Save That Foot. The Consequences of Diabetic Neuropathy and the At Risk Foot. Jack W Hutter DPM, C.ped, FACFAS, FAPWCA, Diplomate, ABPFAS
|
|
|
- Tyler Smith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Save That Foot The Consequences of Diabetic Neuropathy and the At Risk Foot Jack W Hutter DPM, C.ped, FACFAS, FAPWCA, Diplomate, ABPFAS
2 General Comments on Neuropathy In the chronic state is peripheral in presentation Can be unilateral but in diabetes mellitus often both feet are involved Glove and sock presentation Diabetics with long standing disease at greatest risk ( > 15 years ) Poorly controlled blood sugar also a contributing factor
3 Etiology Diabetes is the most common disease state to manifest peripheral neuropathy 70% of diabetics have at least mild to moderate peripheral neuropathy Other conditions include spina bifida, Hansen s disease, SLE, immuno-suppression such as cancer and AIDS, B vitamin deficiency, MS, alcoholism, PVD, CMT
4 Demographics Two forms are early onset type I insulin dependent, adult onset non-insulin dependent 16,000,000 diabetics in the US alone Over 700,000 are newly diagnosed each year US diabetes related medical costs exceed $1.4 million yearly 54,000 diabetes related lower extremity amputations per year, 60% of which are preventable with proper care 70% of amputations are preceded by foot ulceration 50% mortality rate within 3 5 years of amputation
5 Neuropathy Considerations General term literally describes an abnormal neurologic condition Can present more localized ( nerve entrapment ), regionally ( sciatica ), Generally (neuromuscular etiology ), whereas diabetes is peripheral Bilateral glove and sock scenario Gradual onset ( painless, decreased sensation, pins and needles, paresthesia type complaints ), sudden onset associated with severe pain Three simultaneously presenting forms autonomic, sensory and motor The microcellular mechanism of neuropathy is unclear, is related to small vessel arterial disease and an associated disruption of intra/extracellular metabolism and nutrient transfer
6 Clinical Findings in Neuropathy Pedal pulses may be palpable ( small vessel disease ) Skin trophic changes dry, scaly, fissures, thin, atrophic ( autonomic ) Structural abnormalities claw toes, drop foot, forms of equinus ( motor ) Insensate digits or portion of or all of one feet, both feet, ankle ( paresthesia, pins, needles, prickling, burning ( sensory ) The rigid, insensate foot is at a greater risk of ulceration, than a flexible, sensate one
7 The Neuropathy Triad Autonomic presentation skin trophic changes, increased injury susceptibility Sensory presentation decreased touch and pain sensation, reduced ability to recognize trauma, increased risk of undetected ulceration with subsequent infection, often resulting in amputation Motor presentation muscle atrophy, structural deformity, drop foot, increased shear forces, foot slap, drag forces, all of which contribute to increased risk of ulceration
8 In Office Testing for Neuropathy Very important, can be the first indication of neuropathy manifestation and /or the onset of diabetes mellitus Symes Weinstein 10 g ( 5.07 ) monofilament is 95% reliable in testing for sensory neuropathy Tuning fork tests for reduced vibratory sensation, often an early deficit in neuropathy ( the feeling of a body part moving in space sensed at a joint, plays a role if subsequent Charcot changes ) Bioesthesiometer also helpful in assessing reduced vibratory sensation Ankle jerk reflex is absent in advanced neuropathy
9 Symes Weinstein Filament Testing Test for LOPS, developed by Birke at the Hansen s Disease Center Monofilament gives single point perception of touch, lack of which infers lack of protective sensation and sensory neuropathy Points of testing ( toes, forefoot, arch, rearfoot ) Test bilateral Patient should not be watching Do not test at points of callus or thickened skin Record keeping helps to track development of neuropathy
10 Symes-Weinstein Filament, Tuning Fork, Neurologic Hammer
11 Symes -Weinstein monofilament Test points Technique
12 The Beginnings of Catastrophe Foot ulceration is the most severe manifestation of neuropathy There are many contributing factors including anatomy, biomechanics, weight with added shear and friction forces, decreased arterial vascular status especially small vessels, footwear, lack of patient knowledge regarding ulcer etiology, non-compliance months opposite limb breakdown TO SAVE THAT FOOT, ULCER PREVENTION IS GOAL #ONE
13 Contributing Factors to Ulceration Abnormal stress against the skin Low pressure over a long time ex. Improper shoe fit, toe box/toe interface Direct injury pressure ex. trauma, heat, chemicals Repetitive moderate pressure ex. metatarsal head prominence with plantar forefoot loading and callus Inappropriate shoe gear contributes to70% of all foot ulcers
14 Further Ulceration Considerations Biomechanical/structural abnormality contributes to abnormal pressures ( HAV, PGD metatarsals, drop foot ) Forefoot fat pad distal migration seen with HDS creating increased metatarsal pressure Intrinsic muscle atrophy in motor neuropathy leading to claw toe, mallet toe with subsequent loading at distal tip of toes Reduced arterial vascular status especially small vessel disease impairs ability of skin to repair trauma Previous site of ulceration greatest area of re-ulceration due to scar tissue, lack of skin elasticity Lack of patient understanding/knowledge regarding ulcer etiology ( barefoot ambulation, improper shoes, lack of daily self foot assessment, check inside of shoes, importance of tight blood sugar control, proper socks, skin texture management ) Poor nutrition Body weight
15 Assessing Arterial Vascular Status Very important in ulcer development and healing prediction Pedal pulses may be palpable, in fact often bounding in Charcot process Integument exam findings are an indicator of vascular status ( skin texture, temperature,dhg) Systems review may indicate claudication,rest pain, numbness Patient history, cardiac disease often accompanies PAD Body temperature thermography Doppler assessment Oximetry ( Tcom )
16 Non Invasive Vascular Testing Arterial Doppler Non palpable PT, DP mark location with hand held Doppler Strength of whooshing sound can provide a clue as to arterial flow Monophasic, biphasic, triphasic wave form on doppler tracing mirrors pulse strength ABI brachial artery /PT, DP ratio, an indicator of arterial inflow to forefoot (normal 1.0 mmhg, or above ) TBI toe/brachial index an indicator of arterial inflow to digits (normal.75 mmhg or above ) ABI less reliable in diabetics due to vessel incompressibility, arteriosclerosis
17 Non Invasive Vascular Testing Tissue Oximetry T com ( Ptc O2 ), transcutaneous oxygen measurement Tertiary assessment of tissue perfusion ( primary -pedal pulses, secondary ABI, TBI ) More reliable than ABI in diabetic in predicting local arterial vascular status and healing Very important in wound care, indicates amount of O2 perfusion of tissues at the point of the lesion Can also be used if contemplating surgery on a diabetic Values > 40 normal healing, impaired healing, < 30 healing not likely Also used to predict effectiveness of hyperbaric O2 therapy ( O2 challenge during oximetry, Tcom value >200, hyperbaric O2 therapy will be 88% effective )
18 Through the Podiatrist s Eye We see the perils neuropathy when associated with abnormal mechanical forces that lead to ulceration Harris mat used to assess these forces Current research at the Scholl College of Podiatric Medicine using remote sensors to monitor local pressures on the foot and joint movements in predicting and controlling neuropathy associated pathology Evaluation of the wear patterns on shoe gear and insoles provide clues to abnormal forces, future problems Local skin color and texture changes, combined with callus patterns, can be an ominous sign
19 Reading Callus Patterns Creates A Map For Ulcer Prevention Local erythema is an early indicator of abnormal pressure, friction Pain is not a reliable indicator of problems Blistering or hyperkeratosis with subsequent ulceration may follow Plantar metatarsal head level is most common site for ulceration, 3 rd MTPJ #1 > digits > 1 st met head > 5 th met head > midfoot > heel Midfoot pressure less common unless associated with chronic Charcot rocker bottom deformity
20 Callus Pattern Etiologies Metatarsal head level -plantar displaced metatarsals -abnormal metatarsal length pattern -cavus foot with plantar flexed 1 st metatarsal - -rearfoot or forefoot equinus -rigid plantarflexed 1 st metatarsal plus equinus recipe for disaster Hallux Valgus -pinch callus, soft corn, medial pressure lesion Hammer digits -soft corn, dorsal pressure lesion Distal digital lesion -claw toe, mallet toe, sometimes associated with drop foot Heel lesion usually associated with debilitation
21 Comments About Charcot Arthropathy A Periosteal neuropathy ( non cutaneous ), pedal pulses are palpable, often bounding Acute Charcot clinical picture shows extreme local edema, erythema and local temperature increase, but no pain Contrary to osteomyelitis, no break in skin X-rays show destructive changes Triphasic bone scan, bone biopsy diagnostic 30% T MTPJ, 30% MTPJ Healing times RF 12 mo., MF 9 mo., FF 6 mo. Chronic Charcot clinical picture local edema, no local temperature increase, minimal erythema, Ulceration predisposition secondary to rocker bottom deformity and gait disturbance
22 Chronic Charcot foot with rocker bottom deformity
23 Podiatric Intervention to Save That Foot Non Surgical Regular patient visits for podiatric care Patient and family education Appropriate shoes and break in period Diabetic socks Custom multiple density shoe inserts ( remember the callous patterns ) Pedorthic shoe modifications ( remember the callous patterns ) AFO Surgical Preventative intervention Definitive correction, usually amputation Ulcer management, covered in the Wound Care Update lecture Wound closure
24 Non Surgical Foot Ulcer Prevention Thoughts on Patient Education 86% of amputations are preventable with patient education and proper shoe gear Etiology of 1 out of 5 foot ulcers is care giver related Non loading force exercise without increased risk of foot trauma ( walking creates 150% of body weight force, running 300% ) Daily patient self foot exam, with patient aware that the exam may be compromised by the disease process Evaluate the level of understanding of the patient of the disease process ( may need to have family members present at consultation ) Strive to have the patient proactive and motivated at prevention
25 Non Surgical Foot Ulcer Prevention Purposes of Patient Education Improve foot problem knowledge Prevent escalation of a simple problem to a more severe one with early detection Reduce infection, amputation rates Have patient and family involved in the decision making process Self Care Education Foot washing techniques ( no soaking, non drying soap ) Avoid dehydration No adhesives No barefoot ambulation Proper callus, toenail care Daily self foot exam Check inside of shoes before putting them on
26 Non Surgical Foot Ulcer Prevention Appropriate Shoe Gear Off the shelf shoe or custom molded shoe Extra depth with deep round toe box, soft leather or Neoprene upper, crepe outer sole, lace up closure Diabetic socks ( adequate stretch, cushioned heel and forefoot, no seam at toes, toe socks for excessive inter digital maceration ) Shoe fit 1/2in. to ¾ space beyond longest toe Vamp pinch test for adequate width and upper material softness Pedorthic modifications include flared lateral heel and or sole as varus deformities are common in neuropathy, rocker sole, metatarsal bar, stiff shank especially important if FF or mid foot amputation, sole expansion Shoe break in period Shoe stretch if necessary
27 Shoe Gear Hierarchy Logarithm Primary choice Considered when confronted with a mild deformity ( structural deformity without hyperkeratosis or neuropathy) Off the shelf extra depth shoes, custom made multi density padded inserts Secondary choice Considered when confronted with moderate deformity ( pre ulcerative structural deformity with hyperkeratosis and neuropathy ) Off the shelf shoes, custom made multi density padded orthoses, pedorthic shoe modifications Tertiary choice Consider when confronted with severe deformity (structural deformity with ulceration /amputation history and neuropathy ) Custom molded shoes, custom made multidensity padded and modified orthoses, pedorthic shoe modifications Quaternary choice Consider when confronted with most severe deformity, usually either after calcanectomy or Chopart amputation Neuropathic walker, AFO with rigid extension and filler for mid and forefoot
28 The Role of Pedorthics in Foot Ulcer Prevention Diabetic orthoses Full length, total contact, filling in spaces between the shoe and the foot Corrections are added to the bottom or inbetween layers of the orthosis Partial weight bearing casting Material synergy must relieve pressure and shear forces Plastizote, P-cell, Poron, puff, crepe are preferred materials Forefoot block for partial amputation, leave adequate space between block and stump, AFO, dropfoot brace for severe instability, dropfoot
29 The Role of Pedorthics in Foot Ulcer Prevention Shoe modifications External Rocker sole - Charcot, PGD mets, HDS Metatarsal bar - PGD mets Medial buttress PPV + Charcot Stiff shank -FF or MF amp Lateral flare -varus deformity Sole expansion - HAV Negative heel- forefoot offload Internal Sole excavation-charcot Stretching-HAV, HDS
30 When The Best Laid Plans The combination of the patient being unaware of the impending problem and ineffective unloading of pressure sets up the scenario. Trauma>callus>inflammation>hematoma>ulceration >infection>ineffective wound care for multiple reasons>cellulitis, sepsis>gangrene>amputation
31 Surgical Management of Diabetic Foot ulceration management Incision and drainage if abscess Regular in office surgical debridement In hospital or surgery center ulcer excision with resection of tissue and bone These topics will be covered more extensively in the Wound Care lecture Complications Wound closure Primary wound closure if non infected and good wound margins Skin graft ( split thickness, full thickness, rotational, advancement)
32 Surgical Management of Foot Diabetic Complications 1. Preventative intervention with deformity correction Early intervention can be cost effective Onychoplasty for onychocryptosis, toenail dystrophy Digital tendon release for claw toe, mallet toe Metatarsal osteotomy for severe tylomata Bunionectomy for hallux valgus 2. Definitive correction, usually amputation associated with gangrene, osteomyelitis Determining amputation level -Point of demarcation or necrosis - -vascular assessment indicating satisfactory level of circulation for prediction of healing (arterial doppler, oximetry more preferrable) functional considerations are very important, always try to leave the most ambulatory stump, avoid transfer lesion
33 Types of Gangrene Dry Tissue is dry, shriveled and black in color Line of demarcation between viable and dead tissue Non painful May be self limiting Wet Tissue reddish purple in color Moist and swollen, no line of demarcation Painful Tissue necrosis, often associated with infection
34 Levels of Amputation Hallux interphalangeal joint or 1 st MTPJ disarticulation Lesser toe(s) interphalangeal joint - level or lesser MTPJ disarticulation Ray amputation distal metatarsal amputation Distal forefoot amputation midshaft metatarsals 1-5 Lisfranc metatarsal/cunieform joint level Chopart talus/cunieform joint level
35 Ist Ray Amputation Lesser Toe IPJ Amputation
36 Functional Considerations and Amputation Hallux amputation interphalangeal joint level, leave a portion of proximal phalangeal base for sesamoid/fhb function Partial digital amputation for distal toe lesion, consider joining flexor and extensor tendons at interphalangeal joint capsule Single 2nd ray amputation preferred over 2 nd MTPJ disarticulation, less likely to cause HAV In all partial forefoot amputations consider subsequent equinus deformity Calcanectomy will need neuropathic walker or patellar tendon bearing orthosis Always try to leave as much residual stump as functionally acceptable, avoid transfer pressure
37 Case Study The Slippery Slope Initial problem was osteomyelitis under 2 nd MPJ resulting in 2 nd ray amputation Subsequently developed ulceration at tip of 3 rd, 4 th toes which became gangrenous resulting in digital amputations, Currently developed pre - ulcerative transfer lesion under 1st Mpj Also has concurrent Charcot arthropathy left midfoot being treated with a total contact cast Vascular status is excellent Significant neuropathy Poorly controlled blood sugars
38 In Conclusion, To Save That Foot. Neuropathy is a major contributor to diabetic foot complications, many cases of which are preventable Multiple factors contribute to neuropathy Treatment of the neuropathic foot must include patient education combined with pedorthic/podiatric applications Judicious preventative surgical intervention can be helpful in preserving as much of the foot as possible Functional/mechanical considerations must be taken into account when definitive surgery is indicated Post surgical pedorthic/podiatric followup is critical to reduce further complications
39 Acknowledgment to AOPP Thank you!
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped
 Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C. Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot. Glossary of Terms
 Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Podiatry in Practice. Alan M. Singer, DPM, FACFAS
 Podiatry in Practice Alan M. Singer, DPM, FACFAS Podiatry in Practice Alan Singer, D.P.M. UNIVERSITY PODIATRY GROUP Onychomycosis Anti-fungals Onychocryptosis (Ingrown Nails) Ingrown Nails Partial Nail
Podiatry in Practice Alan M. Singer, DPM, FACFAS Podiatry in Practice Alan Singer, D.P.M. UNIVERSITY PODIATRY GROUP Onychomycosis Anti-fungals Onychocryptosis (Ingrown Nails) Ingrown Nails Partial Nail
Care of the Diabetic Patient
 Care of the Diabetic Patient Aarti Deshpande, CPO Clinic Manager Zuckerberg San Francisco General Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, San Francisco March 16, 2017 Diabetes Diabetes
Care of the Diabetic Patient Aarti Deshpande, CPO Clinic Manager Zuckerberg San Francisco General Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, San Francisco March 16, 2017 Diabetes Diabetes
Introduction. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment
 Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith
 Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith Ingrown Toenails Paronychia (infected toenail) Onychomycosis (fungal nails) From improper trimming, leaving nail sharp corners Curved nails Thick (Hypertrophic)
Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith Ingrown Toenails Paronychia (infected toenail) Onychomycosis (fungal nails) From improper trimming, leaving nail sharp corners Curved nails Thick (Hypertrophic)
Aetiology Macroangiopathy occurs mainly distally ie Popliteal artery There is arterial wall calcification Microangiopathy is less common
 DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care
 The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
Charcot Arthropathy of the Foot & Ankle. MTAPA Annual Meeting June 2018 Emily Harnden, MD
 Charcot Arthropathy of the Foot & Ankle MTAPA Annual Meeting June 2018 Emily Harnden, MD Background Disclosures None Learning Objectives Define the disease Recognize presenting signs/symptoms for proper
Charcot Arthropathy of the Foot & Ankle MTAPA Annual Meeting June 2018 Emily Harnden, MD Background Disclosures None Learning Objectives Define the disease Recognize presenting signs/symptoms for proper
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Rapid Foot Screening
 GP Symposium 2015 Workshop Rapid Foot Screening Ms Chelsea Law, Principal Podiatrist Mr Henry Lee, Podiatrist Ms Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Ms Polly Lim, Podiatrist Ms Wong Wan Mun, Podiatrist Mr Yeo Boon
GP Symposium 2015 Workshop Rapid Foot Screening Ms Chelsea Law, Principal Podiatrist Mr Henry Lee, Podiatrist Ms Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Ms Polly Lim, Podiatrist Ms Wong Wan Mun, Podiatrist Mr Yeo Boon
Diabetes Mellitus and the Associated Complications
 Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA
 Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA Charcot 1. What is it? (definition) & Who gets it? (epidemiology
Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA Charcot 1. What is it? (definition) & Who gets it? (epidemiology
High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC
 High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC A new paradigm? Foot ulceration 101 Assessing Perfusion a new challenge Pressure
High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC A new paradigm? Foot ulceration 101 Assessing Perfusion a new challenge Pressure
Surgical Off-loading. Reiber et al Goals of Diabetic Foot Surgery 4/28/2012. The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration
 Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot
 Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
Helen Gelly, MD, FUHM, FCCWS
 Helen Gelly, MD, FUHM, FCCWS Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor that impairs wound healing, making foot wounds one of the major problems of diabetes. Over 60% of lower limb amputations in the US
Helen Gelly, MD, FUHM, FCCWS Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor that impairs wound healing, making foot wounds one of the major problems of diabetes. Over 60% of lower limb amputations in the US
The Diabetic Foot Latest Statistics
 The Diabetic Foot Latest Statistics There are 2.6 million people with diagnosed diabetes in the UK. There are predicted to be 500,000 who have the condition but are unaware of it. There are 11,859 in TH
The Diabetic Foot Latest Statistics There are 2.6 million people with diagnosed diabetes in the UK. There are predicted to be 500,000 who have the condition but are unaware of it. There are 11,859 in TH
Project I - Background Worksheet. Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu. Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers
 Project I - Background Worksheet Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1) Strategic Focus based on the Strategic focus powerpoint presentation and readings a. Team
Project I - Background Worksheet Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1) Strategic Focus based on the Strategic focus powerpoint presentation and readings a. Team
Conservative Management to Restore and Maintain Function in Limb Preservation Patients
 Conservative Management to Restore and Maintain Function in Limb Preservation Patients Tyson Green, DPM Department Chair Imperial Health Center for Orthopaedics Lake Charles, LA Founder & Medical Director
Conservative Management to Restore and Maintain Function in Limb Preservation Patients Tyson Green, DPM Department Chair Imperial Health Center for Orthopaedics Lake Charles, LA Founder & Medical Director
Diabetes - Foot Care
 Diabetes - Foot Care Introduction People with diabetes are more likely than others to have problems with their feet. These problems can lead to dangerous infections of the foot. Recognizing and treating
Diabetes - Foot Care Introduction People with diabetes are more likely than others to have problems with their feet. These problems can lead to dangerous infections of the foot. Recognizing and treating
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태
 Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Podiatric Medicine: Best Foot Forward. Dr. Kevin J. DeAngelis, DPM Brandywine Family Foot Care 213 Reeceville Rd. Suite 13 Coatesville, PA
 Podiatric Medicine: Best Foot Forward Dr. Kevin J. DeAngelis, DPM Brandywine Family Foot Care 213 Reeceville Rd. Suite 13 Coatesville, PA What is a Podiatrist? Specially trained physician specializing
Podiatric Medicine: Best Foot Forward Dr. Kevin J. DeAngelis, DPM Brandywine Family Foot Care 213 Reeceville Rd. Suite 13 Coatesville, PA What is a Podiatrist? Specially trained physician specializing
ORTHOTI MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FEET. Tarun Kumar Kulshreshtha, Clinical Prosthetist & Orthotist, Guest Facutly, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India
 ORTHOTI MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FEET Tarun Kumar Kulshreshtha, Clinical Prosthetist & Orthotist, Guest Facutly, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India INTRODUCTION Diabetic Melitus is a group of metabolic
ORTHOTI MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FEET Tarun Kumar Kulshreshtha, Clinical Prosthetist & Orthotist, Guest Facutly, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India INTRODUCTION Diabetic Melitus is a group of metabolic
10/19/2017. Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI. Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis
 Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis Understand the systemic effects of diabetes on the lower extremity The significance of structural and biomechanical
Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis Understand the systemic effects of diabetes on the lower extremity The significance of structural and biomechanical
Peripheral Neuropathy
 Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Diabetic Foot Complications
 Diabetic Foot Complications Podiatry Specialty Clinic YKHC Bethel, Alaska August 1-3, 2017 Charles C. Edwards, DPM Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Peripheral Neuropathy Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Foot Complications Podiatry Specialty Clinic YKHC Bethel, Alaska August 1-3, 2017 Charles C. Edwards, DPM Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Peripheral Neuropathy Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
DIABETES AND FOOTCARE
 DIABETES AND FOOTCARE Self-Care and Treatment for Healthy Feet Don t Take Your Feet for Granted Every day, you depend on your feet to keep you moving. But when you have diabetes, your feet need special
DIABETES AND FOOTCARE Self-Care and Treatment for Healthy Feet Don t Take Your Feet for Granted Every day, you depend on your feet to keep you moving. But when you have diabetes, your feet need special
Diabetes Foot Care Clinical Pathway Healthcare Provider s Guide
 Diabetes Foot Care Clinical Pathway Healthcare Provider s Guide Diabetes, Obesity & Nutrition Strategic Clinical Network Version 1.0 Acknowledgement This healthcare provider s guide has been adapted from
Diabetes Foot Care Clinical Pathway Healthcare Provider s Guide Diabetes, Obesity & Nutrition Strategic Clinical Network Version 1.0 Acknowledgement This healthcare provider s guide has been adapted from
Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to
 Page 1 The Diabetic Foot Definition Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to the inability of the body's insulin to perform its normal everyday
Page 1 The Diabetic Foot Definition Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to the inability of the body's insulin to perform its normal everyday
Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities
 Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities The following table provides the description for several foot deformities: hammer toe, claw toe, hallux deformity, pes planus, pes cavus and charcot arthropathy.
Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities The following table provides the description for several foot deformities: hammer toe, claw toe, hallux deformity, pes planus, pes cavus and charcot arthropathy.
Forefoot Procedures to Heal and Prevent Recurrence. Watermark. Diabetic Foot Update 2015 San Antonio, Texas
 Forefoot Procedures to Heal and Prevent Recurrence Diabetic Foot Update 2015 San Antonio, Texas J. Randolph Clements, DPM Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics Virginia Tech- Carilion School of Medicine
Forefoot Procedures to Heal and Prevent Recurrence Diabetic Foot Update 2015 San Antonio, Texas J. Randolph Clements, DPM Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics Virginia Tech- Carilion School of Medicine
PRESCRIPTION FOOTWEAR
 PRESCRIPTION FOOTWEAR Standards of Practice for Chiropodists and Podiatrists I. Introduction Prescription footwear is an integral part of patient care for the management of lower extremity pathology and
PRESCRIPTION FOOTWEAR Standards of Practice for Chiropodists and Podiatrists I. Introduction Prescription footwear is an integral part of patient care for the management of lower extremity pathology and
Case Study 2 - Mr J. Medical history
 Case Study 2 - Mr J A 54 year-old male was referred to the podiatrist at Coast Provincial General Hospital Diabetic Clinic, for management of active foot disease. The patient s presenting complaint was
Case Study 2 - Mr J A 54 year-old male was referred to the podiatrist at Coast Provincial General Hospital Diabetic Clinic, for management of active foot disease. The patient s presenting complaint was
Practical advice when treating feet
 Practical advice when treating feet Helen Mandic Clinical Lead Podiatrist in Health Promotion and Student Mentor Department of Podiatry and Foot Health Dawlish Hospital Falls Prevention The Role of the
Practical advice when treating feet Helen Mandic Clinical Lead Podiatrist in Health Promotion and Student Mentor Department of Podiatry and Foot Health Dawlish Hospital Falls Prevention The Role of the
Localized collection of pus in a cavity
 Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Comprehensive Diabetic Foot Exam, WorryFree DME SM Shoe Order Form
 Comprehensive Diabetic Foot Exam, WorryFree DME SM Shoe Order Form First perform CDFE, then use WorryFree DME! Perform CDFE on 50% or more of patients with Medicare and diabetes and qualify for PQRS end
Comprehensive Diabetic Foot Exam, WorryFree DME SM Shoe Order Form First perform CDFE, then use WorryFree DME! Perform CDFE on 50% or more of patients with Medicare and diabetes and qualify for PQRS end
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION. Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot)
 AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
Financial Disclosure. Turf Toe
 Seth O Brien, CP, LP Financial Disclosure Mr. Seth O'Brien has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Turf Toe Common in athletes playing on firm, artificial turf Forceful
Seth O Brien, CP, LP Financial Disclosure Mr. Seth O'Brien has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Turf Toe Common in athletes playing on firm, artificial turf Forceful
National Aboriginal Diabetes Association
 National Aboriginal Diabetes Association 2015 To increase awareness of diabetes and foot care management Disclaimer: This presentation is offered as educational information and shall not be used as a substitute
National Aboriginal Diabetes Association 2015 To increase awareness of diabetes and foot care management Disclaimer: This presentation is offered as educational information and shall not be used as a substitute
Therapeutic Shoes for Diabetics
 Last Review Date: August 11, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.03bC8v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: August 11, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.03bC8v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Address: Left Leg. other: Nails: thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal
 South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot 2011
 DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225 231. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2253 IWGDF GUIDELINES Practical guidelines
DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225 231. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2253 IWGDF GUIDELINES Practical guidelines
3 section of the Foot
 TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
The Diabetic Foot. Michael Anthony, DPM. 422 million diabetic million % adult population 90% Type II
 The Diabetic Foot Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence of Diabetes 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
The Diabetic Foot Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence of Diabetes 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
The Diabetic Foot. Prevalence of Diabetes United States. Prevalence of Diabetes
 The Diabetic Foot Prevalence of Diabetes Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
The Diabetic Foot Prevalence of Diabetes Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists
 EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
Happy Feet: Feeling good about diabe.c foot screening! Family Medicine Forum 2014, Quebec City November 14, 2014
 Happy Feet: Feeling good about diabe.c foot screening! Family Medicine Forum 2014, Quebec City November 14, 2014 Dr. Michael Yan, MD, CCFP Clinical Lecturer, Department of Family Medicine, University of
Happy Feet: Feeling good about diabe.c foot screening! Family Medicine Forum 2014, Quebec City November 14, 2014 Dr. Michael Yan, MD, CCFP Clinical Lecturer, Department of Family Medicine, University of
AGONY FEET. The. of the. Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers
 The AGONY of the FEET Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers By Margaret Falconio-West, BSN, rn, APN/CNS, CWOCN, DAPWCA Nearly 25 percent of people with diabetes will develop a diabetic foot
The AGONY of the FEET Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers By Margaret Falconio-West, BSN, rn, APN/CNS, CWOCN, DAPWCA Nearly 25 percent of people with diabetes will develop a diabetic foot
Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study
 The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
The Journal of Diabetic Foot Complications Transmetatarsal amputation in an at-risk diabetic population: a retrospective study Authors: Merribeth Bruntz, DPM, MS* 1,2, Heather Young, MD 3,4, Robert W.
Front line management of the Diabetic Foot
 Front line management of the Diabetic Foot n o ti e b a i D + s te k o Sm = g in p Am a t u Sam Fratesi MD Smoking + diabetes = amputation Almost 2 million Canadians have diabetes In amputated diabetics
Front line management of the Diabetic Foot n o ti e b a i D + s te k o Sm = g in p Am a t u Sam Fratesi MD Smoking + diabetes = amputation Almost 2 million Canadians have diabetes In amputated diabetics
Index. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 865 869 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alpha-lipoic acid, in diabetic neuropathy, 764 Amputation(s), lower-extremity, in diabetes, 791
Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 865 869 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alpha-lipoic acid, in diabetic neuropathy, 764 Amputation(s), lower-extremity, in diabetes, 791
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
DIABETES AND YOUR FEET
 FOOTNOTES DIABETES AND YOUR FEET Diabetes is chronic disease that occurs when your body s ability to process sugars, starches, and other foods into energy is impaired. Some of the long-term effects of
FOOTNOTES DIABETES AND YOUR FEET Diabetes is chronic disease that occurs when your body s ability to process sugars, starches, and other foods into energy is impaired. Some of the long-term effects of
I have no financial interests to disclose in regards to this lecture.
 Evaluation and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcerations John M. Giurini, D.P.M. Associate Professor in Surgery Harvard Medical School Disclosure Statement I have no financial interests to disclose in regards
Evaluation and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcerations John M. Giurini, D.P.M. Associate Professor in Surgery Harvard Medical School Disclosure Statement I have no financial interests to disclose in regards
Lesser toe deformities
 PATIENT INFORMATION Lesser toe deformities What are lesser toe deformities? Lesser toe deformities are caused by changes in normal anatomy that create an imbalance between the foot s muscle groups (intrinsic
PATIENT INFORMATION Lesser toe deformities What are lesser toe deformities? Lesser toe deformities are caused by changes in normal anatomy that create an imbalance between the foot s muscle groups (intrinsic
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust
 How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT
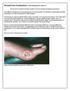 Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
I also call this lecture
 I also call this lecture GO BUCKS!!! My Background Cornerstone University Grand Rapids, MI Kent State University College of Podiatric Medicine (OCPM) Florida Hospital East Orlando 3 year surgical residency
I also call this lecture GO BUCKS!!! My Background Cornerstone University Grand Rapids, MI Kent State University College of Podiatric Medicine (OCPM) Florida Hospital East Orlando 3 year surgical residency
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Common Foot Disorders Justin Wernick, DPM, C.Ped. NY College of Podiatric Medicine Orthopedic Department, New York, NY 2 Common
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Common Foot Disorders Justin Wernick, DPM, C.Ped. NY College of Podiatric Medicine Orthopedic Department, New York, NY 2 Common
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS
 CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
Maintaining Remission Induced Frailty by Offloading Bijan Najafi, PhD. Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas, USA
 Maintaining Remission Induced Frailty by Offloading Bijan Najafi, PhD Professor of Surgery Director of Clinical Research, Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy Director of Interdisciplinary
Maintaining Remission Induced Frailty by Offloading Bijan Najafi, PhD Professor of Surgery Director of Clinical Research, Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy Director of Interdisciplinary
Prevention Of Falls In Older People With Diabetes. Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Toylyn Lee, Snr Physiotherapist
 Prevention Of Falls In Older People With Diabetes Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Toylyn Lee, Snr Physiotherapist Content Assessments - Foot assessment - Physical mobility Management - Footwear/callus - Exercise
Prevention Of Falls In Older People With Diabetes Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Toylyn Lee, Snr Physiotherapist Content Assessments - Foot assessment - Physical mobility Management - Footwear/callus - Exercise
Diabetes Foot Health and Prevention Program:
 Diabetes Foot Health and Prevention Program: A Podiatrist / RN Collaborative Practice Dr. Pamela Monk Visiting Podiatrist drpamelamonk@live.ca(204) 391-9719 Danna Ferry RN Ferry RN Services dlferry@live.ca
Diabetes Foot Health and Prevention Program: A Podiatrist / RN Collaborative Practice Dr. Pamela Monk Visiting Podiatrist drpamelamonk@live.ca(204) 391-9719 Danna Ferry RN Ferry RN Services dlferry@live.ca
Podiatric Medicine: Your Partner in Patient Care
 Podiatric Medicine: Your Partner in Patient Care Craig Herman, D.P.M. Diplomat A.B.P.O.P.P.M. Director of Podiatry, Community Healthcare Network Advanced Foot Care, Bronx, New York; Owner/Operator Diabetes
Podiatric Medicine: Your Partner in Patient Care Craig Herman, D.P.M. Diplomat A.B.P.O.P.P.M. Director of Podiatry, Community Healthcare Network Advanced Foot Care, Bronx, New York; Owner/Operator Diabetes
People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy.
 Form: D-5821 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy. Diabetes raises
Form: D-5821 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy. Diabetes raises
Foot Care. Taking steps towards good FOR AT-RISK FEET. HIGH RISK of developing serious. Person with Diabetes
 Taking steps towards good Person with Diabetes Foot Care FOR AT-RISK FEET Your healthcare professional has found that as a person with Diabetes your feet have a HIGH RISK of developing serious problems
Taking steps towards good Person with Diabetes Foot Care FOR AT-RISK FEET Your healthcare professional has found that as a person with Diabetes your feet have a HIGH RISK of developing serious problems
Injuries to the Foot. NOCROP Sports Medicine and Therapy
 Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Wound Jeopardy: Name That Wound Session 142 Saturday, September 10 th 2011
 Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board (WOCNCB) Certified Foot Care Nurse (CFCN) Detailed Content Outline
 Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board (WOCNCB) Certified Foot Care Nurse (CFCN) Detailed Content Outline Description Domain I: Assessment and Care Planning 010000 40 Task 1: Obtain focused
Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board (WOCNCB) Certified Foot Care Nurse (CFCN) Detailed Content Outline Description Domain I: Assessment and Care Planning 010000 40 Task 1: Obtain focused
Common Injuries & Ailments
 Common Injuries & Ailments Basic Understanding Tendonitis/ Soft tissue injuries Tendonitis is an inflammation of a tendon. It typically has a pattern of pain when it s cool, improves when it warms up,
Common Injuries & Ailments Basic Understanding Tendonitis/ Soft tissue injuries Tendonitis is an inflammation of a tendon. It typically has a pattern of pain when it s cool, improves when it warms up,
Patient Product Information
 Patient Product Information REGEN-D 150 (India's First Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf) Gel for Diabetic Foot Ulcers) Generic name: [Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf)]
Patient Product Information REGEN-D 150 (India's First Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf) Gel for Diabetic Foot Ulcers) Generic name: [Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf)]
Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction
 Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction VOLUME: 23 PUBLICATION DATE: Apr 01 2010 Issue Number: 4 April 2010 Author(s): Lawrence DiDomenico, DPM, FACFAS While tendon transfers have
Essential Insights On Tendon Transfers For Digital Dysfunction VOLUME: 23 PUBLICATION DATE: Apr 01 2010 Issue Number: 4 April 2010 Author(s): Lawrence DiDomenico, DPM, FACFAS While tendon transfers have
Foot Care. Taking steps towards good FOR AT-RISK FEET. HIGH RISK of developing serious. Person with Diabetes
 Taking steps towards good Person with Diabetes Foot Care FOR AT-RISK FEET Your healthcare professional has found that as a person with Diabetes your feet have a HIGH RISK of developing serious problems
Taking steps towards good Person with Diabetes Foot Care FOR AT-RISK FEET Your healthcare professional has found that as a person with Diabetes your feet have a HIGH RISK of developing serious problems
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing
 Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Will it heal? How to assess the probability of wound healing Richard F. Neville, M.D. Professor of Surgery Chief, Division of Vascular Surgery George Washington University Limb center case 69 yr old male
Preservation of the First Ray in Patients with Diabetes
 Preservation of the First Ray in Patients with Diabetes Surgical approaches are often necessary to off-load excessive pressure. By Derek Ley, DPM, and Barry Rosenblum, DPM Introduction In approaching diabetic
Preservation of the First Ray in Patients with Diabetes Surgical approaches are often necessary to off-load excessive pressure. By Derek Ley, DPM, and Barry Rosenblum, DPM Introduction In approaching diabetic
Wound Classification. Overview
 Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Patient & Family Guide. Diabetic Foot Ulcer.
 Patient & Family Guide Diabetic Foot Ulcer 2018 www.nshealth.ca Diabetic Foot Ulcer What is a diabetic foot ulcer? The term foot ulcer is used to describe an open sore that happens below the ankle and
Patient & Family Guide Diabetic Foot Ulcer 2018 www.nshealth.ca Diabetic Foot Ulcer What is a diabetic foot ulcer? The term foot ulcer is used to describe an open sore that happens below the ankle and
Statistics on DM and DFU risk
 Disclosure NOTHING Statistics on DM and DFU risk National Institute of Diabetes Digestive & Kidney Diseases: As of September 2011 an estimated 16 million Americans are known to have diabetes, with many
Disclosure NOTHING Statistics on DM and DFU risk National Institute of Diabetes Digestive & Kidney Diseases: As of September 2011 an estimated 16 million Americans are known to have diabetes, with many
Integumentary Physical Therapy 피부계물리치료학
 Integumentary Physical Therapy 피부계물리치료학 Dong-Ryul Lee, PT, Ph.D. Movement Impairment Specialist & Performance Enhancement Specialist Neurofeedback, Robotics & Virtual Reality Research Specialites: NeuroRehabilitation
Integumentary Physical Therapy 피부계물리치료학 Dong-Ryul Lee, PT, Ph.D. Movement Impairment Specialist & Performance Enhancement Specialist Neurofeedback, Robotics & Virtual Reality Research Specialites: NeuroRehabilitation
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS. Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2
 NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
Case Report: Diabetic Foot
 Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Ana León (2), Juan Ignacio Acosta (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, Sapin; ibv@ibv.upv.es
Sergio Puigcerver (1) ; Juan Carlos González (1) ; Roser Part (1) ; Eduardo Brau (1) ; Ana León (2), Juan Ignacio Acosta (2) (1) Instituto de Biomecánica de Valencia, UPV. Valencia, Sapin; ibv@ibv.upv.es
Diabetic Foot Problems
 http://www.medicine-on-line.com Diabetic foot disease: 1/12 Diabetic Foot Problems Author: Affiliation: Rebecca Wong BN, MSc(Health Care) Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong SAR Introduction Diabetes Mellitus
http://www.medicine-on-line.com Diabetic foot disease: 1/12 Diabetic Foot Problems Author: Affiliation: Rebecca Wong BN, MSc(Health Care) Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong SAR Introduction Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes-Diabetes Mellitus About one in five people with diabetes will enter the hospital for foot problems. DIABETIC FOOT PROBLEMS by Robert
 Diabetes-Diabetes Mellitus About one in five people with diabetes will enter the hospital for foot problems. DIABETIC FOOT PROBLEMS by Robert Frykberg, DPM Foot problems are leading causes of hospitalization
Diabetes-Diabetes Mellitus About one in five people with diabetes will enter the hospital for foot problems. DIABETIC FOOT PROBLEMS by Robert Frykberg, DPM Foot problems are leading causes of hospitalization
BUCKS MSK: FOOT AND ANKLE PATHWAY GP MANAGEMENT. Hallux Valgus. Assessment: Early Management. (must be attempted prior to any referral to imsk):
 Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
Lesser Toe Correction
 Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Lesser Toe Correction Lesser toe deformities are classified
Richard M. Marks, MD Professor and Director Division of Foot and Ankle Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Medical College of Wisconsin Explanation: Lesser Toe Correction Lesser toe deformities are classified
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated June 10,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months.
 Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
Case 57 What is the diagnosis? Insidious onset forefoot pain in a 50 year old female for last 3 months. Diagnosis: II MTP instability Demographics of MT instability Lesser MTP joint instability occurs
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
A Patient s Guide to Bunions. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Bunions Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Bunions Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
fitting shoes, or repetitive stress. It also frequently arises from unknown causes.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, 2013
 Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon. Monday, 29 April 13
 Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April 2013 Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Monday, 29 April 13 Topics Forefoot pain Hindfoot/Ankle pain Hallux rigidus Bunions Toe deformity Mortons
Common Foot and Ankle Pathology DOTS 17th April 2013 Nick Savva Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Surgeon Monday, 29 April 13 Topics Forefoot pain Hindfoot/Ankle pain Hallux rigidus Bunions Toe deformity Mortons
Lesser toe sequential repair
 Lesser toe sequential repair For the correction of lesser toe deformity Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is lesser toe deformity? The lesser toes are those other than your
Lesser toe sequential repair For the correction of lesser toe deformity Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is lesser toe deformity? The lesser toes are those other than your
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief?
 Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
Common Foot and Ankle Conditions: How Can You Find Relief? Your Feet and Ankles are Workhorses They bear a lot of weight They perform various movements Common Conditions That Cause Foot/Ankle Pain Plantar
