Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders
|
|
|
- Emery Cross
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VAHCS Diffuse Regional Rickets and Osteomalacia Scurvy Parathyroid Disorders Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism Renal Osteodystrophy Metabolic Disorders Thyroid disorders Hyper/ hypothyroidism Thyroid acropachy Acromegaly Gaucher s Paget disease Drug-induced bone disorders Bone Fragility Result of alterations in structural and material properties Causes of fragility Increased bone turnover (abnormal remodeling rate) Mineralization defect (abnormal mineral density) Abnormal collagen Lealli PT, et al., Clin Cases in Min and Bone Metabolism 2009; 6(2): Quantity normal (left) versus osteoporotic (right) bone Quality osteomalacic insufficiency fracture Increased radiolucency of bone Plain film finding Obligates search for etiology DEXA diagnosis Osteoporosis Condition characterized by Qualitatively normal bone Quantitatively deficient bone Diagnosis suggested by w/o other etiology Language of Mineralization Unmasking of the trabecular pattern of the hip and Ward s triangle Compressive Tensile Plain Film Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis for Diffuse Findings Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Hyperparathyroidism Osteogenesis imperfecta Multiple myeloma 2 nd metacarpal index Reinforcement lines/ bone bars Bone resorption Unmasking of vertical trabecular pattern and emphasis of endplate 1
2 Differential Diagnosis for Diffuse Findings - Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Abnormal remodeling rate of bone: resorbed at a greater rate than formed Characterized histologically by cortical thinning and enlargement of haversian canals Mechanical properties show less strength and stiffness Most common cause diffuse osteopenia Diagnosis of exclusion (DEXA) Predisposing factors Female gender, age (postmenopausal), low weight, family history, race (caucasian/asian) Dickensen et al., JBJS 1981; 63B(2): Differential Diagnosis for Diffuse Findings - Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Complications can include both posttraumatic and insufficiency type fractures Vertebral involvement association with high frequency femoral fracture Unclear mechanism Hormonal influences Generalized involutional process aging Dietary factors 50% of post-menopausal fractures do not occur in the setting of osteoporosis, confirming that bone density is not the only determinant of bone strength Focus Session 1 84 yo woman with bilateral hip pain Fosamax Induced Stress Fx Link between prolonged bisphosphonate therapy and atypical femur fractures Bisphosphonate may suppress bone turnover Results in skeletal microdamage accumulation Imaging Findings Fractures located cm below lesser trochanter 79% < or = 5 cm below trochanter Medial beak (85%) and varus angulation Skirt of focal buttressing at lateral cortex Increased propensity for bilateral involvement (12/22) All women aged years On alendronate therapy minimum 4 years up to 14 years Chan, et al., AJR; 194:
3 Imaging Findings Fractures located cm below lesser trochanter 79% < or = 5 cm below trochanter Medial beak (85%) and varus angulation Skirt of focal buttressing at lateral cortex Increased propensity for bilateral involvement (12/22) All women aged years On alendronate therapy minimum 4 years up to 14 years Chan, et al., AJR; 194: Imaging Findings Fractures located cm below lesser trochanter 79% < or = 5 cm below trochanter Medial beak (85%) and varus angulation Skirt of focal buttressing at lateral cortex Increased propensity for bilateral involvement (12/22) All women aged years On alendronate therapy minimum 4 years up to 14 years Chan, et al., AJR; 194: MR Imaging Findings Imaging Findings Fractures located cm below lesser trochanter 79% < or = 5 cm below trochanter Medial beak (85%) and varus angulation Skirt of focal buttressing at lateral cortex Increased propensity for bilateral involvement (12/22) All women aged years On alendronate therapy minimum 4 years up to 14 years Chan, et al., AJR; 194: High association of bilateral involvement with limited symptoms indicate screening of both hips Subset of fractures occur well below the lesser trochanter be sure entire femur is evaluated MR findings can be subtle and focused at endosteum Take Home Points Differential Diagnosis for Diffuse Findings - Osteomalacia Osteomalacia Quality - Defect in mineralization due to decreased blood calcium and phosphate (Vitamin D deficiency causing malabsorption) Decreased calcium gives an error in mineralization Abnormally mineralized osteoid is laid down Quantity - Decreased blood calcium induces secondary hyperparathyroidism HPT results in increased bone turnover 3
4 Differential Diagnosis for Diffuse Findings - Osteomalacia Osteomalacia Complications of abnormal osteoid Acetabular protrusio Looser s zones (incomplete fractures) Pubic rami Ribs Margin scapula Proximal ulna Insufficiency fractures Rickets Nonmineralized bone deposited in region of growth-- resulting in IRREGULAR METAPHYSES Osteomalacia Nonmineralized bone deposited in mature cortical + spongy bone COARSE TRABECULAE Differential Diagnosis for Diffuse Findings - Rickets Rickets Abnormal osteoid in deposited in regions of growth (physis) Changes predominate at sites of rapid growth Prox humerus Distal radius Distal femur Tibia Loss zone of provisional Ca++ Fraying and cupping DDX Metaphyseal Irregularity Rickets Hypophosphatasia Metaphyseal Chondrodysplasia DDX Metaphyseal Irregularity Gymnast wrist Rickets Little Leaguer Shoulder Differential Diagnosis Diffuse Findings - Hyperparathyroidism Increased parathyroid hormone production Major consequence increased rate of remodelling Function PTH Increased PTH Increased Vit D Ca HPO4 Primary 90% due to adenoma Secondary Renal dysfunction (often with osteomalacia) 4
5 Differential Diagnosis Diffuse Findings HPT X-Ray Findings Findings Primary Secondary + + Osteosclerosis rare + Bone resorption + + Brown tumor + -- Soft tissue Ca + + Chondrocalcinosis + rare DDx Diffuse Findings HPT Resorption (Primary or Secondary) Subchondral bone Evident at discovertebral junction with Schmorl s nodes formation Result in delamination of cartilage All findings can be seen in both forms DDx Diffuse Findings HPT Resorption (Primary or Secondary) Subligamentous resorption At sites of ligament origins Calcaneus Pelvis Clavicle DDx Diffuse Findings HPT Resorption (Primary or Secondary) Subperiosteal Most common form affects the radial aspect middle phalanges Especially 2 and 3 DDx Diffuse Findings HPT Chondrocalcinosis (Primary) Common association 18-40% reported Pyrophosphate arthropathy Not common with HPTH DDx Diffuse Findings HPT Brown Tumor (Primary) Localized accumulation of osteoclasts Look for other signs of HPTH to make dx Primary HPTH 5
6 DDx Diffuse Findings HPT Osteosclerosis (Secondary) Classic example Rugger jersey spine Patchy or diffuse Secondary HPTH Mechanism unclear PTH can also stimulate osteoblastic activity DDX Regional Disuse osteoporosis Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Transient Regional Osteoporosis Rheumatologic disorder Infection Disuse Osteoporosis Occurs in immobilized regions often due to trauma Can have aggressive appearance DDX Regional Disuse osteoporosis Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Transient Regional Osteoporosis Rheumatologic disorder Infection Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Also known as Sudeck s atrophy, Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, Causalgia Appears to be mediated by sympathetic nervous system Radiographic findings Soft tissue changes Severe extremity osteopenia Scintigraphic findings reveal increased articular uptake Presentation 1 Month F/U 6
7 Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy DDX Regional Disuse osteoporosis Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Transient Regional Osteoporosis Rheumatologic disorder Infection Transient Regional Osteoporosis Transient Osteoporosis of the Hip Painful Marrow Edema Regional Migratory Osteoporosis Transient Regional Osteoporosis Term applied to conditions that share features: Rapidly developing osteoporosis affecting periarticular bone Self-limited and reversible nature Absence of inciting events Nomenclature Require radiographic dx of osteopenia Progression of one form to another Possible relation to RSD/? Transient ischemia Transient Osteoporosis of the Hip History Original description in women 3rd trimester pregnancy Presented with pain, limp Mild increase ESR Self-limited course Patient demographics Young/ middle aged men Similar sxs, labs, course Initial presentation Transient Osteoporosis of the Hip 1 year later 7
8 Transient Osteoporosis MR Findings Transient Osteoporosis? Insufficiency Fracture Regional Migratory Osteoporosis Migratory in nature Patient demographics Men in 4th or 5th decade Presentation Hip less common than distal LE Local pain and swelling limited time Recurrence at different site, same or opposite extremity Diagnosis???? 30 yo pt with sudden onset L hip pain Transient Painful Marrow Edema Diagnosis???? T1 STIR 8 months after initial presentation pt c/o R hip pain 8
9 Regional Migratory Osteoporosis DDX Regional PD STIR Disuse osteoporosis Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Transient Regional Osteoporosis Rheumatologic disorder Infection Rheumatoid Paget s Disease Arthritis Osteitis Deformans Disease of unknown etiology Periarticular osteopenia Erosive changes Soft tissue swelling causing abnormal remodeling of bone Increased bone remodelling, bone hypertrophy and abnormal bone structure Simultaneous osteoclast and osteoblast activity Accelerated bone turnover leads to formation of abnormal woven bone, irregular arrangement of collagen fibers that are not deposited in lamellar fashion Characterized by thickened, disorganized, coarsened trabeculae Epidemiology Caucasian men over 50 years of age Most common in Great Britain, Australia, USA Clinical presentation Painful in 1/4 patients Deforming Distribution Predominates in axial skeleton Radiographic findings showing 3 phases Paget s Disease Lytic Intense osteoclast activity (lysis) Mixed Cortical accretion, enlarging bone Sclerotic Increased size/density of bone Paget s Disease MR Imaging Findings Increased vascularity with vascular lakes 9
10 Paget s Disease MR Imaging Findings Hyperthyroidism Thyroid Disorders Term used to describe the syndrome of thyrotoxicosis as the result of overproduction of hormones by the thyroid gland proper Most common etiologies Toxic diffuse goiter Toxic nodular goiter Single or multiple adenomas Thyroid Acropachy Unusual manifestation of thyroid disease.5-1% pts with thyrotoxicosis Usually observed after treatment No age or sex predilection Clinical findings Exopthalmos Painless soft tissue swelling fingers/toes Pretibial edema Thyroid Acropachy Thyroid Acropachy Radiographic findings virtually diagnostic Periosteal bone formation Diaphyses MC, MT, proximal and middle phalanges Asymmetric (radial side) Soft tissue swelling DDX Periosteal Reaction Hypertrophic Pulmonary Osteoarthropathy Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy Pachydermoperiostosis Venous stasis Infection Focal Inflammation DDX Periosteal Reaction Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy Pachydermoperiostosis Venous stasis Infection Focal Inflammation 10
11 DDX Periosteal Reaction Drug-induced Bone Disorders Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy Pachydermoperiostosis Venous stasis Infection Focal Inflammation Steroids Alcohol Heparin Dilantin Fluorosis AVN AVN Osteomalacia Periostitis Osteosclerosis Ligament ossification Drug-induced Bone Disorders DDX Osteosclerosis Vitamin D Poisoning Vitamin A Poisoning Prostaglandins Periostitis Osteosclerosis Ligament ossification Periostitis Coned epiphpyses (kids) Periostitis (kids) Renal Osteodystrophy Sickle Cell Anemia Mastocytosis Osteopoikilosis Pyknodysostosis Myelofibrosis Mets/Myeloma/Lymphoma Paget s Disease Athletes Fluorosis Mastocytosis Osteopoikilosis Proliferative disorder of mast cells May show osteoporosis or osteosclerosis Multiple bone islands 11
12 Pyknodysostosis Osteosclerosis, short stature, frontal and occipital bossing Autosomal recessive Acro-osteolysis Metabolic Disorders in the Musculoskeletal System Diffuse Regional Rickets and Osteomalacia Scurvy Parathyroid Disorders Hyperparathyroidism Hypoparathyroidism Renal Osteodystrophy Imaging Thyroid disorders Findings Hyper/ hypothyroidism Thyroid acropachy Acromegaly Gaucher s Paget disease Drug-induced bone disorders Broad Based Category Disease Approach Emphasizing DDx Hot Topics 12
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Renal osteodystrophy revisited: A didactic review of imaging, pathophysiology, and differential diagnosis
 Renal osteodystrophy revisited: A didactic review of imaging, pathophysiology, and differential diagnosis Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors:
Renal osteodystrophy revisited: A didactic review of imaging, pathophysiology, and differential diagnosis Poster No.: C-2174 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors:
Metabolic and Endocrine Bone Disease Imaging. Tumoral Calcinosis
 Metabolic and Endocrine Bone Disease Imaging Tumoral Calcinosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is the most common metabolic bone disorder. It has been defined by the National Institutes of Health as an agerelated
Metabolic and Endocrine Bone Disease Imaging Tumoral Calcinosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is the most common metabolic bone disorder. It has been defined by the National Institutes of Health as an agerelated
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Awaisheh. Mousa Al-Abbadi. Abdullah Alaraj. 1 Page
 f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
Osteoporosis. Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease
 Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Osteoporosis and Lupus. Andrew Ruthberg, MD University Rheumatologists
 Osteoporosis and Lupus Andrew Ruthberg, MD University Rheumatologists 1 Forget the medical terminology (osteoporosis, osteopenia, low bone mass, DEXA, DXA, T score etc) The bottom line is that you don
Osteoporosis and Lupus Andrew Ruthberg, MD University Rheumatologists 1 Forget the medical terminology (osteoporosis, osteopenia, low bone mass, DEXA, DXA, T score etc) The bottom line is that you don
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
BONE REMODELLING. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
Skeletal changes in endocrine disorders
 Skeletal changes in endocrine disorders Poster No.: P-0100 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Poster A. C. O'Brien 1, H. L. khosa 2, A. levai 2, N. Ramesh 2 ; 1 Dublin/IE, 2 Portlaoise/IE Keywords:
Skeletal changes in endocrine disorders Poster No.: P-0100 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Poster A. C. O'Brien 1, H. L. khosa 2, A. levai 2, N. Ramesh 2 ; 1 Dublin/IE, 2 Portlaoise/IE Keywords:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis
 Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Case 4 Generalised bone pain
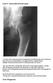 Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders. Nisha Patel, MD
 MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders Nisha Patel, MD 1 Introduction Nearly all imaging modalities evaluate the marrow, which is a site of significant pathology Radiography Nuclear Medicine CT MR 2 Topics
MR Evaluation of Bone Marrow Disorders Nisha Patel, MD 1 Introduction Nearly all imaging modalities evaluate the marrow, which is a site of significant pathology Radiography Nuclear Medicine CT MR 2 Topics
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Diagnostic imaging of. Musculoskeletal diseases
 Diagnostic imaging of Musculoskeletal diseases Investigating methods 1. X ray tha basic technique 2. CT more accurate anatomy, reconstructions 3. MRI bones no, but bone marrow 4. Scintigraphy : osteoblast
Diagnostic imaging of Musculoskeletal diseases Investigating methods 1. X ray tha basic technique 2. CT more accurate anatomy, reconstructions 3. MRI bones no, but bone marrow 4. Scintigraphy : osteoblast
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Metabolic, Endocrine, and Hematologic disease 주선영 가톨릭대학교인천성모병원
 Metabolic, Endocrine, and Hematologic disease 주선영 가톨릭대학교인천성모병원 1 Metabolic disease Ca, P metabolism Vit D metabolism Rickets Nutritional Hypophosphatemic Renal osteodystrophy Hypophosphatasia Hypervitaminosis
Metabolic, Endocrine, and Hematologic disease 주선영 가톨릭대학교인천성모병원 1 Metabolic disease Ca, P metabolism Vit D metabolism Rickets Nutritional Hypophosphatemic Renal osteodystrophy Hypophosphatasia Hypervitaminosis
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Osteoporosis. When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of.
 Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Skeletal Manifestations
 Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older
 Dr Brajesh Nandan Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older patients. Cancers of the breast, prostate,
Dr Brajesh Nandan Skeletal metastases are the most common variety of bone tumors and should always be considered in the differential diagnosis, particularly in older patients. Cancers of the breast, prostate,
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
What is Osteoporosis?
 What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Osteoporosis. Dr. C. C. Visser. MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK) Member: Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK)
 Osteoporosis Dr. C. C. Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK) Member: Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Effect of age on trabecular bone. Fatfree dry bone cylinders obtained
Osteoporosis Dr. C. C. Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK) Member: Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Effect of age on trabecular bone. Fatfree dry bone cylinders obtained
Normal Bone Health and Bone Disease. Mr Ryan Trickett Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon 6 th February 2017
 Normal Bone Health and Bone Disease Mr Ryan Trickett Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon 6 th February 2017 Learning outcomes Understand the structure and function of bone and articular cartilage Explain
Normal Bone Health and Bone Disease Mr Ryan Trickett Consultant Hand and Wrist Surgeon 6 th February 2017 Learning outcomes Understand the structure and function of bone and articular cartilage Explain
Prevention and Treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS 骨質疏鬆的預防與治療
 Prevention and Treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS 骨質疏鬆的預防與治療 Gwo Jaw Wang, M.D. 王國照教授 University of Virginia (U.S.A.) & National Cheng Kung University (Taiwan) Learning Objectives Pathophysiology of osteoporosis
Prevention and Treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS 骨質疏鬆的預防與治療 Gwo Jaw Wang, M.D. 王國照教授 University of Virginia (U.S.A.) & National Cheng Kung University (Taiwan) Learning Objectives Pathophysiology of osteoporosis
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Soft Tissue and Osseous Lesions of the Hip
 Soft Tissue and Osseous Lesions of the Hip Osseous Anatomy Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Osseous Anatomy Osseous Anatomy Gluteus
Soft Tissue and Osseous Lesions of the Hip Osseous Anatomy Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Osseous Anatomy Osseous Anatomy Gluteus
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
1/28/2017. Orthopedic Implications Of Osteoporosis Introduction. Orthopedic Implications Of Osteoporosis Introduction
 The Orthopedic Implications Of Prolonged In Osteoporosis Donald A. Wiss MD Director Of Orthopedic Trauma Cedars Sinai Medical Center Orthopedic Implications Of Osteoporosis Introduction Osteoporosis Most
The Orthopedic Implications Of Prolonged In Osteoporosis Donald A. Wiss MD Director Of Orthopedic Trauma Cedars Sinai Medical Center Orthopedic Implications Of Osteoporosis Introduction Osteoporosis Most
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Case study Group 2 presentation
 Case study Group 2 presentation Patient profile HN 3095-57 Female 60 years old Hometown : Sa Kaeo province Occupation : farmer No drug and food allergy Chief complain Left neck mass 10 years PTA that gradually
Case study Group 2 presentation Patient profile HN 3095-57 Female 60 years old Hometown : Sa Kaeo province Occupation : farmer No drug and food allergy Chief complain Left neck mass 10 years PTA that gradually
Regulation of the skeletal mass through the life span
 Regulation of the skeletal mass through the life span Functions of the skeletal system Mechanical protection skull Movement leverage for muscles Mineral metabolism calcium store Erythropoiesis red blood
Regulation of the skeletal mass through the life span Functions of the skeletal system Mechanical protection skull Movement leverage for muscles Mineral metabolism calcium store Erythropoiesis red blood
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
Know all the bones of the skull, lateral view and frontal view. From the worksheets, one of the earlier ones in this unit.
 Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
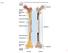 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
1. Define Wolff s Law and give three examples of its application.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.021: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology, IAP 2006 Course Director: Dr. Dwight R. Robinson Final Examination HST.021 February 2, 2001 Name 1. Define
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.021: Musculoskeletal Pathophysiology, IAP 2006 Course Director: Dr. Dwight R. Robinson Final Examination HST.021 February 2, 2001 Name 1. Define
BMD: A Continuum of Risk WHO Bone Density Criteria
 Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis AGING MENOPAUSE OTHER RISK FACTORS RESORPTION > FORMATION Bone Loss LOW PEAK BONE MASS Steven T Harris
Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis AGING MENOPAUSE OTHER RISK FACTORS RESORPTION > FORMATION Bone Loss LOW PEAK BONE MASS Steven T Harris
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Conflict of Interest. Objectives. Learner Outcome
 Foundations of Orthopaedic Nursing Care, Part Four: Metabolic Bone Disease, highlighting Osteoporosis and Paget s Disease Conflict of Interest I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect
Foundations of Orthopaedic Nursing Care, Part Four: Metabolic Bone Disease, highlighting Osteoporosis and Paget s Disease Conflict of Interest I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
The diseases causing insufficiency fractures of the spine in young and middle-aged patients
 The diseases causing insufficiency fractures of the spine in young and middle-aged patients Poster No.: C-2404 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: S. Y. Park, W.
The diseases causing insufficiency fractures of the spine in young and middle-aged patients Poster No.: C-2404 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: S. Y. Park, W.
Trebeculae. Step 4. compact bone. Diploë Pearson Education, Inc.
 Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis
 Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
Practical Management Of Osteoporosis CONFERENCE 2012 Education Centre, Bournemouth.19 November The following companies have given funding towards the cost of this meeting but have no input into the agenda
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Bisphosponate Fractures: Elusive but Dangerous
 Krista Weiss, 2014 Gillian Lieberman, MD October 25, 2013 Bisphosponate Fractures: Elusive but Dangerous Krista Weiss, Tufts Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD Presentation Outline Our Patient:
Krista Weiss, 2014 Gillian Lieberman, MD October 25, 2013 Bisphosponate Fractures: Elusive but Dangerous Krista Weiss, Tufts Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD Presentation Outline Our Patient:
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTEREST PATHOPHYSIOLOGY -MECHANICAL STRESS FRACTURES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITIES
 RELEVANT DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTEREST STRESS FRACTURES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITIES NONE Mark A Foreman M.D. Assistant Professor, UTHSCSA General Orthopedics and Trauma WHAT IS A STRESS FRACTURE? A
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTEREST STRESS FRACTURES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITIES NONE Mark A Foreman M.D. Assistant Professor, UTHSCSA General Orthopedics and Trauma WHAT IS A STRESS FRACTURE? A
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
CIC EDIZIONI INTERNAZIONALI. Bone fragility: current reviews and clinical features. Mini review
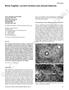 Mini review Paolo Tranquilli Leali, MD, FBSE Carlo Doria, MD, PhD Alexandros Zachos, MD Adriano Ruggiu, MD Fabio Milia, MD Francesca Barca, MD Orthopaedic Department, University of Sassari, Sassari, Italy
Mini review Paolo Tranquilli Leali, MD, FBSE Carlo Doria, MD, PhD Alexandros Zachos, MD Adriano Ruggiu, MD Fabio Milia, MD Francesca Barca, MD Orthopaedic Department, University of Sassari, Sassari, Italy
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health. Noah S. Schenkman, MD
 Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
From Fragile to Firm. Monika Starosta MD. Advocate Medical Group
 From Fragile to Firm Monika Starosta MD Advocate Medical Group Bone Remodeling 10% remodeled each year Calcium homoeostasis Maintain Mechanical strength Replace Osteocytes Release Growth Factors Bone remodeling
From Fragile to Firm Monika Starosta MD Advocate Medical Group Bone Remodeling 10% remodeled each year Calcium homoeostasis Maintain Mechanical strength Replace Osteocytes Release Growth Factors Bone remodeling
Atypical Femoral Fractures Insights and Enigmas
 Atypical Femoral Fractures Insights and Enigmas Madhu Mehta, M.D. Clinical Asst. Prof. of Medicine Department of Immunology/Rheumatology The Ohio State University Abreviations used TFF- Typical femoral
Atypical Femoral Fractures Insights and Enigmas Madhu Mehta, M.D. Clinical Asst. Prof. of Medicine Department of Immunology/Rheumatology The Ohio State University Abreviations used TFF- Typical femoral
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy
 September 2005 Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy Roxanne Landesman, Harvard Medical School Year III Hypothetical Patient A patient presents with persistent right ankle pain, and no history of trauma. As the
September 2005 Hypertrophic Osteoarthropathy Roxanne Landesman, Harvard Medical School Year III Hypothetical Patient A patient presents with persistent right ankle pain, and no history of trauma. As the
Atypical Femoral Fractures With Long Term Bisphosphonates Use
 Atypical Femoral Fractures With Long Term Bisphosphonates Use There has been an increase in the number of atypical femoral fractures in pa4ents on long term bisphosphonate therapy (e.g Fosamax) Accordingly
Atypical Femoral Fractures With Long Term Bisphosphonates Use There has been an increase in the number of atypical femoral fractures in pa4ents on long term bisphosphonate therapy (e.g Fosamax) Accordingly
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines DEXA Scan
 Policy: IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines IEHP considers bone mineral density testing using DEXA medically necessary for members who meet any of the following criteria: Women aged
Policy: IEHP UM Subcommittee Approved Authorization Guidelines IEHP considers bone mineral density testing using DEXA medically necessary for members who meet any of the following criteria: Women aged
Residents Section Pattern of the Month
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Rana et al. Periosteal Reaction Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Rich S. Rana 1 Jim S. Wu Ronald L. Eisenberg Rana RS, Wu JS, Eisenberg
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Rana et al. Periosteal Reaction Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Rich S. Rana 1 Jim S. Wu Ronald L. Eisenberg Rana RS, Wu JS, Eisenberg
Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method
 190.19 - Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method Collagen crosslinks, part of the matrix of bone upon which bone mineral is deposited, are biochemical markers the excretion of which provides a quantitative measurement
190.19 - Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method Collagen crosslinks, part of the matrix of bone upon which bone mineral is deposited, are biochemical markers the excretion of which provides a quantitative measurement
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
