FieldStrength. MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis at Aachen
|
|
|
- Shon McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis at Aachen Montreal MR-OR suite enables intraoperative brain MRI MultiTransmit helps expand the role of MRI in MSK oncology at Leuven Vanderbilt runs dedicated breast MR scanner MultiTransmit propels Erasme to scan all body patients at 3.0T
2 For image-guided biopsies, I believe MR is the best modality to help target the biopsy. I actually see the lesions in the prostate, so I exactly know where I want to position the needle. Felix Schoth, MD, see pages 6-8 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright holder. Philips Medical Systems Nederland B.V. reserves the right to make changes in specifications or to discontinue any product, at any time, without notice or obligation, and will not be liable for any consequences resulting from the use of this publication. Printed in Belgium FieldStrength is also available via the Internet: Editor-in-chief Karen Janssen Editorial team Annemarie Blotwijk, Andre van Est, Paul Folkers (PhD), Liesbeth Geerts (PhD), Diana Hoogenraad, Karen Janssen, Stephen Mitchell, Claus Schaffrath (MD), Marc Van Cauteren (PhD), Jacintha Weezenberg. Contributors Lori Bickford, Lynne Bishop, Ian Crick, PJ Early, Jean-Pierre Farmer (MD), Troy Havens, John G. Huff (MD), Shahid Hussain (MD, PhD), Karen Janssen, Dag Clement Johannessen (MD), Philippe Kindynis (MD), Celso Matos (MD), Yvonne Mekes, Steven Pans (MD), Georgia Papaioannou (MD, PhD), John Penatzer, Thomas Perkins (PhD), Stefanie Remmele (PhD), Felix Schoth (MD), Line Storetvedt, Jeroen Stout, Stefan Sunaert (MD, PhD), Pat Venters, Martin Weibrecht (PhD). Subscriptions Please register on Correspondence FieldStrength@philips.com or FieldStrength, Philips Healthcare, Building QR 0119 P.O. Box , 5680 DA Best, The Netherlands Notice FieldStrength is published three times per year for users of Philips MRI systems. FieldStrength is a professional magazine for users of Philips medical equipment. It provides the healthcare community with results of scientific studies performed by colleagues. Some articles in this magazine may describe research conducted outside the USA on equipment not yet available for commercial distribution in the USA. Some products referenced may not be licensed for sale in Canada.
3 In this issue NetForum Visit the NetForum User Community for downloading ExamCards and viewing application tips, clinical cases, extended versions of FieldStrength articles, and more. Editorial by Pat Venters, Vice President, Oncology Care Cycle Reports from our users MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis Dr. Schoth sees MR-guided prostate biopsy enables fewer core biopsies at Aachen University Hospital. MR-OR suite enables intraoperative brain MRI Dr. Farmer, The Montreal Children s Hospital uses MRI to check completeness of tumor resection during surgery. MultiTransmit propels Erasme to scan all body patients at 3.0T Dr. Matos benefits from high image quality and consistency provided by MultiTransmit for diagnosis and follow-up in oncology patients. Vanderbilt runs dedicated breast MR scanner Dr Huff, Vanderbilt Breast Center, sees advantages of MammoTrak with Achieva for providing comprehensive services to patients. MultiTransmit helps to expand the role of MRI in MSK oncology at Leuven Achieva 3.0T TX is rapidly becoming the default system for all MSK oncology exams according to Dr. Pans. Panorama HFO ideal for fetal and pediatric scans Dr. Papaioannou says Mitera utilizes High Field Open for all MR scans from fetal to adult. Research Philips developing investigational PET/MRI system With the Philips GEMINI TF PET MR patients can undergo PET and MRI during the same procedure which optimizes image fusion. Panorama HFO system aids in radiotherapy planning Ullevål University Hospital initiates Panorama HFO RT system for MR-aided radiotherapy treatment planning. MR used in tumor vascularity research Stefanie Remmele, PhD, and her colleagues have been developing techniques to characterize the microvascular structure of tumors. Clinical Case report High reproducibility makes SmartExam a useful tool in oncology imaging MR News MR in the Oncology Care Cycle New features of NetForum online community Achieva 3.0T TX becomes Europe s first 3.0T mobile MRI mdixon is being developed to simplify and accelerate liver MRI Application tips Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging Calendars Education calendar / Events calendar FieldStrength 3
4 The Oncology Care Cycle Imaging Diagnosis Image-guided intervention Cardiology Oncology Women s Healthcare Diagnosis Outside the Hospital (home, EMS, etc.) Intervention Clinical Decision Support Monitoring Maintenance Patient active pathways Clinical algorithms Monitoring Information transfer Care cycle thinking is integrating Philips strategy and yielding new solutions, new capabilities, and opportunities for new revenue streams. In oncology, that may mean that even if a particular cancer cannot be cured, we can harness the power of the chronic disease model by offering solutions that focus on providing a high quality of living with the disease. To that end, we aim to introduce innovations designed to reduce the debilitating side effects of certain treatments. Based on a deep understanding of insights from clinicians, administrators and patients, we focus on accuracy in diagnostics and therapy, helping the physician to find the cancer sooner, to determine the right treatment regime and to help the patient live longer. One special focus is to provide emerging markets with early detection, diagnostics and therapy solutions that improve access, reduce cost and meet cultural needs. 4 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
5 Our commitment to the care cycle approach continues to drive a deep understanding of medical conditions and how treatment is evolving. We use that understanding to guide prioritization of investments and resources. In addition, we continue to experiment with different business models to maximize our collective ability to capitalize on the opportunity and maintain a sustainable differentiation in the market. The role of MR in the Oncology Care Cycle MRI began to be used clinically in the early eighties as a promising technique because of its excellent soft tissue contrast. Since then, continuous hardware and software developments have helped improve image quality and speed, and expand MR application areas. The role of MRI has evolved from purely diagnostic imaging into a broader role. In the breast cancer care cycle, for example, the MR Elite Breast solution is used in diagnostic imaging, in pre-surgical imaging to look for additional lesions in the affected breast and the contralateral breast, in monitoring and in surveillance after treatment. MRI guidance is used increasingly during breast and prostate biopsy, enabled by Philips Elite Breast and Elite Prostate Clinical solutions. With dedicated software, coils and peripherals, these solutions enable faster, more targeted biopsy procedures. In neuro oncology, pre-surgical fmri (functional MRI) helps locate language areas so neurosurgeons can plan to avoid them during surgery. MRI is even performed intra-operatively during neurosurgery procedures. Throughout the care cycle, Ambient Experience increases the physical and emotional comfort of the patient. This environment can reduce the need for retakes, which lowers cost and improves workflow and clinical results. Dear Friends, It s a pleasure to introduce this issue of FieldStrength, focusing on the role of MR in oncology. The Philips comprehensive care cycle approach has guided Philips strategic thinking in oncology, cardiology and women s healthcare over the past several years. This holistic disease based approach is focused on specific medical conditions, technology independent, and grounded in the needs of multiple stakeholders. The approach extends across multiple care settings and includes transition hand-offs, which can be very complex. We believe this approach yields better solutions, and contributes to lower cost, reduced morbidity and saves lives. Prostate cancer is an area of focus for Philips. Urologists and their patients are sometimes faced with the dilemma of rising PSA levels and negative biopsies. This can lead to uncertainty and anxiety for patients and a series of repeated, inconclusive biopsies. Philips has developed a solution that enables a faster, more targeted MR-guided biopsy procedure. For selected patients, MR imaging, complemented by MR-guided prostate biopsy, can be a valuable alternative, augmenting other imaging tools such as ultrasound. This issue of FieldStrength highlights University Hospital Aachen, performing prostate biopsies, with excellent visualization and targeted needle positioning. Additional MR developments featured are MultiTransmit and SmartExam, enhancing the quality and efficiency of MR imaging in oncology patients. Panorama HFO is also being used in innovative ways, including pediatric and fetal oncology imaging and radiation therapy planning. In addition, Achieva 3.0T is part of an intra-operative MR neurosurgery suite, and finally, the breast MR solution with MammoTrak offers excellent diagnostic imaging and an efficient biopsy process. I m confident you will enjoy reading about these exciting developments and much more! Pat Venters Vice President, Oncology Care Cycle, Philips Healthcare
6 MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis MR-guided prostate biopsy enables fewer core biopsies at RWTH Aachen University Hospital With the advent of MR guidance, prostate biopsy is easier for both patients and physicians. At RWTH Aachen University Hospital (Aachen, Germany), clinicians are performing their first prostate biopsies using the Achieva 3.0T with DynaTRIM prostate biopsy device and DynaCAD prostate biopsy software. Initial results are extremely encouraging. Some time before the biopsy we perform a high resolution diagnostic exam to identify potential lesions, says Felix Schoth, MD, Department of Diagnostic Radiology at RWTH. We use our Achieva 3.0T scanner, along with the SENSE Torso coil and the 3.0T endorectal coil for diagnostic imaging. Felix Schoth, MD For the biopsy procedure the patient lies prone with the DynaTRIM biopsy device and appropriate receive coil in place. DynaTRIM is a fully MR-compatible device for trans-rectal MR biopsy of the prostate. Dr. Schoth performs an anatomical T2 TSE scan and overlays it onto the diagnostic scans acquired previously. Then he identifies the regions of interest in the anatomical scan that he selected from the diagnostic scan. RWTH Aachen University Hospital After a calibration scan we adjust the DynaTRIM device if necessary, and then perform a control scan, which shows us whether we correctly moved the shaft, now pointing toward the region we want to biopsy, explains Dr. Schoth. The DynaCAD biopsy planning software also helps us decide which needle to use, and whether to use a spacer to ensure the correct distance from the shaft to the region we want to target. It s all quite easy to use and intuitive. He punctures up to three regions of the prostate, and usually takes two cores at each location. When moving to the next puncture site he repeats the control scan. I exactly know where I want to position the needle. 6 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
7 Diagnostic exam T2-weighted axial T2-weighted coronal Diagnostic MRI data analysis With MR guidance, especially with a diagnostic scan before, you can better target the lesions. MR-guided biopsy procedure MR-guided biopsy shows Gleason 3+4 T2-weighted axial 73-year-old male with PSA level rising for 5 years, even after short drop following Finasterid therapy. Previous TRUS biopsies were negative. Diagnostic MR images were made with the Endorectal and SENSE Cardiac coil. Images show a suspicious T2-hypointense area in the right apical peripheral zone of the prostate. Biopsy planning screen The biopsy procedure again starts with an anatomic scan to visualize the right apical lesion (marked in image). The biopsy planning screen provides the settings for the biopsy device and the pre-calculated position of the biopsy needle overlaid on the anatomical scans. A Gleason score 3+4 prostate carcinoma was diagnosed from this biopsy. Findings from other biopsied lesions were negative for cancer, some showed prostatitis. In the follow-up, histology of pelvic lymphadenectomy revealed lymph node involvement despite negative abdominal CT. The proposed treatment was external beam radiation therapy. FieldStrength 7
8 After three more negative TRUS biopsies, he was referred to me. With MR guided biopsy we were able to demonstrate the carcinoma. The Achieva 3.0T at University Hospital Aachen is used for prostate biopsy MR helps better visualize regions of interest Dr. Schoth says that MR is superior to ultrasound for visualizing the region of interest and the lesions. For image-guided biopsies, I believe MR is the best modality for overlaying the anatomic scans on the diagnostic scans, to help define the region for the puncture, says Dr. Schoth. I actually see the lesions and suspicious areas in the prostate, so I exactly know where I want to position the needle. With ultrasound, you can collect any number of punctures, but still have a substantial chance that you won t hit the lesion (if it is small), as you re doing it more or less blind. With MR guidance, especially with a diagnostic scan before, you can better target the lesions, he adds. You need fewer core biopsies, so there is a lower risk of complications. You re doing it the intelligent way. First results demonstrate MR benefits One of the first patients who underwent an MR-guided prostate biopsy at RWTH had recurrent negative biopsies and a very high PSA of about 20 for several years. Dr. Schoth explains: In 2006 he had a PSA level of 12.5 and he received an ultrasound-guided biopsy, where it was found that he had an adenomyomatosis and atrophy, and discrete chronic interstitial prostatitis, but they found no carcinoma. After receiving treatment with an anti-androgen medication, his PSA went down to 3.6 but then went up again. His PSA at one point was up to After three more negative biopsies, he was referred to me. Dr. Schoth selected three regions of interest to biopsy with MR guidance, and one proved to indeed have carcinoma. We were able to demonstrate a Gleason score of 7, sampled from a region in the transition zone. Most cancers don t develop there, but in the peripheral zone; even with MR, it is more challenging to image a lesion in the transition zone. Nevertheless, with the histology at hand, a diagnosis was reached and the patient was able to get appropriate treatment. MR-guided prostate biopsy routine in future I think MR-guided prostate biopsy will become widespread for patients who received a number of negative ultrasound guided biopsies, and still have elevated PSA levels, says Dr. Schoth. It could certainly lead to a better workup for the patient. He also envisions a probability map of sorts. Diffusion-weighted imaging is becoming more and more commonly used, and I think we could pull together information from the dynamic scans, the T2 image scans and the DWI scans, and form a probability map for carcinoma. It would be very helpful. 8 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
9 MR-OR suite enables intraoperative brain MRI The Montreal Children s Hospital uses MRI to check completeness of tumor resection during surgery During brain tumor resection it is often difficult to see whether the entire tumor has been removed. Therefore, the neurosurgical MR-OR Suite at The Montreal Children s Hospital includes an Achieva 3.0T scanner prepared for intraoperative MR imaging. Montreal physicians have performed surgery with MR guidance on more than 30 patients, mainly tumor or epilepsy cases, since its installation in late Jean-Pierre Farmer, MD Whether it s for epilepsy or brain tumors, the extent of resection is very important to the patient s outcome, says Jean-Pierre Farmer, MD, Neurosurgeon and Surgeon-in-Chief at The Montreal Children s Hospital of The McGill University Health Centre, and Head of the Department of Pediatric Surgery at McGill University Health Centre. Without imaging during surgery it can be necessary to stop resecting before the whole tumor is removed to reduce the chance of damaging vital areas. We wanted to be able to perform MR imaging during neurosurgery to better assess the extent of resection in children during neurosurgery. This two-fold advantage extensive resection and preserving function is the biggest advantage of the suite, says Dr. Farmer. There are cases where it s crucial that the resection will be as complete as possible. It can spare a child from having to face a second surgery. Whether it s for epilepsy or brain tumors, the extent of resection is very important to the patient s outcome. Floor plan of the MR-OR suite FieldStrength 9
10 For Emilie, the intraoperative MRI had a very big impact. Pre-op Intra-op Post-op MR guidance during neurosurgery Images of a patient with dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNET) and seizures. Note unsuspected deep residual disease on the intraoperative scan and contrast with the post-op scan showing complete resection. On top: MR views used for surgical navigation during neurosurgery procedures. 10 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
11 Impression of the MR-OR suite s two-room concept with the Achieva 3.0T on the left With ultrasound, it looked like a complete resection, but MR still showed deeper roots of the tumor that seemed safe to remove. Advanced equipment enables advanced surgeries The hospital chose a two-room solution, so the MR system is also accessible to patients for diagnostic imaging. In this way, the Achieva 3.0T also helps reduce MRI waiting lists. In addition to the Achieva 3.0T MRI in the scanner room, the OR has a surgical microscope that accepts the BrainLab navigational program. MR images are transposed onto the program, enabling the accurate navigation within the brain during surgery. If a patient underwent an fmri or tractography study, those images can also be overlaid on the navigational scan. We re coupling a navigational scan with the full detailed study we did previously for seeing best detail, says Dr. Farmer. This helps us to extensively resect in specific areas, and also preserve adjacent eloquent areas for the patient s quality of life. For intraoperative MRI a special coil is used, which has two separate halves and is sterilizable for surgical use. First patient a success story The child who cut the ribbon at the opening of the MR-OR suite was Dr. Farmer s first patient, Emilie. She had a low-grade tumor that was causing epilepsy. Because it was low grade and very close to the structure of the brain, it looked very similar to grey matter of the brain during surgery. With ultrasound, it looked like I had a complete resection, but then I took her for an MR scan. To my surprise there were still deeper roots of the tumor and, based on the fiber tracking that we had done previously, they seemed to be safe to remove. Dr. Farmer brought her back to the OR. Because they had only provisionally closed the membrane and the skin, it took no time to re-drape and get to the tumor. We knew exactly where the residual fragment was. We removed the residual fragment and did another MRI to be sure we had removed all we wanted to. So she probably has no residual tumor at all, and her chance of having been cured of the epilepsy is over 90 percent. Time will tell, but it looks very good. For Emilie, the intraoperative MRI had a very big impact. Beyond pediatrics Cases such as Emilie s could become more common in the near future, also for adults. This setup can be used for all types of neurosurgery, says Dr. Farmer. We are looking at other applications as well, particularly skull-base surgery and orthopedic applications. In these cases it s very important that the resection is complete. FieldStrength 11
12 3.0T MultiTransmit propels Erasme to scan all body patients at 3.0T Clinicians at Erasme Hospital Brussels benefit from high image quality and high consistency provided by MultiTransmit for diagnosis and follow-up in oncology patients Since Erasme Hospital received the MultiTransmit upgrade for its Achieva 3.0T system it has seen spectacular results, particularly in abdominal work. Patientadaptive MultiTransmit technology employs multiple, independent RF sources to nullify dielectric shading at its origin. The power, amplitude, phase and waveform of the RF sources automatically adjust to each patient s unique size, shape and relative fat and water quantities to optimize uniformity and consistency. Celso Matos, MD With MultiTransmit, we can scan anyone on our 3.0T system. Erasme Hospital (Cliniques Universitaires de Bruxelles, Hôpital Erasme, ULB, Brussels, Belgium) uses four Philips systems Achieva 3.0T with MultiTransmit, Achieva 1.5T and two Intera 1.5T to perform 1,200 to 1,500 exams each month, including spinal exams done by neuroradiologists. Although the hospital installed its Achieva 3.0T system in 2005 and the field of view is smaller than in newer models, it could readily be upgraded to MultiTransmit. Since the upgrade in late 2009, more than 300 patients have been scanned on the Achieva 3.0T with MultiTransmit. Time savings and improved image quality with MultiTransmit Radiologist Celso Matos, MD, utilizes the Achieva 3.0T with MultiTransmit and the 16-channel SENSE XL Torso coil on average two days a week for abdomen and pelvis scanning. MultiTransmit consistently enhances image and contrast uniformity and improves reproducibility in all clinical sequences, he says. In addition, it allows us to scan faster or with higher resolution, which is specifically an advantage in breath hold T1-weighted sequences. Dual echo (in- and out-of-phase) T1-weighted scans can now be acquired during a single breath hold. T2-weighted TSE can be acquired faster with less blurring, and refocusing control can be avoided, thus increasing the T2 contrast. Coronal views consistently have better signal uniformity, which allows us to explore larger FOVs. MultiTransmit makes our choices easier and more flexible; the examination can be tailored to the specific patient problem. 12 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
13 With MultiTransmit all body scanning may be done at 3.0T Along with Thierry Metens, PhD, Dr. Matos has achieved the greatest results with MultiTransmit in his abdomen exams. We are obtaining excellent abdominal examinations (liver, pancreas and kidneys). Decompensated cirrhotic patients with ascites, and patients with severe acute pancreatitis and large fluid collections can now be scanned with consistent image quality. Dr. Matos says that before MultiTransmit he used to pre-select patients for 3.0T abdominal and pelvic examinations. Especially in liver examinations, we often saw a significant drop in signal intensity in the left liver lobe due to dielectric shading; some regions in the middle of the FOV were quite dark. Patients with cirrhosis and ascites and a lot of fluid in the peritoneum were scanned on our 1.5T system to avoid such problems. Now, with MultiTransmit, we can scan anyone on our 3.0T system. In addition, MultiTransmit s patient adaptive technology reduces local SAR, which in turn shortens scan time by up to 40 percent. So, T2-weighted imaging can be done much faster because the repetition time is significantly reduced. Because of this TR reduction, our pelvis examinations are done significantly faster. Specifically for the high resolution TSE T2-weighted (acquisition voxel size 0.6 x 0.6 x 3 mm), the TR decreases from 6680 ms to 4230 ms, and the examination time goes from 9:47 to 6:12 minutes, while the detailed survey is nowadays performed in 35 seconds, says Dr. Matos. For other anatomic regions we prefer to use MultiTransmit s benefits to scan with higher resolution. We can do better T1-weighted imaging, particularly double-echo T1, which was not possible before. Now we can do that during a single breath hold. Oncology MRI benefits from MultiTransmit Body MRI scanning at Erasme Hospital involves oncology patients. Because of the excellent performance of MultiTransmit the hospital can now use the 3.0T system for all of its oncology patients, not just a selected group, says Dr. Matos. The higher signal at 3.0T is a large advantage in our oncology work, but without MultiTransmit we would not have been able to use our 3.0T system for every case. T2W TSE We can do better T1-weighted imaging, and specifically 3D e-thrive with higher spatial resolution. Chronic obstructive pancreatitis A 44-year-old male addressed for acute abdominal pain and weight loss. He has a history of pulmonary embolism and ongoing anticoagulant therapy. The axial and coronal single-shot respiratory triggered T2-weighted TSE sections show homogeneous signal intensity all over the field-of-view. We noticed the presence of ascites (short arrows in axial) and of a collection with a fluid-fluid level in the duodenal wall (long arrow in axial, asterisk in coronal) related to duodenal hematoma. The pancreatic duct is enlarged and obstructed by a stone (short arrow in coronal). Diagnosis was chronic obstructive pancreatitis and duodenal hematoma. The SENSE Torso XL coil was used. Voxel size 1.2 x 1.6 x 4 mm. MultiTransmit provides high quality diagnostic images in the presence of abdominal collections and ascites in this severely ill patient. FieldStrength 13
14 T2W TSE Delayed e-thrive DWI low b-value Delayed e-thrive Multiple Focal Nodular Hyperplasia A 43-year-old female with abdominal pain and abnormal liver function tests underwent MRI. Axial TSE T2- weighted section through the dome of the liver shows a focal lesion slighty hyperintense to adjacent normal liver tissue (arrow). Contrast between the lesion and the adjacent liver is enhanced at low b-value DWI. Delayed contrast enhanced axial and coronal e-thrive sections show three lesions (in coronal) enhanced relative to adjacent liver which is related to the presence of functional normal hepatocytes in the lesion, characteristic of focal nodular hyperplasia. The low b-value DWI better depicts focal liver lesions than the T2-weighted TSE images. High resolution e-thrive along with liver specific contrast agents produces superb morphologic and functional information facilitating characterization. The SENSE Torso XL coil was used. I ve seen, for instance, that for small lesions within the liver 3.0T MultiTransmit is much better. MultiTransmit is enabling high quality, high resolution imaging that allows us more confidence in diagnosis, follow-up and monitoring. In oncology patients Dr. Matos is now also performing high resolution diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) of the prostate, liver and pancreas. The images are quite impressive. MultiTransmit consistently improves contrast and resolution in all clinical sequences, including DWI. The fat suppression uniformity is improved in those anatomical locations more sensitive to dielectric shading, such as the left liver lobe. Also the reproducibility of apparent diffusion coefficients (ADC) is better, he says. This will certainly have an impact on the follow-up with our oncology patients. We are now doing some studies comparing the signal-to-noise ratio in DWI with and without MultiTransmit, he adds, We know it has improved, but we want to quantify it. Erasme Hospital Brussels 14 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
15 T2W TSE MultiTransmit consistently enhances image and contrast uniformity and improves reproducibility in all clinical sequences. DWI b=150 DWI b=1000 ADC map Delayed e-thrive Focal Nodular Hyperplasia 63-year-old female with history of breast cancer underwent MRI after a focal liver lesion was previously detected with liver US. T2-weighted TSE shows a focal liver lesion located in segment 4, hyperintense to adjacent normal liver tissue (arrow). DWI shows restricted diffusion. The ADC map shows higher ADC of the lesion compared to normal liver. On delayed coronal THRIVE the lesion enhances relative to adjacent liver, which is related to the presence of functional normal hepatocytes. Combining DWI and contrast-enhanced MRI with liver-specific contrast agents potentially improves the specificity of MRI. The SENSE Torso XL coil was used. FieldStrength 15
16 With MultiTransmit our choices are easier and more flexible; the examination can be tailored to the specific patient problem. Future is now wide open for 3.0T imaging MultiTransmit opens the field for more body applications at 3.0T, says Dr. Matos. It will certainly expand whole body applications like 3.0T whole body DWI in oncology patients, and it will allow us to scan more patients. It s particularly useful for the brain, for MSK and abdomen, with much better image quality and improved signal. The 3.0T imaging we re doing now wouldn t be possible without MultiTransmit, he adds. The image quality was previously less reproducible, and not this consistent from one patient to another. I think that 3.0T with MultiTransmit has the potential to become a new standard for MR examinations. T2W TSE 3D multivoxel spectroscopy T2W TSE Rectal cancer and prostate cancer A 77-year-old male underwent MRI to help staging of a neoplasm of the rectum. Axial respiratory triggered T2-weighted TSE shows a rectal neoplasm with anterior wall disruption. The prostate presents heterogeneous morphology in the central zone without clear delineation of a mass. The ADC map shows the rectal lesion and a right side central zone prostate lesion with significantly decreased ADC related to neoplasm (arrows). Spectroscopy of the prostate tissue shows an elevated choline peak and reduced citrate in the area of restricted diffusion within the central zone. Combining DWI and 3D spectroscopy visualizes the prostate lesion in the central zone better than just using T2-weighted sequences. The SENSE Torso XL coil was used. 16 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
17 Vanderbilt runs dedicated breast MR scanner Vanderbilt Breast Center sees advantages of MammoTrak with Achieva for conveniently providing comprehensive services to patients The Vanderbilt Breast Center (Nashville, Tennessee, USA) was established in 1991 in response to a growing need for comprehensive, multidisciplinary breast services. The breast center moved to a new, expanded location in Spring 2009 and now provides clinical and imaging services under one roof, including MRI. John Huff, MD, served as Chief of Breast Imaging at Baptist Hospital (Nashville, Tennessee, USA) and Imaging Director of the Baptist Comprehensive Breast Care Center from 1992 until July 2007, when he joined the Vanderbilt Breast Clinic. Dr. Huff has a special interest in breast MRI and oversaw the development of Specialty MRI, Middle Tennessee s first dedicated breast MRI facility where he served as Medical Director from 2005 to John G. Huff, MD is Associate Professor of Radiology and Imaging Director at Vanderbilt Breast Center. The dedicated MR scanner in the breast center enables us to provide a higher level of personal service to our patients, with greater scheduling flexibility, he says. It allows us to serve out-of-town patients in one location, and we are able to have technologists specialized in breast imaging. Oncology is primary indication Dr. Huff says the Center scans up to 60 patients a month with Achieva 1.5T XR, from referrals including its own clinical services, Vanderbilt primary care providers, and other centers in the area. Our two MRI technologists perform everything from helping the patient undress and starting IV s to scanning and discharging, in 1:30-hour time slots. Putting patients into the magnet feet first is a plus. It allows us to scan patients who would simply not have fit in the bore head first. The Center s main indication for breast MR, about 60 percent, is for patients with a new diagnosis of breast cancer, defining the extent of ipsilateral disease and assessing for contralateral disease. About 15 percent of the volume comes from imaging women who are referred because of their high risk for breast cancer. We also assess implant integrity and determine response to neoadjuvant therapy, Dr. Huff notes. Other indications include positive surgical margins when pre-operative MRI was not performed, scar versus recurrence in patients who have undergone breast conservation, and interval follow-ups of probably benign MRI findings. MammoTrak benefits patients and performance The MammoTrak dockable patient support system with its integrated 7-channel and 16-channel coils is a great improvement over previous configurations, says Dr. Huff. Putting patients into FieldStrength 17
18 T2 SPAIR T1W FFE T1W TSE e-thrive Known left breast malignancy 57-year-old female with recent histologic diagnosis of malignancy in upper outer quadrant of posterior left breast. She presented for an MRI study for determination of extent of disease on the ipsilateral side and possible contralateral involvement. There is heterogeneously dense breast tissue and a strong family history including a brother with a diagnosis of breast cancer. The recently biopsied malignancy in the left breast is well demonstrated, with adjacent marking clip. A small focus in the retroareolar right breast is noted, follow up is recommended. T2 SPAIR T1W FFE T1W TSE e-thrive Right breast mass 36-year-old female with new diagnosis of breast cancer and extremely dense breast tissue presents for evaluation of the extent of disease and evaluation of the contralateral breast. She has not had radiation or chemotherapy yet. A large lobulated mass is seen in the superior lateral right breast corresponding to the known malignancy. No obvious chest wall involvement is seen. Enlarged and morphologically suspicious right axillary lymph nodes are seen. No abnormalities seen in the left breast. 18 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
19 T2 SPAIR T1W FFE T1W TSE e-thrive Patient with reconstructed breast an implants 56-year-old female with bilateral chest wall pain, left greater than right, and intermittent pressure occasionally associated with sensation of left axillary fullness. The patient has a history of extensive multifocal left breast ductal carcinoma in situ. The patient is status post bilateral partial mastectomies 4 years ago with breast reconstruction including tissue expanders and bilateral silicone implants. No suspicious lesions are seen on either side. The silicone implants are well visible in the reconstructed breasts. BI-RADS Category 2. the magnet feet first is a plus. It allows us to scan patients who would simply not have fit in the bore head first. Image quality is excellent and the dockable MammoTrak enables a smooth workflow for biopsy procedures. This Philips solution is really great. The dedicated MR scanner in the breast center enables us to provide a higher level of personal service to our patients, with greater scheduling flexibility. The Center performs one or two breast biopsies a week using the 7-channel coil, which allows biopsy access from a superior or cranial approach in addition to medial and lateral. For diagnostic imaging, the 16-channel coil provides enhanced spatial and temporal resolution for improved visualization of small lesions. Overall, having a dedicated MR system in the breast center is a huge advantage, says Dr. Huff. It s convenient for the patients, and much more private than a hospital MR setting. It facilitates interdisciplinary decision-making and keeps the patient at the center of the management team. We re scanning at 1.5T right now because that s where most of our experience is, and the majority of our clinical needs are met, explains Dr. Huff. But we might consider upgrading to 3.0T in the future. FieldStrength 19
20 MultiTransmit helps expand the role of MRI in MSK oncology at Leuven With faster procedures and reduced artifacts Achieva 3.0T TX is rapidly becoming the default system for all MSK oncology exams and interventions Leuven University Hospital s Radiology Department recently upgraded its Achieva 3.0T to TX performance which includes Philips patient-adaptive MultiTransmit technology embodying parallel RF sources. The boost in performance this upgrade provides has led to a big expansion in the role of MRI in MSK oncology in the department, which now performs all whole body scans and almost all regional scans for bone and soft tissue lesions on its Achieva 3.0T TX. Steven Pans, MD Leuven radiologist Steven Pans, MD, specializes in MSK oncology with a particular interest in MSK interventional procedures including bone-marrow and soft-tissue biopsies. He has long considered MRI to be the preferred modality for MSK oncology because of its excellent soft tissue contrast and its absence of ionizing radiation. The absence of ionizing radiation and the fact that you don t need to use iodized contrast agent makes MRI very interesting for staging and follow up after therapy. Patients certainly feel far more comfortable with it, he says. And its very high sensitivity to bone-marrow pathology compared with CT means that it s an excellent tool for guiding bone-marrow biopsies. For the past four years the department has also been engaged in whole body imaging for which Dr. Pans and his colleagues also prefer to use MRI. This, of course, depends somewhat on the pathology. Sometimes the clinician will prefer a PET or PET/CT exam, but nowadays for multiple myeloma and lymphoma studies and staging of bone metastasis, we are seeing a general changeover from whole body CT to whole body MRI, he observes. Dr. Pans own research interests are also directed towards combining morphological imaging with functional imaging. MR staging benefits from MultiTransmit Since the recent upgrade of the department s Achieva 3.0T system to TX performance, all whole body scans and almost every regional scan for bone marrow and soft tissue lesions are performed on the Achieva with, according to Dr. Pans, very impressive results. One of the major advantages of the new Philips scanner is that we get excellent image quality in whole body scans without the need for any covering coils. Using just the single Integrated Body coil in combination with MultiTransmit, we can perform not only whole body STIR sequences, but also whole body T1 and whole body DWI sequences in the same examination. The combination of these three sequences gives excellent information for staging of suspicious lesions, he explains. We also now find that whereas formerly within an exam time of around 30 to 35 minutes we were only able to perform pre- and post-contrast morphological imaging, the extra time we now gain thanks to MultiTransmit enables us also to perform functional imaging with 4D THRIVE and DWI. Dr. Pans and his colleagues have also noted a significant reduction in artifacts caused by implants. In the past we had some problems with artifacts caused by port-a-caths small chambers or reservoirs implanted under the skin for delivering chemo as well as by titanium braces and screws that may have been inserted into the bones. These were particularly serious with T2 fat saturated sequences, but are now no problem at all. With the TX we get much more homogeneous images than before with better contrast and resolution, he says. 20 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
21 T1 T2 SPAIR Nowadays for many MSK oncology studies, we re seeing a general changeover from whole body CT to whole body MRI. 3 weeks therapy Before therapy T2 SPAIR DWI b1000 ADC 4D THRIVE Perfusion map Ewing sarcoma of ankle T2 SPAIR DWI b1000 ADC 26-year-old male with ankle pain. The intraand extramedullary bone tumor in the distal part of the tibia is hyperintense on the b1000 image. The perfusion map calculated from the 4D THRIVE correlates well with the b1000 image. After 3 weeks chemotherapy, a signal decrease on b1000 and increase of ADC is clearly visible. Performed with 8-channel SENSE Knee coil and patient prone, feet first. MRI helps monitoring response to chemotherapy in adults and children The major cancers the department encounters in its daily work include, in the adult population, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, and all types of benign and malignant bone lesions. One of Dr. Pans particular interests within the department, however, is pediatric imaging especially for lymphoma, bone metastasis, and lesions like Ewing sarcoma and osteosarcoma. Previously we d scan children at the point of diagnosis and just before surgery to have an idea of necrosis or tumor response to chemotherapy. Now on the Achieva 3.0T TX we also perform functional MRI scans at intermediate stages as well to have an idea of how the chemotherapy is progressing. DWI helps for staging and follow-up Almost every patient with bone or soft tissue tumor in their department is scanned with 4D THRIVE and DWI. We re particularly impressed with DWI and WB DWI on the Philips system, he says. Of course, it requires some experience and you need to be careful with T2-shine-through effects when imaging abscesses and imaging hematomas. These entities can cause a hyperintense signal on the diffusion weighted images and they should be best correlated with the perfusion imaging to exclude pseudotumoral lesions or differentiate them from tumoral lesion. But now, having gotten used to it, I think it s an incredibly useful tool. We use it not only for staging and lesion detection but also in follow-up to FieldStrength 21
22 T1 STIR Image fusion for bone metastasis 42-year-old female with breast cancer and pelvic pain. Two bone lesions are seen on the STIR and T1-weighted images. The DWI b1000 image shows a hyperintense signal, which makes the lesion highly suspicious. Image fusion (software on the Philips console) makes it much easier to make out suspicious lesions. SENSE Torso XL coil. DWI b1000 DWI + T1 We re particularly impressed with DWI and WB DWI on the Philips system. have a good idea of tumor relapse, tumor recurrence and tumor response. Normally we use six b values b0, b50, b100, b500, b750 and b1000 to assure a reliable ADC calculation. We prefer to use the calculated ADC value more than the ADC map. What s more, on the Achieva TX, including DWI adds no more than about 3 minutes to the scan, rather than the 10 to 12 minutes extra on a system without MultiTransmit. slice thickness. We also find T1-weighted VISTA sequences very useful, especially in scanning for skip-metastases in patients with Ewing and osteosarcoma. With VISTA you can perform reconstruction in a central coronal or sagittal plane with a 1 to 1.5 mm slice, which is very useful to clinicians as it enables very small skip lesions to be excluded, which can have a big influence on patient outcome. Depending upon indications, Dr. Pans and his colleagues may also combine DWI with perfusion-weighted 4D THRIVE sequences. This adds a total of 3 minutes to the exam but provides a lot of information that can assist the oncologist or surgeon in taking a biopsy from the most viable tumoral parts, or in making a good differential diagnosis, explains Dr. Pans. Depending on the pathology, other sequences may also be included. When scanning for multiple myeloma, for example, we add whole body STIR and whole body T1 scans in the coronal plane with 5 mm Future prospects From his positive experiences with DWI on the Achieva 3.0T TX, Dr. Pans believes these sequences, especially whole body DWI, are likely to play significant roles in MSK oncology imaging in the future. Currently all MSK oncology exams at Leuven include diffusion and perfusion weighted imaging but we re carrying out different studies in our department to determine if, for some tumor types, the perfusion phase could be omitted altogether. Preliminary results appear to confirm that at least for follow up studies on lymphoma, multiple myeloma and Ewing and osteosarcoma, we could indeed rely just on DWI. 22 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
23 With the Achieva 3.0T TX we get much more homogeneous images than before with better contrast and resolution. T1 T1 DWIBS MPR PET Ncl bone scan Bone and liver metastases in breast cancer patient 32-year-old female with breast cancer. PET showed liver metastases and bone metastases on the lumbar spine. Ncl bone scan showed multiple bone metastases in the lumbar spine. Bone metastases in the vertebral bodies of the lumbar spine are visible on T1, STIR and DWIBS images. There is excellent correlation of MR and Ncl bone scans and PET. STIR T1 STIR T1 DWIBS MIP Non-Hodgkin s lymphoma 26-year-old male. Multiple lymphoma bone lesions on the ribs, in the upper arms, pelvis and proximal femur (arrow) are clearly visible on whole body STIR, T1 and DWIBS (3D-MIP reconstruction). FieldStrength 23
24 Panorama HFO ideal for fetal and pediatric scans Mitera utilizes High Field Open for all MR scans in hospital, from fetal to adult Mitera Maternity and General Hospital (Athens, Greece) is home to the largest pediatric unit of any private hospital in Greece. It s also a general hospital with a busy radiology department that uses the Panorama HFO scanner as its sole MR system. The wide range of the 330 pediatric and adult exams performed on Panorama each month include neuro, abdomen, musculoskeletal, angiography, mammography and cardiac. Georgia Papaioannou, MD, PhD Georgia Papaioannou, MD, PhD, Consultant Pediatric Radiologist at Mitera, says the Panorama s biggest advantage is its 360-degree openness. The examinations are quite pleasant for all of our patients, no matter what their age or size. They are provided with a comfortable diagnostic examination with very high image quality. Our anesthetists are also happy when giving medication to our younger patients, because they have room for their equipment, and can still reach the child comfortably. Panorama HFO with AE helped our pregnant patients to feel more comfortable during fetal and maternal scanning. It really makes a difference. Oncology work benefits from high-performance system With image quality comparable to a 1.5T system, Panorama can help detect lesions in all parts of the body. Although oncology work is not the hospital s main focus, Dr. Papaioannou says many of the adult and pediatric cases she sees are oncological in nature. The majority of our adult oncology cases are gynecology cases, such as cervical, endometrial and ovarian lesions and breast lesions. We ve also seen several cases of soft tissue tumors in the extremities and the abdomen. In addition, we ve diagnosed renal cell carcinomas, metastatic and primary tumors of the liver. We deal with pediatric oncology cases as well, both congenital and acquired, she adds. We ve seen CNS gliomas, optic gliomas, benign glioneuronal tumors, rare cases of pineoblastoma and giant cell tumor of the ethmoid cells, hepatic, renal and musculoskeletal tumors. As you can see, our Panorama excels in a wide variety of oncology-related scans with high-quality images on the abdominal area as well. 24 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
25 T2W TSE Post contrast STIR Coronal Post contrast Endometrial cancer stage II 59-year-old post-menopausal female with vaginal bleeding. Endometrial sampling revealed endometrial cancer. MRI of the pelvis was requested to verify operability of the lesion. A solid lesion of abnormal signal intensity and abnormal enhancement was demonstrated at the right anterior part of the uterine body which infiltrates the myometrium, but does not extend to cervix nor does it infiltrate the serosa, in keeping with endometrial Ca stage II (FIGO classification, operable). Findings were confirmed at surgery. The ST Body/Spine M coil was used. High resolution T2W with 4 mm slice thickness was particularly helpful. Our Panorama excels in a wide variety of oncology-related scans. FLAIR Post contrast Post contrast 25-month-old female with pigmented lesions of the skin and strabismus Brain MRI to investigate lesions compatible with neurofibromatosis 1. Images through hypothalamus show areas of bright signal in white matter (UBOs) which enhance post contrast, indicative of infiltrative lesions, and abnormal thickening and enhancement of the posterior part of the optic chiasm in keeping with optic chiasm glioma, which confirms the diagnosis of NF1. A proximal cervical neuroma is also noted at the level of the foramen magnum (right image). MR follow-up is considered essential to evaluate disease progress. Examination performed under sedation (IV administration of propofol). ST SENSE Head coil used. FieldStrength 25
26 T2W 3D T2W VISTA 3D T1W 3-week-old male with seizures Brain US revealed cavum septum agenesis. MRI reveals bilateral schizencephaly with abnormally thickened cortex in keeping with polymicrogyria. Absence of cavum septum is confirmed. Cortical abnormalities as well as peripheral parenchymal lesions are often missed on head US, thus making MRI performance invaluable. Standard neonate protocol was used with ST SENSE Head coil, applying feed and wrap technique. The 3D T2W VISTA images have been very useful in this age group where myelination has not completed yet. Superb images in pediatric and fetal scans Among Mitera s pediatric cases, almost half are neuro scans. We may scan pre-terms or neonates to evaluate neurologic deficits as suggested by their clinical evaluation, or very low birth-weight preterm babies with sonographic and neurologic findings before they go home. We commonly scan children with seizures, headache, visual deficits or hearing loss. The remaining pediatric exams are mainly head and neck, abdominal and musculoskeletal. Since installing the Panorama two and a half years ago, Dr. Papaioannou says Mitera has performed approximately 130 fetal MRI scans, with great results. Usually there is an indication from the obstetric ultrasound; the majority are ventriculomegaly (dilatation of the ventricular system in the brain), where our role is not only to confirm the ultrasound findings but to look for additional anomalies that may alter the prognosis of the fetus. We ve seen several cases of corpus callosum agenesis and anomalies of the posterior fossa. Fetal exams, especially neuro, may become quite demanding, and the Panorama is really ideal for this type of scan with its large opening, which makes the scan a comfortable experience for the mother-to-be and the very good image quality which produces diagnostic results. Panorama shines in special applications In high-end studies such as angiography, enterography, urography, and even cardiac imaging, Panorama s higher field strength is a significant advantage. We perform angiography in adults and children, in cases where we feel it enhances the diagnosis, says Dr. Papaioannou. We don t yet have vast experience in MR angiography, but in the studies we ve performed, we ve been very happy and our tendency is to replace where possible the CTA with MRA; the Panorama works very well for this. Mitera Radiology Department has performed several enterography (MRE) scans to evaluate the small bowel in children and adults with known or investigated inflammatory bowel disease. MRE helps visualize the extent and activity of the disease and its associated complications such as abscesses or fistulas. In MR urography, the Mitera Radiology team uses anatomic sequences, 3D images of the urinary tract and dynamic scans for a complete diagnostic picture of the urinary system, its anatomy, and function. One of Mitera s strong suits is cardiac, and the hospital wanted to assist the cath lab for the benefit of its pediatric patients. To that end, the Mitera Radiology team recently began cardiac MR imaging on their patients. The initial results of cardiac imaging on the Panorama are quite encouraging and rewarding, Dr. Papaioannou says. We hope to continue and even expand this program in the future. Ambient Experience helps enable successful scans Mitera makes good use of Ambient Experience (AE), which projects sound, lights and pictures into the scanner room to help calm and comfort the patient. We have seen that it makes our patients feel more relaxed and calm throughout their scanning experience, says Dr. Papaioannou. We have scanned several claustrophobic patients who had previously tried to be scanned in other systems with no success. We recently scanned a patient with multiple myeloma in her thoracic and lumbar spine, who told me after the scan that it 26 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
27 was a fantastic experience. Listening to the music made her think of nice places she had visited previously, and kept her calm. She was quite happy and optimistic after the scan! Ambient Experience also makes a difference in young children, because they are so relaxed in the Panorama, she says. We also have the MRI kitten scanner for children so they can pretend to scan toys on a small model of a scanner before they enter the room for their own scan. This especially helps children in the borderline ages of five or six. The Panorama s wide patient aperture accommodates larger patients as well, and when combined with AE it encourages very successful scans. We have successfully scanned patients that were very big, and could not fit in a regular scanner, Dr. Papaioannou notes. It has also helped our pregnant patients to feel more comfortable during fetal and maternal scanning. It really makes a difference. Possibilities for future applications Mitera has built a success story on the effectiveness of its fetal and pediatric exams, and several other hospitals around the world are sending staff members for site visits. Our experience with the Panorama HFO has been very satisfying, concludes Dr. Papaioannou. We hope to continue with even more possibilities for other applications in the future. One of these may be a specially designed coil for neonates and infants, similar to the 16-channel pediatric coil applied for Achieva. Additionally, the design of a mirror-system that could be adjusted on the head-coil so as for the patient to be able to watch the AE projections during the scan may improve our applications. T2W 3D T2W VISTA 3D T1W Periventricular cysts in ex-premature neonate Ex-premature low-birth-weight twin female, corrected term age with PVL. History of bilateral grade III IVH and periventricular cysts on head US. 3D T2W VISTA and 3D T1W images delineate accurately the position and size of the periventricular cysts to assist clinical prognosis, target therapy and use as baseline for future studies. The images demonstrate bilateral periventricular porencephalic cysts with corresponding white matter volume loss and dilatation of the trigones bilaterally, worse on the right. Standard neonatal head protocol was used. SSh T2W SSh T2W T1W DWI Fetal corpus callosum agenesis and supratentorial midline cyst Coronal and sagittal SSh T2W images of a 32-week-old gestational age fetus show absence of corpus callosum and additionally presence of a supratentorial midline cyst with content similar to CSF as seen on T1W and DW images. ST Body/Spine M coil was used. SSh T2W is performed on free maternal breathing. FieldStrength 27
28 Clinical Case report High reproducibility makes SmartExam a useful tool in oncology imaging SmartExam is a unique tool that enables standardization of the MRI exam process, from planning to reviewing. It ensures consistent and reproducible MRI results for challenging exams and follow-up studies, independent of scanner, technologist and positioning. This is particularly important in oncology patients for comparing images from initial and follow-up exams, or comparing pre-and post-surgery images. Savings in time and stress for the technologists are an additional benefit of using SmartExam s automated planning. By adding it to ExamCards, one click is enough to perform automatic planning, scanning and processing. SmartExam is available for brain, spine, breast*, shoulder and knee imaging, to provide consistent, high quality images for confident decision making. * SmartExam Breast is only available for Achieva systems. Initial scan after treatment Intera 3.0T, technologist A Follow up 6 months later Achieva 3.0T, technologist B 3 koloms opmaak Glioblastoma multiforme progression 55-year-old male after resection of glioblastoma multiforme and vaccination therapy of recurrent tumor. SmartExam planning allows comparing the exact same slice of two exams performed 6 months apart, on different MR systems, and by different technologists. Same details in both slices (arrows) convincingly show the high reproducibility of SmartExam planning. Green circles indicate a very mild progression of the glioblastoma multiforme. Courtesy of Prof. Stefan Sunaert, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium. Pre operative Post operative Pre/post operative comparison Patient underwent MR exam before and after tumor resection. Even with clear anatomic changes, the reproducibility of SmartExam automatic planning allows good slice-to-slice comparison. Courtesy of Dr. Philippe Kindynis, Clinique Generale-Beaulieu, Geneva, Switzerland. 28 FieldStrength Issue 41 Summer 2010
29 MR news New features of NetForum online community Since recently NetForum has a new look and some new functionality to improve your experience. Some of the new features are mentioned below. Direct access Your preference for the MR, CT or NM community is now stored. Also your preference for the USA or Global site is stored via the Country/Language setting on top of the page. Sharing with peers It s made easy to submit your own content any registered viewer can do this by clicking Submit content on top. Rate the content you re viewing with 1 to 5 in just one click. Update and share your personal profile More ways to find content Sort content by Most recent, Best rated or Most viewed. Search by typing your keyword in the Search box on top of the page. Click on tags in a document to find related content. Clicking on Contributor name works the same. Use the ExamCard index to easily find all available ExamCards. updates of new content Receive updates when new content is published. Activate and set your interests and preferred frequency via My NetForum. Most popular MRI NetForum contributions in first half of ExamCard 1.5T Comprehensive abdomen including MRCP and dynamic liver 2. ExamCard 1.5T Cervical spine mffe 3. Clinical News MRI Textbook - Special price for Philips customers 4. Web Seminar MultiTransmit experiences at University of Vermont 5. Application tip Application tips for prostate imaging - update NetForum Visit the MRI NetForum User Community for downloading ExamCards and viewing application tips, clinical cases, extended versions of FieldStrength articles and more. FieldStrength 29
30 MR news First mobile Achieva 3.0T TX introduced in the UK Mobile MRI unit will provide range of imaging services to centers and hospitals The Philips/Cobalt team toasting the partnership. From left to right: Rob Davies, Philips Regional Manager West and Central UK and Ireland; David Abel Smith, Cobalt Chairman of Trustees; Peter Sharpe, Cobalt Chief Executive Officer; Maarten Barmentlo, Philips VP MRI Systems; Annette Schmidt, Philips MR Business Line UK & Ireland; John Atwill, Philips Managing Director UK & Ireland. Philips Healthcare and leading UK medical charity Cobalt have developed a mobile 3.0T MRI unit to provide a unique mobile MRI service to the National Health Service. Based around the Achieva 3.0T TX, it will be the first mobile 3.0T MRI unit in Europe and the first mobile Achieva 3.0T TX system with MultiTransmit in the world. We are very pleased with this new partnership with Philips. The unit will provide specialist imaging services to Neuro, Oncology and Orthopedic centers, and routine Neuro and MSK imaging to general hospitals, with very high resolution scans in a shorter time than standard 1.5T and 3.0T systems. We ve had a 3.0T system at our imaging center for about three years and although we ve found it extremely beneficial, there have been some limitations with respect to field of view and dielectric shading, says Cobalt CEO Peter Sharpe. That s why we re moving straight to the Achieva 3.0T TX with our new 3.0T mobile unit. The system s greater field of view and excellent image uniformity provided by MultiTransmit technology will allow us to expand the range of patients for whom we can provide 3.0T imaging services. It will enable higher quality images and greater patient throughput up to 40 percent greater with MultiTransmit. 30 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
31 A further benefit of the 3.0T mobile MRI is that it will help advance 3.0T imaging in the UK, reflecting a global trend towards adoption of 3.0T. The time is right to introduce a 3.0T mobile service, said Peter Sharpe. It will enable hospitals to experience 3.0T and allow patients to access facilities not currently available within the NHS. Before Philips introduced the Achieva 3.0T TX s lighter, fourthgeneration 3.0T magnet, with lower-weight magnetic shielding to confine the fringe fields within the unit, weight restrictions on vehicles in the UK precluded a mobile 3.0T system. Joint commitment Although Philips and Cobalt have cooperated closely over many years, the new partnership on the 3.0T mobile system is truly a landmark event, involving shared investment and risk. We are very pleased with this new partnership with Philips, points out Peter Sharpe. We ve had a long and happy association with the company. From our experience, the equipment is outstanding, with the highest levels of innovation and user friendliness. I am also attracted by the company s honesty about their products, their potential and even their limitations. That s an important quality in any partnership. The time is right to introduce a 3.0T mobile service. Third International MR Spectroscopy Workshop September 16-18, 2010, Thailand After two successful events with about 100 participants each in 2008 and 2009, the third International MR Spectroscopy Workshop 2010 will be held in Krabi, Thailand. This workshop is jointly organized by Dr. Jiraporn Laothamatas, MD of the Advanced Diagnostic Imaging and Image-Guided Minimal Invasive Therapy Center (AIMC), Pyathai Hospital and Philips. The course faculty includes speakers from Asia, Dr. Peter Barker from Johns Hopkins University, (Baltimore, Maryland, USA), and Philips clinical scientists. The program includes sessions on spectroscopy at 3.0T and 1.5T, postprocessing, multi-nuclei spectroscopy, clinical MRS applications in CNS, prostate, MSK, breast, liver and pediatric brain. Lectures and interactive case sessions are featured as well, and mini-workshops on workstation postprocessing will be held on the second evening. For more information and registration, please contact nah.lee.tang@philips.com or aimc_team@yahoo.co.th. Note that the number of participants is limited. FieldStrength 31
32 In development mdixon being developed to simplify and accelerate liver MRI The Philips mdixon scan is being designed to create four image types in one breath hold A liver MRI exam typically includes T2-weighted imaging, chemical shift imaging, pre-contrast T1-weighted, and dynamic post-contrast imaging. Currently, three separate scans are required to create these four image datasets. The mdixon sequence is being developed to provide four image types in one breath hold: water and fat images as well as in-phase and opposed-phase images. The mdixon sequence is being developed to provide the same images as the pre-contrast and chemical shift sequences, in only one single scan that fits in a breath hold of about 20 seconds. Because this mdixon scan is designed to be faster, it allows using higher in-plane and through-plane spatial resolution within one breath hold. Shahid Hussain, MD, PhD, University of Nebraska Medical Center, USA and Thomas Perkins, PhD, Senior Clinical Scientist at Philips, are cooperating to optimize the mdixon sequence for liver MRI. Philips mdixon differs from previous Dixon techniques The original Dixon technique requires a time-consuming acquisition of in-phase and opposed-phase gradient echo images. The in-phase and opposed-phase images are then added together to get wateronly images, and subtracted to get fat-only images. These imaging sequences have limited possibilities to simultaneously optimize for spatial resolution, slice thickness, and scan time, and still fit in a single breath hold in the case of liver imaging. The Philips mdixon sequence is based on a unique reconstruction algorithm, offering Schematic comparison of mdixon and standard methods. mdixon produces 4 image types in one breath hold 1 breath hold 3D mdixon in phase image opposed phase image water image fat image Standard method needs 2 breath holds for 3 image types 1 breath hold 2D in/out of phase in phase image opposed phase image 1 breath hold 3D water image water image 32 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
33 mdixon in-phase mdixon opposed phase 2nd and 3rd breath hold 1st breath hold mdixon water mdixon fat mdixon water Arterial mdixon water Delayed mdixon in liver Four different image types are obtained with mdixon in a patient with two liver lesions. The 3D axial 2-point multi-echo FFE mdixon scan was performed in one breath hold using the Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit and the 16-channel SENSE Torso coil. freedom in echo time setting, so that it does allow for optimization of key imaging parameters and still fits in one breath hold. Arbitrary echo times are used to generate reconstructed water-only images, fat-only images, in-phase images and opposed-phase images. Time-consuming fat-suppression RF pulses are not needed, and this gain in speed allows to select better spatial resolution for mdixon than for e-thrive within the same breath hold time. In addition, mdixon performs a special optimization designed to obtain more uniform fat suppression than with e-thrive. On 3.0T systems, a two-point mdixon sequence may be ideal, because at higher field strengths, the frequency difference between fat and water increases, shortening the fat-water amplitude modulation period such that the two acquired mdixon echo times can be short, thus enabling a higher data sampling rate. References 1. S Hussain, T Perkins Preliminary Clinical Experience with a Multiecho 2-Point DIXON (mdixon) Sequence at 3T as an Efficient Alternative for Both the SAR-Intensive Acquired In- And Out-Of-Phase Chemical Shift Imaging as Well as for 3D Fat-Suppressed T1-Weighted Sequences Used for Dynamic Gadolinium-enhanced Imaging Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med, 18:556 (2010) 2. WT Dixon Simple Proton Spectroscopic Imaging Radiology, 153: (1984) 3. H Eggers, B Brendel, G Herigault Comparison of Dixon Methods for Fat Suppression in Single Breath-Hold 3D Gradient-Echo Abdominal MRI Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med., 17:2705 (2009) 4. S Hussain Liver MRI: Correlation with Other Modalities and Histopathology Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg FieldStrength 33
34 Application tips Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging At the Body/Oncology MR Council organized by Philips in August 2009 the needs for a standardized routine protocol for oncology MR imaging were discussed. The group outlined a concise protocol to help in oncology staging. John Penatzer, RT, Philips MR Application Jeroen Stout, Philips MR Application For the abdomen/pelvis area such an examination should be possible within minutes, both at 1.5T and 3.0T. When also the chest needs to be included, 25 minutes exam time was considered acceptable. Apart from the scout and the SENSE reference scan, the ExamCard should include the T1-weighted, T2-weighted fat suppressed, diffusion weighted and post-contrast e-thrive sequences. Basic 1.5T and 3.0T ExamCards were set up with this input and the R2.6.1 versions are shared on NetForum. Below are some tips for optimizing results with these ExamCards. Even taking into consideration the time needed to give breath-hold instructions, the actual time to complete the exam is within minutes at both 1.5T and 3.0T. Parameters in Tips 1-6 below refer to the 1.5T ExamCard. Tip 7 explains where 3.0T is different. 1.5T ExamCard 3.0T ExamCard 34 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
35 Tip 1: Patient positioning Position the SENSE Torso XL coil so that it covers pubic symphysis and includes the complete liver. This should cover the abdomen and pelvis and limit the need for repositioning the coil. Apply the respiratory belt according to instruction in the Application Guides for use with the respiratory triggered scans. Tip 2: Scout scan and reference scan(s) The single shot T2-weighted scout scan provides a fast overview in three planes that can be used in diagnosis and for planning the subsequent scans. It uses 10 mm slices with 2 mm gap, and takes two breath holds of 23 sec. 30 transverse, 10 coronal and 10 sagittal slices are obtained. Tip 3: T1-weighted pre-contrast scan A two station approach is implemented. Planning should be done so that the abdomen is included in the first station and pelvis in the second station. Geolinks are used for consistent positioning of all scans and to aid in the postprocessing of the data. In the 3D T1-TFE scan 60 slices with 2 x 2 x 2.25 mm voxels, overcontiguous are acquired for the abdomen and pelvis, each in a 19 sec. breath hold. Automatic postprocessing of this scan will use MobiView and MPR to reconstruct the coronal images. Abdomen Pelvis Coronal MPR MobiView FieldStrength 35
36 Tip 4: DWIBS with three b-values DWIBS is often very useful to visualize lesions. Many users prefer viewing DWIBS images with an inverse window, as this more closely resembles the images produced by PET. Three different b-values are used. The b0 images resemble T2-weighted fat suppressed imaging. The b1000 provides the strongest contrast. The b100 scan is added because this contrast helps to distinguish blood vessels (dark) from potential lesions (bright). Acquisition of this b-value also allows the user the choice to create maps with either the b0 value and/or b100 as the starting point for ADC calculation. The diffusion weighted scan (DWIBS) is performed with free breathing. Voxel sizes are 3.0 x 3.0 x 7 mm, 35 slices are acquired with no gap. Slab MIPs of the abdomen and pelvis stations are automatically made and then manually stitched with MobiView. DWIBS b=0 DWIBS b=100 DWIBS b=1000 DWIBS b=1000 MobiView (slab MIP) NetForum Visit the MRI NetForum community for downloading ExamCards or for more application tips. 36 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
37 Tip 5: T2-weighted fat suppressed scan A single shot T2-weighted TSE is used with SPAIR fat suppression. Voxel sizes are 1.4 x 1.8 x 7 mm, 30 slices are acquired with 1 mm slice gap. Respiratory triggering is used to acquire one slice per respiration. If navigator is available (Release 2.6 or higher), it can be used as an alternative to the respiratory belt for the upper station. Abdomen Pelvis Tip 6: e-thrive post-contrast scan e-thrive is used for dynamic post-contrast imaging. The 3D T1 TFE scan with fat suppression acquires 2 x 2 x 2.25 mm voxels, 60 overcontiguous slices in two 19 sec. breath holds. Abdomen Pelvis Tip 7: Differences in the 3.0T version of the ExamCard The 3.0T ExamCard has two different reference scans for the two stations. The T1 TFE images have higher resolution: 1.5 x 1.5 x 2 mm, 119 slices in 22 sec. breath holds. The T2-weighted scan has higher in-plane resolution: 1.3 x 1.6 mm. The 3.0T inversion time is longer for DWIBS. e-thrive has higher resolution: 1.5 x 1.5 x 2 mm, 119 slices in 20 sec. breath holds. FieldStrength 37
38 Research Philips developing investigational PET/MR system PET/CT has been used in oncology for nearly 10 years. However, PET/MR may become a viable alternative as MR has some advantages over CT: it does not expose patients to x-ray radiation and it is better at imaging soft tissue. To solve the challenge of avoiding interference of the MRI magnetic field with the PET scanner, Philips has developed a special shielding system for the PET scanner. Dr. Ratib with patient on the table between the MR gantry (left) and the PET gantry in Geneva. The Philips investigational PET/MR combination is called GEMINI TF PET/MR Imaging system. This uses the Achieva 3.0T MRI scanner and the GEMINI TF PET scanner. The PET-MR combination is designed to enable comparison of the metabolic activity visualized by PET and the anatomical images with high soft tissue contrast that MRI provides. MRI Fused PET/MR PET Courtesy University Hospital of Geneva PET/MR combination designed for more consistency between exams In oncology, most patients receive a PET and an MRI scan, but these are usually done at different times, different conditions and different patient positions. This makes it hard to accurately superimpose the images and correlate information from the two imaging technologies. With the Philips GEMINI TF PET/MR patients can be positioned on the examination table and then undergo PET and MRI during the same procedure, which saves time for patients. Performing both exams right after each other provides more consistency in patient positioning and thus helps to produce very good fused images. As metabolic changes often occur when lesions are still too small to be localized, PET scanning could lead to earlier detection of lesions. MRI could then be used to help determine where the lesion is. PET/MR could also be used in monitoring during treatment, to ascertain whether certain drugs decrease tumor size and/or metabolism. The PET/MR system is installed at the University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland which specializes in oncology applications and at the Mount Sinai Medical Center in New York, focused on cardiology. Both sites are key beta partners to drive the clinical validation of a very exciting new technology. 38 FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
39 Research Panorama HFO adds benefits in radiotherapy treatment planning Clinicians at Ullevål University Hospital (Oslo, Norway) are integrating MR into plans The gold standard for radiation treatment planning has always been CT. But now, with Panorama High Field Open and a support kit being developed by Philips, clinicians at Ullevål University Hospital are adding the excellent soft-tissue imaging of MR to RT planning. MR helps better visualize lesion boundaries, making it easier to irradiate the lesion and avoid surrounding tissue. Panorama HFO in RT configuration. The Hospital began using the Panorama HFO in 2007 for RT planning. Since then, more than 900 patients have had the benefits of MR in their treatment plans. Dag Clement Johannessen, MD, oncologist at Ullevål University Hospital uses a combination of MR and CT to help develop RT plans for his prostate patients. MR is better for delineating the prostate, especially the borders with the bladder, the apex and seminal vesicles. We see the structure more clearly with MR, and we use CT for dosimetry. Dose plan prostate, based on CT and MR images. Panorama suited for RT planning So that MR and CT images are aligned when overlaid, Philips developed a laser positioning system that ensures the patient is positioned in the same location in both scans, as well as a flat tabletop for the Panorama. Quality assurance protocols and phantoms are provided for image distortion evaluation and laser alignment. Dedicated software completes the Panorama RT support package. Line Storetvedt, RT, says the Panorama s large patient space is an advantage. We use a lot of materials for patient fixation and it all fits into the Panorama. We also have the capability of moving the isocenter if necessary. Dag Clement Johannessen, MD Line Storetvedt, RT More patients scanned In addition to prostate patients, Ullevål University Hospital is using the setup for treatment planning in bladder, lower rectum and brain patients. The Hospital s diagnostic radiologists use Panorama one day a month, for children and obese or claustrophobic patients who might not be able to be scanned in a cylindrical system. FieldStrength 39
40 Research MR used in tumor vascularity research The quantitative MR project at Philips Research Hamburg works on several approaches involving the use of MRI to investigate ways to quantify tumor vascularization parameters and assess the relation between such parameters and disease development. Stefanie Remmele, PhD The ultimate goal is to provide solutions for noninvasive physiologic measurements that support early detection and staging of diseases, and early assessment of their response to therapy. The MR experiment consists of a diffusion measurement followed by a simultaneous R2 and R2* weighted sequence before and after contrast agent injection. In less than 10 min. it delivers joint information about cellular and vascular tissue properties, i.e. the diffusion constant, the blood volume fraction, and the mean size of vessel radius. Stefanie Remmele, PhD, and her colleagues have been developing MR sequences and postprocessing techniques to characterize the microvascular structure of tumors. The approach quantifies the blood volume and the mean vessel size, which is typically in the order of a few micrometers and thus much smaller than an MR imaging voxel. The hope is that in the future these parameters will help to identify abnormal tissues and could be used for early therapy monitoring and follow-up. There is a particular need for monitoring the effect of antiangiogenic, antivascular drugs, which do not necessarily lead to tumor size regression. It is, however, expected that blood volume and vessel size change within the first hours or days of treatment. The techniques are currently being evaluated in close collaboration with a clinical partner, the University of Münster, Germany. References S. Remmele, J. Ring, J. Sénégas, W. Heindel, W. E. Berdel, C. Bremer, T. Persigehl Simultaneous Blood Volume and Vessel Size Imaging Technique for Localized Therapy Response Detection Proc. ISMRM 17, 2010, #2737 S. Remmele, J. Sénégas, T. Persigehl, C. Bremer, J. Ring Simultaneous vessel size and blood volume measurement in a human tumor outside the brain Proc. ISMRM 18, 2010, # FieldStrength Issue 41 September 2010
41 Receive FieldStrength by Visit to manage your subscription or to preview FieldStrength online. FieldStrength now offers electronic-only subscriptions in an effort to be more environmentally friendly. When a new FieldStrength issue is available, subscribers receive an alert with an overview of the issue s contents and links to the articles online. We encourage existing readers to switch to an subscription, and new readers to register for an subscription. Please consider the environment before printing any document. Blood volume (%) Anatomy Vessel radius (µm) ADC (10-3 mm 2 s -1 ) Blood volume and vessel size measurement results in a human tumor (71-year-old, phleomorphic sarcoma in the left pubic bone). Dedicated postprocessing algorithms based on ΔR2 and ΔR2* relaxometry provide pixelwise estimates (maps) of the blood volume fraction [%], mean vessel radius [μm], and apparent diffusion coefficient [10-3 mm 2 /s]. FieldStrength 41
42 Education calendar 2010 Breast MRI Advanced Breast MRI Workshop Cleveland, OH, USA Date: October 5-7 Two-day course for radiologists, technologists. Participants have basic knowledge of MRI, breast imaging. The course combines lectures and the clinical practice of breast MR. Note that class size for this course is limited. Info: MRI-guided vacuum breast biopsies Bruges, Belgium Date: Nov European Workshop for radiologists with experience in breast imaging. Organized by Dr. Casselman, AZ St. Jan. Info: The Chicago International Breast Course Chicago, IL, USA Date: Sep Oct. 3 Info: Practical breast MRI: case based review Houston, TX, USA Date: October 9-10 Info: Advances in Breast MRI Las Vegas, NV, USA Date: October Info: radiologycme.stanford.edu/dest Musculoskeletal Erasmus Course on Musculoskeletal MRI Leiden, The Netherlands Date: January 24-28, 2011 Info: NetForum Register on NetForum to have free access to online training modules on use of Philips MR scanners and packages, use of coils, use of EWS, MR safety. Cardiac MR Cardiac MR courses at CMR Academy German Heart Institute, Berlin All courses are for cardiologists and radiologists. Some parts will be offered in separate groups. Info: info@cmr-academy.com, Tel Complete course Dates: Oct Dec. 3 and Dec. 3 Jan. 14 Intensive course including hands-on training at the German Heart Institute, and reading and partially quantifying over 250 cases. Compact course Dates: October CMR diagnostics in theory and practice, including performing examinations and case interpretation. CVMRI Practicum: New Techniques and Better Outcomes St. Luke s Episcopal Hospital, Houston, TX, USA Date: October On principles and practical applications of Cardiac MRI. Info: tpratka@sleh.com Tel , Fax: International Cardiac MR course Leeds, England Dates: Oct Deals with theoretical principles and practical applications of Cardiac MRI. Daily practical scanning and postprocessing sessions in small groups. Info: Mgreen@leedscmr.org Erasmus Course on Cardiovascular MRI Leiden, The Netherlands Date: October 8-9 Focuses on clinical applications of cardiac MR. Info: Cardiac MRI Training Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC, USA Date: Three-month fellowship Info: Pamela Wilson Tel Cardiac MR Imaging in Clinical Practice Leeds, England Date: t.b.d. Designed by cardiologists for cardiology trainees and cardiologists. Includes the basics of CMR methodology and its daily applications. Lectures are presented with firmly clinical focus in a case-based format. Info: j.c.beeton@leeds.ac.uk, medmop@leeds.ac.uk Tel Cardiovascular MR training courses and fellowships St. Louis, MO, USA Lecture format (2.5 days) or lecture plus hands-on (4 days). Also offered are hands-on technologist training courses and three-month fellowships. Info: ctrain.wustl.edu, cme@wustl.edu Tel MR Spectroscopy MR Spectroscopy course (1.5T and 3.0T) Zurich, Switzerland Date: summer 2011 Theory sessions and daily practical scanning and post-processing sessions in small groups. Info: education-centre, dmeier@ethz.ch Advanced MR Spectroscopy Cleveland, OH, USA Dates: Sep Oct. 1 MR engineers, research technologists,physicians, and physicists of Philips MR sites, interested in MR spectroscopy. Participants require basic MR scanning experience. Note that class size for this course is limited Info: vicki.milligan@philips.com International MR Spectroscopy Workshop Krabi, Thailand Date: September The program includes spectroscopy at 3.0T and 1.5T, postprocessing, multi-nuclei spectroscopy, clinical MRS applications in CNS, prostate, MSK, breast, liver and pediatric brain. Info: nah.lee.tang@philips.com or aimc_team@yahoo.co.th 42 FieldStrength Issue 41 Summer 2010
43 General MR Essential Guide to Philips in MRI Cheltenham, UK Dates: November Designed for Philips users. Includes 2 days on basics of MR physics and 2 days on advanced concepts. The course can be attended for 2-4 days. Info: philips.mr.training.education@philips.com MRI self-directed visiting fellowship ProScan Education Foundation Cincinnati, OH, USA Date: continuously throughout the year. Info: Visiting_Fellowships-448.html, mrieducation@proscan.com Tel MRI-EDUC MRI in practice Johannesburg, South Africa Date: November Basics of MRI. Designed for Philips users, radiologists and technologists. Info: with forum on mri.spruz.com North American off-site training courses Dates: upon request Info: lori.hawkins@philips.com Tel Fax: MR Basics Cleveland, OH, USA Designed for the novice technologists with little or no previous MR experience. Lectures cover the basic concepts and theory of MRI. This program is entirely didactic and theory based. MR Essentials for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, OH, USA This comprehensive course for technologists covers all basic scanning and system functionality. Lectures cover MRI safety, scan parameters, and pulse sequences. MR Advanced for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, OH, USA Didactic and hands-on course covering advanced applications including advanced scan parameters, pulse sequences, advanced Neuro, Ortho, Body and Breast imaging techniques. Extended MR WorkSpace for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, OH, USA Didactic and hands-on course covering basic system maintenance, EWS functionality, and all MR analysis packages with lectures in Cardiac imaging, fmri and Diffusion Tensor imaging and Fiber Tracking. Cardiac Imaging for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, OH, USA Didactic and hand-on course covering all cardiac views, heart valves, Q-flow, coronary arteries and the postprocessing packages on the EWS. Events calendar 2010 Date Event Location More information Aug 28 Sep 1 European Society of Cardiology ESC Stockholm, Sweden September 9-11 European Society of Head and Neck Radiology ESHNR Vienna, Austria September European Society for Therapuetic Radiology and Oncology ESTRO Barcelona, Spain September Japan Radiological Society Yokohama, Japan September Interventional MRI-Symposium imri Leipzig, Germany radiologie.uniklinikum-leipzig.de/ start/imri/1stannouncement.pdf Sep 30 Oct 2 Japanese Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine JSMRM Tsukuba, Japan October 6-10 American Society of Head and Neck Radiology ASHNR Houston, TX, USA October 6-9 Magnetic Resonance Angiography MRA Club Seoul, South Korea October Journées Françaises de Radiologie JFR Paris, France Oct 31 Nov 4 American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology ASTRO Chicago, IL, USA November American Heart Association AHA Chicago, IL, USA americanheart.org Nov 28 Dec 3 Radiological Society of North America RSNA Chicago, IL, USA FieldStrength 43
44 What inspired our MultiTransmit 3T MRI innovation? No two patients are alike. The Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit automatically adjusts to each patient s unique anatomy. In abdominal imaging, this gives short scan times with high quality image and uniform contrast, even in the most challenging conditions such as patients with ascites. Make diagnoses based on MRI information that is clear, reliable and consistent. It just makes clinical and economic sense for you and your patients. Check out MultiTransmit body imaging results at * Because our innovations are inspired by you
The first MR with IQ. Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam
 The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam Smart Exam reproducibility 2 consistency, and efficiency Philips Intera 1.5T gives you the image quality, patient comfort and range of clinical applications
The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam Smart Exam reproducibility 2 consistency, and efficiency Philips Intera 1.5T gives you the image quality, patient comfort and range of clinical applications
Publication for the Philips MRI Community. New MultiTransmit technology advances 3.0T imaging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 New technology advances 3.0T imaging Tokai University School of Medicine reports significant benefits for image quality and
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 New technology advances 3.0T imaging Tokai University School of Medicine reports significant benefits for image quality and
Large health system benefits from multiple scanners for breast MRI
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 42 DECEMBER 2010 Large health system benefits from multiple scanners for breast MRI Breast MR and MR-guided biopsy are daily practice at WellStar Health
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 42 DECEMBER 2010 Large health system benefits from multiple scanners for breast MRI Breast MR and MR-guided biopsy are daily practice at WellStar Health
Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Fast and easy diagnostic imaging from head to toe
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 50 2014 / 1 Fast and easy diagnostic imaging from head to toe Ingenia 1.5T with dstream provides speed and convenience, IntelliSpace Portal provides flexibility
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 50 2014 / 1 Fast and easy diagnostic imaging from head to toe Ingenia 1.5T with dstream provides speed and convenience, IntelliSpace Portal provides flexibility
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December More patients and high clinical versatility
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 More patients and high clinical versatility Panorama HFO accommodates broader patient group and provides exceptional results
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 More patients and high clinical versatility Panorama HFO accommodates broader patient group and provides exceptional results
FieldStrength. Leuven research is finetuning. whole body staging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 40 May 2010 Leuven research is finetuning 3.0T DWIBS for whole body staging The University Hospital of Leuven is researching 3.0T whole body
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 40 May 2010 Leuven research is finetuning 3.0T DWIBS for whole body staging The University Hospital of Leuven is researching 3.0T whole body
FieldStrength. Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging. SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology. Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
MRI to fit your planning. Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration
 MRI to fit your planning Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration MR Imaging that fits Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration allows radiation oncologists to take full advantage of MRI s excellent
MRI to fit your planning Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration MR Imaging that fits Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration allows radiation oncologists to take full advantage of MRI s excellent
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
An excellent fit to expand the imaging center, Prodiva 1.5T
 An excellent fit to expand the imaging center, Prodiva 1.5T FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - December 2017 www.philips.com/fieldstrength High quality MR imaging combined with a simplified,
An excellent fit to expand the imaging center, Prodiva 1.5T FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - December 2017 www.philips.com/fieldstrength High quality MR imaging combined with a simplified,
Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
FreeWave upgrade enables faster, more powerful imaging
 FreeWave upgrade enables faster, more powerful imaging Western Neurological Associates upgrades Intera 1.5T to Release 2.5 with FreeWave, and sees a significant improvement in image quality and efficiency.
FreeWave upgrade enables faster, more powerful imaging Western Neurological Associates upgrades Intera 1.5T to Release 2.5 with FreeWave, and sees a significant improvement in image quality and efficiency.
Herlev radiation oncology team explains what MRI can bring
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 Herlev radiation oncology team explains what MRI can bring The radiotherapy unit at Herlev University Hospital investigates use of MRI for radiotherapy
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 Herlev radiation oncology team explains what MRI can bring The radiotherapy unit at Herlev University Hospital investigates use of MRI for radiotherapy
Seamless pre-surgical fmri and DTI mapping
 Seamless pre-surgical fmri and DTI mapping Newest release Achieva 3.0T X-series and Eloquence enable efficient, real-time fmri for brain activity mapping in clinical practice at Nebraska Medical Center
Seamless pre-surgical fmri and DTI mapping Newest release Achieva 3.0T X-series and Eloquence enable efficient, real-time fmri for brain activity mapping in clinical practice at Nebraska Medical Center
Ingenia Elition S. 3.0T imaging at your fingertips
 3.0T imaging at your fingertips 3.0T imaging at your fingertips Healthcare is maturing daily setting and adopting new standards in clinical pathways. At the same time, there is a need for high productivity,
3.0T imaging at your fingertips 3.0T imaging at your fingertips Healthcare is maturing daily setting and adopting new standards in clinical pathways. At the same time, there is a need for high productivity,
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR.
 GE Healthcare PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR. MR Radiation Oncology Suite MAXIMIZE YOUR PRECISION. HELP MINIMIZE PATIENT COMPLICATIONS. Our goal in MR radiation oncology is to
GE Healthcare PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR. MR Radiation Oncology Suite MAXIMIZE YOUR PRECISION. HELP MINIMIZE PATIENT COMPLICATIONS. Our goal in MR radiation oncology is to
Optimized. clinical pathway. propels high utilization of PET/MR at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital
 Optimized propels high utilization of PET/MR at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital clinical pathway As one of Europe s largest teaching hospitals, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital is renowned for its innovative research
Optimized propels high utilization of PET/MR at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital clinical pathway As one of Europe s largest teaching hospitals, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital is renowned for its innovative research
FieldStrength. Multi-parametric 3.0T MRI provides excellent prostate imaging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 35 September / October 2008 Multi-parametric 3.0T MRI provides excellent prostate imaging Three different centers show that advances in imaging
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 35 September / October 2008 Multi-parametric 3.0T MRI provides excellent prostate imaging Three different centers show that advances in imaging
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Expanding therapy options for
 MR systems Sonalleve MR-HIFU Expanding therapy options for women s health and oncology 2 Discover the freedom of patient-friendly and non-invasive therapy options Sonalleve MR-HIFU is an innovative therapy
MR systems Sonalleve MR-HIFU Expanding therapy options for women s health and oncology 2 Discover the freedom of patient-friendly and non-invasive therapy options Sonalleve MR-HIFU is an innovative therapy
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed
 A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed The new Philips Ingenia Elition X solution offers cutting-edge MR imaging techniques,
A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed The new Philips Ingenia Elition X solution offers cutting-edge MR imaging techniques,
11/10/2015. Prostate cancer in the U.S. Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning. NIH estimates for 2015.
 Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Temel Tirkes, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Genitourinary Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department
Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Temel Tirkes, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Genitourinary Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department
OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER
 OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER By Dr. John Feller, MD, Radiologist Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA MRI is clinically accepted as the best imaging modality for displaying anatomical
OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER By Dr. John Feller, MD, Radiologist Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA MRI is clinically accepted as the best imaging modality for displaying anatomical
Ingenia 3.0T excels in cardiac imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 45 2012/1 Ingenia 3.0T excels in cardiac imaging St. Luke s Episcopal Hospital sees huge advantages in image quality, workflow Publication for the Philips
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 45 2012/1 Ingenia 3.0T excels in cardiac imaging St. Luke s Episcopal Hospital sees huge advantages in image quality, workflow Publication for the Philips
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
High performance ultrasound
 High performance ultrasound Philips HD7 XE ultrasound system Redefining high definiti Superb image quality and an array of advanced performance features deliver high definition imaging qualities in a system
High performance ultrasound Philips HD7 XE ultrasound system Redefining high definiti Superb image quality and an array of advanced performance features deliver high definition imaging qualities in a system
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
is time consuming and expensive. An intra-operative assessment is not going to be helpful if there is no more tissue that can be taken to improve the
 My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
Ingenia MR-RT. MR Systems. The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning
 Ingenia MR-RT MR Systems The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning Table of contents Experience the difference MRI makes 3 A comprehensive MR-sim solution 4 Position with precision 6 Tailored
Ingenia MR-RT MR Systems The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning Table of contents Experience the difference MRI makes 3 A comprehensive MR-sim solution 4 Position with precision 6 Tailored
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions
 Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
UVM brain MRI protocols upgraded with latest methods
 UVM brain MRI protocols upgraded with latest methods FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - March 2017 UVM appreciates latest neuro MR methods for diagnosing and workflow The MRI staff at University
UVM brain MRI protocols upgraded with latest methods FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - March 2017 UVM appreciates latest neuro MR methods for diagnosing and workflow The MRI staff at University
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors
 Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards
 I s s u e 3 1 - M a rc h 2 0 0 7 F i e l d Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards Drs. Mukherji, Parmar create Achieva 3.0T ExamCards
I s s u e 3 1 - M a rc h 2 0 0 7 F i e l d Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards Drs. Mukherji, Parmar create Achieva 3.0T ExamCards
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Field Strength. Achieva 3.0T excels in wide range of applications. Fletcher Allen Health Care finds many uses for versatile system
 Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Achieva 3.0T excels in wide range of applications Fletcher Allen Health Care finds many uses for versatile system This article is part of Field
Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Achieva 3.0T excels in wide range of applications Fletcher Allen Health Care finds many uses for versatile system This article is part of Field
MR neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves
 Publication for the Philips I Community ISSE 50 2014 / 1 neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves Shandong edical Imaging esearch Institute explores DWIBS for neurography in extremities
Publication for the Philips I Community ISSE 50 2014 / 1 neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves Shandong edical Imaging esearch Institute explores DWIBS for neurography in extremities
Prostate MRI Hamidreza Abdi, MD,FEBU Post Doctoral Fellow Vancouver Prostate Centre UBC Department of Urologic Sciences May-20144
 Prostate MRI Hamidreza Abdi, MD,FEBU Post Doctoral Fellow Vancouver Prostate Centre UBC Department of Urologic Sciences May-20144 Objectives: Detection of prostate cancer the need for better imaging What
Prostate MRI Hamidreza Abdi, MD,FEBU Post Doctoral Fellow Vancouver Prostate Centre UBC Department of Urologic Sciences May-20144 Objectives: Detection of prostate cancer the need for better imaging What
Staging Colorectal Cancer
 Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
Fusion Ultrasound: Characterization of Abdominal Masses with MR, CT, PET, and Contrast Ultrasound
 Fusion Ultrasound: Characterization of Abdominal Masses with MR, CT, PET, and Contrast Ultrasound Mollie Rashid, MD Corinne Deurdulian, MD Hisham Tchelepi, MD Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern
Fusion Ultrasound: Characterization of Abdominal Masses with MR, CT, PET, and Contrast Ultrasound Mollie Rashid, MD Corinne Deurdulian, MD Hisham Tchelepi, MD Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern
ACR MRI Accreditation Program. ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update. Educational Objectives. ACR accreditation. History. New Modular Program
 ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
Elastography in the. technically difficult patient. EPIQ ultrasound system. Ultrasound
 Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Radiation Oncology. The conf ident path to treatment Philips Radiation Oncology Solutions
 Radiation Oncology The conf ident path to treatment Philips Radiation Oncology Solutions The confident path to treatment Philips Radiation Oncology Solutions Imaging Image registration Contouring Treatment
Radiation Oncology The conf ident path to treatment Philips Radiation Oncology Solutions The confident path to treatment Philips Radiation Oncology Solutions Imaging Image registration Contouring Treatment
Worldwide Leading Academic Center Gets a Lift in Advanced MR Imaging
 Worldwide Leading Academic Center Gets a Lift in Advanced MR Imaging As one of the largest and most authoritative scientific medical centers in Europe, Erasmus University Medical Center (Rotterdam, Netherlands),
Worldwide Leading Academic Center Gets a Lift in Advanced MR Imaging As one of the largest and most authoritative scientific medical centers in Europe, Erasmus University Medical Center (Rotterdam, Netherlands),
Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner. Answers for life.
 Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner Answers for life. 1 ACQUIRE An automated whole breast solution. Reduced acquisition time.
Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner Answers for life. 1 ACQUIRE An automated whole breast solution. Reduced acquisition time.
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
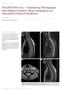 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results
 Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions
 PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions General Q: Is FDG PET specific for cancer? A: No, it is a marker of metabolism. In general, any disease that causes increased metabolism can result in increased FDG uptake
PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions General Q: Is FDG PET specific for cancer? A: No, it is a marker of metabolism. In general, any disease that causes increased metabolism can result in increased FDG uptake
MRI enters Emergency Department for fast, confident decisions
 MRI enters Emergency Department for fast, confident decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2016 www.philips.com/fieldstrength When MRI is the preferred choice, ED patients can
MRI enters Emergency Department for fast, confident decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2016 www.philips.com/fieldstrength When MRI is the preferred choice, ED patients can
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Imaging in Epilepsy. Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015
 Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours. Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany
 PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
For a legacy that lives large: Think Big. Philips CT Big Bore. Computed tomography
 Computed tomography For a legacy that lives large: Think Big Philips CT Big Bore The big question The world of cancer care is rapidly changing. The number of new cancer cases is expected to rise by about
Computed tomography For a legacy that lives large: Think Big Philips CT Big Bore The big question The world of cancer care is rapidly changing. The number of new cancer cases is expected to rise by about
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators: Use cases
 Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators: Use cases 2014 Date: October 2014 Version: Owner: Status: v01 Ministry of Health Cancer Services Final Citation: Ministry of Health. 2014. Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators:
Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators: Use cases 2014 Date: October 2014 Version: Owner: Status: v01 Ministry of Health Cancer Services Final Citation: Ministry of Health. 2014. Faster Cancer Treatment Indicators:
difference in MR oncology
 Melany Atkins, M airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Tom Schrack, ARMRIT, S airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Making a difference in MR oncology imaging Oncologic imaging represents
Melany Atkins, M airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Tom Schrack, ARMRIT, S airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Making a difference in MR oncology imaging Oncologic imaging represents
RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS)
 Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS) RIS 34001 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY 1 Credit Provides an introduction to diagnostic medical sonography.
Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS) RIS 34001 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY 1 Credit Provides an introduction to diagnostic medical sonography.
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging. Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital
 Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Lung Perfusion Analysis New Pathways in Lung Imaging Case Study Brochure PLA 309 Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2012 all rights reserved. Design and specifications
Using MRI only in prostate cancer radiotherapy workflow
 Using MRI only in prostate cancer radiotherapy workflow FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - February 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength MR-only simulation streamlines workflow for prostate cancer
Using MRI only in prostate cancer radiotherapy workflow FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - February 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength MR-only simulation streamlines workflow for prostate cancer
Advancing critical clinical decisions
 Radiation Oncology Computed Tomography Big Bore RT Advancing critical clinical decisions Pursuit of the successful outcome Powerful technology delivers Radiation therapy can be effective in helping your
Radiation Oncology Computed Tomography Big Bore RT Advancing critical clinical decisions Pursuit of the successful outcome Powerful technology delivers Radiation therapy can be effective in helping your
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
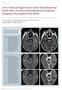 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Emerging Referral Patterns for Whole-Body Diffusion Weighted Imaging (WB-DWI) in an Oncology Center
 Emerging Referral Patterns for Whole-Body Diffusion Weighted Imaging (WB-DWI) in an Oncology Center Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Petralia 1, G. Conte 1, S.
Emerging Referral Patterns for Whole-Body Diffusion Weighted Imaging (WB-DWI) in an Oncology Center Poster No.: C-1296 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Petralia 1, G. Conte 1, S.
Welcome to a better way for YOU and YOUR patient.
 Welcome to a better way for YOU and YOUR patient. The Next Generation of Prostate Care from Invivo Current methods of prostate cancer screening, such as prostate-specifi c antigen (PSA) tests and digital
Welcome to a better way for YOU and YOUR patient. The Next Generation of Prostate Care from Invivo Current methods of prostate cancer screening, such as prostate-specifi c antigen (PSA) tests and digital
Versatile, affordable ultrasound. Philips HD6 ultrasound system. The print quality of this copy is not an accurate representation of the original.
 Versatile, affordable ultrasound Philips HD6 ultrasound system Multiple purpose, singular focus Philips HD6 ultrasound system provides a range of capabilities and features that make it suitable for a wide
Versatile, affordable ultrasound Philips HD6 ultrasound system Multiple purpose, singular focus Philips HD6 ultrasound system provides a range of capabilities and features that make it suitable for a wide
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
MultiTransmit 4D brings robustness to 3.0T cardiac imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 44 SUMMER 2011 MultiTransmit 4D brings robustness to 3.0T cardiac imaging Bonn clinicians see a reduction in artifacts and inhomogeneities as a significant
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 44 SUMMER 2011 MultiTransmit 4D brings robustness to 3.0T cardiac imaging Bonn clinicians see a reduction in artifacts and inhomogeneities as a significant
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Prostate Case Scenario 1
 Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Introducing Wollongong Diagnostics Corrimal
 Introducing Wollongong Diagnostics Corrimal 432-434 PRINCES HIGHWAY, CORRIMAL NSW 2518 www.wollongongdiagnostics.com.au WELCOME TO SERVICES MR MSK Neurology Prostate Body Imaging MULTISLICE CT CT angiography
Introducing Wollongong Diagnostics Corrimal 432-434 PRINCES HIGHWAY, CORRIMAL NSW 2518 www.wollongongdiagnostics.com.au WELCOME TO SERVICES MR MSK Neurology Prostate Body Imaging MULTISLICE CT CT angiography
Breast Cancer. What is breast cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Breast cancer is a malignant tumor in or around breast tissue. It usually begins as a lump or calcium deposit that develops from abnormal cell growth. Most breast lumps
Designed for first-time-right imaging and increased patient comfort for a faster workflow *. Ingenia 1.5T S. MR systems
 1 Premium IQ defined as increased SNR and speed and improved fat-free and motion-free imaging obtained on dstream with ds SENSE, mdixon and MultiVane XD compared to Achieva with SENSE, Dixon and Propeller.
1 Premium IQ defined as increased SNR and speed and improved fat-free and motion-free imaging obtained on dstream with ds SENSE, mdixon and MultiVane XD compared to Achieva with SENSE, Dixon and Propeller.
SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR. Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum. YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024)
 SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024) Course Directors: David W. Trost, MD, Franz Kainberger, MD Faculty: Gerd Bodner, MD, Marius
SALZBURG WEILL CORNELL/NYPH SEMINAR Diagnostic Imaging 3-Year Curriculum YEAR 1 (i.e. 2015, 2018, 2021, 2024) Course Directors: David W. Trost, MD, Franz Kainberger, MD Faculty: Gerd Bodner, MD, Marius
ADI Procedure Codes. August 2016 Revised April 2017 Page 1 of 7 ADI Procedure Codes
 Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
Code Description 70450 CT Head without contrast 70460 CT Head with contrast 70470 CT Head with & without contrast 70480 CT Orbit, et al without contrast 70481 CT Orbit, et al with contrast 70482 CT Orbit,
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Case Scenario 1. 4/19/13 Bone Scan: No scintigraphic findings to suggest skeletal metastases.
 Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
3D Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS): The dense breast screening tool and its potential role for preoperative staging
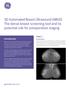 3D Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS): The dense breast screening tool and its potential role for preoperative staging Introduction Breast cancer is by far the most common cancer amongst women across Europe,
3D Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS): The dense breast screening tool and its potential role for preoperative staging Introduction Breast cancer is by far the most common cancer amongst women across Europe,
Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine
 Ultrasound Customer story Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine Philips Affiniti ultrasound for elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) Where Sonography Institute, Uster, Switzerland
Ultrasound Customer story Simplifying liver assessment in internal medicine Philips Affiniti ultrasound for elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) Where Sonography Institute, Uster, Switzerland
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Product Category CPT Code CPT Code Description Radiology MR 70336 MRI Temporomandibular Joint(s), (TMJ) Radiology CT 70450 CT Head or
Powered by. Dedicated MRI
 Powered by Dedicated MRI Provides the latest software and hardware upgrade configuration powered by exp technology: boosting productivity, increasing image quality, and adding new acquisition techniques.
Powered by Dedicated MRI Provides the latest software and hardware upgrade configuration powered by exp technology: boosting productivity, increasing image quality, and adding new acquisition techniques.
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI BREAST CANCER. The incidence of getting breast cancer is 1:19 in Malaysia
 Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
PET IMAGING (POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPY) FACT SHEET
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
