Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
|
|
|
- Julian Hopkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton - cartilages, ligaments and other stabilizing connective tissues The 5 primary functions of the skeletal system are: 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) and lipids (yellow marrow) 3. Blood cell production (red marrow) 4. Protection 5. Leverage (force of motion) II. The Gross Anatomy of Bones, p. 180 Objectives: 1. Classify bones according to shapes and internal tissues. 2. Identify the major types of bone markings. Bone Shapes, p. 180 The 6 major bone shapes are: 1. Long bones 2. Flat bones 3. Sutural bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Short bones 6. Sesamoid bones Figure 6-1a Long bones are long and thin. They are found in arms, legs, hands, feet, fingers and toes. Figure 6-1b Flat bones are thin with parallel surfaces. They are found in the skull, sternum, ribs and scapula. Figure 6-1c Sutural bones are small, irregular bones between the flat bones of the skull. Figure 6-1d Irregular bones are complex shapes such as spinal vertebrae and pelvic bones.
2 Figure 6-1e Short bones are small and thick, including ankle and wrist bones. Figure 6-1f Sesamoid bones are small, flat bones that develop inside tendons near joints of knees, hands and feet. Bone Markings, p. 181 The surface features of bones include depressions or grooves where tendons, ligaments and neighboring bones attach, and tunnels where blood and nerves enter the bone. Table 6-1 describes 19 types of surface features and their functions. Bone Structure, p. 183 Figure 6-2a The femur is a long bone. The long shaft is the diaphysis. The wide part at each end, where the femur articulates with other bones, is the epiphysis. The area where the two connect is the metaphysis. The heavy wall of the diaphysis is made of compact or dense bone. Inside is a central space called the marrow cavity. The epiphysis is made mostly of spongy (cancellous) bone with an open network structure, covered with a thin layer of compact bone called the cortex. Figure 6-2b The parietal bone of the skull is a flat bone, consisting of a sandwich of spongy bone between 2 layers of compact bone. III. Bone Histology, p. 184 Objectives: 1. Identify cell types and functions in bone 2. Compare structures and functions of compact bone and spongy bone Osseous tissue is dense, supportive connective tissue containing specialized cells. The matrix of bone tissue is solid because of the calcium salts deposited around protein fibers in its ground substance. The 4 characteristics of bone tissue are: 1. Dense matrix containing deposits of calcium salts
3 2. The matrix contains bone cells within lacunae, which are organized around blood vessels. 3. Canaliculi form pathways for blood vessels to exchange nutrients and wastes. 4. Outer surfaces of bones are covered by periosteum consisting of outer fibrous and inner cellular layers. The Matrix of Bone, p. 184 Two-thirds of bone matrix is made of calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2, which reacts with calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2 to form crystals of hydroxyapatite, Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, which incorporates other calcium salts and ions as it crystallizes. About 1/3 of bone is protein fibers (collagen). Bone cells are only about 2% of bone mass. The Cells of Bone, p. 184 Bone contains 4 types of cells: 1. osteocytes 2. osteoblasts 3. osteoprogenitor cells 4. osteoclasts Figure 6-3a Osteocytes are mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix. Each osteocyte lives in a lacuna between layers (lamellae) of matrix. Canaliculi through the lamellae allow osteocytes to connect at gap junctions between cytoplasmic extensions. Osteocytes do not divide. The main functions of osteocytes are: 1. To maintain the protein and mineral content of the matrix. 2. To help repair damaged bone (can revert to osteoblast or osteoprogenitor). Osteoblasts are immature bone cells that secrete the matrix by the process of osteogenesis (secretion of proteins and other inorganic compounds of the matrix). Before calcium salts are deposited (forming bone), the matrix is called osteoid. When osteoblasts are surrounded by bone, they become osteocytes. Osteoprogenitor cells are mesenchymal stem cells that divide to produce osteoblasts. Located in the inner, cellular layer of periosteum (endosteum). Assist in repairing bone fractures. Osteoclasts are giant, mutlinucleate cells that secrete acids and protein-digesting enzymes which dissolve bone matrix and release stored minerals (the process of osteolysis).
4 Osteoclasts are derived from the stem cells that produce macrophages. Bone building and bone recycling must be kept in balance. When osteoclasts break down bone faster than osteocytes build bone, bones become weak. Bones get stronger with exercise, which causes osteocytes to build bone. The Structure of Compact Bone, p. 185 Figure 6-5 The basic unit of mature compact bone is a longitudinal unit called the osteon, in which osteocytes are arranged in concentric circles (concentric lamellae) around a central canal containing blood vessels. Perpendicular to the central canal are perforating canals which carry blood vessels deep into the bone and bone marrow. All osteons in long bones run the length of the bone, strengthening the bone in that direction. A layer of circumferential lamellae wraps around the circumference of the long bone and binds all together. The Structure of Spongy Bone, p. 186 Figure 6-6 Spongy bone does not have osteons. Its matrix forms an open network of trabeculae. Spongy bone has no blood vessels in its trabeculae. The space between trabeculae is filled with another tissue, red bone marrow, which has blood vessels and supplies nutrients to the osteocytes. Red bone marrow is red because it forms red blood cells. In other bones, spongy bone may hold yellow bone marrow, which is yellow because it stores fat. Figure 6-7 The femur transfers weight from the hip joint along its length to the knee joint, causing stretching or tension on the outside of the shaft (lateral), and compression on the inside (medial). The Periosteum and Endosteum, p. 188 Figure 6-8 The periosteum covers all bones except the parts of joints enclosed within the joint capsule. It has an outer fibrous layer and an inner cellular layer.
5 The collagen fibers of the periosteum connect the collagen fibers of the bone with those of joint capsules, attached tendons and ligaments (perforating fibers). The periosteum has 3 functions: 1. isolates bone from surrounding tissues 2. provides a route for circulatory and nervous supply 3. participates in bone growth and repair Figure 6-8b Endosteum is an incomplete cellular layer covering the trabeculae of spongy bone in the marrow cavity, and line central canals. Endosteum contains osteoblasts, osteoprogenitor cells and osteoclasts, and is active in bone growth and repair. IV. Bone Formation and Growth, p. 189 Objectives: 1. Compare intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification 2. The timing of bone formation and growth, and differences in internal structure of adult bones Human bones grow until about age 25. The process of replacing other tissues with bone (bone formation or osteogenesis) is called ossification. The process of depositing calcium salts (calcification) occurs during ossification and in other tissues. The 2 main forms of ossification are: 1. intramembranous ossification 2. endochondral ossification Intramembranous Ossification, p. 189 Figure 6-9 Intramembranous ossification, also called dermal ossification because it occurs in the dermis, produces dermal bones such as the mandible and clavicle. There are 3 main steps in intramembranous ossification: 1. Mesenchymal cells aggregate, differentiate into osteoblasts, and begin ossification. The location where ossification begins is the ossification center, from which developing bone grows out in projections called spicules. 2. Blood vessels grow into the area to supply the osteoblasts. Spicules connect, trapping blood vessels inside bone. 3. Spongy bone develops, which can be remodeled into osteons of compact bone, periosteum or marrow cavities. Endochondral Ossification, p. 191
6 Most bones originate as hyaline cartilage which becomes ossified through the process of endochondral ossification. Figure 6-10a (steps 1-6) The growth and ossification of a long bone occurs in 6 steps: 1. Chondrocytes in the center of the hyaline cartilage enlarge and form struts which begin to calcify. The enlarged chondrocytes die, leaving cavities in the cartilage. 2. Blood vessels grow around the edges of the cartilage. Cells in the perichondrium change to osteoblasts, producing a layer of superficial bone around the shaft which will continue to grow and become compact bone (appositional growth). 3. Blood vessels enter the cartilage, bringing fibroblasts that become osteoblasts. Spongy bone develops at the primary ossification center. 4. Remodeling creates a marrow cavity. Bone replaces cartilage at the metaphyses. 5. Capillaries and osteoblasts enter the epiphyses, creating secondary ossification centers. 6. The epiphyses fill with spongy bone. The cartilage remaining within the joint cavity is the articulation cartilage. The cartilage at the metaphysis is the epiphyseal cartilage. Figure 6-11 When the long bone stops growing, after puberty, the epiphyseal cartilage disappears -- but its location is visible on X-rays as an epiphyseal line. Figure 6-10a (step 2) Appositional Growth: The growth of compact bone on the surface (periosteum) of the bone, continues to thicken and strengthen the long bone with layers of circumferential lamellae. The Blood and Nerve Supplies, p. 193 Figure 6-12 As the long bone matures, osteoclasts enlarge the marrow cavity, and osteons form around blood vessels in the compact bone. Three major sets of blood vessels develop: 1. The nutrient artery and vein: a single pair of large blood vessels that enter the diaphysis through the nutrient foramen. (The femur has more than 1 pair.) 2. Metaphyseal vessels supply the epiphyseal cartilage, where bone growth occurs. 3. Periosteal vessels provide blood to the superficial osteons and the secondary ossification centers. The periosteum also contains networks of lymphatic vessels and sensory nerves. V. The Dynamic Nature of Bone, p. 194
7 Objectives: 1. The remodeling and homeostatic mechanisms of the skeletal system 2. The effects of nutrition, hormones, exercise and aging on bone. 3. The types of fractures and how they heal. The adult skeleton must maintain itself and replace mineral reserves. The process that recycles and renews bone matrix is remodeling. Bone remodeling involves osteocytes, osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Key Bone is continually remodeled, recycled and replaced. The rate of turnover varies. When deposition is greater than removal, bones get stronger. When removal is faster than replacement, bones get weaker. Effects of Exercise on Bone, p. 194 Mineral recycling allows bones to adapt to stress. Heavily stressed bones become thicker and stronger. Degenerative changes in the skeleton occur after relatively short periods of inactivity. Up to 1/3 of bone mass can be lost in just a few weeks without stress. Key What you don t use, you lose. The stresses applied to bones during physical activity are essential to maintaining bone strength and mass. Hormonal and Nutritional Effects on Bone, p. 194 Normal bone growth and maintenance requires some nutritional and hormonal factors: 1. A dietary source of calcium and phosphate salts, plus small amounts of magnesium, fluoride, iron and manganese. 2. The hormone calcitriol, made in the kidneys, is essential to proper absorption of calcium and phosphorus by the digestive tract. Calcitriol synthesis requires vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). 3. Vitamins: Vitamin C is required for collagen synthesis, and stimulates osteoblast differentiation. Vitamin A stimulates osteoblast activity. Vitamins K and B12 help synthesize bone proteins. 4. Growth hormone and thyroxine stimulate bone growth. 5. Sex hormones: Estrogens and androgens stimulate osteoblasts for bone growth. 6. Calcitonin and parathyroid hormone regulate calcium and phosphate levels in body fluids. Table 6-2 shows the major hormones involved in bone growth and maintenance. The Skeleton as a Calcium Reserve, p. 196
8 Figure 6-13 Our bones are storage areas for many metabolically active minerals, particularly calcium. Calcium (stored in bones) is the most abundant mineral in the body. Calcium ions are important to membranes and to the intracellular activities of neurons and muscle cells, especially heart cells. Calcium ion concentrations in body fluids must be closely regulated. Calcium ion homeostasis is maintained by the hormones calcitonin and parathyroid hormone, which control calcium ion storage, absorption and excretion. Three sites are controlled: 1. bones, where calcium is stored 2. digestive tract, where calcium is absorbed 3. kidneys, where calcium is excreted Figure 6-14a Parathyroid hormone (PTH), produced by parathyroid glands located in the neck, increases calcium ion levels in body fluids by: 1. stimulating osteoclasts (release calcium stored in bone) 2. increasing intestinal absorption of calcium ions (through its effect on calcitriol) 3. decreasing the rate of calcium excretion at the kidneys. Figure 6-14b Calcitonin, secreted by C cells (parafollicular cells) in the thyroid, decreases calcium ion levels in body fluids by: 1. inhibiting osteoclast activity 2. increasing calcium ion excretion at the kidneys Key Calcium and phosphate ions circulating in the blood are constantly being lost in the urine. These ions must be replaced to maintain homeostasis. If they aren t obtained from the diet, they will be released from storage in the skeleton, making bones weaker. Exercise and a diet with plenty of calcium are necessary to keep bones strong. Fracture Repair, p. 198 Fractures are cracks or breaks in bones caused by physical stress. Fractures are repaired in 4 steps: Figure 6-15a 1. Bleeding produces a clot called the fracture hematoma, establishing a fibrous network. Bone cells in the area die. Figure 6-15b
9 2. Cells of the endosteum and periosteum divide and migrate into the fracture zone. Calluses stabilize the break: A collar of cartilage and bone (external callus) surrounds the break, and an internal callus develops in the marrow cavity. Figure 6-15c 3. Osteoblasts replace the central cartilage of the external callus with spongy bone. Figure 6-15d 4. Osteoblasts and osteocytes continue to remodel the fracture for up to a year, reducing the bone calluses. Figure 6-16 The major types of fractures are: 1. Pott s fracture 2. comminuted fractures 3. transverse fractures 4. spiral fractures 5. displaced fractures 6. Colles fracture 7. greenstick fracture 8. epiphyseal fractures 9. compression fractures VI. Aging and the Skeletal System, p. 199 Objective: 1. The effects of the aging process on the skeletal system The bones of the skeleton become thinner and weaker with age. Reduction in bone mass (osteopenia) begins between ages 30 and 40. Women lose about 8% of bone mass per decade, men about 3%. Epiphyses, vertebrae and jaws are most affected, resulting in fragile limbs, reduction in height, and tooth loss. Osteoporosis is the condition of severe bone loss, extensive enough to impair normal function. Over age 45, 29% of women and 18% of men have osteoporosis. Estrogens and androgens contribute to maintaining bone mass. Bone loss in women accelerates after menopause. Cancerous tissues release a chemical (osteoclast-activating factor) that stimulates osteoclasts and produces severe osteoporosis. SUMMARY In chapter 6 we learned about: - Bone shapes, markings and structure.
10 - The matrix of osseous tissue. - Types of bone cells. - The structures of compact bone. - The structures of spongy bone. - The periosteum and endosteum. - The processes of ossification and calcification. - Intramembranous ossification. - Endochondrial ossification. - Blood and nerve supplies to bone. - Bone minerals, recycling and remodeling. - The effects of exercise on bone. - Hormonal and nutritional effects on bone. - The skeleton as calcium storage. - Fracture repair. - The effects of aging on the skeletal system.
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Module 2:! Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A! Semester 1! !!! !!!! Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb!
 Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Functional Musculoskeletal Anatomy A Module 2: Hard Tissues, Distal Upper Limb & Neurovascular Supply of Upper Limb Semester 1 1 18. Bone Tissue & Growth of Bones 18.1 Describe the structure of bone tissue
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Skeletal System Learning Outcomes 6-1 Describe the primary
Chapter 6. Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Chapter 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Skeletal System The Skeletal System Includes: Bones of the
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 6 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1. irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) The is between the shaft and end. It contains cartilage that is
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 6 SI 1 1. List 5 functions of bones: 2. Classify bones according to shape: give descriptions and examples: long short flat irregular ectopic: sutural (Wormian) ectopic: sesamoid 3. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION
 2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
2 PROCESSES OF BONE OSSIFICATION ENDOCHONDRAL OSSIFICATION 6 STEPS 1. CARTILAGE ENLARGES, BY APPOSITIONAL GROWTH; CHONDROCYTES AT CENTER OF CARTILAGE GROW IN SIZE; MATRIX REDUCES IN SIZE & SPICULES CALCIFY;
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System. Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Osseous Tissue and Skeletal Structure Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The skeletal system is made of: Skeletal bones Cartilage
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides. Chapter 6
 Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Skeletal Tissue Study Slides Chapter 6 Functions of the skeletal system include all of the following, except A. support. B. storage. C. protection. D. blood cell production. E. movement. ANSWER Functions
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
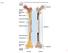 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
Chapter 6: SKELETAL SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS A. Support B. Protection C. Movement D. Mineral storage E. Lipid storage (Fig. 6.8b) F. Blood cell production (Fig. 6.4) II. COMPONENTS A. Cartilage 1. Hyaline 2.
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805 - AB) PAUL ANDERSON 2011 KEY CONCEPTS Unit 6 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A Overview of The Skeletal System 1. Definition: Anatomically the SKELETAL SYSTEM consists of bones, cartilages,
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Chapter 6 Skeletal System
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Chapter 6 Skeletal System Functions of the skeletal system/bone 1. Support skeletal system is the internal framework of the body 2. Protection protects internal organs 3. Movement muscles & bones work
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 6 The Skeletal System: Bone Tissue Introduction The skeletal system has 6 important functions: Provides support Protects the internal organs (brain,
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Chapter 6 Bones and Bone Tissue Chapter Outline Module 6.1: Introduction to Bones as Organs (Figures 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4) A. The skeletal system includes the bones, joints, and their associated supporting
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Bones and Bone Structure
 6 Bones and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Introduction to the Structure and Growth of Bones Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the two main divisions of the skeleton, and list
6 Bones and Bone Structure Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Section 1: Introduction to the Structure and Growth of Bones Learning Outcomes 6.1 Describe the two main divisions of the skeleton, and list
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Types of Bones. 5 basic types of bones: Sutural bones - in joint between skull bones
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bone and their cartilage, ligaments & tendons. Dynamic and ever changing throughout life Skeleton contains all 4 tissue types; Epithelial, connective, muscle and
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07. Bone Function BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. Body Movement interacts with muscles bones act as rigid bar of a lever
 Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
Page 1 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of
SKELETAL SYSTEM CHAPTER 07 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 07 SKELETAL SYSTEM Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill.
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum. Osseous tissue For the body and soft organs. Magnesium, sodium, fluoride Levers for muscle action
 10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
10/1/2016 Cranium Facial s Skull Clavicle Scapula Sternum Rib Humerus Vertebra Radius Ulna Carpals Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) The Skeletal System Vertebral column Sacrum Phalanges Metacarpals Femur
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue. Functions of Bone. Bones
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose,
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
Exam Name 1) An open or fracture projects through the skin. 1) 2) The humerus is an example of a(n) bone. 2) A) flat B) sesamoid C) long D) short E) irregular 3) Accelerated closure of the epiphyseal plates
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1)
 NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
NOTES: Skeletal System (Ch 5, part 1) Individual bones are the organs of the skeletal system. A bone contains very active tissues. BONE STRUCTURE: *Bone structure reflects its function. Parts of a long
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Anatomy & Physiology
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 6 The Skeletal System Paul Anderson 2011 Skeletal System: Components Bones major organs of system, have all functions of system. Cartilages connect & protect bones at
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Skeletal System. Bio 105
 Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Skeletal System Bio 105 Outline I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline. Skeletal System. Tendons link the skeletal and the muscular systems.
 Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Outline Skeletal System Bio 105 I. Overview of the skeletal system II. Function of bones III. Bone structure IV. Bone cells V. Cartilage VI. Tendons and Ligaments VII. Joints VIII. Bone development IX.
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
Trebeculae. Step 4. compact bone. Diploë Pearson Education, Inc.
 Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Bone. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44789 1 Bone OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m44789 1 Bone OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Bone Development. Two Types of OssificaDon 10/18/14. Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages. Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B
 Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Bone Development 6 Bones and Skeletal Tissues: Part B Osteogenesis ( ) bone Dssue formadon Stages Bone formadon begins in the 2nd month of development Postnatal bone growth undl early adulthood Bone remodeling
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Skeletal Tissue: Cartilage and Bone This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Overview of the Skeleton, Classification and Structure of Bones and Cartilages,
Chapter 6. Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
Chapter 6 Bone Tissue Functions of the Skeleton support hold the body up, supports muscles, mandible and maxilla support teeth protection brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs movement limb movements, breathing,
The Skeletal S 1Jstem
 . / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
. / : /~ 4,.',ifṾI : /'i I,"~ ~". ~ /', - 1"';-- '"i-:~.~ I!.,J'" The Skeletal S 1Jstem ". P 'J : ~lj:::' ~,- The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body-cartilage
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
OpenStax-CNX module: m Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin. Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax. Abstract
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m63474 1 Bone Structure * Ildar Yakhin Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Copy and Return to Teacher. The Skeletal System
 Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Copy and Return to Teacher The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system o Bones (skeleton) o Joints o Cartilages o Ligaments Divided into two divisions o Axial skeleton o Appendicular
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58082 1 Human Biology Chapter 15.3: Bone Structure * Willy Cushwa Based on Bone Structure by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Skeletal System Functions
 Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
Chapter 6 Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue 6-1 Skeletal System Functions Support. Bone is hard and rigid; cartilage is flexible yet strong. Cartilage in nose, external ear, thoracic cage and trachea.
The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the erect body. The mandible (jawbone) supports the teeth.
 Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support EXAMPLES: The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight
Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support EXAMPLES: The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight
Skeletal System. Skeletal System 12/15/15. Bone Classification
 Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the
Skeletal System Composed of the body s bones and associated ligaments, tendons, and cartilages. Functions: 1. Support The bones of the legs, pelvic girdle, and vertebral column support the weight of the
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
Unit 5 Skeletal System Nov 21 10:24 PM I. Functions A. Support: > internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > protects vital organs C. Movement: > provides attach
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 2: Skeletogenesis Aug. 18, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Student will describe Development of Bone - the general anatomy of bone
