Erythema nodosum or Erythema induratum: An Important Distinction for Appropriate Treatment
|
|
|
- Nathan Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report Med Principles Pract 1998;7: Received: July 6, 1997 Revised: October 26, 1997 A.N. Malaviya a, b Suad Abdeend c M.A.F. Qurtom b S. Al-Ghuriear b H.I. Kablawi b a Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, and Departments of b Medicine, and c Pathology, Mubarak Al-Kabeer Hospital, Ministry of Health, Kuwait OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Key Words Panniculitis Bazin s disease Erythema nodosum Erythema nodosum or : An Important Distinction for Appropriate Treatment OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Abstract Objective and Importance: The objective of this case report is to draw the attention of the readers to a commonly seen disorder, namely panniculitis. Clinically, the condition resembles cellulitis, that often causes a diagnostic problem. The report hightlights the importance of accurate diagnosis of panniculitis and its subtypes for its proper management. Clinical Presentation: Two patients with clinically typical lesions of panniculitis on their lower extremities are described. The lesions in these 2 patients had marked clinical resemblance to cellulitis. However, with the help of biopsy and histopathological examination it was possible to accurately diagnose the distinct forms of panniculitis in these patients. It helped in the correct management of the patients with satisfactory outcome. Conclusion: It is concluded that in patients with lesions resembling cellulitis, especially on the shin, the possibility of panniculitis must be considered. The experience with these 2 patients highlights the need for accurate histological characterization as an essential step in the diagnosis and proper management of different forms of panniculitides. OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Introduction Nonsuppurative inflammation in subcutaneous tissue is called panniculitis [1 6]. It is often associated with constitutional and rheumatic symptoms. In this category erythema nodosum (EN), a form of septal panniculitis without vasculitis, is the commonest variety seen in clinical practice [1 6]. It is a frequently diagnosed condition in Kuwait [7, 8]. However, the clinical and morphologic picture of the lesion may not be specific of this condi- ABC Fax karger@karger.ch S. Karger AG, Basel /98/ $15.00/0 Accessible online at: Prof. A.N. Malaviya, MD, FACP, FACR Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine Kuwait University, PO Box Safat (Kuwait) Fax , !anand@hsc.kuniv.edu.kw1
2 tion and some of the patients may have other forms of panniculitis including erythema induratum (EI), a form of panniculitis associated with vasculitis of medium- or small-sized arteries or veins in the panniculus, in conjunction with an adjacent suppurative and/or granulomatous panniculitis [4], a histology believed to be rather specific for tuberculosis [1 6]. This disease has often been called Bazin s disease after the name of the person who described it for the first time [cited in ref. 8]. In this report, we present 2 patients who had lesions on the legs associated with constitutional and rheumatic symptoms that were first considered EN. One of them suffered protracted fluctuating illness due to lack of accurate early diagnosis. However, the histological study of the lesion in both of them showed features of EI that led to the diagnosis of tuberculosis. With appropriate treatment, both the patients recovered from their illness. This report highlights the fact that for achieving proper diagnosis and treatment in patients with any form of panniculitis, histopathological categorization of the lesion may be necessary. Case Reports Case 1 A 33-year-old Indian man presented with a history of an unusual skin lesion on his legs of 2-year duration. In the beginning, he noticed vague pains in the lower part of his legs associated with mild constitutional symptoms including muscular aches and pains, mild arthralgias, with occasional feverish feeling. He was treated symptomatically and felt better. However, soon he noticed a few reddish-purplish nodules on the legs that were tender. Lesions quickly increased in number, became bigger and a few of them ulcerated. Over the next several months he consulted a number of clinics and hospitals. A diagnosis of chronic nodularulcerative skin condition was made, and he was given symptomatic and antibiotic treatment without definite relief. The constitutional symptoms became worse. He continued with fluctuating constitutional symptoms Fig. 1. Photograph of the legs showing skin nodules with ill-defined margins merging with each other with hyperpigmented, stretched and shiny overlying skin with a distinct erythematous-purplish hue. Some scarring of the healed ulcerated nodules is also visible. and leg ulcers that healed on a few occasions, but reappeared soon. This process went on for almost 2 years. However, because of exacerbation in the nodulo-ulcerative skin condition with increasing constitutional symptoms and vague rheumatic pains he was referred to this hospital for opinion. On examination there were a few palpable discrete nontender 0.5- to 1-cm-size lymph nodes in the left axilla. There were bilateral skin nodules, about 3 4 on each leg. Margins of the nodules were ill-defined and appeared to merge with each other. The skin over the nodules was hyperpigmented with a distinct erythematous-purplish hue and appeared stretched and shiny. There were scars over some of the nodules while a few of them had superficial chronic nonhealing ulcers (fig. 1). Routine investigations showed the following results: ESR 40 mm Erythema nodosum versus Med Principles Pract 1998;7:
3 Fig. 2. Epithelial cells (arrows) at the periphery of the granulomas invading the subcutaneous fat. Lymphocytes are seen at the outside of the lesion. HE.! 200. Fig. 3. Fibrinoid necrosis of the wall of a vein with inflammatory cells and necrotic debris within an area of panniculitis. HE.! st hour (normal range in males 1 50 years 0 20), normal complete blood count, normal serum biochemistry including liver enzymes, renal profile and serum proteins, normal immunological tests including rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody, C-reactive protein, and cryoproteins. Screening for hepatitis B and C was negative. Biopsy of the subcutaneous nodules along with the overlying skin was carried out. Histopathology showed the main lesion in the lower dermis and subcutis, consisting of lobular panniculitis with confluent areas of necrotizing granulomas comprising of epitheloid cells (fig. 2), and occasional Langerhans giant cells. The granulomas were surrounding necrotic adipocytes. There was necrotizing vasculitis affecting some vessels characterized by fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall (fig. 3), showing infiltration with mononuclear nuclear inflammatory cells. The surrounding tissue showed suppurative panniculitis in which neutrophils and debris were present within the necrotic fat (fig. 4). Acid-fast stains were, however, negative for acid-fast bacilli. The patient was given standard triple-drug antituberculous therapy consisting of isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide. He tolerated medicines well and his liver function tests remained normal during the followup. In about 3 weeks he noticed improvement in the constitutional symptoms, and the lesions on the legs started to heal in about 5 6 weeks. By 3 months the leg 300 Med Principles Pract 1998;7: Malaviya/Abdeend/Qurtom/ Al-Ghuriear/Kablawi
4 Fig. 4. Neutrophils are seen in the area of panniculitis giving rise to suppurative changes. HE.! 200. Fig. 5. Photograph of the legs showing sparse erythematous elevated skin nodules over both shins (arrows) that were tender. lesions had completely healed. However, the pigmentation and the stretched shiny appearance of the overlying skin persisted. The medicines were discontinued after a total of 9 months of treatment. Till the time of this writing the patient had completed a follow-up of 9 months since the medicines were discontinued, and remained in completely normal health. Case 2 A 50-year-old Iranian man presented with a 4-week history of constitutional symptoms consisting of fever, night sweats, marked fatigue, loss of appetite and 10 kg weight loss. Over the last 3 days he had noticed painful raised nodular reddish lesions on his shins. Simultaneously with the appearance of the lesions on the legs, he also noted painful swellings in his ankles. He had a past history of brucellosis diagnosed and treated in Iran 24 years ago. Positive physical findings included fever (38.4 C), emaciation, nontender matted lymph nodes 1 2 cm in size in both cervical areas, follicular tonsillitis, and sparse tender erythematous elevated skin nodules over both the shins (fig. 5). Both the ankles were mildly swollen and tender. Abdominal examination showed a 16-cm tender smooth hepatomegaly. The spleen was not palpable. Investigations showed the following results: WBC 19 (normal range 4 10)! 10 9 /l with differential count granulocytes Erythema nodosum versus Med Principles Pract 1998;7:
5 Fig. 6. Vasculitis with marked inflammation with neutrophils many of which have broken down to nuclear debris. HE.! 200. Fig. 7. Multiple epitheloid cell granulomas (arrows) surrounding fat cells within the areas of panniculitis. HE.! % (normal range 45 74), lymphocytes 15% (normal range 16 45), monocytes 0.4% (normal range 4 10), hemoglobin 110 g/l (normal range ), platelets 428! 10 9 /l (normal range ), ESR 120 mm 1st hour (normal range in males 1 50 years 0 20). The routine and microscopic urine examination was normal. The serum biochemistry including liver enzymes, renal profile and serum proteins were normal except alkaline phosphatase that was 146 units/l (normal range 2 120), serum albumin 25 g/l (normal range 35 55), total serum globulin 35 g/l (normal range 20 30). Coagulation profile was normal. Immunological tests including rheumatoid factor, antinuclear antibody and C-reactive protein tests were negative. Blood, urine, sputum and throat swab smears and cultures did not show positive tests for any pathogens. Blood smears were negative for any parasites. Sputum culture for acid-fast bacilli was also negative. Virological studies including those for cytomegalovirus (specific IgM and IgG antibodies) and Epstein-Barr virus (specific IgM and IgG antibodies and Monospot test ) yielded negative results. Brucella agglutination test was negative. Echocardiogram was normal. Abdominal ultrasound examination and plain roentgenogram of the chest was normal. A Mantoux test with 1 unit purified-protein derivative gave a strongly positive reaction of 37! 37 mm of induration after 48 h. Screening for hepatitis B and C was negative. Biopsy of the subcutaneous nod- 302 Med Principles Pract 1998;7: Malaviya/Abdeend/Qurtom/ Al-Ghuriear/Kablawi
6 ules along with the overlying skin was carried out. The histopathology showed focal leukocytoclastic vasculitis (fig. 6) involving small arteries and veins characterized by fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall with mononuclear inflammatory cell infiltration and nuclear debris. There was thrombotic occlusion within the lumen of these vessels. There were small foci of panniculitis with epitheloid cell granulomas (fig. 7). Foreign-body type of giant cells were seen around sutural material. The surrounding dermal collagen showed areas of fibrinoid necrosis. Mild mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate was present around some of the skin appendages. The histological features were those of leukocytoelastic vasculitis and papulonecrotic tuberculid. Lymph node biopsy showed typical features of tuberculous lymphadenitis with multiple large confluent epitheloid cell granulomas and Langerhans giant cells, and it tested positive for acid-fast bacilli on special stains. The patient was given triple-drug antituberculous therapy consisting of isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide. He tolerated the medicines well. Over a period of 2 weeks he started to gain weight and the fever subsided. At the time of discharge the investigations showed ESR 90 mm Hg, hemoglobin 122 g/l, WBC 10.4! 10 9 /l, granulocytes 69%, lymphocytes 22%, platelets 428! 10 9 /l. Liver function monitoring did not show any abnormality. At the follow-up visit 4 weeks after discharge, he was found to have improved in his general health and felt normal. He had not repeated the investigations that were suggested and informed that he was leaving for his home country. He was advised to continue medicines for a minimum of 6 9 months and to be under the care of a local doctor for proper follow-up. Discussion The 2 cases presented in this report illustrate the problems in the diagnosis of panniculitis. What clinically appears as panniculitis may necessitate histological categorization. Although EN, a septal panniculitis without vasculitis, is the most common form, the morphological picture may not be specific for this condition. The lesion could be due to any of the several underlying conditions, including EI, a lobular panniculitis with vasculitis, that is often associated with an underlying focus of tuberculosis [1 6]. The examples of these patients highlight the need for histopathological study that, in these 2 cases, led to the diagnosis of mycobacterial infection. Therefore, histopathology is recommended for achieving the proper diagnosis and treatment in those patients where the cause of panniculitis is not obvious. Panniculitis is a generic term used for inflammation in the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the body [9]. Most authorities now classify panniculitides into four categories based upon histopathological criteria, namely: (i) septal panniculitis without vasculitis; (ii) lobular panniculitis without vasculitis; (iii) mixed septal and lobular panniculitis but without vasculitis, and (iv) panniculitis with vasculitis [1, 2]. Clinically the lesions of different varieties of panniculitides may look alike with nodular indurated erythematous inflamed areas in the subcutaneous tissue. The overlying skin may show different features in different stages of the lesions. Thus, the skin may appear inflamed, or it may have a brawny indurated appearance, or it may appear ecchymotic, or become scaly when healing. However, there are certain features that help in clinical distinction between different categories of panniculitides. These include: (i) sex of patient EN is predominantly a disease of women, if seen in men, Lofgren s syndrome (acute sarcoidosis with bilateral hilar lymph nodes, EN-type lesions on shin and inflammatory peripheral arthritis) or Behçet s disease are the most likely underlying cause [1]; Vilanova s disease, a chronic relapsing form of EN (also called erythema migrans chronicum [1]), is seen only in women. The other features include: (ii) appearance and feel of the lesion; (iii) number and distribution of the lesions (EN lesions are almost entirely limited to shin); (iv) presence or absence of ulceration (EN lesions never ulcerate while those in other forms of panniculitis may ulcerate), and (v) scarring (a prominent feature of panniculitis Erythema nodosum versus Med Principles Pract 1998;7:
7 associated with Behçet s disease). Increased awareness of the distinguishing clinical features between different forms of panniculitides would help in deciding in whom histopathological categorization is necessary for achieving proper diagnosis. Among the various categories of panniculitides, EN is the commonest form seen in clinical practice [1 6]. Therefore, characteristic clinical features of EN may be taken as a reference point. Deviation from this clinical pattern should be a guide for obtaining histopathological confirmation of the actual category of panniculitis. Characteristic clinical features of EN are a predominance of this in young females and an acute appearance of one or a few tender erythematous nodules on the anterior tibial surface that are better palpated than visualized. Overlying skin appears inflamed and feels indurated. As the lesions age, the nodules soften and become less palpable, a peculiar ecchymotic purplish discoloration appears and scaling of the skin may become prominent. (It is not uncommon for such patients to get the label of cellulitis and to receive antibiotics empirically.) Over the next 4 6 weeks the lesions eventually heal without suppuration or scarring. Although EN is usually an acute process, as discussed above, a chronic relapsing variant of EN is not uncommon. It is much more common in middleaged women [1, 2]. Clinically, the lesions look very similar to those seen in the acute condition. However, ankle arthritis (unilateral or bilateral) is a unique feature associated in many of these cases [5]. This type of arthritis may sometimes appear a few days before the appearance of the EN nodules. In contrast, the clinical features of EI include occurrence without any sex predilection, superficial resemblance of the lesions to EN occurring predominantly on the anterior tibial region, but the lesions may occur at other sites in the body, often with ulceration and suppuration, and healing with scarring. However, the actual diagnosis is made on a constellation of histological features consisting of vasculitis of medium- or small-sized arteries or veins in the panniculus in conjunction with an adjacent suppurative and/or granulomatous panniculitis [4]. In both the cases reported here, the clinical features were against the diagnosis of EN. Thus in case 1, the lesions had shown repeated ulcerations and extensive scarring in the lower regions of both legs, features not seen in EN (fig. 1). In case 2, the nodules had extended up to the midthighs, a most unusual occurrence for lesions of EN. Of course, the diagnosis of EI was established on histological examination showing the characteristic histopathology in both cases (fig. 2 4, 6, 7). In case 1, a skin and subcutaneous tissue biopsy provided the essential clue to tuberculosis as the etiology of the underlying disorder. Had the biopsy not been performed, tuberculosis might not have been recognized even at this late stage. Moreover, there is a tendency among clinicians to give corticosteroids in recalcitrant skin lesions especially if they appear to be due to some form of immunological reaction. EN is one such lesion where steroids are often used if the lesion becomes chronic or recurrent. Had empiric corticosteroid therapy been prescribed to these patients, an exacerbation of their mycobacterial infection could have resulted. In many cases with EI, it may not always be easy to demonstrate the causative agent, i.e. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Therefore, it was fortunate that in both the cases presented here, it was possible to diagnose tuberculosis with a fair degree of certainty. In case 1, the typical histopathology along with the therapeutic response that was confirmed in the prolonged follow-up left no doubt on the diagnosis of tuberculosis. In case 2, acid-fast bacilli were demonstrated in the lymph node biopsy. This is important because Whitfield has de- 304 Med Principles Pract 1998;7: Malaviya/Abdeend/Qurtom/ Al-Ghuriear/Kablawi
8 scribed almost identical patients without any evidence of tuberculosis [cited in ref. 8]. For this reason, the modern view is to call such lesions nodular vasculitis representing a hypersensitivity reaction manifested by medium-sized vessel vasculitis in which the adjacent panniculus becomes involved in the inflammatory process and becomes necrotic. Once the diagnosis of nodular vasculitis is made histologically, all efforts should be made to look for the evidence of tuberculosis. In this regard, the availability of a polymerase chain reaction has been reported to be of help in improving the diagnosis of tuberculosis in those cases where smears and cultures may be negative [10]. Unfortunately, this could not be done in case 1 due to some practical difficulties. In summary, panniculitis, i.e. inflammatory lesions of the panniculus, is common in clinical practice and it entails a wide spectrum of differential diagnosis. EN being the commonest form of panniculitis seen in practice, there is a tendency among clinicians to label all forms of panniculitides as EN. The present report emphasizes the importance of using the generic term panniculitis for most such patients until careful clinical examination, often combined with histopathological and microbiological studies, had established the exact diagnostic category of panniculitis. This approach is recommended in order to avoid using certain drugs (e.g. steroids) empirically that can have deleterious effects on the clinical outcome. Acknowledgment The help provided by Ms. Lynn Marie Lund, Lecturer, Department of English, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Kuwait University, in the preparation of the manuscript, is gratefully acknowledged. OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO References 1 Callen JP, Zax RH: Panniculitis; in Maddison PJ, Isenberg DA, Woo P, Glass DN (eds): Oxford Textbook of Rheumatology, ed 2. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1993, pp Callen JP: Panniculitis; in Klippel JH, Dieppe PA (eds): Rheumatology. London, Mosby-Year Book Europe, 1994, George DL: Arthritis with skin and nail changes; in Klippel JH, Dieppe PA (eds): Rheumatology. London, Mosby-Year Book Europe, 1994, pp Patterson JW: Differential diagnosis of panniculitis. Adv Dermatol 1991; 6: Soter NA, Franks AG Jr: The skin and rheumatic diseases; in Kelly W, Harris E Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge C (eds): Textbook of Rheumatology, ed 4. Philadelphia, Saunders, 1993, pp Moschella S, Hawley H: Dermatology, ed 3. Philadelphia, Saunders, 1992, pp Malaviya AN, Al-Awadi A, Al-Saeid K, Al-Jarallah K, Shehab D: Letter from Kuwait. Br J Rheumatol 1996; 35: Rayan TJ: Cutaneous vasculitis; in Chapino RH, Burton JL, Ebling FJG (eds): Textbook of Dermatology, ed 5. Cambridge, Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1992, pp Patterson JW: Panniculitis: A guide to differential diagnosis. J Assoc Military Dermatol 1983;9: Penneys NS, Leonardi CL, Cook S, Blauvelt A, Rosenberg S, Eells LD, Konwiser M, Aaronson CM: Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in DNA in five different types of cutaneous lesions by the polymerase-chain reaction. Arch Dermatol 1993;129: Erythema nodosum versus Med Principles Pract 1998;7:
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Clinicopathologic Evaluation of Nodular Cutaneous Lesions of Behçet Syndrome
 Anatomic Pathology / NODULAR CUTANEOUS LESIONS OF BEHÇET SYNDROME Clinicopathologic Evaluation of Nodular Cutaneous Lesions of Behçet Syndrome Cuyan Demirkesen, MD, 1 Nükhet Tüzüner, MD, 1 Cem Mat, MD,
Anatomic Pathology / NODULAR CUTANEOUS LESIONS OF BEHÇET SYNDROME Clinicopathologic Evaluation of Nodular Cutaneous Lesions of Behçet Syndrome Cuyan Demirkesen, MD, 1 Nükhet Tüzüner, MD, 1 Cem Mat, MD,
Bilateral multiple choroidal granulomas and systemic vasculitis as presenting features of tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
 Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
CPC. Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand
 CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
CPC Chutika Srisuttiyakorn, M.D. Kobkul Aunhachoke, M.D. Phramongkutklao Hospital Bangkok, Thailand A 53 year-old woman with fever, facial swelling and rashes on face, trunk and upper extremities for 3
Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases
 Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 246 251 CASE REPORT Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases RASHMI JINDAL* & NADIA SHIRAZI** *Department of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy, Himalayan
Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 246 251 CASE REPORT Uncommon clinical presentations of leprosy: apropos of three cases RASHMI JINDAL* & NADIA SHIRAZI** *Department of Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy, Himalayan
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Collar stud abscess an interesting case report
 Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
manifestations are uncommon. Initial descriptions of the disease (Rosai and Dorfman, 1969) specifically
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
العصوي الوعاي ي الورام = angiomatosis Bacillary
 1 / 7 BACILLARY ANGIOMATOSIS Epidemiology BA is most commonly seen in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a CD4 count less than 50 cells/mm 3, with an incidence of 1.2 cases per
1 / 7 BACILLARY ANGIOMATOSIS Epidemiology BA is most commonly seen in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and a CD4 count less than 50 cells/mm 3, with an incidence of 1.2 cases per
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 5 No 2:16, December Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris Pathak D.* and Thapa A** Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 5 (2): 16 * Consultant Dermatologist, Delhi Dermatology Group Kubba,
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris Pathak D.* and Thapa A** Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 5 (2): 16 * Consultant Dermatologist, Delhi Dermatology Group Kubba,
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA
 CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA Report of two Cases with Clinical and Diagnostic Implications Presented By Dr. Amar Sholapurkar Under the guidance of Dr.Ausaf Ahsan Department of Oral Medicine & Radiology, MCODS,
CHEILITIS GRANULOMATOSA Report of two Cases with Clinical and Diagnostic Implications Presented By Dr. Amar Sholapurkar Under the guidance of Dr.Ausaf Ahsan Department of Oral Medicine & Radiology, MCODS,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma
 Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma Introduction Pages with reference to book, From 280 To 282 Irshad Nabi Soomro ( Department of Pathology, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma Introduction Pages with reference to book, From 280 To 282 Irshad Nabi Soomro ( Department of Pathology, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Elsevier B.V.; この論文は出版社版でありま Right 引用の際には出版社版をご確認ご利用ください This is
 Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa
 Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa Hywel Davies BSc ( ),Andrew J Unwin BSc, Nick P H Morgan BSc Windsor Knee Clinic, Windsor, United Kingdom Correspondence: Hywel Davies, Windsor
Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa Hywel Davies BSc ( ),Andrew J Unwin BSc, Nick P H Morgan BSc Windsor Knee Clinic, Windsor, United Kingdom Correspondence: Hywel Davies, Windsor
Enlarging TB Lymph Node Improving or Deteriorating? History. History. Physical examination. Distribution of lymph nodes
 Enlarging TB Lymph Node Improving or Deteriorating? Dr. Lilian Lee Dr. Hamilton Hui Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine United Christian Hospital 30 August 2006 Enlarging TB lymph node - Improving
Enlarging TB Lymph Node Improving or Deteriorating? Dr. Lilian Lee Dr. Hamilton Hui Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine United Christian Hospital 30 August 2006 Enlarging TB lymph node - Improving
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
VCRC-OMERACT ANCA-Vasculitis Outcome Measure Initiative Comparative Outcome Measure Exercise-Training Cases
 Introduction to Training Cases The purpose of this preliminary exercise is to familiarize you with the rules and logistics of the five instruments under study. Please do not read the Training Cases until
Introduction to Training Cases The purpose of this preliminary exercise is to familiarize you with the rules and logistics of the five instruments under study. Please do not read the Training Cases until
Rheumatologic Emergencies It s not just swollen joints. Joanne Homik Rheumatologist University of Alberta
 Rheumatologic Emergencies It s not just swollen joints Joanne Homik Rheumatologist University of Alberta Or is it? Disclosures No relevant conflicts of interest regarding the content of this presentation
Rheumatologic Emergencies It s not just swollen joints Joanne Homik Rheumatologist University of Alberta Or is it? Disclosures No relevant conflicts of interest regarding the content of this presentation
Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
 To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
Kawasaki Disease. 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD. Children s Specialty Group. All rights reserved.
 Kawasaki Disease 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD Disclosures We have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Describe the characteristic signs and symptoms of Kawasaki
Kawasaki Disease 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD Disclosures We have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Describe the characteristic signs and symptoms of Kawasaki
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months
 A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy
 Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 180 185 CASE REPORT Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy GEETI KHULLAR*, TARUN NARANG*, KUSUM SHARMA**, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA***
Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 180 185 CASE REPORT Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy GEETI KHULLAR*, TARUN NARANG*, KUSUM SHARMA**, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA***
More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa
 More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure None Classification/Overview 1) Necrobiotic/Palisading
More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure None Classification/Overview 1) Necrobiotic/Palisading
Multiple Skin Colored Nodules on both Legs in Patient with Positive QuantiFERON R -TB Gold Test
 pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 29, No. 1, 2017 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.95 CASE REPORT Multiple Skin Colored Nodules on both Legs in Patient with Positive QuantiFERON R -TB
pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 29, No. 1, 2017 https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.1.95 CASE REPORT Multiple Skin Colored Nodules on both Legs in Patient with Positive QuantiFERON R -TB
Sarcoidosis with Skin Manifestations - Two Case Reports and Review of Literature
 Sarcoidosis with Skin Manifestations - Two Case Reports and Review of Literature Pages with reference to book, From 162 To 164 Shamaila Siddiqi, Aleern Qureshi ( Departments of Dermatology, The Aga Khan
Sarcoidosis with Skin Manifestations - Two Case Reports and Review of Literature Pages with reference to book, From 162 To 164 Shamaila Siddiqi, Aleern Qureshi ( Departments of Dermatology, The Aga Khan
RHEUMATIC FEVER AND POST-STREPTOCOCCAL REACTIVE ARTHRITIS
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it RHEUMATIC FEVER AND POST-STREPTOCOCCAL REACTIVE ARTHRITIS What is it? Rheumatic fever has been defined as a disease triggered by infection caused by streptococcus.
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it RHEUMATIC FEVER AND POST-STREPTOCOCCAL REACTIVE ARTHRITIS What is it? Rheumatic fever has been defined as a disease triggered by infection caused by streptococcus.
Kikuchi s disease (necrotizing lymphadenitis) presenting as acneiform eruption
 Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery (2012) 16, 67 71 King Saud University Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery www.ksu.edu.sa www.jssdds.org
Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery (2012) 16, 67 71 King Saud University Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery www.ksu.edu.sa www.jssdds.org
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2).
 22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Sarcoidosis. Julia Rhiannon Harborview/UW Rheumatology November 2010
 Sarcoidosis Julia Rhiannon Harborview/UW Rheumatology November 2010 julrhi@uw.edu outline Introduction/Epi/Genetics Clinical features Acute/Lofgren s vs chronic Pathogenesis Treatment sarc eidos osis flesh
Sarcoidosis Julia Rhiannon Harborview/UW Rheumatology November 2010 julrhi@uw.edu outline Introduction/Epi/Genetics Clinical features Acute/Lofgren s vs chronic Pathogenesis Treatment sarc eidos osis flesh
Acute miliary tuberculosis in a five-month-old boy
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 138-142 Case Report Acute miliary tuberculosis in a five-month-old boy FC Ip and KC Lee A five-month-old boy presented with fever and multiple cutaneous papular
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 138-142 Case Report Acute miliary tuberculosis in a five-month-old boy FC Ip and KC Lee A five-month-old boy presented with fever and multiple cutaneous papular
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
 Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 177-183 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Report Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature 1 2 3
Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 177-183 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Report Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature 1 2 3
DISCUSSION BY: Dr M. R. Shakeebi, MD, Rheumatologist
 Case presentations Related to some Rheumatic Diseases Lab & Clinic i Programs, Tuesday, April 24, 2012 COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD, Immunologist COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD,
Case presentations Related to some Rheumatic Diseases Lab & Clinic i Programs, Tuesday, April 24, 2012 COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD, Immunologist COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD,
Case Rep Dermatol 2009;1:66 70 DOI: / Key Words Coma Blister Barbiturate Overdose Meningoencephalitis
 66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
66 Coma Blisters Joana Rocha a Teresa Pereira a Filipa Ventura a Fernando Pardal b Celeste Brito a Departments of a Dermatology and b Pathology, Hospital de São Marcos, Braga, Portugal Key Words Coma Blister
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Superficial Granulomatous Pyoderma of the Face: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Superficial Granulomatous Pyoderma of the Face: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Sarah M. Persing, MPH, a and Donald Laub Jr, MD, FACS a,b a University of Vermont College of Medicine, Burlington;
Superficial Granulomatous Pyoderma of the Face: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Sarah M. Persing, MPH, a and Donald Laub Jr, MD, FACS a,b a University of Vermont College of Medicine, Burlington;
Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania
 Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 37/Aug 21, 2014 Page 9580
 THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
THE SPECTRUM OF CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY IN CHILDREN: A STUDY IN RURAL NORTH INDIA Pawan Tiwari 1, Satya Kiran Kapoor 2, Madhu Tiwari 3, Yogesh Yadav 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Pawan Tiwari, Satya Kiran
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123
 BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
BSD Self Assessment Workshop 7 th July 2013 CASE 27 RAC6123 M55. 4/7 tender lesions on knee, legs and arms. Also iritis/ weight loss/headache, synovitis.?vasculitis. Sarcoidosis. Biopsy from left elbow
Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion
 Original article: Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion Kavita S Kore, Guruprasad Antin,
Original article: Combined efficacy of pleural fluid lymphocyte neutrophil ratio and pleural fluid adenosine deaminase for the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion Kavita S Kore, Guruprasad Antin,
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Vasculitis Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Hypersensitivity vasculitis/microscopic
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Infections and nonmicrobial inflammatory stimuli can cause leukocytosis (as seen in Lab 1) as well as lymph node enlargement (lymphadenopathy).
 LAB 5: LYMPHOID TISSUE AND SKIN The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the lymphoid tissue and skin. The lymphoid organs include the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Abnormalities in the lymph
LAB 5: LYMPHOID TISSUE AND SKIN The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the lymphoid tissue and skin. The lymphoid organs include the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Abnormalities in the lymph
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS. Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology
 SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
Case Report Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Using Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis: A Case Study
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2015, Article ID 723726, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/723726 Case Report Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Using Polymerase Chain Reaction
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2015, Article ID 723726, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/723726 Case Report Diagnostic Challenges of Tuberculous Lymphadenitis Using Polymerase Chain Reaction
Case Report Traumatic Haemorrhagic Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Underlying Infectious Mononucleosis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2017, Article ID 3097414, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3097414 Case Report Traumatic Haemorrhagic Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Underlying Infectious Mononucleosis
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2017, Article ID 3097414, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3097414 Case Report Traumatic Haemorrhagic Cervical Lymphadenopathy with Underlying Infectious Mononucleosis
So, this is a group of patients that were treated with an anti-inflammatory drug in development within Eli Lilly. The name of the compound was an
 Thank you, Mark and thank you all for being here and sticking with it. This is going to be a little bit of a detour to the left side of the first slide that Mark showed, which is a hypersensitivity allergic-type
Thank you, Mark and thank you all for being here and sticking with it. This is going to be a little bit of a detour to the left side of the first slide that Mark showed, which is a hypersensitivity allergic-type
Lymphatic System Disorders
 Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphomas Malignant neoplasms involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes Specific causes not identified // Higher risk in adults who received radiation during childhood
Lymphatic System Disorders Lymphomas Malignant neoplasms involving lymphocyte proliferation in lymph nodes Specific causes not identified // Higher risk in adults who received radiation during childhood
Kikuchi s Disease. Safaa AlKhawaja* Khatoon Ali** Shameem Shareef ***
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2006 Kikuchi s Disease Safaa AlKhawaja* Khatoon Ali** Shameem Shareef *** Fifteen year old male presented with high grade intermittent fever and cervical
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 3, September 2006 Kikuchi s Disease Safaa AlKhawaja* Khatoon Ali** Shameem Shareef *** Fifteen year old male presented with high grade intermittent fever and cervical
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
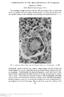 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management
 Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management Poster No.: C-1418 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Song, B. K. Seo, K. R. Cho, O. H. Woo, Y.-S. Kim ; 1 1
Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management Poster No.: C-1418 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Song, B. K. Seo, K. R. Cho, O. H. Woo, Y.-S. Kim ; 1 1
Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders. Raymond P. Wood. History
 Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders Raymond P. Wood Dysfunction of the salivary glands is usually manifested in one of two ways: swelling of the gland, either diffuse or discrete, or by dry mouth (xerostomia).
Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders Raymond P. Wood Dysfunction of the salivary glands is usually manifested in one of two ways: swelling of the gland, either diffuse or discrete, or by dry mouth (xerostomia).
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Name the condition: Canine sterile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet s syndrome)
 5-year-old male miniature Schnauzer dog with acute onset of severe macular erythema and multiple tender violaceus plaques all over the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Canine
5-year-old male miniature Schnauzer dog with acute onset of severe macular erythema and multiple tender violaceus plaques all over the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis? 1. Canine
In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between
 In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between the two, we also propose a classification system for
In our paper, we suggest that tuberculosis and sarcoidosis are two ends of the same spectrum. Given the pathophysiological and clinical link between the two, we also propose a classification system for
Vasculitis. Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology. Vasculitis
 Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Edward Dwyer, M.D. Division of Rheumatology VASCULITIS is a primary inflammatory disease process of the vasculature Determinants of the Clinical Manifestations of : Target organ involved Size of vessel
Buerger s disease manifesting nodular erythema with livedo reticularis
 .Case Report Buerger s disease manifesting nodular erythema with livedo reticularis Tetsuo Takanashi*, **, Reiko Horigome***, Yasuaki Okuda*, Masato Nose**** Masayuki Matsuda**, Shu-ichi Ikeda** *Department
.Case Report Buerger s disease manifesting nodular erythema with livedo reticularis Tetsuo Takanashi*, **, Reiko Horigome***, Yasuaki Okuda*, Masato Nose**** Masayuki Matsuda**, Shu-ichi Ikeda** *Department
Rheumatic Fever And Post-streptococcal Reactive Arthritis
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Rheumatic Fever And Post-streptococcal Reactive Arthritis Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS RHEUMATIC FEVER 1.1 What is it? Rheumatic fever is a disease caused by
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Rheumatic Fever And Post-streptococcal Reactive Arthritis Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS RHEUMATIC FEVER 1.1 What is it? Rheumatic fever is a disease caused by
Vasculitis and Vasculitides. OMONDI OYOO Physician/Rheumatologist; Senior Lecturer, Department of Medicine University of Nairobi
 Vasculitis and Vasculitides OMONDI OYOO Physician/Rheumatologist; Senior Lecturer, Department of Medicine University of Nairobi Definition Presence of leucocytes in the vessel wall with reactive damage
Vasculitis and Vasculitides OMONDI OYOO Physician/Rheumatologist; Senior Lecturer, Department of Medicine University of Nairobi Definition Presence of leucocytes in the vessel wall with reactive damage
Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies
 Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies Directions: Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements in this section is followed by answers or by completions of the statement.
Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies Directions: Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements in this section is followed by answers or by completions of the statement.
Mohammad Reza Shakibi M.D Kerman university of medical sciences (KMU) Shafa Hospital, Rheumatology ward
 VASCULITIS SYNDROMES Mohammad Reza Shakibi M.D Kerman university of medical sciences (KMU) Shafa Hospital, Rheumatology ward ILLUSTRATED CASE 1 A 56 years old lady refered me for prolonged fever, arthritis
VASCULITIS SYNDROMES Mohammad Reza Shakibi M.D Kerman university of medical sciences (KMU) Shafa Hospital, Rheumatology ward ILLUSTRATED CASE 1 A 56 years old lady refered me for prolonged fever, arthritis
Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report
 Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report Surendra Prakash Vyas 1, Dharm Chand Kothari 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner, India 2, Resident, Department
Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report Surendra Prakash Vyas 1, Dharm Chand Kothari 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner, India 2, Resident, Department
الفتوي الاصفر الحبيبوم = Xanthogranuloma_Juvenile JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9
 JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
Liver disease in brucellosis. A clinical and pathological study of 40 cases
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (June 1982) 58, 346-350 PAPERS Liver disease in brucellosis. A clinical and pathological study of 40 cases F. CERVANTES J. CARBONELL S. WEBB M. BRUGUERA L. FORCE Department
Postgraduate Medical Journal (June 1982) 58, 346-350 PAPERS Liver disease in brucellosis. A clinical and pathological study of 40 cases F. CERVANTES J. CARBONELL S. WEBB M. BRUGUERA L. FORCE Department
A Female Van Driver with a Swollen Arm
 A Female Van Driver with a Swollen Arm Charles D Forbes,* William F Jackson,** A 28-year-old female van driver presented with a 5 day history of a swollen, painful left arm. The swelling had started shortly
A Female Van Driver with a Swollen Arm Charles D Forbes,* William F Jackson,** A 28-year-old female van driver presented with a 5 day history of a swollen, painful left arm. The swelling had started shortly
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers. Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities. Evidence of healed ulcers. Dermatitis. Normal ABI.
 Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Case presentation. Dr Rammohan Reddy 1 st year PG, Dept of DVL, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally.
 Case presentation Dr Rammohan Reddy 1 st year PG, Dept of DVL, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. Name : XXX Age : 33 years Sex : Female Occupation : Farmer IP no : 201608905 DOA : 15-02-2016
Case presentation Dr Rammohan Reddy 1 st year PG, Dept of DVL, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. Name : XXX Age : 33 years Sex : Female Occupation : Farmer IP no : 201608905 DOA : 15-02-2016
Citation The Journal of dermatology, 37(1), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Case of localized scleroderma assoc Muroi, Eiji; Ogawa, Fumihide; Yamao Sato, Shinichi Citation The Journal of dermatology, 37(1), Issue Date 2010-01 URL
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Case of localized scleroderma assoc Muroi, Eiji; Ogawa, Fumihide; Yamao Sato, Shinichi Citation The Journal of dermatology, 37(1), Issue Date 2010-01 URL
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA. April 16, 2008
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSIONS LYMPHOMA April 16, 2008 FACULTY COPY GOAL: Learn the appearance of normal peripheral blood elements and lymph nodes. Recognize abnormal peripheral blood
Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
number Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي
 number 12 Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي Morphology of Granulomatous Inflammations The first image (left) shows a lung alveolus in which necrosis is taking place. The image below it shows the
number 12 Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي Morphology of Granulomatous Inflammations The first image (left) shows a lung alveolus in which necrosis is taking place. The image below it shows the
5.1 Breast, Anatomy. 70
 Chapter 5 Breast 5.1 Breast, Anatomy Breasts, also called Mamma are mammary glands, subcutaneously placed on the ventral side of the trunk in mammalian species, and develop for the sole purpose of secreting
Chapter 5 Breast 5.1 Breast, Anatomy Breasts, also called Mamma are mammary glands, subcutaneously placed on the ventral side of the trunk in mammalian species, and develop for the sole purpose of secreting
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center
 LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August 2015; 2(8) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.672
 CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
Cardiac Sarcoidosis. Millee Singh DO Non Invasive Cardiology First Coast Heart and Vascluar
 Cardiac Sarcoidosis Millee Singh DO Non Invasive Cardiology First Coast Heart and Vascluar Introduction Multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown etiology characterized by noncaseating granulomas in
Cardiac Sarcoidosis Millee Singh DO Non Invasive Cardiology First Coast Heart and Vascluar Introduction Multisystem granulomatous disease of unknown etiology characterized by noncaseating granulomas in
UC Davis Dermatology Online Journal
 UC Davis Dermatology Online Journal Title Sweet syndrome with panniculitis, arthralgia, episcleritis, and neurologic involvement precipitated by antibiotics Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9tm147p2
UC Davis Dermatology Online Journal Title Sweet syndrome with panniculitis, arthralgia, episcleritis, and neurologic involvement precipitated by antibiotics Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/9tm147p2
Abstracting Hematopoietic Neoplasms
 CASE 1: LYMPHOMA PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 43yo male with a history of lower gastrointestinal bleeding and melena undergoing colonoscopy and biopsy to rule out neoplasm versus inflammation. Patient had no other
CASE 1: LYMPHOMA PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 43yo male with a history of lower gastrointestinal bleeding and melena undergoing colonoscopy and biopsy to rule out neoplasm versus inflammation. Patient had no other
Refractory Hand Ulceration: A Case of Chronic Ulceration and Sporotrichoid Spread in a Fish Tank Hobbyist following Mycobacterium marinum Infection
 137 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
137 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis: A Case Detected by Breast Cancer Screening Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
