Asthma 2009: Latest in Diagnostic and Treatment Options
|
|
|
- Carol Helen Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Asthma 2009: Latest in Diagnostic and Treatment Options Wendy L. Wright, MS, APRN, BC, FAANP Family Nurse Practitioner Owner - Wright & Associates Family Healthcare Amherst, NH Adjunct Faculty - University of Wyoming Fay W. Whitney School of Nursing Partner Partners in Healthcare Education Objectives Upon completion, the participant will be able to: 1. Identify statistics related to incidence/prevalence of asthma 2. Discuss the signs and symptoms of asthma 3. Discuss treatment options for asthma Asthma Wright,
2 Asthma is... Derived from the Greek word for panting or breathlessness Recurrent airflow obstruction caused by chronic airway inflammation with a superimposed bronchospasm Leads to wheezing, breathlessness and a cough Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Update on Selected Topics NIH, NHLBI. June NIH publication no Prevalence of Asthma Impacts approximately 21 million individuals in the United States Most common chronic disease of childhood affecting 6 million children Before adolescence, 2 times more common in boys Increasing incidence of this disease 76% increase in the prevalence of asthma within the past decade Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Update on Selected Topics NIH, NHLBI. June NIH publication no Impact of Asthma Most frequent cause for hospitalization in children (470,000 each year) Emergency room visits and hospitalizations are increasing Most frequent cause of childhood death, particularly amongst certain groups (children, african americans) ,000 people die yearly from asthma Mannino DM, Homa DM, Akinbami LJ, et al. Surveillance for asthma-united States, MMWR Surveill Summ. 2002;51:1-13. Wright,
3 Why Is the Death Rate Increasing? Multifactorial Asthma is increasing Asthma is more severe Poor management of the disease Poor patient compliance Inadequate patient and provider response to signs of worsening trouble Misconceptions and Facts Asthma symptoms can begin at any age Most often misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed in the elderly Fail to report symptoms because it is thought to be normal Attribute the symptoms to comorbid diseases Mannino DM, Homa DM, Akinbami LJ, et al. Surveillance for asthma-united States, MMWR Surveill Summ. 2002;51:1-13. Misconceptions Most people think that children will outgrow asthma Children who suffer from intermittent wheezes have a 50% chance or better of outgrowing this disease Children with persistent wheezing have only a 5% chance of outgrowing this disease Fuerra S, Wright AL, Morgan WJ, et al. Persistence of asthma symptoms: role of obesity and onset of puberty. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170: Wright,
4 Pathophysiology of Asthma Genetic predisposition Chromosome: 5Q31-Q33 Results from repeated exposure to allergens in the individual already equipped with the genetic predisposition Upon exposure to an allergen, there is a release of IgE antibodies IgE antibody binds with the antigen Pathophysiology of Asthma IgE/allergen complex - then attaches itself to the mast cells on the nasal and bronchial mucosa Release of numerous chemical mediators Histamine Histamine is stored mainly in the mast cell Circulated in the blood via the basophil Causes an increase in blood flow to the affected area. Responsible for the increased nasal discharge, edematous mucous membranes, sneezing, itchy nose and eyes, and hives Also associated with airway inflammation and bronchoconstriction Wright,
5 Components of Asthma Asthma Triggers Allergens Exercise Irritants Viruses Weather Smooth Muscle Dysfunction Hypertrophy Hyperplasia Inflammatory Mediator Release Bronchial Constriction Architectural t Changes Bronchial Hyperreactivity Inflammation Mucus Secretion Epithelial Damage Edema Impaired Ciliary Function Inflammatory Cell Infiltration Adapted from Creticos. Adv Stud Med. 2002;2(14): Symptoms Exacerbations Consequences of Inflammation in Asthma Stimulus (Antigen, virus, pollutant, occupational agent) Altered airway physiology Airflow obstruction Acute Inflammation Resolution Airway dysfunction Chronic Inflammation Injury Repair Permanently altered lung function Remodeling (fixed changes in the structure of airway) Asthma: Pathophysiologic Features and Changes in Airway Morphology Airway lumen narrowing Mucous gland hypertrophy and hyperplasia Edema Mucus hypersecretion Thickening of basement membrane Epithelial damage Airway smoothmuscle hypertrophy, hyperplasia, and bronchoconstriction ti Inflammatory cell infiltration Vascular dilation Goblet cell hyperplasia Adapted from Expert Panel Report. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma. NIH, NHLBI NIH publication Wright,
6 Cross Section of Bronchiole Showing Bronchospasm Color Atlas of Respiratory Disease. Volume 2, Epithelial Damage in Asthma Normal Jeffery P. In: Asthma, Academic Press Asthmatic Basement Membrane Thickening Jeffery P. In: Asthma, Academic Press Wright,
7 Triggers Inhalant allergens are the most common triggers for both asthma House dust Pollens Mold spores Animal and insect emanations Cockroach feces Triggers Chemicals Perfumes Foods Sulfites (wine), shrimp, dried fruit, processed potatoes, beer Viruses or infections Cold air Triggers Tobacco smoke Pollution Work exposures Exercise Wright,
8 Gastroesophageal Reflux - A Significant Factor in Children 84 healthy infants and children referred for an evaluation of daily wheezing All evaluated for reflux 64% had positive evaluations for reflux After 3 months on anti-reflux treatment, 64.8% of the infants/children were able to discontinue all daily asthma medications (including nebulized flunisolide) Sheikh S. et. Al. Pediatric Pulmonology Sep; 28(3): Asthma is... A disease of: Inflammation Primary Process Hyperresponsiveness Airway bronchoconstriction Excessive mucous production Diagnosis of Asthma Wright,
9 Diagnosis of Asthma History and Physical Examination Spirometry is needed to make diagnosis Monitoring: Peak Flow Meters Symptoms and Signs of Asthma in Children and Adults Coughing, particularly at night or after exercise Wheezing Chest tightness SOB Cold that lingers x months Methods for Measuring Airway Caliber Maximum PEFR airflow achieved Home FVC, FEV 1 FEF 25%-75% Office/Clinic Airway Resistance Clinic/Laboratory Wright,
10 2008 Fitzgerald Health Education Associates, Inc. 28 Asthma Findings Typically, reversibility of 12% or greater after administration of a bronchodilator aerosol is consistent with asthma. Conboy-Ellis, Kathleen. Asthma: Pathogenesis and Management. The Nurse Practitioner: November 2006; Vol.31, No Rate of Decline in FEV FEV 1 /Ht 3 (L/m 3 ) Normal subjects (n=186) 0.2 Asthma patients (n=66) Age (Yrs.) Adapted from Peat. Eur J Respir Dis. 1987;70:171. Wright,
11 Changes With Age in FEV 1 According to Smoking and Asthma Status Male Smokers No asthma (n=9332) Asthma (n=630) Male Nonsmokers No asthma (n=5480) Asthma (n=314) 1.3 Height- Adjusted d FEV 1 (liters) 1.3 Height- Adjusted 1.1 FEV 1 (liters) Age (yr) Age (yr) Lange et al. N Engl J Med. 1998;339: The Biggest Predictor of Sudden Death from Asthma History of hospitalization with or without intubation These individuals are at a significant risk for a serious exacerbation again Hyperinflation Diaphragm is down to the 11 th ribs Most patients with asthma have normal x-rays Asthma Wright,
12 Chronic Asthma Changes Increased AP Lateral diameter The way you know that AP/Lat diameter is increased is by this clear space between the sternum and the ascending aorta Flat diaphragms Treatment of Asthma Evolution of Asthma Paradigms Symptoms Bronchial Hyperreactivity Fixed Obstruction Relieve Symptoms Prevent Symptoms Prevent Attacks Prevent Symptoms Prevent Attacks Prevent Remodeling Wright,
13 Environmental Control: A Useful but Often Ignored Step Dust Mite Avoidance Bed linens must be laundered 1-2 times/week Maintain humidity at <50% Encase pillows and mattresses Frequent vacuuming Remember: 30 minutes after vacuuming: increased dust mite emanations in the air Individuals with significant asthma should avoid vacuuming or avoid the room for 30 minutes after vacuuming Environmental Control: A Useful but Often Ignored Step Pollen Avoidance Air-conditioning Minimize outdoor exposures during times of highest pollen counts Keep bedroom windows closed Air filters Environmental Control Animal Avoidance Keep animals out of the bedroom If the family has a cat, weekly washing of the cat significantly reduces the allergen load May have to remove animals from home Dry clean upholstery and carpets Cover with an air filter any ducts leading into the bedroom Wright,
14 Environmental Control Mold Avoidance Children/adolescents with allergic rhinitis and/or asthma should not be sleeping in a damp basement Clean moldy surfaces Avoid houseplants Avoid chores that involve damp grass, leaves Environmental Control Avoidance of Non-allergic Triggers Strong emotions Smoke: No smoking in house or car Pollution Cold air Odors Exercise Childhood Asthma Control Can Predict Adult Lung Status Study of 119 asthmatic children during 1966 and 1969 Ages: 5-14 were evaluated using FEV1 Follow-up performed years later and years later Children who were well controlled during childhood had the smallest decline in total lung volume during adulthood Wright,
15 How Are We Doing With Treatment? Study looking at treatment of children over 10 year period showed an increase in the number of prescriptions for beta agonists 4.0% up to 8.1% However, despite the significant increase in beta agonist prescriptions, there was only a slight increase in anti-inflammatory medications prescribed (even amongst children using 2+ rescue inhalers/month) 0.4% up to 2.4% Goodman, DC et. Al. Pediatrics 1999 Aug; 104(2) Stepwise Approach for Managing Asthma in Patients Aged 12 Years: NAEPP EPR-3 Guidelines Severe Persistent Mild Intermittent Persistent Step 2 Step 1 Preferred: Preferred: Low-dose inhaled SABA prn corticosteroid (ICS) Alternative: Mast cell stabilizer (Cromolyn nedocromil), leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRA), or theophylline Moderate Persistent Step 3 Preferred: Medium-dose ICS or Low-dose ICS + LABA Alternative: Low-dose ICS and either LTRA, theophylline, or zileuton Step 4 Preferred: Medium-dose dose ICS + LABA Alternative: Medium-dose ICS and either LTRA, theophylline, or zileuton Step 5 Preferred: High-dose ICS + LABA and omalizumab use can be considered for patients who have allergies. Step 6 Preferred: High-dose ICS + LABA + oral corticosteroid and consider omalizumab for patients who have allergies 44 Step Approach to Therapy If control is not achieved with therapy, step up the therapy Once control is sustained for a minimum of 3 months, can consider stepping down the therapy Regardless, therapy should be reviewed q 6 months Wright,
16 Major Focus in EPR-3 Controlling asthma is a major focus of the EPR-3 guidelines 46 National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute; National Asthma Education and Prevention Program; Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Asthma, Full Report Monitoring Control in Clinical Practice: Asthma Control Test for Patients Aged 12 Years 1 1. Asthma Control Test copyright, QualityMetric Incorporated 2002, All rights reserved. 2. Available at: Accessed February 5, Level of Control Based on Composite Score 2 20 = Controlled = Not Well Controlled 15 = Very Poorly Controlled Regardless of patient s self assessment of control in Question 5 Wright,
17 Short Acting Inhaled Beta 2 Agonists Albuterol (Proventil HFA) 90mcg/puff, 200 puffs 2 puffs q 4-6 hours or 2 puffs 15 minutes before exercise Onset: 5 minutes Short Acting Beta-2 Agonist Levalbuterol (Xopenex HFA) 1 2 inhalations every 4 6 hours prn Short-Acting Beta-2 Agonists Usage of these medications more than 2 times/week is indicative of poor control Regular, scheduled use of these medications is usually not recommended Wright,
18 Long-Acting Controller Medications Maintenance or Prevention is the Key Good management is the key to preventing exacerbations and hospitalizations As with any disease, preventing the problem is always better than treating it Corticosteroids Most potent and effective antiinflammatory medication currently available Wright,
19 Inhaled Corticosteroids Examples Beclomethasone (Beclovent, Vanceril) Budesonide (Pulmicort turbuhaler) Flunisolide (Aerobid) Fluticasone (Flovent) Triamcinolone Acetonide (Azmacort) Mometasone (Asmanex) Inhaled Corticosteroids Side effects Pharyngitis Dysphonia Oral Candidiasis i Precautions High dosages: Increased systemic absorption leading to HPA axis suppression Not indicated for an acute exacerbation To Reduce Side Effects of Inhaled Corticosteroids Administer with spacers or holding chambers Rinse mouth after inhalation Use lowest possible dose to maintain control Children - monitor growth Wright,
20 Schenkel, E. et. al 98 patients randomized to either placebo or mometasone furoate aqueous nasal spray Ages: 3-9 years After 1 year, there was no suppression of height in the children using the nasal corticosteroid when compared with the child using placebo Pediatrics Vol 105 No. 2 February 2000, p. 22 Remember... Poorly controlled asthma often delays growth In general, children with asthma tend to have longer periods of reduced growth rates prior to puberty Mast Cell Stabilizers Cromolyn Sodium (Intal) Indications Asthma prophylaxis Prevention of bronchoconstriction before exposure to suspected allergen Best for mild-moderate disease May be the initial choice for children Wright,
21 Mast Cell Stabilizers Mechanism of Action Reduces the production of histamine and prevents the release from the mast cell MDI or Nebulizer Solution MDI: > 5 years: 2 puffs po qid Nebulizer Solution: >2 years: 1 ampule qid Begin to work within 15 minutes of inhalation but can take up to 2 weeks to become effective Mast Cell Stabilizer Side effects Generally well tolerated Side effects occur in 1:10,000 Cough Wheezing Rash Nausea Category B Non-steroidal Inhaled Antiinflammatory Medication Nedocromil Sodium (Tilade) Best for mild - moderate disease Works by reducing the production of histamine and by preventing the release from the mast cells MDI: >6 years: 2 sprays qid Nebulizer: >2 years 0.5% solution; 1 ampule qid Wright,
22 Nedocromil Sodium (Tilade) Side effects Unpleasant taste Precautions Not for an acute exacerbation Category B Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Cysteinyl leukotriene production in the body has been associated with airway edema, smooth muscle constriction and the inflammatory process These medications block the leukotriene receptors which in turn is able to prevent inflammation and bronchoconstriction Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists (Zafirlukast) Accolate 10mg bid for ages mg bid for 12 and older Studied in children as young as 5 Avoid food 1 hour before and 2 hours after taking: Food decreases the bioavailability of Accolate Metabolism: Metabolized through the CY P450 2C9 and 3A4 pathways Major pathways in the body Numerous other medications use this same pathway Wright,
23 Zafirlukast (Accolate) Drug/Drug Interactions Aspirin: Increased zafirlukast levels by 40% Erythromycin: 40% decrease in zafirlukast Theophylline: Postmarketing reports of increased theophylline levels Coumadin: 35% increase in PT/INR Zafirlukast (Accolate) Side effects Headache (12.9%) Dizziness Nausea Churg Strauss syndrome Pregnancy: B Precautions Not for an acute exacerbation Montelukast (Singulair) (Montelukast) Singulair 4 mg Granules once daily: months 4 mg tablet t for children 2-5 years of age 5mg qhs for ages mg qhs for ages 15 and older Wright,
24 Montelukast (Singulair) Drug Interactions Metabolized through CYP2A6 (minor pathway) Phenobarbital: decreases montelukast but no dosage adjustment is required Side effects: headache, fatigue, dizziness, Churg-Strauss Precautions Not for an acute exacerbation Category: B Methylxanthines Theophylline Theo-24, Theo-Dur, Uni-Dur, Slo-Bid Bronchodilates and increases the force with which the diaphragm contracts 6 years and older Difficult to manage and as a result has not really gained wide spread acceptance Indicated for individuals with moderate to severe asthma Numerous drug interactions Theophylline Numerous medications, foods and chemicals interact with theophylline All of the following decrease theophylline levels Smoking (cigarettes and marijuana) High protein/low carbohydrate diet Phenytoin Phenobarbital Carbamazepine Ketoconazole Diuretics Wright,
25 Theophylline Theophylline levels (normal 6-15mcg/dL) 15-25: GI upset, N/V, diarrhea, abdominal pain 25-35: Tachycardia, occasional PVC s >35: Ventricular tachycardia, seizures Category: C Long Acting Inhaled Beta 2 Agonist Salmeterol (Serevent) Diskus >4 years of age-1 puff po q 12 hours No role for acute exacerbations Seems to help children affected by the nocturnal cough and wheezing Good for prevention of exercise induced asthma Long Acting Inhaled Beta 2 Agonist Foradil Aerolizer > 5 years of age: 1 inhalation every 12 hours Also may be used for prevention of EIB Wright,
26 Omalizumab (Xolair) Indicated for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to severe persistent asthma who have a positive skin test or in vitro reactivity to a perennial aeroallergen And whose symptoms are inadequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroids SC injection Omalizumab (Xolair) Recombinant DNA-derived humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to human immunoglobulin E (IgE). Inhibits the binding of IgE to the high-affinity IgE receptor on the surface of mast cells and basophils Limits the degree of release of mediators of the allergic response. Last. Don t forget to treat the nose 85% of individuals with asthma have concomitant allergic rhinitis Wright,
27 Acute Asthma Exacerbation Management Acute Asthma Exacerbation Measure FEV1 Inhaled short acting beta 2 agonist: Up to three treatments of 2-4 puffs by MDI at 20 minute intervals OR a single nebulizer Can repeat x 1 2 provided patient tolerates Prednisone What dose and schedule?? Management of Moderate Exacerbations: Response from ED Treatment Good Response Symptom relief sustained x 1hr; FEV1 or PEF 70% D/C home Continue SABA & oral corticosteroid Consider inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) Patient education / asthma action plan 81 Wright,
28 Management of Moderate Exacerbations: Response from ED Treatment Incomplete Response Mild-moderate symptoms, FEV1 or PEF 40-69% SABA, oxygen, oral or IV corticosteroids t id Can D/C home Poor Response Marked symptoms, PEF <40% Repeat SABA immediately ED / 911; oral corticosteroid 82 Key Differences in the EPR-3 Report Point of discharge FEV1 or PEF 70% predicted Response sustained 60 minutes after last treatment Normal physical exam Continued ED treatment needed FEV1 or PEF 40-69% predicted Consider adjunct therapies FEV1 or PEF <40% predicted 83 Thank you for your time and attention. Wendy L. Wright, MS, APRN, BC, FAANP WendyARNP@aol.com Wright,
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Foundations of Pharmacology
 Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Pharmacologic Management of Asthma Objectives: 1. Review the physiological basis for asthma therapy 2. Discuss the differences between SABA and LABA 3. Discuss the role of inhaled and oral systemic corticosteroids
Allergies and Asthma 5/21/2013. Objectives. Allergic Rhinitis (AR): Risk Factor for ASTHMA. Rhinitis and Asthma
 Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Asthma. Definition. Symptoms
 Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES. School Nurses November 2015
 ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
ASTHMA BEST PRACTICES FOR SCHOOL NURSES School Nurses November 2015 1 BACKGROUND AND CURRENT STATS General definitions and explanations 2 Incidence of Asthma Centers for Disease Control (CDC) - 1 in 12
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
(pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:
 (pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:_ Date: I am being seen on: a) self referral _ b) physician referral from Dr. Please share the main reasons for your office visit today (check all those that apply):
(pedi) Patient Name: date of birth:_ Date: I am being seen on: a) self referral _ b) physician referral from Dr. Please share the main reasons for your office visit today (check all those that apply):
Asthma medications: Know your options - MayoClinic.com. Asthma medications: Know your options
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Pediatric Asthma Management
 Pediatric Asthma Management APRN Conference February 2016 Cheryl Kerrigan, MSN, CPNP Aimee Tiller RN, AE-C The Plan Definition Pathophysiology review Triggers & Risk Factors Incidence and Prevalence Making
Pediatric Asthma Management APRN Conference February 2016 Cheryl Kerrigan, MSN, CPNP Aimee Tiller RN, AE-C The Plan Definition Pathophysiology review Triggers & Risk Factors Incidence and Prevalence Making
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
From Chronic Lung Disease of Infancy to Asthma
 From Chronic Lung Disease of Infancy to Asthma Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP Certified Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Pediatric Lung Care Bon Secours Medical Group St. Mary s Hospital 1 Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP
From Chronic Lung Disease of Infancy to Asthma Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP Certified Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Pediatric Lung Care Bon Secours Medical Group St. Mary s Hospital 1 Mollie V. Anderson, CPNP
Key features and changes to these four components of asthma care include:
 Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Adults Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions regarding
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Adults Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and other clinicians in making decisions regarding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma Education. The Keys to Asthma Prevention and Control. what to do when one s asthma is flared! Lucile Packard Children s Hospital.
 Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
Home Management Plan. Cover Page
 Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Adults and Children with Asthma
 Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Adults and Children with Asthma - 2005 Criteria that suggest the diagnosis of Asthma: The symptoms of dyspnea, cough and/or wheezing,
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Adults and Children with Asthma - 2005 Criteria that suggest the diagnosis of Asthma: The symptoms of dyspnea, cough and/or wheezing,
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Breathe Easy. Living with Asthma
 Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Meeting the Challenges of Asthma
 Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Taking Control of Asthma Through Proper Medication Selection and the Use of Asthma Action Plans Julie M. Koehler, Pharm.D., FCCP
 Taking Control of Asthma Through Proper Medication Selection and the Use of Asthma Action Plans Julie M. Koehler, Pharm.D., FCCP Associate Dean for Clinical Education and External Affiliations & Professor
Taking Control of Asthma Through Proper Medication Selection and the Use of Asthma Action Plans Julie M. Koehler, Pharm.D., FCCP Associate Dean for Clinical Education and External Affiliations & Professor
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
10/18/2012. Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C
 Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Penn State University Children s Hospital JODIE STABINSKI CRNP MSN AE-C Daily: Long-Term Control Corticosteroids (inhaled and systemic) Long-acting beta 2 -agonists (Serevent, Foradil) Methylxanthines
Childhood Asthma. The pathophysiology of asthma is an interplay. CME Case Study. Case Study. By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC
 CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Asthma. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing worldwide, but why this is happening is not known.
 Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma. Basic Information About Asthma. What is asthma? Who is at risk? What are the most common triggers for asthma symptoms?
 In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016?
 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017
 Protocol Title: Adult Asthma Protocol Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based
Protocol Title: Adult Asthma Protocol Effective Date: 4/27/2016 Version: 1.0 Approval By: CCC Clinical Delivery Steering Planned Review Date: 4/27/2017 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based
Breathe Easy ACTIVITIES. A Family Guide to Living with Asthma F O R T H E K ! I D S
 Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
II: Moderate Worsening airflow limitations Dyspnea on exertion, cough, and sputum production; patient usually seeks medical
 Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Table 3.1. Classification of COPD Severity Stage Pulmonary Function Test Findings Symptoms I: Mild Mild airflow limitations +/ Chronic cough and sputum production; patient unaware of abnormal FEV 1 80%
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Adult Asthma Clinical Practice Guideline Summary
 Adult Asthma Clinical Practice Guideline Summary The following evidence-based guideline was developed to assist Primary Care physicians and other clinicians in the management of asthma in adults. It was
Adult Asthma Clinical Practice Guideline Summary The following evidence-based guideline was developed to assist Primary Care physicians and other clinicians in the management of asthma in adults. It was
LivingWith Asthma. A Guide to Understanding Asthma...
 A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
Staying Healthy. with Asthma. Illustrations by paulsharp.com
 Staying Healthy with Asthma Illustrations by paulsharp.com Lungs & Asthma What is Asthma? Inflammation or swelling of airways that leads to: 1) Mucous production deep inside the airways. 2) Temporary difficulty
Staying Healthy with Asthma Illustrations by paulsharp.com Lungs & Asthma What is Asthma? Inflammation or swelling of airways that leads to: 1) Mucous production deep inside the airways. 2) Temporary difficulty
Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit)
 Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Objectives. Asthma in Primary Care. Definition. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology
 Objectives Asthma in Primary Care Jed Grant, PA-C Program Director, SJVC PA Program Staff PA, AMCH Emergency Department Apply the NAEPP guideline measures of severity and control including current impairment
Objectives Asthma in Primary Care Jed Grant, PA-C Program Director, SJVC PA Program Staff PA, AMCH Emergency Department Apply the NAEPP guideline measures of severity and control including current impairment
How to Manage Asthma
 How to Manage Asthma Table of Contents I. What is Asthma? Page 2 II. How Do Your Lungs Work Page 2 III. What Triggers an Asthma Attack? Page 3 IV. How to Control Asthma Triggers Page 3 V. Your Peak Flow
How to Manage Asthma Table of Contents I. What is Asthma? Page 2 II. How Do Your Lungs Work Page 2 III. What Triggers an Asthma Attack? Page 3 IV. How to Control Asthma Triggers Page 3 V. Your Peak Flow
Asthma. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know
 1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma ASTHMA. Current Strategies for Asthma and COPD
 Current Strategies for Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor of Medicine Chair, Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco (UCSF) San Francisco,
Current Strategies for Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor of Medicine Chair, Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco (UCSF) San Francisco,
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
31 - Respiratory System
 31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
Some Facts About Asthma
 Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP?
 THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING Presented by:
 MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
Pediatric and Adult. Disclosure. Asthma. Learning Objectives. EPR-3: What s Changed? Asthma: Pediatric and Adult
 Asthma: Pediatric and Adult Americo D. Fraboni, MD, FAAFP Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Family Practice & Community Health University of Minnesota Medical School Minneapolis, Minnesota Disclosure
Asthma: Pediatric and Adult Americo D. Fraboni, MD, FAAFP Assistant Clinical Professor Department of Family Practice & Community Health University of Minnesota Medical School Minneapolis, Minnesota Disclosure
Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath.
 Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath. AccuNeb inhalation 0.021% solution: 0.63mg/3mL 3-4 times solution
Inhaled bronchodilators relax constricted airways and treat the noisy part of asthma: coughing, wheezing, choking and shortness of breath. AccuNeb inhalation 0.021% solution: 0.63mg/3mL 3-4 times solution
Asthma. Don Hayes, Jr., MD, FAAP, FACP
 Asthma Don Hayes, Jr., MD, FAAP, FACP Director, University of Kentucky Asthma Center Kentucky Children s Hospital & Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Internal Medicine University of Kentucky College
Asthma Don Hayes, Jr., MD, FAAP, FACP Director, University of Kentucky Asthma Center Kentucky Children s Hospital & Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Internal Medicine University of Kentucky College
I have no perceived conflicts of interest or commercial relationships to disclose.
 ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management
 Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Asthma for Primary Care: Assessment, Control, and Long-Term Management Learning Objectives After participating in this educational activity, participants should be better able to: 1. Choose the optimal
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Learning Objective. Asthma. Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Asthma 2/22/2017
 Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Marianne Curran, PA C 3/1/17 Learning Objective Discuss the pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of Definition many variations Chronic Disorder with Reversible (Intermittent
Management of Asthma in Adults and Children in the Primary Care Setting PRACTICE GUIDELINE
 Management of Asthma in Adults and Children in the Primary Care Setting PRACTICE GUIDELINE Practice Guidelines: Guidelines are intended to be flexible. They serve as reference points or recommendations,
Management of Asthma in Adults and Children in the Primary Care Setting PRACTICE GUIDELINE Practice Guidelines: Guidelines are intended to be flexible. They serve as reference points or recommendations,
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients. Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources
 Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medications for Managing COPD in Hospice Patients Jim Joyner, PharmD, CGP Director of Clinical Operations Outcome Resources Goal of medications in COPD Decrease symptoms and/or complications Reduce frequency
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
Web E-Mial Registration Form. Med practitioner s name. Med practitioner s phone. Name/location of the clinic
 AsthmaCare Program Buteyko Clinic USA, LLC Web www.asthmacare.us E-Mial info@asthmacare.us Workshop Date Workshop location Registration Form The purpose of this form is to assist AsthmaCare practitioner
AsthmaCare Program Buteyko Clinic USA, LLC Web www.asthmacare.us E-Mial info@asthmacare.us Workshop Date Workshop location Registration Form The purpose of this form is to assist AsthmaCare practitioner
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma. April 21, Spring Managed Care Forum
 Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians
 Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Asthma in Adults Melissa Ngai, Pharm.D Candidate Peter J. Hughes, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham,
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Asthma in Adults Melissa Ngai, Pharm.D Candidate Peter J. Hughes, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham,
Provider Respiratory Inservice
 Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Provider Respiratory Inservice 2 Welcome Opening Remarks We will cover: Definition of Asthma & COPD Evidence based guidelines for diagnosis, evaluation, and management of asthma Evidence based guidelines
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II
 Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Asthma Clinical Guideline
 These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They are not intended to replace a clinician s judgment or
These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They are not intended to replace a clinician s judgment or
Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes:
 Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
ASTHMA CONTROL. Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms.
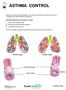 ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD
 Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor
Primary Care Medicine: Concepts and Controversies Wed., February 17, 2010 Fiesta Americana Puerto Vallarta, Mexico Update on Asthma and COPD Talmadge E. King, Jr., M.D. Krevins Distinguished Professor
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies
 Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS*
 FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS* 0 4 Years Age and Adults Potential Adverse Effects Inhaled Corticosteroids (See Figure 18, Estimated Comparative Daily Dosages for ICSs. ) Oral
FIGURE 17. USUAL DOSAGES FOR LONG-TERM CONTROL MEDICATIONS* 0 4 Years Age and Adults Potential Adverse Effects Inhaled Corticosteroids (See Figure 18, Estimated Comparative Daily Dosages for ICSs. ) Oral
Asthma. Clinical Problem and Management Issues
 University of Michigan Health System Guidelines for Clinical Care Asthma Guideline Team Team Leader Sean K Kesterson, MD General Medicine Team Members Joyce E Kaferle, MD Family Medicine Jill A Noble,
University of Michigan Health System Guidelines for Clinical Care Asthma Guideline Team Team Leader Sean K Kesterson, MD General Medicine Team Members Joyce E Kaferle, MD Family Medicine Jill A Noble,
Q: Should patients with mild asthma
 1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
