HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL, PUDUCHERRY
|
|
|
- Melanie Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.06 Research Article HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF GRANULOMATOUS LESIONS IN A TEACHING HOSPITAL, PUDUCHERRY Sandhya Panjeta Gulia, M. Lavanya, Archana V., S. P. Arun Kumar, Kalaivani Selvi Department of Pathology, Sri Venkateshwaraa Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Ariyur, Pondicherry, India; JIPMER, Pondicherry, India. ABSTRACT Aims: The present study is done to study the frequency, morphology and to find out the etiology of granulomatous lesions by clinicopathologic correlation wherever possible. Materials and methods: A retrospective analysis of 75 biopsy sections was done from August 00 July 04. Diagnosis was confirmed by haematoxylin and eosine stained slides alongwith the special stains wherever required. Results: A total of 75 cases of granulomatous lesions were identified of which 4(56.0%) were malesand 33(44.0%) were females. Granulomas due to tuberculosis accounted for the majority of the types of granulomas,i.e,46 cases(6.33%), followed by 7 (9.33%)cases of foreign body granulomas, 5 (6.67%) fungal granulomas, 4 (5.33%) actinomycosis, granulomas of unknown etiology were 4(5.33%) cases of granulomatous synovitis, (.33%) cases of granulomatous cystitis and 5 (6.67%) cases of non infectious skin granulomas. The granulomatous skin lesions reported were mostly infectious 3(4.0%) leprosy, (.67%) lupus vulgaris, 3(4.0%)cases of actinomycosis, (.33%) scrofuloderma, and fungal granulomas (.67%) subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis (.33%) maduramycosis, (.33%) chromoblastomycosis, (.33%)zygomycosis; 5(6.67%)non infectious skin granulomas reported as granuloma annulare, erythema nodosum and acne agmeneta. Granulomatous lesions of the genitourinary tract constituted 8(0.67%) cases 3 (4.0%) tuberculosis of cervix and fallopian tube, 4 (5.33%) tuberculousepididymoorchitis and scrotal abscess; (.33%) granulomatous cystitis. Tuberculous lesions affecting the gastrointestinal tract were 3(4.0%)cases of fistula in ano, (.33%) appendicular tuberculosis and (.33%) case rectum.(.33%) case each of tuberculosis of spine and actinomycosis of tonsil was reported. AFB stain was positive in 4 (30.43%) cases of tuberculosis. Conclusion: Tuberculosis was the commonest cause of granulomatous lesion and lymph nodes were the most common site affected. Epithelioid type of granuloma was the most common morphology. Key Words: Epithelioid, Granuloma, Lymph nodes, Tuberculosis INTRODUCTION Granulomas are a characterstic microscopic finding of chronic inflammation. Granulomatous inflammation is considered as a response to pathogens and persistent irritants of exogenous and endogenous origin []. Granulomas are discrete collections of histiocytes with admixture of multinucleated giant cells and inflammatory cells []. The granulomas are formed as a result of series of events that involves the interplay of antigen (persistent endogenous / exogenous) resulting in activation of cell mediated type IV hypersensitivity reaction, activation of macrophages, T and B cell responses with release of chemical mediators of inflammation mainly cytokines. Classification of granulomas based on etiology could be: bacterial, fungal, viral/chlamydial, helminthic, foreign body type and unknown cause [3]. According to the morphology granulomas can be classified as: epithelioid, histiocytic, foreign body, necrobiotic/palisading and mixed inflammatory [3]. It is imperative to find out the correct etiology of the granulomatous lesions to start the appropriate treatment so correlating the clinical history with the histopathological findings proves to be valuable in establishing the correct diagnosis in majority of the cases. The present study was undertaken to find out the frequency, morphology and etiology where ever possible, Corresponding Author: Corresponding Dr. Sandhya Panjeta Author: Gulia, Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sri Venkateshwaraa Medical College Hospital and Research Anil Centre, Pawar, Ariyur, Assistant Pondicherry, Professor, India, Department sandhya_path@yahoo.com of Zoology, D.A.V. College for Girls, Yamunanagar (Haryana); Mobile: ; sumanil7@yahoo.co.in Received: Revised: Accepted: Received: Revised:.7.04 Accepted: Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05 78
2 of granulomatous lesions in the teaching hospital, and to compare with the similar studies. MATERIALS AND METHODS A retrospective study conducted in the department of Pathology, Sri Venkateshwaraa Medical College Hospital & Research Centre, Puducherry on the biopsies recieved from August 00 July 04 to analyse the frequency of granulomatous lesion. Alongwith routine haematoxylin and eosine stained sections, special stains like acid fast stain, fitefaraco and PAS stain was done wherever required. RESULTS A total of 75 cases of granulomatous lesions were identified out of which 4(56.0%) were male patients and 33(44.0%) were females with M:F ratio of being.7:. The maximum number of cases, 8 (37.33%), were reported in the age group of 30 years; only one case was less than 0 years and 5 (6.67%) cases were more than 60 years age(table ). Table : Showing distribution of granulomas according to the age group: Age group(yrs) No. of cases % < > Total cases Granulomas due to tuberculosis (Fig. ) accounted for the majority,i.e,46 cases(6.33%), followed by foreign body granulomas 7 (9.33%), fungal granulomas 5 (6.67%), actinomycosis4 (5.33%). Among the seven cases of foreign body granulomas, the most common etiologic agent was ruptured epidermal cyst with keratin and cholesterol granuloma in 4(5.33%) cases and xanthoma in 3(4.0%)cases. Granulomas of unknown etiology were 4(5.33%) cases of granulomatous synovitis, (.33%) case of granulomatous cystitis and 5 (6.67%) cases of non infectious skin granulomas. Figure : Shows percentage of types of granulomas According to the site of distribution (Table )the majority of cases of tuberculosis, 8(4%),were reported in the lymph nodes with 8 (44.44%) cases positive for acid fast stain. Bones and soft tissues accounted for total of 7(.67%) cases of granulomatous lesions reported as tuberculousosteomyelitis, soft tissue tuberculosis, foreign body granulomas and granulomatous synovitis with no case showing acid fast positivity. Table : Showing sitewise distribution of granulomatous lesions S. no Site Diagnosis No. % Special stains. Lymph node Tuberculosis cases AFS +. Bone Tb Osteomyelitis Soft tissue Foreign body granuloma Tuberculosis 4. Skin Leprosy Lupus vulgaris Scrofuloderma Actinomycosis Madura mycosis Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis Chromoblastomycosis Acne agmineta Erythema nodosum Granuomaannulare Zygomycosis Spine Tuberculosis FFS + AFS + Gram + PAS+ PAS+ PAS+ 6. Rectum Tuberculosis.33 AFS + 7. Synovium Granulomatous synovitis Cervix Tuberculosis Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05
3 9. Testis Tb epididymoorchitis AFS + 0. Tonsil Actinomycosis.33 Gram +. Fistula in ano. Scrotal abscess Tuberculosis Tuberculosis Appendix Tuberculosis Fallopian tube 5. Urinary bladder Total cases Tuberculosis.67 Granulomatous cystitis The granulomatous skin lesions reported were mostly infectious 3(4.0%) leprosy, (.67%)lupus vulgaris which showed acid fast positivity in both cases, 3(4.0%) cases of actinomycosis, (.33%) case ofscrofuloderma, and 5 (6.67 %) cases of fungal granulomas, (.67%) subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis, (.33%)case of maduramycosis,(.33%) case of chromoblastomycosis, (.33%)case of zygomycosis; 5(6.67%)cases of non infectious skin granulomas reported as granuloma annulare, erythema nodosum and acne agmeneta. Granulomatous lesions of the genitourinary tract constituted 8(0.67%) cases 3 (4.0%) tuberculosis of cervix and fallopian tube, 4 (5.33%) tuberculousepididymoorchitis and scrotal abscess; (.33%) granulomatous cystitis. Tuberculous lesions affecting the gastrointestinal tract were 3(4.0%)cases of fistula in ano, (.33%) appendix and (.33%) case in rectum. (.33%) case each of tuberculosis of spine and actinomycosis of tonsil were reported. DISCUSSION Majority of granulomatous lesions in our study were seen among the males 4 (56%) as compared to the females 33 (44%) with maximum number of cases in the age group of 30 years. These results were similar to the studies done by Adhikari RC et al [4], Permi HS et al [5] and Pawale JS [3] and Patel et al [6]. The present study showed that the etiology of the majority of granulomatous lesions was infectious in 57 (76%) cases which is in accordance to the study done by Bal et al [7]. In the present study the majority of the granulomas, 8(4%) cases, were reported in lymph nodes similar to the findings of Adhikari [4] who also reported lymph nodes (4.%) as the commonest site of granulomas followed by skin and subcutaneous tissue (.0%), bones and joints (.5%), respiratory system (7.7%) and gastrointestinal tract (5.5%). Whereas Permi HS et al [5] in his study reported majority of the granulomas in skin and subcutaneous tissue with 68(4.7%) cases followed by lymph nodes in 59(.46%)cases. In the study done by Permi HS [5] in 0, lymph node tuberculosis was reported in 53(40.76%) cases, tuberculosis of bones and synovium in 35(6.9%)cases, cutaneous tuberculosis in 4(3.08%),intestinal tuberculosis in 4(0.76%),sinus tract in 4(3.08%) cases, fallopian tube in (.54%), bladder in 3 (.30%) and kidney, lung, breast, epididymis in (0.76%) case each. Patel et al [6] in 03 reported 55% granulomas in lymph nodes, 5% respiratory tract, 8% skin, 5% GIT, 9% bones and joints, 0% head and neck, 6% reproductive system and 4% others. Whereas in the present study lymph node tuberculosis was reported in 8(4.0%)cases, skin and soft tissue tuberculosis in 9 (.0%) cases, tuberculous osteomyelitis in 7(9.33%) cases, tuberculosis of rectum in (.33%) case, appendicular tuberculosis in (.33%), tuberculosis in female genital tract in 3(4.0%) cases, and tuberculosisin male genital tract in 4(5.33%) cases. Adults seem to develop tuberculousepididymoorchitis by direct spread from the urinary tract [8]. The usual presentation is painful inflamed scrotal swelling that is difficult to differentiate from acute epididymo orchitis [9]. The diagnosis requires comprehensive evaluations histology,cytology and microbiological investigations and further clinical follow up to avoid complications [0]. The most common cause of granuloma in our study was found to be tuberculosis in 6.33% cases which is similar to the findings of the studies done by Adhikari RC [4] et al in 6.7%, Permi HS [5] reported in 47.6%, Pawale JS in 49.4% [3] and Patel et al in 06 (8%) cases [6] who also reported tuberculosis as the commonest cause of granuloma. In the study conducted by Pawale et al [3],ZN stain was positive in 9(.6%) out of 84 casesof tubercular granuloma. Whereas it was positive in 9(7%) out of 8 cases in the study of Krishnaswamy et al []. The study done by Permi HS [5] demonstrated tubercle bacilli in 7(0.74%) out of 30 cases. Whereas the findings of the present study are in contrast to the other studies where out of the total 46 cases of tubercular granulomas, acid fast stain was positive in 4(30.43%) and negative in 3 (69.57%)cases. The liquefaction of necrotic focus is considered to be associated with increased proliferation of AFB and infiltration of neutrophils with a high degree of hypersensitivity reaction []. In the study done by Chakrabarti et al [3] it was found out that culture positivity was found only in 3% cases of tuberculosis because of dead and altered organisms in the tissues. Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05 80
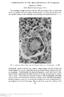
4 The most common type of granuloma reported in the present study is necrotizing epithelioid type in 46 (6.33%) cases (Fig. ) with the other types being epithelioid with suppuration (usually seen in fungal granulomas) 5 (6.67%), foreign body granulomas 7 (9.33%), necrobiotic granuloma (.67%) cases and also mixed inflammatory type (where the differential diagnosis of fungal infections and tuberculosis should be considered ) and histiocytic granulomas. In tuberculosis different types of granulomas can be encountered on histopathology like epithelioid granuloma without necrosis, chronic nonspecific granuloma, chronic nonspecific inflammation, epithelioid granuloma with necrosis and abscess [3]. Adhikari RC [4] also reported epithelioid granuloma as the commonest type in his study. Pawale JS [3] described tuberculoid granuloma 98 (57.65%), histiocytic granulomas in 9 (7.06%), foreign body granulomas in 7 (0.00%), ill defined granulomas in 3 (7.65%), mixed inflammatory granulomas in (6.47%) and necrobiotic granulomas in (.8%). The commonest morphological pattern found in the study done by Permi HS et al [5] was epithelioid 65 (60% ), foreign body 35 (.7%), ill defined 9 (0.54%), histiocytic 3 (8.36%), mixed inflammatory 9 (6.9%) and necrobiotic granulomas in 4 (.45%) cases. Apart from tuberculosis, epithelioid granulomas are also seen in sarcoidosis, leprosy, fungal infections, crohns disease and tumor associated; epithelioid granulomas with suppuration can be seen in fungal infection, tuberculosis, catscratch disease and leishmaniasis; histiocytic granulomas found in parasitic infestation and fungal infections; foreign body granulomas seen as a reaction to foreign body; mixed inflammatory granulomas seen in parasiticinfestation, tuberculosis, leishmaniasis and chalazion [4]. In the skin granulomas of unknown etiology, (.67%) cases each of granuloma annulare and erythema nodosum and (.33%) case of acne agminata were reported. A case of perforating granuloma annulare was reported in 38 years male with multiple punched out ulcers over the trunk and proximal extremities covered by black eschar for which clinical differential diagnosis of ecthymagangrenosum and papulonecrotictuberculid was suggested. The biopsy picture showed degenerated collagen and mucin material surrounded by histiocytes. The mucin nature was suggested by PAS stain (Fig. 3) which showed a strong positivity. These findings were similar to those described by Pawale et al in their study [3]. These findings were similar to the observation made by Gautam et al [4],Billet A et al [5] and Joana Alexandra [6] reported 4(3.7%) cases of granuloma annulare. Figure 3: (H&E. 0x) shows degenerated PAS positive collagen and mucin material in a case of perforating granuloma annulare. Acne agminata is idiopathic in etiology, though the histopathology shows tuberculoid granulomas, all other relevant investigations for tuberculosis were negative in the case similar to the case reported by Sule [7]. Figure : (H&E, 0x) shows lymph node structure replaced by multiple granulomas due to tuberculosis. Out of the 30 cases of leprosy the fitefaraco stain was positive in 7(56.66%) and negative in 3(43.33%) cases in the study done by Pawale [3] whereas in the study done by Nayak et al it was positive in 5(44.64%) and negative in 3(55.35%) cases [8]. It was positive in only 9(5.7%) cases and negative in 3(55.36%) cases in the study done by Permi HS et al [5].Whereas in our study, the stain was positive in one case of borderline tuberculoid leprosy (Fig. 4)& (Fig. 5). 8 Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05
5 zygomycosis, and (.33%) chromoblastomycosis. The H & E stained sections of zygomycosis showed presence of broad septate hyphae with focal bulbous dilatations which was more evidently depicted in PAS stain. It was found that the patient was having diabetes mellitus due to which he developed secondary fungal lesion of cutaneous zygomycosis / mucormycosis. The microscopic picture of chromoblastomycosis sections revealed microabscessesand granulomatous infiltrate in the dermis with multiple brown coloured copper penny bodies. Figure 4: (H&E, 0x) shows structure of skin with underlying dermis showing periappendegeal granulomas in case of borderline tuberculoid leprosy. Figure 6: ( H& E, 0x) shows pigmented brown fungal colony in the centre (Madura mycosis) surrounded by mixed inflammatory cells. Figure 5: (Fitefaraco stain, 00x) shows structure of skin with underlying dermis showing aggregates and clusters of pink rod shaped lepra bacilli. The commonest fungal lesion found in the study done by Pawale et al were 3(30%) cases of madura mycosis followed by cases(0%) rhinosporiodosis, (0%) cases of P.boydii and one case each of histoplasmosis and mucormycosis [3] whereas in the study done by Chavan SS et al rhinosporiodosis formed the majority, 34 (68%), of cases of fungal granulomas followed by madura mycosis in 8(6%)cases [9]. In the study done by Permi HS et al [5] fungal infections were aspergillus in 6(5%),rhinosporiodosis 4(6.6%), chromoblastomycosis in 3(.5%), pseudolleshcheriaboydii in (8.33%), subcutaneous entomphothormycosis in (4.6%),mucormycosis in (8.33%),cryptococci in (8.33%), madura mycosis in (4.6%) and candida in (4.6%) case. In the study by Gautam K et al, cutaneous chromoblastomycosis comprised.8% cases [4]. Whereas our study showed (.67%) cases of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis, (.33%) madura mycosis (Fig. 6), (.33%) All 4(5.33%)cases of actinomycosis showed suppurative granulomas with central actinomycotic colonies seen on Haematoxylin & Eosine(Fig. 7) stained slides were confirmed by gram staining which showed gram positive filaments. These findings are comparable to the findings ofpawale JS [3], Permi HS et al [5], Mirza M et al [0] which was similar in our study. It is always advisable to search for the organisms in the centre of necrotic granulomas rather than peripheral viable and inflammatory tissue. Figure 7: (H&E, 0x) Actinomycosis: shows suppurative granulomas composed of sulphur granules(filaments) arranged radially with club shaped eosinophilic material. Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05 8
6 In the study conducted by Permi HS [5], foreign body granulomas were encountered in 3 cases epidermal cyst with keratin and cholesterol granulomas in 3(56.5%) cases, xanthomas 4(7.4%) cases, sinus tract in (8.7%) cases, bile induced granulomas in (8.7%) cases and gouty arthritis in (8.7%) cases. In our study 7 cases of foreign body granulomas were reported and the probable etiologies identified were foreign body reaction to keratin and cholesterol, xanthogranuloma, suture granuloma and granuloma in the sinus tract. In the study of Permi HS et al [5],(8.0%) cases of granulomas were of unknown etiology, PawaleJS et al [3] reported (6.47%) cases of granulomas of unknown etiology, i.e, granulomatous mastitis, granuloma annulare, sarcoidosis, granulomatous orchitis, granuloma in the pleura and mastoid antrum. The granulomas where etiology could not be found out in our study were 5(6.67%)cases 4 (5.33%) cases of granulomatous synovitis, (.67%) cases of granuloma annulare, (.33%) case of acne agminata and (.33%) case of granulomatous cystitis. The etiology could not be established by doing stains like ZN and PAS hence they were grouped as granulomatous lesions [3,5] The definitive diagnosis to find out the exact etiology of granuloma formation could be made in 70 (93.33 %) cases out of total of 75 cases in the present study after doing special stains. After relevant special stains the etiological diagnosis could be confirmed in 95% cases in the study done by Patel et al [6]. Even after doing the special stains, in some cases, it is not possible to find out the etiology of the granulomatous lesion. hence ancillary studies of culture, serology, PCR may be required for confirmation. CONCLUSION The most common cause of granulomatous lesion in our study was tuberculosis with lymph node being the most common site. Majority of the granulomas had infectious etiology. According to the morphology epithelioid type was the predominant granuloma followed by foreign body type. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references in this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to the authors/publishers/editors of all those articles,journals and books from where the literature for this has been reviewed and discussed. REFERENCES. Mariano M. Does macrophage deactivating factor play a role in the maintainence and fate of infectious granulomata? Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, 86:485487,99.. Weedon D. The granulomatous reaction pattern. In: Weedon D(ed). Skin Pathology, nd ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone;00.pp Jayashree Pawale, Rekha Purani, MH Kulkarni. A Histopathological study of Granulomatous Inflammations with an attempt to find the Aetiology. JCDR 0;5(): Adhikari RC, Shrestha KB, Savami G. Granulomatous inflammation: A histopathological study. Journal of Pathology of Nepal 03;3: Harish S. Permi, Jayaprakash Shetty K, Shetty K Padma, Teerthanath S, Michelle Mathias, Sunil Kumar Y, Kishan Prasad HL,Chandrika. A Histopathological Study of Granulomatous Inflammation. NUJHS 0;(): Vaidehi Patel, Jasmin Jasani, RajolI. Desai. The histopathological study of granulomatous diseases in various organs to find the exact etiology of granulomas. IJBAR 03;4(7): BalA, Mohan H, Dhami GP. Infectious granulomatous dermatitis: aclinocopathologic study. Indian J Dermatol 006;5: Madeb R, Marshall J, Nativ O, Erturk E. Epididymal tuberculosis: case report and review of the literature. Urology 005;65(4): Keyur N. Surati, Kaushal D. Suthar, Jainam K Shah. Isolated Tuberculous EpididymoOrchitis: A Rare and Instructive Case Report. SEAJCRR 0;(3): Vishnu Prasad Shenoy, Shashidhar Viswanath, Annet D Souza, Indira Bairy, Joseph Thomas. Isolated tuberculousepididymoorchitis: an unusual presentation of tuberculosis. J Infect DevCtries 0;6():994.. Krishnaswamy H, Job CK. The role of Ziehl Neelson and Flourescent stains in tissue sections in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis, 974;(0):8.. Kunh, IIIC and Askin, F.B. Andersons Pathology, edited by J.M. Kissane, 8 th Ed., Mosby Co, St. Louis, 985, Ashish Kumar Chakrabarti, Krishna Kumar Halder, Shikha Das, Subrata Chakrabarti. Morphological Classification of Tuberuclous Lesions: Preliminary Observations. Ind. JTub 994;4(39): Gautam K, Pai RR, Bhat S. Granulomatous lesions of the skin. Journal of Pathology of Nepal 0;: Billet A,Viseux V,Chaby G,DascotteBarbeau E,Gontier MF, Deneoux JP, Lok C. Perforating granuloma annulare with transfollicular perforation. Ann DermatolVenereol 005;3(89): Joana Alexandra Devesa Parente, Jose Alberto Machado Dores, Joao Manuel Pires Arhana. Generalized Perforating Granuloma Annulare: Case Report. Annal Dermatovenerol Croat 0;0(4): Sule RR, Athavale NV, Gharpuray MB. Lupus miliaris disseminates faciei. Ind J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 99;58: Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05
7 8. Nayak SV, Shivrudrappa AS, Mukamil AS. Role of fluorescent microscopy in detecting Mycobacterium leprae in tissue sections. Annals of diagnostic pathology 003;7(): Chavan SS. A clinicopathlogical study of fungal lesions encountered in tissue sections (dissertation unpublished), Hubli, Karnataka university, Mirza M, Sarwar M. Recurrent cutaneous actinomycosis. Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences 003;9:303. Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 7 Issue 9 May 05 84
A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION
 Original Article Abstract : A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION 2 4 3 3 Harish S. Permi, Jayaprakash Shetty K., Shetty K. Padma, Teerthanath S., 3 2 1 5 Michelle Mathias, Sunil Kumar
Original Article Abstract : A HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATION 2 4 3 3 Harish S. Permi, Jayaprakash Shetty K., Shetty K. Padma, Teerthanath S., 3 2 1 5 Michelle Mathias, Sunil Kumar
Granulomatous reaction - a histopathological study: a retrospective and prospective study of 5 years
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20150136 Granulomatous reaction - a histopathological
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20150136 Granulomatous reaction - a histopathological
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Granulomatous Lesions: A Diagnostic Challenge To Dermatopathologists
 Original Research Article Granulomatous Lesions: A Diagnostic Challenge To Dermatopathologists Karuna Gupta 1, Anita Kumari 2, Kalpana Mangal 3* 1 Professor, 2 PG Resident (3rd year), 3* Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Granulomatous Lesions: A Diagnostic Challenge To Dermatopathologists Karuna Gupta 1, Anita Kumari 2, Kalpana Mangal 3* 1 Professor, 2 PG Resident (3rd year), 3* Assistant Professor,
Histopathological Study of Infectious Granulomatous Skin Lesions
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1874 Histopathological Study of Infectious Granulomatous Skin Lesions Ratnakar M Potekar 1, Anita P Javalgi 2 *, Lynda Dennis Rodrigues 1 and Raga Sruthi Dwarampudi
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1874 Histopathological Study of Infectious Granulomatous Skin Lesions Ratnakar M Potekar 1, Anita P Javalgi 2 *, Lynda Dennis Rodrigues 1 and Raga Sruthi Dwarampudi
Clinico-Pathological Study of Cutaneous Granulomatous Lesions- a 5 yr Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
 54 Original Article Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(1): 54-60 http://www.ijp.iranpath.org/ Clinico-Pathological Study of Cutaneous Granulomatous Lesions- a 5 yr Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
54 Original Article Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(1): 54-60 http://www.ijp.iranpath.org/ Clinico-Pathological Study of Cutaneous Granulomatous Lesions- a 5 yr Experience in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Spectrum of granulomatous lesions in a tertiary care hospital
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00113.7 Spectrum of lesions in a tertiary care hospital R. Vimal Chander 1,*, P. Jayaganesh 2, Tejaswini Punuru Reddy 3, Chitra Srinivasan 4 1 Assistant
Original Research Article DOI: 10.5958/2394-6792.2016.00113.7 Spectrum of lesions in a tertiary care hospital R. Vimal Chander 1,*, P. Jayaganesh 2, Tejaswini Punuru Reddy 3, Chitra Srinivasan 4 1 Assistant
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months
 A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
A 40-year old male with follicular papule and pustule at central face area for 3 months GMS- Neg AFB-Neg Fite stain - neg HISTOPATHOLOGICAL DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS CASEOUS GRANULOMA INFECTION -MYCOBACTERIUM
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC LYMPHADENOPATHY.
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 01 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 16/10/13 Revised on: 18/11/13 Accepted on: 20/12/13 FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNAC) AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN PAEDIATRIC Heming Agrawal,
Short Communication Cytomorphological patterns in the Diagnosis of Tuberculous lymphadenitis Khanna A 1, Khanna M 2, Manjari M 3
 Short Communication Cytomorphological patterns in the Diagnosis of Tuberculous lymphadenitis Khanna A 1, Khanna M 2, Manjari M 3 1 Dr Ashish Khanna Associate Professor, Microbiology 2 Dr Menka Khanna Associate
Short Communication Cytomorphological patterns in the Diagnosis of Tuberculous lymphadenitis Khanna A 1, Khanna M 2, Manjari M 3 1 Dr Ashish Khanna Associate Professor, Microbiology 2 Dr Menka Khanna Associate
Original Article Morphological study of different granulomatous lesions of the skin M Naved Uz Zafar, Saleem Sadiq*, M Arif Memon**
 Original Article Morphological study of different granulomatous lesions of the skin M Naved Uz Zafar, Saleem Sadiq*, M Arif Memon** Pathology Department, Sindh Medical College/Dow University of Health
Original Article Morphological study of different granulomatous lesions of the skin M Naved Uz Zafar, Saleem Sadiq*, M Arif Memon** Pathology Department, Sindh Medical College/Dow University of Health
An institution-based observational study to identify sensitive histopathological parameters in leprosy
 Research Article An institution-based observational study to identify sensitive histopathological parameters in leprosy Amit S Mistry, Santoshdev P Rathod, Pooja Agarwal Department of Dermatology, AMC-MET
Research Article An institution-based observational study to identify sensitive histopathological parameters in leprosy Amit S Mistry, Santoshdev P Rathod, Pooja Agarwal Department of Dermatology, AMC-MET
Journal of Medical Science & Technology
 Page40 Journal of Medical Science & Technology Case Report Open Access Diverse Presentation of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Sandhya Panjeta Gulia* 1, Naseem Noorunnisa 1,Madhusudan Chaudhury 1,C D Balakrishnan
Page40 Journal of Medical Science & Technology Case Report Open Access Diverse Presentation of Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis Sandhya Panjeta Gulia* 1, Naseem Noorunnisa 1,Madhusudan Chaudhury 1,C D Balakrishnan
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/24 Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study K Florence, K Suresh, K Lavanya Department
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/24 Cytopathological Study of Lymph Node Lesions - A 2 Years Retrospective Study K Florence, K Suresh, K Lavanya Department
More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa
 More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure None Classification/Overview 1) Necrobiotic/Palisading
More Non-infectious Granulomatous Diseases! Karolyn Wanat, MD Assistant Professor, Dermatology & Pathology University of Iowa Conflicts of Interest/Disclosure None Classification/Overview 1) Necrobiotic/Palisading
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in an immunocompromised host
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2014) 22, 85-89 Case Report Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in an immunocompromised host YXE Tay, JY Pan, SSJ Lee Phaeohyphomycosis is an infection caused by dematiaceous
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2014) 22, 85-89 Case Report Cutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in an immunocompromised host YXE Tay, JY Pan, SSJ Lee Phaeohyphomycosis is an infection caused by dematiaceous
Chronic inflammation. 07-Dec-15. Macrophage Tissue destruction
 Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
number Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي
 number 12 Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي Morphology of Granulomatous Inflammations The first image (left) shows a lung alveolus in which necrosis is taking place. The image below it shows the
number 12 Done by Corrected by Doctor موسى العبادي Morphology of Granulomatous Inflammations The first image (left) shows a lung alveolus in which necrosis is taking place. The image below it shows the
Correlation of clinical and histopathological classification of Leprosy in post elimination era
 Indian J Lepr 2012, 84 : 271-275 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Correlation of clinical and histopathological classification of Leprosy in post elimination era
Indian J Lepr 2012, 84 : 271-275 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Correlation of clinical and histopathological classification of Leprosy in post elimination era
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi
 number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
number 11 Done by Husam Abu-Awad Corrected by Muhammad Tarabieh Doctor Mousa Al-Abbadi The possible outcomes of an acute inflammation are the following: 1- A complete resolution in which the tissue returns
Clinical Study Screening for Tuberculosis and Its Histological Pattern in Patients with Enlarged Lymph Node
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Pathology Research International Volume 2011, Article ID 417635, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/417635 Clinical Study Screening for Tuberculosis and Its Histological Pattern in
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Pathology Research International Volume 2011, Article ID 417635, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/417635 Clinical Study Screening for Tuberculosis and Its Histological Pattern in
Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report
 Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report Surendra Prakash Vyas 1, Dharm Chand Kothari 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner, India 2, Resident, Department
Lupus Vulgaris of Elbow A Case Report Surendra Prakash Vyas 1, Dharm Chand Kothari 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Sardar Patel Medical College, Bikaner, India 2, Resident, Department
A Retrospective Histological Evaluation of Non-neoplastic Superficial Lymphadenopathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 1 A Retrospective Histological Evaluation of Non-neoplastic Superficial Lymphadenopathy S Chhabra, H Mohan, A Bal Citation S Chhabra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 1 A Retrospective Histological Evaluation of Non-neoplastic Superficial Lymphadenopathy S Chhabra, H Mohan, A Bal Citation S Chhabra,
Histomorphological Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 26, No. 1, March 2004 Histomorphological Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis Ashok Kumar Malik,MD, MNAMS, FRCPath* Lily Pal, MD** Wig JD, MS, FRCS*** Objective:To study
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 26, No. 1, March 2004 Histomorphological Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis Ashok Kumar Malik,MD, MNAMS, FRCPath* Lily Pal, MD** Wig JD, MS, FRCS*** Objective:To study
Scenario of Histoid Hansen at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India
 Indian J Lepr 2018, 90 : 235-240 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Series Scenario of Histoid Hansen at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India 1 2 3 R Subha, M Ananthi, V
Indian J Lepr 2018, 90 : 235-240 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Series Scenario of Histoid Hansen at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India 1 2 3 R Subha, M Ananthi, V
Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy
 Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 180 185 CASE REPORT Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy GEETI KHULLAR*, TARUN NARANG*, KUSUM SHARMA**, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA***
Lepr Rev (2015) 86, 180 185 CASE REPORT Disseminated cutaneous BCG infection following BCG immunotherapy in patients with lepromatous leprosy GEETI KHULLAR*, TARUN NARANG*, KUSUM SHARMA**, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA***
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
An unusual presentation of lupus vulgaris in pediatric patient: A clinico- histopathological diagnosis
 Patel K, Kumar VH, Gandhi D, Aswani H, Savjiani N, Kumar D. An unusual presentation of lupus vulgaris in pediatric Case Report An unusual presentation of lupus vulgaris in pediatric patient: A clinico-
Patel K, Kumar VH, Gandhi D, Aswani H, Savjiani N, Kumar D. An unusual presentation of lupus vulgaris in pediatric Case Report An unusual presentation of lupus vulgaris in pediatric patient: A clinico-
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Laboratory Evaluation of a New Rapid Slide Culture (RSC) Technique for Diagnosis of Extra-
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Laboratory Evaluation of a New Rapid Slide Culture (RSC) Technique for Diagnosis of Extra-
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
India s Hidden Disease: Retrospective Study of Hansen Disease In A Tertiary Care Hospital. Evelyn Elizabeth Ebenezer*, Vimal Chander and S.
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1671 India s Hidden Disease: Retrospective Study of Hansen Disease In A Tertiary Care Hospital Evelyn Elizabeth Ebenezer*, Vimal Chander and S. Chitra Department of
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1671 India s Hidden Disease: Retrospective Study of Hansen Disease In A Tertiary Care Hospital Evelyn Elizabeth Ebenezer*, Vimal Chander and S. Chitra Department of
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Superficial Granulomatous Pyoderma of the Face: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Superficial Granulomatous Pyoderma of the Face: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Sarah M. Persing, MPH, a and Donald Laub Jr, MD, FACS a,b a University of Vermont College of Medicine, Burlington;
Superficial Granulomatous Pyoderma of the Face: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Sarah M. Persing, MPH, a and Donald Laub Jr, MD, FACS a,b a University of Vermont College of Medicine, Burlington;
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Actinomycosis A Common Incidental Diagnosis at Different Sites
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 2 Ver. V (February. 2017), PP 61-65 www.iosrjournals.org Actinomycosis A Common Incidental
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 2 Ver. V (February. 2017), PP 61-65 www.iosrjournals.org Actinomycosis A Common Incidental
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 5 No 2:16, December Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris Pathak D.* and Thapa A** Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 5 (2): 16 * Consultant Dermatologist, Delhi Dermatology Group Kubba,
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising on Extensive and Chronic Lupus Vulgaris Pathak D.* and Thapa A** Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 5 (2): 16 * Consultant Dermatologist, Delhi Dermatology Group Kubba,
Mandakini Patel, Komal Patel, Sonal Italiya, Kumarbhargav Kaptan Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Surat, Gujarat, India
 IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOSIS IN LYMPH NODE CYTOLOGY BY BLEACH METHOD FOR DETECTION OF ACID FAST BACILLI IN COMPARISON TO CONVENTIONAL ZIEHL NEELSEN STAINING METHOD Mandakini Patel, Komal Patel, Sonal
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TUBERCULOSIS IN LYMPH NODE CYTOLOGY BY BLEACH METHOD FOR DETECTION OF ACID FAST BACILLI IN COMPARISON TO CONVENTIONAL ZIEHL NEELSEN STAINING METHOD Mandakini Patel, Komal Patel, Sonal
ACCME/Disclosures. Two Patients and a Caveat 4/13/2016. Patient #1: 13 y/o boy with IPEX syndrome; s/p BMT
 Two Patients and a Caveat The Use and Misuse of Molecular Methods in Mycobacterial Infections Gary W. Procop, MD Director, Molecular Microbiology Infectious Disease Pathologist Cleveland Clinic ACCME/Disclosures
Two Patients and a Caveat The Use and Misuse of Molecular Methods in Mycobacterial Infections Gary W. Procop, MD Director, Molecular Microbiology Infectious Disease Pathologist Cleveland Clinic ACCME/Disclosures
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2).
 22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues. Introduction. Histochemical Stains Used to Detect Fungi. Histopathologic Diagnoses
 The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues Gary W. Procop, MD Chair, Clinical Pathology Staff, Anatomic Pathology Director, Molecular Microbiology, Mycology, and Parasitology Cleveland
The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues Gary W. Procop, MD Chair, Clinical Pathology Staff, Anatomic Pathology Director, Molecular Microbiology, Mycology, and Parasitology Cleveland
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology
 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lecture (14) Dr.Baha, AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Robert Koch 1843-1910 German physician Became famous for isolating the anthrax bacillus (1877), tuberculosis bacillus (1882)
Subcutaneous Mycosis
 Subcutaneous Mycosis Fungal infections 1. Superficial mycosis. 2. Coetaneous mycosis: Dermatophytoses. 3. Subcutaneous mycosis. 4. Systemic mycosis. 5. Opportunistic mycosis. Subcutanus mycoses Fungal
Subcutaneous Mycosis Fungal infections 1. Superficial mycosis. 2. Coetaneous mycosis: Dermatophytoses. 3. Subcutaneous mycosis. 4. Systemic mycosis. 5. Opportunistic mycosis. Subcutanus mycoses Fungal
2/18/19. Case 1. Question
 Case 1 Which of the following can present with granulomatous inflammation? A. Sarcoidosis B. Necrobiotic xanthogranulma C. Atypical mycobacterial infection D. Foreign Body Reaction E. All of the above
Case 1 Which of the following can present with granulomatous inflammation? A. Sarcoidosis B. Necrobiotic xanthogranulma C. Atypical mycobacterial infection D. Foreign Body Reaction E. All of the above
Elsevier B.V.; この論文は出版社版でありま Right 引用の際には出版社版をご確認ご利用ください This is
 Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
Title Refractory cutaneous lichenoid sarc tranilast. Author(s) Nakahigashi, Kyoko; Kabashima, Kenj Utani, Atsushi; Miyachi, Yoshiki Citation Journal of the American Academy of 63(1): 171-172 Issue Date
K Kakkad, T Padhi,K Pradhan, K C Agrawal
 Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 97-103 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A Study of Clinical, Bacteriological & Histopathological Correlation in Leprosy Cases attending
Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 97-103 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A Study of Clinical, Bacteriological & Histopathological Correlation in Leprosy Cases attending
Type II reaction without erythema nodosum leprosum masquerading as lymphoma
 Lepr Rev (2012) 83, 378 383 CASE REPORT Type II reaction without erythema nodosum leprosum masquerading as lymphoma RAHUL MAHAJAN*, SUNIL DOGRA*, INDERJEET KAUR*, SAVITA YADAV*, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA** & ANIL
Lepr Rev (2012) 83, 378 383 CASE REPORT Type II reaction without erythema nodosum leprosum masquerading as lymphoma RAHUL MAHAJAN*, SUNIL DOGRA*, INDERJEET KAUR*, SAVITA YADAV*, UMA NAHAR SAIKIA** & ANIL
DETERMINATION OF SEX USING DRY ADULT HUMAN SACRUM- A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article DETERMINATION OF SEX USING DRY ADULT HUMAN SACRUM- A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY Nisha Yadav 1, Kopal Saini 1, Kalpana Patil 2 1 Department
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article DETERMINATION OF SEX USING DRY ADULT HUMAN SACRUM- A MORPHOMETRIC STUDY Nisha Yadav 1, Kopal Saini 1, Kalpana Patil 2 1 Department
Leprosy. Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Leprosy Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Leprosy - Overview Slow progressive infection
Leprosy Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Leprosy - Overview Slow progressive infection
CLINICAL PROFILE REVIEW OF PATIENTS WITH THROMBOCYTOPENIA: A STUDY OF 100 CASES AT A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article CLINICAL PROFILE REVIEW OF PATIENTS WITH THROMBOCYTOPENIA: A STUDY OF 100 CASES AT A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE Shah H. R. 1, Vaghani
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Research Article CLINICAL PROFILE REVIEW OF PATIENTS WITH THROMBOCYTOPENIA: A STUDY OF 100 CASES AT A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE Shah H. R. 1, Vaghani
Correlation of clinical features, histopathology and demonstration of Lepra bacilli.
 A study of Leprosy cases: Correlation of clinical features, histopathology and demonstration of Lepra bacilli. Dr. Shilpa Taviyad 1*, Dr. Shilpa Dr. Gauravi Dhruva 5 1 Third year resident, 2,3 Associate
A study of Leprosy cases: Correlation of clinical features, histopathology and demonstration of Lepra bacilli. Dr. Shilpa Taviyad 1*, Dr. Shilpa Dr. Gauravi Dhruva 5 1 Third year resident, 2,3 Associate
Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report
 Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management
 Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management Poster No.: C-1418 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Song, B. K. Seo, K. R. Cho, O. H. Woo, Y.-S. Kim ; 1 1
Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management Poster No.: C-1418 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Song, B. K. Seo, K. R. Cho, O. H. Woo, Y.-S. Kim ; 1 1
Characteristic. Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils
 ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
ACUTE INFLAMMATION Characteristic Course of disease:short Days--one month Changes : Alteration, exudation Tissue destruction Inflammation cells: major neutrophils TYPES Serous Inflammation Fibrinous Inflammation
INFECTIOUS SCROTAL CONDITIONS
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology INFECTIOUS SCROTAL CONDITIONS Mustafa SECIL, MD Professor of Radiology, Dokuz Eylul University Faculty of Medicine Department of Radiology
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology INFECTIOUS SCROTAL CONDITIONS Mustafa SECIL, MD Professor of Radiology, Dokuz Eylul University Faculty of Medicine Department of Radiology
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Mycology. BioV 400. Subcutaneous Mycoses. Ecological associations. Geographic distribution World-wide
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
Collar stud abscess an interesting case report
 Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Volume 2 issue 2 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Collar stud abscess an interesting case report Kameshwaran Kannappan Punniyakodi * Balasubramanian Thiagarajan* *Stanley Medical College Chennai, Tamilnadu Abstract
Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017
 Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017 Clay J. Cockerell, M.D. Director, Cockerell Dermatopathology Director, Division of Dermatopathology UT Southwestern Medical Center July 2017 No relevant
Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017 Clay J. Cockerell, M.D. Director, Cockerell Dermatopathology Director, Division of Dermatopathology UT Southwestern Medical Center July 2017 No relevant
Address for correspondence: Dr. PVS Prasad, 88 AUTA Nagar, Sivapuri Post, Annamalai Nagar , Tamil Nadu, India.
 Brief Report Fine needle aspiration cytology in leprosy P. V. S. Prasad, Raj Varghese George, P. K. Kaviarasan, P. Viswanathan 1, Rehana Tippoo 1, C. Anandhi 2 Departments of Dermatology Venereology and
Brief Report Fine needle aspiration cytology in leprosy P. V. S. Prasad, Raj Varghese George, P. K. Kaviarasan, P. Viswanathan 1, Rehana Tippoo 1, C. Anandhi 2 Departments of Dermatology Venereology and
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis
 Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Unit VIII Problem 6 Pathology: Meningitis - Important terms: Meningitis: it is inflammation of meninges (coverings of the central nervous system) caused by infection. They are classified to: Pachymeningitis:
Clinicopathological correlation of Hansen s disease: a retrospective study of skin biopsies
 Original Research Article Clinicopathological correlation of Hansen s disease: a retrospective study of skin biopsies Banushree CS 1,*, Ramachandra V. Bhat 2, Udayashankar C 3 1 Associate Professor, 2
Original Research Article Clinicopathological correlation of Hansen s disease: a retrospective study of skin biopsies Banushree CS 1,*, Ramachandra V. Bhat 2, Udayashankar C 3 1 Associate Professor, 2
Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma
 Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma Introduction Pages with reference to book, From 280 To 282 Irshad Nabi Soomro ( Department of Pathology, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Arthritis and Rosai-Dorfman Disease of the Skin: A Diagnostic Dilemma Introduction Pages with reference to book, From 280 To 282 Irshad Nabi Soomro ( Department of Pathology, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Currently, there are about 15 million TB patients including 11 million of working age.
 Currently, there are about 15 million TB patients including 11 million of working age. The vast majority of infected people (90%) the disease does not progress. Predicted by WHO in the next twenty years
Currently, there are about 15 million TB patients including 11 million of working age. The vast majority of infected people (90%) the disease does not progress. Predicted by WHO in the next twenty years
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
 Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 177-183 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Report Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature 1 2 3
Indian J Lepr 2016, 88 : 177-183 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Case Report Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Misdiagnosed as Leprosy. Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature 1 2 3
Role of S-100 Immunostaining in Differentiation of Borderline Leprosy from Other Granulomatous Diseases of Skin
 Indian J Lepr 2018, 90 : 289-296 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Role of S-100 Immunostaining in Differentiation of Borderline Leprosy from Other Granulomatous
Indian J Lepr 2018, 90 : 289-296 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Role of S-100 Immunostaining in Differentiation of Borderline Leprosy from Other Granulomatous
Evaluation of the diagnostic value of immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization in the pediatric leprosy
 Indian J Lepr 203, 85 : 93- Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Evaluation of the diagnostic value of immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization in the pediatric
Indian J Lepr 203, 85 : 93- Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article Evaluation of the diagnostic value of immunocytochemistry and in situ hybridization in the pediatric
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
Mast cells in leprosy
 Original article: Mast cells in leprosy *Dr. Navdeep Kaur, 1 Dr. S.S. Hiremath, 2 Dr. Suresh K.K. 3 1Post Graduate, 2 Professor, 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, JJM Medical College, Davangere, Karnataka,
Original article: Mast cells in leprosy *Dr. Navdeep Kaur, 1 Dr. S.S. Hiremath, 2 Dr. Suresh K.K. 3 1Post Graduate, 2 Professor, 3 Professor, Department of Pathology, JJM Medical College, Davangere, Karnataka,
Clinicopathologic Self-Assessment
 Clinicopathologic Self-Assessment Handout Symposium (S003), July 27 th 2017 Maija Kiuru MD PhD Assistant Professor, Departments of Dermatology & Pathology University of California Davis CASE 1: History
Clinicopathologic Self-Assessment Handout Symposium (S003), July 27 th 2017 Maija Kiuru MD PhD Assistant Professor, Departments of Dermatology & Pathology University of California Davis CASE 1: History
The Clarion International Multidisciplinary Journal
 The Clarion Volume 4 Number 2 (2015) PP 1-5 The Clarion International Multidisciplinary Journal ISSN : 2277-1697 Value of fine needle aspiration cytology(fnac) in the diagnosis of Tubercular lymphadenitis
The Clarion Volume 4 Number 2 (2015) PP 1-5 The Clarion International Multidisciplinary Journal ISSN : 2277-1697 Value of fine needle aspiration cytology(fnac) in the diagnosis of Tubercular lymphadenitis
Actinomycosis of Thoracic Spine A Rare Case
 Actinomycosis of Thoracic Spine A Rare Case Nanda Patil 1, Avinash Mane 2, Rashmi L. Sonawane 3, Suchi Gadhiya 4 Abstract: Introduction: Actinomycosis is a chronic suppurative infection caused by Actinomyces
Actinomycosis of Thoracic Spine A Rare Case Nanda Patil 1, Avinash Mane 2, Rashmi L. Sonawane 3, Suchi Gadhiya 4 Abstract: Introduction: Actinomycosis is a chronic suppurative infection caused by Actinomyces
Accepted for publication 24 January Lepr Rev (2013) 84, 51 64
 Lepr Rev (2013) 84, 51 64 A study on histological features of lepra reactions in patients attending the Dermatology Department of the Government Medical College, Calicut, Kerala, India SASIDHARANPILLAI
Lepr Rev (2013) 84, 51 64 A study on histological features of lepra reactions in patients attending the Dermatology Department of the Government Medical College, Calicut, Kerala, India SASIDHARANPILLAI
Acute miliary tuberculosis in a five-month-old boy
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 138-142 Case Report Acute miliary tuberculosis in a five-month-old boy FC Ip and KC Lee A five-month-old boy presented with fever and multiple cutaneous papular
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 138-142 Case Report Acute miliary tuberculosis in a five-month-old boy FC Ip and KC Lee A five-month-old boy presented with fever and multiple cutaneous papular
Histological Spectrum of Pure Neuritic Leprosy:
 Department of Histopathology Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research Chandigarh,India Histological Spectrum of Pure Neuritic Leprosy: Experience at Tertiary Care Centre Dr Uma Nahar INTRODUCTION
Department of Histopathology Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research Chandigarh,India Histological Spectrum of Pure Neuritic Leprosy: Experience at Tertiary Care Centre Dr Uma Nahar INTRODUCTION
Subcutaneous Fungi 10/13/2009. General Characteristics. Pathogenesis. Epidemiology. Laboratory Diagnosis. Specimens. Growth rate: 1-4 weeks
 General Characteristics Growth rate: 1-4 weeks Subcutaneous Fungi Clinical Laboratory Science Program Carol Larson MSEd, MT(ASCP) Dematiaceous septate hyphae Hyaline septate hyphae Branching GPR Epidemiology
General Characteristics Growth rate: 1-4 weeks Subcutaneous Fungi Clinical Laboratory Science Program Carol Larson MSEd, MT(ASCP) Dematiaceous septate hyphae Hyaline septate hyphae Branching GPR Epidemiology
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Spectrum of clinical presentations
 Spectrum of clinical presentations Case History A 7-day-old male patient born full-term via uncomplicated vaginal delivery was seen for multiple erythematous red-brown purpuric lesions that were present
Spectrum of clinical presentations Case History A 7-day-old male patient born full-term via uncomplicated vaginal delivery was seen for multiple erythematous red-brown purpuric lesions that were present
Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
ISPUB.COM. A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHOD
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY: A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL IN LYMPHADENOPTHY
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Mahesh S Patil and Anand A S, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2014 Mahesh S Patil and Anand A S, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION
1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive abdominal distension 3 months Failure
 Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
Dr Rajasree S Dr Srinivas S, Dr Bagdi RK, Dr Satheesh C Apollo Childrens Hospital, Chennai 1 yr old girl presented with Fever on and off 3 months H/o frequent semisolid bulky stools 3 months Progressive
Bilateral multiple choroidal granulomas and systemic vasculitis as presenting features of tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
 Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Tuberculosis and Johne s Disease
 Tuberculosis and Johne s Disease Prof. R. S. Chauhan Joint Director, Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar 243 122 (India) TUBERCULOSIS Tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial disease of animals caused
Tuberculosis and Johne s Disease Prof. R. S. Chauhan Joint Director, Indian Veterinary Research Institute Izatnagar 243 122 (India) TUBERCULOSIS Tuberculosis is a chronic bacterial disease of animals caused
Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Non-Neoplastic Adrenal Pathology Rajesh Kumar, M.D., and Pranab Dey, M.D., F.R.C.PATh*
 Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Non-Neoplastic Adrenal Pathology Rajesh Kumar, M.D., and Pranab Dey, M.D., F.R.C.PATh* Background: The incidence of many fungal and parasitic lesions are on the rise
Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Non-Neoplastic Adrenal Pathology Rajesh Kumar, M.D., and Pranab Dey, M.D., F.R.C.PATh* Background: The incidence of many fungal and parasitic lesions are on the rise
Indian Journal of Medical Research and Pharmaceutical Sciences August 2015; 2(8) ISSN: ISSN: Impact Factor (PIF): 2.672
 CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
CASE REPORT OF TUBERCULOUS SUBDELTOID BURSITIS WITH RICE BODIES Dr. Jhatoth Venkateshwarlu*, Dr. Tandra Venkateshwararao, Dr. K. Ramkumar Reddy, Dr. K.Venkatswamy, Dr. M.Sudhir MS Orthopaedics, Associate
Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania
 Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
Tropical Medicine and International Health VOLUME I NO. 2 PP 243-250 APRIL 1996 Necrotizing and suppurative lymphadenitis in Leishmania major infections A. Gaafar r, A. Ismai13, A. Y. El Kadaro4, Elsir
Figure 7.1 Figure 7.2 Figure 7.3
 CASE 7 Patient: A 63 year-old Thai female from Pathumthani Chief Complaint: Progressive facial eruption in 1 month Present Illness: The lesions involved only facial area without itching or pain. No associated
CASE 7 Patient: A 63 year-old Thai female from Pathumthani Chief Complaint: Progressive facial eruption in 1 month Present Illness: The lesions involved only facial area without itching or pain. No associated
MAGNITUDE OF PULMONARY DISEASES - INCIDENTALLY DIAGNOSED ON AUTOPSY AT LARGEST HOSPITAL & MEDICAL COLLEGE OF RAJASTHAN
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.6 Original Research Article MAGNITUDE OF PULMONARY DISEASES - INCIDENTALLY DIAGNOSED ON AUTOPSY AT LARGEST HOSPITAL & MEDICAL COLLEGE OF RAJASTHAN
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.6 Original Research Article MAGNITUDE OF PULMONARY DISEASES - INCIDENTALLY DIAGNOSED ON AUTOPSY AT LARGEST HOSPITAL & MEDICAL COLLEGE OF RAJASTHAN
Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract
 Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
FNAC IN TUBERCULOUS LYMPHADENITIS: EXPERIENCE FROM A TERTIARY LEVEL REFERRAL CENTRE
 Original 102 Article FNAC IN TUBERCULOUS LYMPHADENITIS: EXPERIENCE FROM A TERTIARY LEVEL REFERRAL CENTRE Paliwal Nidhi 1, Thakur Sapna 1, Mullick Shalini 2 and Gupta Kumud 3 (Received on 20.1.2011. Accepted
Original 102 Article FNAC IN TUBERCULOUS LYMPHADENITIS: EXPERIENCE FROM A TERTIARY LEVEL REFERRAL CENTRE Paliwal Nidhi 1, Thakur Sapna 1, Mullick Shalini 2 and Gupta Kumud 3 (Received on 20.1.2011. Accepted
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification. Taxonomic Systems for Identification of the Anamorphs of Conidiogenous Fungi
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
