PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN
|
|
|
- Rosemary James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 246 PATHWAY OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE, CHIASM, AND TRACT*t BY J. REIMER WOL-TER AND ROMAN R. KNOBLICH From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Pathology of the University of Michigan Hospital, Ann Arbor THE pathway of the centrifugal (efferent, antidromic) nerves has been studied histologically in the optic nerves, chiasm, and optic tracts of a patient who had both eyes enucleated 50 years before. Centrifugal fibres in the optic nerve of animals have been known to exist for a long time (Cajal, 1894; Dogiel, 1895), and this fact is supported by recent physiological observations (Granit, 1955; Dodt, 1956). There can no longer be much doubt that a great number of centrifugal nerves also exists in the human optic nerve. Numerous remaining nerve fibres in two atrophic nerve stumps eleven and sixteen years after enucleation were the first evidence (Wolter and Liss, 1956). Subsequently, the terminal branches of centrifugal nerves were demonstrated in the normal human retina and optic nerve (Liss and Wolter, 1956; Wolter, 1957a) and it was concluded that at least some of the centrifugal nerves supply blood vessels. The observation of interrupted neurites in the human nerve fibre layer with terminal swellings pointing away from the optic disc was further evidence of the presence of centrifugal fibres (Wolter, 1956). Attempts at regeneration of centrifugal fibres were observed in a child's optic nerve stump eleven days after enucleation (Wolter, 1960) and later the reactions of these fibres could be studied four days after enucleation (Pfister and Wolter, 1963) in another case. A peculiar proliferation (hyper-regeneration) of centrifugal nerves was observed around blood vessels and micro-aneurysms in advanced diabetic retinopathy (Woltei, 1961). Very recently the remaining centrifugal nerves in the human optic disc were examined histologically ten days after complete occlusion of the central retinal artery that caused necrosis of the ganglion cells and all centripetal (afferent) retinal nerves (Wolter, n.d.). This latter study allowed for the conclusions that there are several morphologically different types of centrifugal nerves and that about 10 per cent. of the nerves in the normal human optic disc are centrifugal in nature. Case Report A 79-year-old Negro male died on December 12, 1963, at Hurley Hospital in Flint, Michigan, of cachexia and liver cirrhosis with ascites and hydrothorax. Surgical absence of both eyes was observed at necropsy-along with much other pathology that is of no interest in this study. The history revealed that in 1913 the patient injured his right eye with a branch while hunting. * Received for publication August 4, f This study was supported by Grant No. B-2873 of the U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare. 246
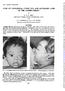
2 FIG. 1 Gross view of the chiasm with the atrophic optic nerves (n), the pituitary stalk (p), and the internal carotid artery (i). x 3. PATHWA Y OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES FIG. 2.-One of the serial frozen sections through the chiasm (ch), with end of the optic nerves (n), and the optic tracts (t). Frozen section, Hortega stain, photomicrograph x 10. FIG. 4.-Nerve fibres with myelin swellings on an irregular course in the right optic nerve next to the chiasm. Frozen section, Hortega stain, photomicrograph x 450. FIG. 3.-Nerve fibres with pearl-string-like myelin swellings on a parallel course in the right optic nerve stump. Frozen section, Hortega stain, photomicrograph x 450. Removal of this eye was advised, but the patient refused. Sympathetic ophthalmitis developed and involved the other eye. Finally, both eyes had to be removed. Fifty years after the bilateral enucleation the brain with the atrophic chiasm and optic nerve stumps (Fig. 1) was obtained for this study. Pathological Findings.-The brain was fixed in formalin. Frozen sections were cut of the optic nerve stumps, the chiasm (Fig. 2), and the optic tracts. The Hortega silver carbonate technique for staining nerves (Scharenberg and Zeman, 1952) was used. Both optic nerve stumps still contained many nerve fibres (Figs 2 and 3). The axons of these nerves were continuous and stained well. Their myelin sheath, however, was of irregular distribution with nodular swellings and areas of attenuation alternating. In the areas of the nodular myelin swellings the axon usually also exhibited some swelling and an irregular course (Figs 4, 8, 247
3 248 A. 61. J. R. WOLTER AND R. R. KNOBLICH r~ ~~~~~~~~ K r. FIG. 5.-Thin "unmyelinated" FIG. 6. Terminal bulb of nerves criss-crossing between interrupted thin nerve (t) in chiasm and pituitary stalk. Fro- the chiasm pointing tozen section, Hortega stain, wards the optic nerve photomicrograph x 400. stump. Frozen section, Hortega stain, photomicrograph x 400. I s f X t FIG. 7.-Two thin "unmyelinated" nerves (arrows) joining the other fibres of the left optic nerve stump. Frozen section, Hortega stain, photomicrograph x 400. Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 May Downloaded from FIG. 8.-Nerves with nodular myelin swellings in right optic tract. Frozen section, Hortega stain, photomicrograph- x 500. FIG. 9.-More distinct stain of axons showing irregularities within the areas of nodular swellings of nerves in the left optic tract next to lateral geniculate body. Two hyaline bodies (arrows) are also seen. Frozen section. Hortega stain, photomicrograph x 500. on 7 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 PATHWA Y OF CENTRIFUGAL FIBRES and 9). This degenerative change of optic nerve fibres with nodular myelin swellings has been recognized before and has been called "pearl-string-like T T nerve degeneration" (Wolter, 1957b). Other nerves -fibre tracts next to the optic tract, for example- / did not show this pearl-string-like change. There were also numerous hyaline bodies of nerve fibre p origin (Wolter and Liss, 1959) all through optic nerves, chiasm, and optic tracts of this case. Mixed \ _ with the majority of nerve fibres with pearl-stringlike degeneration were fewer neurites that had d \/ / virtually no myelin sheath. These "unmyelinated" neurites seemed to increase in number as one pro- C H gressed from the distal ends of the optic nerve stumps towards the chiasm. All nerves of the optic nerve stumps were arranged in the regular pattern of fibres / on a parallel course (Fig. 3). The pattern of the nerve fibres with nodular myelin N N swellings became more irregular next to the chiasm (Fig. 4). At the chiasm about half of these neurites were seen to cross from the optic tract of the other FIG. 10.-Drawing to give impression of the side. The other half was seen to come more or less course of the two types of centrifugal nerves. directly from the optic tract of the same side. One type (with myelin nodules) goes from optic the. of,liere tracts (T) by way of chiasm (CH) to the At the back Of the chiasm tnere were some thin nerves (N). The other thin nerve type comes optic "unmyelinated" nerve fibres criss-crossing and into the chiasm from pituitary stalk (P). The extending into the chiasm from a posterior direction location of numerous degeneration bulbs of (Fig. 5). A reconstruction showed that these nerves interrupted thin nerves is indicated. came from the pituitary stalk. We could not be certain from what direction these thin fibres came in the pituitary stalk, but our impression was that they were ascending. A few of the thin fibres which were seen to come from the pituitary stalk and to join the chiasm were interrupted and showed rather large terminal swellings (Fig. 6). All these terminal swellings pointed towards the optic nerve stumps. In the optic nerve stumps the same thin "unmyelinated" nerves could be recognized (Fig. 7). Most of the nerves of the optic nerve stumps-and all fibres with the pearl-string-like myelin swellings- could be traced into the optic tracts. They were still present in the optic tracts in a region immediately adjacent to the lateral geniculate bodies (Figs 8 and 9). The drawing (Fig. 10) is to explain the course of the centrifugal nerves found in this case. Discussion The centrifugal (efferent) and centripetal (afferent) fibres of the normal human optic nerve, chiasm, and tract look alike in a histological section. Therefore, it is impossible with present-day techniques to find the pathway of the centrifugal nerves in a normal human brain. The period of 50 years after bilateral enucleation in the present case must have caused complete atrophy of all centripetal nerves. All remaining nerves in the optic nerves, chiasm, and tracts must, therefore, be centrifugal in nature. It is already known that the centrifugal nerves show only partial or no retrograde degeneration (Wolter and Liss, 1956). Thus, this case represents a unique opportunity to study the pathway of the centrifugal fibres of the human optic nerve. At first, this study revealed that continuous centrifugal nerve fibres survived in the optic nerve stumps 50 years after bilateral enucleation. Most of the remaining fibres in the optic nerve stumps of the present case showed a peculiar pearl-string-like 249
5 250 J. R. WOLTER AND R. R. KNOBLICH degenerative change of their myelin sheath that also involved the axon. This change is well known to us from atrophic optic nerves due to other causes (Wolter, 1957b; Wolter and Liss, 1959) and it serves very well in this study for an easy recognition of the remaining optic nerve fibres all the way up to the lateral geniculate body. All fibres with the pearl-string-like myelin change could be traced to the optic tracts next to the lateral geniculate bodies. It cannot be said as yet whether the fibres originate there or whether they just pass through the lateral geniculate body and really have another origin. About half of the fibres with the pearl-string-like change were seen to cross in the chiasm while the other half remained uncrossed. In the optic nerve these fibres formed no distinct bundle, but were distributed about evenly. Additional thin fibres virtually without a myelin sheath were found in both optic nerve stumps. These fibres could be traced into the chiasm. All these "unmyelinated" fibres, however, were seen to come into the chiasm from a posterior directionfrom the region of the pituitary stalk-and not from the optic tracts. No fibres of this type were found in the optic tracts. In this case it has not been possible to trace the thin centrifugal nerves which come from the pituitary stalk to their origin. These nerves are of the greatest interest, of course. Extensive hyper-regeneration of terminal centrifugal nerves around blood vessels and micro-aneurysms was demonstrated several years ago as "the only specific pathologic change of diabetic retinopathy" (Wolter, 1961). The presence of such fibres connecting pituitary stalk and eye could perhaps also be important in relation to the fact that removal of the pituitary gland or pituitary stalk section has both been found to improve advanced diabetic retinopathy. Summary Nerve fibres were still present in the optic nerve stumps 50 years after bilateral enucleation and represent new evidence for the existence of centrifugal fibres in the human eye. These nerves were traced back through the chiasm into the optic tracts. About half of them were seen to cross at the chiasm while the other half was observed to come from the same side. Additional "unmyelinated" fibres found in the optic nerve stumps were seen to come from the pituitary stalk. REFERENCES DODT, E. (1956). J. Neurophysiol., 19, 301. DOGIEL, A. S. (1895). Arch. Mikr. Anat., 44, 622. GRANIT, R. (1955). J. Neurophysiol., 18, 388. Liss, L., and WOLTER, J. R. (1956). Klin. Mbl. Augenheilk., 129, 793. PFISTER, R. R., and WOLTER, J. R. (1963). Neurology (Minneap.), 13, 38. RAMON Y CAJAL, S. (1894). "Die Retina der Wirbelthiere". Bergmann, Wiesbaden. SCHARENBERG, K., and ZEMAN, W. (1952). Arch. Psychiat. Nervenkr., 188, 430. WOLTER, J. R. (1956). von Graefes Arch. Ophthal., 158, 235. (1957a). Ibid., 158, 524. (1957b). Ibid., (1960). A.M.A. Arch. Ophthal., 64, 697. (1961). Amer. J. Ophthal., 51, "Centrifugal Nerves at the Optic Disk". Submitted as a thesis for American Ophthalmological Society. [Not yet published.] and Liss, L. (1956). von Graefes Arch. Ophthal., 158, 1. (1959). A.M.A. Arch. Ophthal., 61, 780.
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Electron Microscopic Demonstration of Centrifugal Nerve Fibers in the Human Optic Nerve
 Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal. 210, 3141 (1979) Graefes Archiv fijr klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie 9 by Springer-Verlag 1979 Electron Microscopic Demonstration of Centrifugal
Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal. 210, 3141 (1979) Graefes Archiv fijr klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie 9 by Springer-Verlag 1979 Electron Microscopic Demonstration of Centrifugal
HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS. photocoagulation of the rabbit's retina.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 577. COMMUNICATIONS PHOTOCOAGULATION OF THE RETINA* OPHTHALMOSCOPIC AND HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS BY A. LAVYEL Haifa, Israel SINCE the introduction of the photocoagulator by Meyer-Schwickerath
Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 823 Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma F. H. STEFANI AND ELISABETH ROTHEMUND From the University Eye Clinic and the Max Planck Institute ofpsychiatry, Munich, Federal Republic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 823 Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma F. H. STEFANI AND ELISABETH ROTHEMUND From the University Eye Clinic and the Max Planck Institute ofpsychiatry, Munich, Federal Republic
Efferent innervation of the retina
 Efferent innervation of the retina II. Morphologic study of the monkey retina' Francisco M. Honrubia and James H. Elliott Silver impregnation of the monkey's retina has been employed to study the presence
Efferent innervation of the retina II. Morphologic study of the monkey retina' Francisco M. Honrubia and James H. Elliott Silver impregnation of the monkey's retina has been employed to study the presence
NEUROGLIAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE HUMAN
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 601. NEUROGLIAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE HUMAN RETINAL CAPILLARY NETWORK* BY C. A. ERSKINE School of Anatomy, Trinity College, Dublin THE investigation described in this paper
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 601. NEUROGLIAL RELATIONSHIPS IN THE HUMAN RETINAL CAPILLARY NETWORK* BY C. A. ERSKINE School of Anatomy, Trinity College, Dublin THE investigation described in this paper
CAROTID-OPHTHALMIC ANASTOMOSES*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1956) 40, 497. CAROTID-OPHTHALMIC ANASTOMOSES* FREQUENCY OF EXTERNAL CAROTID AND OPHTHALMIC ARTERY ANASTOMOSES BY MICHAEL SHEAt Toronto, Canada ANATOMICAL studies in man on the degree
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1956) 40, 497. CAROTID-OPHTHALMIC ANASTOMOSES* FREQUENCY OF EXTERNAL CAROTID AND OPHTHALMIC ARTERY ANASTOMOSES BY MICHAEL SHEAt Toronto, Canada ANATOMICAL studies in man on the degree
Band atrophy of the optic nerve: A report on different anatomical locations in three patients
 Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology (2013) 27, 65 69 Case Report Band atrophy of the optic nerve: A report on different anatomical locations in three patients Alberto Gálvez-Ruiz, MD a,b, ; Nawal Arishi, MD
Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology (2013) 27, 65 69 Case Report Band atrophy of the optic nerve: A report on different anatomical locations in three patients Alberto Gálvez-Ruiz, MD a,b, ; Nawal Arishi, MD
The Neuron. Consists Of: - cell body. - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin. dendrites Axon terminal. Cell body. nucleus. axon.
 The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
The Neuron Consists Of: - cell body - Dendrites - axon - axon terminal - myelin dendrites Axon terminal Cell body nucleus myelin axon THE SYNAPSE Definition: It is a point of contact between the axon of
Concentric "Microwaves" of Henle's Fiber Layer: Associated with Horizontal Folding
 Albrecht von Graefes Arch Klin Ophthalmol. (1981) 216:31-39 Graefes Archiv for klinische und experimenlelle Ophthalmologie 9 Springer-Verlag 1981 Concentric "Microwaves" of Henle's Fiber Layer: Associated
Albrecht von Graefes Arch Klin Ophthalmol. (1981) 216:31-39 Graefes Archiv for klinische und experimenlelle Ophthalmologie 9 Springer-Verlag 1981 Concentric "Microwaves" of Henle's Fiber Layer: Associated
T HE visual field changes that accompany
 J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / September, 1969 The Arterial Supply of the Human Optic Chiasm RICHARD BERGLAND, M.D.,* AND BRONSON S. RAY, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), New York Hospital-Cornell
J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / September, 1969 The Arterial Supply of the Human Optic Chiasm RICHARD BERGLAND, M.D.,* AND BRONSON S. RAY, M.D. Department of Surgery (Neurosurgery), New York Hospital-Cornell
STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 343. STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY* OBSERVATIONS BY MEANS OF THE PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE BY ANTONIO A. ROSSI From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London (Director of Research,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 343. STRUCTURE OF THE VITREOUS BODY* OBSERVATIONS BY MEANS OF THE PHASE-CONTRAST MICROSCOPE BY ANTONIO A. ROSSI From the Institute of Ophthalmology, London (Director of Research,
_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... I~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~...x'..'.i ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA*
 '..,S''''. t ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. g.# lgl,~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.%. : Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 164. ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA* BY ALY MORTADA Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
'..,S''''. t ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. g.# lgl,~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.%. : Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 164. ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA* BY ALY MORTADA Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
CENTRAL RETINAL ARTERY AND CENTRAL OPTIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 21. CENTRAL RETINAL ARTERY AND CENTRAL OPTIC NERVE ARTERY* BY J. FRANqOIS AND A. NEETENS From the. Ophthalmological Clinic, University of Ghent, Belgium (Director: Prof. J.
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 21. CENTRAL RETINAL ARTERY AND CENTRAL OPTIC NERVE ARTERY* BY J. FRANqOIS AND A. NEETENS From the. Ophthalmological Clinic, University of Ghent, Belgium (Director: Prof. J.
ADENOMA OF THE LIMBAL CONJUNCTIVA*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 237. ADENOMA OF THE LIMBAL CONJUNCTIVA* BY J. FRAN(OIS AND M. RABAEY From the Ophthalmological Clinic of the University of Ghent Director: Prof. J. Franpois, M.D. ADENOMATA of the
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 237. ADENOMA OF THE LIMBAL CONJUNCTIVA* BY J. FRAN(OIS AND M. RABAEY From the Ophthalmological Clinic of the University of Ghent Director: Prof. J. Franpois, M.D. ADENOMATA of the
2. GOVT ACCESSION NO AD djjjt. Approved for public release; distribution unlimited.
 UNCLASSIFIED SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE (When Data Enle.ed; t. REPORT NUMBER REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE SAM TR 81-358 4. TITLE (and Subtitle) 2. GOVT ACCESSION NO AD djjjt READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE
UNCLASSIFIED SECURITY CLASSIFICATION OF THIS PAGE (When Data Enle.ed; t. REPORT NUMBER REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE SAM TR 81-358 4. TITLE (and Subtitle) 2. GOVT ACCESSION NO AD djjjt READ INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE
(ALBERS-SCHONBERG DISEASE)*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 218. NEURO-HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN OSTEOPETROSIS (ALBERS-SCHONBERG DISEASE)* BY F. VRABEC AND J. SEDLA(KOVA From the Eye Clinic of the Medical Faculty of Hygiene of the Charles
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 218. NEURO-HISTOLOGICAL FINDINGS IN OSTEOPETROSIS (ALBERS-SCHONBERG DISEASE)* BY F. VRABEC AND J. SEDLA(KOVA From the Eye Clinic of the Medical Faculty of Hygiene of the Charles
EXUDATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* SPONTANEOUS CHANGES AND EFFECTS OF A CORN OIL DIET
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 666. EXUDATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* SPONTANEOUS CHANGES AND EFFECTS OF A CORN OIL DIET BY R. C. KING, J. H. DOBREE, D'A. KOK, W. S. FOULDS, AND W. G. DANGERFIELD St. Bartholomew's
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 666. EXUDATIVE DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* SPONTANEOUS CHANGES AND EFFECTS OF A CORN OIL DIET BY R. C. KING, J. H. DOBREE, D'A. KOK, W. S. FOULDS, AND W. G. DANGERFIELD St. Bartholomew's
OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 242. OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS* BY J. R. HUDSON Institute of Ophthalmology, London HAEMOCHROMATOSIS is a rare condition, the chief clinical features of which are
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 242. OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS* BY J. R. HUDSON Institute of Ophthalmology, London HAEMOCHROMATOSIS is a rare condition, the chief clinical features of which are
the rhesus monkey Blood supply of the ciliary ganglion in histochemical studies, and studies of the comparative anatomy of the ciliary ganglion and
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (i 969) 53, 753 Blood supply of the ciliary the rhesus monkey M. ELISKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Medical Faculty, Caroline University, Prague ganglion in In our study of the central retinal
Brit. J. Ophthal. (i 969) 53, 753 Blood supply of the ciliary the rhesus monkey M. ELISKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Medical Faculty, Caroline University, Prague ganglion in In our study of the central retinal
C:\Documents and Settings\sstensaas\Desktop\dental visual 2010\VisualPath dental 2010.docVisualPath dental 2010.doc
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas April 8, 2010, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15, Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch 7 THE VISUAL PATHWAY Objectives: 1. Describe the pathway of visual information from
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas April 8, 2010, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15, Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch 7 THE VISUAL PATHWAY Objectives: 1. Describe the pathway of visual information from
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
non-perforating injury
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
ABSTRACT. 2. METhODS 3. RESULTS
 Laser induced retinal nerve fiber layer (NFL) damage H. Zwick, D.A. Gagliano, J.A. Zuclich, B.E. Stuck, M. Belkin USArmy Medical Research Detachment Walter Reed Army Institute of Research San Antonio,
Laser induced retinal nerve fiber layer (NFL) damage H. Zwick, D.A. Gagliano, J.A. Zuclich, B.E. Stuck, M. Belkin USArmy Medical Research Detachment Walter Reed Army Institute of Research San Antonio,
[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the
![[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the [1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the](/thumbs/84/89127006.jpg) 'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
Reappraisal of the retinal cotton-wool spot: a discussion paper
 682 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 74 September 1981 Reappraisal of the retinal cotton-wool spot: a discussion paper David McLeod BSC FRCS Moorfields Eye Hospital, London EC] V 2PD In
682 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 74 September 1981 Reappraisal of the retinal cotton-wool spot: a discussion paper David McLeod BSC FRCS Moorfields Eye Hospital, London EC] V 2PD In
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
COMMUNICATIONS. ARTERITIS*t CILIARY ARTERY INVOLVEMENT IN GIANT CELL. generalized vascular disease was emphasized by Cooke, Cloake, Govan, and
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 505 COMMUNICATIONS CILIARY ARTERY INVOLVEMENT IN GIANT CELL ARTERITIS*t BY P. A. MAcFAUL Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THIS condition
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 505 COMMUNICATIONS CILIARY ARTERY INVOLVEMENT IN GIANT CELL ARTERITIS*t BY P. A. MAcFAUL Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THIS condition
Haemorrhagic glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 444 Haemorrhagic glaucoma Comparative study in diabetic and nondiabetic patients P. H. MADSEN From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Internal Medicine, the University Hospital,
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 444 Haemorrhagic glaucoma Comparative study in diabetic and nondiabetic patients P. H. MADSEN From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Internal Medicine, the University Hospital,
The Visual System. Anatomical Overview Dr. Casagrande January 21, 2004
 The Visual System Anatomical Overview Dr. Casagrande January 21, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN How the Brain Works Useful Additional Reading: Adler,
The Visual System Anatomical Overview Dr. Casagrande January 21, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN How the Brain Works Useful Additional Reading: Adler,
Vaso-glial connections in the rabbit
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, I Communications Vaso-glial connections in the rabbit retina BRENDA TRIPATHI AND NORMAN ASHTON Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, I Communications Vaso-glial connections in the rabbit retina BRENDA TRIPATHI AND NORMAN ASHTON Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The
The 7 th lecture. Anatomy and Physiology For the. 1 st Class. By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza
 The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
The 7 th lecture In Anatomy and Physiology For the 1 st Class By Dr. Ala a Hassan Mirza Nervous System (part I) The Nerve Tissue and the Nervous System The Tissues of the Body There are 4 types of tissues
VISUAL PROGNOSIS OF PROLIFERATING DIABETIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 611. VISUAL PROGNOSIS OF PROLIFERATING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* BY WILLIAM PARKES BEETHAM From the Harvard Medical School, the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, and the New
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 611. VISUAL PROGNOSIS OF PROLIFERATING DIABETIC RETINOPATHY* BY WILLIAM PARKES BEETHAM From the Harvard Medical School, the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, and the New
EFFECT OF REPEATED TRAUMATIZATION OF THE CEN'I'RAL STUMP OF THE HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE ON DEGENERATION AND REGENERArrTON OF rrrs FIBERS AND CELLS
 Reprinted from THE ANATOM1CAL RECORD Vol. 43, No, 1, June, ] 929 EFFECT OF REPEATED TRAUMATIZATION OF THE CEN'I'RAL STUMP OF THE HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE ON DEGENERATION AND REGENERArrTON OF rrrs FIBERS AND CELLS
Reprinted from THE ANATOM1CAL RECORD Vol. 43, No, 1, June, ] 929 EFFECT OF REPEATED TRAUMATIZATION OF THE CEN'I'RAL STUMP OF THE HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE ON DEGENERATION AND REGENERArrTON OF rrrs FIBERS AND CELLS
ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Lesson 33. Objectives: References: Chapter 16: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 16:
 Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Lesson 33 Lesson Outline: Nervous System Structure and Function Neuronal Tissue Supporting Cells Neurons Nerves Functional Classification of Neuronal Tissue Organization of the Nervous System Peripheral
Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma
 Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
Introduction to Nervous Tissue
 Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
CONJUNCTIVAL ANGIOSCOPY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 479 CONJUNCTIVAL ANGIOSCOPY* BY PAUL WEINSTEIN AND JOSEPH FORGACS From the Department of Ophthalmology, Budapest University ACCORDING to Rollin (1934), Pletnava (1938), and Sedan
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 479 CONJUNCTIVAL ANGIOSCOPY* BY PAUL WEINSTEIN AND JOSEPH FORGACS From the Department of Ophthalmology, Budapest University ACCORDING to Rollin (1934), Pletnava (1938), and Sedan
Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS /16/2018. Dr/ Marwa Abdellah EOS When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases???
 When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
When do you ask Fluorescein angiography for optic disc diseases??? 1 NORMAL OPTIC DISC The normal optic disc on fluorescein angiography is fluorescent due to filling of vessels arising from the posterior
WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1955), 39, 374. HEREDITARY POSTERIOR POLAR CATARACT WITH REPORT OF A PEDIGREE* BY C. G. TULLOH London K HEREDITARY, developmental, posterior polar cataract has been encountered in a
1/10/2013. What do neurons look like? Topic 14: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves. How do neurons work? The nervous impulse. Specialized Neurons
 Topic 4: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves What do neurons look like? Neurons What do they look like? How do they work? Neuronal and spinal organization What is the difference between neuron & nerve? How
Topic 4: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves What do neurons look like? Neurons What do they look like? How do they work? Neuronal and spinal organization What is the difference between neuron & nerve? How
Ocular findings in children with sickle
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 644 Ocular findings in children with sickle cell haemoglobin C disease in Jamaica PATRICK I. CONDON, ROBERT GRAY, AND GRAHAM R. SERJEANT From the Medical Research Council,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 644 Ocular findings in children with sickle cell haemoglobin C disease in Jamaica PATRICK I. CONDON, ROBERT GRAY, AND GRAHAM R. SERJEANT From the Medical Research Council,
Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14
 Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14 Overview of the Nervous System Every minute of every day, your nervous system is sending and receiving countless messages about what is happening both inside and
Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14 Overview of the Nervous System Every minute of every day, your nervous system is sending and receiving countless messages about what is happening both inside and
Recurrence of astrocytoma of optic nerve after 48 years
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1976) 6o, 539 Recurrence of astrocytoma of optic nerve after 48 years JOAN MULLANEY, J. WALSH, W. R. LEE, AND J. H. ADAMS From the National Ophthalmic Pathology Laboratory of Ireland,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1976) 6o, 539 Recurrence of astrocytoma of optic nerve after 48 years JOAN MULLANEY, J. WALSH, W. R. LEE, AND J. H. ADAMS From the National Ophthalmic Pathology Laboratory of Ireland,
non-occipital lobe lesions
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 4I6 The Riddoch phenomenon revealed in non-occipital lobe lesions R. J. ZAPPIA, J. MI. ENOCH, R. STAMPER, J. Z. WINKELMAN, AND A. J. GAY From the Departments of Ophthalmology
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 4I6 The Riddoch phenomenon revealed in non-occipital lobe lesions R. J. ZAPPIA, J. MI. ENOCH, R. STAMPER, J. Z. WINKELMAN, AND A. J. GAY From the Departments of Ophthalmology
Visually evoked cortical potentials in the evaluation of homonymous and bitemporal visual field defects
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I976) 6o, 273 Visually evoked cortical potentials in the evaluation of homonymous and bitemporal visual field defects H. G. H. WILDBERGER,* G. H. M. VAN LITH, R. WIJNGAARDE, AND G. T.
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I976) 6o, 273 Visually evoked cortical potentials in the evaluation of homonymous and bitemporal visual field defects H. G. H. WILDBERGER,* G. H. M. VAN LITH, R. WIJNGAARDE, AND G. T.
Peripheral retina in myopia
 Brit. _J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 300 Peripheral retina in myopia With particular reference to retinal breaks S. W. HYAMS AND E. NEUMANN From the Department of Ophthalmology, Rothschild Government-Municipal
Brit. _J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 300 Peripheral retina in myopia With particular reference to retinal breaks S. W. HYAMS AND E. NEUMANN From the Department of Ophthalmology, Rothschild Government-Municipal
Sudden Vision Loss. Brendan Girschek, MD, FRCSC, FACS Vitreoretinal Surgery Cedar Valley Medical Specialists
 Sudden Vision Loss Brendan Girschek, MD, FRCSC, FACS Vitreoretinal Surgery Cedar Valley Medical Specialists My Credentials -Residency in Ophthalmology at the LSU Eye Center in New Orleans, LA -Fellowship
Sudden Vision Loss Brendan Girschek, MD, FRCSC, FACS Vitreoretinal Surgery Cedar Valley Medical Specialists My Credentials -Residency in Ophthalmology at the LSU Eye Center in New Orleans, LA -Fellowship
RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA* A NEW THERAPEUTIC APPROACH
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 144. RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA* A NEW THERAPEUTIC APPROACH BY LALIT P. AGARWAL, S. R. K. MALIK, MADAN MOHAN, AND P. R. KARWAL From the Department of Ophthalmology, All-India Institute
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 144. RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA* A NEW THERAPEUTIC APPROACH BY LALIT P. AGARWAL, S. R. K. MALIK, MADAN MOHAN, AND P. R. KARWAL From the Department of Ophthalmology, All-India Institute
D."espite numerous anatomic and physiologic
 Trigeminal pathway for afferent fibers from the oculomotor nerves William S. Joffe, Andrew J. Gay, and C. Courtney Antrim Stimulation studies in the cat have shown that the afferent fibers for the oculorespiratory
Trigeminal pathway for afferent fibers from the oculomotor nerves William S. Joffe, Andrew J. Gay, and C. Courtney Antrim Stimulation studies in the cat have shown that the afferent fibers for the oculorespiratory
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 7 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Introduction The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental
Graefe's Archive. Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:55-60 Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Artificial anterior chamber for the growing of membranes on lens implants*
Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma*
 Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:101-105 Graefe's Archive for CliniCal and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma* J. Reimer Wolter
Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (1983) 221:101-105 Graefe's Archive for CliniCal and Experimental Ophthalmology Springer-Verlag 1983 Cystoid macular edema associated with limbal melanoma* J. Reimer Wolter
optic nerve contains myelinated fibres of graded size. Arey and his electro-physiological work on the optic nerve has been completed
 AN ANALYSIS OF FIBRE-SIZE IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE 457 AN ANALYSIS OF FIBRE-SIZE IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE* BY L. W. CHACKO DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY, UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD DATA on the fibre-size " spectrum
AN ANALYSIS OF FIBRE-SIZE IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE 457 AN ANALYSIS OF FIBRE-SIZE IN THE HUMAN OPTIC NERVE* BY L. W. CHACKO DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY, UNIVERSITY OF OXFORD DATA on the fibre-size " spectrum
LOOKING AT BLINDNESS FROM NEUROLOGIST S PERSPECTIVE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk LOOKING AT BLINDNESS FROM NEUROLOGIST S PERSPECTIVE Author : LAURENT S GAROSI Categories : Vets Date : June 23, 2008 LAURENT
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk LOOKING AT BLINDNESS FROM NEUROLOGIST S PERSPECTIVE Author : LAURENT S GAROSI Categories : Vets Date : June 23, 2008 LAURENT
THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. February 16, 2012 Objectives: THE VISUAL PATHWAY FOR DENTAL STUDENTS A. Draw the expected visual fields seen in classic lesions of the nerve, chiasm, thalamus, optic
RETINAL NEUROPATHOLOGY OF LATE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 277. RETINAL NEUROPATHOLOGY OF LATE INFANTILE AMAUROTIC IDIOCY*t BY From the Department of Ophthalmology and the Pediatric Neurology Unit of the Department of Pediatrics of
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 277. RETINAL NEUROPATHOLOGY OF LATE INFANTILE AMAUROTIC IDIOCY*t BY From the Department of Ophthalmology and the Pediatric Neurology Unit of the Department of Pediatrics of
HOMONYMOUS VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS Perimetric findings and corresponding neuro-imaging results
 Homonymous visual field defects 511 HOMONYMOUS VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS Perimetric findings and corresponding neuro-imaging results JAN SCHILLER 1, TRAUGOTT J. DIETRICH 1, LIESE LORCH 1, MARTIN SKALEJ 2, CHRISTOPH
Homonymous visual field defects 511 HOMONYMOUS VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS Perimetric findings and corresponding neuro-imaging results JAN SCHILLER 1, TRAUGOTT J. DIETRICH 1, LIESE LORCH 1, MARTIN SKALEJ 2, CHRISTOPH
Preliminary report on effect of retinal panphotocoagulation on rubeosis iridis and
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1977, 61, 278-284 Preliminary report on effect of retinal panphotocoagulation on rubeosis iridis and neovascular glaucoma LEILA LAATIKAINEN From Moorfields Eye Hospital,
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1977, 61, 278-284 Preliminary report on effect of retinal panphotocoagulation on rubeosis iridis and neovascular glaucoma LEILA LAATIKAINEN From Moorfields Eye Hospital,
Fundoscopic features in standard and red-free illumination in three patients with congenital hemiplegia
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 537 Homonymous hemioptic hypoplasia Fundoscopic features in standard and red-free illumination in three patients with congenital hemiplegia W. F. HOYT,* E. N. RIOS-MONTENEGRO,t
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 537 Homonymous hemioptic hypoplasia Fundoscopic features in standard and red-free illumination in three patients with congenital hemiplegia W. F. HOYT,* E. N. RIOS-MONTENEGRO,t
Traumatic optic pathway degeneration
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 233 Traumatic optic pathway degeneration Antegrade and retrograde GEORGE H. KURZ, JUN OGATA, AND ELLIOT M. GROSS From the Departments of Ophthalmology, Pathology, and Forensic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 233 Traumatic optic pathway degeneration Antegrade and retrograde GEORGE H. KURZ, JUN OGATA, AND ELLIOT M. GROSS From the Departments of Ophthalmology, Pathology, and Forensic
Investigations. The blood count was normal with an erythrocyte. sedimentation rate of 5 mm. ist hr, and negative Waaler-
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
RADIAL PERIPAPLLARY CAPILLARIES OF THE RETINA*tt
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 26 RADIAL PERIPAPLLARY CAPILLARIES OF THE RETINA*tt HI. POSSIBLE ROLE IN BJERRUM SCOTOMA BY MORTON ALTERMAN AND PAUL HENKIND From the Department of Ophthalmology, New York
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 26 RADIAL PERIPAPLLARY CAPILLARIES OF THE RETINA*tt HI. POSSIBLE ROLE IN BJERRUM SCOTOMA BY MORTON ALTERMAN AND PAUL HENKIND From the Department of Ophthalmology, New York
On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. One of the present authors, KIKUCHI, has reported in detail on the innervation
 Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 19, n. 3 (May 1960). P. 437-446. Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku Univ., Sendai. On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. Mizuho KIKUCHI, Shunsaku HATAKEYAMA,
Arch. hist. jap. Vol. 19, n. 3 (May 1960). P. 437-446. Anat. Labor. of Prof. H. SETO, Tohoku Univ., Sendai. On the Nerve Supply of the Radix Linguae of Newborn Dog. Mizuho KIKUCHI, Shunsaku HATAKEYAMA,
New vessel formation in retinal branch vein occlusion
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I 976) 6o, 8io New vessel formation in retinal branch vein occlusion JOHN S. SHILLING AND EVA M. KOHNER From the Retinal Diagnostic Unit, Moorfields Eye Hospital, London Neovascularization
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I 976) 6o, 8io New vessel formation in retinal branch vein occlusion JOHN S. SHILLING AND EVA M. KOHNER From the Retinal Diagnostic Unit, Moorfields Eye Hospital, London Neovascularization
CENTRAL AREOLAR CHOROIDAL SCLEROSIS* A HISTO-PATHOLOGICAL STUDY
 Brit. J. Op/ithal. (1953), 37, 140. CENTRAL AREOLAR CHOROIDAL SCLEROSIS* A HISTO-PATHOLOGICAL STUDY BY NORMAN ASHTON Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London THE history and clinical
Brit. J. Op/ithal. (1953), 37, 140. CENTRAL AREOLAR CHOROIDAL SCLEROSIS* A HISTO-PATHOLOGICAL STUDY BY NORMAN ASHTON Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London THE history and clinical
MESHWORK*t NODULAR DYSTROPHY OF THE TRABECULAR
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 31. NODULAR DYSTROPHY OF THE TRABECULAR MESHWORK*t BY J. S. SPEAKMAN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto THE description of the microscopic structure of individual
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 31. NODULAR DYSTROPHY OF THE TRABECULAR MESHWORK*t BY J. S. SPEAKMAN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto THE description of the microscopic structure of individual
16. which is not synthesised in postganglionic sympathetic neurons a. L-dopa b. DA c. NA d. A e. ACh
 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Visual pathways a. Have P cells that are associated with colour b. Utilize the primary colours, red, yellow and blue c. Have simple cells which respond to all light stimuli d. Pass through
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Visual pathways a. Have P cells that are associated with colour b. Utilize the primary colours, red, yellow and blue c. Have simple cells which respond to all light stimuli d. Pass through
following its stimulation. joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to
 612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 597. A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF THE IRIS WITH PIGMENTATION OF THE SCLERA AND PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA* BY V. CAVKA Beograd, Yugoslavia THE significance of pigmentation
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1961) 45, 597. A NEW CLINICAL FORM OF HETEROCHROMIA OF THE IRIS WITH PIGMENTATION OF THE SCLERA AND PIGMENTARY GLAUCOMA* BY V. CAVKA Beograd, Yugoslavia THE significance of pigmentation
CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME
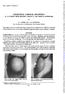 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 631 CONGENITAL CORNEAL OPACITIES*t IN A PATIENT WITH RIEGER'S ANOMALY AND DOWN'S SYNDROME BY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Royal Hospital, Sheffield THIS report concerns
Angle recession and secondary glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 6o8 Angle recession and secondary glaucoma D. MOONEY Kent County Ophthalmic and Aural Hospital, Maidstone In a previous article (Mooney, I972), the incidence and extent of
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 6o8 Angle recession and secondary glaucoma D. MOONEY Kent County Ophthalmic and Aural Hospital, Maidstone In a previous article (Mooney, I972), the incidence and extent of
(Received 8 March 1965)
 J. Physiol. (1965), 180, pp. 837-845 837 With 1 plate and 4 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECT OF OCCLUDING THE RETINAL AND CHOROIDAL CIRCULATIONS ON THE ELECTRO- RETINOGRAM OF MONKEYS BY
J. Physiol. (1965), 180, pp. 837-845 837 With 1 plate and 4 text-figures Printed in Great Britain THE EFFECT OF OCCLUDING THE RETINAL AND CHOROIDAL CIRCULATIONS ON THE ELECTRO- RETINOGRAM OF MONKEYS BY
Why does the writer above love running so much? One of the reasons. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure. Reader s Guide. Exploring Psychology
 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Reader s Guide Main Idea Learning about the nervous system helps us know how messages that are sent to the brain cause behavior. Vocabulary central nervous system
D URING the study of a fairly large material of microscopical sections of
 ARACHNOIDAL PROLIFERATIONS WITH CYST FORMATION IN HUMAN SPINAL NERVE ROOTS AT THEIR ENTRY INTO THE INTERVERTEBRAL FORAMINA PRELIMINARY REPORT BROR REXED, M.D. Department of Histology, Karolinska Instituter,
ARACHNOIDAL PROLIFERATIONS WITH CYST FORMATION IN HUMAN SPINAL NERVE ROOTS AT THEIR ENTRY INTO THE INTERVERTEBRAL FORAMINA PRELIMINARY REPORT BROR REXED, M.D. Department of Histology, Karolinska Instituter,
Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms
 J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
J. clin. Path. (964), 7, Histology of the aortic media in dissecting aneurysms GERALD MANLEY From the Department of Pathology, The Radcliffe nfirmary, Oxford SYNOPSS Sections of the ascending aorta of
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Symptoms of spinal cord injury:
 Symptoms of spinal cord injury: involuntary muscle spasms loss of voluntary movement sensation, balance control of breathing autonomic functions (blood pressure) bladder, sexual, bowel control All due
Symptoms of spinal cord injury: involuntary muscle spasms loss of voluntary movement sensation, balance control of breathing autonomic functions (blood pressure) bladder, sexual, bowel control All due
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 11 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A This is Your Brain on Music Assignment 1 With your
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Pathogenesis of cupping of the optic disc
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 863 Pathogenesis of cupping of the optic disc SOHAN SINGH HAYREH Department of Ophthalmology, University of Iowa, U.S.A. Optic disc cupping (ODC) is a classical feature of
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 863 Pathogenesis of cupping of the optic disc SOHAN SINGH HAYREH Department of Ophthalmology, University of Iowa, U.S.A. Optic disc cupping (ODC) is a classical feature of
Lattice degeneration in a family
 Brit. jt. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 566 Lattice degeneration in a family With retinal detachment and cataract I. LEWKONIA, M. S. DAVIES, AND J. D. SALMON Moorfields Eye Hospital, High Holborn, London, W.C.
Brit. jt. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, 566 Lattice degeneration in a family With retinal detachment and cataract I. LEWKONIA, M. S. DAVIES, AND J. D. SALMON Moorfields Eye Hospital, High Holborn, London, W.C.
(Received 12 April 1938)
 206 J. Physiol. (I938) 93, 206-2I4 6II.83:6II.314:6I2.392.OI3 A DEGENERATIVE CHANGES IN THE AXIS CYLINDERS OF THE DENTAL NERVES, DUE TO DIETS DEFICIENT IN VITAMIN A AND CAROTENE BY J. D. KING, W. LEWINSKY
206 J. Physiol. (I938) 93, 206-2I4 6II.83:6II.314:6I2.392.OI3 A DEGENERATIVE CHANGES IN THE AXIS CYLINDERS OF THE DENTAL NERVES, DUE TO DIETS DEFICIENT IN VITAMIN A AND CAROTENE BY J. D. KING, W. LEWINSKY
function after direct surgcal intervention for posterior communicating aneurysms
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I97), i i Analysis of the recovery of third nerve function after direct surgcal intervention for posterior communicating aneurysms M. C. GAYSON, S.. SONI, AND V. A. SPOONE University
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I97), i i Analysis of the recovery of third nerve function after direct surgcal intervention for posterior communicating aneurysms M. C. GAYSON, S.. SONI, AND V. A. SPOONE University
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology
 Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
Pearls, Pitfalls and Advances in Neuro-Ophthalmology Nancy J. Newman, MD Emory University Atlanta, GA Consultant for Gensight Biologics, Santhera Data Safety Monitoring Board for Quark AION Study Medical-legal
SEGMENTAL LESIONS OF THE RETINAL ARTERIES*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 562. SEGMENTAL LESIONS OF THE RETINAL ARTERIES* BY R. K. BLACH London FEW cases with segmental lesions of the retinal arteries have been described. Suganuma (1927) reported
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 562. SEGMENTAL LESIONS OF THE RETINAL ARTERIES* BY R. K. BLACH London FEW cases with segmental lesions of the retinal arteries have been described. Suganuma (1927) reported
E, Ixperimental allergic encephalomyelitis
 Experimental allergic optic neuritis in guinea pigs: preliminary report Narsing A. Rao, Mark O. M. Tso," and Lorenz E. Zimmerman An experimental model for acute allergic optic neuritis was produced in
Experimental allergic optic neuritis in guinea pigs: preliminary report Narsing A. Rao, Mark O. M. Tso," and Lorenz E. Zimmerman An experimental model for acute allergic optic neuritis was produced in
Coagulative necrosis in a malignant melanoma of the choroid at the macula with extensive subretinal hemorrhage
 Coagulative necrosis in a malignant melanoma of the choroid at the macula with extensive subretinal hemorrhage Robert D. Yee, Robert Y. Foos, and Bradley R. Straatsma The authors present a case report
Coagulative necrosis in a malignant melanoma of the choroid at the macula with extensive subretinal hemorrhage Robert D. Yee, Robert Y. Foos, and Bradley R. Straatsma The authors present a case report
STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF RETINAL NEOVASCULARIZATION ROLE OF LACTIC ACID*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 75. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF RETINAL NEOVASCULARIZATION ROLE OF LACTIC ACID* BY G. IMRE 2nd Department of Ophthalmology, University Medical School, Budapest, Hungary ACCORDING
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 75. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF RETINAL NEOVASCULARIZATION ROLE OF LACTIC ACID* BY G. IMRE 2nd Department of Ophthalmology, University Medical School, Budapest, Hungary ACCORDING
sheath syndrome Bilateral superior oblique tendon of uniovular twins Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one Brit. J. Ophthal.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 466 Bilateral superior oblique tendon sheath syndrome Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one of uniovular twins RONALD F. LOWE Melbourne, Australia Brown (I950) defined
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 466 Bilateral superior oblique tendon sheath syndrome Occurrence and spontaneous recovery in one of uniovular twins RONALD F. LOWE Melbourne, Australia Brown (I950) defined
