following its stimulation. joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to
|
|
|
- Melissa Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 612.44: THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for publication 2nd July 1937.) THE extensive literature dealing with the innervation of the thyroid has been reviewed by Marine [1922], Crawford and Hartley [1925], Smith and Moloy [1930], and, especially from the anatomical viewpoint, by Teitelbaum [1934]. Our present conception of this innervation is largely based on the work of Nonidez [1931]. By careful dissection and serial sections, using foetuses and puppies, Nonidez found a distinct nerve bundle entering the thyroid gland, which received branches from the superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic and from the superior laryngeal branch of the vagus, these tributaries uniting to form a common trunk, which passed into the gland along the course of the superior thyroid artery and its branches. The research here recorded was directed towards the identification of this nerve bundle in the adult dog and the elicitation of results following its stimulation. ANATOMICAL OBSERVATIONS. Initial dissections were carried out on a specimen preserved with formalin and glycerine, with arterial injection of dye. After the usual exposure the two lobes of the thyroid were dissected, care being taken to avoid severing any nerves. No nerves could be found entering the substance of the gland directly, but a small bundle of nerve fibres joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to this vessel. On each side this nerve bundle ended in twigs, which entered the gland along with the arterial branches. The nerve was traced cephalad on each side, as it courses in the fascia between the carotid artery and the larynx, and its upper origin followed, after reflecting muscles and other structures which intervened. The nerve was found to derive fibres from the superior cervical ganglion at its 1 The experiments recorded in this paper were carried out by the first-named author as part of his work for the degree of Bachelor of Science in Medicine of the University of Manitoba. VOL. XXVII., NO
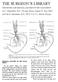
2 210 Ross and Moorhouse junction with the vago-sympathetic trunk, and from the superior laryngeal branch of the vagus, as Nonidez has described. The nerve was sometimes found to receive branches from the vago-sympathetic trunk as well as the above-named branches. Including post-mortem material and the subjects of the operative experiments to be described, the right thyroid nerve was found by dissection in 20 out of 22 dogs, and the left thyroid nerve in 11 out of 13 dogs. In 2 animals neither right nor left nerve could be found; these were small dogs, and the nerve was probably missed because of its insignificant size. The nerve was found most easily in large young dogs, and in later experiments such animals were selected for this work. Search in the fascia between the common carotid artery and the larynx, just cephalad to the superior thyroid artery, usually revealed the nerve. The nerves on both sides can be reached by using a transverse incision of 2-1 inches at the level of the cricoid cartilage. For prolonged electrical stimulation and for the recording of the blood-flow further dissection is required to expose the nerve and the thyroid veins. The origin of ten thyroid nerves was carefully traced. These were found to have a contribution from the superior cervical ganglion in every case. The superior laryngeal branch TUYPOID NEP\/1 of the vagus supplied twigs in nine cases IN TwE DOG out of ten. The vagus, either from the...v vaqu3 Ncrvc ganglion nodosum or from the vago upcrior Cervical sympathetic trunk, gave direct branches Ganqhonlol S4mpathCfC in four cases. One nerve had a com IConnecctions bctween&c~t andvqo. S4mpG MM Trunk munication from the external laryngeal Ncrvcs t. Wa of Carotid nerve, as well as its branch from the Artcrqat Bifurcation superior cervical ganglion and the vago- --- Supcrior Lar4Wnqel sympathetic trunk. Another nerve, whose l/-----twypoid NEP'J( beginning was not traced, had a com- Common Carotid Artcr4municating twig from the external laryngeal '.uperior Thqroid ABcri near the entrance of that nerve into the a'd Larqnqca.1 branch.-thqroid Gland laryngeal muscles. The course of the nerve (Rlqht Lobe) was usually at first posterior to the internal carotid artery, then medial to this vessel Fic. 1.-Mounted dissection showing usual arrangement of and between the common carotid and the thyroid innervation. larynx to the superior thyroid artery. The terminal branchings were fibres which entered the superior lobe of the gland with the branches of the superior thyroid artery. A thorough search was made in all the dissections for nerves apart from this bundle, but none were found. It is possible that some small fibres course to the gland along with other blood-vessels, but it appears that the thyroid nerve constitutes the chief supply. Fig. 1 is a photograph of a mounted and labelled dissection and shows the nerve with its branches as most usually found.
3 The Thyroid Nerve in the Dog and its Function 211 PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPERIMENTS. The rate of blood-flow through the gland was studied in 6 dogs to ascertain the results of stimulation of the nerves. The dogs were FIa. 2.-Perfused thyroid gland. Stimulation of thyroid nerve. FIG. 3.-Stimulation of the thyroid nerve after ergotoxine. The drop record of the right-hand tracing is somewhat faint, and dots have been placed above each drop signal. anawsthetised with morphine and urethane, and the nerves exposed as described. The veins at the lower pole of the gland were cannulated,
4 212 Ross and Moorhouse and the outflow was collected in a vessel filled with a saturated solution of magnesium sulphate, with a drop record of the overflow. Blood pressure was recorded by a mercury manometer. In some experiments the gland was perfused with defibrinated blood at constant pressure and body temperature, with a drop record of the venous outflow. The thyroid nerve and its branches were stimulated with faradic current from a Harvard inductorium with 3 volts in the circuit. Results. Stimulation of the thyroid nerve consistently produced a slowing of the blood-flow through the thyroid both in the intact and perfused gland. This effect was recorded many times, and a typical tracing is shown in fig. 2. The slowing of flow occurred in dogs with intact thyroids independently of changes in the blood-pressure, which were usually insignificant. The constriction was uninfluenced by the injection of atropine or small doses of ergotoxine. With larger dosage FiG. 4.-Stimulation of branch from external laryngeal nerve. indicates the duration of the stimulus. The top tracing of the latter drug stimulation of the thyroid nerve resulted in an acceleration of blood-flow (fig. 3). Constriction effects following the stimulation of the cervical sympathetic have been previously noted by Mason, Markowitz, and Mann [1930], using a plethysmograph method. Stimulation of the vagi did not give consistent results. With the gland intact such stimulation produces passive changes secondary to blood-pressure variations. A dilator response was occasionally recorded on ipsilateral vagus stimulation with the perfused gland. A noteworthy response was obtained in the dog mentioned, in which a communicating branch joined the thyroid nerve from the external laryngeal. Stimulation of this branch caused a slight but definite acceleration of the blood-flow repeatedly (fig. 4). Pilocarpine caused dilatation, and adrenalin a constriction of the vessels. These experiments seem to afford satisfactory evidence that the
5 The Thyroid Nerve in the Dog and its Function 213 thyroid nerve contains both constrictor and dilator fibres. It is possible that the nervous control of the gland, by impulses passing along this nerve, may, through regulation of its blood-flow, play a definite role in the rate of discharge into the general circulation. The results point to the predominance of a sympathetic constrictor effect with the ordinary methods of stimulation. HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES. In 3 dogs the right thyroid nerve was cut, and several weeks later the animals were killed and the thyroids examined histologically. In several experiments all isthmus connexions between the right and left glands were severed, and the right thyroid nerve electrically stimulated for 2 to 3 hours. After this procedure the glands were histologically examined and compared. No significant difference could be detected in the tissue of the glands thus treated. Probably experiments of a much greater duration will be needed to produce demonstrable changes. SUMMARY. The thyroid nerve described by Nonidez in puppies and canine foetuses has been found in adult dogs. It is usually made up of nerve fibres derived from the superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic and from the superior laryngeal branch of the vagus. The vagus fibres may arise from the ganglion nodosum or the vago-sympathetic trunk, and occasionally from the external laryngeal nerve. The thyroid nerve terminates in, branches which enter the thyroid with the branches of the superior thyroid artery. Stimulation of the thyroid nerve consistently slows the flow of blood through the gland. Acceleration of the blood-flow has been obtained by stimulating the ipsilateral vagus and, in one instance, fibres from the external laryngeal nerve. These results, indicating that the thyroid has a constant constrictor and some dilator innervation, suggest an indirect nervous control of the output of thyroid hormone into the blood-stream. Histological changes in the thyroid, after electrical stimulation of the thyroid nerve for some hours, could not be demonstrated. Section of the nerve, allowing time for degeneration, produced no demonstrable histological change.
6 214 The Thyroid Nerve in the Dog and its Function REFERENCES. CRAWFORD, J. H., and HARTLEY, J. N. J. (1925). J. exp. Med. 42, 179. MARINE, D. (1922). Phy8iol. Rev. 2, 521. MASON, J. B., MARKOWITZ, J., and MANN, F. C. (1930). Amer. J. Physiol. 94, 125. NONIDEZ, J. F. (1931). Amer. J. Anat. 48, 299. SMITH, I. H., and MOLOY, H. C. (1930). Anat. Ree. 45, 393. TEITELBAUM, H. A. (1934). Bull. Sch. Med. Univ. Maryland, 18, 77.
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
University College, Cork.)
 612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
(From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION
 Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the
![[1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the [1920], in studies on the human pleural membrane, pointed out the](/thumbs/84/89127006.jpg) 'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
'ca -.101 6II.25:6II.OI8.86 NERVES AND NERVE ENDINGS IN THE VISCERAL PLEURA OF THE CAT. BY A. I. G. McLAUGHLIN. (From the Unit Laboratories, University College Hospital Medical School.) (Received September
published by Hektoen and SchuIhof (1), and since the appearance
 ON THE INNERVATION AND SECRETORY PATH OF THE THYROID GLAND. BY C. S. HICKS (Beit Memorial Fellow). (From the Biochemistry Laboratories, Cambridge, and Physiology Department, University of Adelaide.) IN
ON THE INNERVATION AND SECRETORY PATH OF THE THYROID GLAND. BY C. S. HICKS (Beit Memorial Fellow). (From the Biochemistry Laboratories, Cambridge, and Physiology Department, University of Adelaide.) IN
McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of
![McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of McSwiney and Wadge [1930] described the effects on the stomach of](/thumbs/83/87976616.jpg) 6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
6I2.328:6I2.898 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. II. The effect of stimulation of the peri-arterial nerves on the stomach and small intestine. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND J. M. ROBSON. (Department
ansesthesia; an oncometer was used for measurement of the splenic Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
6I2.4I3:6I2.I43 CAUSE OF RHYTHMICAL. CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN. BY J. BARCROFT AN Y. NISIMARU' (Okayama). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) Roy [1881] was the first to discover the rhythmical
show-n to give off a branch, and sometimes two or three branches, to
 THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
blood-vessels of the isolated perfused lungs of the rat. Both Hirakawa
 547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 119-125. LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS BY N. ASSARSON AND N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden (Received October 8, 1963)
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 119-125. LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS BY N. ASSARSON AND N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden (Received October 8, 1963)
gland, the tongue and the sweat glands of the cat. The submaxillary
 306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
D."espite numerous anatomic and physiologic
 Trigeminal pathway for afferent fibers from the oculomotor nerves William S. Joffe, Andrew J. Gay, and C. Courtney Antrim Stimulation studies in the cat have shown that the afferent fibers for the oculorespiratory
Trigeminal pathway for afferent fibers from the oculomotor nerves William S. Joffe, Andrew J. Gay, and C. Courtney Antrim Stimulation studies in the cat have shown that the afferent fibers for the oculorespiratory
University of Leeds.)
 6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
it by the sympathetic nerve.
 OBSERVATIONS ON AUGMENTED SALIVARY SECRETION. BY G. V. ANREP. * (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) IN 1889 Langley described a peculiar effect of stimulation of the cerebral
OBSERVATIONS ON AUGMENTED SALIVARY SECRETION. BY G. V. ANREP. * (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) IN 1889 Langley described a peculiar effect of stimulation of the cerebral
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
experimer,ts, and more particularly from the fact that adrenalin apnoea
 THE ACTION OF ADRENALIN ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. BYA. ST G. HUGGETT (Beit Memorial Research Fellow) AND J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) IN a previous
THE ACTION OF ADRENALIN ON THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. BYA. ST G. HUGGETT (Beit Memorial Research Fellow) AND J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) IN a previous
striking difference between these two animals in respect of the sympathetic
 THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Since, for many months after section of the right vagus in the neck,
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
Circulation," Anrep and Starling(l) were unable to obtain evidence of
 CARDIOVASCULAR REFLEXES. BY I. DE BURGH DALY AND E. B. VERNEY (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Physiology Institute, Cardi.) DURING an investigation of the "Central and Reflex Regulation of the
CARDIOVASCULAR REFLEXES. BY I. DE BURGH DALY AND E. B. VERNEY (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (From the Physiology Institute, Cardi.) DURING an investigation of the "Central and Reflex Regulation of the
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Schaper (1892), in his studies of the histology of the 'glandula carotica',
 347 J. Physiol. (I952) II7, 347-358 THE BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE CAROTID BODY IN DOGS AND RABBITS CATS, BY D. CHUNGCHAROEN, M. DE BURGH DALY AND A. SCHWEITZER From the Department of Physiology, University College,
347 J. Physiol. (I952) II7, 347-358 THE BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE CAROTID BODY IN DOGS AND RABBITS CATS, BY D. CHUNGCHAROEN, M. DE BURGH DALY AND A. SCHWEITZER From the Department of Physiology, University College,
administration of adrenaline or in cases of increased perfusion pressure. approximately the same within fairly wide variations of the systemic
 6I2. I72. I THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE BLOOD IN THE CORONARY BLOOD VESSELS. BY G. V. ANREP, A. BLALOCK AND M. HAMMOUDA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) As a result of experiments on perfused
6I2. I72. I THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE BLOOD IN THE CORONARY BLOOD VESSELS. BY G. V. ANREP, A. BLALOCK AND M. HAMMOUDA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) As a result of experiments on perfused
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta.
 Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
Multiple Neurovascular... Pit Baran Chakraborty, Santanu Bhattacharya, Sumita Dutta. Fig-3: Showing high formation of Median nerve. Fig-1: Showing atypical formation of cords of Brachial plexus. 1 = Upper
however, to have been directly studied in any of the numerous observations
 ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
6I :6I2.I83 BY ALISON S. DALE. concluded that the apparent vaso-constriction obtained by F r6 hli c h and
 6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus.
 THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
SUPERSENSITIVITY OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND FOLLOWING EXCLUSION OF THE POSTGANGLIONIC PARASYMPATHETIC NEURONE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 356. SUPERSENSITIVITY OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND FOLLOWING EXCLUSION OF THE POSTGANGLIONIC PARASYMPATHETIC NEURONE BY N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 356. SUPERSENSITIVITY OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND FOLLOWING EXCLUSION OF THE POSTGANGLIONIC PARASYMPATHETIC NEURONE BY N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University
Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands
 Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
UNCERTAINTY as to the completeness
 Functional Analysis of the Vasomotor Innervation of the Dog's Hind Footpad By W. C. RANDALL, PH.D., W. F. ALEXANDER, PH.D., J. W. COX, M.D., AND A. B. HERTZMAN, PH.D. Vascular responses in the large central
Functional Analysis of the Vasomotor Innervation of the Dog's Hind Footpad By W. C. RANDALL, PH.D., W. F. ALEXANDER, PH.D., J. W. COX, M.D., AND A. B. HERTZMAN, PH.D. Vascular responses in the large central
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
ISOLATED AND INNERVATED ATRIA AND VESSELS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 117. THE ACTION OF SYMPATHETIC BLOCKING AGENTS ON ISOLATED AND INNERVATED ATRIA AND VESSELS BY S. HUKOVIC* From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (RECEIVED
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 117. THE ACTION OF SYMPATHETIC BLOCKING AGENTS ON ISOLATED AND INNERVATED ATRIA AND VESSELS BY S. HUKOVIC* From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (RECEIVED
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
King's College, London.)
 THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
tone. The observations were taken to mean that sympathetic stimulation was
 289 J. Physiol. (1942) IOI, 289-303 577.I74.5:6I2.823.5 AN ACTION OF ADRENALINE ON TRANSMISSION IN SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA, WHICH MAY PLAY A PART IN SHOCK BY EDITH BCLBRING AND J. H. BURN, From the Department
289 J. Physiol. (1942) IOI, 289-303 577.I74.5:6I2.823.5 AN ACTION OF ADRENALINE ON TRANSMISSION IN SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA, WHICH MAY PLAY A PART IN SHOCK BY EDITH BCLBRING AND J. H. BURN, From the Department
Prom the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
 365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
365 J. Physiol. (I95I) II3, 365-37I EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE ON CORONARY FLOW AND HEART CONTRACTION, AS RECORDED CONCURRENTLY IN THE ISOLATED RABBIT HEART BY F. C. LU* AND K. I. MELVILLE Prom the Department
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
Histology. Dr.shatarat
 Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
Histology Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Cells of the adenohypophysis adenohypophysis Dr.shatarat Dr.shatarat Adenohypophysis high power acidopill basophill Chromophobes Dr.shatarat 1-Chromophils
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland
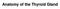 Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
612.I73:6I2.I3. mammary and mediastinal vessels tied off. The thoracic wall on the left
 612.I73:6I2.I3 CARDIAC OUTPUT AND BLOOD DISTRIBUTION. By H. BAR CROFT (Harmsworth Scholar, St Mary's Hospital, London). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE methods for the measurement of
612.I73:6I2.I3 CARDIAC OUTPUT AND BLOOD DISTRIBUTION. By H. BAR CROFT (Harmsworth Scholar, St Mary's Hospital, London). (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THE methods for the measurement of
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
(Received June 7, 1934.)
 121 6I2.792.8:6I2.OI8 THE CHEMICAL TRANSMISSION OF SECRETORY IMPULSES TO THE SWEAT GLANDS OF THE CAT. BY H. H. DALE AND W. FELDBERG. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, Hampstead, London,
121 6I2.792.8:6I2.OI8 THE CHEMICAL TRANSMISSION OF SECRETORY IMPULSES TO THE SWEAT GLANDS OF THE CAT. BY H. H. DALE AND W. FELDBERG. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, Hampstead, London,
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON VASOMOTOR REFLEXES.
 577.174.6:612.181 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON VASOMOTOR REFLEXES. By LIANG-WEI CHU and FONG-YEN Hsu. From the Institute of Psychology, Academia Sinica, Nanking. (Received for publication 23rd October 1937.)
577.174.6:612.181 THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON VASOMOTOR REFLEXES. By LIANG-WEI CHU and FONG-YEN Hsu. From the Institute of Psychology, Academia Sinica, Nanking. (Received for publication 23rd October 1937.)
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 5. NERVES Q1. Which of the following classifications of the nervous systems is correct? A. The autonomic nervous system is composed of the brain, cranial nerves and spinal nerves.
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
CARDIAC OUTPUT DURING EXCITATION OF CHEMO-
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 372. CARDIAC OUTPUT DURING EXCITATION OF CHEMO- REFLEXES IN THE CAT BY GWENDA R. BARER AND E. NUSSER From the Nuffield Institute for Medical Research, University of Oxford
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 372. CARDIAC OUTPUT DURING EXCITATION OF CHEMO- REFLEXES IN THE CAT BY GWENDA R. BARER AND E. NUSSER From the Nuffield Institute for Medical Research, University of Oxford
The sympathetic nerve fibres which originate in the thoracic part of. postganglionic but does not affect preganglionic nerve fibres, Langley has
 532 PHYSIOLOGY: S. J. MELTZER PROC. N. A. S. ARE THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANLIA INDISPENSABLE TO THE MAINTENANCE OF LIFE? By S. J. MULTZUR ROCKUPSLLUR INSTITUTh FOR MUDICAL RuSZARCH Read before the Academy,
532 PHYSIOLOGY: S. J. MELTZER PROC. N. A. S. ARE THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANLIA INDISPENSABLE TO THE MAINTENANCE OF LIFE? By S. J. MULTZUR ROCKUPSLLUR INSTITUTh FOR MUDICAL RuSZARCH Read before the Academy,
Grossman, 1953), and there is little information so far concerning its function
 52 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 52-57 A SURGICAL APPROACH TO THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANGLION AND RELATED STRIJCTURES IN THE SHEEP BY THE LATE A. B. APPLETON* AND G. M. H. WAITES From the Zoological Society of
52 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 52-57 A SURGICAL APPROACH TO THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANGLION AND RELATED STRIJCTURES IN THE SHEEP BY THE LATE A. B. APPLETON* AND G. M. H. WAITES From the Zoological Society of
Cannon(3) and Elliott(4). The action of these fibres has thrown a new
 ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
INTRAHEPATIC VASCULAR PATHWAYS. By W. H. H. ANDREWS
 INTRAHEPATIC VASCULAR PATHWAYS. By W. H. H. ANDREWS and I. DEL Rio LOZANO. From the Department of Pharmacology, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London, W. 2. (Received for publication 15th September
INTRAHEPATIC VASCULAR PATHWAYS. By W. H. H. ANDREWS and I. DEL Rio LOZANO. From the Department of Pharmacology, St. Mary's Hospital Medical School, London, W. 2. (Received for publication 15th September
(Received 17 July 1945)
 392 J. Physiol. (1946) I04, 392-403 547 * 435-292: 612. I7 THE STIMULATING ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINE ON THE HEART BY R. J. S. McDOWALL, King's College, London (Received 17 July 1945) In 1882 Gaskell, when
392 J. Physiol. (1946) I04, 392-403 547 * 435-292: 612. I7 THE STIMULATING ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINE ON THE HEART BY R. J. S. McDOWALL, King's College, London (Received 17 July 1945) In 1882 Gaskell, when
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
physiological stimulus of expansion and collapse of the lungs, respectively.
 446 J. Physiol. (I943) IOI, 446-459 6I2.288 THE ORIGIN OF THE INFLATION AND THE DEFLATION PULMONARY REFLEXES BY M. HAMMOUDA, ADLI SAMAAN AND W. H. WILSON From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine,
446 J. Physiol. (I943) IOI, 446-459 6I2.288 THE ORIGIN OF THE INFLATION AND THE DEFLATION PULMONARY REFLEXES BY M. HAMMOUDA, ADLI SAMAAN AND W. H. WILSON From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine,
ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA
 1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
Nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerves and anatomical findings during thyroid surgery: report of three cases
 Kato et al. Surgical Case Reports (2016) 2:44 DOI 10.1186/s40792-016-0170-5 CASE REPORT Nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerves and anatomical findings during thyroid surgery: report of three cases Kumiko
Kato et al. Surgical Case Reports (2016) 2:44 DOI 10.1186/s40792-016-0170-5 CASE REPORT Nonrecurrent inferior laryngeal nerves and anatomical findings during thyroid surgery: report of three cases Kumiko
Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011
 Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011 The AV node is the soul of the heart, and whoever understands its anatomy and electrophysiology
Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011 The AV node is the soul of the heart, and whoever understands its anatomy and electrophysiology
however, reduced after parasympathetic denervation [Nordenfelt et al., 1960]. opposite to those caused by parasympathetic denervation.
![however, reduced after parasympathetic denervation [Nordenfelt et al., 1960]. opposite to those caused by parasympathetic denervation. however, reduced after parasympathetic denervation [Nordenfelt et al., 1960]. opposite to those caused by parasympathetic denervation.](/thumbs/90/101412039.jpg) CHOLINE ACETYLASE IN SALIVARY GLANDS OF THE CAT AFTER SYMPATHETIC DENERVATION. By IVAR NORDENFELT. From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden. (Received for publication 20th April 1964)
CHOLINE ACETYLASE IN SALIVARY GLANDS OF THE CAT AFTER SYMPATHETIC DENERVATION. By IVAR NORDENFELT. From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden. (Received for publication 20th April 1964)
Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid. Chapter 133: Anatomy. Daniel O. Graney, Ronald C. Hamaker. Development of the Thyroid Gland
 Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid Chapter 133: Anatomy Daniel O. Graney, Ronald C. Hamaker Development of the Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland begins as an endodermal bud from the floor of the pharynx between
Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid Chapter 133: Anatomy Daniel O. Graney, Ronald C. Hamaker Development of the Thyroid Gland The thyroid gland begins as an endodermal bud from the floor of the pharynx between
(From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE OXYGEN EXCHANGE OF THE SUPRARENAL GLAND. BY K. 0. NEUMAN. (From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, Cambridge.) THIS paper deals with the question of the amount of oxygen taken in by a unit weight of the
THE OXYGEN EXCHANGE OF THE SUPRARENAL GLAND. BY K. 0. NEUMAN. (From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, Cambridge.) THIS paper deals with the question of the amount of oxygen taken in by a unit weight of the
J. Physiol. (I956) I33,
 232 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 232-242 A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF THE PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE AORTIC NERVE ON THE REFLEX DEPRESSOR RESPONSES By W. W. DOUGLAS, J. M. RITCHIE AND W. SCHAUMANN*
232 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 232-242 A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF THE PATTERN OF ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE AORTIC NERVE ON THE REFLEX DEPRESSOR RESPONSES By W. W. DOUGLAS, J. M. RITCHIE AND W. SCHAUMANN*
Junctional Tissues of Human Heart
 1 Junctional Tissues of Human Heart Mr. Rupajit Das, Associate Professor, M.B.B. College, Agartala Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation
1 Junctional Tissues of Human Heart Mr. Rupajit Das, Associate Professor, M.B.B. College, Agartala Cardiac muscle consists essentially of certain specialised structures which are responsible for initiation
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
skeletal muscle, it was concluded that the vasodilatation is brought about by
 289 J. Physiol. (I954) I23, 289-3 THE EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON THE BLOOD VESSELS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN THE CAT. AN INVESTIGATION OF VASOMOTOR AXON REFLEXES BY S. M. HILTON From the Physiological Laboratory,
289 J. Physiol. (I954) I23, 289-3 THE EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON THE BLOOD VESSELS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN THE CAT. AN INVESTIGATION OF VASOMOTOR AXON REFLEXES BY S. M. HILTON From the Physiological Laboratory,
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Did you ever stop to think about what happens under the collar?
 Did you ever stop to think about what happens under the collar? For humans we know that only 1 whiplash accident can cause long-term pain and suffering. The dog s anatomy is basically the same as ours.
Did you ever stop to think about what happens under the collar? For humans we know that only 1 whiplash accident can cause long-term pain and suffering. The dog s anatomy is basically the same as ours.
6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) heart-lung preparation. The object of this communication is to show that
 6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33 III. THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. The dependence of changes in the coronary blood flow on cardiac and local vascular factors. BY H. HA.USLER (Rockefeller Travelling Fellow). (From the Physiological
6iI.I32.2:6I2.I33 III. THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. The dependence of changes in the coronary blood flow on cardiac and local vascular factors. BY H. HA.USLER (Rockefeller Travelling Fellow). (From the Physiological
Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions.
 Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
Section 1 Anatomy Chapter 1. Trachea 1 Candidate s instructions Look at this cross-section taken at the level of C5. Answer the following questions. Pretracheal fascia 1 2 5 3 4 Questions 1. Label the
THE ACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Brit. J. Pharinacol. (1963), 20, 171-177. THE ACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM BY G. F. ABERCROMBIE AND B. N. DAVIES From the Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. Pharinacol. (1963), 20, 171-177. THE ACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM BY G. F. ABERCROMBIE AND B. N. DAVIES From the Department of Physiology,
THE NATURE OF THE ATRIAL RECEPTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR A REFLEX INCREASE IN ACTIVITY IN EFFERENT CARDIAC SYMPATHETIC NERVES
 Quaterly Journal of Experimental Physiology (1982), 67, 143-149 Printed in Great Britain THE NATURE OF THE ATRIAL RECEPTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR A REFLEX INCREASE IN ACTIVITY IN EFFERENT CARDIAC SYMPATHETIC
Quaterly Journal of Experimental Physiology (1982), 67, 143-149 Printed in Great Britain THE NATURE OF THE ATRIAL RECEPTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR A REFLEX INCREASE IN ACTIVITY IN EFFERENT CARDIAC SYMPATHETIC
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam
 Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
Many authors (Hering, 1927; Koch 1931; Heymans, Bouckaert & Regniers,
 259 J. Physiol. (I949) I09, 259-27I 6I2.0I4.424.089:6I2.I4 PRESSOR RESPONSES TO ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE CAROTID SINUS NERVE IN CATS BY E. NEIL AND C. R. M. REDWOOD Department of Physiology, School
259 J. Physiol. (I949) I09, 259-27I 6I2.0I4.424.089:6I2.I4 PRESSOR RESPONSES TO ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF THE CAROTID SINUS NERVE IN CATS BY E. NEIL AND C. R. M. REDWOOD Department of Physiology, School
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Vasculature and innervation of the heart. A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department
 Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
INTRA HEPATIC PATTERN OF PORTAL VEIN IN DOG S LIVER: A CORROSION CAST STUDY
 Original Research Article INTRA HEPATIC PATTERN OF PORTAL VEIN IN DOG S LIVER: A CORROSION CAST STUDY Shikha Sharma *1, Tejendra Singh, Ekramuddin, Bhawani Shankar Modi. ABSTRACT Introduction: The variations
Original Research Article INTRA HEPATIC PATTERN OF PORTAL VEIN IN DOG S LIVER: A CORROSION CAST STUDY Shikha Sharma *1, Tejendra Singh, Ekramuddin, Bhawani Shankar Modi. ABSTRACT Introduction: The variations
THE SACRAL PARASYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE COLON
 THE SACRAL PARASYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE COLON RUSSELL T. WOODBURNE Department of Anatomy, University of Michigan Hedical School, Ann Arbofi TWO FIGURES Autonomic nerves distribute by a variety of
THE SACRAL PARASYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE COLON RUSSELL T. WOODBURNE Department of Anatomy, University of Michigan Hedical School, Ann Arbofi TWO FIGURES Autonomic nerves distribute by a variety of
CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
The arteries of the human kidney
 J. Anat. (1966), 100, 4, pp. 881-894 881 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain The arteries of the human kidney BY H. FINE AND E. N. KEEN Department of Anatomy, University of Natal INTRODUCTION A study
J. Anat. (1966), 100, 4, pp. 881-894 881 With 8 figures Printed in Great Britain The arteries of the human kidney BY H. FINE AND E. N. KEEN Department of Anatomy, University of Natal INTRODUCTION A study
Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1961, 5(
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Responsiveness of the Denervated Ad Author(s) Yamashita, Kazukuni; Jinnai, Seiich Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1961, 5( Issue Date 1961-03-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/15441
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Responsiveness of the Denervated Ad Author(s) Yamashita, Kazukuni; Jinnai, Seiich Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1961, 5( Issue Date 1961-03-25 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/15441
Rosenthal(4), Hill(5), Lumsden(6), J. F. and C. Heymans(l, Gesell(7m, C. F. Schmidt(s)). These facts are taken by several authors
 6I2.288:6II.I33 6I2.284.2:577.I74.5 SINUS CALOTICUS AND RESPIRATORY REFLEXES. I. Cerebral blood flow and respiration. Adrenaline apnceal. BY C. HEYMANS AND JEAN J. BOUCKAERT. (From the Department of Pharmacology,
6I2.288:6II.I33 6I2.284.2:577.I74.5 SINUS CALOTICUS AND RESPIRATORY REFLEXES. I. Cerebral blood flow and respiration. Adrenaline apnceal. BY C. HEYMANS AND JEAN J. BOUCKAERT. (From the Department of Pharmacology,
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
of the Axillary Artery
 Variation in the Origins of the Branches of the Axillary Artery DONALD F. HUELKE Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan Variability in the origin of certain
Variation in the Origins of the Branches of the Axillary Artery DONALD F. HUELKE Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan Variability in the origin of certain
