ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY of The respiratory system
|
|
|
- Branden Ernest Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
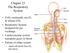
2 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY of The respiratory system 1. Nose and Sinuses 2. Pharynx (Throat) 3. Larynx (Voice Box) 4. Trachea (Windpipe) 5. Bronchi and Bronchioles 6. Lungs
3 Nose First passage for breathing Organ of Smell Contain hairs to filter, and warm incoming air Contains mucus producing goblet cells trap irritants and moisten/lubricate nose Character and resonance to voice and speech Nasal mucosa
4 Sinuses Hollow spaces - Decrease the weight of the Skull Give resonance to voice
5 Pharynx (Throat) Nasopharynx: respiratory function Oropharynx: Respiratory & digestive function Laryngopharynx: Respiratory & vocal function
6 Larynx (Voice Box) Connects pharynx to trachea Epiglottis - covers larynx during swallowing Contains two vocal cords which vibrate together to make voice
7 Trachea and Bronchi Trachea is the wind pipe and it divides into: Right and Left primary bronchus these further divide into Secondary bronchi Cartilage rings Bronchioles : branch 14 times to a final terminal bronchiole
8 Lungs Responsible for gas- exchange
9 Upper & Lower Respiratory System Upper respiratory system refers to nose, pharynx & associated structures (tonsils & sinuses). Lower respiratory system refers to larynx, trachea, bronchi & lungs.
10 Respiratory tract functions mucus cilia Epithelium with goblet cells Bronchial muscle
11 Overview of Cough
12 COUGH A protective and a physiological response Involves rapid expulsion of air from respiratory airway which expel irritants and excessive secretions from respiratory tract Goodman & Gilman (1996), pg 551 Satoskar (1997), pg 318
13 Cough receptors There are two kinds of receptors in the respiratory tract which can initiate cough. The Mechanoceptors Stimulated by stretch impulses as seen in bronchospasm, bronchoconstriction or sudden airflow changes or by non irritating foreign particles. The Chemoreceptors Stimulated by irritant stimuli - dust, pathogens, allergens, chemicals, odors, irritating foreign particles and mucus. These chemoreceptors are also directly stimulated by Histamine which is released from mast cells in upper airway in response to the above irritant stimuli Therefore irritants not only stimulate airway receptors directly but also cause mast cells present in the upper airway to release histamine which further stimulates airway receptors
14 Cough Reflex mechanism Histamine Foreign particles Irritants Airway Chemoceptors Airway Mechanoceptors Cholinergic, vagal pathway Effective cough Patent airway Ciliary action Impulse to Larynx, Intercostal / abdominal muscles Diaphragm Cough Center in Brain stem Stimulation of CNS receptors - cough excitability
15 Dry Cough Needs to be suppressed Cough suppressants have a major role Seen commonly in Upper Respiratory tract infections: Viral colds due to post nasal drip Pharyngitis Tonsillitis Laryngitis Airway Allergies TB Should aggressively be suppressed as: Cause Sleep impairment and fatigue Risk - Hernias, fresh surgeries, etc Irritation and interference in work Useless as no sputum to be expelled Productive cough Should not be suppressed It should be aided - in bringing out mucus by Maintaining bronchodilation Thinning mucus consistency Ensuring ciliary movement Improving expectoration Seen commonly in Lower Respiratory tract infections: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Acute and Chronic bronchitis Asthmatic Bronchitis Emphysema Pneumonia Bronchiectasis Tuberculosis & Smoking
16 Management of cough Dry cough This should be done by suppressing cough at 2 levels: A) Peripheral To suppress the stimulation of Airway receptors B) Central Suppression of cough center Productive cough This should be done by A) Decreasing mucus viscosity mucolytics B) Improving expectoration of mucus C) Maintaining bronchial patency to expel mucus effectively (bronchodilator)
17 Ideal Dry cough formulation Effective cough suppression peripherally and centrally: CPM DXM Soothing agent To provide soothing action as well as reduce throat pain and soreness Menthol
18 DEXTROMETHORPHAN Acts on cough center: Inhibits incoming cough stimuli Raises threshold of cough and Suppress cough reflex Does not suppress Voluntary cough No dependence, respiratory depression or constipating properties (as seen in Codiene) Efficacy on par with narcotic anti tussive (codiene) Acts within min and action lasts for 4-6 hours. Considered treatment of choice for suppressing dry cough Dose : 10 to 30 mg orally every 4 to 8 hourly (max mg/day)
19 Chlorpheniramine Maleate Inhibits cough by both peripheral and central mechanisms. Peripheral: Decreases histamine induced airway cough receptor stimulation Decreases cholinergic transmission of nerve impulses to the cough reflex. Central: Binds to CNS receptors and controls cough excitability. (Therefore complements central action of Dextromethorphan on cough centre) Dose : 4 mg every 4 to 6 hourly (max, 24 mg/day)
20 20 Menthol: A Soothing Agent Produces cooling, soothing sensation Mild anesthetic action decreases throat pain and soreness and airway cough receptor stimulation
21 MOA Histamine Foreign particles Irritants Cough suppressed CPM Airway Chemoceptors Airway Mechanoceptors Cholinergic, vagal pathway CPM Effective cough Patent airway Ciliary action Impulse to Larynx, Intercostal / abdominal muscles Diaphragm x DX M Cough Center in Brain stem CPM Stimulation of CNS receptors - cough excitability
22 New ZEDEX DC for DXM and CPM ; DC for DUAL CONTROL of Cough!! Each 5ml contains: DXM 10mg and CPM 2mg DCGI approved Dose Adults: 10ml TID Children above 6 years: 5 ml TID 2-6 years : 2.5 ml TID
23 Overview of Common Cold
24 Common cold Most common colds are caused either by Viral infections (Rhinovirus, Coronavirus) or reaction to various substances like dust, pollen etc. Usually resolve spontaneously in 7 to 10 days, with some symptoms possibly lasting for up to 2-3 weeks. Treatment is symptomatic. Average two to four times a year in individual adults and up to 6-12 in individual children. Risk factors Air- conditioned crowded places Constant touching of nose Improper hygiene in sneezing, coughing and hand washing Seasonal change, humidity and pollution Improper diet Low immunity
25 Pathophysiology Mast cells are present on all interfaces with external environment especially upper airway (nose and throat) and skin. They release Histamine when stimulated by pathogens and irritants as in common colds Histamine acts through H1 receptors in nasal mucosa and throat
26 Actions of Histamine Dilation of Blood Vessels Redness Congestion Increase in blood vessel permeability - fluid leakage into mucosa Swelling Congestion Increase in Mucus secretion by stimulation of goblet cells Mucus tickling down throat (post nasal drip) especially at night Running nose Cough, throat irritation/sore throat Stimulation of nasal nerve receptors (free nerve endings) and airway chemoreceptors which cause irritation and itching Sneezing Irritation Itching Irritating Cough
27 Symptoms of common cold Running Nose- Nasal discharge Mucus production by goblet cells stimulated by histamine Mucus maybe watery, or purulent and thick
28 Nasal Congestion and Stuffiness Dilation of blood vessels Fluid leakage into mucosa - swelling Accumulation of mucus Nasal irritation & itching Stimulation of nerve endings by Histamine as well as mucus Common Cold
29 Irritation of Nasal mucosa by foreign particles, irritants or mucus pieces Mast cells release Histamine and stimulate nerve endings in nose Sneezing Signals being sent to the Brain to initiate the sneeze through the 5 th cranial (Trigeminal) nerve The brain relates this initial signal and sends response Activates the facial and throat muscles and creates a large opening of the nasal and oral cavities Powerful release of air and particles (FB and mucus). The powerful sneeze involves numerous organs of the upper body the face, throat, and chest muscles
30 Sinusitis Nasal congestion blocks sinus openings Leads to impaired drainage Nasal and heavy voice Headache and Heaviness of head especially on looking down
31 COLD PATHOLOGY & TREATMENT Pathology Sneezing, running nose, and nasal/throat irritation (due to histamine release from mast cells) Nasal congestion due to dilated blood vessels Decrease viscosity and break down nasal mucus secretions Decrease associated throat pain and fever Soothing and local anesthetic action Treatment Anti histamine CPM Decongestant Phenylephrine Mucolytic Sodium citrate Antipyretic-Analgesic PCM Soother Menthol
32 H1 Antihistaminics 1 st Generation (cross BBB) Highly sedative: Diphenhydramine, Promethazine, Hydroxyzine Moderately sedative: Cinnarazine, Meclizine, Buclizine Mildly sedative: Chlorpheniramine maleate, Triprolidine 2nd Generation: Cetrizine, Terfenidine, Loratidine, Azelastine, Astemazole, and Mizolastine, Olopatidine 3 rd Generation : (active enantiomers or metabolites): Levocetrizine, Desloratidine and Fexofenadine
33 Chlorpheniramine maleate 1 st generation Antihistamine Very effective and most widely accepted Has good oral bioavailability (30-50% compared to 4-5% for triprolidine) Decreases sneezing, running nose and nasal irritation mediated by histamine from mast cells Decreases peripheral airway irritation and cough impulse transmission, and also lowers central cough excitability decreases associated cough with cold especially due to PND
34 Why CPM in cold? 1 st generation Anti-histamines like CPM are preferred over later generation ones like levocetrizine, in cough-cold formulations: In cough and cold patients, the main problem is lack of sleep/rest due to nasal congestion as well as irritating cough due to post nasal discharge when they lie down. CPM is mildly sedative compared to other 1 st generation antihistamines maintains a good balance between inducing sleep at night and maintaining day time activity. 1 st gen AH combine better with decongestants due to similar dosing schedule- A cough-cold syrup is usually meant for multiple (2-3 times) dosing in a day as the soothing action of the syrup base and menthol at regular intervals contributes significantly to relief. Only 1 st generation H1 Antihistamines have central effects like cough suppression and decrease in headache therefore they are preferred in combination cold-cough medicines
35 Decongestants They are vasoconstricting agents and act by counteracting the vasodilation caused by histamine. Antihistaminics prevent further action of histamine but cannot reverse the vasodilation already caused by it for which a vasoconstricting decongestant is required. These dilated nasal vessels are the main cause of nasal stuffiness. Systemic/ Oral agents: Phenylephrine, Pseudoephedrine and Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) Topical agents: Naphazoline, Oxymetazoline, Xylometazoline (can cause rebound congestion) PPA is now not preferred due to the risk of stroke associated with it
36 PHENYLEPHRINE It acts via (Alpha 1) receptors in blood vessels and brings about vasoconstriction It is an effective nasal decongestant (Clin Ther Jun;29(6): ) It also decreases swelling of nasal mucosa and improves sinus drainage It can also decrease mucus production due to reduced blood supply to goblet cells It does not display any cardiac or CNS action at clinical doses. It should be avoided in hypertensives as it can raise BP After congestion or rebound congestion is not a problem as seen with topical agents Long term use of topical decongestants can lead to compromised mucociliary action and mucosal atrophy. This is not seen in oral agents.
37 SODIUM CITRATE It has mucolytic action and helps to break down nasal mucus and reduce its viscosity This helps in easier clearing of mucus
38 PARACETAMOL Cold and URTI in children is frequently associated with fever Paracetamol is the most widely accepted Anti-pyretic in children Post nasal drip is common in children and causes throat irritation, soreness, cough and throat pain. Throat pain and sore throat can lead to discomfort and crying in young children and affect their eating and feeding Paracetamol s analgesic properties helps to reduce throat pain and soreness
39 39 Menthol: A Soothing Agent Produces cooling, soothing sensation Mild anesthetic action further decreases throat pain and soreness and airway cough receptor stimulation
40 New Zedex P For Pediatric cold and cough Each 5 ml contains: CPM 0.5mg Phenylephrine 5mg Sodium Citrate 60mg Paracetamol 125mg Menthol 1mg DCGI approved Dose in children> 2 years = 5ml 6 hourly
41 Dry Cough & Cold Continuum
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Therapeutic Agents for the Respiratory System
 Therapeutic Agents for the Respiratory System Chapter 19 1 Structure and Function of the Respiratory System Respiratory system resembles large inverted tree Large trunk: Trachea Two main branches: Bronchi
Therapeutic Agents for the Respiratory System Chapter 19 1 Structure and Function of the Respiratory System Respiratory system resembles large inverted tree Large trunk: Trachea Two main branches: Bronchi
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Drugs Used to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Drugs Used to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD COPD is a chronic, irreversible obstruction of airflow that is usually progressive. Symptoms include cough, excess mucus production,
Drugs Used to Treat Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) COPD COPD is a chronic, irreversible obstruction of airflow that is usually progressive. Symptoms include cough, excess mucus production,
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
How to spot allergies. What are allergies? What can your patients do about allergies? How allergies cause sinusitis. Module 5 Allergies
 Module 5 Allergies What are allergies? Allergies occur when a patient s immune system has a hypersensitive response to a substance that the body comes into contact with 1a. These substances, called allergens,
Module 5 Allergies What are allergies? Allergies occur when a patient s immune system has a hypersensitive response to a substance that the body comes into contact with 1a. These substances, called allergens,
Structural Plan. Respiratory System. ose. Upper Respiratory Tract. Upper Respiratory Tract ose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, and larynx
 Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
RESPIRATORY CONDITIONS
 RESPIRATORY CONDITIONS 1 RESPIRATORY STRUCTURES & FUNCTIONS THE RESPIRATORY TRACT Mouth UPPER Respiratory Tract LOWER Respiratory Tract Nose Pharynx (Larynx) Larynx Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles Alveoli/Lungs
RESPIRATORY CONDITIONS 1 RESPIRATORY STRUCTURES & FUNCTIONS THE RESPIRATORY TRACT Mouth UPPER Respiratory Tract LOWER Respiratory Tract Nose Pharynx (Larynx) Larynx Trachea Bronchi/Bronchioles Alveoli/Lungs
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Chapter 23 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O 2 & release CO 2 Respiratory System designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell
Respiratory System. Respiratory System Overview. Component 3/Unit 11. Health IT Workforce Curriculum Version 2.0/Spring 2011
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE. Learning Objectives. Pronunciation Guide Click on the megaphone icon before each item to hear the pronunciation.
 ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
COUGH PROF. G. ZULIANI
 COUGH PROF. G. ZULIANI Definitions Cough is a 3-phase expulsive motor act characterized by: 1. an inspiratory effort (inspiratory phase), followed by 2. a forced expiratory effort against a closed glottis
COUGH PROF. G. ZULIANI Definitions Cough is a 3-phase expulsive motor act characterized by: 1. an inspiratory effort (inspiratory phase), followed by 2. a forced expiratory effort against a closed glottis
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
A Winter Free of Cold Understanding the Common Cold and Flu. Camille Aizarani, MD Family Medicine Specialist
 A Winter Free of Cold Understanding the Common Cold and Flu Camille Aizarani, MD Family Medicine Specialist Outline Introduction Is it a cold or flu? The Common Cold Symptoms of Common Cold Tansmission
A Winter Free of Cold Understanding the Common Cold and Flu Camille Aizarani, MD Family Medicine Specialist Outline Introduction Is it a cold or flu? The Common Cold Symptoms of Common Cold Tansmission
Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from?
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM How You Breathe Why do you breathe? What is oxygen used for? Where does CO2 come from? Respiration: exchange of gases between air & your body cells 1. Outside air (O2) lungs metabolism
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
CARE CUP CARE CODEINE 15MG/5ML ORAL SOLUTION SUGAR FREE 200ML
 OTC CARE CUP040029 CUP002119 CARE CODEINE 15MG/5ML ORAL SOLUTION SUGAR FREE 200ML CARE CODEINE LINCTUS 200ML Codeine Phosphate reduces the urge to cough and so helps to soothe dry or irritating coughs.
OTC CARE CUP040029 CUP002119 CARE CODEINE 15MG/5ML ORAL SOLUTION SUGAR FREE 200ML CARE CODEINE LINCTUS 200ML Codeine Phosphate reduces the urge to cough and so helps to soothe dry or irritating coughs.
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human body systems Questionnaires, coding schemes, analysis and results
 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 1 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I nt r oduc t i on TextBook Readings Pages 830 through 845. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
Gas exchange Regulate blood ph Voice production Olfaction Innate immunity
 Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Respiration Functions Gas exchange: Grab O 2, eject CO 2 Regulate blood ph: Alters CO 2 levels Voice production: air movement past vocal cords Olfaction: in nasal cavity Innate immunity: physical protection
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Inspiration. Expiration
 Muscular breathing movements and recoil of elastic tissues create the changes in pressure that result in ventilation. Pulmonary ventilation involves three different pressures: When the respiratory system
Muscular breathing movements and recoil of elastic tissues create the changes in pressure that result in ventilation. Pulmonary ventilation involves three different pressures: When the respiratory system
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Remember the Respiratory System
 Remember the Respiratory System BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Rhino Nare(s) Epistaxis ENT or EENT Acute vs Chronic respiratory system 2 STANDARDS 11) Outline the gross normal
Remember the Respiratory System BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Rhino Nare(s) Epistaxis ENT or EENT Acute vs Chronic respiratory system 2 STANDARDS 11) Outline the gross normal
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
PATHOLOGY & PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Disorders of the Respiratory System Infections Degenerative Tumours Immune Trauma Congenital Upper respiratory
INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Return to Syllabus INTRODUCTION TO UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT DISEASES General Goal: To know the major mechanisms of defense in the URT, the major mechanisms invaders use
Respiratory system. Applied Anatomy &Physiology
 Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Allergy and inflammation
 and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
and inflammation 1 Allergic population hyper-producers of IgE consistently increasing western societies: ~20% of general population 2 Allergic population 3 Allergic triggers 4 Allergic triggers abnormal
