DEVELOPMENT OF DRUG DEVICE COMBINATION PRODUCTS I. INHALED THERAPEUTIC PRODUCTS IN THE US MARKET Rohinton Toddywala, Ph.D., MBA
|
|
|
- Cory Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEVELOPMENT OF DRUG DEVICE COMBINATION PRODUCTS I. INHALED THERAPEUTIC PRODUCTS IN THE US MARKET Rohinton Toddywala, Ph.D., MBA INTRODUCTION The benefits of inhaled therapy for the treatment of lung and systemic diseases have been recognized for many years. In comparison with oral or parenteral formulations, therapeutic doses of drug can be delivered locally into the airways to cause local effects within the lung or systemic effects throughout the body. In many cases, systemic effects can are minimized along with rapid onset and duration of action. Today, inhaled drugs such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids are gold standards for the treatment of diseases such as Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Systemic therapy of Cystic Fibrosis, Diabetes, Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH), Influenza and Schizophrenia are now available via aerosol delivery. Several new frontiers for treatment of diseases such as Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Diabetes, Ventilator Associated Pneumonia, Migraine and Multi Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis are currently under research. Inhaled therapy is delivered to the patients using devices to generate the aerosol of appropriate particle size. Several devices called Nebulizers deliver medication as a solution or suspension. Such devices are sold separately from the drug. The medication sold in the form of a nebule or respule. From a regulatory perspective the drug is approved separately from the nebulizer and the physician has the option of choosing the nebulizer of their choice to prescribe to the patient. There are several types of inhalation therapeutic devices that deliver medication as a Drug/Device Combination Product. These include the Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers (pmdi s), Dry Powder Inhalers (DPI s) and Solution/Suspension delivering devices that are integrated with the drug. Table 1 lists some characteristics of an Ideal Inhaler. Table 1: Ideal Characteristics of Inhalers 1 Dose reliability and reproducibility High lung-deposition efficiency Mass Median Aerodynamic Diameter <5 microns Simple to use and handle Short treatment time Portable Multiple-dose capability Durable Cost-effective Minimal/ drug released to ambient-air bacterial contamination through the use life of product Patient and Health care professional friendly In the United States, inhaled therapeutics are classified as Combination Products from a regulatory perspective. Combination products are generally complex in nature. This review details the different inhaled products that are currently in the market as well as outlines the different considerations in the development of these combination products. PRODUCT TYPES Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers: A metered-dose inhaler (MDI) is a device that delivers a specific amount of medication to the lungs, in the form of a short burst of aerosolized medicine. Pressurized MDI products contain therapeutically active ingredients dissolved or suspended in a propellant, a mixture of propellants, or a mixture of solvents, propellants, and/or other excipients in compact pressurized aerosol dispensers 2. The formulation of a pmdi usually contains the drug dissolved or suspended in a solvent and a propellant. The device component of a pmdi consists of a canister, a metering valve and the actuator. A dose counter may or may not be built into the actuator or may be placed separately on the device. One device (Aerospan
2 HFA, Meda Pharmaceuticals) incorporates a small chamber in the actuator. A pmdi product may discharge up to several hundred metered doses of one or more drug substances. Depending on the product, each actuation may contain from a few micrograms (mcg) up to milligrams (mg) of the active ingredients delivered in a volume typically between 25 and 100 microliters 2. Pressurized MDI s have been the dominant means of delivery of drug to the lungs for the last 30 years, and world-wide 2, they still constitute a majority of the global market. Table 2 shows the advantages and disadvantages of pmdi s. In terms of effectiveness and usability pmdi s exhibit several disadvantages over other similar aerosol products. The most prescribed pmdis are inefficient and are not user friendly. Results for MDIs showed that between 8 16% of the metered dose was deposited in the lungs 3. Pressurized MDIs require good co-ordination between dose activation and inhalation in order to ensure correct inhalation and deposition of the drug. Poor coordination is frequent and associated with poor disease control 4. Pressurized MDI s also require an optimal inspiratory flow, a full inspiration from functional residual capacity and breath hold of at least 6 seconds 5. Therefore, correct use of these inhalers requires intensive training by the physician and regular technique re-testing may also be necessary 6. Some suspension-based p-mdi s require shaking before use in order to thoroughly mix drug and propellant. Patients often forget this which may make drug delivery unreliable. It is reported that many as 90% of patients cannot use their MDI correctly 7. Common mistakes include failure to continuously inhale slowly after activation of the inhaler, failure to exhale fully before the inhalation 7,8, activation the inhaler before inhalation or at the end of inhalation and concluding inhaler activation while holding breath 8,9. Deposition rates with MDIs depend on inhalation technique 10. MDIs can be used with a valved-holding chamber device to improve drug deposition in the lungs, but this device is very bulky. However, use of an MDI without a valved-holding chamber device results in high deposition of the therapeutic agent in the mouth and pharynx 11. It is worth noting that there are significant differences in dose output from different combinations of MDIs and spacers 12.Finally, while most new pmdi s include a dose counter, several older formulations still do not have a dose counter making it difficult for the patient to determine when their canister is empty. Table 2: Advantages and Disadvantages of pmdis 13 Advantages Compact, Portable, Robust, Convenient, Unobtrusive, Multidose Shorter treatment times compared to traditional Nebulizers Good Delivered Dose Content Uniformity Aerosol is independent of patient s inhalation Inexpensive to manufacture in bulk Pressurized contents prevent ingress of microbes Disadvantages Many patients cannot use correctly and may receive low and/or variable lung dose t Breath Actuated Lung deposition could be lower compared to DPI s Difficult to deliver larger doses Need Priming and in some cases shaking prior to actuation Many pmdi s do not have a dose counter Several pmdi s have to be used with valvedholding chambers to remove larger particles Table 3 shows the pmdi products currently available in the US market. With the removal of the older generation chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) based products over the past decade; the use of pmdi s has reduced in the United States. Dry Powder Inhalers and other newer dosage forms have emerged as the dosage forms of choice for development by the pharmaceutical companies.
3 Table 3: Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers (pmdi s) in the United States Marketplace Product Name Disease State Drug Device Manufacturer Dose [mcg/puff] Number of Actuations Inactive Ingredients Advair HFA Asthma Fluticasone Propionate and Salmeterol Xinafoate GlaxoSmithKline 45/21, 115/21, 230/ HFA 134a Only Aerospan HFA Asthma Flunisolide Meda 80 60,120 Ethanol + HFA 134a Alvesco Asthma Ciclesonide Sunovion Pharmaceuticals 80, Ethanol + HFA 134a Asmanex HFA Asthma Mometasone furoate Merck 110, HFA-227, Ethanol and Oleic acid Atrovent HFA Asthma Ipratropium Bromide Boehringer Ingelheim Sterile Water + Dehydrated Alcohol + Anhydrous Citric Acid + HFA 134a Bevespi Aerosphere Dulera COPD Asthma Glycopyrrolate and Fomoterol Fumarate Mometasone furoate and fomoterol fumarate Aerosol Canister with or without Dose Counter Pearl Therapeutics 9/ Merck 5/100, 5/ and 120 HFA134a, porous particles (comprised fo DSPC and calcium choride) HFA-227, Anhydrous Alcohol, Oleic Acid Flovent HFA Asthma Fluticasone Propionate GlaxoSmithKline 44, 100, HFA 134a Only ProAir HFA Asthma Albuterol Sulfate Teva Ethanol (11.5% w/w) + HFA 134a Proventil HFA Asthma Albuterol Sulfate Merck Ethanol (15% w/w) + Oleic Acid (About 0.1% w/w) + HFA 134a Qvar 40, Qvar 80 Asthma Beclomethasone Dipropionate Teva 40, Ethanol + HFA 134a Symbicort Asthma Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate AstraZeneca 80/4.5, 160/ PEG PVP K25 + HFA 227ea Ventolin HFA Asthma Albuterol Sulfate GlaxoSmithKline HFA 134a Only Xopenex HFA Asthma Levalbuterol Tartrate Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Ethanol + Oleic Acid + HFA 134a
4 Dry Powder Inhalers: A Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI) is a device that delivers medication to the lungs in the form of a dry powder. Most DPI formulations consist of micronized drug blended with larger carrier particles, which enhance flow, reduce aggregation, and aid in dispersion. A combination of intrinsic physicochemical properties, particle size, shape, surface area, and morphology affects the forces of interaction and aerodynamic properties, which in turn determine fluidization, dispersion, delivery to the lungs, and deposition in the peripheral airways. When a DPI is actuated, the formulation is fluidized and enters the patient s airways. Under the influence of inspiratory airflow, the drug particles separate from the carrier particles and are carried deep into the lungs, while the larger carrier particles impact on the oropharyngeal surfaces and are cleared. If the cohesive forces acting on the powder are too strong, the shear of the airflow may not be sufficient to separate the drug from the carrier particles, which results in low deposition efficiency.. The critical factors driving the therapeutic effectiveness of a respiratory drug through a Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI) is the generation of an inhalation flow rate sufficient to trigger the dose and disaggregate the drug, thus producing a particulate of optimal size able to reach the therapeutic target within the lung. Dry Powder Inhalers can be easy to use and portable. Such an inhaler can be manufactured easily and can be relatively low in terms of cost. DPIs, as a class of delivery device, have numerous advantages over pmdis. They are breath activated, precluding the need for the patient to co-ordinate actuation with inhalation. This assists the effective drug delivery to the lungs. As a general rule, DPI s offer a higher lung deposition than pmdi s. Additionally, patients often express a preference for DPIs. For example, in elderly patients breath-activated inhalers are used correctly and are preferred by patients over pmdis 14. DPIs do have some limitations of design, cost effectiveness and user-friendliness. Table 4 shows the advantages and disadvantages of DPIs and Table 6 shows the DPI products currently available in the US market. Table 4: Advantages and Disadvantages of DPIs 13 Advantages Quick and convenient to use Usually compact and portable Little or no patient coordination of breathing required propellants needed Could deliver relatively higher doses than pmdi s Formulations can be relatively stable in a dry form Disadvantages Aerosol formation and deposition may depend on inspiratory effort Unit dose DPS s could be perceived as inconvenient Powders may be moisture sensitive providing inconsistent therapy There are many different types of DPI s. If patients are taking different types, there could be confusion in instructions Development and manufacture is usually more complex and expensive There are several DPIs currently on the market or being developed by the pharmaceutical industry. These devices are divided into single-unit dose devices, multi-dose reservoir device and multi-unit dose devices. Table 5 shows the different technologies of DPI s. The Neohaler, Aerolizer and Podhaler are examples of single-unit dose devices. Doses are individually loaded into gelatin capsules or blisters, each of which is loaded into the inhaler immediately before use. With multi-dose reservoir devices the drug is metered from a reservoir of freely flowing powder. Examples of these devices are Flexhaler, Pressair, RespiClick and Twisthaler. The Ellipta, Diskhaler and Diskus are examples of multi-unit dose devices. They contain a series of capsules or blisters within the devices. As one dose is delivered, the next dose is ready for delivery. Single-Unit Dose Devices require that a new capsule be inserted into device prior to inhalation. This makes this device cumbersome to use, makes dose-counting difficult and can give rise to higher dose variability. Further, higher temperatures can soften capsules making their perforation difficult. Finally, a high inspiratory flow must be achieved to generate a fine particle fraction 15.
5 Multi-Dose Devices offer good deposition with sufficient inspiratory flow. Such devices are prone to being affected by higher humidity conditions 16. These devices also Turbuhalers also require a relatively high inspiratory flow of 60 l/min for optimal drug delivery. This may not be achievable, especially in younger children, elderly patients and other patients with a low peak inspiratory flow rate. The particle size inhaled is very much dependent on the patients inspiratory flow rate 17. Finally, these devices require dose priming which may result in patient confusion. Multi-Unit Dose Devices offer some advantages over the Single-unit and Multi-dose devices. However, in some cases the metered dose is not completely emptied as the patient is not able to inspire fully. The mouthpiece is also not user friendly, and it is costly to produce because of the level of complexity. Finally, these devices also require a high inspiratory flow in order to achieve proper dosing which may not be feasible for certain populations of patients or certain disease states. Table 5: Dry Powder Inhaler Technologies DPI Technology Neohaler Drug (Product) Company How it works Indacaterol (Arcapta ) Glycopyrrolate (Seebri ) Glycopyrrolate /Indacaterol (Utibron ) Aerolizer Fomoterol (Foradil ) Merck Handihaler Tiotropium (Spiriva ) Boehringer Ingelheim Podhaler Tobramycin (Tobi ) vartis Cartridge Device Staccato Device Single-Unit Dose vartis Plastic device to inhale medication that uses a capsule. A capsule is placed in the device. When the buttons are pressed, the capsule is pierced and medication can be inhaled. These devices are breath activated. Insulin (Afrezza ) Mannkind Plastic device to inhale medication that uses a cartridge. The cartridges are color coded by dose. The cartridge is inserted into the device, a mouthpiece cover is removed and medication can be inhaled. The device is breath actuated. Loxapine (Adasuve ) Alexza This device generates aerosol by evaporation and condensation. The device contains a thin film which is heated. The drug evaporates and condenses as an aerosol. The device is breath actuated Multi-dose Reservoir Flexhaler Budesonide (Pulmicort) Astra Zeneca Plastic device that contains several doses of medication. Each dose is loaded by turning the bottom grip on one side and then back. The device is breath actuated. Pressair Aclidinium (Tudorza ) Astra Zeneca Plastic device that contains several doses of medication. Each dose is loaded by pressing the button. The device is breath actuated. RespiClick Albuterol (ProAir ) Teva Plastic device that contains several doses of medication. Each dose is loaded by opening the cap. The device is breath actuated. Twisthaler Mometasone (Asmanex ) Merck Plastic device that contains several doses of medication. Each dose is loaded by lifting the cap. The device is breath actuated. Multi-Unit dose Accuhaler Salmeterol (Serevent) Diskus Fluticasone/ Salmaterol (Advair ) Fluticasone (Flovent ) Diskhaler Zanamivir (Relenza ) Ellipta Fluticasone/Umeclidium/Vilanterol (Trelegy) Umeclidium/ Vilanterol (Anoro ) Fluticasone (Arnuity ) Fluticasone/ Vilanterol (Breo ) Umecldinium (Incruse ) GlaxoSmith -Kline Plastic device with multiple blisters. Each blister is loaded to expose the medication prior to inhalation. These devices are breath actuated.
6 Table 6: Dry Powder Inhalers (DPI s) in the United States Market Product Name Disease State Drug Device Manufacturer Dose per puff Number of Doses Inactive Ingredients Adasuve Schizophrenia Loxapine Advair Diskus Afrezza Anoro Ellipta Asthma Diabetes COPD Fluticasone Propionate and Salmeterol Xinafoate Recombinant Human Insulin Umeclidinium bromide and Vilanterol trifenatate Single-Unit Dose Thin Film Multi- Dose - Single-Unit Dose - Cartridge Multi-Unit Dose - Arcapta Neohaler COPD Indacaterol Maleate Single-Unit Dose - Capsule Arnuity Ellipta Asthma Fluticasone Furoate Multi-Unit Dose - Asmanex Multi-Dose Reservoir Twisthaler Asthma Mometasone Furoate - Powder Dose Dispenser Breo Ellipta Asthma/COPD Fluticasone Furoate and Vilanterol Trifenatate Flovent Diskus Asthma Fluticasone Propionate Foradil Aerolizer Asthma Formoterol Fumarate Incruse Ellipta COPD Umeclidinium bromide Multi-Unit Dose - Multi-Unit Dose - Single Unit Dose - Capsule Multi-Unit Dose - Proair Multi-Dose Reservoir RespiClick Asthma Albuterol Sulfate - Powder Dose Dispenser Multi-Dose Reservoir Pulmicort Flexhaler Asthma Budesonide - Powder Dose Dispenser Relenza Diskhaler Influenza Zanamivir Multi-Unit Dose - Seebri Neohaler COPD Glycopyrrolate Single-Unit Dose - Capsule Alexza GlaxoSmithKline Mannkind 10 mg base 100/50, 250/50, 500/50 mcg 4,8,12 units 5 units per carton 60 60,90, 120 cartridges GlaxoSmithKline 62.5/25 mcg 30 vartis 75 mcg base 30 Capsules GlaxoSmithKline 100, 200 mcg 30 Merck GlaxoSmithKline GlaxoSmithKline ne Lactose (contains milk proteins) Fumaryl Diketopiperazine, Polysorbate 80 Lactose Monohydrate (contains milk protein), Magnesium Stearate Lactose Monohydrate (contains trace levels of milk protein) Lactose Monohydrate (contains milk protein) 110, 220 mcg 30 Lactose (contains milk 220 mcg 60, 120 proteins) 100/25, 200/25 mcg 50, 100, 250 mcg Merck 12 mcg 60 capsules GlaxoSmithKline 62.5 mcg Teva 90 mcg 200 AstraZeneca 90, 180 mcg 60, 120 GlaxoSmithKline 5 mg/dose 20 vartis 15.6 mcg 60 Capsules Lactose Monohydrate (contains milk protein), Magnesium Stearate Lactose (contains milk proteins) Lactose (contains milk proteins) Lactose Monohydrate (contains milk protein), Magnesium Stearate Lactose (may contain milk proteins) Lactose (contains milk proteins) Lactose (contains milk proteins) Lactose Monohydrate (contains milk protein), Magnesium Stearate
7 Product Name Disease State Drug Device Manufacturer Dose per puff Serevent Multi-Unit Dose - Asthma Salmeterol Xinafoate Accuhaler Spiriva Handihaler Asthma Tiotropium Bromide Single-Unit Dose - Capsule Trelegy Ellipta COPD Fluticasone Furoate, Umeclidinium and Vilanterol Trifenatate Tobi Podhaler Cystic Fibrosis Tobramycin Tudorza Pressair COPD Aclidinium Bromide Utibron Neohaler COPD Glycopyrrolate and Indacaterol maleate Multi-Unit Dose - Single-Unit Dose - Capsule Multi-Dose Reservoir - Powder Dose Dispenser Single-Unit Dose - Capsule Number of Doses GlaxoSmithKline 50 mcg 60 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals GlaxoSmithKline 18 mcg 30 Strip 1:100 mcg Fluticasone Furoate; Strip 2: 62.5 mcg Umeclidinium /25 mcg Vilanterol Trifenatate 30 blisters vartis 28 mg 56 capsules Inactive Ingredients Lactose (contains milk proteins) Lactose (contains milk proteins) Strip 1: Fluticasone furoate- Lactose monohydrate (12.3 mg) Strip 2: Umeclidinium bromide/vilanterol trifenatate - magnesium stearate (75 mcg), and lactose monohydrate (12.3 mg) 1,2-distearoyl-sn- glycero-3- phosphocholine (DSPC), Calcium Chloride, and Sulfuric Acid (for ph adjustment) Astra Zeneca 400 mcg 30 and 60 Lactose Monohydrate vartis 15.6/27.5 mcg 60 Capsules Lactose Monohydrate (contains milk protein), Magnesium Stearate
8 Solution/Suspension Combination Products: Soft-Mist Inhalers Soft-Mist Inhalers (SMIs) use liquid formulations similar to those in nebulizers, but are generally multidose devices that have the potential to compete with pmdis and DPIs. SMI s contains sufficient doses of a formulation for one-month s dosing, stored in a fluid reservoir 18. Currently there is one device in the market called the Respimat. The Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler is powered by the energy of a compressed spring inside the inhaler; no propellants are required. Individual doses are delivered via a nozzle system as a slow-moving aerosol cloud (hence the term soft mist ). The velocity of the spray from and SMI is similar to a pmdi 19, however, scintigraphy studies have shown that lung deposition can be significantly higher than that of a pmdi 20. SMIs are a press and breathe device, and the correct inhalation technique closely resembles that used with a pmdi. While coordination between firing and inhaling is required, the low spray velocity and long duration of the aerosol cloud (typically s) enables patients to coordinate firing and inhaling more easily than with a pmdi 21. Table 7 shows the advantages and disadvantages of SMIs. Table 7: Advantages and Disadvantages of SMIs 22 Advantages Compact and Portable Multi-dose Device Convenient Do not contain propellants Lower particle sizes Lower spray velocity compared to pmdis Relatively higher lung deposition Easier to use than pmdis. Valved-holding chamber not required Disadvantages t breath-actuated Complicated method for preparation of first dose Additional actuation required if device is not used for a long period of time Require preservatives like benzalkonium chloride. Long term effects of inhaled preservatives are not known Nebulizers combined with Drugs Other than the traditional delivery systems discussed above, there are some drugs that are approved with specific nebulizers. One such product, Ventavis, is approved for the delivery of inhaled iloprost using the i-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD ) System. The device is a vibrating mesh device and is breath actuated. Software in the i-neb AAD System analyzes the patient s breathing pattern and pulses aerosol only during inspiration, thereby avoiding aerosol waste during expiration. The device can also log information. Studies have shown a significantly high lung deposition with this device. Table 8 shows the advantages and disadvantages of the i-neb system. Table 8: Advantages and Disadvantages of i-neb 23 Advantages Slow and deep breathing possible for optimal lung deposition Breath actuation prevents drug exposure to caregivers Allows patient feedback thru visual and tactile signals Patient compliance thru logging system Small amount of drug wastage due to low residual volumes Disadvantages Bulky system t easy to use Vibrating-mesh devices tend to clog Cannot be used for children < 2 years of age or with mechanically ventilated patients Several drugs cannot be mixed together Table 9 shows the Solution/Suspension Combination Products that are available in the US market.
9 Table 9: Solution/Suspension Combination Products in the United States Marketplace Product Name Disease State Drug Device Manufacturer Dose per puff Number of Doses Inactive Ingredients Combivent Respimat COPD Albuterol Sulfate and Ipratropium Bromide Respimat with cartridge Spiriva Respimat Asthma, COPD Tiotropium Bromide Respimat with cartridge Striverdi Respimat COPD Olodaterol hydrochloride Stiolto Respimat COPD Olodaterol hydrochloride and Tiotropium Bromide Respimat with cartridge Respimat with cartridge Cayston Cystic Fibrosis Aztreonam Altera Nebulizer Nebupent Tyvaso Ventavis Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Pentamidine Isethionate Treprostinil Soft Mist Inhalers Boehringer Ingelheim Boehringer Ingelheim Boehringer Ingelheim Boehringer Ingelheim Nebulizers combined with Drugs Respigard II Nebulizer Customized Nebulizer Gilead Sciences, Inc. Fresenius Kabi GlaxoSmithkline Iloprost i-neb AAD System Actelion 120/20 mcg 120 actuations 12.5 and 25 mcg 60 actuations 2.5 mcg base 60 actuations 2.5 mcg base/2.5 mcg base 60 actuations 75 mg/vial mg/vial mg/ml; 2.9 ml ampoule 10/20 mcg/ml; 1 ml ampule 28 ampules 30 ampules Water, Benzalkonium Chloride, Disodium Edetate, Water, Benzalkonium Chloride, Disodium Edetate, Water, Benzalkonium Chloride, Disodium Edetate, Anhydrous Citric Acid Water, Benzalkonium Chloride, Disodium Edetate, Lyophilized product with Lysine. Sodium Chloride (diluent) Lyophilized product to be diluted with 6 ml of Sterile Water for injection Sodium Chloride, Sodium Citrate, Sodium Hydroxide,, and Water for injection. Tromethamine, Ethanol, Sodium Chloride, for ph adjustment, and Water for Injection
10 Nebulized Products: Nebulizers convert a liquid into a aerosol for medical purposes. These products are still widely in use for inhaled therapeutics in medical practice in hospitals as well as for individual use. Nebulizers work on several different principles. Those driven by compressed air are termed jet nebulizers while those powered by a vibrating piezoelectric crystal are termed ultrasonic nebulizers. Jet nebulizers can be constant output, breath enhanced or breath actuated. In a constant output nebulizer, the aerosol is delivered at a constant rate through a venturi effect. In a breath-enhanced nebulizer, the air is added during inhalation that enhances the aerosol output during inhalation. Breath actuated nebulizers operate only during inhalation providing less wastage of medication during exhalation. Ultrasonic nebulizers employ a piezoelectric crystal that vibrates. The droplets are then forced through a mesh creating the aerosol. Table 10 shows the advantages and disadvantages of nebulizers: Table 10: Advantages and Disadvantages of Nebulized Products Advantages Disadvantages Jet Nebulizers are usually cheaper alternatives to traditional pmdis and Dry Powder Inhalers Jet nebulizers are generally bulky and require an external power source making them nonportable propellants needed Nebulizers and the drugs are sold separately allowing the physicians/patients to mix and match different nebulizers with different drugs Can be used with solution and suspension formulations Relatively larger volumes can be nebulized allowing for larger doses to be nebulized. The devices are generally approved as a 510(k) while the drugs are approved separately using an NDA/ANDA route. Several generic alternatives are available since formulations and approvals may be less complicated. Treatment times are generally significantly longer than pmdis or Dry Powder Inhalers Vibrating-mesh devices tend to clog Vibrating-mesh devices generally provide larger particle sizes Jet Nebulizers tend to have a significantly higher residual volume left in the nebulizer of wasted drug Continuous Jet nebulization can be inhaled by caregivers Table 11 shows the Nebulization Drugs that are available in the US market. These drugs are not associated with any one specific device and as such are not considered Drug-Device Combination Products. SUMMARY Inhalation is an effective route of drug administration for treating diseases. This route ensures that drugs are delivered directly to their site of action where they exert the required local effect. Inhaled Therapeutics are currently being used for the treatment of many respiratory diseases and are now successfully being used for other non-respiratory diseases. This paper reviews the varied products that are in the market today. Future papers will review the requirements required to develop Drug-Device combination products.
11 Table 11: Nebulization Drugs in the US Marketplace Drug Product Name Manufacturer Strength Concentration [mg/ml]. of ml per Vial Reference Listed Drug (RLD) Inactive Ingredients Acetylcysteine Albuterol Sulfate Arformoterol Tartrate Acetylcysteine Acetylcysteine Acetylcysteine Acetylcysteine AccuNeb Albuterol Sulfate AccuNeb Albuterol Sulfate Luitpold Pharmaceuticals Inc Hospira Inc, Alvogen Inc, Roxane Laboratories, Inc Luitpold Pharmaceuticals Inc Hospira Inc, Alvogen Inc, Roxane Laboratories, Inc Dey Pharma (Mylan) Nephron Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Watson Laboratories, Inc Dey Pharma (Mylan) Nephron Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Watson Laboratories, Inc 10% % 200 EQ 0.021% Base EQ 0.042% Base 30 ml Albuterol Sulfate Nephron Corp EQ 0.083% Albuterol Sulfate The Ritedose Corp Base Brovana Sunovion Pharmaceuticals EQ 0.015MG Base/2ML 15 2 Edetate disodium, hihydrate, Sodium Hydroxide and Edetate disodium, hihydrate, Sodium Hydroxide and Sodium Chloride and Sulfuric acid Sodium Chloride and Sulfuric acid Sodium Chloride and Sulfuric Acid Isotonic Saline Solution, phadjusted to 5.0 with Citric Acid and Sodium Citrate Pulmicort Budesonide AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP Sandoz Inc, Impax Laboratories, Inc, Apotex Ijc, Teva Pharmaceuticals 0.25MG/2ML Disodium Edetate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Citrate, Citric Acid, Polysorbate 80 and Water for Injection Budesonide Pulmicort Budesonide Pulmicort AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP Sandoz Inc, Impax Laboratories Inc, Apotex Inc, Teva Pharmaceuticals AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP 0.5MG/2ML MG/2ML 1 2 Disodium Edetate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Citrate, Citric Acid, Polysorbate 80 and Water for Injection Disodium Edetate, Sodium Chloride, Sodium Citrate, Citric
12 Drug Product Name Manufacturer Strength Cromolyn Sodium Budesonide Cromolyn Sodium Cromolyn Sodium Teva Pharmaceuticals, Sandoz Inc Teva Pharmaceuticals USA Mylan Speciality LP, Wockhardt Concentration [mg/ml]. of ml per Vial 10MG/ML 10 1 Reference Listed Drug (RLD) Inactive Ingredients Acid, Polysorbate 80 and Water for Injection Purified Water Formoterol Perforomist Dey Pharma (Mylan) 0.02MG/2ML 20 2 Sterile aqueous solution with NaCl, ph-adjusted to 5.0 with Citric Acid and Sodium Citrate Ipratropium Bromide and Albuterol Sulfate Ipratropium Bromide and Albuterol Sulfate Nephrom Pharmaceuticals Corporation, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Watson Pharmaceuticals, Cipla Ltd, The Ritedose Corp EQ 0.083% Base; 0.017% (0.5/2.5) 3 Isotonic Saline Solution and Ipratropium Bromide The Ritedose Corp Ipratropium Bromide Levalbuterol Ipratropium Bromide Xopenex Inhalation Solution Levalbuterol Hydrochloride Xopenex Inhalation Solution Levalbuterol Hydrochloride Xopenex Inhalation Solution Nephron Corp, Bausch and Lomb Pharmaceuticals Inc, Watson Laboratories Inc, Landela Pharmaceutical, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd. Oak Pharmaceuticals Inc Subsidiary of Akron Inc The Ritedose Corp, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Cipla Ltd, Myan Speciality, Impax Laboratories Oak Pharmaceuticals Inc Subsidiary of Akron Inc The Ritedose Corp, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Cipla Ltd, Myan Speciality, Impax Laboratories Oak Pharmaceuticals Inc Subsidiary of Akron Inc 0.02% (0.5/2.5) 2.5 EQ % Base EQ 0.021% Base EQ 0.042% Base Sodium Chloride and Sodium Chloride and Sodium Chloride and Sodium Chloride and
13 Drug Product Name Manufacturer Strength Concentration [mg/ml]. of ml per Vial Reference Listed Drug (RLD) Inactive Ingredients Pentetate Zinc (or calcium) Trisodium Ribavirin Tobramycin Levalbuterol Hydrochloride Xopenex Inhalation Solution Levalbuterol Hydrochloride Pentetate Zinc (or calcium) Trisodium Virazole Ribavirin Tobi Tobramycin The Ritedose Corp, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Cipla Ltd, Myan Speciality, Impax Laboratories Oak Pharmaceuticals Inc Subsidiary of Akron Inc EQ 0.25% Teva Pharmaceuticals, Base Mylan Speciality Hameln Pharma Plus Gmbh Valeant Pharmaceuticals international Navinta LLC vartis Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Akron Inc, Amneal Pharmaceuticals, Katibis Pak 1.25/ Sodium Chloride and EQ 1GM Base/ML(EQ 200 MG Base/ML n/a Lyophilized product to be diluted with sterile water for injection or sterile water for 6GM/Vial 6GM/Vial inhalaiton n/a 300MG/5ML Sodium chloride, WFI, Sulfuric Acid and NaOH Tobramycin Bethkis (to be used with Pari LC Plus nebulizer) Chiesi USA Inc 300MG/4ML Sodium Chloride, sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide
14 REFERENCES 1 Rau J L Design principles of liquid nebulization devices currently in use. Respir Care 2002; 47(11): FDA Guidance for the Industry Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) and Dry Powder Inhaler (DPI) Products; Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls Documentation October O Connor B, The ideal Inhaler: design and characteristics to improve outcomes, Respiratory Medicine (2004), Supplement A, S10-S16. 4 Giraud V, Roche N. Misuse of corticosteroid metered-dose inhaler is associated with decreased asthma stability. Eur Respir J 2002;19: Ernst P. Inhaled drug delivery: a practical guide to prescribing inhaler devices. Can Respir J 1998;5: Kamps A, Brand P, Roorda R. Determinants of correct inhalation technique in children attending a hospital-based asthma clinic. Acta Paediatr 2002;91: Erickson S, Horton A, Kirking D. Assessing metered dose inhaler technique: comparison of observation versus patient self-report. J Asthma 1998;35: van Beerendonk I, Mesters I, Mudde A, Tan T. Assessment of the inhalation technique in outpatients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using a metered-dose inhaler or dry powder device. J Asthma 1998;35: Larsen J, Hahn M, Ekholm B, Wick K. Evaluation of conventional press-and-breath metered-dose inhaler technique in 501 patients. J Asthma 1994;31: Crompton G. Problems patients have using pressurized aerosol inhalers. Eur Respir Dis 1982;119: Hirst P, Pitcairn G, Richards J, et al. Deposition and pharmacokinetics of an HFA formulation of triamcinolone acetonide delivered by pressurised metered dose inhaler. J Aerosol Med 2001;14: Berg E, Madsen J, Bisgaard H. In vitro performance of three combinations of spacers and pressurised metered dose inhalers for treatment in children. Eur Respir J 1998;12: Newman S, Peart J, Pressurized Metered Dose Inhalers, Respiratory Drug Delivery, Essential Theory and Practice, RDD Online, 2009: Chapman K, Love L, Brubaker H. A comparison of breath activated and conventional metered-dose inhaler inhalation techniques in elderly patients. Chest 1993;104: Chew N, Chan H. In vitro aerosol performance and dose uniformity between the Foradil Aerolizer and the Oxis Turbuhaler. J Aerosol Med 2001;14: Meakin B, Cainey J, Woodcock P. Effect of exposure to humidity on terbutaline delivery from Turbuhaler dry powder inhalation devices. Eur Respir J 1993;6:760 1.
15 17 Everard M, Devadason S, Souef P. Flow early in the inspiratory manoeuvre affects the aerosol particle size distribution from a Turbuhaler. Respir Med 1997;91: Zierenberg B. Optimizing the in vitro performance of Respimat. J Aerosol Med 1999; 12: Suppl. 1, S19 S Hochrainer D, Holz H. Comparison of the aerosol velocity and spray duration of Respimat1 Soft MistTM inhaler and pressurised metered dose inhalers. J Aerosol Med 2005; 18: Newman SP. Use of gamma scintigraphy to evaluate the performance of new inhalers. J Aerosol Med 1999; 12: Suppl. 1, S25 S Dalby R, Spallek M, Voshaar T. A review of the development of Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler. Int J Pharm 2004; 283: Newman S, Inhaler treatment options in COPD, Eur Respir Rev 2005; 14: 96, Dhand R., Intelligent Nebulizers in the Age of the Internet: The I-neb Adaptive Aerosol Delivery (AAD) System, J. Aerosol Med. Nad Pul Drug Del., 2010; 23: i-iii.
Ferris State University College of Pharmacy MPA CE Symposium 2016 Paul Thill, PharmD, BCPS
 Ferris State University College of Pharmacy MPA CE Symposium 2016 Paul Thill, PharmD, BCPS Objectives Categorize the new asthma and COPD inhalers in to existing or newly created categories Discuss the
Ferris State University College of Pharmacy MPA CE Symposium 2016 Paul Thill, PharmD, BCPS Objectives Categorize the new asthma and COPD inhalers in to existing or newly created categories Discuss the
Select Inhaled Respiratory Agents
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
First to Market or 505 (b)2 CMC Considerations IPAC-RS/UF Orlando Inhalation Conference Orlando, Florida
 First to Market or 505 (b)2 CMC Considerations IPAC-RS/UF Orlando Inhalation Conference Orlando, Florida Prasad Peri, Ph.D., Branch Chief, ONDQA, FDA March 19, 2014 1 Topics for discussion Introduction
First to Market or 505 (b)2 CMC Considerations IPAC-RS/UF Orlando Inhalation Conference Orlando, Florida Prasad Peri, Ph.D., Branch Chief, ONDQA, FDA March 19, 2014 1 Topics for discussion Introduction
MDI Bonanza. Dwayne Griffin, DO
 MDI Bonanza Dwayne Griffin, DO Bonanza 3. A MDI costing $200 - $500 per month SISYPHUS MDI Griffin Mountain Evolution of Deliver Systems for COPD in the US 2003 2009 2011 2013 2004 2012 2014 Prescribing
MDI Bonanza Dwayne Griffin, DO Bonanza 3. A MDI costing $200 - $500 per month SISYPHUS MDI Griffin Mountain Evolution of Deliver Systems for COPD in the US 2003 2009 2011 2013 2004 2012 2014 Prescribing
TRELEGY ELLIPTA (fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol) aerosol powder
 TRELEGY ELLIPTA (fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol) aerosol powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
TRELEGY ELLIPTA (fluticasone-umeclidinium-vilanterol) aerosol powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
The Medical Letter. on Drugs and Therapeutics
 The Medical Letter publications are protected by US and international copyright laws. Forwarding, copying or any other distribution of this material is strictly prohibited. For further information call:
The Medical Letter publications are protected by US and international copyright laws. Forwarding, copying or any other distribution of this material is strictly prohibited. For further information call:
COPD Medicine. No one ever showed me how to use this. Wendy Happel; RRT, COPD Educator Krystal Fedoris; RRT-NPS, BA, COPD Educator
 Medicine. No one ever showed me how to use this. Wendy Happel; RRT, Educator Krystal Fedoris; RRT-NPS, BA, Educator 1 Taking prescriptions correctly Taking prescriptions can be a challenge Busy schedules
Medicine. No one ever showed me how to use this. Wendy Happel; RRT, Educator Krystal Fedoris; RRT-NPS, BA, Educator 1 Taking prescriptions correctly Taking prescriptions can be a challenge Busy schedules
Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath.
 Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath. AccuNeb inhalation 0.021% solution: 0.63mg/3mL 3-4 times solution
Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath. AccuNeb inhalation 0.021% solution: 0.63mg/3mL 3-4 times solution
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens
 A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP 3 Main Categories Inhaled Respiratory Drugs Binds to beta-2 receptors Relaxation of smooth muscles in the lung
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP 3 Main Categories Inhaled Respiratory Drugs Binds to beta-2 receptors Relaxation of smooth muscles in the lung
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Supporting Evidence: Diagnosis and Management of Asthma The subdivision of this section is: Appendix B Tables Copyright 2016 by 1 Eleventh Edition/December 2016 Appendix B Asthma Summary Tables Class:
Supporting Evidence: Diagnosis and Management of Asthma The subdivision of this section is: Appendix B Tables Copyright 2016 by 1 Eleventh Edition/December 2016 Appendix B Asthma Summary Tables Class:
Your Inhaler Devices & You
 1 Your Inhaler Devices & You COUNSEL ON THE APPROPRIATE USE OF A: METERED DOSE INHALER (MDI) DRY POWDER INHALER (DPI) DISCUSS THE APPROPRIATE USAGE OF A PEAK FLOW METER AND SPACER/HOLDING CHAMBER DEVICE
1 Your Inhaler Devices & You COUNSEL ON THE APPROPRIATE USE OF A: METERED DOSE INHALER (MDI) DRY POWDER INHALER (DPI) DISCUSS THE APPROPRIATE USAGE OF A PEAK FLOW METER AND SPACER/HOLDING CHAMBER DEVICE
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens
 Adverse Effects of Inhaled Medications A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP June 28, 2017 Drug Category Beta 2 agonists antagonists Adverse Effects
Adverse Effects of Inhaled Medications A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP June 28, 2017 Drug Category Beta 2 agonists antagonists Adverse Effects
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens
 A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP October 23, 2017 Learning Objectives Be able to list at least 3 major adverse effects of inhaled medications
A Visual Approach to Simplifying Respiratory Drug Regimens Stephanie Cheng, PharmD, MPH, BCGP October 23, 2017 Learning Objectives Be able to list at least 3 major adverse effects of inhaled medications
Correct Use of Inhaler Devices
 PL Detail-Document #300206 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER February 2014 Correct Use of
PL Detail-Document #300206 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER February 2014 Correct Use of
AIRDUO RESPICLICK (fluticasone-salmeterol) aerosol DULERA (mometasone furoate and formoterol fumarate dihydrate) aerosol
 DULERA (mometasone furoate and formoterol fumarate dihydrate) aerosol Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
DULERA (mometasone furoate and formoterol fumarate dihydrate) aerosol Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
QUANTITY LIMIT CRITERIA. BROVANA (arformoterol tartrate) SEREVENT DISKUS (salmeterol) STRIVERDI RESPIMAT (olodaterol)
 Carelirst. +.V Family of health care plans DRUG CLASS COMBINATIONS QUANTITY LIMIT CRITERIA LONG ACTING BETA2-ADRENERGIC AGONIST, ORAL INHALATION BRAND NAME (generic) LONG-ACTING BETA2-ADRENERGIC AGONISTS:
Carelirst. +.V Family of health care plans DRUG CLASS COMBINATIONS QUANTITY LIMIT CRITERIA LONG ACTING BETA2-ADRENERGIC AGONIST, ORAL INHALATION BRAND NAME (generic) LONG-ACTING BETA2-ADRENERGIC AGONISTS:
A Patient s Guide to Aerosol Medication Delivery
 A Patient s Guide to Aerosol Medication Delivery 3rd Edition Prepared by: Tim Op t Holt, EdD, RRT, AE-C, FAARC Kimberly Wiles, RRT, CPFT Ellen Becker, PhD, RRT, RRT-NPS, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC Edited by: Timothy
A Patient s Guide to Aerosol Medication Delivery 3rd Edition Prepared by: Tim Op t Holt, EdD, RRT, AE-C, FAARC Kimberly Wiles, RRT, CPFT Ellen Becker, PhD, RRT, RRT-NPS, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC Edited by: Timothy
COPD Update. Plus New and Improved Products for Inhaled Therapy. Catherine Bourg Rebitch, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Associate Professor
 COPD Update Plus New and Improved Products for Inhaled Therapy Catherine Bourg Rebitch, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Associate Professor Disclosure The presenter has nothing to disclose concerning possible financial
COPD Update Plus New and Improved Products for Inhaled Therapy Catherine Bourg Rebitch, PharmD, BCACP Clinical Associate Professor Disclosure The presenter has nothing to disclose concerning possible financial
INHALERS for COPD INTRODUCTION. Types of inhalers. Inhaler technique. MDIs for COPD WET AEROSOLS. Dr Christopher Worsnop
 INHALERS for COPD Dr Christopher Worsnop Department of Respiratory Medicine Austin Hospital INTRODUCTION Most drugs for COPD are given via inhalers. This reduces the dose that needs to be given and delivers
INHALERS for COPD Dr Christopher Worsnop Department of Respiratory Medicine Austin Hospital INTRODUCTION Most drugs for COPD are given via inhalers. This reduces the dose that needs to be given and delivers
BREEZHALER. Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate)
 Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate) BREEZHALER Please date initial after you have directly observed
Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate) BREEZHALER Please date initial after you have directly observed
BREEZHALER. Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate)
 Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate) BREEZHALER Please date initial after you have directly observed
Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate) BREEZHALER Please date initial after you have directly observed
BREEZHALER. Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate)
 Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate) BREEZHALER Please date initial after you have directly observed
Medications available: Onbrez (indacaterol maleate) Seebri (glycopyrronium bromide) Ultibro (glycopyrronium bromide/ (indacaterol maleate) BREEZHALER Please date initial after you have directly observed
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS
 NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
NEBULIZERS, METERED DOSE INHALERS, AND DRY POWDER INHALERS Douglas S. Gardenhire, Ed.D, RRT-NPS MODULE 1 Manipulate Small Volume Nebulizers by Order or Protocol 1 Objectives for Module 1 At the end of
STRIVERDI RESPIMAT (olodaterol hcl) aerosol
 STRIVERDI RESPIMAT (olodaterol hcl) aerosol Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
STRIVERDI RESPIMAT (olodaterol hcl) aerosol Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Impact of a Comprehensive COPD Therapeutic Interchange Program on 30-Day Readmission Rates in Hospitalized Patients
 Impact of a Comprehensive COPD Therapeutic Interchange Program on 30-Day Readmission Rates in Hospitalized Patients Maren A. McGurran, PharmD, BCPS; Lisa M. Richter, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP; Nathan D. Leedahl,
Impact of a Comprehensive COPD Therapeutic Interchange Program on 30-Day Readmission Rates in Hospitalized Patients Maren A. McGurran, PharmD, BCPS; Lisa M. Richter, PharmD, BCPS, BCCCP; Nathan D. Leedahl,
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU
 Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
Delivering Aerosol Medication in ICU 18th Aug 2017 Lau Chee Lan Pharmacist HCTM PPUKM ASMIC 2017 Aerosol Therapy Part of the treatment for a variety of respiratory disease * asthma and chronic obstructive
What You Need to Know about Metered-Dose Inhalers and the HFA Propellant
 What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
What You Need to Know about Metered- Inhalers and the HFA Propellant There are a number ways to deliver inhaled medication. They include: Metered-dose inhaler () Metered-dose inhaler with spacer/holding
10/18/2012. Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C
 Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Common Inhaled Asthma Medications Dose Comparison and Tips for Use
 Detail-Document #210303 This Detail-Document accompanies the related article published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER March 2005 ~ Volume 21 ~ Number 210303 Common Inhaled Asthma Medications
Detail-Document #210303 This Detail-Document accompanies the related article published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER March 2005 ~ Volume 21 ~ Number 210303 Common Inhaled Asthma Medications
Guide to Inhaled Treatment Choices
 Guide to Inhaled Treatment Choices Note: this is guidance only, it is important to consider which device is best suited to the patient. This may NOT be the first line choice (but should be on the joint
Guide to Inhaled Treatment Choices Note: this is guidance only, it is important to consider which device is best suited to the patient. This may NOT be the first line choice (but should be on the joint
Guide to Inhaled Treatment Choices
 Guide to Inhaled Treatment Choices Note: this is guidance only, it is important to consider which device is best suited to the patient. This may NOT be the first line choice (but should be on the joint
Guide to Inhaled Treatment Choices Note: this is guidance only, it is important to consider which device is best suited to the patient. This may NOT be the first line choice (but should be on the joint
Pulmonary Disease Aerosol Delivery Devices A Guide for Physicians, Nurses, Pharmacists, and Other Health Care Professionals
 Pulmonary Disease Aerosol Delivery Devices A Guide for Physicians, Nurses, Pharmacists, and Other Health Care Professionals 3rd Edition Karen L. Gregory, DNP, APRN, CNS, RRT, AE-C, FAARC Lori Wilken, PharmD,
Pulmonary Disease Aerosol Delivery Devices A Guide for Physicians, Nurses, Pharmacists, and Other Health Care Professionals 3rd Edition Karen L. Gregory, DNP, APRN, CNS, RRT, AE-C, FAARC Lori Wilken, PharmD,
Asthma/COPD Update with Inhaler Workshop
 Asthma/COPD Update with Inhaler Workshop October 8, 2017 Nathan Samsa, DO, Pharm D, RPh, FACOI None Disclosures Agenda Asthma Updates COPD Updates Inhaler Workshop Asthma Updates Asthma Updates SMART Trial
Asthma/COPD Update with Inhaler Workshop October 8, 2017 Nathan Samsa, DO, Pharm D, RPh, FACOI None Disclosures Agenda Asthma Updates COPD Updates Inhaler Workshop Asthma Updates Asthma Updates SMART Trial
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: (Seebri Neohaler) Reference Number: CP.CPA.150 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy
Clinical Policy: (Seebri Neohaler) Reference Number: CP.CPA.150 Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 11.17 Line of Business: Commercial Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy
Inhaled Corticosteroid Dose Comparison in Asthma
 This Clinical Resource gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in April 2017 ~ Resource #330402 Inhaled Corticosteroid Dose Comparison in Asthma The chart below provides
This Clinical Resource gives subscribers additional insight related to the Recommendations published in April 2017 ~ Resource #330402 Inhaled Corticosteroid Dose Comparison in Asthma The chart below provides
Drug Effectiveness Review Project Summary Report
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma/COPD Update with Inhaler Workshop
 Asthma/COPD Update with Inhaler Workshop October 8, 2017 Nathan Samsa, DO, Pharm D, RPh, FACOI None Disclosures Agenda Asthma Updates COPD Updates Inhaler Workshop Medication Acronyms SABA: Short acting
Asthma/COPD Update with Inhaler Workshop October 8, 2017 Nathan Samsa, DO, Pharm D, RPh, FACOI None Disclosures Agenda Asthma Updates COPD Updates Inhaler Workshop Medication Acronyms SABA: Short acting
Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management. Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018
 Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest 2 Objectives Summarize
Up in FLAMES: Stable Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Management Colleen Sakon, PharmD BCPS September 27, 2018 Disclosures I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest 2 Objectives Summarize
The Latest Medications A Pharmacological Update for RTs
 The Latest Medications A Pharmacological Update for RTs Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Georgia State University Objectives
The Latest Medications A Pharmacological Update for RTs Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Georgia State University Objectives
Appendix M: Device Technique
 Nursing Care of Dyspnea: The 6th Vital Sign in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Appendix M: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Medications come in many forms.
Nursing Care of Dyspnea: The 6th Vital Sign in Individuals with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Appendix M: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Medications come in many forms.
Aerosol Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists
 A Guide To Aerosol Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists 4th Edition Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Dave Burnett, PhD, RRT, AE-C Shawna Strickland, PhD, RRT-NPS, RRT-ACCS, AE-C, FAARC
A Guide To Aerosol Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists 4th Edition Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Dave Burnett, PhD, RRT, AE-C Shawna Strickland, PhD, RRT-NPS, RRT-ACCS, AE-C, FAARC
The ideal inhaler: design and characteristics to improve outcomes
 Respiratory Medicine (2004) Supplement A, S10 S16 ARTICLE IN PRESS The ideal inhaler: design and characteristics to improve outcomes Brian J. O Connor* Department of Respiratory Medicine and Allergy, Guy
Respiratory Medicine (2004) Supplement A, S10 S16 ARTICLE IN PRESS The ideal inhaler: design and characteristics to improve outcomes Brian J. O Connor* Department of Respiratory Medicine and Allergy, Guy
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline. MedStar Health
 Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of COPD 2016 Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions
MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINES ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE DATE: 07/05/18 SECTION: DRUGS LAST REVIEW DATE: LAST CRITERIA REVISION DATE: ARCHIVE DATE:
 CINQAIR (reslizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
CINQAIR (reslizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
Respiratory Inhalers. Identification Guide Version 3
 Respiratory Inhalers Identification Guide Version 3 This booklet has been prepared by NHSGGC Medicines Information. Endorsed by NHSGGC Respiratory Managed Clinical Network, February 2017. Designed by Medical
Respiratory Inhalers Identification Guide Version 3 This booklet has been prepared by NHSGGC Medicines Information. Endorsed by NHSGGC Respiratory Managed Clinical Network, February 2017. Designed by Medical
primer on inhalers and nebulizers
 CREDIT: 2.0 Continuing Education EARN CE CREDIT FOR THIS ACTIVITY AT WWW.DRUGTOPICS.COM AN ONGOING CE PROGRAM OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT SCHOOL OF PHARMACY AND DRUG TOPICS educational objectives
CREDIT: 2.0 Continuing Education EARN CE CREDIT FOR THIS ACTIVITY AT WWW.DRUGTOPICS.COM AN ONGOING CE PROGRAM OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT SCHOOL OF PHARMACY AND DRUG TOPICS educational objectives
Breakout Session # A 12:45 1:25. New Methods of Medication Delivery to the Lungs: Say Goodbye to the MDI as we know it
 Breakout Session # A 12:45 1:25 New Methods of Medication Delivery to the Lungs: Say Goodbye to the MDI as we know it Michael J. Welch MD, FAAP, FAAAAI, CPI Co-director, Allergy & Asthma Medical Group
Breakout Session # A 12:45 1:25 New Methods of Medication Delivery to the Lungs: Say Goodbye to the MDI as we know it Michael J. Welch MD, FAAP, FAAAAI, CPI Co-director, Allergy & Asthma Medical Group
Question I was one of the first dry power devices available in the US Flovent, Serevent and Advair are all available in this device
 What Device am I Class Side Effects History Potpourri Monitoring Tools 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 WHAT KIND OF DEVICE AM I? I was one of the first dry power
What Device am I Class Side Effects History Potpourri Monitoring Tools 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20 20 20 30 30 30 30 30 40 40 40 40 40 50 50 50 50 50 WHAT KIND OF DEVICE AM I? I was one of the first dry power
THE COPD PRESCRIBING TOOL
 THE COPD PRESCRIBING TOOL Revised edition, 2017 www.bpac.org.nz/copd CLASSIFICATION The COPD prescribing tool This tool provides pharmacological treatment options for patients with COPD based on their
THE COPD PRESCRIBING TOOL Revised edition, 2017 www.bpac.org.nz/copd CLASSIFICATION The COPD prescribing tool This tool provides pharmacological treatment options for patients with COPD based on their
REVISED RESPIRATORY MEDICATION USE QUESTIONNAIRE
 REVISED RESPIRATORY MEDICATION USE QUESTIONNAIRE ID NUMBER: 0a) Date of Collection / / 0b) Staff Code Instructions: This form should be completed during the participant s clinic visit. 1) Are you regularly
REVISED RESPIRATORY MEDICATION USE QUESTIONNAIRE ID NUMBER: 0a) Date of Collection / / 0b) Staff Code Instructions: This form should be completed during the participant s clinic visit. 1) Are you regularly
FASENRA (benralizumab)
 FASENRA (benralizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
FASENRA (benralizumab) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs
Respiratory Medications and Devices Update 2/15
 Respiratory Medications and Devices Update 2/15 Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Wendy Brown, Pharm.D., MPAS, PA-C, AE-C Objectives! Review mechanism of action for asthma pharmacologic agents! Describe key patient
Respiratory Medications and Devices Update 2/15 Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Wendy Brown, Pharm.D., MPAS, PA-C, AE-C Objectives! Review mechanism of action for asthma pharmacologic agents! Describe key patient
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medicaid P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
New and Novel Medications for Respiratory Care
 New and Novel Medications for Respiratory Care JASON MOORE, PHARM.D. BCCCP CLINICAL STAFF PHARMACIST STORMONT-VAIL HEALTH Objectives Quick overview of the newest FDA-approved repiratory-related medications
New and Novel Medications for Respiratory Care JASON MOORE, PHARM.D. BCCCP CLINICAL STAFF PHARMACIST STORMONT-VAIL HEALTH Objectives Quick overview of the newest FDA-approved repiratory-related medications
Inhalation devices, proper technique and cleaning
 Preventing Your Symptoms and Taking Your Medications Inhalation devices, proper technique and cleaning Knowing how to use your medications properly is important because inhaled drugs are meant to get directly
Preventing Your Symptoms and Taking Your Medications Inhalation devices, proper technique and cleaning Knowing how to use your medications properly is important because inhaled drugs are meant to get directly
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol
 Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
Inhaled Corticosteroids Drug Class Prior Authorization Protocol Line of Business: Medi-Cal P&T Approval Date: February 21, 2018 Effective Date: April 1, 2018 This policy has been developed through review
2008 IPAC-RS Conference Doing the Right Thing Science, Quality and Patient Focus
 2008 IPAC-RS Conference Doing the Right Thing Science, Quality and Patient Focus Patient Perspective Alpha-1 1 Foundation John W. Walsh Patient Focus Personal perspective Challenges and lessons Importance
2008 IPAC-RS Conference Doing the Right Thing Science, Quality and Patient Focus Patient Perspective Alpha-1 1 Foundation John W. Walsh Patient Focus Personal perspective Challenges and lessons Importance
End Stage COPD Guidance Document
 End Stage COPD Guidance Document Suggested Guidelines for the Determination of Hospice Eligibility A patient with severe chronic pulmonary disease that meets the following criteria may be eligible for
End Stage COPD Guidance Document Suggested Guidelines for the Determination of Hospice Eligibility A patient with severe chronic pulmonary disease that meets the following criteria may be eligible for
The Novolizer s : overcoming inherent problems of dry powder inhalers
 Respiratory Medicine (2004) Supplement A, S17 S21 ARTICLE IN PRESS The Novolizer s : overcoming inherent problems of dry powder inhalers Dieter Kohler* Chefarzt Innere Medizin und Pneumologie, Fachkrankenhaus
Respiratory Medicine (2004) Supplement A, S17 S21 ARTICLE IN PRESS The Novolizer s : overcoming inherent problems of dry powder inhalers Dieter Kohler* Chefarzt Innere Medizin und Pneumologie, Fachkrankenhaus
reslizumab (Cinqair )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Asthma & COPD Medication Review. Hutchison Disclosures 2/16/2017. Objectives
 Asthma & COPD Medication Review Anna Meador, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Professor/ Pharmacy Director McWhorter School of Pharmacy/ Christ Health Center Amber Hutchison, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Clinical Professor
Asthma & COPD Medication Review Anna Meador, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Professor/ Pharmacy Director McWhorter School of Pharmacy/ Christ Health Center Amber Hutchison, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Clinical Professor
A Guide to Aerosol Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists, 3rd Edition
 A Guide to Aerosol Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists, 3rd Edition Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Arzu Ari PhD, PT, RRT, CPFT, FAARC Dean Hess, PhD, RRT, FAARC Timothy R. Myers, MBA,
A Guide to Aerosol Delivery Devices for Respiratory Therapists, 3rd Edition Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Arzu Ari PhD, PT, RRT, CPFT, FAARC Dean Hess, PhD, RRT, FAARC Timothy R. Myers, MBA,
Clinical Policy: Roflumilast (Daliresp) Reference Number: CP.PMN.46 Effective Date: Last Review Date: 08.18
 Clinical Policy: (Daliresp) Reference Number: CP.PMN.46 Effective Date: 11.01.11 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: (Daliresp) Reference Number: CP.PMN.46 Effective Date: 11.01.11 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
GMMMG Asthma Formulary Inhaler Options August 2017
 Regular Preventer Beclometasone Beclometasone Beclometasone Brand name Qvar Easi-Breathe Clenil Modulite Easyhaler Device MDI MDI DPI Strengths 50 microgram 100 microgram 200 microgram Adult asthma 2 inhalations
Regular Preventer Beclometasone Beclometasone Beclometasone Brand name Qvar Easi-Breathe Clenil Modulite Easyhaler Device MDI MDI DPI Strengths 50 microgram 100 microgram 200 microgram Adult asthma 2 inhalations
How can I benefit most from my COPD medications?
 Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
Fact Sheet: COPD Medications and Delivery Devices How can I benefit most from my COPD medications? COPD medications can improve your symptoms. By taking the right medication at the right time, you can
GMMMG COPD Formulary Inhaler Options October 2017
 BNF 3.1.1 Adrenocepter agonists (SABA) Salbutamol Salbutamol Terbutaline Brand name Airsalb Ventolin Evohaler Bricanyl Turbohaler Device MDI MDI Dry powder Strengths 100 microgram 100 microgram 500 microgram
BNF 3.1.1 Adrenocepter agonists (SABA) Salbutamol Salbutamol Terbutaline Brand name Airsalb Ventolin Evohaler Bricanyl Turbohaler Device MDI MDI Dry powder Strengths 100 microgram 100 microgram 500 microgram
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD
 How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
How to Use Inhaled Medications for Asthma and COPD This information is not intended to diagnose health problems or to take the place of medical advice or care you receive from your physician or other health
How to Use Inhaled Medications
 How to Use Inhaled Medications FOR ASTHMA AND COPD introduction Inhaled medications are an important part of controlling and treating asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The medication
How to Use Inhaled Medications FOR ASTHMA AND COPD introduction Inhaled medications are an important part of controlling and treating asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The medication
COPD Device Workshop. Summary. Role of inhaler device in COPD. Why use inhaler device in COPD?
 Part 1 Role of inhaler device in COPD COPD Device Workshop Dr Philip Lee Respiratory and Sleep Physician St George Hospital, Sydney Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Incorrect inhaler technique-adverse clinical outcomes
Part 1 Role of inhaler device in COPD COPD Device Workshop Dr Philip Lee Respiratory and Sleep Physician St George Hospital, Sydney Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Incorrect inhaler technique-adverse clinical outcomes
Test Your Inhaler Knowledge
 A Breath of Fresh Air: Updates in COPD Management Jennifer Austin Szwak, PharmD, BCPS, DPLA University of Chicago Medicine The speaker has nothing to disclose Abbreviations COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary
A Breath of Fresh Air: Updates in COPD Management Jennifer Austin Szwak, PharmD, BCPS, DPLA University of Chicago Medicine The speaker has nothing to disclose Abbreviations COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary
Incorporating Newer Therapies and Strategies to Improve COPD Outcomes: A Practical Guide for Pharmacists. Learning Objectives.
 Incorporating Newer Therapies and Strategies to Improve COPD Outcomes: A Practical Guide for Pharmacists Learning Objectives Identify the risk factors for COPD and the clinical features that differentiate
Incorporating Newer Therapies and Strategies to Improve COPD Outcomes: A Practical Guide for Pharmacists Learning Objectives Identify the risk factors for COPD and the clinical features that differentiate
Appendix E: Device Technique
 Adult Asthma Care Guidelines for Nurses: Promoting Control of Asthma Appendix E: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Adapted with permission from The Lung Association: www.lung.ca/asthma/manage/devices.html
Adult Asthma Care Guidelines for Nurses: Promoting Control of Asthma Appendix E: Device Technique Medications: Inhalation Devices Adapted with permission from The Lung Association: www.lung.ca/asthma/manage/devices.html
Practical Problems With Aerosol Therapy in COPD. Joseph L Rau PhD RRT FAARC
 Special Articles Practical Problems With Aerosol Therapy in COPD Joseph L Rau PhD RRT FAARC Introduction Problems With Use of MDIs Synchronizing Inhalation With MDI Actuation Lack of a Dose Counter Medical
Special Articles Practical Problems With Aerosol Therapy in COPD Joseph L Rau PhD RRT FAARC Introduction Problems With Use of MDIs Synchronizing Inhalation With MDI Actuation Lack of a Dose Counter Medical
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Use of Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler in COPD patients
 REVIEW Use of Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler in COPD patients Paula Anderson Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Central Arkansas Veterans Healthcare
REVIEW Use of Respimat Soft Mist Inhaler in COPD patients Paula Anderson Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Central Arkansas Veterans Healthcare
COPD: Treatment Update Property of Presenter. Not for Reproduction. Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health
 COPD: Treatment Update Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory board, consultant, multi-center trial, research funding, Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB), or
COPD: Treatment Update Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory board, consultant, multi-center trial, research funding, Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB), or
Reference Guide for Caring for Pediatric Patients with Asthma
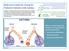 Reference Guide for Caring for Pediatric Patients with Asthma Co-Chair: Nancy Cantey Banasiak, DNP, PPCNP-BC, APRN Co-Chair: Deborah Hickman, DNP, APRN-CNP, CPNP-PC, NNP-BC Asthma and Allergy SIG Members
Reference Guide for Caring for Pediatric Patients with Asthma Co-Chair: Nancy Cantey Banasiak, DNP, PPCNP-BC, APRN Co-Chair: Deborah Hickman, DNP, APRN-CNP, CPNP-PC, NNP-BC Asthma and Allergy SIG Members
COPD Medications Coverage Summary Non-Insured Health Benefits Coverage SABA Bricanyl turbuhaler Yes Yes
 COPD Medications Coverage Summary Drug Non-Insured Health Benefits Coverage SABA Bricanyl turbuhaler Yes Yes Ventolin MDI + generics Yes Yes Ventolin Diskus NO NO Yukon Pharmacare/Chronic Disease Program
COPD Medications Coverage Summary Drug Non-Insured Health Benefits Coverage SABA Bricanyl turbuhaler Yes Yes Ventolin MDI + generics Yes Yes Ventolin Diskus NO NO Yukon Pharmacare/Chronic Disease Program
Individualizing and Optimizing Asthma Care. CFW 2018 Friday, April 13, 9:45 11:15 am Renaissance Austin Hotel in Austin, Texas
 Individualizing and Optimizing Asthma Care CFW 2018 Friday, April 13, 9:45 11:15 am Renaissance Austin Hotel in Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Hawkins has disclosed that he has no actual or potential
Individualizing and Optimizing Asthma Care CFW 2018 Friday, April 13, 9:45 11:15 am Renaissance Austin Hotel in Austin, Texas Speaker Disclosure Dr. Hawkins has disclosed that he has no actual or potential
Learning Objectives 4/26/2012. Review normal lung function and COPD pathophysiology Discuss pharmacological management
 Marliese Gibson PharmD HospiScript, a Catalyst Rx Company May 16, 2012 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Learning Objectives Review normal lung function and COPD pathophysiology Discuss pharmacological
Marliese Gibson PharmD HospiScript, a Catalyst Rx Company May 16, 2012 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Learning Objectives Review normal lung function and COPD pathophysiology Discuss pharmacological
A Breath of Fresh Air? An update of novel inhalers used for the treatment of asthma and COPD
 A Breath of Fresh Air? An update of novel inhalers used for the treatment of asthma and COPD Chris Federico PharmD, BCACP RIPF Kimberly McDonough Spring Seminar May 4, 2016 Disclosure I have no actual
A Breath of Fresh Air? An update of novel inhalers used for the treatment of asthma and COPD Chris Federico PharmD, BCACP RIPF Kimberly McDonough Spring Seminar May 4, 2016 Disclosure I have no actual
Drug Class Monograph
 Drug Class Monograph Class: Inhaled Corticosteroids Drugs: Aerospan (flunisolide), Advair Diskus, Advair HFA (fluticasone/salmeterol), Alvesco (ciclesonide), Arnuity Ellipta (fluticasone furoate), Asmanex
Drug Class Monograph Class: Inhaled Corticosteroids Drugs: Aerospan (flunisolide), Advair Diskus, Advair HFA (fluticasone/salmeterol), Alvesco (ciclesonide), Arnuity Ellipta (fluticasone furoate), Asmanex
Formulation Considerations for Inhaled Products
 Formulation Considerations for Inhaled Products Formulation Considerations of Inhaled Products Inhalation Therapy Nebulizers and Formulations Dry Powder Inhalers and Formulations Metered Dose Inhalers
Formulation Considerations for Inhaled Products Formulation Considerations of Inhaled Products Inhalation Therapy Nebulizers and Formulations Dry Powder Inhalers and Formulations Metered Dose Inhalers
COPD The New Epidemic. Peter Lin MD CCFP Director Primary Care Initiatives Canadian Heart Research Centre
 COPD The New Epidemic Peter Lin MD CCFP Director Primary Care Initiatives Canadian Heart Research Centre Conflict Disclosure Information Speaker: Dr. Peter Lin Title of Talk: COPD The New Epidemic Financial
COPD The New Epidemic Peter Lin MD CCFP Director Primary Care Initiatives Canadian Heart Research Centre Conflict Disclosure Information Speaker: Dr. Peter Lin Title of Talk: COPD The New Epidemic Financial
SELECTING A DOSAGE FORM FOR DRUG DELIVERY TO THE LUNGS
 SELECTING A DOSAGE FORM FOR DRUG DELIVERY TO THE LUNGS Poonam Sheth, PharmD, PhD, Research Scientist, Inhalation Matthew T. Marmura, Research Scientist, Inhalation Recipharm is frequently asked to help
SELECTING A DOSAGE FORM FOR DRUG DELIVERY TO THE LUNGS Poonam Sheth, PharmD, PhD, Research Scientist, Inhalation Matthew T. Marmura, Research Scientist, Inhalation Recipharm is frequently asked to help
COPD Update: Focus on Intensifying LABA, LAMA and ICS Therapy
 Update: Focus on Intensifying LABA, LAMA and ICS Therapy B.C. Provincial Academic Detailing Service February 2017 Background In Canada, approximately 20 inhaled medications are approved to treat Chronic
Update: Focus on Intensifying LABA, LAMA and ICS Therapy B.C. Provincial Academic Detailing Service February 2017 Background In Canada, approximately 20 inhaled medications are approved to treat Chronic
University System of Georgia Prior Authorization, Step Therapy and Quantity Limit List (Updated 1/1/2016)
 University System of Georgia, Step Therapy and Quantity Limit List (Updated 1/1/2016) (PA) Your doctor will need to obtain a prior authorization for the drugs listed below, before your prescription drug
University System of Georgia, Step Therapy and Quantity Limit List (Updated 1/1/2016) (PA) Your doctor will need to obtain a prior authorization for the drugs listed below, before your prescription drug
I have no conflicts of interest or financial relationships to disclose!
 I have no conflicts of interest or financial relationships to disclose! Timothy R. Hudd BS, PharmD, RPh, AE-C Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice MCPHS University Boston, MA Clinical Pharmacist Primary
I have no conflicts of interest or financial relationships to disclose! Timothy R. Hudd BS, PharmD, RPh, AE-C Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice MCPHS University Boston, MA Clinical Pharmacist Primary
Using Inhaled Corticosteroids as Needed for Asthma: giving patients relief or leaving them breathless?
 Using Inhaled Corticosteroids as Needed for Asthma: giving patients relief or leaving them breathless? Lindsay Thomas, Pharm.D. PGY2 Ambulatory Care Resident Department of Pharmacotherapy and Pharmacy
Using Inhaled Corticosteroids as Needed for Asthma: giving patients relief or leaving them breathless? Lindsay Thomas, Pharm.D. PGY2 Ambulatory Care Resident Department of Pharmacotherapy and Pharmacy
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Asthma/COPD P&T DATE 12/14/2017 CLASS:
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Asthma/COPD P&T DATE 12/14/2017 CLASS: LOB: Respiratory Disorders Medi-Cal REVIEW HISTORY (MONTH/YEAR) 12/17,12/16, 5/15,
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Asthma/COPD P&T DATE 12/14/2017 CLASS: LOB: Respiratory Disorders Medi-Cal REVIEW HISTORY (MONTH/YEAR) 12/17,12/16, 5/15,
Dose. Route. Units. Given. Dose. Route. Units. Given
 Chapter 4 Respiratory Andrew Stanton SALBUTAMOL (in acute asthma) 5 in acute asthma Nebulised (driven by oxygen not air) 4 6 hourly In acute severe asthma not responding to initial treatment or in life-threatening
Chapter 4 Respiratory Andrew Stanton SALBUTAMOL (in acute asthma) 5 in acute asthma Nebulised (driven by oxygen not air) 4 6 hourly In acute severe asthma not responding to initial treatment or in life-threatening
Advance in inhaler technique: changes in delivery devices, Authorized Generics, and Advance in technology for monitoring inhaler adherence
 Advance in inhaler technique: changes in delivery devices, Authorized Generics, and Advance in technology for monitoring inhaler adherence Bruce Brown, MS, RRT, AE-C Nemours Healthcare System Disclosures
Advance in inhaler technique: changes in delivery devices, Authorized Generics, and Advance in technology for monitoring inhaler adherence Bruce Brown, MS, RRT, AE-C Nemours Healthcare System Disclosures
Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) In Vitro Measures to Confirm Patient Perceptions: HFA vs. CFC
 Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) In Vitro Measures to Confirm Patient Perceptions: HFA vs. CFC William H. Doub, Ph.D. Division of Pharmaceutical Analysis (DPA) US FDA/CDER/OPS/OTR The information presented
Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) In Vitro Measures to Confirm Patient Perceptions: HFA vs. CFC William H. Doub, Ph.D. Division of Pharmaceutical Analysis (DPA) US FDA/CDER/OPS/OTR The information presented
Orally Inhaled Corticosteroids to 2022
 Greystone Research Associates 1+603-595-4340 April 2015 Orally Inhaled Corticosteroids to 2022 Drugs, Devices, Markets and Forecasts Contents A Comprehensive Market Analysis Report Scope & Overview 2 Table
Greystone Research Associates 1+603-595-4340 April 2015 Orally Inhaled Corticosteroids to 2022 Drugs, Devices, Markets and Forecasts Contents A Comprehensive Market Analysis Report Scope & Overview 2 Table
ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS. Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK
 THE PRESS-AND-BREATHE pmdi ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK steve.newman@physics.org Compact, portable, convenient Asthma
THE PRESS-AND-BREATHE pmdi ADDITIONAL TECHNOLOGIES FOR PRESSURIZED METERED DOSE INHALERS Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Nottingham, UK steve.newman@physics.org Compact, portable, convenient Asthma
Pulmonary deposition of inhaled drugs
 Pulmonary deposition of inhaled drugs Federico Lavorini Dept. Experimental and Clinical Medicine Careggi University Hospital Florence - Italy Presenter Disclosures F.L. has received in the last 5 years
Pulmonary deposition of inhaled drugs Federico Lavorini Dept. Experimental and Clinical Medicine Careggi University Hospital Florence - Italy Presenter Disclosures F.L. has received in the last 5 years
Asthma COPD Update 2018
 Asthma COPD Update 2018 Roger Hefflinger, Pharm.D. Clinical Associate Professor ISU COP Clinical Teaching Pharmacist Family Medicine Residency of Idaho In support of improving patient care, Idaho State
Asthma COPD Update 2018 Roger Hefflinger, Pharm.D. Clinical Associate Professor ISU COP Clinical Teaching Pharmacist Family Medicine Residency of Idaho In support of improving patient care, Idaho State
An update on inhalation devices
 OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
OPTIMIZING INHALED DRUG DELIVERY An update on inhalation devices Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. History of spacers... 1 3. Working of a spacer... 2 4. Advantages of spacer devices... 3 5. Who should
