LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Disease and Disorders of the Musculoskeletal System. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
|
|
|
- Jane Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Disease and Disorders of the Musculoskeletal System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraph 1-1 through LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify the causes of deviations from normal musculoskeletal functioning Identify the types of joint pain Define and identify the causes, signs/symptoms, and treatment for these musculoskeletal diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporosis. Septic arthritis. Gout. Bursitis. Tendinitis/tenosynovitis. Spasmodic torticollis (wryneck). Low back pain. Ganglion. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Chondromalacia patellae. Osteomyelitis. SUGGESTION After completing the assignment, complete the exercises of this lesson. These exercises will help you to achieve the lesson objectives. MD
2 LESSON 1 DISEASES AND DISORDERS OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Section 1. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 1-1. INTRODUCTION The musculoskeletal system is a complex system of bones, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and other connective tissue. It is this system that gives the body form and shape. This system is subject to a variety of diseases some of which are not well understood. As a medical noncommissioned officer (NCO), you will often need to distinguish the characteristics of musculoskeletal diseases CAUSES OF DEVIATIONS FROM NORMAL MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONING Disease, defects, and trauma are the major causes of musculoskeletal system malfunction. Diseases such as arthritis, osteoporosis (imbalance between bone formation and reabsorption), and tumors interfere with proper musculoskeletal functioning. Other defects such as cysts and congenital problems can cause malfunctioning. Trauma to the body such as fractures, sprains, dislocations, subluxations, and strains also cause musculoskeletal system dysfunction TYPES AND EXAMPLES Section II. JOINT PAIN The skeletal system is made up of many separate bones held together at joints by flexible connective tissue. The movements that allow us to change position by moving the bony parts of our bodies occur at the joints (also called articulations). Joints are classified by function also taking into account the degree of movement the joint permits. Classified by function there are these types of joints: synarthroses (immovable joints), amphiarthroses (slightly movable joints), and diarthroses (freely movable joints). Additionally, joints are classified by connections: fibrous joints (no joint cavity and bones held together by connective tissue), cartilaqinous joints (no joint cavity and bones held together by cartilage), and synovial ioints (joint cavity and bones forming joint are united by accessory ligaments). Joints are subject to pain that can be classified as monarticular pain and polyarticular pain MONARTICULAR PAIN Monarticular pain is pain that occurs in one joint. Causes of monarticular pain include: MD
3 a. Mechanical Cause. A direct blow to the joint will cause pain. Also, injuries to other body parts that are close to the joint may cause pain in the joint. b. Osteoarthritis. This is the most common form of arthritis and is a deterioration of the joint cartilage and the formation of new bone at the margins and subchondral areas of the joints. Joint pain is the most common symptom of this condition. c. Tumors. A tumor, an overgrowth of tissue, can occur at a joint. The tumor may be benign or malignant, causing pain in either case. d. Pyogenic Cause. Pyogenic refers to a pus-forming infection. It can be acute (sudden onset) or chronic (ongoing but milder). In either case, if this occurs at a joint, there will be pain. e. Metabolic Cause. Metabolism refers to the chemical processes taking place in the body's living tissues, processes needed to maintain life. Increased production of uric acid and calcium can result in joint pain. f. Avascular Necrosis Cause. This refers to the death of tissue due to poor circulation, this tissue having no blood vessels g. Neuropathic Cause. Joint pain can be associated with nervous system disease POLYARTICULAR PAIN Here, pain occurs in several joints. Types of polyarticular pain include acute polyarticular pain and subacute pain. Conditions in which there is acute polyarticular pain include rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematous, metabolic-caused joint pain, viral infection, and rheumatic fever. a. Rheumatoid Arthritis. In this chronic, systemic, inflammatory disease, the joints are affected. Initially, the affected joints may only feel stiff when the individual gets up in the morning. Later, joints become painful and tender, especially joints of the wrists, knees, elbows, and ankles. b. Systemic Lupus Erythematous. This is an inflammatory infectious tissue disease that bears some similarities to rheumatoid arthritis. Joint pain and stiffness are the first and most common symptoms of the disease. c. Metabolic Caused Joint Pain. These disorders can produce monarticular and polyarticular pain. MD
4 d. Viral Infection Process. Diseases in this category range from the common cold and influenza to chicken pox, German measles, and herpes simplex. All are viral infections. e. Rheumatic Fever. This fever characteristically follows a streptococcal infection. A common complaint among many patients is migratory joint pain SUBACUTE PAIN This type of pain is chronic but does not have the characteristics of deformity of the area with the exception that there is swelling. Subacute pain can be a symptom of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematous, and metabolic-caused joint pain. Subacute pain can also be characteristic of ankylosing spondylitis, a progressive chronic disease of the small vertebral joints of the spine. Section III. SPECIFIC MUSULOSKELETAL DISEASES 1-7. RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic, inflammatory disease that attacks outer body joints and the surrounding muscles, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. RA is characterized by recurrent inflammation involving the synovial joints or the lining of those joints. If untreated, fibrous tissue in the joints calcifies, and the patient is unable to move the affected joints. The cause of RA is unknown; however, one theory is that infectious, genetic, and endocrine factors help determine whether a person will develop rheumatoid arthritis. a. Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis. If RA is untreated, the inflammatory process in the joints progresses in four stages. (1) Stage 1. Congestion and edema of the synovial membrane and joint capsule cause synovitis (inflammation of the membranes lining a joint). (2) Stage 2. Pannus (thickened layers of granulated tissue) forms, covers, and invades cartilage, and finally destroys the joint capsule and bone. (3) Stage 3. Fibrous ankylosis (abnormal immobility and fixation of a joint caused by the presence of fibrous bands between the bones forming the joint) takes place closing the joint and causing the joint to be immovable. It is in this stage that visible deformities can be seen. (4) Stage 4. Fibrous tissue calcifies in this stage, and the affected joint becomes totally immovable. MD
5 b. Signs/Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Included are the following: (1) Easily fatigued and general feeling of being unwell. (2) Persistent low-grade fever. (3) Weight loss and general weakness. Anemia. (4) Painful joint swelling. hand. (5) Subcutaneous nodules over bony prominences such as knuckles of the (6) Enlarged lymph nodes. c. Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Initially, the patient must understand that this is a chronic disease necessitating a major change in life-style. The patient will need to learn how to perform daily activities without putting undue stress on arthritic joints. Follow this treatment: (1) Instruct the patient to rest at specific periods of the day on a regular basis to control fatigue. (2) Apply splints carefully to provide rest for painful joints. (3) Refer the patient to a physical therapist--who can, among other things, teach the patient how to function without putting undue stress on his joints. (4) Control the patient's pain by these methods. (a) ASA--high dosage can be given. Salicylates reduce inflammation and relieve joint pain. Stop when the patient hears ringing in his ears. Most adults can tolerate 4-6 g daily. (b) Nonsteroid anti-inflammatory medication can be given; for example, indomethacin (Indocin ) (c) Gold compounds. These are effective against active joint inflammation only. Nonanalgesics can produce remission. Water soluble gold compounds can be given intramuscularly weekly. (d) Moist heat. Hot soaks, paraffin baths, and whirlpool therapy are usually effective for patients with chronic arthritis. MD
6 1-8. OSTEOPOROSIS Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disorder. The rate of bone resorption accelerates at the same time the rate of bone formation slows down. The result is a loss of bone mass. The bones that are affected by this disease lose calcium and phosphate a salt that causes the bones to become porous, brittle, and abnormally vulnerable to fracture. This condition affects the entire skeletal system eventually allowing the spine to curve, the thorax to drop, and the ribs to fall on the pelvic rim. a. Cause of Osteoporosis. Included are the following: (1) A mild but prolonged lack of adequate calcium intake (2) Decrease or loss of anabolic sex hormone (anabolism = formation of living tissue from simple substances). (3) Bone atrophy (wasting and loss of function) of the hands, wrists, or feet following minor injuries. (Also called Sudeck's atrophy) (4) Excess of catabolic hormones (body compounds which breakdown chemical substances into more basic parts). (5) Malabsorption syndrome (body's ability to absorb nutritional elements is impaired). b. Signs/Symptoms of Osteoporosis. Included are: (1) Pain in the lumbar spine. (2) Tendency to kyphosis (an exaggeration of the thoracic curve of the vertebral column resulting in a round-shouldered or hunched back appearance. (3) Kidney stones from hypercalciuria (too much calcium in the urine). c. Treatment of Osteoporosis. Follow these instructions: (1) Follow a high protein diet, supplementary calcium, and multivitamin pills. (2) Increase fluid intake. (3) Sleep on a firm surface. (4) Increase physical activity. MD
7 NOTE: Among the factors implicated in bone loss are a decrease in estrogen in women, calcium deficiency, malabsorption of calcium, vitamin D deficiency, loss of muscle mass, and inactivity SEPTIC ARTHRITIS (SA) Septic arthritis is a medical emergency, a condition caused by bacteria invading a joint and then causing the synovial lining of the joint to become inflamed. The bacterial organisms can enter the joint cavity causing liquid from that cavity to escape into a body cavity; the liquid containing bacteria causes pus formation. Septic arthritis can lead to ankylosis (abnormal immobility and fixation of a joint). This disease can even be fatal if bacterial organisms enter the body systems. a. Signs/Symptoms of Septic Arthritis. The onset of SA is sudden with these signs and symptoms: intense pain, inflammation swelling of the affected joint, and lowgrade fever. SA can develop in any joint, but it usually attacks large joints and small peripheral joints. b. Treatment of Septic Arthritis. (1) Administer antibiotic therapy by phvsician's orders; for example, Gramnegative penicillin, gram-positive nafcillin, or gram-negative bacilli ampicillin. (2) To relieve pain, you may give codeine or propoxyphene. (3) Monitor progress of the patient by frequent analysis of joint fluid cultures, synovial fluid leukocyte counts, and glucose determinations GOUT This condition is a metabolic disease characterized by an excess of uric acid in the urine. Gout usually occurs in the feet and legs and causes joints to be painfully arthritic. a. Normal Causes of Gout. Normally, nucleic acids are catabolized, and uric acid is produced as waste. Some individuals produce too much uric acid while others excrete too little uric acid. In both cases, uric acid accumulates in the body and tends to solidify into crystals that are deposited in the joints and kidney tissue. Gouty arthritis is the term for the condition caused wthen these crystals are deposited in joints. b. Other Causes of Gout. The tendency to gout can be inherited. Other causes of gout include renal problems (kidney problems) and overuse of diuretics. Dehydration and starvation make the condition worse. Individuals who have gout can be gout free for years. The condition is not necessarily constant. MD
8 c. Signs/Symptoms of Gout. Note the following: (1) Sudden onset of severe pain in peripheral joints. (2) Metatarsophalangeal joint of great toe (see figure 1-1) is most susceptible to gout. (3) Affected joints are hot, tender, inflamed, dusky-red, or cyanotic. (4) The patient may have a fever of 101ºF to 103ºF. (5) Recurring episodes of gout attack the same joints. Figure 1-1. Metatarsophalangeal joint of great toe. MD
9 d. Treatment of Gout. Follow this treatment: (1) Advise avoidance of alcohol and purine-rich foods. (2) Encourage large fluid intake. (3) By physician's order, may administer nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory indomethacin medication such as Indocin. (4) By physician's order, may give uriocsurics such as allopurinol (Zyloprim ) and colchicine. NOTE: See paragraph 2-14 for more information about gout BURSITIS a. General Information. The bursae are closed sacs lubricated by small amounts of synovial fluid. This fluid helps muscles and tendons move over bony prominences (pieces of bone that stick out). Bursitis is the inflammation of a bursa or of several bursae. When bursitis occurs, it usually occurs in these bursae: the subdeltoid, the olecranon, the trochanteric, the calcaneal, or the prepatellar bursae. These are all areas where tendons pass over bony prominences. Housemaid's knee is a typical example of bursitis. b. Causes. Bursitis affects individuals who spend a great deal of time on their knees regardless of whether they do housework or some other type of endeavor. Additional causes of bursitis include trauma, an acute or chronic infection (including syphilis and tuberculosis), rheumatoid arthritis, and gout. c. Signs/Symptoms of Bursitis. Included are the following: (1) Pain at the affected site. (2) Tenderness at the affected site. (3) Limited range of motion. (4) Swelling at the site. (5) Redness at the site. MD
10 d. Treatment of Bursitis. Possible treatments include: (1) Physical therapy. This prevents limiting adhesions from developing. (2) By physician's orders, these procedures may be performed: (a) Needle aspiration of joint. This procedure may be necessary to relieve pressure, to evacuate blood, or to get a fluid sample for laboratory studies. (b) Intrabursal injection. Hydrocortisone and one percent procaine may be injected to relieve pain. (c) Systemic corticosteriods may be injected to reduce inflammation TENDINITIS/TENOSYNOVITIS These conditions are much the same. inflammation of the lining of the tendon sheath and the enclosed tendon surrounding certain joints. Wrists, shoulders. elbows (tennis elbow), finger joints (trigger finger), ankles, and associated tendons are affected. a. Signs/Symptoms of Tendinitis/ Tenosynovitis. Included are: (1) Swelling due to fluid accumulation. (2) Fluid accumulation in the affected tendon sheaths. (3) Inflammation of the tendons. (4) Irregular contours of the tendons. Friction rubs. (5) Pain on movement. b. Treatment of Tendinitis. The same treatment is advised as for bursitis in paragraph 1-11d. c. Treatment for Tenosynovitis (Tennis Elbow). The goal is to relieve pain. (1) By physician's orders, these medications may be given: (a) Medications such as corticosteriods can be given. (b) Aspirin or indomethacin for pain. (2) Apply an immobilizing splint from the distal forearm to the elbow. (In two to three weeks, this treatment usually relieves pain.) MD
11 (3) Physical therapy such as manipulation and massage. (4) Use a "tennis elbow strap" to relieve strain on the affected forearm muscles/tendons. Wrap the strap snugly around the forearm SPASMODIC TORTICOLLIS (WRYNECK) Torticollis is the shortening of superficial and deep muscles of the neck. Spasmodic torticollis, also known as wryneck, refers to these muscles contracting spasmodically. Spasms. Spasms occur in the sternomastoid, trapezius, and other neck muscles. The result is that the head bends to the affected side, and the chin rotates to the opposite side. The head is in an unnatural position. Causes of this condition include basal ganglia disease, central nervous system infections, tumors in the bones or soft tissues of the neck, and psychological disturbances. a. Signs/Symptoms of Spasmodic Torticollis. Signs and symptoms may occur suddenly or gradually. The condition affects males and females equally. The individual may find the condition occurring occasionally and mildly, or the condition may be permanent, causing a deformity in the person's posture. b. Treatment of Spasmodic Torticollis. Follow this treatment: (1) Remove local causes of the condition. (2) Apply tactile pressure to the same side of the jaw as the head rotation. (3) Refer the patient for psychiatric counseling LOW BACK PAIN Pain that occurs in the low lumbar, lumbosacral, or sacroiliac region of the back is all termed low back pain. a. Cause of Low Back Pain. Causes include the following: (1) Degenerative joint disease of the lumbosacral area. (2) Ruptured discs in the spinal column. (3) Fractures, infection, and tumors of the back, pelvis, or retroperitoneum. (4) Traumatic ligament rupture. (5) Muscle tears. MD
12 (6) Congenital defects. (7) Obesity. (8) Pregnancy. b. Treatment of Low Back Pain. Included are the following: (1) Muscle relaxants such as methocarbamol (Robaxin ). (2) Local heat on the affected area. (3) Aspirin. (4) Bed rest GANGLION (5) Lumbosacral corset. (6) Physical therapy. A ganglion may be a collection of nerve cell bodies outside of the brain or the spinal cord. Here, the meaning is a cystic swelling resembling a tumor. This cystic swelling can occur on a tendon sheath or a joint capsule. Ganglions can be caused by contusions, repeated strains, or a weak area in a joint capsule or tendon sheath. Ganglions are most common in the wrist. a. Signs/Symptoms of Ganglion. A firm lump or protrusion and a non-tender cyst are indications of a ganglion. b. Treatment of a Ganglion. If the tumor is benign, leave it alone. It can be aspirated. If the ganglion is a cyst which is surgically removed, there is a fifty percent chance that the cyst will return CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME This musculoskeletal condition is the most common of the trapped nerve syndromes. The median nerve at the wrist is compressed within the carpal tunnel. The median nerve, tendons, and blood vessels pass through the carpal tunnel at the wrist on the way to the fingers and thumb. The compression causes sensory and motor changes in the hand. The general population in- the 40 to 50 year age group is most likely to have this syndrome, and five times as many women have the condition as men. Carpal tunnel syndrome can develop during pregnancy. For those who use their hands strenuously (sustained grasping, twisting, or flexing the hands done by assembly line workers, for example), the disorder worsens. MD
13 a. Signs/Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Symptoms are often worse at night and may be relieved if the patient shakes his hands vigorously or dangles his hands at his sides. Included are the following: (1) Pain in the hands. (2) Weakness in the hands. (3) Paresthesia (abnormal sensation such as burning, tingling, numbness) in the hands. (4) Eventually, pain may spread to the forearm and even the shoulders. b. Treatment. Begin conservative treatment which is to splint the wrist in the neutral position at night. Try this for one to two weeks. If this treatment is unsuccessful, refer the patient to orthopedics CHONDROMALACIA PATELLAE Figure 1-2. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Chondromalacia refers to an abnormal softening of cartilage. Chondromalacia patellae refers to the rapid erosion and fragmentation of cartilage around the knee. The condition is most common in young men. There may be a momentary "catching" of the knee while climbing stairs. Passive motion is not painful. MD
14 a. Signs/Symptoms of Chondromalacia Patellae. Included are the following: (1) Compression of the patellae (kneecap) is painful. (2) A grating sound is heard when the patella is palpated. b. Treatment of Chondromalacia Patellae. Rest is the first treatment. Surgery may be necessary to remove articular cartilage OSTEOMYELITIS This condition is an inflammatory process involving the bone. Osteomyelitis can be chronic or acute and is a pus-producing bone infection. Causes of osteomyelitis include disease-causing bacteria, lesions, trauma, and sickle cell anemia. a. Signs/Symptoms of Osteomyelitis. Included are the following: (1) Fever. (2) Malaise. (3) Localized pain. (4) Swelling. (5) Weakness. (6) Surrounding tissue dies. b. Treatment of Osteomyelitis. Treatment includes administering large doses of antibiotics intravenously and bed rest CLOSING STATEMENT Musculoskeletal diseases are common and many are chronic requiring long-term or minimally effective therapy. The diseases studied in this lesson are common in all populations and will require medical and/or surgical treatments which you may need to directly or indirectly provide. Continue with Exercises Return to Table of Contents MD
15 EXERCISE, LESSON 1 INSTRUCTIONS. Complete the following exercises by writing the word or term that properly completes the incomplete statement or by writing the answer in the space provided at the end of the exercise. After you have completed all the exercises, turn to the "Solution to Exercise" at the end of the lesson and check your answers. 1. List the five parts of the musculoskeletal system. a.. b.. c.. d.. e.. 2. List three major causes of musculoskeletal system malfunction. a.. b.. c.. 3. Monarticular pain is pain that occurs in. 4. Polyarticular pain is pain that occurs in. 5. Pain with a pyogenic cause is pain resulting from. 6. Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematous. and ankylosing spondylitis are all examples of pain. MD
16 7. List three signs/symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. a.. b.. c.. 8. Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disorder in which the rate of bone resorption accelerates at the same time that the. 9. A high protein diet, fluid intake, sleeping on a firm surface, and are treatments for osteoporosis. 10. Bacteria invading a joint and causing the synovial lining of the joint to become inflamed is a description of the disease. 11. Gout is characterized by. 12. Needle aspiration of a bursitis sufferer's joint may be necessary for the following three reasons: a.. b.. c The goal in the treatment of tennis elbow (tenosynovitis) is. 14. In the condition, superficial and deep neck muscles contract spasmodically causing the head to bend to one side and the chin to rotate to the opposite side. MD
17 15. Ruptured discs in the spinal column; fractures. infections, and tumors of the back, pelvis, or retroperitoneum; and degenerative joint disease of the lumbosacral area can all cause. 16. The individual has a benign ganglion. What is the treatment? 17. If the median nerve of the wrist is compressed within the carpal tunnel, an individual may suffer from. 18. Rapid erosion and fragmentation of cartilage around the knee are characteristic of. 19. Osteomyelitis, condition caused by a pus-producing infection, is best treated by and bed rest. 20. List the three regions of the back in which low back pain occurs. a.. b.. c.. Check Your Answers on Next Page MD
18 SOLUTIONS TO EXERCISES, LESSON 1 1. Bones. Muscles. Ligaments. Tendons. Connective tissue. (para 1-1). 2. Disease. Defects. Trauma. (para 1-2). 3. One joint. (para 1-4). 4. Several joints. (para 1-5). 5. A pus-forming infection. (para 1-4d). 6. Subacute. (para 1-6). 7. Any three of the following: Easily fatigued. General feeling of being unwell. Weight loss. General weakness. Anemia. Painful joint swelling. Subcutaneous nodule over bony prominences. Enlarged lymph nodes. (para 1-7c) 8. Rate of bone formation slows down. (para 1-8). 9. Increased; increased physical activity. (para 1-8b). 10. Septic arthritis (para 1-10). 11. Uric acid accumulating in the body and tending to solidify into crystals that are deposited in the joints and kidney tissue. (para 1-10a). 12. Relieve pressure. Evacuate blood. Obtain a fluid sample for laboratory studies. (para 1-11d) MD
19 13. To relieve pain. (para 1-12c). 14. Spasmodic torticollis. (para 1-13). 15. Lower back pain. (para 1-14a). 16. Leave it alone. (para 1-15b). 17. Carpal tunnel syndrome. (para 1-16). 18. Chondromalacia patellae. (para 1-17). 19. Administering large doses of antibiotics intravenously. (para 1-18b). 20. Low lumbar. Lumbosacral. Sacroiliac. (para 1-14). Return to Table of Contents MD
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS
 U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM I SUBCOURSE MD0577 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
U.S. ARMY MEDICAL DEPARTMENT CENTER AND SCHOOL FORT SAM HOUSTON, TEXAS 78234-6100 THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM I SUBCOURSE MD0577 EDITION 100 DEVELOPMENT This subcourse is approved for resident and correspondence
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Car a e e o f o th f e th e Pati Pa e ti n e t n wi w th i th a Mus u c s u c l u o l s o k s e k l e e l t e al a l Dis i o s r o de d r
 Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Function of the bones Support Protection Movement Mineral storage Hemopoiesis Slide 2 Functions of the muscles
Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Function of the bones Support Protection Movement Mineral storage Hemopoiesis Slide 2 Functions of the muscles
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Functions of Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
The Skeletal System 5PART F. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by
 Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis
 Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Presented by Chris Hudd
 Presented by Chris Hudd Study design dot points: causes of potential acute and chronic injuries and illness associated with the muscular and skeletal systems such as arthritis, osteoporosis and other musculoskeletal
Presented by Chris Hudd Study design dot points: causes of potential acute and chronic injuries and illness associated with the muscular and skeletal systems such as arthritis, osteoporosis and other musculoskeletal
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis
 Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
Chiropractic Healthcare
 ebook 2 Chiropractic Healthcare Four symptoms explained Introduction 3 Chapter 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 4 Chapter 2 Common Shoulder Pain Issues 8 Chapter 3 Headaches and Chiropractic Care 14 Chapter 4
ebook 2 Chiropractic Healthcare Four symptoms explained Introduction 3 Chapter 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 4 Chapter 2 Common Shoulder Pain Issues 8 Chapter 3 Headaches and Chiropractic Care 14 Chapter 4
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
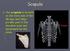 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 42 Caring for Clients with Musculoskeletal Trauma Musculoskeletal Trauma Tissue is subjected to more
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 42 Caring for Clients with Musculoskeletal Trauma Musculoskeletal Trauma Tissue is subjected to more
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow
 Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Module Eight. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
SKELETAL SYSTEM- JOINTS
 Bell Work Write the new standard, underlined portions only necessary. Then write down the following terms: Synarthroses-immoveable joint connected by tough fibrous connective tissue. Amphiarthroses-partially
Bell Work Write the new standard, underlined portions only necessary. Then write down the following terms: Synarthroses-immoveable joint connected by tough fibrous connective tissue. Amphiarthroses-partially
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education
 Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Regional Pain Syndromes Introduction: At some time in the course of life, virtually everyone will experience pain in a tendon, muscle, or
Arthritis and Rheumatology Clinics of Kansas Patient Education Regional Pain Syndromes Introduction: At some time in the course of life, virtually everyone will experience pain in a tendon, muscle, or
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Joints. Articulations Arthroses
 Joints Articulations Arthroses 1 Joints, defined Points of contact between Two bones Bone and teeth Joint classification: 2 schemes Functional classification degree of movement permitted Structural classification
Joints Articulations Arthroses 1 Joints, defined Points of contact between Two bones Bone and teeth Joint classification: 2 schemes Functional classification degree of movement permitted Structural classification
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Soft Tissue Rheumatism. Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group
 Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Mechanical Injury. Trauma 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Mechanical Injury Force or mechanical energy is that which changes the state of rest or uniform motion of matter. When a force is
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Mechanical Injury Force or mechanical energy is that which changes the state of rest or uniform motion of matter. When a force is
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
For more information call , or visit
 Target Coding ICD-10 List for Chiropractic HEADACHE G43: Migraine G43.0: Migraine without aura (common migraine) G43.009: Migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus (migraine without
Target Coding ICD-10 List for Chiropractic HEADACHE G43: Migraine G43.0: Migraine without aura (common migraine) G43.009: Migraine without aura, not intractable, without status migrainosus (migraine without
Rheumatology & Immunology. Regional pain syndromes to be covered today. Some definitions. Tendinitis. Bursitis. History. History. Exam.
 Rheumatology & Immunology Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating soft tissue syndromes are not! Soft tissue syndromes one of the most common reasons patients present to their doctor.
Rheumatology & Immunology Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating soft tissue syndromes are not! Soft tissue syndromes one of the most common reasons patients present to their doctor.
Localized collection of pus in a cavity
 Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Arthritis. that affects the joints.
 Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Spine Conditions and Treatments. Your Guide to Common
 Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems
 Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system
 1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
Chapter 8: Exercise for Those with Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Chapter 8: Exercise for Those with Disorders of the Skeletal System Williamson, P. (2010). Exercise for Special Populations. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Bone tissue Classified as compact
Chapter 8: Exercise for Those with Disorders of the Skeletal System Williamson, P. (2010). Exercise for Special Populations. Baltimore, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Bone tissue Classified as compact
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
3 section of the Foot
 TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
Musculoskeletal Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma
 Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement Learn About: How Your Knee Works Knee Related Problems Candidates for Knee Replacement Surgery What to Expect From Your Artificial Knee Preparing for Knee Replacement Your Surgery
Total Knee Replacement Learn About: How Your Knee Works Knee Related Problems Candidates for Knee Replacement Surgery What to Expect From Your Artificial Knee Preparing for Knee Replacement Your Surgery
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS. Ms. Doshi
 CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
The Spine.
 The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
Bell Work. Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies.
 Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA
 Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA Osteoarthritis: What Is It? Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of
Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA Osteoarthritis: What Is It? Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of
Chapter 09 Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
May 2014 Knife-free Relief for Knee Arthritis More than a million surgeries are
 Knife-free Relief for Knee Arthritis More than a million surgeries are performed every year to help people suffering from arthritis of the knee. While such surgery is sometimes the best option, two studies
Knife-free Relief for Knee Arthritis More than a million surgeries are performed every year to help people suffering from arthritis of the knee. While such surgery is sometimes the best option, two studies
Skeletal system. Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments
 Skeletal System 1 Skeletal system Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments Functions: Support (structural support of whole body) Storage of minerals (calcium) Storage of
Skeletal System 1 Skeletal system Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments Functions: Support (structural support of whole body) Storage of minerals (calcium) Storage of
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination
 History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination Introduction A thorough rheumatologic assessment is performed within the context of a good general evaluation of the patient. The patient should be undressed
History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination Introduction A thorough rheumatologic assessment is performed within the context of a good general evaluation of the patient. The patient should be undressed
Complications of Treatment: Nonsurgical and Surgical
 Complications of Treatment: Nonsurgical and Surgical Whenever orthopedic surgeons discuss a treatment with patients we must always consider the risks and complications of any treatment we recommend. Part
Complications of Treatment: Nonsurgical and Surgical Whenever orthopedic surgeons discuss a treatment with patients we must always consider the risks and complications of any treatment we recommend. Part
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
BACK PAIN. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 BACK PAIN Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or a licensed healthcare
BACK PAIN Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or a licensed healthcare
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy
 Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT
 TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP AND KNEE JOINT TUBERCULOSIS OF HIP JOINT Occurrence-15% of all osteo articular tuber culosis Next common after spinal TB AETIO PATHOGENESIS Most common cause Mycobacterium tuberculosis
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
CHAPTER IV PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. BONES AND JOINTS Structure and function of bone(skeleton): Bone is a strong and durable type of connective tissue. It consists
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
The Articular System OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES. A. Completion
 C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
What Is Back Pain? Fast Facts: An Easy-to-Read Series of Publications for the Public. Who Gets Back Pain? What Are the Causes of Back Pain?
 Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
ARTHRITIS TREAT PAINS & ACHES NATURALLY BY DR. MEENA.K SR. NATUROPATH, JNI
 ARTHRITIS TREAT PAINS & ACHES NATURALLY BY DR. MEENA.K SR. NATUROPATH, JNI PAIN An unpleasant sensation that can range from mild, localized discomfort to agony. Pain process an injury to joints the damaged
ARTHRITIS TREAT PAINS & ACHES NATURALLY BY DR. MEENA.K SR. NATUROPATH, JNI PAIN An unpleasant sensation that can range from mild, localized discomfort to agony. Pain process an injury to joints the damaged
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
Chapter 43. Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder
 Chapter 43 Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Support Protection Movement
Chapter 43 Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Support Protection Movement
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Musculoskeletal System Objectives:
 Lemone and Burke Chapters 40-41 Musculoskeletal System Objectives: Review Anatomy and physiology Describe normal MS assessment Describe age related changes Discuss tests and nursing interventions Recognize
Lemone and Burke Chapters 40-41 Musculoskeletal System Objectives: Review Anatomy and physiology Describe normal MS assessment Describe age related changes Discuss tests and nursing interventions Recognize
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend
 Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Additional File 1. ICD9 Codes for chronic pain related diagnoses Dx Diagnosis Description Codes
 Additional File 1. ICD9 Codes for chronic pain related diagnoses Dx Diagnosis Description Dx Diagnosis Description Codes Codes 327.52 Sleep related leg cramps 717 Old bucket handle tear of medial 333.84
Additional File 1. ICD9 Codes for chronic pain related diagnoses Dx Diagnosis Description Dx Diagnosis Description Codes Codes 327.52 Sleep related leg cramps 717 Old bucket handle tear of medial 333.84
Musculoskeletal Assessment ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 Health Assessment - 1 - Lab 8: Musculoskeletal Assessment University of Kerbala / College of Nursing Adult Nursing Department Health Assessment Musculoskeletal Assessment ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The musculoskeletal
Health Assessment - 1 - Lab 8: Musculoskeletal Assessment University of Kerbala / College of Nursing Adult Nursing Department Health Assessment Musculoskeletal Assessment ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The musculoskeletal
Brisbin Family Chiropractic
 Information reviewed with patient: Dr. Initials Today s Date Brisbin Family Chiropractic Name: Sex: Male Female Address: City: Postal Code: Home Ph# Work# Ext# Cell# Preferred number (circle one) Home
Information reviewed with patient: Dr. Initials Today s Date Brisbin Family Chiropractic Name: Sex: Male Female Address: City: Postal Code: Home Ph# Work# Ext# Cell# Preferred number (circle one) Home
Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? 2. What are the ingredients of Algaea-X? 3. How does Algaea-X work?
 Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? Algaea-X is a topical cream developed to help relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and helps the regeneration of damaged cartilage. Developed by utilizing
Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? Algaea-X is a topical cream developed to help relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and helps the regeneration of damaged cartilage. Developed by utilizing
Chiropractic Glossary
 Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
PAIN. Headache. enstrual Pain. Low Back Pain. Osteoarthritis. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Sprains and Strains. Taking Care of. Pain of
 Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
GONSTEAD. Think of an Adjustment as " Tuning " a piano, Adjusting each String so it produces the Perfect Tone. DIVERSIFIED
 We use a number of highly-effective adjusting approaches to help improve spinal biomechanics and reduce nervous system interference. The approach we use is based on our judgment and years of experience.
We use a number of highly-effective adjusting approaches to help improve spinal biomechanics and reduce nervous system interference. The approach we use is based on our judgment and years of experience.
Benefits of Aspiration and Injection JOINT INJECTIONS. Injection Indications. Mechanism of Action 1/11/2016
 Benefits of Aspiration and Injection JOINT INJECTIONS Mark Niedfeldt, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Decrease or resolution of pain Decrease or resolution of inflammation Decrease or resolution of effusion
Benefits of Aspiration and Injection JOINT INJECTIONS Mark Niedfeldt, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Decrease or resolution of pain Decrease or resolution of inflammation Decrease or resolution of effusion
