic status, poor housing conditions with poor or noventilation and sun light. Most of the females are from interior Lahore where people live in small houses with large number of family members sleeping together in the same room. Sinus were found to be most common mode of presentation in our study. In patients 13 were with painless sinus with 1.90%, next one was with swelling and pain six patients (28.57%), one with painful sinus and one patient with pathological fracture and pain. This comparison shows that sinus is more common symptom in this part of the world. The reason might be late presentation of the patients. Nearly all of our patients had initial treatment with NSAID, which offered some relief of pain or swelling and decrease in discharge. The repeated use of these drugs created a false sense of security until it became apparent that their continued use had failed to provide complete relieve, then they decided to come in hospital for consultation. The poor awareness of the patients about the disease can be assessed from this that one patient had sinus which was secondary to incision and drainage done by a local Jarah. One patient thirteen years of age had sinus on forearm since last four months, then he got fracture of radius and ulna, later it was diagnosed as a case of dysphysial tuberculosis. No patient presented within a week. Majority of the patients visited Orthopaedic department after four weeks with an average duration of symptoms about.92 months. About seven months of treatment from local G.P (General Practioner), Bone Setter and Jarah they visited hospital and consulted orthopaedic surgeon. So advancement in early diagnosis of disease can be made by improving the knowledge at G.P level. Previous Studies had Presentation in this Ratio Year No. of Patients Sinus Pain and Swelling Abscess Mis. Zareena Niazi Vohra Rajeev Total Cases Metaphysis Diaphysis Epiphysis Mis. M.N Rasool
4 4 MURTAZA CHEEMA Eighteen lesion were detected in metaphyseal area (85.71%) and only three in dyaphyseal area (14.29%), showing metaphysis to be favourable site for tuberculosis. This is same observation made by M.N Rasool in 1994 in a study of tuberculosis in children. The metaphysis of the long bones is often the site of infection. This predilection is probabely due to vascular structure of long bones in this region (Edeikin et al 193). Tubercle bacilli lodge in the small terminal branches of the arteries of the metaphysis and grow, caseate and produce the lesion. Lower limbs of body were found to be more succeptible to tuberculosis than upper limb. Sixteen lesions (72.73%) were present in lower limb and six in upper limb (27.27%). Distribution of bones in body was like this. Lower Limbs Bone Involved No. of Cases Percentage Tibia Femur Fibula Metatarsal Cuboid 0 Upper Limb Bone Involved No. of Cases Percentage Ulna Metacarpal Radius Two patients had multifocal disease. These findings are in accordance with the incidence percentage of the study by (Hugh. G et al 199). Tuberculosis was reported in all bones of the body but tibia and its metaphysis was found most common and vulnerable site for infection. In this study ninteen patients had solitary lesions and only two had multifocal disease. M.N. Rasool (1994) Total Cases 13 Solitary Multifocal The multifocal form is exceptional even in endemic countries of tuberculosis. It constitutes less than 5% of all cases of osseous tuberculosis (Moujtahid. M et al 1995). According to Kumar and Saxena in 1988 bones lesions are usually solitary because sensitisation of the patient to the tubercle bacilli occurs before the onset of skeletal disease. However if the host immunity is poor and the immune response has been altered the lesion may multiply. Since tubercle bacilli are blood born, individual lesions start at different sites and multifocal lesions may be seen at different stages of development. Two patients with multifocal disease were interesting for brief discription. A thirteen years old female presented in OPD with complaint of sinus over right ankle, swelling arround left knee and pain in front of chest associated with pain in dorsal spine. On xray cystic lesions were found in left proximal fibula and fifth rib and osteolytic defect in right distal fistula. Xray of spine was normal but bone scan showed increase uptake in D910 vertebrae proving bone scan to be more sensitive than xray. Pain in dorsal spine was relieved after six weeks of taking chemotherapy. A 42 years old male patient presented with pain and swelling over left knee and a small sinus in front of chest. Xray showing an osteolytic defect at subchondral area and ecentrically located resembling to Giant Cell Tumor, second lesion was present in fifth rib. After investigation and confirmation with histopathology and P.C.R, it was diagnosed as tuberculous osteomyelitis, chemotherapy was started and the patient recovered. Majority of our patients 14 (.%) had lesion less than 5 cm in size. Six (28.57%) had lesion in between 510 cm and only one (4.7%) had a lesion more than 10 cm. Size of the lesion depends upon chronicity of the disease i.e the delay in proper diagnosis or delay in getting proper treatment. The general health of the patient, associated symptoms, superadded infection, nutritional and immunological status of the patient, all contributed to the smaller or larger size of the lesion. Radiological picture of the lesion was different in different patients table 11.. Osteolytic defect with cortical erosion was most common in 12 (57.14%), followed by cystic expansion of bone or Brodies abscess in 7 (33.33%). While in 2 patients (%) findings were closely related to chronic pyogenic osteomyelitis with sequestrum. In majority of cases the gross appearance of material obtained during biopsy was caseous in
5 STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS 5 nature 14 (.%), followed by caseous material associated with pus in three patients (%). One had (4.7%) granulation with caseation, 2 (%) had pus, debris and sequestrum per operatively and one patient had fleshy appearance closely resembling to Giant Cell Tumor Table The gross appearance of material depends on the condition of the wound / sinus, duration of illness, general health of the patient, previous treatment. Site of lesion and size also contribute to gross appearance of biopsy material. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Osseous tuberculosis is common in young adult, females, living in poor housing conditions, houses with poor or no ventilation and with out sun light. Persons with low socioeconomic setup are mainly affected. It is more common in wall city. In our society patients are not aware about the severity of the disease as most of them reported in the hospital at later stage average duration was.92 months. All of our patients wasted about 7 months by visiting local doctors, Bone Setter or Jarah. Nearly all of them had initial treatment with nonsterided antiinflammatory drugs and antibiotics which offered some relief of pain and swelling or both. So repeated use of these drugs created a false sense of security until it became apparent that their continued use had failed to provide complete... REFERENCES 1.
A STUDY OF NON-SPINAL, EXTRA-ARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL OF LAHORE - PAKISTAN
 F:/Biomedica Vol.22 Jan. Jun. 20/Bio10 (B) A STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL OF LAHORE PAKISTAN G. M. CHEEMA, KHALID AWAN, I. A. BHUTTA, M. KHALID SAYED
F:/Biomedica Vol.22 Jan. Jun. 20/Bio10 (B) A STUDY OF NONSPINAL, EXTRAARTICULAR, OSSEOUS TUBERCULOSIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL OF LAHORE PAKISTAN G. M. CHEEMA, KHALID AWAN, I. A. BHUTTA, M. KHALID SAYED
Modes of Presentation, Diagnostic Pitfalls and Treatment of Non- Spinal Extra-Articular Osseous Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Modes of Presentation, Diagnostic Pitfalls and Treatment of Non- Spinal Extra-Articular Osseous Tuberculosis M.SAEED AKHTAR, KHALID MAHMOOD AWAN, MUHAMMAD AKRAM, ASIF HANIF, ARIF RASHEED
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Modes of Presentation, Diagnostic Pitfalls and Treatment of Non- Spinal Extra-Articular Osseous Tuberculosis M.SAEED AKHTAR, KHALID MAHMOOD AWAN, MUHAMMAD AKRAM, ASIF HANIF, ARIF RASHEED
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A CASE REPORT Babu B. Hundekar 1
 TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji
 Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Osteomyelitis in infancy and childhood: A clinical and diagnostic overview M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Osteomyelitis is a relative common disease in infancy
Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis in children
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(3):336-40 Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis in children Anil Agarwal, Shariq Azam Khan, Nadeem Akhtar Qureshi Department of Orthopaedics, CNBC, Geeta Colony,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2011;19(3):336-40 Multifocal osteoarticular tuberculosis in children Anil Agarwal, Shariq Azam Khan, Nadeem Akhtar Qureshi Department of Orthopaedics, CNBC, Geeta Colony,
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
 PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery
 Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY
 CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation
 Case Reports in Pulmonology, Article ID 685406, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/685406 Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation Balaji
Case Reports in Pulmonology, Article ID 685406, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/685406 Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation Balaji
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Acute Osteomyelitis: similar to septic arthritis but up to 40% may be afebrile swelling overlying the bone & tenderness
 Osteomyelitis / Bone and Joint Infections Bone infections in children are usually from haematogenous bacterial seeding to a single joint, usually the lower limbs, but may be multifocal. Approximately 10%
Osteomyelitis / Bone and Joint Infections Bone infections in children are usually from haematogenous bacterial seeding to a single joint, usually the lower limbs, but may be multifocal. Approximately 10%
TB or not TB? That should be the question
 TB or not TB? That should be the question SH Liyanage, CM Gupte ( ), A Cobb, MC Beverly Department of Orthopaedics Ealing University Hospital Uxbridge Rd, Southall, Middlesex UB13HW United Kingdom Correspondence:
TB or not TB? That should be the question SH Liyanage, CM Gupte ( ), A Cobb, MC Beverly Department of Orthopaedics Ealing University Hospital Uxbridge Rd, Southall, Middlesex UB13HW United Kingdom Correspondence:
Keywords: Tubercular osteomyelitis, Extrapulmonary, Sequestrectomy
 Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. PRIMARY TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS
Orthopaedics Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 4, July-Aug 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. PRIMARY TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Osteo-articular TB in Children
 Osteo-articular TB in Children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa Questions Spinal TB is the most common
Osteo-articular TB in Children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa Questions Spinal TB is the most common
Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all):
 Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Acutely Limping Child and Septic Arthritis Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all): History Careful history of any significant
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Acutely Limping Child and Septic Arthritis Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all): History Careful history of any significant
Collar stud abscess an interesting case report
 Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Topics. Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities. Detection of Infection. Role of Imaging in Extremity Infection. Detection of Infection
 Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Spina Ventosa in a Young Adult: Report of Two Cases
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(3):444-448 Spina Ventosa in a Young Adult: Report of Two Cases Vishnu Senthil, Anil K Bhat, Ashwath Acharya Department of Orthopaedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal-576104,
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(3):444-448 Spina Ventosa in a Young Adult: Report of Two Cases Vishnu Senthil, Anil K Bhat, Ashwath Acharya Department of Orthopaedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal-576104,
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August 2015; 2(8) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.672
 CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
Manage TB Dr. Dina Nair National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai. Lecture 07 Clinical manifestations of TB Session 02
 Manage TB Dr. Dina Nair National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai Lecture 07 Clinical manifestations of TB Session 02 Hello, welcome to the second session on Clinical manifestations of tuberculosis.
Manage TB Dr. Dina Nair National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis, Chennai Lecture 07 Clinical manifestations of TB Session 02 Hello, welcome to the second session on Clinical manifestations of tuberculosis.
Bilateral multiple choroidal granulomas and systemic vasculitis as presenting features of tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
 Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Unusual Presentation of Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Osteomyelitis in Immunocompetent Saudi Child: A Case Report Al zomor AO 1 $
 Unusual Presentation of Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Osteomyelitis in Immunocompetent Saudi Child: A Case Report Al zomor AO 1 $, Bukhari EE 2, Alfrayh A. 3 1 Department of Pediatric Infectious Diseases,
Unusual Presentation of Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) Osteomyelitis in Immunocompetent Saudi Child: A Case Report Al zomor AO 1 $, Bukhari EE 2, Alfrayh A. 3 1 Department of Pediatric Infectious Diseases,
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - well-defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Types of bone/joint infections. Bone and Joint Infections. Septic Arthritis. Pathogenesis. Pathogenesis. Bacterial arthritis: predisposing factors
 Bone and Joint Infections Types of bone/joint infections Arthritis (infective/septic) Osteomyelitis Prosthetic bone and joint infections Septic Arthritis Common destructive athroplasty Mono-articular Poly-articular
Bone and Joint Infections Types of bone/joint infections Arthritis (infective/septic) Osteomyelitis Prosthetic bone and joint infections Septic Arthritis Common destructive athroplasty Mono-articular Poly-articular
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
Mycobacterial Lymphadenitis in Childhood
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 7. Mycobacterial Lymphadenitis in Childhood A. MACKELLAR, H. B. HILTON, and P. L. MASTERS From Princess Margaret Hospital for Children, Perth, Western Australia In Western
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 7. Mycobacterial Lymphadenitis in Childhood A. MACKELLAR, H. B. HILTON, and P. L. MASTERS From Princess Margaret Hospital for Children, Perth, Western Australia In Western
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1
 Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1 Hee-Jin Park, M.D., Sung-Moon Lee, M.D., Hee-Jung Lee, M.D., Jung-Sik Kim, M.D., Hong Kim, M.D. Primary lymphoma of bone is uncommon
Disseminated Primary Non-Hodgkin s Lymphoma of Bone : A Case Re p o r t 1 Hee-Jin Park, M.D., Sung-Moon Lee, M.D., Hee-Jung Lee, M.D., Jung-Sik Kim, M.D., Hong Kim, M.D. Primary lymphoma of bone is uncommon
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 59. 151-157, 1996 CASE REPORTS GIANT CELL-RICH OSTEOSARCOMA: A CASE REPORT KEIJI SATO!, SHIGEKI YAMAMURA!, HISASHI IWATA!, HIDESHI SUGIURA 2, NOBUO NAKASHIMA 3 and TETSURO NAGASAKA
Mohammad Ashraf. - Bahaa Najjar. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 4 - Mohammad Ashraf - Bahaa Najjar - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Fractures (cont d). Healing of fractures: There are a lot of factors determine the proper healing of the fracture. For example: Displaced
- 4 - Mohammad Ashraf - Bahaa Najjar - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Fractures (cont d). Healing of fractures: There are a lot of factors determine the proper healing of the fracture. For example: Displaced
SMALL ROUND BLUE CELL LESION OF BONE
 DISCLOSURE SMALL ROUND BLUE CELL LESION OF BONE Dr. Alistair Jordan University of South Alabama No financial support or endorsement OBJECTIVES Describe the more common small round cell lesions of bone
DISCLOSURE SMALL ROUND BLUE CELL LESION OF BONE Dr. Alistair Jordan University of South Alabama No financial support or endorsement OBJECTIVES Describe the more common small round cell lesions of bone
Isolated Tubercular Osteomyelitis of Scapula A Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
 Editorial Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2013 Oct-Dec;3(4): Page 7-11 Isolated Tubercular Osteomyelitis of Scapula A Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature Abstract Gopisankar Balaji
Editorial Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2013 Oct-Dec;3(4): Page 7-11 Isolated Tubercular Osteomyelitis of Scapula A Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature Abstract Gopisankar Balaji
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF LOWER END OF FEMUR IN A SKELETALLY IMMATURE-A RARE CASE
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF LOWER END OF FEMUR IN A SKELETALLY IMMATURE-A RARE CASE *Surojit Mondal 1, Aniket Chowdhury 2 and Goutam Bandyopadhyay 3 1 Department of Orthopaedics, B.S.Medical College, Bankura,
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF LOWER END OF FEMUR IN A SKELETALLY IMMATURE-A RARE CASE *Surojit Mondal 1, Aniket Chowdhury 2 and Goutam Bandyopadhyay 3 1 Department of Orthopaedics, B.S.Medical College, Bankura,
A Case Report of an Unusual Case of Tuberculous Osteomyelitis Causing Spontaneous Pathological Fracture of Humerus in a Middle Aged Female
 Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2017 Jan Feb: 7(1):41 45 A Case Report of an Unusual Case of Tuberculous Osteomyelitis Causing Spontaneous Pathological Fracture of Humerus in a Middle Aged
Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2017 Jan Feb: 7(1):41 45 A Case Report of an Unusual Case of Tuberculous Osteomyelitis Causing Spontaneous Pathological Fracture of Humerus in a Middle Aged
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
PSOAS ABSCESS. Dr Noman Ullah Wazir
 PSOAS ABSCESS Dr Noman Ullah Wazir Psoas Major muscle The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Psoas Major
PSOAS ABSCESS Dr Noman Ullah Wazir Psoas Major muscle The psoas major is a long fusiform muscle located on the side of the lumbar region of the vertebral column and brim of the lesser pelvis. Psoas Major
Advertisement. Osteochondroma
 Advertisement Osteochondroma An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
Advertisement Osteochondroma An osteochondroma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor that develops during childhood or adolescence. It is an abnormal growth that forms on the surface of a bone near the growth
BONES & JOINTS INFECTION BONE TUMOURS
 BONES & JOINTS INFECTION BONE TUMOURS IMPORTANT SERIOUS CONSEQUENCE PLEASE DON T MISS!! EARLY DIAGNOSIS & PROPER TREATMENT HOW?? AWARE of THEIR EXISTENCE (Knowledge) PREPARE for THEIR OCCURRENCE A HIGH
BONES & JOINTS INFECTION BONE TUMOURS IMPORTANT SERIOUS CONSEQUENCE PLEASE DON T MISS!! EARLY DIAGNOSIS & PROPER TREATMENT HOW?? AWARE of THEIR EXISTENCE (Knowledge) PREPARE for THEIR OCCURRENCE A HIGH
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Management of infected custom mega prosthesis by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gudaru K et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3874-3878 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151459
CASE STUDY: PRO-DENSE Injectable Regenerative Graft Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor
 : PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
: PRO-DENSE Used to Backfill a Bone Cavity Following Resection of a Giant Cell Tumor Contributed by: Matthew J. Seidel, MD* Lauren A. Schwartz, NP Scottsdale, AZ *Dr. Seidel is a paid consultant for Wright
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION. Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics
 BONE AND JOINT INFECTION Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics www.ortopedia.dote.hu Order of verbal exams: The students are able to register for the exam on the Neptun system. The students pick two titles,
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics www.ortopedia.dote.hu Order of verbal exams: The students are able to register for the exam on the Neptun system. The students pick two titles,
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO :
 CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
CASE NO: 1 PATIENT DETAILS : Name : XXXX Age : 53yr Sex : Female Occupation : Housewife Date Of Admission :11/06/15 Residence : Nalgonda IP NO : 201518441 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : - Pain in the right knee since
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Case 4 Generalised bone pain
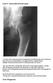 Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
CASE PRESENTATION. Dr. Faseeh Shahab PGY3 Orthopaedic Resident, Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, PAKISTAN
 CASE PRESENTATION Dr. Faseeh Shahab PGY3 Orthopaedic Resident, Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, PAKISTAN CASE PRESENTATION - History Ms. SB, 30yo Afghan National Presented with 3 months history of Swelling
CASE PRESENTATION Dr. Faseeh Shahab PGY3 Orthopaedic Resident, Khyber Teaching Hospital, Peshawar, PAKISTAN CASE PRESENTATION - History Ms. SB, 30yo Afghan National Presented with 3 months history of Swelling
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN. Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool
 MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN Dr Caren Landes Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS Common and uncommon infections Common and uncommon presentations Imaging
Case Report Sequential MR Images and Radiographs of Epiphyseal Osteomyelitis in the Distal Femur of an Infant
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 672815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/672815 Case Report Sequential MR Images and Radiographs of Epiphyseal Osteomyelitis in the Distal Femur
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2013, Article ID 672815, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/672815 Case Report Sequential MR Images and Radiographs of Epiphyseal Osteomyelitis in the Distal Femur
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor Camilla Rodrigues, MD co-author Abstract Most individuals who get exposed
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD Author and Series Editor Camilla Rodrigues, MD co-author Abstract Most individuals who get exposed
Surgical and orthotic possibilities of bone tumour pain management
 Surgical and orthotic possibilities of bone tumour pain management Chaloupka, R., Grosman, R., Repko, M., Tichý, V. Ortopedická klinika FN Brno-Bohunice Ortopedická klinika, FN Brno, Jihlavská 20, 625
Surgical and orthotic possibilities of bone tumour pain management Chaloupka, R., Grosman, R., Repko, M., Tichý, V. Ortopedická klinika FN Brno-Bohunice Ortopedická klinika, FN Brno, Jihlavská 20, 625
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT. Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad
 Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Tuberculosis otitis media
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2013; 9 (5): 329-333 Tuberculosis otitis media Poon Seong LIM, Bee See GOH, Lokman SAIM Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2013; 9 (5): 329-333 Tuberculosis otitis media Poon Seong LIM, Bee See GOH, Lokman SAIM Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
OSTEOMYELITIS EXPERIENCE IN THE STOCKHOLM REGION OVER THE YEARS
 BCG OSTEOMYELITIS EXPERIENCE IN THE STOCKHOLM REGION OVER THE YEARS 1961-1974 S. BERGDAHL, M. FELLANDER and B. ROBERTSON, STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN Eighteen cases of bone and joint tuberculosis in children were
BCG OSTEOMYELITIS EXPERIENCE IN THE STOCKHOLM REGION OVER THE YEARS 1961-1974 S. BERGDAHL, M. FELLANDER and B. ROBERTSON, STOCKHOLM, SWEDEN Eighteen cases of bone and joint tuberculosis in children were
Tibia metaphysis fracture icd 9
 Tibia metaphysis fracture icd 9 The Borg System is 100 % Tibia metaphysis fracture icd 9 S82.244F is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Tibia metaphysis fracture icd 9 The Borg System is 100 % Tibia metaphysis fracture icd 9 S82.244F is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Correlation Of Immunological And Pathological Parameters In Extra-Pulmonary Tuberculosis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 3 Ver. IV (Mar. 2016), PP 14-25 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation Of Immunological And Pathological
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 3 Ver. IV (Mar. 2016), PP 14-25 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation Of Immunological And Pathological
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Table 1. Hospital. Wrightington Hospital 24. Manchester Royal Infirmary 17
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 982, 4, -6 Bone and joint tuberculosis in Greater Manchester 969-79 PAUL NEWTON, J. SHARP,' AND K. L. BARNES2 From the 'Rheumatology Unit, University Hospital ofsouth
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 982, 4, -6 Bone and joint tuberculosis in Greater Manchester 969-79 PAUL NEWTON, J. SHARP,' AND K. L. BARNES2 From the 'Rheumatology Unit, University Hospital ofsouth
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Release Notes and Installation Instructions. Medtech32. ACC Subsidy Updates
 Release Notes and Installation Instructions Medtech32 ACC Subsidy Updates General Practitioners, Medical Specialists, Nurses, Podiatrists and Specified Treatment Providers (April 2014) These Release Notes
Release Notes and Installation Instructions Medtech32 ACC Subsidy Updates General Practitioners, Medical Specialists, Nurses, Podiatrists and Specified Treatment Providers (April 2014) These Release Notes
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA. Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009
 EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: Objective for Portfolio #1: Part I: Skeletal Stations Station A: Bones of the Body
 SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
SKELETAL STRUCTURES Objectives for Exam #1: 1. Provide information on the various structures and functions of the skeletal system. 2. Describe various skeletal system disorders, including imaging techniques
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Endovascular and surgical treatment of giant pelvic tumor
 Endovascular and surgical treatment of giant pelvic tumor Mitrev Z., MD FETCS; Anguseva T., MD; Milev I., MD; Zafiroski G., PhD MD Center for Cardiosurgery, Filip the II, Skopje, Macedonia Background Giant
Endovascular and surgical treatment of giant pelvic tumor Mitrev Z., MD FETCS; Anguseva T., MD; Milev I., MD; Zafiroski G., PhD MD Center for Cardiosurgery, Filip the II, Skopje, Macedonia Background Giant
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Presacral Cold Abscess a Rare and Special Case of Skeletal Tuberculosis
 : D Radiology, Diagnostic Imaging and Instrumentation Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
: D Radiology, Diagnostic Imaging and Instrumentation Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist
 A Patient s Guide to Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Scaphoid Fracture of the Wrist 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Case Report A Rare Case of Tuberculosis with Sacrococcygeal Involvement Miming a Neoplasm
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7286806, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7286806 Case Report A Rare Case of Tuberculosis with Sacrococcygeal Involvement Miming a Neoplasm Walid
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7286806, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7286806 Case Report A Rare Case of Tuberculosis with Sacrococcygeal Involvement Miming a Neoplasm Walid
Women s Imaging ICD-10-CM
 Women s Imaging ICD-10-CM Clinical Documentation Guides Brought to you by www.codingstrategies.com The Resource for Physician and Outpatient Coding, Compliance & ICD-10-CM OTHER CLINICAL DOCUMENTATION
Women s Imaging ICD-10-CM Clinical Documentation Guides Brought to you by www.codingstrategies.com The Resource for Physician and Outpatient Coding, Compliance & ICD-10-CM OTHER CLINICAL DOCUMENTATION
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
CHAPTER 8 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower extremities and the shoulder and hip girdles. B. The appendicular skeleton functions primarily
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Equine Skeletal System
 Equine Skeletal System EQS 110 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Functions of the Skeletal System... 3 Skeletal Strength... 3 Bone
Equine Skeletal System EQS 110 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Functions of the Skeletal System... 3 Skeletal Strength... 3 Bone
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anesthesia Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes
 Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2015 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Resequenced
Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2015 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Resequenced
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Sue Greenhalgh Consultant Physiotherapist March 18th
 Sue Greenhalgh Consultant Physiotherapist March 18th Caused by the Myobacterium Tuberculosis well known to Hippocrates Sir Percival Pott gave a very good description of the disease in 1779 Consumption
Sue Greenhalgh Consultant Physiotherapist March 18th Caused by the Myobacterium Tuberculosis well known to Hippocrates Sir Percival Pott gave a very good description of the disease in 1779 Consumption
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of the Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Cluster - 26 ORTHOPEDICS. X Ray of Affected Limb, MIR of Shoulder
 Sr.No Package no 1708 26.1 Orthopeidc 1709 26.2 Orthopeidc Sub speciality Procedure name Pre-Operative Investigation AC joint reconstruction/ Stabilization/ Acromionplasty (Nonoperative management is recommended
Sr.No Package no 1708 26.1 Orthopeidc 1709 26.2 Orthopeidc Sub speciality Procedure name Pre-Operative Investigation AC joint reconstruction/ Stabilization/ Acromionplasty (Nonoperative management is recommended
Equine Skeletal System
 Equine Skeletal System EQS 110 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Functions of the Skeletal System... 3 Skeletal Strength... 3 Bone
Equine Skeletal System EQS 110 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Functions of the Skeletal System... 3 Skeletal Strength... 3 Bone
Bacteriological Profile of Post Traumatic Osteomyelitis in a Tertiary Care Centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 367-372 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.044
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 367-372 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.044
FOLLICULAR / OVULATION STUDY USG HIP JOINT (LEFT) USG HIP JOINT (RIGHT) USG KNEE JOINT (LEFT) USG KNEE JOINT (RIGHT) USG KUB USG MUSKULOSKELETAL USG
 RADIOLOGY TESTS SONOGRAPHY,COLOR DOPPLER 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN TWINS 3D/4D USG PELVIS ABDOMEN & PELVIS USG ABDOMEN UPPER USG ANKLE JOINT (LEFT) USG ANKLE JOINT (RIGHT) USG B SCAN BREAST
RADIOLOGY TESTS SONOGRAPHY,COLOR DOPPLER 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN TWINS 3D/4D USG PELVIS ABDOMEN & PELVIS USG ABDOMEN UPPER USG ANKLE JOINT (LEFT) USG ANKLE JOINT (RIGHT) USG B SCAN BREAST
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION
 GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
GIANT CELL TUMOR OF TENDON SHEATH A CYTO HISTO CORRELATION Dr.S.SRIKANTH, Assistant Professor.Dept of Patholgy. Dr.SMITHA VADANA, Resident.Dept of pathology. Dr.R.SUHELA. Resident.Dept Of Pathology. Prathima
