Models of Imitation and Mirror Neuron Activity. COGS171 FALL Quarter 2011 J. A. Pineda
|
|
|
- Asher Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Models of Imitation and Mirror Neuron Activity COGS171 FALL Quarter 2011 J. A. Pineda
2 Basis for Models Since a majority of mirror neurons have been found in motor areas (IFG and IPL), it is reasonable to envision a role for mirror neurons in motor control. One possibility is that these neurons implement an internal model for control. The CNS uses internal models for movement planning, control, and learning A Forward model is one that predicts the sensory consequences of a motor command; while An Inverse model transforms a desired sensory state into a motor command that can achieve it. Hurley and others propose that mirror neurons are involved in inverse modeling
3 The Shared Circuits Mode (Hurley) An abstract/conceptual explananon of how behaviors like imitanon and mindreading can be enabled by subpersonal mechanisms of control, mirroring, and simulanon. It is aimed at a middle, funcnonal level of descripnon, that is, between the level of neural implementanon and the level of conscious percepnons and intennonal acnons. It avoids the common concepnon of percepnon and acnon as separate and peripheral to central cogninon (the sandwich model).
4 AssumpNons 1. PercepNon is an acnve process and cogninon is embodied and situated. Embodied basis for cogninon are representanons rooted in sensorimotor representanons Situated - knowing is inseparable from doing in that all knowledge is situated in acnvity bound to social, cultural and physical contexts. 2. PercepNon- acnon mechanisms connect with the dynamics of self- other. 3. PercepNon- acnon mechanisms are mulnfuncnonal and reusable (i.e., they are layered)
5 Layer 1: Basic AdapNve Feedback Control SCM begins with specific comparator (error correcnon or supervised learning network; STS?) feedback control system. A comparator system generates outputs that are means to a target, by establishing an associanon between outputs and their results. Enables dynamic online motor control via sensorimotor feedback (embodied acnons)
6 Layer 2: SimulaNve predicnon of effects for improved control Real- Nme feedback can be slow and produce overshoonng. Control funcnons can be speeded and smoothed by adding online predicnons of sensory feedback from ongoing motor output (Forward model) Efference copy of output is made
7 Layer 3: Mirroring for priming, emulanon, and imitanon (beginning of circuit sharing) In the next iteranon of the model, not only does efference copy produce simulated input in forward models, but these input signals can now evoke mirroring efference or motor output (reverse model). This runs the predicnve simulanons of forward models in reverse. observing movements generates motor signals in the observer that tend to cause similar movements enabling copying/imita6on.
8 Layer 4: Monitored output inhibinon combined with simulanve predicnon and/or simulanve mirroring Layer 4 introduces the capacity to inhibit actual output and monitor this inhibinon while instrumental associanons are acnvated. This capacity for monitored inhibinon supports self- other disnncnon and could enable acnon understanding.
9 Layer 5: Counterfactual input simulanon Finally, the system can be taken offline for input as well as output. Adds the funcnon of monitored simulanon of input specifying possible observed acnons, which allows for counterfactual reasoning. Counterfactual inputs can simulate different possible acts by others and their results.
10 Advantages of SCM Explains the possibility of imitanon, mindreading and intelligent social interacnon Built ennrely on the foundanon of sensorimotor circuits (embodied) that are adapnve and responsive to world events (situated) Does not require the inheritance of semannc content from one level to another, but rather it s built around the inheritance of funcnon
11 Many QuesNons To Be Answered How is a precise visual descripnon of one s own body mentally produced given a motor command (forward problem) What are the corncal mechanisms that support the processing stages that transform rennal input caused by an acnon observanon into mirror neuron responses? how is the retinal image transformed to motor commands in a precise way (inverse problem) What is encoded by the mirror neuron acnvity? Is it the motor command, the meaning or the intennon of the observed acnon?
12 Models 1. STS acts as a comparator for the mirror neuron- projected acnon code that matches the observed acnon code best. This can be used for subsequent imitanon. 2. Furthermore, the STS- F5 circuit can be run in the reverse direcnon (inverse modeling) to map the observed acnon into motor codes (mirror acnvity) so that a rough motor representanon of the observed act becomes available for imitanon. According to this hypothesis, the F5- STS circuitry must be capable of producing detailed visual representanon of the self- acnons.
13 Bridging Visual and Motor Representations Visual information external cues Posterior STS Sensorimotor cortex Ventral PMC/ Posterior IFG (F5) Rostral IPL Human PF/PFG
14 Models (cont) Others have proposed that the forward and inverse computanons required can be carried out by the cerebellum and PPC (posterior parietal cortex), respecnvely. Models of imitanon generally make a couple of wrong assumpnons: 1. that mirror neurons are responsible for generanng acnons and 2. that area F5 is composed only of mirror neurons.
15 A Modular Architecture for ImitaNon (Demiris and Johnson, 2003) The key structure is formed by a bafery of behaviors (modules) paired with forward models, where each behavior module receives informanon about the current state (and possibly the target goal), and outputs the motor commands that is necessary to achieve the associated behavior
16 A Modular Architecture for ImitaNon (Demiris and Johnson, 2003) Assumes that the demonstrator s current state is available to it. When the demonstrator executes a behavior, the perceived states are fed into the imitator s available behavior modules in parallel which generate motor commands that are sent to the forward models. The forward models predict the next state based on the incoming motor commands, which are then compared with the actual demonstrator s state at the next Nme step. The error signal resulnng from this comparison is used to derive a confidence value for each behavior (module). The behavior with the highest confidence value (i.e. the one that best matches the demonstrator s behavior) is selected for imitanon.
17 A Modular Architecture for ImitaNon (cont.) (Demiris and Johnson, 2003) If an observed behavior is not in the exisnng repertoire, none of the exisnng behaviors reach a high confidence value, indicanng that a new behavior should be added to the exisnng behavior set. This is achieved by extracnng representanve postures while the unknown behavior is demonstrated, and construcnng a behavior module to go through the representanve postures extracted.
18 An EvoluNonary Model Borenstein and Ruppin (2005) used evolunonary algorithms to explain MNs and imitanon An evolunonary algorithm maintains a populanon of structures ( individuals ) that evolves according to rules of selecnon, recombinanon, mutanon and survival. Aher many generanons one expects to find a set of high performing individuals which represent close- to opnmal solunons to the original problem. Using a 1- hidden layer feedforward neural net, Borenstein and Ruppin (2005) defined individuals as simple agents that could sense the state of the world and the acnon of a teaching agent (inputs) and generate acnons (outputs).
19 An EvoluNonary Model (cont) A populanon of 200 individuals evolving over 2000 generanons developed those who could learn to imitate the teacher The hidden units revealed those which were acnve both when observing the teacher and when execunng the correct acnon (although not all acnons were mirrored!)
20 Hebbian Learning: AssociaNve or Content- Addressable Memory Models Key feature: a parnal representanon of a stored pafern is sufficient to reconstruct the whole. When the organism generates motor commands the representanon of this command and the sensed effects of the command (in somatosensory, visual and auditory areas) are associated within the mirror neuron system. Then, later when the system is presented with a snmulus that parnally matches one of the stored paferns (i.e. vision or audinon of an acnon alone) the associated motor command representanon is retrieved automancally. This representanon can be used (with addinonal circuitry) to mimic the observed movement.
21 Hebbian Learning: AssociaNve or Content- Addressable Memory Models The learned association enabled neurons of the hidden layer of the network to behave as mirror neurons The hidden units could become active with one of motor, vision or language inputs
22 MNS Model (Oztop and Arbib, 2002) A systems level model that takes a developmental point of view and explains how the mirror neurons are developed during infancy Proposes that MNs are ininally evolved to support motor control The temporal profile of the features an infant experiences during self- executed grasps provides the training snmuli for the mirror neuron system to develop Its focus is how mirror neurons may learn to recognize the hand- state trajectories (hand- object relanonships) for an acnon already within the repertoire and not for a novel acnon.
23 Model Distal reach Proximal reach
24 DefiniNons F4 controls proximal movements F5 controls distal movements Inferotemporal (IT)/caudal Intraparietal sulcus (cips) - Provide visual input (what/where informanon) to anterior intraparietal area (AIP) AIP - extracts the affordances the object offers for grasping
Evolving Imitating Agents and the Emergence of a Neural Mirror System
 Evolving Imitating Agents and the Emergence of a Neural Mirror System Elhanan Borenstein and Eytan Ruppin,2 School of Computer Science, Tel Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 6998, Israel 2 School of Medicine,
Evolving Imitating Agents and the Emergence of a Neural Mirror System Elhanan Borenstein and Eytan Ruppin,2 School of Computer Science, Tel Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 6998, Israel 2 School of Medicine,
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Mirror neurons and imitation: A computationally guided review
 Neural Networks 19 (2006) 254 271 2006 Special issue Mirror neurons and imitation: A computationally guided review Erhan Oztop a,b, *, Mitsuo Kawato a,b, Michael Arbib c www.elsevier.com/locate/neunet
Neural Networks 19 (2006) 254 271 2006 Special issue Mirror neurons and imitation: A computationally guided review Erhan Oztop a,b, *, Mitsuo Kawato a,b, Michael Arbib c www.elsevier.com/locate/neunet
Observational Learning Based on Models of Overlapping Pathways
 Observational Learning Based on Models of Overlapping Pathways Emmanouil Hourdakis and Panos Trahanias Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas (FORTH) Science and Technology
Observational Learning Based on Models of Overlapping Pathways Emmanouil Hourdakis and Panos Trahanias Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas (FORTH) Science and Technology
Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain
 Motivating Questions Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory COGS1 class How do our brains perceive the mental states of others
Motivating Questions Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory COGS1 class How do our brains perceive the mental states of others
A Dynamic Model for Action Understanding and Goal-Directed Imitation
 * Manuscript-title pg, abst, fig lgnd, refs, tbls Brain Research 1083 (2006) pp.174-188 A Dynamic Model for Action Understanding and Goal-Directed Imitation Wolfram Erlhagen 1, Albert Mukovskiy 1, Estela
* Manuscript-title pg, abst, fig lgnd, refs, tbls Brain Research 1083 (2006) pp.174-188 A Dynamic Model for Action Understanding and Goal-Directed Imitation Wolfram Erlhagen 1, Albert Mukovskiy 1, Estela
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation. Tom Hartley
 Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
The Concept of Simulation in Control-Theoretic Accounts of Motor Control and Action Perception
 The Concept of Simulation in Control-Theoretic Accounts of Motor Control and Action Perception Mitchell Herschbach (mherschb@ucsd.edu) Department of Philosophy, University of California, San Diego, 9500
The Concept of Simulation in Control-Theoretic Accounts of Motor Control and Action Perception Mitchell Herschbach (mherschb@ucsd.edu) Department of Philosophy, University of California, San Diego, 9500
Emergence of Self Awareness in Robots Based on Predictive Learning
 and Social Cognition Emergence of Self Awareness in Robots Based on Predictive Learning Yukie Nagai Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University Cognitive Neuroscience Robotics ISSA Summer School Center
and Social Cognition Emergence of Self Awareness in Robots Based on Predictive Learning Yukie Nagai Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University Cognitive Neuroscience Robotics ISSA Summer School Center
ArteSImit: Artefact Structural Learning through Imitation
 ArteSImit: Artefact Structural Learning through Imitation (TU München, U Parma, U Tübingen, U Minho, KU Nijmegen) Goals Methodology Intermediate goals achieved so far Motivation Living artefacts will critically
ArteSImit: Artefact Structural Learning through Imitation (TU München, U Parma, U Tübingen, U Minho, KU Nijmegen) Goals Methodology Intermediate goals achieved so far Motivation Living artefacts will critically
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Robot Trajectory Prediction and Recognition based on a Computational Mirror Neurons Model
 Robot Trajectory Prediction and Recognition based on a Computational Mirror Neurons Model Junpei Zhong, Cornelius Weber, and Stefan Wermter Department of Computer Science, University of Hamburg, Vogt Koelln
Robot Trajectory Prediction and Recognition based on a Computational Mirror Neurons Model Junpei Zhong, Cornelius Weber, and Stefan Wermter Department of Computer Science, University of Hamburg, Vogt Koelln
Cognitive Neuroscience History of Neural Networks in Artificial Intelligence The concept of neural network in artificial intelligence
 Cognitive Neuroscience History of Neural Networks in Artificial Intelligence The concept of neural network in artificial intelligence To understand the network paradigm also requires examining the history
Cognitive Neuroscience History of Neural Networks in Artificial Intelligence The concept of neural network in artificial intelligence To understand the network paradigm also requires examining the history
Ch.20 Dynamic Cue Combination in Distributional Population Code Networks. Ka Yeon Kim Biopsychology
 Ch.20 Dynamic Cue Combination in Distributional Population Code Networks Ka Yeon Kim Biopsychology Applying the coding scheme to dynamic cue combination (Experiment, Kording&Wolpert,2004) Dynamic sensorymotor
Ch.20 Dynamic Cue Combination in Distributional Population Code Networks Ka Yeon Kim Biopsychology Applying the coding scheme to dynamic cue combination (Experiment, Kording&Wolpert,2004) Dynamic sensorymotor
Hierarchical dynamical models of motor function
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Neurocomputing 70 (7) 975 990 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom Hierarchical dynamical models of motor function S.M. Stringer, E.T. Rolls Department of Experimental Psychology, Centre for
ARTICLE IN PRESS Neurocomputing 70 (7) 975 990 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom Hierarchical dynamical models of motor function S.M. Stringer, E.T. Rolls Department of Experimental Psychology, Centre for
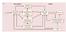 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
LEAH KRUBITZER RESEARCH GROUP LAB PUBLICATIONS WHAT WE DO LINKS CONTACTS
 LEAH KRUBITZER RESEARCH GROUP LAB PUBLICATIONS WHAT WE DO LINKS CONTACTS WHAT WE DO Present studies and future directions Our laboratory is currently involved in two major areas of research. The first
LEAH KRUBITZER RESEARCH GROUP LAB PUBLICATIONS WHAT WE DO LINKS CONTACTS WHAT WE DO Present studies and future directions Our laboratory is currently involved in two major areas of research. The first
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system
 Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system Parallel pathways from the retina to the cortex Visual input is initially encoded in the retina as a 2D distribution of intensity. The retinal
Parallel processing strategies of the primate visual system Parallel pathways from the retina to the cortex Visual input is initially encoded in the retina as a 2D distribution of intensity. The retinal
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders
 Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Embodied Me. 28. Embodied Mental Imagery in Cognitive Robots. Part F 28. Alessandro Di Nuovo, Davide Marocco, Santo Di Nuovo, Angelo Cangelosi
 69 Embodied Me 28. Embodied Mental Imagery in Cognitive Robots Alessandro Di Nuovo, Davide Marocco, Santo Di Nuovo, Angelo Cangelosi This chapter is focused on discussing the concept of mental imagery
69 Embodied Me 28. Embodied Mental Imagery in Cognitive Robots Alessandro Di Nuovo, Davide Marocco, Santo Di Nuovo, Angelo Cangelosi This chapter is focused on discussing the concept of mental imagery
Learning Classifier Systems (LCS/XCSF)
 Context-Dependent Predictions and Cognitive Arm Control with XCSF Learning Classifier Systems (LCS/XCSF) Laurentius Florentin Gruber Seminar aus Künstlicher Intelligenz WS 2015/16 Professor Johannes Fürnkranz
Context-Dependent Predictions and Cognitive Arm Control with XCSF Learning Classifier Systems (LCS/XCSF) Laurentius Florentin Gruber Seminar aus Künstlicher Intelligenz WS 2015/16 Professor Johannes Fürnkranz
ARTICLE IN PRESS Neuroscience Letters xxx (2012) xxx xxx
 Neuroscience Letters xxx (2012) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Neuroscience Letters jou rn al h om epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neulet Review Mirror neurons: Functions, mechanisms
Neuroscience Letters xxx (2012) xxx xxx Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Neuroscience Letters jou rn al h om epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neulet Review Mirror neurons: Functions, mechanisms
Manuscript. Do not cite. 1. Mirror neurons or emulator neurons? Gergely Csibra Birkbeck, University of London
 Manuscript. Do not cite. 1 Mirror neurons or emulator neurons? Gergely Csibra Birkbeck, University of London Mirror neurons are cells in the macaque brain that discharge both when the monkey performs a
Manuscript. Do not cite. 1 Mirror neurons or emulator neurons? Gergely Csibra Birkbeck, University of London Mirror neurons are cells in the macaque brain that discharge both when the monkey performs a
Mirror Neurons: Functions, Mechanisms and Models
 Mirror Neurons: Functions, Mechanisms and Models Erhan Oztop 12*, Mitsuo Kawato 2, Michael A. Arbib 3 1 Ozyegin University, Istanbul, Turkey 2 Advanced Telecommunications Institute International, Kyoto,
Mirror Neurons: Functions, Mechanisms and Models Erhan Oztop 12*, Mitsuo Kawato 2, Michael A. Arbib 3 1 Ozyegin University, Istanbul, Turkey 2 Advanced Telecommunications Institute International, Kyoto,
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch!
 Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
PERCEPTION AND ACTION
 PERCEPTION AND ACTION Visual Perception Ecological Approach to Perception J. J. Gibson in 1929 Traditional experiments too constrained Subjects cannot move their heads Study of snapshot vision Perception
PERCEPTION AND ACTION Visual Perception Ecological Approach to Perception J. J. Gibson in 1929 Traditional experiments too constrained Subjects cannot move their heads Study of snapshot vision Perception
Action Understanding and Imitation Learning in a Robot-Human Task
 Action Understanding and Imitation Learning in a Robot-Human Task Wolfram Erlhagen 1, Albert Mukovskiy 1,EstelaBicho 2, Giorgio Panin 3, Csaba Kiss 3, Alois Knoll 3, Hein van Schie 4, and Harold Bekkering
Action Understanding and Imitation Learning in a Robot-Human Task Wolfram Erlhagen 1, Albert Mukovskiy 1,EstelaBicho 2, Giorgio Panin 3, Csaba Kiss 3, Alois Knoll 3, Hein van Schie 4, and Harold Bekkering
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Seventh Edition. The Nervous System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
A Dynamic Neural Network Model of Sensorimotor Transformations in the Leech
 Communicated by Richard Andersen 1 A Dynamic Neural Network Model of Sensorimotor Transformations in the Leech Shawn R. Lockery Yan Fang Terrence J. Sejnowski Computational Neurobiological Laboratory,
Communicated by Richard Andersen 1 A Dynamic Neural Network Model of Sensorimotor Transformations in the Leech Shawn R. Lockery Yan Fang Terrence J. Sejnowski Computational Neurobiological Laboratory,
Visuomotor development
 Chapter 3 Visuomotor development Sensorimotor coordination has been an active research topic for both neuroscience and artificial intelligence over the last decade. The integration of sensory information
Chapter 3 Visuomotor development Sensorimotor coordination has been an active research topic for both neuroscience and artificial intelligence over the last decade. The integration of sensory information
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Timing and the cerebellum (and the VOR) Neurophysiology of systems 2010
 Timing and the cerebellum (and the VOR) Neurophysiology of systems 2010 Asymmetry in learning in the reverse direction Full recovery from UP using DOWN: initial return to naïve values within 10 minutes,
Timing and the cerebellum (and the VOR) Neurophysiology of systems 2010 Asymmetry in learning in the reverse direction Full recovery from UP using DOWN: initial return to naïve values within 10 minutes,
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A Computational Model For Action Prediction Development
 A Computational Model For Action Prediction Development Serkan Bugur 1, Yukie Nagai 3, Erhan Oztop 2, and Emre Ugur 1 1 Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey. 2 Ozyegin University, Istanbul, Turkey. 3
A Computational Model For Action Prediction Development Serkan Bugur 1, Yukie Nagai 3, Erhan Oztop 2, and Emre Ugur 1 1 Bogazici University, Istanbul, Turkey. 2 Ozyegin University, Istanbul, Turkey. 3
Oscillatory Neural Network for Image Segmentation with Biased Competition for Attention
 Oscillatory Neural Network for Image Segmentation with Biased Competition for Attention Tapani Raiko and Harri Valpola School of Science and Technology Aalto University (formerly Helsinki University of
Oscillatory Neural Network for Image Segmentation with Biased Competition for Attention Tapani Raiko and Harri Valpola School of Science and Technology Aalto University (formerly Helsinki University of
Learning and representation of causative motor actions: a neural network model and its use in an embodied theory of language
 Learning and representation of causative motor actions: a neural model and its use in an embodied theory of language Jeremy Lee-Hand (leehandjeremy@gmail.com) and Alistair Knott (alik@cs.otago.ac.nz) Department
Learning and representation of causative motor actions: a neural model and its use in an embodied theory of language Jeremy Lee-Hand (leehandjeremy@gmail.com) and Alistair Knott (alik@cs.otago.ac.nz) Department
The evolution of imitation and mirror neurons in adaptive agents
 Cognitive Systems Research 6 (2005) 229 242 www.elsevier.com/locate/cogsys The evolution of imitation and mirror neurons in adaptive agents Action editor: Luc Berthouze Elhanan Borenstein a, *, Eytan Ruppin
Cognitive Systems Research 6 (2005) 229 242 www.elsevier.com/locate/cogsys The evolution of imitation and mirror neurons in adaptive agents Action editor: Luc Berthouze Elhanan Borenstein a, *, Eytan Ruppin
Mirror neurons. Romana Umrianova
 Mirror neurons Romana Umrianova The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations Giacomo Rizzolatti and Corrado Sinigaglia Mechanism that unifies action
Mirror neurons Romana Umrianova The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations Giacomo Rizzolatti and Corrado Sinigaglia Mechanism that unifies action
The mirror-neuron system: a Bayesian perspective
 CE: madhu ED: Susan Koshy Op: srini WNR: LWW_WNR_4050 COMMISSIONED REVIEW NEUROREPORT The mirror-neuron system: a Bayesian perspective James M. Kilner, Karl J. Friston and Chris D. Frith WellcomeTrust
CE: madhu ED: Susan Koshy Op: srini WNR: LWW_WNR_4050 COMMISSIONED REVIEW NEUROREPORT The mirror-neuron system: a Bayesian perspective James M. Kilner, Karl J. Friston and Chris D. Frith WellcomeTrust
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization
 Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
The Motor Systems. What s the motor system? Plan
 The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
Visual Selection and Attention
 Visual Selection and Attention Retrieve Information Select what to observe No time to focus on every object Overt Selections Performed by eye movements Covert Selections Performed by visual attention 2
Visual Selection and Attention Retrieve Information Select what to observe No time to focus on every object Overt Selections Performed by eye movements Covert Selections Performed by visual attention 2
HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL. Emmanuel Guigon
 HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL Emmanuel Guigon Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et de Robotique Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS / UMR 7222 Paris, France emmanuel.guigon@upmc.fr e.guigon.free.fr/teaching.html
HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL Emmanuel Guigon Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et de Robotique Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS / UMR 7222 Paris, France emmanuel.guigon@upmc.fr e.guigon.free.fr/teaching.html
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS. specifications
 NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
The Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes. Anatomy of the Frontal Lobes 3/2/2011. Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions. Readings: KW Ch.
 The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
The Frontal Lobes Readings: KW Ch. 16 Portrait: Losing Frontal-Lobe Functions E.L. Highly organized college professor Became disorganized, showed little emotion, and began to miss deadlines Scores on intelligence
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
LEC 1B ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Cogs 17 * UCSD
 LEC 1B ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Cogs 17 * UCSD Cerebral Cortex A 6-layer sheet of cells, unfolded = < 1 m square X 3 mm thick Cortex 6 layers of cells Nissl Stain for Cell Bodies Info projected to
LEC 1B ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Cogs 17 * UCSD Cerebral Cortex A 6-layer sheet of cells, unfolded = < 1 m square X 3 mm thick Cortex 6 layers of cells Nissl Stain for Cell Bodies Info projected to
Giacomo Rizzolatti - selected references
 Giacomo Rizzolatti - selected references 1 Rizzolatti, G., Semi, A. A., & Fabbri-Destro, M. (2014). Linking psychoanalysis with neuroscience: the concept of ego. Neuropsychologia, 55, 143-148. Notes: Through
Giacomo Rizzolatti - selected references 1 Rizzolatti, G., Semi, A. A., & Fabbri-Destro, M. (2014). Linking psychoanalysis with neuroscience: the concept of ego. Neuropsychologia, 55, 143-148. Notes: Through
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
neurons: how kids learn
 mirror neurons: how kids learn Table of Contents 1 2 mirror neurons The Neuron What is a Mirror Neuron Research language development Mimicry Mapping 3 actions and intentions Understanding Intentions 4
mirror neurons: how kids learn Table of Contents 1 2 mirror neurons The Neuron What is a Mirror Neuron Research language development Mimicry Mapping 3 actions and intentions Understanding Intentions 4
Degree of freedom problem
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
Computational Thinkers: The Emulator Example. (Based on Clark and Grush)
 Computational Thinkers: The Emulator Example (Based on Clark and Grush) 1 Realism about Computational Thinkers: The claim that the human brain and CNS, in at least some of its functioning, actually IS
Computational Thinkers: The Emulator Example (Based on Clark and Grush) 1 Realism about Computational Thinkers: The claim that the human brain and CNS, in at least some of its functioning, actually IS
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
PHY3111 Mid-Semester Test Study. Lecture 2: The hierarchical organisation of vision
 PHY3111 Mid-Semester Test Study Lecture 2: The hierarchical organisation of vision 1. Explain what a hierarchically organised neural system is, in terms of physiological response properties of its neurones.
PHY3111 Mid-Semester Test Study Lecture 2: The hierarchical organisation of vision 1. Explain what a hierarchically organised neural system is, in terms of physiological response properties of its neurones.
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
Cognitive Neuroscience Section 4
 Perceptual categorization Cognitive Neuroscience Section 4 Perception, attention, and memory are all interrelated. From the perspective of memory, perception is seen as memory updating by new sensory experience.
Perceptual categorization Cognitive Neuroscience Section 4 Perception, attention, and memory are all interrelated. From the perspective of memory, perception is seen as memory updating by new sensory experience.
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Reading Assignments: Lecture 5: Introduction to Vision. None. Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence
 Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Hierarchically Organized Mirroring Processes in Social Cognition: The Functional Neuroanatomy of Empathy
 Hierarchically Organized Mirroring Processes in Social Cognition: The Functional Neuroanatomy of Empathy Jaime A. Pineda, A. Roxanne Moore, Hanie Elfenbeinand, and Roy Cox Motivation Review the complex
Hierarchically Organized Mirroring Processes in Social Cognition: The Functional Neuroanatomy of Empathy Jaime A. Pineda, A. Roxanne Moore, Hanie Elfenbeinand, and Roy Cox Motivation Review the complex
The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function
 The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function Raviraj Nataraj, Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, William H. Seitz, MD, Zong-Ming Li. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA. Disclosures:
The Effects of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome on the Kinematics of Reach-to-Pinch Function Raviraj Nataraj, Peter J. Evans, MD, PhD, William H. Seitz, MD, Zong-Ming Li. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA. Disclosures:
using deep learning models to understand visual cortex
 using deep learning models to understand visual cortex 11-785 Introduction to Deep Learning Fall 2017 Michael Tarr Department of Psychology Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition this lecture A bit out
using deep learning models to understand visual cortex 11-785 Introduction to Deep Learning Fall 2017 Michael Tarr Department of Psychology Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition this lecture A bit out
Cell Responses in V4 Sparse Distributed Representation
 Part 4B: Real Neurons Functions of Layers Input layer 4 from sensation or other areas 3. Neocortical Dynamics Hidden layers 2 & 3 Output layers 5 & 6 to motor systems or other areas 1 2 Hierarchical Categorical
Part 4B: Real Neurons Functions of Layers Input layer 4 from sensation or other areas 3. Neocortical Dynamics Hidden layers 2 & 3 Output layers 5 & 6 to motor systems or other areas 1 2 Hierarchical Categorical
Big Ideas. (e.g. puberty, immune function (autoimmune disorders)) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
M.Sc. in Cognitive Systems. Model Curriculum
 M.Sc. in Cognitive Systems Model Curriculum April 2014 Version 1.0 School of Informatics University of Skövde Sweden Contents 1 CORE COURSES...1 2 ELECTIVE COURSES...1 3 OUTLINE COURSE SYLLABI...2 Page
M.Sc. in Cognitive Systems Model Curriculum April 2014 Version 1.0 School of Informatics University of Skövde Sweden Contents 1 CORE COURSES...1 2 ELECTIVE COURSES...1 3 OUTLINE COURSE SYLLABI...2 Page
Mechanosensation. Central Representation of Touch. Wilder Penfield. Somatotopic Organization
 Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Motor Theories of Cognition
 Motor Theories of Cognition In his Essay Towards a New Theory of Vision (1709) Berkeley uses a motor representation to describe depth perception. Motor theory in Movement and Mental Imagery (1916) by Margeret
Motor Theories of Cognition In his Essay Towards a New Theory of Vision (1709) Berkeley uses a motor representation to describe depth perception. Motor theory in Movement and Mental Imagery (1916) by Margeret
Active Sites model for the B-Matrix Approach
 Active Sites model for the B-Matrix Approach Krishna Chaithanya Lingashetty Abstract : This paper continues on the work of the B-Matrix approach in hebbian learning proposed by Dr. Kak. It reports the
Active Sites model for the B-Matrix Approach Krishna Chaithanya Lingashetty Abstract : This paper continues on the work of the B-Matrix approach in hebbian learning proposed by Dr. Kak. It reports the
WELCOME, THIS WEB CONFERENCE WILL BEGIN SOON
 WELCOME, THIS WEB CONFERENCE WILL BEGIN SOON LOGIC MODELS FOR PREVENTION PROGRAMMING I CALCASA 1215 K Street Suite 1850 Sacramento, CA 95814 Website: calcasa.org Facebook: www.facebook.com/calcasa Twi;er:
WELCOME, THIS WEB CONFERENCE WILL BEGIN SOON LOGIC MODELS FOR PREVENTION PROGRAMMING I CALCASA 1215 K Street Suite 1850 Sacramento, CA 95814 Website: calcasa.org Facebook: www.facebook.com/calcasa Twi;er:
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Human Paleoneurology and the Evolution of the Parietal Cortex
 PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
PARIETAL LOBE The Parietal Lobes develop at about the age of 5 years. They function to give the individual perspective and to help them understand space, touch, and volume. The location of the parietal
Nervous System. The Peripheral Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Reflexes Pathways
 Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
Imitating others by composition of primitive actions: a neuro-dynamic model
 Imitating others by composition of primitive actions: a neuro-dynamic model Hiroaki Arie a, Takafui Arakaki b, Shigeki Sugano b, Jun Tani a a Brain Science Institute, RIKEN b Department of Advanced Mechanical
Imitating others by composition of primitive actions: a neuro-dynamic model Hiroaki Arie a, Takafui Arakaki b, Shigeki Sugano b, Jun Tani a a Brain Science Institute, RIKEN b Department of Advanced Mechanical
11/2/2011. Basic circuit anatomy (the circuit is the same in all parts of the cerebellum)
 11/2/2011 Neuroscientists have been attracted to the puzzle of the Cerebellum ever since Cajal. The orderly structure, the size of the cerebellum and the regularity of the neural elements demands explanation.
11/2/2011 Neuroscientists have been attracted to the puzzle of the Cerebellum ever since Cajal. The orderly structure, the size of the cerebellum and the regularity of the neural elements demands explanation.
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Neurobiology guides robotics
 M. Mahdi Ghazaei Ardakani Neurobiology guides robotics As robotic technology moves toward more anthropomorphic structures with increased complexity, it is reasonable to consider controllers inspired by
M. Mahdi Ghazaei Ardakani Neurobiology guides robotics As robotic technology moves toward more anthropomorphic structures with increased complexity, it is reasonable to consider controllers inspired by
ANTICIPATING DYNAMIC LOADS IN HANDLING OBJECTS.
 ANTICIPATING DYNAMIC LOADS IN HANDLING OBJECTS. Alan M. Wing Sensory Motor Neuroscience Centre, The University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK. a.m.wing@bham.ac.uk J. Randall Flanagan
ANTICIPATING DYNAMIC LOADS IN HANDLING OBJECTS. Alan M. Wing Sensory Motor Neuroscience Centre, The University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT, UK. a.m.wing@bham.ac.uk J. Randall Flanagan
A Scientific Model of Consciousness that Explains Spirituality and Enlightened States
 A Scientific Model of Consciousness that Explains Spirituality and Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D. Physics degrees from Stanford and MIT consciousness@frankheile.com April 2016 Outline Part 1: Agents
A Scientific Model of Consciousness that Explains Spirituality and Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D. Physics degrees from Stanford and MIT consciousness@frankheile.com April 2016 Outline Part 1: Agents
Title: Computational modeling of observational learning inspired by the cortical underpinnings of human primates.
 Title: Computational modeling of observational learning inspired by the cortical underpinnings of human primates. Authors: Emmanouil Hourdakis (ehourdak@ics.forth.gr) Institute of Computer Science, Foundation
Title: Computational modeling of observational learning inspired by the cortical underpinnings of human primates. Authors: Emmanouil Hourdakis (ehourdak@ics.forth.gr) Institute of Computer Science, Foundation
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions.
 Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
Neuroscience Tutorial
 Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Perception & Attention
 Perception & Attention Perception is effortless but its underlying mechanisms are incredibly sophisticated. Biology of the visual system Representations in primary visual cortex and Hebbian learning Object
Perception & Attention Perception is effortless but its underlying mechanisms are incredibly sophisticated. Biology of the visual system Representations in primary visual cortex and Hebbian learning Object
A model to explain the emergence of reward expectancy neurons using reinforcement learning and neural network $
 Neurocomputing 69 (26) 1327 1331 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom A model to explain the emergence of reward expectancy neurons using reinforcement learning and neural network $ Shinya Ishii a,1, Munetaka
Neurocomputing 69 (26) 1327 1331 www.elsevier.com/locate/neucom A model to explain the emergence of reward expectancy neurons using reinforcement learning and neural network $ Shinya Ishii a,1, Munetaka
 BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 1 Brain and Its Vital Functions Student s Name Institution Name Professor s Name Course Title BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 2 The brain is the integral organism and all its
BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 1 Brain and Its Vital Functions Student s Name Institution Name Professor s Name Course Title BRAIN AND ITS VITAL FUNCTIONS 2 The brain is the integral organism and all its
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
0-3 DEVELOPMENT. By Drina Madden. Pediatric Neuropsychology 1
 0-3 DEVELOPMENT By Drina Madden DrinaMadden@hotmail.com www.ndcbrain.com 1 PHYSICAL Body Growth Changes in height and weight are rapid in the first two years of life. Development moves from head to tail
0-3 DEVELOPMENT By Drina Madden DrinaMadden@hotmail.com www.ndcbrain.com 1 PHYSICAL Body Growth Changes in height and weight are rapid in the first two years of life. Development moves from head to tail
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense
 The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
Exploring the Functional Significance of Dendritic Inhibition In Cortical Pyramidal Cells
 Neurocomputing, 5-5:389 95, 003. Exploring the Functional Significance of Dendritic Inhibition In Cortical Pyramidal Cells M. W. Spratling and M. H. Johnson Centre for Brain and Cognitive Development,
Neurocomputing, 5-5:389 95, 003. Exploring the Functional Significance of Dendritic Inhibition In Cortical Pyramidal Cells M. W. Spratling and M. H. Johnson Centre for Brain and Cognitive Development,
Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex. 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations. 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage
 Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual,
Topic 11 - Parietal Association Cortex 1. Sensory-to-motor transformations 2. Activity in parietal association cortex and the effects of damage Sensory to Motor Transformation Sensory information (visual,
Intelligent Control Systems
 Lecture Notes in 4 th Class in the Control and Systems Engineering Department University of Technology CCE-CN432 Edited By: Dr. Mohammed Y. Hassan, Ph. D. Fourth Year. CCE-CN432 Syllabus Theoretical: 2
Lecture Notes in 4 th Class in the Control and Systems Engineering Department University of Technology CCE-CN432 Edited By: Dr. Mohammed Y. Hassan, Ph. D. Fourth Year. CCE-CN432 Syllabus Theoretical: 2
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Hemispheric Specialization (lateralization) Each lobe of the brain has specialized functions (Have to be careful with this one.)
 Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Cerebral Cortex Principles contralaterality the right half of your brain controls the left half of your body and vice versa. (contralateral control.) Localization of function Specific mental processes
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
