The Skeletal System 5PART F. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
|
|
|
- Griffin Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5PART F
2 Joints Articulations of bones Functions of joints Hold bones together Allow for mobility Ways joints are classified Functionally Structurally
3 Functional Classification of Joints Synarthroses Immovable joints Amphiarthroses Slightly moveable joints Diarthroses Freely moveable joints
4 Structural Classification of Joints Fibrous joints Generally immovable Cartilaginous joints Immovable or slightly moveable Synovial joints Freely moveable
5 Summary of Joint Classes [Insert Table 5.3 here] Table 5.3
6 Fibrous Joints Bones united by fibrous tissue Example: Sutures Syndesmoses Allows more movement than sutures Example: Distal end of tibia and fibula
7 Fibrous Joints Figure 5.28a b
8 Cartilaginous Joints Bones connected by cartilage Example: Pubic symphysis Intervertebral joints
9 Cartilaginous Joints Figure 5.28c e
10 Synovial Joints Articulating bones are separated by a joint cavity Synovial fluid is found in the joint cavity
11 Synovial Joints Figure 5.28f h
12 Features of Synovial Joints Articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage) covers the ends of bones A fibrous articular capsule encloses joint surfaces A joint cavity is filled with synovial fluid Ligaments reinforce the joint
13 Structures Associated with the Synovial Joint Bursae flattened fibrous sacs Lined with synovial membranes Filled with synovial fluid Not actually part of the joint Tendon sheath Elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon
14 The Synovial Joint Figure 5.29
15 Types of Synovial Joints Figure 5.30a c
16 Types of Synovial Joints Figure 5.30d f
17 Inflammatory Conditions Associated with Joints Bursitis inflammation of a bursa usually caused by a blow or friction Tendonitis inflammation of tendon sheaths Arthritis inflammatory or degenerative diseases of joints Over 100 different types The most widespread crippling disease in the United States
18 Clinical Forms of Arthritis Osteoarthritis Most common chronic arthritis Probably related to normal aging processes Rheumatoid arthritis An autoimmune disease the immune system attacks the joints Symptoms begin with bilateral inflammation of certain joints Often leads to deformities
19 Clinical Forms of Arthritis Gouty arthritis Inflammation of joints is caused by a deposition of uric acid crystals from the blood Can usually be controlled with diet
20 Developmental Aspects of the Skeletal System At birth, the skull bones are incomplete Bones are joined by fibrous membranes called fontanels Fontanels are completely replaced with bone within two years after birth
21 Ossification Centers in a 12-week-old Fetus Figure 5.32
22 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Fetus Birth Long bones are formed of hyaline cartilage Flat bones begin as fibrous membranes Flat and long bone models are converted to bone Fontanels remain until around age 2
23 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Adolescence Epiphyseal plates become ossified and long bone growth ends Size of cranium in relationship to body 2 years old skull is larger in proportion to the body compared to that of an adult 8 or 9 years old skull is near adult size and proportion Between ages 6 and 11, the face grows out from the skull
24 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Figure 5.33a
25 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Figure 5.33b
26 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Curvatures of the spine Primary curvatures are present at birth and are convex posteriorly Secondary curvatures are associated with a child s later development and are convex anteriorly Abnormal spinal curvatures (scoliosis and lordosis) are often congenital
27 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Figure 5.16
28 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Osteoporosis Bone-thinning disease afflicting 50% of women over age 65 20% of men over age 70 Disease makes bones fragile and bones can easily fracture Vertebral collapse results in kyphosis (also known as dowager s hump) Estrogen aids in health and normal density of a female skeleton
29 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Figure 5.34
30 Skeletal Changes Throughout Life Figure 5.35
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Carpals Tarsals Classification of Bones Flat bones Thin, flattened, and usually curved
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones
The Skeletal System. Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
 5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
Chapter 5- The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5- The Skeletal System I. The skeletal system A. Parts of the skeletal system 1. Bones (skeleton) 2. Joints 3. Ligaments 4. Cartilage B. Two subdivisions of the skeleton 1. Axial skeleton 2. Appendicular
Chapter 5- The Skeletal System I. The skeletal system A. Parts of the skeletal system 1. Bones (skeleton) 2. Joints 3. Ligaments 4. Cartilage B. Two subdivisions of the skeleton 1. Axial skeleton 2. Appendicular
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System. Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Why do we need the skeletal system?
 EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
Articulations (Joints) Can t We Just All Keep it Together
 Articulations (Joints) Can t We Just All Keep it Together Joints With one exception (the hyoid bone), every bone in the body is connected to or forms a joint with at least one other bone. Functions of
Articulations (Joints) Can t We Just All Keep it Together Joints With one exception (the hyoid bone), every bone in the body is connected to or forms a joint with at least one other bone. Functions of
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Chapter 5. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Our Bones - Introduction Identify 2 main functions of our skeletal system. Look for ligaments and tendons. What does each connect? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkvcg
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Our Bones - Introduction Identify 2 main functions of our skeletal system. Look for ligaments and tendons. What does each connect? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkvcg
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R. Joints: Part A. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by
 Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
Joints Outline 8.1 Joints are classified into three structural and three functional categories (p. 251; Table 8.1) A. Joints are classified by structure and by function: Structural classification focuses
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Chapter 6
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
KEY TO OBJECTIVES CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 1. Define the term articulation. A joint (articulation) is the site where two bones come together. 2. Distinguish between the structural and functional classification of joints, and relate the terms that
1. Define the term articulation. A joint (articulation) is the site where two bones come together. 2. Distinguish between the structural and functional classification of joints, and relate the terms that
Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) No bones about it! Joints. Cartilages. Ligaments
 No bones about it! Have to reference book OFTEN for pictures & names of bones for nearly all homework Should immediately be familiar with major bone names Thigh = femur Arm = humerus Lower jaw = mandible
No bones about it! Have to reference book OFTEN for pictures & names of bones for nearly all homework Should immediately be familiar with major bone names Thigh = femur Arm = humerus Lower jaw = mandible
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM (M.C. FLATH, Ph.D.)
 CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM (M.C. FLATH, Ph.D.) KEY TO OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. A joint (articulation) is the site where two bones come together. 2. Distinguish between
CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM (M.C. FLATH, Ph.D.) KEY TO OBJECTIVES: 1. Define the term articulation. A joint (articulation) is the site where two bones come together. 2. Distinguish between
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
Skeletal System: Articulations (Chapter 9) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Sources for figures and content: Marieb, E. N. Human Anatomy
9.1 Joints. Objectives Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints
 Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
Joints 9.1 Joints Describe the structural and functional classifications of joints Joints have both structural and functional classifications: The criteria for classifying joints structurally are anatomical
Joints. Articulations Arthroses
 Joints Articulations Arthroses 1 Joints, defined Points of contact between Two bones Bone and teeth Joint classification: 2 schemes Functional classification degree of movement permitted Structural classification
Joints Articulations Arthroses 1 Joints, defined Points of contact between Two bones Bone and teeth Joint classification: 2 schemes Functional classification degree of movement permitted Structural classification
Joints. Agenda. Joints. Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations
 Joints Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations Agenda Joint Basics Classification Structural Joint Details Joint Stability Movements of Synovial Joints Shape Classification of Synovial
Joints Structural and Functional Classification of Articulations Agenda Joint Basics Classification Structural Joint Details Joint Stability Movements of Synovial Joints Shape Classification of Synovial
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
Introduction. Physiology. Classification of Bones. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Skeletal System and Joint Movements.
 Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
The Skeletal System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Non Synovial: JOINTS Synovial or Non Synovial (Fibrous or Cartilaginous) Characteristics Fibrous Cartilaginous
 Joints part 2 JOINTS Synovial or Non Synovial (Fibrous or Cartilaginous) Non Synovial: Characteristics Fibrous Cartilaginous Designed for Suture Jts of Skull No motion Vert. Body w/ disc Stability protects
Joints part 2 JOINTS Synovial or Non Synovial (Fibrous or Cartilaginous) Non Synovial: Characteristics Fibrous Cartilaginous Designed for Suture Jts of Skull No motion Vert. Body w/ disc Stability protects
Skeletal system. Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments
 Skeletal System 1 Skeletal system Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments Functions: Support (structural support of whole body) Storage of minerals (calcium) Storage of
Skeletal System 1 Skeletal system Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments Functions: Support (structural support of whole body) Storage of minerals (calcium) Storage of
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) Answers to Activity Questions
 Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Elaine N. Marieb Tenth Edition
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Tenth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Tenth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Overview of the Components of the MSS
 Overview of the Components of the MSS Lecture Objectives Discuss the components and functions of the MSS. Describe the relation between bones and skeletal muscles in producing body movements. Identify
Overview of the Components of the MSS Lecture Objectives Discuss the components and functions of the MSS. Describe the relation between bones and skeletal muscles in producing body movements. Identify
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Introduction 1. List the functions of joints. 2. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
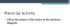 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
UNIT 2 - CHAPTER 8: JOINTS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES:
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 8.1 Types of Joints 1. Explain how joints can be classified according to the type of tissue that binds the bones together and the degree of movement possible at the joint. (p. 268) 2.
SKELETAL SYSTEM- JOINTS
 Bell Work Write the new standard, underlined portions only necessary. Then write down the following terms: Synarthroses-immoveable joint connected by tough fibrous connective tissue. Amphiarthroses-partially
Bell Work Write the new standard, underlined portions only necessary. Then write down the following terms: Synarthroses-immoveable joint connected by tough fibrous connective tissue. Amphiarthroses-partially
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Introduction. Fibrous Joints. 8.1: Types of Joints. Cartilaginous Joints. Fibrous Joints 12/14/2016. Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Introduction Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Joints (Articulations): Functional junctions between bones Bind
Introduction Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Joints (Articulations): Functional junctions between bones Bind
The Articular System OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES. A. Completion
 C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
C H A P T E R 8 The Articular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Name and describe the three types of joints. 2. Name the two types of synarthroses joints. 3. Name
Lecture 9: Arthrology
 Lecture 9: Arthrology M/O Chapter 9 45. Classify joints based on the degree of movement allowed and give examples of each classification. 46. Classify joints based on anatomical structure and give examples
Lecture 9: Arthrology M/O Chapter 9 45. Classify joints based on the degree of movement allowed and give examples of each classification. 46. Classify joints based on anatomical structure and give examples
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints. Structural Classifica5on of Joints 10/26/14
 Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints. Structural Classifica5on of Joints. Fibrous Joints. Fibrous Joints: Sutures 10/26/14
 Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Joints (Ar5cula5ons) 8 Joints: Part A site where two or more bones meet Func5ons of joints: Give skeleton Hold skeleton together Func5onal Classifica5on of Joints Based on amount of allowed by the joint
Student Objectives. When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives:
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Articulations Chapter 9
 Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Lecture 13 Bones. Function of Bones. Bones and Cartilages of the Human Body
 Lecture 13 Bones Function of Bones Support form the framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs Protection provide a protective case for the brain, spinal cord, and vital organs Movement provide
Lecture 13 Bones Function of Bones Support form the framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs Protection provide a protective case for the brain, spinal cord, and vital organs Movement provide
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together.
 Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Definition: A joint or articulation is a place in the body where two bones come together. CLASSES OF JOINTS. 1. Joints are classified according to how the bones are held together. 2. The three types of
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
The Skeletal System: Structure, Function, and Diseases of the bones and joints
 The Skeletal System: Structure, Function, and Diseases of the bones and joints Is this the correct anatomical position? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages
The Skeletal System: Structure, Function, and Diseases of the bones and joints Is this the correct anatomical position? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 9 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 229) 1. A joint or articulation or arthrosis is a point of contact between neighboring bones, between cartilage and bones, or
Chapter 9 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 229) 1. A joint or articulation or arthrosis is a point of contact between neighboring bones, between cartilage and bones, or
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems
 Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17
 B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 10/10 10/11 - B 10/12 - A 10/13 - B 10/14 - A NO SCHOOL Unit quiz Presentations 10/17 - B 10/18 - A 10/19 -
B DAYS SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT GUIDE DUE THURSDAY 11/17 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 10/10 10/11 - B 10/12 - A 10/13 - B 10/14 - A NO SCHOOL Unit quiz Presentations 10/17 - B 10/18 - A 10/19 -
Objectives. Review the gross anatomy and physiology of the axial skeleton by labeling a diagram and completing a group research activity.
 Bell Work Read and highlight the review worksheets given to you paying attention to the functions of the skeletal system, bone structure, and types of bones. The Skeletal System Standards Review the gross
Bell Work Read and highlight the review worksheets given to you paying attention to the functions of the skeletal system, bone structure, and types of bones. The Skeletal System Standards Review the gross
JOINTS (ARTICULATIONS)
 CJ Shuster A & P I Note Series Articulations 1 JOINTS (ARTICULATIONS) - JOINTS or ARTICULATIONS - sites where 2 or more bones meet. Hold skeleton together & give it motility (by using muscles). All locomotion
CJ Shuster A & P I Note Series Articulations 1 JOINTS (ARTICULATIONS) - JOINTS or ARTICULATIONS - sites where 2 or more bones meet. Hold skeleton together & give it motility (by using muscles). All locomotion
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Bio 5/6 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide
 Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Joints. Ar*cula*ons of bones Func*ons of joints. Ways joints are classified. Hold bones together Allow for mobility. Func*onally Structurally
 Joints Ar*cula*ons of bones Func*ons of joints Hold bones together Allow for mobility Ways joints are classified Func*onally Structurally Func*onal Classifica*on of Joints Synarthroses immovable joints
Joints Ar*cula*ons of bones Func*ons of joints Hold bones together Allow for mobility Ways joints are classified Func*onally Structurally Func*onal Classifica*on of Joints Synarthroses immovable joints
The SKELETAL System. The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion.
 The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
By Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the term Joint. Describe the classification of the 3 types of joints & give an example of each. Describe
By Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the term Joint. Describe the classification of the 3 types of joints & give an example of each. Describe
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Unit 5: SKELETAL SYSTEM (a) NRSG231 Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi Skeletal System: Contents Functions of the Skeletal System Fracture Structure of Bone Tissue Articulations & Joint Bone Development and Growth
Articulations. Articulation. Joint between bones. Does not mean movement! Some joints are immovable; sutures.
 Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Skeletal System. By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
UNIT 5 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Nov 20 12:02 PM I. Functions A. Support: Internal framework, Structure, Anchors & Supports soft tissue/organs B. Protection: Protects vital organs C. Movement: Provide attach
MECHANICS OF MOVEMENT
 MECHANICS OF MOVEMENT Tissues and Structures Involved Muscle Nerve Bone Cartilage What are Tendons? Role of Joints Mechanics of Joints Making it all work Nerve and Muscle-- --the Motor Unit Motor neurons
MECHANICS OF MOVEMENT Tissues and Structures Involved Muscle Nerve Bone Cartilage What are Tendons? Role of Joints Mechanics of Joints Making it all work Nerve and Muscle-- --the Motor Unit Motor neurons
Extension: The Role of the Skeleton
 Extension: The Role of the Skeleton Jellyfish, sea anemones, and various kinds of worms accomplish movement by muscle alone. Animals capable of more rapid movements have muscles linked to a structural
Extension: The Role of the Skeleton Jellyfish, sea anemones, and various kinds of worms accomplish movement by muscle alone. Animals capable of more rapid movements have muscles linked to a structural
Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction. Sentenced to Life in the Joint
 Arthrology Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction Sentenced to Life in the Joint Kinesiology study of musculo-skeletal movement Articulations any point where two bones meet (joint)
Arthrology Arthrology the study of joint structure, function and dysfunction Sentenced to Life in the Joint Kinesiology study of musculo-skeletal movement Articulations any point where two bones meet (joint)
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
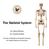 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
Unit 5 Skeletal System
 Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Unit 5 Skeletal System I. Functions A. Support: > Internal framework, structure, anchors & supports soft tissue organs B. Protection: > Protects vital organs C. Movement: > Provides attach point for muscles
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
The Skeletal System: Structure, Function, and Diseases of the bones and joints
 The Skeletal System: Structure, Function, and Diseases of the bones and joints Is this the correct anatomical position? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages
The Skeletal System: Structure, Function, and Diseases of the bones and joints Is this the correct anatomical position? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System
 Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System Part 1: Classifying Joints & Joint Movements Interactive pages 269-278 Types of Joints (AKA: Articulations) Structural Classification (type of tissue that binds the
Ch. 8 Joints of the Skeletal System Part 1: Classifying Joints & Joint Movements Interactive pages 269-278 Types of Joints (AKA: Articulations) Structural Classification (type of tissue that binds the
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS. Ms. Doshi
 CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
The Skeletal System: Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 8 The Skeletal System: Articulations Introduction The body cannot move without joints Movements are linked to the range of joint action Joints (arthroses) are connections between bones that may or may
8 The Skeletal System: Articulations Introduction The body cannot move without joints Movements are linked to the range of joint action Joints (arthroses) are connections between bones that may or may
Bell Work. Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies.
 Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Arthrology joint, articulation or union between two or more bones Classification by degree of movement or tissue that bind the bones together
 ARTICULATIONS OF THE SPINE AND THORAX Pages 8-12, 42 and 57 Arthrology joint, articulation or union between two or more bones Classification by degree of movement or tissue that bind the bones together
ARTICULATIONS OF THE SPINE AND THORAX Pages 8-12, 42 and 57 Arthrology joint, articulation or union between two or more bones Classification by degree of movement or tissue that bind the bones together
Chapter 9 Joints. Classification of Joints. Fibrous Joints. Structural classification based upon: Functional classification based upon movement:
 Chapter 9 Joints Joints hold bones together but permit movement Point of contact between 2 bones between cartilage and bone between teeth and bones Arthrology = study of joints Kinesiology = study of motion
Chapter 9 Joints Joints hold bones together but permit movement Point of contact between 2 bones between cartilage and bone between teeth and bones Arthrology = study of joints Kinesiology = study of motion
Muscle Tissue. Isometric Contraction. Isotonic Contractions 11/22/2016. Muscles. Anatomy Two Joints And Movements
 Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
INJURY ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT
 INJURY ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT UNIT THREE Despite the certified athletic trainer s best efforts toward injury prevention, injuries do still occur. It is important for the ATC to be able to recognize,
INJURY ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT UNIT THREE Despite the certified athletic trainer s best efforts toward injury prevention, injuries do still occur. It is important for the ATC to be able to recognize,
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system.
 L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
Chapter 5. Joint Classifications. Synarthroses. Amphiarthroses Slightly movable joints such as: Synchondroses 1 st sternocostal
 Chapter 5 Joint Classifications Synarthroses immovable Amphiarthroses slightly movable Diarthroses (synovial) freely movable Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Articulations Synarthroses Immovable joints such
Chapter 5 Joint Classifications Synarthroses immovable Amphiarthroses slightly movable Diarthroses (synovial) freely movable Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Articulations Synarthroses Immovable joints such
The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide
 DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
3/15/15. Chapter 8: Joints. Classification of Joints. Classification of Joints. } Objectives. } Functional Classifications
 Chapter 8: Joints Classification of Joints } Objectives } Define Joint or Articulation } Classify Joints by Structure and by Function } Describe the general structure, know the properties of, and provide
Chapter 8: Joints Classification of Joints } Objectives } Define Joint or Articulation } Classify Joints by Structure and by Function } Describe the general structure, know the properties of, and provide
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
Outline. Skeletal System. Functions of Bone. Bio 105: Skeletal System 3/17/2016. The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam
 Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Bio 105: Skeletal System Lecture 8 Chapter 5 The material from this lecture packet will be on the lecture exam The identification that you do after this lecture will be on the lab exam Outline I. Overview
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling
 Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
Bone Formation, Growth, and Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation)
