Clinical features and management of type I gastric carcinoids
|
|
|
- Archibald Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clin J Gastroenterol (2014) 7: DOI /s CLINICAL REVIEW Clinical features and management of type I gastric carcinoids Yuichi Sato Received: 20 August 2014 / Accepted: 2 September 2014 / Published online: 17 September 2014 Ó Springer Japan 2014 Abstract Type I gastric carcinoids (TIGCs) are related to chronic atrophic gastritis and are characterized by hypergastrinemia and hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like cells. TIGCs are the most frequently diagnosed of all gastric carcinoids, accounting for about %. Endoscopically, TIGCs are present as small (\10 mm), polypoid lesions or, more frequently, as smooth, rounded submucosal lesions. Histologically, TIGCs arise in the deep mucosa, with some invading the submucosa. Most TIGCs are well-differentiated tumors, with metastasis being rare. Therefore, patients with TIGCs generally have an excellent prognosis. Among the currently available treatment options are total gastrectomy, partial resection, antrectomy, endoscopic resection, and endoscopic surveillance, although no consensus has been reached on their optimal management. Further studies are needed to develop better management options for patients with TIGC. Keywords Gastric carcinoid Gastric neuroendocrine tumor Type-A gastritis Helicobacter pylori Introduction Carcinoids arise from cells of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and are, therefore, also called neuroendocrine Y. Sato (&) Department of Gastroenterology, Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Asahimachi-dori, Niigata , Japan yuichi@med.niigata-u.ac.jp tumors [1]. The incidence of gastric carcinoids (GC) among all gastrointestinal carcinoids (GICs) has gradually increased [2 4], making it important to understand the clinical features and management of GCs. GCs can be classified into three distinct subgroups, with Table 1 showing the clinical characteristics of these three types [5 11]. Type I GCs (TIGCs) arise in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis (CAG), including autoimmune gastritis (AIG; i.e. type A gastritis) and Helicobacter pyloriassociated atrophic gastritis [12, 13]. TIGCs are associated with hypergastrinemia and hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells. TIGCs are often small (\10 mm), occurring as multiple tumors in individual patients, and are located in the gastric fundus or corpus. Most tumors are limited to the mucosa or submucosa. TIGCs are the most frequently diagnosed of all GCs, accounting for about %. TIGCs tend to display a nearly benign behavior with a low risk for progression or metastasis. Type II GCs are rare and account for 5 6 % of all GCs. They are associated with gastrin-producing neoplasms in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia/zollinger Ellison syndrome. Similar to TIGCs, type II GCs are small and multiple, associated with hypergastrinemia and hyperplasia of ECL cells, and considered benign. In contrast, type III GCs are sporadic carcinoids without specific background factors, therefore, occurring under normogastrinemic conditions. Type III GCs are often single and large tumors, accounting for % of all GCs. These tumors behave more aggressively, with higher rates of metastasis and regional lymph node involvement. In Japan, TIGCs constitute 87.1 % of all GCs [14]. This review focuses on the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of TIGCs.
2 382 Clin J Gastroenterol (2014) 7: Table 1 Characteristics of gastric carcinoid tumors GC gastric carcinoid Characteristic Type I GCs Type II GCs Type III GCs Proportion of GCs (%) Associated disease Chronic atrophic gastritis (type A gastritis, H. pylori) Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 1/gastrinoma Gender Females [ males Females = males Females \ males Number of Multiple Multiple Solitary tumors Size of Often small (\10 mm) Often small (\10 mm) Often [20 mm tumors Histology Well-differentiated Well-differentiated From well- to poorly differentiated WHO grading Depth of invasion None G1 tumor G1 tumor G1/G2/G3 (NEC) tumor Mucosa or submucosa Mucosa or submucosa Any depth Serum gastrin Increased Increased Normal Gastric ph Low High Normal Risk of 2 5 % % [50 % metastasis Prognosis Excellent Good Poor Epidemiology Pathophysiology GCs are rare tumors, although their incident rates have gradually increased. For example, over a 35-year period, the incidence of GC in the United States has increased nearly tenfold [2], while the incidence of GC in the UK hasincreased23-foldinmenand47-foldinwomen[3]. As of 1999, the percentage of GCs among all gastric malignancies in the United States increased from 0.3 to 1.77 % over 50 years, and the percentage of GCs among all GICs increased from 2.4 to 8.7 % over 30 years [4]. More recent reports have revealed that the ratio of GCs to all GICs has increased further, at rates of 12 % in the UK [3], 23 % in Austria [15], 14.6 % in Korea [16], 11.9 % in the United States [17], and 15.1 % in Japan [14]. Although these increases in the incidence of GCs may be due in part to a true increase in the incidence, they may also be due to improvements in diagnostic technology, including endoscopy, and an increased awareness of GCs. Since no specific symptoms are associated with TIGC, most TIGCs are detected incidentally during endoscopy. TIGCs are more prevalent in women than in men [9, 12], owing to the greater incidence of AIG in women [18]. In Japan, however, TIGC is more common in men than in women [19], perhaps owing to the lower rates of cooccurrence of TIGC and AIG. On ingestion of food, antral G cells in the stomach secrete gastrin, which binds to cholecystokinin-2 (CCK-2) receptors located on the membranes of ECL cells, leading to histamine release. Histamine binds to H2 receptors on gastric parietal cells to produce hydrochloric acid. In the AIG, anti-parietal cell antibodies act on gastric parietal cells, leading to achlorhydria, which induces G cell hyperplasia and their secretion of additional gastrin, resulting in hypergastrinemia. Gastrin stimulates gastric epithelial cell proliferation and acts as a trophic factor for ECL cells, leading to ECL cell hyperplasia. Therefore, in some patients, hypergastrinemia can lead to TIGC development. Since only some patients with AIG develop TIGC, other cofactors, such as Reg [20], mcl-1 [21], and MEN-1 gene mutation [22], may play a role in the development of TIGC. In H. pylori associated gastritis, H. pylori induces hypergastrinemia [23, 24]. H. pylori infection is a risk factor for the development of gastric mucosal atrophy, resulting in low acid output [25]. Antibodies against H. pylori may act as autoantibodies to parietal cells [26 28]. Additionally, hypergastrinemia related to H. pylori infection would be due to up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-a and interleukin-b and down-regulation of somatostatin [29]. Furthermore, H. pylori lipopolysaccharide stimulates DNA
3 Clin J Gastroenterol (2014) 7: synthesis in ECL cells, suggesting that it may act on ECL cell hyperplasia [30]. H. pylori infection may, therefore, be a risk factor for TIGC by inducing hypergastrinemia [13, 31]. In either AIG or H. pylori-associated gastritis, under the condition of CAG, a lack of gastric acid production results in hyperplasia of G cells and hypergastrinemia, leading to TIGC development. Diagnosis Most patients with TIGCs do not complain of flushing or any other symptoms related to carcinoid syndrome [32, 33]. However, patients with TIGC have nonspecific symptoms, such as nausea, abdominal pain, and/or dyspepsia [34], or pernicious anemia complicated by AIG. Therefore, TIGCs are detected incidentally during screening by esophagogastroduodenal endoscopy. Endoscopically, TIGC is present as polypoid lesions or, more frequently, as smooth and rounded submucosal lesions [35]. TIGCs are often found in the gastric corpus or fundus, are small in size (\10 mm), and multiple. Narrow band imaging and high resolution magnification endoscopy may be helpful for the endoscopic diagnosis of TIGC [36]. Histologically, TIGCs are composed of small uniform cells in nests and infiltrating strands, or with an anastomosing ribbon-like, tubular, or acinar pattern. These tumors arise in the deep mucosa, in some cases invading the submucosa. Moreover, these tumors are covered by normal mucosa, requiring deeper biopsy to remove specimens adequate for diagnosis. Sampling biopsy should not include only the TIGC lesion, but also both the antrum and the corpus/fundus to assess for the presence of atrophic gastritis and precursor lesions of TIGCs [37]. Hyperplastic and dysplastic ECL cells are considered precursors of ECL cell carcinoids [38] and are often detected in biopsy specimens from non-tumor mucosa adjacent to tumors. The 2010 World Health Organization (WHO) classification system has defined ECL cell hyperplasia as diffuse, linear, micronodular, or adenomatoid hyperplasia, whereas ECL cell dysplasia is characterized by enlarged or fused micronodules, microinvasion, or newly formed stroma [1, 39]. Nodules that increase in size to [0.5 mm or invade the submucosa are classified as microcarcinoids (\0.5 cm) or plain carcinoids (C0.5 cm) [1]. GCs are classified histologically by grade and differentiation. The 2010 WHO classification system grades GCs by counting mitoses and by the Ki67 index: G1,\2 mitoses per 10 high power fields (HPF) (=2 mm 2 ) and/or a Ki67 index B2 %; G2, 2 20 mitoses per 10 HPF and/or a Ki67 index of 2 20 %; or G3, [20 mitoses per 10 HPF and/or a Ki67 index [20 % [40]. Most TIGCs are classified as G1 tumors. Endoscopic ultrasonography is useful for assessing the depth of gastric wall invasion of tumors[1 cm in size [41]. CT or MRI scan can provide useful information in patients with metastatic disease. The role of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in assessing TIGCs is unclear [42]. Octreoscan can be used to assess metastases and somatostatin receptor status if treatment with somatostatin receptor antagonist is being considered [43]. However, Octreoscan is generally unavailable in Japan. Prognosis Since most TIGCs are G1 tumors and are limited to the mucosa or submucosa, patients with TIGCs generally have an excellent prognosis. Endoscopic resection of localized T1 lesions can achieve a close to 100 % survival rate [44]. A recent report of a large series of patients with TIGC found that the rate of lymph node metastases was 5.3 % and the rate of tumor-associated death was 1.07 % [45]. Tumor size and depth predict lymph node metastasis [46]. Although most patients with TIGCs classified as G1 had an excellent prognosis, those with TIGCs classified as G2 and G3 had poorer or very severe prognosis, respectively [45]. Metastatic TIGC is related to be a tumor size C1 cm, an elevated Ki-67 index and high serum gastrin levels [47]. Therefore, assessment of tumor size, depth, and histological stage may be predictive of patient prognosis. Management The clinical management and treatment of patients with TIGC depend on tumor size and the presence of risk factors, including muscle wall infiltration, increased proliferation, and/or metastasis. Hitherto, endoscopic resection has been recommended for patients with a few (\3 5 lesions) small (\1 cm) TIGCs, whereas antrectomy or local resection is recommended for patients with many ([3 5 lesions) or large ([1 cm) TIGCs [48]. However, resent studies revealing the generally indolent nature of TIGCs led to a shift in management and treatment. Patients with small tumors and lacking risk factors have been managed by simple observation, without endoscopic or surgical resection [12, 19, 32, 37, 49, 50]. In contrast, the ENETS guidelines have recommended that all TIGCs should be removed whenever possible, although tumor development has not been found to be less favorable in patients with tumors \10 mm left in place [37]. NCCN guidelines [50] have recommended that patients with locoregional
4 384 Clin J Gastroenterol (2014) 7: TIGC B 20 mm in size undergo (a) endoscopic surveillance every 6 12 months, and (b) endoscopic resection, if feasible, with biopsy of the tumor and adjacent mucosa. The treatment of TIGCs mm in size is unclear. In the WHO classification, GCs 1 cm in size is the cut-off defining T1 and T2 tumors. ENETS guidelines have suggested endoscopic removal of TIGCs larger than 10 mm in size without invasion of the muscularis propria and lymph nodes, and surgical resection of tumors with involvement beyond the submucosa or lymph nodes or with distant disease [37]. However, NCCN guidelines have recommended either endoscopic resection or observation of local TIGCs mm in diameter. ENETS guidelines recommend endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) of TIGCs that have not invaded the muscularis propria. However, TIGCs frequently invade the submucosa [19], making it difficult to remove TIGCs completely, even small ones, by snare polypectomy or conventional EMR. In contrast, endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) is a feasible technique for the removal of tumors present in the submucosal layer, such as TIGCs. Recent reports have revealed that the complete resection rate of GC tumors was higher with ESD than with EMR [51, 52]. Surgical resection is generally recommended for TIGCs larger than 20 mm in diameter or those that extend deeper than the submucosa [37, 50]. Moreover, the latest ENETS guidelines endorsed the use of surgery in patients with lymph node or distant disease spread, and in those with poorly differentiated neoplasms [37]. Surgery should include local resection and antrectomy to reduce gastrin levels. However, antrectomy may not be effective in preventing recurrence and/or metastasis [53]. Patients with locoregionally unresectable and/or metastatic TIGCs should be treated with somatostatin analogs (SSAs) and/or undergo complete resection of the primary tumor and metastases. Treatment with SSAs has been shown effective in reducing the number and size of TIGCs [54 56]. SSAs act on G cells to inhibit gastrin secretion and have a role in reducing ECL cell hyperplasia. However, use of SSAs cannot be recommended, because their effects are short-term, with tumor progression occurring after the completion of SSA treatment [57]. Recently, natazepide (YF476), a peripheral gastrin (CCK-B) receptor antagonist, has been reported to inhibit acid secretion and ECL cell proliferation and to reduce the size and number of TIGCs [58]. Large, long-term, follow-up studies are needed to determine the efficacy of this CCK-B receptor antagonist in the treatment of TIGCs. After treatment, the ENETS guidelines recommend endoscopic surveillance every 12 months in patients with tumor recurrence, and every 24 months in patients without tumor recurrence [37]. NCCN guidelines have recommended that patients with small (B20 mm) TIGCs who did not require endoscopic resection or treatment should be evaluated by patient history and physical examination every 6 12 months [50]. Moreover, in the absence of tumor recurrence or progression, follow-up endoscopies should be performed every 6 12 months for the first 3 years and annually thereafter [50]. However, an optimal follow-up schedule has not yet been established as a clinical standard. Conclusion TIGCs are related to CAG with hypergastrinemia and hyperplasia of ECL cells. The incidence of GCs has significantly increased, with the great majority of GCs being TIGCs. TIGCs are present as small (\10 mm) and multiple lesions endoscopically, and are generally limited to the mucosa or submucosa. TIGCs tend to display a nearly benign behavior with a low risk for progression or metastasis. Several treatment options are currently available for TIGCs, but their optimal management has not been established. Further studies on TIGCs are needed to develop new promising management for patients with these tumors. Disclosures Conflict of Interest: interest. Yuichi Sato decrear that he has no conflict of Human/Animal Rights: All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5). Informed Consent: This study does not apply to giving Informed Consent because the present manuscript is a review article. References 1. Solcia E, Arnold R, Capella C, et al. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the stomach. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND editors WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: IARC, p Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, et al. One hundred years after carcinoid : epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26: Ellis L, Shale MJ, Coleman MP. Carcinoid tumors of the gastrointestinal tract: trends in incidence in England since Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105: Modlin IM, Lye KD, Kidd M. A 50-year analysis of 562 gastric carcinoids: small tumor or larger problem? Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99: Rindi G, Luinetti O, Cornaggia M, et al. Three subtypes of gastric argyrophil carcinoid and the gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma: a clinicopathological study. Gastroenterology. 1993; 104:
5 Clin J Gastroenterol (2014) 7: Nikou GC, Angelopoulos TP. Current concepts on gastric carcinoid tumors. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012; Article ID Basuroy R, Srirajaskanthan R, Prachalias A, et al. Review article: the investigation and management of gastric neuroendocrine tumours. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;39: Li TT, Qiu F, Qian ZR, et al. Classification, clinicopathologic features and treatment of gastric neuroendocrine tumors. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20: Massironi S, Sciola V, Spampatti MP, et al. Gastric carcinoids: between underestimation and overtreatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15: Zhang L, Ozao J, Warner R, Divino C. Review of the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management of type I gastric carcinoid tumor. World J Surg. 2011;35: Kaltsas G, Grozinsky-Glasberg S, Alexandraki KI, et al. Current concepts in the diagnosis and management of type 1 gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014;81: Scherübl H, Cadiot G, Jensen RT, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the stomach (gastric carcinoids) are on the rise: small tumors, small problems? Endoscopy. 2010;42: Sato Y, Iwafuchi M, Ueki J, et al. Gastric carcinoid tumors without autoimmune gastritis in Japan: a relationship with Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47: Ito T, Sasano H, Tanaka M, et al. Epidemiological study of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2010;45: Niederle MB, Hackl M, Kaserer K, Niederle B. Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours: the current incidence and staging based on the WHO and European Neuroendocrine Tumour Society classification: an analysis based on prospectively collected parameters. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17: Cho MY, Kim JM, Sohn JH, et al. Current trends of the incidence and pathological diagnosis of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (gep-nets) in korea : multicenter study. Cancer Res Treat. 2012;44: Lawrence B, Gustafsson BI, Chan A, et al. The epidemiology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011;40: Soykan I, Yakut M, Keskin O, et al. Clinical profiles, endoscopic and laboratory features and associated factors in patients with autoimmune gastritis. Digestion. 2012;86: Sato Y, Imamura H, Kaizaki Y, et al. Management and clinical outcomes of type I gastric carcinoid patients: retrospective, multicenter study in Japan. Dig Endosc. 2014;26: Higham AD, Bishop LA, Dimaline R, et al. Mutations of RegI alpha are associated with enterochromaffin-like cell tumor development in patients with hypergastrinemia. Gastroenterology. 1999;116: Pritchard DM, Berry D, Przemeck SM, et al. Gastrin increases mcl-1 expression in type I gastric carcinoid tumors and a gastric epithelial cell line that expresses the CCK-2 receptor. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;295:G D Adda T, Keller G, Bordi C, Höfler H. Loss of heterozygosity in 11q13-14 regions in gastric neuroendocrine tumors not associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 syndrome. Lab Invest. 1999;79: Chittajulla RS, Ardill JES, McColl KEL. The degree of hypergastrinemia induced by Helicobacter pylori is the same in duodenal ulcer patients and asymptomatic volunteers. Eur J Gastroenterol. 1992;4: Smith JTL, Pounder RE, Nwokolo CU. Inappropriate hypergastrinemia in asymptomatic healthy subjects infected with Helicobacter pylori. Gut. 1990;31: El-Omar EM, Oien K, El-Nujumi A, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastric acid hyposecretion. Gastroenterology. 1997;113: Faller G, Steininger H, Kränzlein J, et al. Antigastric autoantibodies in Helicobacter pylori infection: implications of histological and clinical parameters of gastritis. Gut. 1997;41: Claeys D, Faller G, Appelmelk BJ, et al. The gastric H, K? ATPase is a major autoantigen in chronic Helicobacter pylori gastritis with body mucosa atrophy. Gastroenterology. 1998;115: Negrini R, Savio A, Poiesi C, et al. Antigenic mimicry between Helicobacter pylori and gastric mucosa in the pathogenesis of body atrophic gastritis. Gastroenterology. 1996;111: Calam J, Gibbons A, Healey ZV, et al. How does Helicobacter pylori cause mucosal damage? Its effect on acid and gastrin physiology. Gastroenterology. 1997;113:S Kidd M, Miu K, Tang LH, et al. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide stimulates histamine release and DNA synthesis in rat enterochromaffin- like cells. Gastroenterology. 1997;113: Solcia E, Rindi G, Fiocca R, et al. Distinct patterns of chronic gastritis associated with carcinoid and cancer and their role in tumorigenesis. Yale J Biol Med. 1992;65: Ravizza D, Fiori G, Trovato C, et al. Long-term endoscopic and clinical follow-up of untreated type 1 gastric neuroendocrine tumours. Dig Liver Dis. 2007;39: Borch K, Ahrén B, Ahlman H, et al. Gastric carcinoids: biologic behavior and prognosis after differentiated treatment in relation to type. Ann Surg. 2005;242: Granberg D, Wilander E, Stridsberg M, et al. Clinical symptoms, hormone profiles, treatment, and prognosis in patients with gastric carcinoids. Gut. 1998;43: Ichikawa J, Tanabe S, Koizumi W, et al. Endoscopic mucosal resection in the management of gastric carcinoid tumors. Endoscopy. 2003;35: Singh R, Yao K, Anagnostopoulos G, et al. Microcarcinoid tumor diagnosed with high-resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging. Endoscopy. 2008;40(Suppl 2):E Delle Fave G, Kwekkeboom DJ, Van Cutsem E, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines for the management of patients with gastroduodenal neoplasms. Neuroendocrinology. 2012;95: La Rosa S, Vanoli A. Gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms and related precursor lesions. J Clin Pathol. 2014; 22 Jul. doi: / jclinpath Solcia E, Bordi C, Creutzfeldt W, et al. Histopathological classification of nonantral gastric endocrine growths in man. Digestion. 1988;41: Rindi G, Arnold R, Bosman FT, et al. Nomenclature and classification of neuroendocrine neoplasms of the digestive system. In: Bosman FT, Carneiro F, Hruban R, Theise ND, editors. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. Lyon: International Agency for Research on cancer (IARC); p Karaca C, Turner BG, Cizginer S, Forcione D, Brugge W. Accuracy of EUS in the evaluation of small gastric subepithelial lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;71: Bushnell DL, Baum RP. Standard imaging techniques for neuroendocrine tumors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2011;40: Gibril F, Reynolds JC, Lubensky IA, et al. Ability of somatostatin receptor scintigraphy to identify patients with gastric carcinoids: a prospective study. J Nucl Med. 2000;41: O Toole D, Delle Fave G, Jensen RT. Gastric and duodenal neuroendocrine tumours. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;26: La Rosa S, Inzani F, Vanoli A, et al. Histologic characterization and improved prognostic evaluation of 209 gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms. Hum Pathol. 2011;42: Saund MS, Al Natour RH, Sharma AM, et al. Tumor size and depth predict rate of lymph node metastasis and utilization of
6 386 Clin J Gastroenterol (2014) 7: lymph node sampling in surgically managed gastric carcinoids. Ann Surg Oncol. 2011;18: Grozinsky-Glasberg S, Thomas D, Strosberg JR, et al. Metastatic type 1 gastric carcinoid: a real threat or just a myth? World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19: Gilligan CJ, Lawton GP, Tang LH, et al. Gastric carcinoid tumors: the biology and therapy of an enigmatic and controversial lesion. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90: Hosokawa O, Kaizaki Y, Hattori M, et al. Long-term follow up of patients with multiple gastric carcinoids associated with type A gastritis. Gastric Cancer. 2005;8: Kulke MH, Benson AB 3rd, Bergsland E, et al. National comprehensive cancer networks. neuroendocrine tumors. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2012;10: Sato Y, Takeuchi M, Hashimoto S, et al. Usefulness of endoscopic submucosal dissection for type I gastric carcinoid tumors compared with endoscopic mucosal resection. Hepatogastroenterology. 2013;60: Kim HH, Kim GH, Kim JH, Choi MG, Song GA, Kim SE. The efficacy of endoscopic submucosal dissection of type I gastric carcinoid tumors compared with conventional endoscopic mucosal resection. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014; doi: /2014/ Epub 17 Feb Gladdy RA, Strong VE, Coit D, Allen PJ, et al. Defining surgical indications for type I gastric carcinoid tumor. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16: Thomas D, Tsolakis AV, Grozinsky-Glasberg S, et al. Long-term follow-up of a large series of patients with type 1 gastric carcinoid tumors: data from a multicenter study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013;168: Grozinsky-Glasberg S, Kaltsas G, Gur C, et al. Long-acting somatostatin analogues are an effective treatment for type 1 gastric carcinoid tumours. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;159: Campana D, Nori F, Pezzilli R, et al. Gastric endocrine tumors type I: treatment with long-acting somatostatin analogs. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008;15: Jianu CS, Fossmark R, Syversen U, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients treated for 1 year with octreotide long-acting release for enterochromaffin-like cell carcinoids. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2011;46: Fossmark R, Sørdal Ø, Jianu CS, et al. Treatment of gastric carcinoids type 1 with the gastrin receptor antagonist netazepide (YF476) results in regression of tumours and normalisation of serum chromogranin A. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;36:
Is Endoscopic Resection for Type 1 Gastric Neuroendocrine Tumors Essential for Treatment?: Multicenter, Retrospective Long-term Follow-up Results
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1738-3331, http://dx.doi.org/10.7704/kjhugr.2016.16.1.13 The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, 2016;16(1):13-18 Is Endoscopic Resection for Type
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1738-3331, http://dx.doi.org/10.7704/kjhugr.2016.16.1.13 The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, 2016;16(1):13-18 Is Endoscopic Resection for Type
CASE REPORT. Introduction. Case Report. Kimitoshi Kubo 1, Noriko Kimura 2, Katsuhiro Mabe 1, Yusuke Nishimura 1 and Mototsugu Kato 1
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0842-18 Intern Med 57: 2951-2955, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Synchronous Triple Gastric Cancer Incorporating Mixed Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Tumor Completely
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0842-18 Intern Med 57: 2951-2955, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Synchronous Triple Gastric Cancer Incorporating Mixed Adenocarcinoma and Neuroendocrine Tumor Completely
Original Report. Carcinoid Tumors of the Stomach: A Clinical and Radiographic Study
 Aaron J. Binstock 1 C. Daniel Johnson 1 David H. Stephens 1 Ricardo V. Lloyd 2 Joel G. Fletcher 1 Received July 25, 2000; accepted after revision September 29, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
Aaron J. Binstock 1 C. Daniel Johnson 1 David H. Stephens 1 Ricardo V. Lloyd 2 Joel G. Fletcher 1 Received July 25, 2000; accepted after revision September 29, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID
 ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID Manoop S. Bhutani, MD, FASGE, FACG, FACP, AGAF, Doctor Honoris Causa Professor of Medicine Eminent Scientist of the Year 2008, World
ENDOLUMINAL APPROACH FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF GASTROINTESTINAL CARCINOID Manoop S. Bhutani, MD, FASGE, FACG, FACP, AGAF, Doctor Honoris Causa Professor of Medicine Eminent Scientist of the Year 2008, World
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role
 Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Carcinoid Tumors: The Beginning and End. Surgical Oncology Update 2011 Chris Baliski MD, FRCS BC Cancer Agency, CSI October 21, 2011
 Carcinoid Tumors: The Beginning and End Surgical Oncology Update 2011 Chris Baliski MD, FRCS BC Cancer Agency, CSI October 21, 2011 1 st described by Oberndofer(1907) Karzinoide = cancer like Arise from
Carcinoid Tumors: The Beginning and End Surgical Oncology Update 2011 Chris Baliski MD, FRCS BC Cancer Agency, CSI October 21, 2011 1 st described by Oberndofer(1907) Karzinoide = cancer like Arise from
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors
 Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors Jaume Capdevila, MD, PhD Vall d'hebron University Hospital Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO)
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors Jaume Capdevila, MD, PhD Vall d'hebron University Hospital Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO)
Gastric endocrine tumors type I: treatment with long-acting somatostatin analogs
 Endocrine-Related Cancer (2008) 15 337 342 Gastric endocrine tumors type I: treatment with long-acting somatostatin analogs D Campana 1, F Nori 1, R Pezzilli 1, L Piscitelli 1, D Santini 2, E Brocchi 1,
Endocrine-Related Cancer (2008) 15 337 342 Gastric endocrine tumors type I: treatment with long-acting somatostatin analogs D Campana 1, F Nori 1, R Pezzilli 1, L Piscitelli 1, D Santini 2, E Brocchi 1,
Endoscopic Treatment of Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumors
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2013;46:656-661 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.6.656 Open Access Endoscopic Treatment of Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumors Sang
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2013;46:656-661 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2013.46.6.656 Open Access Endoscopic Treatment of Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumors Sang
Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the stomach
 Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the stomach Oldrich Louthan Background. Gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms of type 1 and type 3 are different entities and as such require different therapeutical strategies.
Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the stomach Oldrich Louthan Background. Gastric neuroendocrine neoplasms of type 1 and type 3 are different entities and as such require different therapeutical strategies.
Gastric and Oesophageal Neuroendocrine tumours. Dr Tim Bracey, Consultant Pathologist MBChB PhD MRCS FRCPath
 Gastric and Oesophageal Neuroendocrine tumours Dr Tim Bracey, Consultant Pathologist MBChB PhD MRCS FRCPath Intestinal (and BO) endocrine cells in crypt bases NE cell (granules towards vessels) Paneth
Gastric and Oesophageal Neuroendocrine tumours Dr Tim Bracey, Consultant Pathologist MBChB PhD MRCS FRCPath Intestinal (and BO) endocrine cells in crypt bases NE cell (granules towards vessels) Paneth
Commonly Encountered Neuro-Endocrine Tumors of the Gut
 Commonly Encountered Neuro-Endocrine Tumors of the Gut Moderators: Giuseppe Aliperti, MD Steven Edmundowicz, MD Panelists Douglas O. Faigel, MD Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Oregon
Commonly Encountered Neuro-Endocrine Tumors of the Gut Moderators: Giuseppe Aliperti, MD Steven Edmundowicz, MD Panelists Douglas O. Faigel, MD Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Oregon
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Color Codes Pathology and Genetics Medicine and Clinical Pathology Surgery Imaging
 Saturday, November 5, 2005 8:30-10:30 a. m. Poorly Differentiated Endocrine Carcinomas Chairman: E. Van Cutsem, Leuven, Belgium 9:00-9:30 a. m. Working Group Sessions Pathology and Genetics Group leaders:
Saturday, November 5, 2005 8:30-10:30 a. m. Poorly Differentiated Endocrine Carcinomas Chairman: E. Van Cutsem, Leuven, Belgium 9:00-9:30 a. m. Working Group Sessions Pathology and Genetics Group leaders:
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Neuroendocrine Tumor of Unknown Primary Accompanied with Stomach Adenocarcinoma
 J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(4):234-238 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.4.234 Case Report Neuroendocrine Tumor of Unknown Primary Accompanied with Stomach Adenocarcinoma Ho-Yeun Kim, Sung-Il Choi 1,
J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(4):234-238 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.4.234 Case Report Neuroendocrine Tumor of Unknown Primary Accompanied with Stomach Adenocarcinoma Ho-Yeun Kim, Sung-Il Choi 1,
Surgical Management of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gut. Richard Hodin MD Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Surgical Management of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gut Richard Hodin MD Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Sites of GI Carcinoid Tumors Small intestine 44% Rectum
Surgical Management of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gut Richard Hodin MD Professor of Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Sites of GI Carcinoid Tumors Small intestine 44% Rectum
Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case
 Case Report Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case Yuanliang Li, Xin Su, Huangying Tan Department of Integrative Oncology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Correspondence
Case Report Type 2 gastric neuroendocrine tumor: report of one case Yuanliang Li, Xin Su, Huangying Tan Department of Integrative Oncology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China Correspondence
Endoscopic argon plasma therapy for neuroendocrine type I gastric tumors
 Original articles Endoscopic argon plasma therapy for neuroendocrine type I gastric tumors Rodrigo Castaño, MD, Claudia Vargas, MD, Juan Camilo Pérez Cadavid, MD, Juan Pablo Dueñas, MD, Mario Hernán Ruiz,
Original articles Endoscopic argon plasma therapy for neuroendocrine type I gastric tumors Rodrigo Castaño, MD, Claudia Vargas, MD, Juan Camilo Pérez Cadavid, MD, Juan Pablo Dueñas, MD, Mario Hernán Ruiz,
Gastrinoma: Medical Management. Haley Gallup
 Gastrinoma: Medical Management Haley Gallup Also known as When to put your knife down Gastrinoma Definition and History Diagnosis Historic Management Sporadic vs MEN-1 Defining surgical candidates Nonsurgical
Gastrinoma: Medical Management Haley Gallup Also known as When to put your knife down Gastrinoma Definition and History Diagnosis Historic Management Sporadic vs MEN-1 Defining surgical candidates Nonsurgical
The pathology of neuroendocrine tumours of the gut
 The pathology of neuroendocrine tumours of the gut Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester & Cheltenham, UK Histopathology Regional Teaching Bristol May 11 2016 The pathology of neuroendocrine tumours (NETs)
The pathology of neuroendocrine tumours of the gut Professor Neil A Shepherd Gloucester & Cheltenham, UK Histopathology Regional Teaching Bristol May 11 2016 The pathology of neuroendocrine tumours (NETs)
Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 6, No. 2, April 2012, pp. 270-274 CASE REPORT Regression of Advanced Gastric MALT Lymphoma after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Soo-Kyung Park, Hwoon-Yong Jung, Do Hoon Kim,
Unexpected Findings at Endoscopy
 The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
The Endoscopic Incidentaloma: What to Tell Your Patient t with Unexpected Endoscopic Findings: Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia, Silent Ileitis, Carcinoid David Greenwald, MD Montefiore Medical Center Albert
Kentaro Tominaga, Kenya Kamimura, Junji Yokoyama and Shuji Terai
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1700-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy and Double-balloon Enteroscopy for the Diagnosis of Multiple Carcinoid Tumors in the Small Intestine:
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1700-18 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Capsule Endoscopy and Double-balloon Enteroscopy for the Diagnosis of Multiple Carcinoid Tumors in the Small Intestine:
Recent Studies on Digestive. System Anatomy
 Chapter 1 Recent Studies on Digestive Study on Morphology and Pathogenesis of Type 1 ECL- Cell Gastric Carcinoids Vuka Katic Department in Policlinic Human, University of Niš, Serbia. Email : vuka.katic@gmail.com
Chapter 1 Recent Studies on Digestive Study on Morphology and Pathogenesis of Type 1 ECL- Cell Gastric Carcinoids Vuka Katic Department in Policlinic Human, University of Niš, Serbia. Email : vuka.katic@gmail.com
NET und NEC. Endoscopic and oncologic therapy
 NET und NEC Endoscopic and oncologic therapy Classification well-differentiated NET - G1 and G2 - carcinoid poorly-differentiated NEC - G3 - like SCLC well differentiated NET G3 -> elevated proliferation
NET und NEC Endoscopic and oncologic therapy Classification well-differentiated NET - G1 and G2 - carcinoid poorly-differentiated NEC - G3 - like SCLC well differentiated NET G3 -> elevated proliferation
Rare GI Malignancies
 Rare GI Malignancies Jordan Karlitz, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology Director, Hereditary GI Cancer and Genetics Program Tulane University School of Medicine Outline Gastrointestinal
Rare GI Malignancies Jordan Karlitz, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology Director, Hereditary GI Cancer and Genetics Program Tulane University School of Medicine Outline Gastrointestinal
Subepithelial Lesions of the Gut: When Should I Worry?
 Subepithelial Lesions of the Gut: When Should I Worry? President, ASGE Chairman, GI & Hepatology Scottsdale, AZ Faigel.douglas@mayo.edu Case 55 yo male with reflux EGD for Barrett s Screening SET, mucosal
Subepithelial Lesions of the Gut: When Should I Worry? President, ASGE Chairman, GI & Hepatology Scottsdale, AZ Faigel.douglas@mayo.edu Case 55 yo male with reflux EGD for Barrett s Screening SET, mucosal
Case Report Intramucosal Signet Ring Cell Gastric Cancer Diagnosed 15 Months after the Initial Endoscopic Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 479625, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/479625 Case Report Intramucosal Signet Ring Cell Gastric Cancer Diagnosed
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 479625, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/479625 Case Report Intramucosal Signet Ring Cell Gastric Cancer Diagnosed
NeuroEndocrine Tumors Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges: introduction
 NeuroEndocrine Tumors Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges: introduction Prof Eric Van Cutsem, MD, PhD Gastroenterology/Digestive Oncology Leuven, Belgium Eric.VanCutsem@uzleuven.be Diagnostic & therapeutic
NeuroEndocrine Tumors Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges: introduction Prof Eric Van Cutsem, MD, PhD Gastroenterology/Digestive Oncology Leuven, Belgium Eric.VanCutsem@uzleuven.be Diagnostic & therapeutic
Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection: A single-center retrospective study
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Endoscopic Resection of Ampullary Neuroendocrine Tumor
 CASE REPORT Endoscopic Resection of Ampullary Neuroendocrine Tumor Hiroyuki Fukasawa, Shigetaka Tounou, Masashi Nabetani and Tomoki Michida Abstract We report the case of a 57-year-old man with a 1.0-cm
CASE REPORT Endoscopic Resection of Ampullary Neuroendocrine Tumor Hiroyuki Fukasawa, Shigetaka Tounou, Masashi Nabetani and Tomoki Michida Abstract We report the case of a 57-year-old man with a 1.0-cm
Diagnosis and Management of Rectal Neuroendocrine Tumors
 FOCUSED REVIEW SERIES: Endoscopic approaches to Neuroendocrine Tumors Clin Endosc 2017;50:530-536 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.134 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Diagnosis and
FOCUSED REVIEW SERIES: Endoscopic approaches to Neuroendocrine Tumors Clin Endosc 2017;50:530-536 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.134 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Diagnosis and
Endoscopic treatment of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine tumors (GI-NETs)
 Endoscopic treatment of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine tumors (GI-NETs) Apostolos Tsolakis M.D., Ph.D. apostolos.tsolakis@ki.se or apobtsol@hotmail.com Dept. of Oncology and Pathology, Karolinska Institute,
Endoscopic treatment of Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine tumors (GI-NETs) Apostolos Tsolakis M.D., Ph.D. apostolos.tsolakis@ki.se or apobtsol@hotmail.com Dept. of Oncology and Pathology, Karolinska Institute,
Endoscopic approach to subepithelial lesions
 513538TAG7310.1177/1756283X13513538Therapeutic Advances in GastroenterologyL Menon and JM Buscaglia research-article2013 Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology Review Endoscopic approach to subepithelial
513538TAG7310.1177/1756283X13513538Therapeutic Advances in GastroenterologyL Menon and JM Buscaglia research-article2013 Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology Review Endoscopic approach to subepithelial
NICaN Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumour SACT protocols. 1.0 Dr M Eatock Final version issued
 Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Pancreatic Neuro-endocrine Tumours Dr Martin Eatock, Consultant Medical Oncologist & on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group,
Reference No: Title: Author(s) Systemic Anti-Cancer Therapy (SACT) Guidelines for Pancreatic Neuro-endocrine Tumours Dr Martin Eatock, Consultant Medical Oncologist & on behalf of the GI Oncologists Group,
Imaging of Neuroendocrine Metastases
 Imaging of Neuroendocrine Metastases Aoife Kilcoyne, Shaunagh McDermott, Colin McCarthy,Manuel Patino, Dushyant Sahani, Michael Blake Abdominal Imaging Division Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosure
Imaging of Neuroendocrine Metastases Aoife Kilcoyne, Shaunagh McDermott, Colin McCarthy,Manuel Patino, Dushyant Sahani, Michael Blake Abdominal Imaging Division Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosure
Introduction of GB polyp
 Management of Gallbladder Polyp as Physician's View Sang Hyub Lee, MD, PhD Seoul National University College of Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Department of Internal Medicine Division
Management of Gallbladder Polyp as Physician's View Sang Hyub Lee, MD, PhD Seoul National University College of Medicine Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Department of Internal Medicine Division
A case of local recurrence and distant metastasis following curative endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer
 Gastric Cancer (2015) 18:188 192 DOI 10.1007/s10120-014-0341-7 CASE REPORT A case of local recurrence and distant metastasis following curative endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer
Gastric Cancer (2015) 18:188 192 DOI 10.1007/s10120-014-0341-7 CASE REPORT A case of local recurrence and distant metastasis following curative endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer
Endoscopic Resection of a Rectal. Carcinoid Tumor with an Esophageal. Variceal Ligation Device. Report of a Case and Literature Review
 2006 7 28-32 Endoscopic Resection of a Rectal Carcinoid Tumor with an Esophageal Variceal Ligation Device Report of a Case and Literature Review Wei-Feng Feng, An-Liang Chou, Jen-En Tzeng, and Kuo-Chih
2006 7 28-32 Endoscopic Resection of a Rectal Carcinoid Tumor with an Esophageal Variceal Ligation Device Report of a Case and Literature Review Wei-Feng Feng, An-Liang Chou, Jen-En Tzeng, and Kuo-Chih
Jeffrey L. Winslow, MD, 1 Thomas D. Trainer, MD, 1 and Richard B. Colletti, MD 2. Abstract
 Anatomic Pathology / COLLAGENOUS GASTRITIS Collagenous Gastritis A Long-Term Follow-up With the Development of Endocrine Cell Hyperplasia, Intestinal Metaplasia, and Epithelial Changes Indeterminate for
Anatomic Pathology / COLLAGENOUS GASTRITIS Collagenous Gastritis A Long-Term Follow-up With the Development of Endocrine Cell Hyperplasia, Intestinal Metaplasia, and Epithelial Changes Indeterminate for
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Treatment Strategy for Non-curative Resection of Early Gastric Cancer. Jun Haneg Lee. Sungkyunkwan University, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul Korea
 Treatment Strategy for Non-curative Resection of Early Gastric Cancer Jun Haneg Lee. Sungkyunkwan University, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul Korea Classic EMR/ESD data analysis style Endoscopic resection
Treatment Strategy for Non-curative Resection of Early Gastric Cancer Jun Haneg Lee. Sungkyunkwan University, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul Korea Classic EMR/ESD data analysis style Endoscopic resection
Surveillance of Small Rectal Carcinoid Tumors in the Absence of Metastatic Disease
 Ann Surg Oncol (2012) 19:3486 3490 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2442-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE ENDOCRINE TUMORS Surveillance of Small Rectal Carcinoid Tumors in the Absence of Metastatic Disease Sara E. Murray, MD
Ann Surg Oncol (2012) 19:3486 3490 DOI 10.1245/s10434-012-2442-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE ENDOCRINE TUMORS Surveillance of Small Rectal Carcinoid Tumors in the Absence of Metastatic Disease Sara E. Murray, MD
PNET 3/7/2015. GI and Pancreatic NETs. The Postgraduate Course in Breast and Endocrine Surgery. Decision Tree. GI and Pancreatic NETs.
 GI and Pancreatic NETs The Postgraduate Course in Breast and Endocrine Surgery Disclosures Ipsen NET Advisory Board Marines Memorial Club and Hotel San Francisco, CA Eric K Nakakura San Francisco, CA March
GI and Pancreatic NETs The Postgraduate Course in Breast and Endocrine Surgery Disclosures Ipsen NET Advisory Board Marines Memorial Club and Hotel San Francisco, CA Eric K Nakakura San Francisco, CA March
ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology
 ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology Jun Haeng Lee, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Biopsy: M/D adenocarcinoma ESD: SRC >>
ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology Jun Haeng Lee, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Biopsy: M/D adenocarcinoma ESD: SRC >>
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors (Carcinoid Tumors) of the Stomach
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors (Carcinoid Tumors) of the Stomach Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition,
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors (Carcinoid Tumors) of the Stomach Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition,
SCOPE TODAYS SESSION. Case 1: Case 2. Basic Theory Stuff: Heavy Stuff. Basic Questions. Basic Questions
 MONDAY TEACHING SCOPE TODAYS SESSION Case 1: Basic Questions Case 2 Basic Questions Basic Theory Stuff: AJCC TNM + Stage Group for Carcinoid of the Appendix Management of Carcinoid of the Appendix (NCCN)
MONDAY TEACHING SCOPE TODAYS SESSION Case 1: Basic Questions Case 2 Basic Questions Basic Theory Stuff: AJCC TNM + Stage Group for Carcinoid of the Appendix Management of Carcinoid of the Appendix (NCCN)
NEUROENDOCRINE CARCINOID TUMORS PANCREATIC NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS
 University of Miami Jackson Memorial Hospital Role of the Surgeon in the Approach to Neuroendocrine tumors Dido Franceschi, MD Professor of Surgery University of Miami Karzinoide Siegfried Oberndorfer,
University of Miami Jackson Memorial Hospital Role of the Surgeon in the Approach to Neuroendocrine tumors Dido Franceschi, MD Professor of Surgery University of Miami Karzinoide Siegfried Oberndorfer,
Oberndofer 1907 Illeal Serotonin Secreting Tumor Carcinoid (Karzinoide)
 GEP-NET Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Oberndofer 1907 Illeal Serotonin Secreting Tumor Carcinoid (Karzinoide) 1 Histogenesis 16 different
GEP-NET Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Oberndofer 1907 Illeal Serotonin Secreting Tumor Carcinoid (Karzinoide) 1 Histogenesis 16 different
GI CARCINOID Dr Mussawar Iqbal Consultant Oncologist Hull and East Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust
 GI CARCINOID Dr Mussawar Iqbal Consultant Oncologist Hull and East Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust Introduction Carcinoid was old term, introduced in 1906 by German pathologist Cancinoma like More recent
GI CARCINOID Dr Mussawar Iqbal Consultant Oncologist Hull and East Yorkshire Hospitals NHS Trust Introduction Carcinoid was old term, introduced in 1906 by German pathologist Cancinoma like More recent
Endoscopic Biopsy in Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Retrospective Study
 Endoscopic Biopsy in Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Retrospective Study Xiao Han, Yun Cui, Chuanhua Yang*, Weili Sun, Jianghong Wu, Yunjie Gao, Hanbing Xue, Xiaobo Li, Lei Shen, Yanshen Peng,
Endoscopic Biopsy in Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Retrospective Study Xiao Han, Yun Cui, Chuanhua Yang*, Weili Sun, Jianghong Wu, Yunjie Gao, Hanbing Xue, Xiaobo Li, Lei Shen, Yanshen Peng,
Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in histologically poorly differentiated type early gastric cancer
 498 Original article Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in histologically poorly differentiated type early gastric cancer Authors C. Kunisaki 1, M. Takahashi 2, Y. Nagahori 3, T. Fukushima 3, H. Makino
498 Original article Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in histologically poorly differentiated type early gastric cancer Authors C. Kunisaki 1, M. Takahashi 2, Y. Nagahori 3, T. Fukushima 3, H. Makino
Medicine. Gang Xu, MD a, Peipei Wang, MD b, Yao Xiao, MD a, Xin Wu, MD b, Guole Lin, MD b, Clinical Case Report. 1.
 Clinical Case Report Medicine Local resection of rectal neuroendocrine tumor with first clinical manifestation of giant liver metastasis by transanal endoscopic microsurgery A case report Gang Xu, MD a,
Clinical Case Report Medicine Local resection of rectal neuroendocrine tumor with first clinical manifestation of giant liver metastasis by transanal endoscopic microsurgery A case report Gang Xu, MD a,
3/22/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Grading G1. Grading. Ki67 index V.
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship
Surgical Therapy of GEP-NET: An Overview
 Surgical Therapy of GEP-NET: An Overview Pierce K.H Chow MBBS, MMed, FRCSE, FAMS, PhD Professor, Duke-NUS Graduate School of Medicine Senior Consultant Surgeon, Singapore General Hospital Visiting Senior
Surgical Therapy of GEP-NET: An Overview Pierce K.H Chow MBBS, MMed, FRCSE, FAMS, PhD Professor, Duke-NUS Graduate School of Medicine Senior Consultant Surgeon, Singapore General Hospital Visiting Senior
Peptic ulcer disease. Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531
 Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Peptic ulcer disease Nomin-Erdene. D SOM-531 Learning objectives Stomach gross anatomy PUD Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Diagnosing Treatment Complicated ulcer disease Surgical procedures
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors (Carcinoid Tumors) of the Stomach
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors (Carcinoid Tumors) of the Stomach Protocol applies to well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the stomach. Carcinomas
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Neuroendocrine Tumors (Carcinoid Tumors) of the Stomach Protocol applies to well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the stomach. Carcinomas
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R
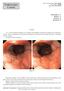 Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Endoscopic Corner Sirimontaporn N, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Vol. 11 No. 3 Sept. - Dec. 2010 171 Sirimontaporn N Klaikaew N Imraporn B Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 47- year-old female presented to the
Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer. Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
Characteristics and treatment of patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction: an analysis of 13 cases
 Original Article Characteristics and treatment of patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction: an analysis of 13 cases Yingzhi Qin 1 *, Chao Guo 1 *, Xiaoyan Chang 2, Yeye Chen
Original Article Characteristics and treatment of patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction: an analysis of 13 cases Yingzhi Qin 1 *, Chao Guo 1 *, Xiaoyan Chang 2, Yeye Chen
Cross-sectional Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract
 Cross-sectional Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract Eric J. May 1, Shannon P. Sheedy 1, Joel G. Fletcher 1, Mark J. Truty 2, Thomas C. Smyrk 3, Jeff L. Fidler 1 1. Radiology,
Cross-sectional Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract Eric J. May 1, Shannon P. Sheedy 1, Joel G. Fletcher 1, Mark J. Truty 2, Thomas C. Smyrk 3, Jeff L. Fidler 1 1. Radiology,
A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma. in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis. of Lymph Node Metastasis
 Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL NEUROENDOCRINE GASTRO-ENTERO-PANCREATIC TUMOURS GI Site Group Neuroendocrine gastro-entero-pancreatic tumours Authors: Dr.
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GASTROINTESTINAL NEUROENDOCRINE GASTRO-ENTERO-PANCREATIC TUMOURS GI Site Group Neuroendocrine gastro-entero-pancreatic tumours Authors: Dr.
Composite neuroendocrine carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with regional lymph node metastasis: a case report
 Fujihara et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:227 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1775-z CASE REPORT Composite neuroendocrine carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with regional lymph node
Fujihara et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:227 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1775-z CASE REPORT Composite neuroendocrine carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma with regional lymph node
Factors Affecting Survival in Neuroendocrine Tumors: A 15-Year Single Center Experience
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:00/00/0000 Acceptance:00/00/0000 : A 15-Year Single Center Experience Abdullah Sakin 1 *, Makbule Tambas 2, Saban Secmeler 3, Orçun Can 3, Serdar Arici 3,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:00/00/0000 Acceptance:00/00/0000 : A 15-Year Single Center Experience Abdullah Sakin 1 *, Makbule Tambas 2, Saban Secmeler 3, Orçun Can 3, Serdar Arici 3,
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States
 Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
Ethnic Distribution of Atrophic Autoimmune Gastritis in the United States Robert M. Genta, Regan Allen, Massimo Rugge Miraca Life Sciences Research Institute, Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas UTSW University
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R
 170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
Overview on Gastric Cancer
 Chapter 1 Gastric neuroendocrine tumors Elife Sahan 1 *; Nusret Erdogan 2 1 Department of Pathology, Taksim s Training and Research Hospital, İstanbul, Turkey 2 Department of Pathology Laboratory Techniques,
Chapter 1 Gastric neuroendocrine tumors Elife Sahan 1 *; Nusret Erdogan 2 1 Department of Pathology, Taksim s Training and Research Hospital, İstanbul, Turkey 2 Department of Pathology Laboratory Techniques,
A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in The Netherlands
 World J Surg (2018) 42:490 497 DOI 10.1007/s00268-017-4278-y ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in The Netherlands
World J Surg (2018) 42:490 497 DOI 10.1007/s00268-017-4278-y ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in The Netherlands
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID. Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
Treatment algorithm Neuroendocrine tumours. Gregory Kaltsas Endocrine Unit, Department of Pathophysiology, University of Athens, Greece
 Treatment algorithm Neuroendocrine tumours Gregory Kaltsas Endocrine Unit, Department of Pathophysiology, University of Athens, Greece Outline Presenting a meaningful algorithm Means used to develop algorithm
Treatment algorithm Neuroendocrine tumours Gregory Kaltsas Endocrine Unit, Department of Pathophysiology, University of Athens, Greece Outline Presenting a meaningful algorithm Means used to develop algorithm
Immunohistochemical consistency between primary tumors and lymph node metastases of gastric neuroendocrine carcinoma
 Uchiyama et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:115 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Immunohistochemical consistency between primary tumors and lymph node metastases
Uchiyama et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:115 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Immunohistochemical consistency between primary tumors and lymph node metastases
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ENETS Consensus Guidelines Update for Gastroduodenal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
 Consensus Guidelines Published online: January 19, 2016 Consensus Guidelines Update for Gastroduodenal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms G. Delle Fave a D. O Toole b A. Sundin c B. Taal d P. Ferolla e J.K. Ramage
Consensus Guidelines Published online: January 19, 2016 Consensus Guidelines Update for Gastroduodenal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms G. Delle Fave a D. O Toole b A. Sundin c B. Taal d P. Ferolla e J.K. Ramage
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
 British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Br J Clin Pharmacol (2016) 1 CLINICAL TRIALS Netazepide, a gastrin/cholecystokinin-2 receptor antagonist, can eradicate gastric neuroendocrine tumours in patients
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology Br J Clin Pharmacol (2016) 1 CLINICAL TRIALS Netazepide, a gastrin/cholecystokinin-2 receptor antagonist, can eradicate gastric neuroendocrine tumours in patients
Multifocal Gastric Carcinoid Tumor in a Patient with Pernicious Anemia Receiving Lansoprazole
 Digestive Diseases and Sciences, Vol. 50, No. 3 (March 2005), pp. 509 513 ( C 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10620-005-2466-3 CASE REPORT Multifocal Gastric Carcinoid Tumor in a Patient with Pernicious Anemia Receiving
Digestive Diseases and Sciences, Vol. 50, No. 3 (March 2005), pp. 509 513 ( C 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10620-005-2466-3 CASE REPORT Multifocal Gastric Carcinoid Tumor in a Patient with Pernicious Anemia Receiving
IN THE DEVELOPMENT and progression of colorectal
 Digestive Endoscopy 2014; 26 (Suppl. 2): 73 77 doi: 10.1111/den.12276 Treatment strategy of diminutive colorectal polyp
Digestive Endoscopy 2014; 26 (Suppl. 2): 73 77 doi: 10.1111/den.12276 Treatment strategy of diminutive colorectal polyp
Gastric mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma occurring 30 years after a gastroenterostomy
 Case report Gastric mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma occurring 30 years after a gastroenterostomy Mihaela Mădălina Gavrilescu 1,2, Ionuț Huțanu*,1,2, Ana-Maria Mușină 1,2, Mihaela Buna-Arvinte 1,2,
Case report Gastric mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinoma occurring 30 years after a gastroenterostomy Mihaela Mădălina Gavrilescu 1,2, Ionuț Huțanu*,1,2, Ana-Maria Mușină 1,2, Mihaela Buna-Arvinte 1,2,
Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories
 Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Polyps in general: is a descriptive term of forming a mass that is exophytic & polypoid.
 ميحرلا نمحرلا هللا مسب Gastric Tumors: Benign tumours & tumor-like conditions: -Mucosal: Gastric polyps (they are uncommon) -Mesenchymal tumours: Leiomyoma & Lipoma (can occur anywhere in the body) Malignant:
ميحرلا نمحرلا هللا مسب Gastric Tumors: Benign tumours & tumor-like conditions: -Mucosal: Gastric polyps (they are uncommon) -Mesenchymal tumours: Leiomyoma & Lipoma (can occur anywhere in the body) Malignant:
David Lewin MD Medical University of South Carolina
 Top 10 Advances in GI Pathology David Lewin MD Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Overview Top Articles/ presentations in the following areas Imaging (3) Molecular (2) Therapeutics (3)
Top 10 Advances in GI Pathology David Lewin MD Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Overview Top Articles/ presentations in the following areas Imaging (3) Molecular (2) Therapeutics (3)
Diagnosing and monitoring NET
 Diagnosing and monitoring NET Inaccurate or delayed diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors (NET) is common, because many NET are small and asymptomatic. 1 When symptoms are present, they are usually nonspecific
Diagnosing and monitoring NET Inaccurate or delayed diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors (NET) is common, because many NET are small and asymptomatic. 1 When symptoms are present, they are usually nonspecific
Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer
 Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Xiang Hu*, Liang Cao*, Yi Yu. Introduction
 Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal Neoplasms: A Single Center Clinical Experience in China
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
Neuroendocrine tumors of GI and Pancreatobiliary tracts. N. Volkan Adsay, MD
 Neuroendocrine tumors of GI and Pancreatobiliary tracts N. Volkan Adsay, MD New (2017) WHO WHO 2017 (endocrine book; for pancreas) WHO 2017 (endocrine book; for pancreas) PD-NE ca WD-NE Tumor Intended
Neuroendocrine tumors of GI and Pancreatobiliary tracts N. Volkan Adsay, MD New (2017) WHO WHO 2017 (endocrine book; for pancreas) WHO 2017 (endocrine book; for pancreas) PD-NE ca WD-NE Tumor Intended
EUS FNA NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS. A. Ginès Endocopy Unit Hospital Cínic. Barcelona (Spain)
 EUS FNA NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS A. Ginès Endocopy Unit Hospital Cínic. Barcelona (Spain) GI NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS GENERAL CONCEPTS Rare neoplasms arising from the neuroendocrine cells of the GI tract Include:
EUS FNA NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS A. Ginès Endocopy Unit Hospital Cínic. Barcelona (Spain) GI NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS GENERAL CONCEPTS Rare neoplasms arising from the neuroendocrine cells of the GI tract Include:
ESMO Preceptorship Gastrointestinal Tumours Valencia October 2017
 www.esmo.org ESMO Preceptorship Valencia 06-07 October 2017 Gastrointestinal Tumours I have no conflicts of interest to declare Fátima Carneiro Gastrointestinal tumours Multidisciplinary management, standards
www.esmo.org ESMO Preceptorship Valencia 06-07 October 2017 Gastrointestinal Tumours I have no conflicts of interest to declare Fátima Carneiro Gastrointestinal tumours Multidisciplinary management, standards
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum
 2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
2012 66 4 351 356 Serotonin- and Somatostatin-Positive Goblet Cell Carcinoid of the Duodenum a b* c c c a a b d a c b d 352 Ohara et al. received remedies at another hospital. Hematemesis then recurred
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
