The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
|
|
|
- Arabella Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2
2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain, more than 50% of neurons of the entire brain Structural regularity Control fine movement coordination, balance and muscle tone. Influences the motor systems by evaluating the disparities between intention and action. Adjusts the operation of motor centers in the cortex and the brain stem while a movement is in progress. 3 The relationship of the cerebellum to the cortical motor area Premotor area Supplementary motor cortex Primary motor cortex Cerebral Cortex Thalamus Cerebellar Thalamus cortex Relay nuclei Cerebellum 4
3 Three aspects of organization 1. Input: from brain stem and cortex, extensive information about the goals, commands, and feedback signals associated with the programming and execution of movement. 2. Output: motor and premotor systems of the cortex and brain stem. 3. Synaptic plasticity supports motor adaptation and learning. 5 Structure of the Cerebellum 6
4 Structure of the Cerebellum Dorsal View Cortex: vermis Hemisphere: intermediate lobe lateral lobe Deep nuclei: Dentate nucleus Cerebellar peduncles Interposed nuclei Fastigial nucleus flocculonodular lobe 7 Structure of the Cerebellum Midsagittal View Midbrain Pons Folium Brain stem Medulla 8
5 Overview of cerebellar control of movement Vestibular afferents Head and proximal body (visual, auditory, vestibular) Flocculonodular lobe Vermis Lateral vestibular nuclei Fastigial nucleus Balance and eye movement Brain stem (medial descending system) Posture, gaze 9 Overview of cerebellar control of movement limbs (somatosensory) Cerebral cortex Intermediate hemisphere Lateral hemisphere Interposed nucleus Dentate nucleus Corticospinal and rubrospinal systems (lateral descending system) Motor, premotor and prefrontal cortices Limbs and digits movement Planning and mental rehearsal of complex movement 10
6 Common Symptoms Related to Cerebellar Lesions Hypotonia a diminished resistance to passive limb displacement Ataxia lack of coordination Intention tremors during movement 11 Structure of the Cerebellar Cortex surface Stellate cell Molecular layer Basket cell Purkinje cell layer Purkinje cell Golgi cell Granule cell glomerulus Granule cell layer Climbing fiber Mossy fiber 12
7 Micro-Circuitry of the Cerebellum Input to the cerebellum: mossy fiber and climbing fiber, both are excitatory (glutamate) Output from the cerebellar cortex: Purkinje cell axon, inhibitory (GABA) Output from the cerebellum: cerebellar deep nuclei, excitatory 13 Micro-Circuitry of the Cerebellum Purkinje cell 2-dimensional dendritic tree The only output of the cerebellar cortex Receives input from climbing fiber and parallel fiber (granule cell axon) Granule cell Small, large quantity Input: mossy fiber Output: parallel fiber to Purkinje cells 14
8 Two excitatory pathways in the cerebellar cortex 1 Mossy fiber Granule cells Parallel fiber Purkinje cells output Climbing fiber 2 1: one parallel fiber thousands of Purkinje cells one Purkinje cell 200,000 parallel fiber Simple spike in Purkinje cell evoked by mossy fiber input 2: one climbing fiber 1-10 Purkinje cells one Purkinje cell one climbing fiber, many synapses complex spikes in Purkinje cell 15 Local inhibitory pathways in the cerebellar cortex Lateral inhibition by Stellate cell and basket cell, - Parallel fiber Stellate, basket Purkinje cell Golgi cell: inhibit granule cells, negative feedback - Parallel fiber Golgi cell granule cell 16
9 Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellar cortex pf Golgi cell - Granule cell Stellate/ Basket Purkinje cell - - Deep nuclei Climbing fiber Mossy fiber Output of the cerebellum 17 The cerebellum and motor learning Model suggested by Marr and Albus (1970s) The climbing fiber weakens the parallel fiber Purkinje cell synapse in a process called long-term depression (LTD). (Masao Ito, 1980s) pf active no LTD pf & cf both active repeatedly LTD (associative plasticity) The climbing fiber compares what is intended with what has happened and provides an error signal that would depress the parallel fibers that are active concurrently and allow correct movement to occur. 18
10 The cerebellum and motor learning 19 The cerebellum and motor learning 20
The Cerebellum. Outline. Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo
 Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
The Cerebellum. Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
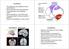 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Functions. Traditional view: Motor system. Co-ordination of movements Motor learning Eye movements. Modern view: Cognition
 The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
Cerebellum 1/20/2016. Outcomes you need to be able to demonstrate. MHD Neuroanatomy Module
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Connection of the cerebellum
 CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
Abdullah AlZibdeh. Dr. Maha ElBeltagy. Maha ElBeltagy
 19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
11/2/2011. Basic circuit anatomy (the circuit is the same in all parts of the cerebellum)
 11/2/2011 Neuroscientists have been attracted to the puzzle of the Cerebellum ever since Cajal. The orderly structure, the size of the cerebellum and the regularity of the neural elements demands explanation.
11/2/2011 Neuroscientists have been attracted to the puzzle of the Cerebellum ever since Cajal. The orderly structure, the size of the cerebellum and the regularity of the neural elements demands explanation.
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
THE CEREBELLUM SUDIVISIONS, STRUCTURE AND CONNECTIONS
 THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
THE CEREBELLUM. - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum
 CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum
 The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU)
 Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? 1 Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU) Cerebellum The Little Brain 2 The Cerebellum takes ~10% of the Brain in Volume Small but Hefty
Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? 1 Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU) Cerebellum The Little Brain 2 The Cerebellum takes ~10% of the Brain in Volume Small but Hefty
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus. Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS
 Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS May 30, 2016 Overview Structure Response properties Hypothesized roles in hearing Review of VCN-DCN circuits and projections Structure
Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus Amanda M. Lauer, Ph.D. Dept. of Otolaryngology-HNS May 30, 2016 Overview Structure Response properties Hypothesized roles in hearing Review of VCN-DCN circuits and projections Structure
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
FUNCTION: It COORDINATES movement HOW IT WORKS
 CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
Cerebellum: Origins and Development
 Cerebellum: Origins and Development Found in all vertebrates Dorsal lip of developing medulla (rhombencephalon) Near terminations of vestibular (VIII) and lateral line afferents, which sense fluid displacement
Cerebellum: Origins and Development Found in all vertebrates Dorsal lip of developing medulla (rhombencephalon) Near terminations of vestibular (VIII) and lateral line afferents, which sense fluid displacement
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
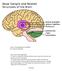 Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
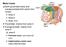 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum
 Outline Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum 陽明大學醫學院腦科所陳昌明副教授 Anatomy Cerebellar cortex Neuronal circuitry Cerebellar connections Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Neocerebellum Other cerebellar functions
Outline Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum 陽明大學醫學院腦科所陳昌明副教授 Anatomy Cerebellar cortex Neuronal circuitry Cerebellar connections Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Neocerebellum Other cerebellar functions
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
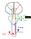 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Neural Basis of Motor Control. Chapter 4
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
The Motor Systems. What s the motor system? Plan
 The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
FIRST PROOF. Cerebellum. Article Number : EONS : 0736
 Cerebellum THE HUMAN CEREBELLUM ( little brain ) is a significant part of the central nervous system both in size and in neural structure. It occupies approximately one-tenth of the cranial cavity, sitting
Cerebellum THE HUMAN CEREBELLUM ( little brain ) is a significant part of the central nervous system both in size and in neural structure. It occupies approximately one-tenth of the cranial cavity, sitting
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Fundamental Neuroscience (2 nd Edition): Section V. MOTOR SYSTEMS Chapter 32: Cerebellum James C. Houk and Enrico Mugnaini
 Fundamental Neuroscience (2 nd Edition): Section V. MOTOR SYSTEMS Chapter 32: Cerebellum James C. Houk and Enrico Mugnaini The cerebellum (Latin for little brain ) is a strategic part of the nervous system.
Fundamental Neuroscience (2 nd Edition): Section V. MOTOR SYSTEMS Chapter 32: Cerebellum James C. Houk and Enrico Mugnaini The cerebellum (Latin for little brain ) is a strategic part of the nervous system.
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
C14 / CNS / MC3. What two stuctures make up the central nervous system?
 C14 / CNS / MC3 What two stuctures make up the central nervous system? The CNS starts embryonic development as a neural tube. What adult structures develop from the neural tube? What structures are part
C14 / CNS / MC3 What two stuctures make up the central nervous system? The CNS starts embryonic development as a neural tube. What adult structures develop from the neural tube? What structures are part
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Spinal Interneurons. Control of Movement
 Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector
 At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector Normal condition, using fingers and wrist Using elbow as folcrum Using shoulder as folcrum (outstretched
At the highest levels of motor control, the brain represents actions as desired trajectories of end-effector Normal condition, using fingers and wrist Using elbow as folcrum Using shoulder as folcrum (outstretched
Neocortex. Cortical Structures in the Brain. Neocortex Facts. Laminar Organization. Bark-like (cortical) structures: Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12
 Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
CEREBRAL CORTEX CHAPTER. caudate nucleus. nucleus. Key Terms. Chapter 13 in a Nutshell REB RAL RES
 caudate nucleus CHAPTER Key Terms anatomy of the cortex hemisphere asymmetry Brodmann areas motor and premotor areas rnotor body maps corticospinal tract neuronal population studies cortical inputs and
caudate nucleus CHAPTER Key Terms anatomy of the cortex hemisphere asymmetry Brodmann areas motor and premotor areas rnotor body maps corticospinal tract neuronal population studies cortical inputs and
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems
 NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
2401 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
Dr. Chris Doumen Week 7 2401 : Anatomy/Physiology The Cerebrum Central Nervous System TextBook Readings Pages 434-456 and 460-461 Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture is worth a thousand
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
10/31/2011. Principal Cell Plasticity. Bastian: Sensory Consequence of Movement of Tail
 In the previous lecture we learned how Mormyrid electric fish produce an electromotor command and then receive an electrosensory response after a delay. The motor output and the sensory response are time-locked
In the previous lecture we learned how Mormyrid electric fish produce an electromotor command and then receive an electrosensory response after a delay. The motor output and the sensory response are time-locked
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves
 CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1 As with sensory input, motor output is organized in central nervous system Peripheral Nervous system divides efferent signals somatotopically
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1 As with sensory input, motor output is organized in central nervous system Peripheral Nervous system divides efferent signals somatotopically
Embryological origin of thalamus
 diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
diencephalon Embryological origin of thalamus The diencephalon gives rise to the: Thalamus Epithalamus (pineal gland, habenula, paraventricular n.) Hypothalamus Subthalamus (Subthalamic nuclei) The Thalamus:
Control over movement is exerted by
 CHAPTER 16 INITIATION AND CONTROL OF MOVEMENT Control over movement is exerted by all parts of the nervous system, not just those identified as "motor" in textbooks. The participation of motoneurons in
CHAPTER 16 INITIATION AND CONTROL OF MOVEMENT Control over movement is exerted by all parts of the nervous system, not just those identified as "motor" in textbooks. The participation of motoneurons in
