Use of oral corticosteroids in the United Kingdom
|
|
|
- Brendan Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q J Med 2000; 93: Use of oral corticosteroids in the United Kingdom T.P. VAN STAA1,2, H.G.M. LEUFKENS2, L.ABENHAIM3,4,B.BEGAUD5, B. ZHANG1 and C. COOPER6 From 1Procter & Gamble Pharmaceuticals, Staines, UK, 2Department of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacotherapy, University of Utrecht, The Netherlands, 3Centre for Clinical Epidemiology and Community Studies, Sir Mortimer B. Davis-Jewish General Hospital, Montreal, 4Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics, McGill University, Montreal, Canada, 5Centre de Pharmacovigilance, CHU, Bordeaux, France, and 6MRC Environmental Epidemiology Unit, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, UK Received 4 August 1999 and in revised form 19 November 1999 Summary Administration of oral corticosteroids is associated adult GPRD population. The highest use (2.5%) with the development of osteoporosis and an was by people between 70 and 79 years of age. increased risk of fractures. However, the size of the Respiratory disease was the most frequently treated sub-population who would benefit from preventive recorded indication for oral corticosteroid treatment therapy remains uncertain. The objective of (40%). Patients with arthropathies were most likely this study was to investigate the usage pattern of to use long-term, continuous treatment, and patients oral corticosteroids in a large sample representative with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease least of the general population in England and Wales. likely (19.3% and 6.1%, respectively, used oral Information was obtained from the General Practice corticosteroids for more than 2 years). The overall Research Database (GPRD) which contains medical use of bone-active medication (oestrogens, bisphosrecords of general practitioners. Oral corticosteroid phonates, vitamin D, and calcitonin) during oral users were patients aged 18 years or older who corticosteroid treatment was low (between 4.0% received one or more prescriptions for oral cortico- and 5.5%). The current population in the UK at risk steroids. Over 1.6 million oral corticosteroid of developing corticosteroid-induced fractures might prescriptions were issued to the cohort of be as large as Identification of these oral corticosteroid users. At any point in time, oral patients will be important for implementing prevent- corticosteroids were being used by 0.9% of the total ive strategies in a cost-effective manner. Introduction Administration of oral corticosteroids has been asso- after suffering the fracture.2 Despite the increased ciated with the development of osteoporosis and an recent awareness of corticosteroid-induced osteo- increased risk of fracture. In a large population-based porosis,3 15 the size of this population at risk remains case-control study, it was found that the risk of hip unclear. The objective of this study was to investigate fracture doubled during oral corticosteroid treatment the usage patterns of oral corticosteroids in a large when compared with age- and sex-matched nonfracture sample representative of the general population in controls.1 Hip fracture is the most severe of England and Wales; information was obtained from the fractures related to osteoporosis, and around the General Practice Research Database (GPRD) 20% of all hip fracture patients die within 6 months which contains the computerized medical records of Address correspondence to Professor C. Cooper, MRC Environmental Epidemiology Unit, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton SO16 6YD Association of Physicians 2000
2 106 T.P. van Staa et al. a large group of medical practices in England and corticosteroid prescription at least 6 months after Wales. There was particular interest in estimating the they were registered at the practice or after the prevalence of oral corticosteroid usage, as well as practice enrolled in GPRD were considered to have the dose and natural history of utilization. started a new course of treatment. The morbidity recorded at the date of starting the oral corticosteroids was categorized according to the International Methods Classification of Diseases (9th revision) categories. Patients were also classified according to the pres- The General Practice Research Database ence of concomitant disease. This classification was The current study included 683 practices from differperiod from 6 months before commencing treatment based on the clinical details recorded during the ent geographic areas in the UK, registered with the General Practice Research Database (GPRD). The until the cessation of oral corticosteroid treatment. data recorded in the GPRD include demographic These concomitant disorders included chronic information, prescription details, clinical events, preinflammatory skin disorders ( ), arthropathies obstructive pulmonary disease (ICD codes ), ventive care provided, specialist referrals, hospital admissions and their major outcomes Clinical ( ), peripheral nervous system disorders data are stored and retrieved by means of OXMIS ( ) and non-infectious enteritis/colitis codes for diseases that are cross-referenced to the ( ). International Classification of Diseases (ICD-9).17,20 Each entry into GPRD is internally validated by Statistical methods cross-checking within the practice and by comparisons with external statistics Only data from A point prevalence estimate for oral corticosteroid practices that pass this quality control are compiled use in the total adult GPRD population was estimated within the GPRD database. Several independent by dividing the total duration of oral corticosteroid validation studies have confirmed a high level of use by the total observation time of GPRD. This completeness and validity of GPRD,22 25 which is prevalence estimate provides a cross-sectional meas- owned by the Department of Health in the UK. ure of oral corticosteroid use. The total duration of oral corticosteroid use for this analysis was based on the length of use with each individual prescription. Study population and methods Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted in The study sample was selected from the GPRD to order to estimate the duration of a course of oral comprise a large retrospective cohort study aiming corticosteroid treatment. Patients were considered to to evaluate the relationship between oral corticoa have discontinued treatment if they did not receive steroid use and fracture risk.26 Oral corticosteroid repeat prescription within 3 months after the last users were defined as permanently registered patients oral corticosteroid prescription. Patients who trans- aged 18 years or older who received one or more ferred out, who died within 3 months of their last prescriptions for oral corticosteroids during the period prescription, or who received their last prescription of time from the enrolment date of their practice in in the last 3 months of the study were censored. GPRD up to the end of data collection (December 1997). The average for this time period was 4.7 years. For each oral corticosteroid user, the daily corticosteroid dose over the total treatment period Results was estimated by dividing the total amount of We identified oral corticosteroid users in prescribed prednisolone (or equivalent dose) in milligrams GPRD. Over 1.6 million oral corticosteroid prescrip- by the treatment time.27 The treatment time tions were issued to these oral corticosteroid was taken as the time from the first oral corticosteroid users. Within this cohort, people received prescription until 31 days after the last prescription. one prescription during follow-up, people Three dose categories were assigned: low dose received two prescriptions and people (2.5 mg per day), medium ( mg per day) and received three or more prescriptions. The mean and high dose (7.5 mg per day or more). median numbers of prescriptions were 6.8 and 2.0 The indication for oral corticosteroid treatment prescriptions, respectively. Prednisolone was the was obtained by reviewing the morbidity recorded most frequently prescribed oral corticosteroid (90.8% at the date on which a new course of treatment was of all prescriptions). Hydrocortisone and dexamethasone started. At the commencement of new drug treatment, were given in 3.1% and 2.0% of prescriptions, the general practitioners are required to record respectively. The average dose over the follow-up the indication for treatment on the same date in the period (from first prescription to last prescription) medical record. Patients who received their first oral was 8.1 mg/day.
3 Use of oral corticosteroids 107 The prevalence of oral corticosteroid use in the a short period of time. Treatment was continued for total adult GPRD population is shown in Figure 1. >6 months in only 22.1% of patients and for >5 The use of oral corticosteroids varied substantively years in only 4.3%. The utilization pattern was over age, but was similar between males and females. similar for both sexes, but elderly patients used oral At any point in time, oral corticosteroids were being corticosteroids for longer periods than younger used by 0.9% of the GPRD population (females and patients. Oral corticosteroid treatment was continued males combined). The highest use was by patients for over 2 years by 20.0% of the oldest men and between 70 and 79 years of age (2.5%) and the 20.1% of the oldest women, compared to 2.8% of lowest among patients between 20 and 29 years of the youngest men and 2.0% of the youngest women. age (0.2%). Of the three dose categories, the intermediate In a separate analysis, we examined the impact of dose ( mg daily) was used most dose on the continuation of oral corticosteroid treat- frequently (0.4% of the population). The prevalence ment. Patients on higher doses of oral corticosteroids of higher-dose therapy (>7.5 mg daily) was 0.3%, were more likely to continue treatment for longer and that of lower-dose treatment (<2.5 mg daily) periods of time: 17.5% of these patients continued was 0.1%. For all three dose categories, patients treatment for >2 years compared to only 1.1% of aged years were using oral corticosteroids the low-dose patients. most frequently (0.9% in the high-, 1.3% in the Figure 2 shows the percentage of people who intermediate- and 0.3% in the low-dose group). The continued oral corticosteroid treatment stratified by lowest use was found in patients aged 20 to 29 years concomitant disease. Patients with arthropathies were (0.08% in the high-, 0.09% in the intermediate- and most likely to continue treatment: 19.3% used oral 0.05% in the low-dose group). corticosteroids for >2 years. Patients with chronic The most frequently recorded indication for oral obstructive pulmonary disease were least likely to corticosteroid treatment was respiratory disease: continue treatment (6.1% for >2 years). around 40% of the patients had respiratory diseases The concomitant use of bone-active treatments recorded (Table 1) and 13% had associated res- (hormone replacement therapy, bisphosphonates, vitamin piratory symptoms. Cutaneous or musculoskeletal D, and calcitonin) was also examined. The disorders were recorded in around 6% of the oral overall use of bone-active medication (any type) corticosteroid users. during oral corticosteroid treatment was very low, Most patients received corticosteroid treatment for ranging from 4.0% to 5.5%. As shown in Figure 3, Figure 1. Use of oral corticosteroids in the total GPRD population, stratified by dose, age and gender.
4 108 Table 1 Indication for oral corticosteroid treatment T.P. van Staa et al. Indication ICD code No. of people (%) Respiratory system (39.9%) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (30.5%) Other disease respiratory system (6.8%) Acute respiratory infection (2.5%) Disease skin and subcutaneous tissue (6.2%) Other inflammatory disease skin (3.5%) Other disease skin (2.6%) Disease musculoskeletal and connective tissue (6.2%) Rheumatism excluding back (4.0%) Arthropathies (1.8%) Disease nervous system (3.4%) Peripheral nervous disease (1.8%) Eye/adnexa disorders (0.7%) Digestive system (2.8%) Non-infectious enteritis and colitis (1.5%) Neoplasms (2.3%) Diseases circulatory system (1.9%) Disease arteries/capillaries (1.0%) Injury and poisoning (1.3%) Unknown (20.4%) Total number of persons (6 months retrospective information) Discussion bisphosphonate and vitamin D use became more prevalent over the duration of oral corticosteroid treatment, particularly in the intermediate corticocorticosteroids We have evaluated the utilization patterns of oral steroid dose categories. The use of bisphosphonates in a large cohort representative of the increased among users of high doses of oral corticocorticosteroids general population of England and Wales. Oral steroids from 0.6% in the first 3 months to 2.4% at are used frequently, especially by the 5 years of treatment. At 5 years, the highest use of elderly. The likelihood of long-term oral corticobisphosphonates was observed among the women steroid use was related to age and concomitant aged years using high doses of oral corticohave disease. High doses of oral corticosteroids, which steroids (6.4%, 8.4%, 9.8% and 5.9% in the women the largest associated fracture risk, were used aged 45 to 54, 55 to 64, 65 to 74, and 75 to 84 by 0.9% of the people aged 70 years or older. The years, respectively). Similarly, the use of vitamin D use of bone-active treatments to prevent or treat the increased from 0.4% at the beginning to 1.1% at 5 adverse skeletal effects of oral corticosteroids was, years of high-dose oral corticosteroid treatment. The however, very low. women aged 45 to 84 years showed the highest use The widespread use of oral corticosteroids, par- (2.7%, 2.9%, 1.7% and 2.6% in the women aged ticularly in the elderly population, indicates the need 45 to 54, 55 to 64, 65 to 74, and 75 to 84 years, to quantify precisely the risk of corticosteroidrespectively). Concomitant use of calcitonin was very induced fractures and to identify the patients at low in all three dose groups. The use of HRT did highest risk of developing such fractures. Although not change substantially over duration of oral corticodecades, oral corticosteroids have been used for the last 5 steroid treatment. The low-dose group had the highest there are few data on the magnitude of risk HRT use compared to the high-dose group, an of corticosteroid-induced fractures and the determinobservation accounted for by the different proporbone ants of this risk. Most information on the adverse tions of women in each of the three dose groups, effects of oral corticosteroids has been obtained and the use of HRT for non-osteoporosis indications. from studies that evaluated changes in bone density HRT use was the highest among the women aged during oral corticosteroid treatment.10,11 There has years. Of the women aged years, been only one large study focusing on hip fracture, 30.2% received one or more HRT prescriptions and it was not able to provide information on during oral corticosteroid treatment. For the women the relationship of fracture risk to dose or duration aged years, this figure was 15.9%. of oral corticosteroid use.1 In our study, all oral
5 Use of oral corticosteroids 109 Figure 2. Percentage of patients who continued oral corticosteroid treatment over time, stratified by concomitant disease. after commencement of oral corticosteroid treatment.26 To quantify more precisely the number of patients at risk of developing corticosteroid-induced fractures, these findings will need to be confirmed. Recent UK guidelines indicate that treatment for corticosteroid-induced osteoporosis should be considered if oral corticosteroids are to be used for >6 months at doses of 7.5 mg per day or more.28 It is unclear whether other characteristics predispose patients to increased risks of corticosteroid-induced fracture. Three small studies have evaluated fractures rates in subgroups of oral corticosteroid users. These studies only evaluated age and gender and had inconsistent results, possibly due to the small numbers of patients Our results indicate great heterogeneity in the population using oral corticosteroids. They were used for a broad range of indications, at different doses, for varying durations and by patients of different age, gender and medical histories. In order to individualize and target preventive therapy with bone-active drugs, identification of patients at high risk for corticosteroid-induced fractures is needed. Given this widespread use in different patient groups, there is a need for further studies on the individual susceptibility to corticosteroid-induced fractures. The use of oral corticosteroids in the UK has been addressed in two previous studies. These were crosssectional surveys which included only a few hundred patients, one conducted in a hospital and the other in eight general practices of a single region.32,33 The hospital study reported that the most common indications for oral corticosteroids were chest disease (39.2%) and neoplasm (7.9%).32 The results of the primary-care study were different: here the most frequent indications were rheumatoid arthritis (23.1%) and polymyalgia rheumatica (21.7%); chest disease accounted for 19.5% of oral corticosteroid use.33 Comparison with the results of our study is difficult given the differences in design and setting. Our study used a large longitudinal cohort with accrual of the study population over several years of observation. When weighting patients according to duration of use, respiratory disease accounted for 26.0% of oral corticosteroid use and musculoskeletal corticosteroid users had a significantly increased risk of hip fracture (OR=1.61) relative to controls.26 The risk of hip fracture was not significantly elevated among low-dose oral corticosteroid users, increased (OR=1.77) with a daily prednisolone dose of mg, and was highest (OR=2.27) with doses disease for 15.7% in our study. Patients with shortterm of 7.5 mg daily or higher.26 exposure are more likely to be included in such Of the adult GPRD population, 0.9% were using longitudinal studies compared with cross-sectional oral corticosteroids. Extrapolation of these figures to studies. The greater frequency of pulmonary disease the UK population as a whole (approximately 44.4 in our study is most likely to be explained by this million adults in 1996) suggests that around difference in study design. Furthermore, our study people currently use corticosteroids; are was conducted in a large group of general practices taking doses >7.5 mg prednisolone daily, and have which have registered a patient population that is done so for >6 months; are using cortico- known to be broadly representative of the population steroids at doses >2.5 mg prednisolone or equivalent of England and Wales.17,19,21 daily. Fracture rates appear to increase even for Our classification of the indication was limited by those using lower doses of oral corticosteroids (at the observation that the indication for oral cortico- doses between mg) and also increase shortly steroid treatment was not specified in the medical
6 110 T.P. van Staa et al. Figure 3. Trends in bone-active treatments over duration of oral corticosteroid use. of the patients who did not have their indication specified. In conclusion, we have shown that oral corticosteroids are widely used over a broad range of indications for varying durations of time. The current population at risk of developing corticosteroid- induced fractures in the UK might be as large as individuals. Bone-active drugs are used infrequently among oral corticosteroid users. Further studies to characterize the risk factors for fracture in corticosteroid users, and measures to identify and treat those subjects at the highest risk of future fracture, are urgently required. records of 20% of the patients. The physicians of GPRD are expected to record the indication on the date of starting the treatment. For repeat prescriptions, it is normally only necessary to enter the indication the first time the drug is being used. The reason for not specifying the indication for treatment in 20% of the patients is unknown. One possible explanation may be that oral corticosteroids may have already been previously prescribed, prior to the start of data collection for GPRD. Consistent with our results on indication for treatment, respiratory disease was the most frequently recorded condition (in the 6 months prior to start of oral corticosteroids) among the 20%
7 Use of oral corticosteroids 111 Acknowledgements Funds for this study were provided by Procter & Gamble Pharmaceuticals. We thank EPIC, the GPRD licence holder, for their support. The manuscript was prepared by Mrs G. Strange. References 18. Mann RD, Hall G, Chukwujindu J. Research implications of computerised primary care. Post Marketing Surveillance 1992; 5: Hollowell J. General Practice Research Database (GPRD): Scope and quality of data. London, Office of Population Censuses and Statistics, Anonymous. The general practice research database: information for researchers. London, Office for National Statistics, Walley T, Mantgani A. The UK General Practice Research Database. Lancet 1997; 350: Cooper C, Coupland C, Mitchell M. Rheumatoid arthritis, corticosteroid therapy and hip fracture. Ann Rheum Dis 22. Jick H, Jick SS, Derby LE. Validation of Information recorded 1995; 54: on general practitioner based computerised data resource in 2. Kanis JA, Pitt FA. Epidemiology of osteoporosis. Bone 1992; the United Kingdom. Br Med J 1991; 302: :S7 S Jick H, Terris BZ, Derby LE, Jick SS. Further validation of 3. Spector TD, Sambrook PN. Steroid osteoporosis. Br Med J information recorded on a general practitioner based 1993; 307: computerised data resource in the United Kingdom. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 1992; 1: Compston JE. Review article: osteoporosis, corticosteroids and inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 24. Nazareth I, King M, Haines A, Rangel L, Myers S. Accuracy 1995; 9: of diagnosis of psychosis on general practice computer system. Br Med J 1993; 307: Cooper C, Kirwan JR. The risk of local and systemic corticosteroid administration. Bailliere Clin Rheumatol 25. van Staa TP, Abenhaim L. The quality of information 1990; 4: recorded on a UK database of primary care records: a study of hospitalization due to hypoglycemia and other 6. Cooper C. Osteoporosis in rheumatological practice: conditions. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 1994; 3: questions to be answered. Ann Rheum Dis 1995; 54: van Staa TP, Abenhaim L, Zhang B, Leufkens B, Cooper C. 7. Dequeker J, Westhovens R. Low dose corticosteroid Use of oral corticosteroids and risk of fractures. J Bone associated osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis and its Miner Res 2000; in press. prophylaxis and treatment: Bones of contention. J Rheumatol 1995; 22: British Medical Association and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. British National Formulary Number 8. Dequeker J, Verwilghen MJ, Westhovens R. Osteoporosis in 32 (September 1996). Wallingford, UK, Pharmaceutical rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1995; 13 Suppl. Press, :S Henderson NK, Sambrook PN. Relationship between 28. Eastell R, Reid DM, Compston J, Cooper C, Fogelman I, osteoporosis and arthritis and effect of corticosteroids and Francis RM, Hosking DJ, Purdie DW, Ralston SH, Reeve J, other drugs on bone. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1996; 8: Russell RGG, Stevenson JC, Torgerson DJ. A UK consensus group on management of glucocorticoid induced 10. Lukert B. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. In: osteoporosis: an update. J Intern Med 1998; 244: Marcus R, Feldman D, Kelsey J, eds. Osteoporosis. San Diego, Academic Press, 1996: McDougall R, Sibley J, Haga M, Russell A. Outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving prednisone 11. Reid IR. Gluco-corticoid-induced osteoporosis and other compared to matched controls. J Rheumatol 1994; forms of secondary osteoporosis. In: Meunier PJ, ed. 21: Osteoporosis: diagnosis and management. London, Martin Dunitz, 1998: Laan RFJM, Van Riel PLCM, Van Erning LJThO, Lemmens JAM, Ruijs SHJ, Van de Putte LBA. Vertebral osteoporosis in 12. Sambrook PN, Jones G. Corticosteroid Osteoporosis. Br rheumatoid arthritis patients: Effect of low dose prednisone J Rheumatol 1995; 34:8 12. therapy. Br J Rheumatol 1992; 31: Sambrook PN. Corticosteroid Induced Osteoporosis. 31. Butler RC, Davie MWJ, Worsfold M, Sharp CA. Bone J Rheumatol 1996; 23 (Suppl 45): mineral content in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: 14. Picado C, Luengo M. Corticosteroid-induced bone loss. Relationship to low-dose steroid therapy. Br J Rheumatol Drug Saf 1996; 15: ; 30: Weisman MH. Corticosteroids in the treatment of rheumatic 32. Peat DI, Healy S, Reid DM, Ralston SH. Steroid induced diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 1995; 7: osteoporosis: an opportunity for prevention? Ann Rheum 16. Hall G. Pharmacoepidemiology using a UK Database of Dis 1995; 54:66 8. Primary Care Records. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 1992; 33. Walsh LJ, Wong CA, Pringle M, Tattersfield AE. Use of oral 1:33 7. corticosteroids in the community and the prevention of 17. Lis Y, Mann RD. The Vamp Research Multi-purpose secondary osteoporosis: a cross sectional study. Br Med J Database in the U.K. J Clin Epidemiol 1995; 48: ; 313:344 6.
Public health impact of adverse bone effects of oral corticosteroids
 Public health impact of adverse bone effects of oral corticosteroids T. P. van Staa, 1,2 L. Abenhaim, 3,4 C. Cooper, 5 B. Zhang 2 & H. G. M. Leufkens 1 1 Department of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacotherapy,
Public health impact of adverse bone effects of oral corticosteroids T. P. van Staa, 1,2 L. Abenhaim, 3,4 C. Cooper, 5 B. Zhang 2 & H. G. M. Leufkens 1 1 Department of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacotherapy,
Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Risk of Fractures
 Bone Vol. 27, No. 4 October 2000:563 568 Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Risk of Fractures T. P. VAN STAA, 1 H. G. M. LEUFKENS, 1 and C. COOPER 2 1 Department of Pharmacoepidemiology and
Bone Vol. 27, No. 4 October 2000:563 568 Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Risk of Fractures T. P. VAN STAA, 1 H. G. M. LEUFKENS, 1 and C. COOPER 2 1 Department of Pharmacoepidemiology and
Incidence and Natural History of Paget s Disease of Bone in England and Wales ABSTRACT
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 17, Number 3, 2002 2002 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Incidence and Natural History of Paget s Disease of Bone in England and Wales T.P. VAN
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 17, Number 3, 2002 2002 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Incidence and Natural History of Paget s Disease of Bone in England and Wales T.P. VAN
Anna Hansell, Jen Hollowell, Tom Nichols, Rosie McNiece, David Strachan
 Thorax 1999;54:413 419 413 Department of Public Health Sciences, St George s Hospital Medical School, Cranmer Terrace, London SW17 RE, UK A Hansell T Nichols D Strachan General Practice Research Database,
Thorax 1999;54:413 419 413 Department of Public Health Sciences, St George s Hospital Medical School, Cranmer Terrace, London SW17 RE, UK A Hansell T Nichols D Strachan General Practice Research Database,
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency London, 20 January 2010 Doc. Ref. EMA/CHMP/EWP/15912/2010 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) CONCEPT PAPER ON THE NEED FOR AN ADDENDUM ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION
European Medicines Agency London, 20 January 2010 Doc. Ref. EMA/CHMP/EWP/15912/2010 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) CONCEPT PAPER ON THE NEED FOR AN ADDENDUM ON THE CLINICAL INVESTIGATION
Use of a-blockers and the risk of hip/femur fractures
 Journal of Internal Medicine 2003; 254: 548 554 Use of a-blockers and the risk of hip/femur fractures P. C. SOUVEREIN 1,T.P.VANSTAA 1,2,A.C.G.EGBERTS 1,J.J.M.C.H.DELAROSETTE 3, C. COOPER 2 & H. G. M. LEUFKENS
Journal of Internal Medicine 2003; 254: 548 554 Use of a-blockers and the risk of hip/femur fractures P. C. SOUVEREIN 1,T.P.VANSTAA 1,2,A.C.G.EGBERTS 1,J.J.M.C.H.DELAROSETTE 3, C. COOPER 2 & H. G. M. LEUFKENS
The Cost-Effectiveness of Bisphosphonates in Postmenopausal Women Based on Individual Long-Term Fracture Risks
 Volume ** Number ** ** VALUE IN HEALTH The Cost-Effectiveness of Bisphosphonates in Postmenopausal Women Based on Individual Long-Term Fracture Risks Tjeerd-Peter van Staa, MD, MA, PhD, 1,2 John A. Kanis,
Volume ** Number ** ** VALUE IN HEALTH The Cost-Effectiveness of Bisphosphonates in Postmenopausal Women Based on Individual Long-Term Fracture Risks Tjeerd-Peter van Staa, MD, MA, PhD, 1,2 John A. Kanis,
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on
 Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Application for Endorsement of CQI (Clinical Audit) Activities for MOPS Credits Allocation
 Application for Endorsement of CQI (Clinical Audit) Activities for MOPS Credits Allocation Below is the form you need to fill out. NAME Health Hawke s Bay DATE NOVEMBER 2012 TITLE OF ACTIVITY OSTEOPOROSIS
Application for Endorsement of CQI (Clinical Audit) Activities for MOPS Credits Allocation Below is the form you need to fill out. NAME Health Hawke s Bay DATE NOVEMBER 2012 TITLE OF ACTIVITY OSTEOPOROSIS
Preliminary Communication
 Preliminary Communication Prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a re audit of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan access and management guideline compliance Aim: To evaluate the current
Preliminary Communication Prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: a re audit of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan access and management guideline compliance Aim: To evaluate the current
INHALED AND NASAL CORTICOSTEROID USE AND THE RISK OF FRACTURE. Online data supplement.
 INHALED AND NASAL CORTICOSTEROID USE AND THE RISK OF FRACTURE. Online data supplement. Samy Suissa, PhD, Marc Baltzan, MD, MSc, Richard Kremer, MD, Pierre Ernst, MD, MSc 26 METHODS Source of data We used
INHALED AND NASAL CORTICOSTEROID USE AND THE RISK OF FRACTURE. Online data supplement. Samy Suissa, PhD, Marc Baltzan, MD, MSc, Richard Kremer, MD, Pierre Ernst, MD, MSc 26 METHODS Source of data We used
O n 21 September 1948 Philip Showalter Hench, a rheumatologist
 32 EXTENDED REPORT Prevalence of long term steroid treatment and the frequency of decision making to prevent steroid induced osteoporosis in daily clinical practice B Gudbjornsson, U I Juliusson, F V Gudjonsson...
32 EXTENDED REPORT Prevalence of long term steroid treatment and the frequency of decision making to prevent steroid induced osteoporosis in daily clinical practice B Gudbjornsson, U I Juliusson, F V Gudjonsson...
RESEARCH. Predicting risk of osteoporotic fracture in men and women in England and Wales: prospective derivation and validation of QFractureScores
 Predicting risk of osteoporotic fracture in men and women in England and Wales: prospective derivation and validation of QFractureScores Julia Hippisley-Cox, professor of clinical epidemiology and general
Predicting risk of osteoporotic fracture in men and women in England and Wales: prospective derivation and validation of QFractureScores Julia Hippisley-Cox, professor of clinical epidemiology and general
Epidemiology of Influenza in the United Kingdom A/H1N1, or swine flu, in Mexico has heightened awareness of the multifaceted and
 Epidemiology of Influenza in the United Kingdom 1996-2007 Introduction The recent international concern related to an important outbreak of influenza A/H1N1, or swine flu, in Mexico has heightened awareness
Epidemiology of Influenza in the United Kingdom 1996-2007 Introduction The recent international concern related to an important outbreak of influenza A/H1N1, or swine flu, in Mexico has heightened awareness
Use of oral glucocorticoids and risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in a population based case control study
 859 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Use of oral glucocorticoids and risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in a population based case control study P C Souverein, A Berard, T P Van Staa, C Cooper,
859 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Use of oral glucocorticoids and risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in a population based case control study P C Souverein, A Berard, T P Van Staa, C Cooper,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Vertebral Fracture Risk With Long-term Corticosteroid Therapy
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Vertebral Fracture Risk With Long-term Corticosteroid Therapy Prevalence and Relation to Age, Bone Density, and Corticosteroid Use Vasi Naganathan, FRACP; Graeme Jones, FRACP, MD;
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Vertebral Fracture Risk With Long-term Corticosteroid Therapy Prevalence and Relation to Age, Bone Density, and Corticosteroid Use Vasi Naganathan, FRACP; Graeme Jones, FRACP, MD;
Trends in the treatment of osteoporosis and types of drug treatments prescribed in general practice in England and Wales, 1994 to 1998
 Trends in the treatment of osteoporosis and types of drug treatments prescribed in general practice in England and Wales, 1994 to 1998 Katie Bailey, Charlotte Ellis Office for National Statistics, Azeem
Trends in the treatment of osteoporosis and types of drug treatments prescribed in general practice in England and Wales, 1994 to 1998 Katie Bailey, Charlotte Ellis Office for National Statistics, Azeem
nogg Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK
 nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
nogg NATIONAL OSTEOPOROSIS GUIDELINE GROUP Guideline for the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men from the age of 50 years in the UK Produced by J Compston, A Cooper,
Trends in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Management Among Seniors in Ontario,
 Trends in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Management Among Seniors in Ontario, 1996-2012 Jordan M Albaum 1, Linda E Lévesque 2, Andrea S Gershon 3, Yan Yun Liu 1, Suzanne M Cadarette 1 1 Leslie Dan
Trends in Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis Management Among Seniors in Ontario, 1996-2012 Jordan M Albaum 1, Linda E Lévesque 2, Andrea S Gershon 3, Yan Yun Liu 1, Suzanne M Cadarette 1 1 Leslie Dan
Use of inhaled and oral glucocorticoids, severity of inflammatory disease and risk of hip/femur fracture: a population-based case control study
 Original Article doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01754.x Use of inhaled and oral glucocorticoids, severity of inflammatory disease and risk of hip/femur fracture: a population-based case control study F.
Original Article doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01754.x Use of inhaled and oral glucocorticoids, severity of inflammatory disease and risk of hip/femur fracture: a population-based case control study F.
Horizon Scanning Centre March Denosumab for glucocorticoidinduced SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 6329
 Horizon Scanning Centre March 2014 Denosumab for glucocorticoidinduced osteoporosis SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 6329 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature
Horizon Scanning Centre March 2014 Denosumab for glucocorticoidinduced osteoporosis SUMMARY NIHR HSC ID: 6329 This briefing is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature
Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis: results of a 1-year study
 Rheumatol Int (2006) 26: 427 431 DOI 10.1007/s00296-005-0004-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J. D. Ringe Æ H. Faber Æ P. Farahmand Æ A. Dorst Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis:
Rheumatol Int (2006) 26: 427 431 DOI 10.1007/s00296-005-0004-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J. D. Ringe Æ H. Faber Æ P. Farahmand Æ A. Dorst Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis:
SYNTHESIS OF CHOLESTEROL IS REduced
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Use of Statins and Risk of s Tjeerd-Pieter van Staa, MD, PhD Sebastiaan Wegman, BSc Frank de Vries, BSc Bert Leufkens, PhD Cyrus Cooper, MA, DM, FRCP SYNTHESIS OF CHOLESTEROL IS REduced
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Use of Statins and Risk of s Tjeerd-Pieter van Staa, MD, PhD Sebastiaan Wegman, BSc Frank de Vries, BSc Bert Leufkens, PhD Cyrus Cooper, MA, DM, FRCP SYNTHESIS OF CHOLESTEROL IS REduced
C aring for patients with interstitial lung disease is an
 980 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK J Gribbin, R B Hubbard, I Le Jeune, C J P Smith, J West, L J Tata... See end of article
980 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Incidence and mortality of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis in the UK J Gribbin, R B Hubbard, I Le Jeune, C J P Smith, J West, L J Tata... See end of article
Improving trends in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis management: 2002 to 2006
 Improving trends in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis management: 2002 to 2006 A. Mohammad, J.G. Ryan, N. Ralph, C. Ryan, P.G. O Connell 1 Department of Rheumatology and 2 Department of Medicine, Beaumont
Improving trends in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis management: 2002 to 2006 A. Mohammad, J.G. Ryan, N. Ralph, C. Ryan, P.G. O Connell 1 Department of Rheumatology and 2 Department of Medicine, Beaumont
Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 1. Title: Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis 2. Background: The population of older individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
1. Title: Safety and effectiveness of biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis 2. Background: The population of older individuals with rheumatoid arthritis
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 21 July 2010
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 21 July 2010 ACTONEL 5 mg, film-coated tablet B/14 (CIP code: 354 362-3) ACTONEL 30 mg, film-coated tablet B/28 (CIP
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 21 July 2010 ACTONEL 5 mg, film-coated tablet B/14 (CIP code: 354 362-3) ACTONEL 30 mg, film-coated tablet B/28 (CIP
C olorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most feared
 1573 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE 5-Aminosalicylate use and colorectal cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease: a large epidemiological study T P van Staa, T Card, R F Logan, H G M Leufkens... See end
1573 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE 5-Aminosalicylate use and colorectal cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease: a large epidemiological study T P van Staa, T Card, R F Logan, H G M Leufkens... See end
Learning Objectives. ! Students will become familiar with the 3 treatment solutions for osteoporosis. ! Students should be able to define osteoporosis
 Learning Objectives! Students should be able to define osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some risk factors of osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some of the people in the
Learning Objectives! Students should be able to define osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some risk factors of osteoporosis! Students should be able to identify some of the people in the
Measuring drug exposure: rationale and methods
 Measuring drug exposure: rationale and methods Hubert G. Leufkens Declaration of interests Chairman of the Dutch Medicines Evaluation Board (MEB), since mid 2007. Professor of Pharmacoepidemiology, Utrecht
Measuring drug exposure: rationale and methods Hubert G. Leufkens Declaration of interests Chairman of the Dutch Medicines Evaluation Board (MEB), since mid 2007. Professor of Pharmacoepidemiology, Utrecht
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CHRISTOPHER J. EDWARDS, 1 CYRUS COOPER, 1 DAVID FISHER, 2 MAX FIELD, 3 TJEERD P. VAN STAA, 4 INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 57, No. 7, October 15, 2007, pp 1151 1157 DOI 10.1002/art.23003 2007, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Importance of the Disease
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 57, No. 7, October 15, 2007, pp 1151 1157 DOI 10.1002/art.23003 2007, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Importance of the Disease
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them. Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey
 Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Changes in hip fracture rate before and after total knee replacement due to osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study
 Changes in hip fracture rate before and after total knee replacement due to osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study Daniel Prieto-Alhambra,1 3 M Kassim Javaid,1 Joe Maskell,1,4 Andrew Judge,1 Michael
Changes in hip fracture rate before and after total knee replacement due to osteoarthritis: a population-based cohort study Daniel Prieto-Alhambra,1 3 M Kassim Javaid,1 Joe Maskell,1,4 Andrew Judge,1 Michael
Bisphosphonate treatment break
 Bulletin 110 December 2015 Bisphosphonate treatment break Bisphosphonates have been widely used in the treatment of osteoporosis with robust data demonstrating efficacy in fracture risk reduction over
Bulletin 110 December 2015 Bisphosphonate treatment break Bisphosphonates have been widely used in the treatment of osteoporosis with robust data demonstrating efficacy in fracture risk reduction over
L ower limb fractures account for approximately one third
 368 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology of lower limb fractures in general practice in the United Kingdom J A Kaye, H Jick... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr James A Kaye,
368 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology of lower limb fractures in general practice in the United Kingdom J A Kaye, H Jick... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr James A Kaye,
Osteoporosis as a Focus for Practice Improvement
 Osteoporosis as a Focus for Practice Improvement Karen E. Hansen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Rheumatology and Endocrine Sections University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis as a Focus for Practice Improvement Karen E. Hansen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Rheumatology and Endocrine Sections University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Downloaded from:
 Douglas, IJ; Evans, SJ; Pocock, S; Smeeth, L (2009) The risk of fractures associated with thiazolidinediones: a self-controlled caseseries study. PLoS medicine, 6 (9). e1000154. ISSN 1549-1277 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000154
Douglas, IJ; Evans, SJ; Pocock, S; Smeeth, L (2009) The risk of fractures associated with thiazolidinediones: a self-controlled caseseries study. PLoS medicine, 6 (9). e1000154. ISSN 1549-1277 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000154
3-Year Results of a Member and Physician Intervention to Reduce Risk Associated With Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis in a Health Plan
 RESEARCH 3-Year Results of a Member and Physician Intervention to Reduce Risk Associated With Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis in a Health Plan Mona M. Chitre, PharmD, CGP, and William Hayes, BS ABSTRACT
RESEARCH 3-Year Results of a Member and Physician Intervention to Reduce Risk Associated With Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis in a Health Plan Mona M. Chitre, PharmD, CGP, and William Hayes, BS ABSTRACT
Critique of evidence put forward by Servier suggesting an association between acid-suppressive medication and fracture risk. Dr Myfanwy Lloyd Jones
 Critique of evidence put forward by Servier suggesting an association between acid-suppressive medication and fracture risk Dr Myfanwy Lloyd Jones February 2008 Background Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Critique of evidence put forward by Servier suggesting an association between acid-suppressive medication and fracture risk Dr Myfanwy Lloyd Jones February 2008 Background Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
T he effect of systemic corticosteroid use on the risk of
 1247 EXTENDED REPORT A population based case-control study of cataract and inhaled corticosteroids L Smeeth, M Boulis, R Hubbard, A E Fletcher... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
1247 EXTENDED REPORT A population based case-control study of cataract and inhaled corticosteroids L Smeeth, M Boulis, R Hubbard, A E Fletcher... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Drug Evaluation
 Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Drug Evaluation Martin Wong MD, MPH School of Public Health and Primary Care Faculty of Medicine Chinese University of Hog Kong Outline of Content Introduction: what is
Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Drug Evaluation Martin Wong MD, MPH School of Public Health and Primary Care Faculty of Medicine Chinese University of Hog Kong Outline of Content Introduction: what is
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Chest pain and subsequent consultation for coronary heart disease:
 Chest pain and subsequent consultation for coronary heart disease: a prospective cohort study Peter R Croft and Elaine Thomas ABSTRACT Background Chest pain may not be reported to general practice but
Chest pain and subsequent consultation for coronary heart disease: a prospective cohort study Peter R Croft and Elaine Thomas ABSTRACT Background Chest pain may not be reported to general practice but
An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice
 professional Darren Parker An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice Background Osteoporosis is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in Australia, and is predicted to
professional Darren Parker An audit of osteoporotic patients in an Australian general practice Background Osteoporosis is a major contributor to morbidity and mortality in Australia, and is predicted to
The 2017 CMS Merit-based Incentive Payment System includes 2 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measures.
 The 2017 CMS Merit-based Incentive Payment System includes 2 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measures. Measure Specifications for Registry Reporting MIPS #271: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive
The 2017 CMS Merit-based Incentive Payment System includes 2 inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) measures. Measure Specifications for Registry Reporting MIPS #271: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Preventive
The Association Between Corticosteroid Use and Development of Fractures Among IBD Patients in a Population-Based Database
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 98, No. 8, 2003 2003 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0002-9270(03)00441-6 The Association
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 98, No. 8, 2003 2003 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0002-9270(03)00441-6 The Association
Osteoporosis is estimated to develop in 1 out of 4 women over the age of 50. Influence of bone densitometry results on the treatment of osteoporosis
 Influence of bone densitometry results on the treatment of osteoporosis Nicole S. Fitt, * Susan L. Mitchell, * Ann Cranney, Karen Gulenchyn, Max Huang, * Peter Tugwell Abstract Background: Measurement
Influence of bone densitometry results on the treatment of osteoporosis Nicole S. Fitt, * Susan L. Mitchell, * Ann Cranney, Karen Gulenchyn, Max Huang, * Peter Tugwell Abstract Background: Measurement
National Dementia Intelligence Network briefing
 Reasons why people with dementia are admitted to a general hospital in an emergency National Dementia Intelligence Network briefing Introduction In recent years there have been a number of national reports
Reasons why people with dementia are admitted to a general hospital in an emergency National Dementia Intelligence Network briefing Introduction In recent years there have been a number of national reports
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention
 Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention NATIONAL GUIDELINE SUMMARY This guideline was developed using an evidence-based methodology by the KP National Osteoporosis/Fracture Prevention Guideline Development Team
Economic Burden of Musculoskeletal Diseases in Canada
 Economic Burden of Musculoskeletal Diseases in Canada Presented by Sylvie Desjardins, Policy Research Unit, Public Health Agency of Canada October 23 rd, 2006 1 Fact Sheet MSK has the higher prevalence
Economic Burden of Musculoskeletal Diseases in Canada Presented by Sylvie Desjardins, Policy Research Unit, Public Health Agency of Canada October 23 rd, 2006 1 Fact Sheet MSK has the higher prevalence
Assessment and management of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
 PRESCRIBING IN PRACTICE n Assessment and management of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis Gerald Tracey and Tehseen Ahmed Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIO) is the most prevalent form of secondary
PRESCRIBING IN PRACTICE n Assessment and management of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis Gerald Tracey and Tehseen Ahmed Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIO) is the most prevalent form of secondary
BMJ Open. The Incidence of Eating Disorders in the UK in : findings from the General Practice Research Database
 The Incidence of Eating Disorders in the UK in 000-00: findings from the General Practice Research Database Journal: Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-00 Article Type: Research Date Submitted by the Author: -Jan-0
The Incidence of Eating Disorders in the UK in 000-00: findings from the General Practice Research Database Journal: Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-00 Article Type: Research Date Submitted by the Author: -Jan-0
RESEARCH. Unintended effects of statins in men and women in England and Wales: population based cohort study using the QResearch database
 Unintended effects of statins in men and women in England and Wales: population based cohort study using the QResearch database Julia Hippisley-Cox, professor of clinical epidemiology and general practice,
Unintended effects of statins in men and women in England and Wales: population based cohort study using the QResearch database Julia Hippisley-Cox, professor of clinical epidemiology and general practice,
Validation of QFracture. Analysis prepared for NICE 2011
 Validation of QFracture compared with FRAX Analysis prepared for NICE 2011 Authors: Julia Hippisley-Cox & Carol Coupland Email: Julia.hippisley-cox@nottingham.ac.uk Julia Hipisley-Cox, University of Nottingham,
Validation of QFracture compared with FRAX Analysis prepared for NICE 2011 Authors: Julia Hippisley-Cox & Carol Coupland Email: Julia.hippisley-cox@nottingham.ac.uk Julia Hipisley-Cox, University of Nottingham,
Recent trends in physician diagnosed COPD in women and men in the UK
 Thorax 2000;55:789 794 789 Department of Worldwide Epidemiology, GlaxoWellcome Research and Development, Middlesex, UK J B Soriano W C Maier P Egger G Visick Department of Medical Data Sciences B Thakrar
Thorax 2000;55:789 794 789 Department of Worldwide Epidemiology, GlaxoWellcome Research and Development, Middlesex, UK J B Soriano W C Maier P Egger G Visick Department of Medical Data Sciences B Thakrar
Research in Real Life
 Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
The risk of acute pancreatitis associated with acid-suppressing drugs
 The risk of acute pancreatitis associated with acid-suppressing drugs I. A. Eland, 1 C. Huerta Alvarez, 2 B. H. CH. Stricker 1,3 & L. A. GarcõÂa RodrõÂguez 2 1 Pharmaco-epidemiology Unit, Departments of
The risk of acute pancreatitis associated with acid-suppressing drugs I. A. Eland, 1 C. Huerta Alvarez, 2 B. H. CH. Stricker 1,3 & L. A. GarcõÂa RodrõÂguez 2 1 Pharmaco-epidemiology Unit, Departments of
Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:509-515 Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Joo-Hyun
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:509-515 Are glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis recommendations sufficient to determine antiosteoporotic treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Joo-Hyun
Name of Policy: Zoledronic Acid (Reclast ) Injection
 Name of Policy: Zoledronic Acid (Reclast ) Injection Policy #: 355 Latest Review Date: May 2011 Category: Pharmacy Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Name of Policy: Zoledronic Acid (Reclast ) Injection Policy #: 355 Latest Review Date: May 2011 Category: Pharmacy Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
8/6/2018. Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? Disclosure. Objectives. Overview
 Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Disclosure Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis: overlooked and undertreated? I have no financial disclosure relevant to this presentation Tasma Harindhanavudhi, MD Division of Diabetes and Endocrinology
Following the health of half a million participants
 Following the health of half a million participants Cathie Sudlow UK Biobank Scientific Conference London, June 2018 Follow-up of participants in very large prospective cohorts Aim: identify a wide range
Following the health of half a million participants Cathie Sudlow UK Biobank Scientific Conference London, June 2018 Follow-up of participants in very large prospective cohorts Aim: identify a wide range
PFIZER INC. What is the difference in incidence of fracture in women who ever or never used DMPA for contraception?
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
Use of combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases
 open access Use of combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the and databases Yana Vinogradova, Carol Coupland, Julia Hippisley-Cox Division of
open access Use of combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the and databases Yana Vinogradova, Carol Coupland, Julia Hippisley-Cox Division of
Disclosures Fractures:
 Disclosures Fractures: A. Schwartz Epidemiology and Risk Factors Research Funding: GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Ann V. Schwartz, PhD Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Outline Fracture incidence
Disclosures Fractures: A. Schwartz Epidemiology and Risk Factors Research Funding: GlaxoSmithKline, Merck Ann V. Schwartz, PhD Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Outline Fracture incidence
The Accuracy of Administrative Data Diagnoses of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases
 The Accuracy of Administrative Data Diagnoses of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases SASHA BERNATSKY, TINA LINEHAN, and JOHN G. HANLY ABSTRACT. Objective. To examine the validity of case definitions
The Accuracy of Administrative Data Diagnoses of Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases SASHA BERNATSKY, TINA LINEHAN, and JOHN G. HANLY ABSTRACT. Objective. To examine the validity of case definitions
Downloaded from:
 Herrett, E; Thomas, SL; Schoonen, WM; Smeeth, L; Hall, AJ (2010) Validation and validity of diagnoses in the General Practice Research Database: a systematic review. British journal of clinical pharmacology,
Herrett, E; Thomas, SL; Schoonen, WM; Smeeth, L; Hall, AJ (2010) Validation and validity of diagnoses in the General Practice Research Database: a systematic review. British journal of clinical pharmacology,
EFFECT OF HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY ON BONE MASS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS TREATED WITH AND WITHOUT STEROIDS
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Volume 37 Number 10, October 1994, pp 1499-1505 0 1994, American College of Rheumatology 1499 EFFECT OF HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY ON BONE MASS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Volume 37 Number 10, October 1994, pp 1499-1505 0 1994, American College of Rheumatology 1499 EFFECT OF HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY ON BONE MASS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS PATIENTS
Statins and newly diagnosed diabetes
 DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02142.x British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Statins and newly diagnosed diabetes Susan S. Jick & Brian D. Bradbury Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program, 11 Muzzey
DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02142.x British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Statins and newly diagnosed diabetes Susan S. Jick & Brian D. Bradbury Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program, 11 Muzzey
Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis
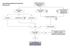 Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Patient may present as a fragility fracture or risk fracture Fragility fracture age 50 Clinical risk factors aged 50 Very strong clinical risk factors
Case Finding and Risk Assessment for Osteoporosis Patient may present as a fragility fracture or risk fracture Fragility fracture age 50 Clinical risk factors aged 50 Very strong clinical risk factors
Discontinuation and restarting in patients on statin treatment: prospective open cohort study using a primary care database
 open access Discontinuation and restarting in patients on statin treatment: prospective open cohort study using a primary care database Yana Vinogradova, 1 Carol Coupland, 1 Peter Brindle, 2,3 Julia Hippisley-Cox
open access Discontinuation and restarting in patients on statin treatment: prospective open cohort study using a primary care database Yana Vinogradova, 1 Carol Coupland, 1 Peter Brindle, 2,3 Julia Hippisley-Cox
Cataracts are a major public health problem,
 Eur Respir J 2006; 27: 1168 1174 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00043005 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Low-dose inhaled and nasal corticosteroid use and the risk of cataracts P. Ernst*,#, M. Baltzan*,",+,
Eur Respir J 2006; 27: 1168 1174 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00043005 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Low-dose inhaled and nasal corticosteroid use and the risk of cataracts P. Ernst*,#, M. Baltzan*,",+,
O. Bruyère M. Fossi B. Zegels L. Leonori M. Hiligsmann A. Neuprez J.-Y. Reginster
 DOI 10.1007/s00296-012-2460-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the proportion of patients potentially treated with an anti-osteoporotic drug using the current criteria of the Belgian national social security
DOI 10.1007/s00296-012-2460-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the proportion of patients potentially treated with an anti-osteoporotic drug using the current criteria of the Belgian national social security
Disclosures Fractures: A. Schwartz Epidemiology and Risk Factors Consulting: Merck
 Disclosures Fractures: A. Schwartz Epidemiology and Risk Factors Consulting: Merck Ann V. Schwartz, PhD Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Outline Fracture incidence and impact of fractures
Disclosures Fractures: A. Schwartz Epidemiology and Risk Factors Consulting: Merck Ann V. Schwartz, PhD Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics UCSF Outline Fracture incidence and impact of fractures
Isle of Wight Joint Strategic Needs Assessment: Core Dataset 2009
 Isle of Wight Joint Strategic Needs Assessment: Core Dataset 2009 Domain: Burden of Ill Health Indicator: Hospital Admissions - Top 10 Causes Sub-Domain: Misc Indicator References: JSNA Core Dataset number
Isle of Wight Joint Strategic Needs Assessment: Core Dataset 2009 Domain: Burden of Ill Health Indicator: Hospital Admissions - Top 10 Causes Sub-Domain: Misc Indicator References: JSNA Core Dataset number
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 : assessing the risk of fragility fracture bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new
: assessing the risk of fragility fracture bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new
Ibuprofen versus other non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs: use in general practice and patient perception
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 187±191. Ibuprofen versus other non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs: use in general practice and patient perception C. J. HAWKEY 1,D.J.E.CULLEN 1,9,G.PEARSON 1,S.HOLMES
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: 187±191. Ibuprofen versus other non-steroidal anti-in ammatory drugs: use in general practice and patient perception C. J. HAWKEY 1,D.J.E.CULLEN 1,9,G.PEARSON 1,S.HOLMES
HOMEOPATHY WITHIN THE NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICE, UK
 HOMEOPATHY WITHIN THE NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICE, UK Some people take the position that public money should not be spent on homeopathy because there is no proof that it works or tax-payers money shouldn t
HOMEOPATHY WITHIN THE NATIONAL HEALTH SERVICE, UK Some people take the position that public money should not be spent on homeopathy because there is no proof that it works or tax-payers money shouldn t
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary. Adalimumab (Humira) for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. National Horizon Scanning Centre.
 Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Adalimumab (Humira) for juvenile idiopathic arthritis June 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Adalimumab (Humira) for juvenile idiopathic arthritis June 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time
Online supplementary material
 Online supplementary material Add-on long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) in a separate inhaler as asthma step-up therapy versus increased dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or ICS/LABA combination inhaler
Online supplementary material Add-on long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) in a separate inhaler as asthma step-up therapy versus increased dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or ICS/LABA combination inhaler
2013 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) (for patients 18 and older)
 2013 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) (for patients 18 and older) Physician Name: Patient Name: Last First MI Date of Birth: / / mm dd yyyy Gender:
2013 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) (for patients 18 and older) Physician Name: Patient Name: Last First MI Date of Birth: / / mm dd yyyy Gender:
Practical Management of Steroids in Non-Endocrine Practice
 Practical Management of Steroids in Non-Endocrine Practice Dr Miguel Debono MD MRCP PhD Consultant Physician in Endocrinology and Honorary Senior Lecturer February 2016 Outline Epidemiology of steroids
Practical Management of Steroids in Non-Endocrine Practice Dr Miguel Debono MD MRCP PhD Consultant Physician in Endocrinology and Honorary Senior Lecturer February 2016 Outline Epidemiology of steroids
Research Article The United Kingdom 2009 Swine Flu Outbreak As Recorded in Real Time by General Practitioners
 Epidemiology Research International Volume 211, Article ID 381597, 6 pages doi:1.1155/211/381597 Research Article The United Kingdom 29 Swine Flu Outbreak As Recorded in Real Time by General Practitioners
Epidemiology Research International Volume 211, Article ID 381597, 6 pages doi:1.1155/211/381597 Research Article The United Kingdom 29 Swine Flu Outbreak As Recorded in Real Time by General Practitioners
2014 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) (for patients aged 18 and older)
 2014 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) (for patients aged 18 and older) Physician Name: Patient Name: Last First MI Date of Birth: / / mm dd yyyy
2014 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) (for patients aged 18 and older) Physician Name: Patient Name: Last First MI Date of Birth: / / mm dd yyyy
GSK Medicine: salmeterol, Salmeterol+Fluticasone proprionate, fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone
 GSK Medicine: salmeterol, Salmeterol+Fluticasone proprionate, fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone Study No.: WWE111984/WEUSRTP2640/EPI40528 Title: The Asthma Death Case Control Study (ADCCS): Association
GSK Medicine: salmeterol, Salmeterol+Fluticasone proprionate, fluticasone propionate, beclomethasone Study No.: WWE111984/WEUSRTP2640/EPI40528 Title: The Asthma Death Case Control Study (ADCCS): Association
Boehringer Ingelheim Page 6 of 178 Study report for non-interventional studies based on existing data BI Study Number
 Page 6 of 178 report for non-interventional studies based on existing data BI Number 1160.144 c14462719-01 International GmbH or one or more of its affiliated companies 1. ABSTRACT Title of study: Keywords:
Page 6 of 178 report for non-interventional studies based on existing data BI Number 1160.144 c14462719-01 International GmbH or one or more of its affiliated companies 1. ABSTRACT Title of study: Keywords:
The prevalence and history of knee osteoarthritis in general practice: a case control study
 The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
Clinical Specialist Statement Template
 Clinical Specialist Statement Template Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can
Clinical Specialist Statement Template Thank you for agreeing to give us a statement on your organisation s view of the technology and the way it should be used in the NHS. Healthcare professionals can
Impact of Chronic Conditions on Health-Related Quality of Life
 BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Conditions on Health-Related Quality of Life Chronic joint pain conditions have an important impact on health-related quality of life Note: a larger negative
BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Conditions on Health-Related Quality of Life Chronic joint pain conditions have an important impact on health-related quality of life Note: a larger negative
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY POSITION STATEMENT. Committee on Rheumatologic Care
 AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY POSITION STATEMENT SUBJECT: PRESENTED BY: FOR DISTRIBUTION TO: Bone Mineral Density Measurement and the Role of Rheumatologists in the Management of Osteoporosis Committee
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF RHEUMATOLOGY POSITION STATEMENT SUBJECT: PRESENTED BY: FOR DISTRIBUTION TO: Bone Mineral Density Measurement and the Role of Rheumatologists in the Management of Osteoporosis Committee
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Outcomes in Male COPD Patients After Treatment With Different Glucocorticoid Regimens*
 Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Outcomes in Male COPD Patients After Treatment With Different Glucocorticoid Regimens* Emile F. Dubois, MD, FCCP; Esther Röder, MD; P. N. Richard Dekhuijzen, MD, PhD; Aeilco
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Outcomes in Male COPD Patients After Treatment With Different Glucocorticoid Regimens* Emile F. Dubois, MD, FCCP; Esther Röder, MD; P. N. Richard Dekhuijzen, MD, PhD; Aeilco
Scottish Burden of Disease Study, Rheumatoid arthritis technical overview
 Scottish Burden of Disease Study, 2015 Rheumatoid arthritis technical overview This resource may also be made available on request in the following formats: 0131 314 5300 nhs.healthscotland-alternativeformats@nhs.net
Scottish Burden of Disease Study, 2015 Rheumatoid arthritis technical overview This resource may also be made available on request in the following formats: 0131 314 5300 nhs.healthscotland-alternativeformats@nhs.net
Cohort linkage studies in England
 Cohort linkage studies in England Tim Millar, Reader in Substance Use & Addictions, University of Manchester Martin White, Drugs & Alcohol Team, Public Health England Number of drug related deaths: opioids
Cohort linkage studies in England Tim Millar, Reader in Substance Use & Addictions, University of Manchester Martin White, Drugs & Alcohol Team, Public Health England Number of drug related deaths: opioids
Review of bisphosphonate prescribing May 2014
 Title of Project: NHS Dumfries & Galloway Review of bisphosphonate prescribing May 2014 1 Reason for the review The aim of this audit is to review patients prescribed a bisphosphonate for the prophylaxis
Title of Project: NHS Dumfries & Galloway Review of bisphosphonate prescribing May 2014 1 Reason for the review The aim of this audit is to review patients prescribed a bisphosphonate for the prophylaxis
R ecent reports suggest that the worldwide incidence and
 267 EXTENDED REPORT Gout epidemiology: results from the UK General Practice Research Database, 199 1999 T R Mikuls, J T Farrar, W B Bilker, S Fernandes, H R Schumacher Jr, K G Saag... See end of article
267 EXTENDED REPORT Gout epidemiology: results from the UK General Practice Research Database, 199 1999 T R Mikuls, J T Farrar, W B Bilker, S Fernandes, H R Schumacher Jr, K G Saag... See end of article
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE. Opinion. 29 November 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 29 November 2006 HEXATRIONE 2% suspension for injection (intra-articular) Box containing one 2-ml vial - CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE Opinion 29 November 2006 HEXATRIONE 2% suspension for injection (intra-articular) Box containing one 2-ml vial - CIP code:
I mmunosuppressive pulse treatment with intravenous
 940 EXTENDED REPORT Bone loss in patients treated with pulses of methylprednisolone is not negligible: a short term prospective observational study G Haugeberg, B Griffiths, K B Sokoll, P Emery... See
940 EXTENDED REPORT Bone loss in patients treated with pulses of methylprednisolone is not negligible: a short term prospective observational study G Haugeberg, B Griffiths, K B Sokoll, P Emery... See
Observational studies on homeopathy
 Observational studies on homeopathy To healthcare providers, patients and clinicians, what matters most is not necessarily how well a treatment performs under the artificially controlled conditions on
Observational studies on homeopathy To healthcare providers, patients and clinicians, what matters most is not necessarily how well a treatment performs under the artificially controlled conditions on
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk. Costing report. Implementing NICE guidance
 Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Costing report Implementing NICE guidance August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 1 of 15 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Osteoporosis: assessing
Osteoporosis: fragility fracture risk Costing report Implementing NICE guidance August 2012 NICE clinical guideline 146 1 of 15 This costing report accompanies the clinical guideline: Osteoporosis: assessing
Center for Rheumatology, Maxima Medical Center Eindhoven, The Netherlands; 4
 High incidence rate of vertebral fractures during chronic prednisone treatment, in spite of bisphosphonate or alfacalcidol use. Extension of the Alendronate or alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis-trial
High incidence rate of vertebral fractures during chronic prednisone treatment, in spite of bisphosphonate or alfacalcidol use. Extension of the Alendronate or alfacalcidol in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis-trial
