IN VIVO MUTAGENIC EFFECT OF VERY LOW DOSE RADIATION
|
|
|
- Kelly Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 4 Issue 4 Article IN VIVO MUTAGENIC EFFECT OF VERY LOW DOSE RADIATION Pamela J Sykes Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia Tanya K Day Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia Sarah J Swinburne Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia Joanne M Lane Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia Alexander A Morley Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia See next page for additional authors Follow this and additional works at: Recommended Citation Sykes, Pamela J; Day, Tanya K; Swinburne, Sarah J; Lane, Joanne M; Morley, Alexander A; Hooker, Anthony M; and Bhat, Madhava (2006) "IN VIVO MUTAGENIC EFFECT OF VERY LOW DOSE RADIATION," Dose-Response: An International Journal: Vol. 4 : Iss. 4, Article 8. Available at: This Article is brought to you for free and open access by ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dose-Response: An International Journal by an authorized editor of ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst. For more information, please contact scholarworks@library.umass.edu.
2 IN VIVO MUTAGENIC EFFECT OF VERY LOW DOSE RADIATION Authors Pamela J Sykes, Tanya K Day, Sarah J Swinburne, Joanne M Lane, Alexander A Morley, Anthony M Hooker, and Madhava Bhat This article is available in Dose-Response: An International Journal:
3 Sykes et al.: In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation Dose-Response, 4(4): , 2006 Formerly Nonlinearity in Biology, Toxicology, and Medicine Copyright 2006 University of Massachusetts ISSN: DOI: /dose-response Sykes IN VIVO MUTAGENIC EFFECT OF VERY LOW DOSE RADIATION Pamela J. Sykes, Tanya K. Day, Sarah J. Swinburne, Joanne M. Lane, Alexander A. Morley, Antony M. Hooker Department of Haematology and Genetic Pathology, Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia Madhava Bhat Department of Medical Physics, Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide, South Australia Almost all of our knowledge about the mutational effect of radiation has come from high dose studies which are generally not relevant to public exposure. The pkz1 mouse recombination mutagenesis assay enables study of the mutational effect of very low doses of low LET radiation (μgy to cgy range) in a whole animal model. The mutational endpoint studied is chromosomal inversion which is a common mutation in cancer. We have observed 1) a non-linear dose response of induced inversions in pkz1 mice exposed to a wide dose range of low LET radiation, 2) the ability of low priming doses to cause an adaptive response to subsequent higher test doses and 3) the effect of genetic susceptibility where animals that are heterozygous for the Ataxia Telangiectasia gene (Atm) exhibit different responses to low dose radiation compared to their normal litter-mates. Keywords: Chromosomal inversion, X-radiation, Transgenic mouse mutagenesis model, Adaptive response INTRODUCTION It is known that as the dose of ionising radiation increases then the number of mutations resulting from that exposure increases. The relationship between dose of ionising radiation and DNA damage appears to be linear at high doses. The linear no threshold (LNT) model predicts that this relationship is also linear at low doses and that any dose above zero will result in some DNA damage. Almost all of the data on mutation in response to ionising radiation comes from studies of high doses. However, the population is normally unlikely to be exposed to high doses of radiation. There is little evidence that low doses of radiation (less than 0.1 Gy) are mutagenic and there is some suggestion that low doses of radiation may even be beneficial (Pollycove and Feinendegen 2003). It is important to determine whether there is a threshold dose at which no DNA damage occurs. There is, however, a paucity of in vivo or in vitro assays with the sensitivity to detect mutagenic responses to low doses of radiation. The majority of in vivo mouse studies showing the mutagenic Address correspondence to A/Professor Pamela J Sykes, Department of Haematology and Genetic Pathology, Flinders University and Medical Centre, Bedford Park, South Australia 5042 Australia. Phone: ; fax: ; pam.sykes@flinders.edu.au 309 Published by ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst,
4 Dose-Response: An International Journal, Vol. 4 [2014], Iss. 4, Art. 8 P. J. Sykes and others effect of X-radiation have used doses > 1 Gy (Winegar et al. 1994; Gossen et al. 1995). The pkz1 transgenic recombination mutagenesis model has proven to be a sensitive model for detecting chromosomal inversions in spleen in response to very low doses of three known chemical carcinogens, cyclophosphamide (Sykes et al. 1998), etoposide (Hooker et al. 2002) and mitomycin C (unpublished results). In the case of cyclophosphamide the model has been shown to be 4 orders of magnitude more sensitive at detecting inversions than other mouse models are at detecting point mutations (Kohler et al. 1991; Sykes et al. 1998). The mice contain a transgene which has the E. coli β-galactosidase gene (lacz) in reverse orientation to a chicken β-actin promoter complex. The lacz gene is flanked by the mouse V κ21c and J κ5 immunoglobulin recombination signal sequences (Matsuoka et al. 1991). When an inversion event occurs, facilitated by the mouse recombination signal sequences, the lacz gene is brought into correct juxtaposition with respect to the promoter complex and expression of the E. coli β-galactosidase message can occur (Fig 1). The E. coli β-galactosidase protein can then be detected in tissues in the animals by staining with the chromogenic substrate X-gal. Cells that undergo inversion events exhibit blue staining. The number of inversion events is determined by the ratio of the number of blue staining cells to the total number of cells counted. Inversion events have been detected in a wide range of pkz1 tissues, with most studies to date concentrating on spleen tissue. We set out to determine if the pkz1 recombination mutagenesis model would provide a sensitive mutation assay in response to single whole body doses of low dose, low LET radiation in order to determine if the LNT model applies at doses < 0.1 Gy. We also utilised the pkz1 model to study adaptive response and genetic susceptibility in response to low dose radiation exposure. FIGURE 1: The pkz1 transgenic mouse construct. LacZ, E. coli, β-galactosidase gene; EP, chicken β- actin enhancer/promoter complex; Ex1 and Ex2, chicken β-actin exons 1 and 2; V K21C and J K5, mouse immunoglobulin recombination signal sequences
5 Sykes et al.: In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation METHODS Mice A colony of pkz1 mice was maintained by breeding pkz1 mice to C57/BL6J mice. Double transgenic mice were bred by crossing pkz1 heterozygous mice with Atm heterozygous knock-out mice (Elson et al. 1994). Mice were screened for the presence of the lacz transgene and the Atm knock-out construct in DNA from tail clippings using polymerase chain reactions specific for the E. coli lacz gene and the Atm knock-out construct. Irradiation of Mice The mice were irradiated using a Philips deep X-ray unit. The machine was operated at 250 kv and 12 ma, HVL of 3 mm Cu, Source to Surface Distance (SSD) ranged from cm and field size was 25 cm x 25 cm. The X-ray machine output was calibrated according to IPEMB protocol (Institution of Physics and Engineering in Medicine and Biology 1996). This dosimetry system has a calibration factor that is traceable to the Australian Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety Agency. Irradiation was carried out after placing mice in a perspex mouse holder. Radiation doses less than 0.01 Gy were delivered at a SSD of 291 cm and using additional lead filters to reduce the dose rate. The control mice were also placed in the perspex holder for the same period of time but without the irradiator turned on. After irradiation the mice were returned to their normal housing cages where they were housed for three days. For adaptive response experiments, mice were exposed to a low priming dose of radiation and then a higher test dose 4 hours later. Control mice included sham-treated mice as well as priming dose only and test dose only. Histochemical Detection of Inversion Events The mice were euthanased by CO 2 asphyxiation and dissected. The spleen was snap frozen in OCT cryoprotectant embedding compound (Tissue-Tek) and stored at -20ºC. Frozen tissue sections were cut on a cryostat and stained for β-galactosidase (β-gal) expression using the method described in Sykes et al (1998). Briefly, 5 μm frozen spleen sections were fixed in glutaraldehyde, stained with X-gal and counter-stained with neutral red. E. coli β-galactosidase expressing cells (ie blue staining cells) were counted using light microscopy. Sixty random fields within each spleen were screened. The number of blue staining cells/total number of cells screened, were recorded. pkz1 transgenic mouse brain sections, which exhibit strong E. coli β-gal staining (Matsuoka et al. 1991), were used as a positive staining control. Spleen sections from a non-trans- 311 Published by ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst,
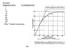
6 Dose-Response: An International Journal, Vol. 4 [2014], Iss. 4, Art. 8 genic mouse were used as a negative control. All slides were coded by another individual in the laboratory and then the slides were scored blind. The data were analysed using a two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test. RESULTS Threshold At high doses of radiation (> 0.1 Gy) an increase in chromosomal inversions was observed compared with the endogenous inversion frequency. Between 0.1 mgy and 100 mgy a decrease in inversions below endogenous frequency was observed, and at very low doses (< 0.01 mgy) an increase in inversions was again detected until the frequency returned to the endogenous frequency observed in the sham-treated animals. Adaptive Response Mice were treated with 0.01 Gy priming dose and then 1 Gy challenge dose 4 hours later. Control groups included sham-treated, priming alone and challenge alone. No difference was observed in mutation frequency between sham-treated animals and those receiving 0.01 Gy. There was a trend towards an increase in inversion frequency for the 1 Gy treatment groups. The groups that received a priming dose of 0.01 Gy followed by a challenge dose of 1 Gy 4 hours later showed a decrease in inversions to a level below endogenous frequency. Genetic Susceptibility pkz1 mice which have two normal copies of the Atm gene and pkz1 mice that were heterozygous knock-out for the Atm gene were exposed to 15 mgy of X-radiation. The sham-treated Atm heterozygous knock-out mice had an endogenous inversion frequency similar to the Atm normal pkz1 mice. Irradiated Atm heterozygous knock-out mice did however demonstrate fewer inversions after exposure to 15 mgy X-radiation than the Atm normal pkz1 mice. DISCUSSION P. J. Sykes and others The results presented here indicate that the pkz1 model will be a useful whole animal model for studying the mutagenic effect of low dose radiation. We observed an inversion response after exposure to doses of radiation that are orders of magnitude lower than have previously been reported. The dose-response observed was non-linear at doses less than 0.1 Gy. At very low doses and at high doses an increase in inversions was observed, and at intermediate doses a decrease below endogenous inversion frequency was observed. The shape of the dose-response observed is shown in Figure 2. The only report of a whole animal model exhibiting an induc
7 Sykes et al.: In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation FIGURE 2: Low dose radiation dose-response curve. Inversions were induced in pkz1 spleen at very low and at high doses of radiation exposure. Intermediate doses of radiation caused a decrease below endogenous inversion frequency. The straight line represents the LNT theory. tion of mutations at X-radiation doses of < 0.1 Gy was by Scheistl et al. (1994) where they found a linear dose-response relationship between 1 cgy and 1 Gy. The mechanism behind the non-linear response observed here is not known. The responses seen at the lowest doses must involve the bystander effect as not all cells will sustain direct DNA damage from the low dose radiation. Inversions will result when stem and loop structures are resolved by non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair. NHEJ will almost always result in a change to the DNA sequence and is therefore potentially mutagenic. An increase in inversions suggests an increase in NHEJ repair, and a decrease in inversions suggests a decrease in NHEJ repair. If double-strand DNA breaks are not repaired in a cell as a result of down-regulated NHEJ then the cell may apoptose, and therefore any mutations that have occurred in that cell will not become fixed. It is possible that the amount of DNA damage sustained at very low doses may not be enough to elicit a down-regulation of NHEJ. At high doses the cells may respond by up-regulating NHEJ in order to repair the very large number of DNA double-strand breaks that are sustained. The relevance of these results to human health will hinge on elucidating the down-stream effects of reduction and induction of inversion events at such low doses. The adaptive response can be defined as a change in sensitivity to radiation damage induced by a low dose, which is delivered prior to a larger challenge dose (Wolff 1998). This has the potential to affect the risk estimation of radiation exposure. The risk of damage from high dose radiation exposure may be decreased if there has been prior exposure to low dose radiation, affecting the validity of the risk predicted using the LNT theory. Our results strongly suggest that a low priming dose of Published by ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst,
8 Dose-Response: An International Journal, Vol. 4 [2014], Iss. 4, Art. 8 P. J. Sykes and others Gy is capable of reducing the frequency of inversions caused by a subsequent challenge dose of 1 Gy. The aim here was to determine if inversions could be used as an end-point to study adaptive response at doses of radiation that are lower than have previously been reported. These experiments suggest that the pkz1 mouse mutation model is an appropriate whole animal system for measurement of the adaptive radiation response. The priming dose (0.01 Gy) used in these experiments is amongst the lowest priming dose reported to be capable of inducing an adaptive response in either in vivo or in vitro studies (reviewed in Wolff 1998). The decrease in mutation frequency that we observed in the experiments performed here is also amongst the largest decrease in mutation frequency below that induced by the challenge dose to have been reported. Different individuals in the population will have different genetic susceptibilities to DNA damaging agents such as ionising radiation based on their ability to repair damaged DNA. Individuals homozygous for ATM mutations are sensitive to ionizing radiation. There is some evidence that individuals in the population who are carriers for an ATM mutation (approximately 1% of the population) may be more sensitive to radiation than normal individuals. Mouse Atm heterozygotes have an increased rate of cataract development after Gy radiation exposure (Worgul et al. 2002) and decreased life span after exposure to 4 Gy (Barlow et al. 1999) compared with normal mice. In addition, lymphocytes from human ATM heterozygotes exhibit greater cell death in response to low dose-rate radiation than normal individuals (West 1995). We utilised the pkz1 mouse model to determine whether carrying one defective Atm gene resulted in increased susceptibility to low dose radiation damage. Animals that were heterozygous for loss of function of an Atm gene exhibited a reduction in inversions below that of endogenous inversion frequency after a low dose radiation exposure compared with sham-treated heterozygous animals and also their normal litter-mates. The ATM protein plays an important role in both homologous recombination and NHEJ (Valerie and Povkirk 2003). A reduction in ATM protein in heterozygous animals may therefore lead to a reduction in NHEJ. Further study is required to determine the relevance of the reduction in NHEJ in ATM heterozygotes to human health. DNA double strand breaks are known to be the major lesion induced after X-irradiation. The pkz1 mutagenesis model allows measurement of inversion events, which arise through the repair of DNA double strand breaks. In spleen tissue in the pkz1 model, inversion events may be recognized and repaired using the RAG1/RAG2 mediated NHEJ machinery which is important in both repair of DNA double strand breaks and in the normal development of B- and T-cell receptors (reviewed in Lieber 1998). Investigation of the important enzymes in the NHEJ pathway (for example RAG-1, RAG-2, DNA-PK, Ku 70, Ku 86), will hopefully lead to further
9 Sykes et al.: In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation clues about the underlying mechanism of changes in inversions identified in the pkz1 mouse spleen in response to low dose radiation. The results presented here indicate that the pkz1 mouse model has the sensitivity to enable study of low dose radiation exposure which is relevant to human population exposure. The model can also be used to study adaptive response and genetic susceptibility in response to low dose radiation exposure. Our data using DNA inversions as a mutagenic endpoint indicate that the dose response to X-radiation is not linear and that the validity of the LNT model needs to be revisited. This will have an important impact when setting exposure limits and conditions for safe occupational and medical radiation exposure. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We wish to thank Professor Martin Lavin (Queensland Institute of Medical Research) for kindly providing heterozygous Atm mice to establish the pkz1/atm mouse colony. Research funded by the Low Dose Radiation Research Program, Biological and Environmental Research (BER), U.S. Department of Energy, grant # DE-FG02-01ER REFERENCES In vivo mutagenic effect of very low dose radiation Barlow C, Eckhaus MA, Schaffer AA and Wynshaw-Boris A Atm haploinsufficiency results in increased sensitivity to sublethal doses of ionizing radiation in mice. Nature Genet 21: Elson A, Wang Y, Daugherty CJ, Morton CC, Zhou F, Campos-Torres J and Leder P Pleiotropic defects in ataxia telangiectasia protein-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93: Gossen JA, Martus HJ, Wei JY and Vijg J Spontaneous and X-ray-induced deletion mutations in a LacZ plasmid-based transgenic mouse model. Mutat Res 331: Hooker AM, Horne R, Morley AA and Sykes PJ Dose-dependent increase or decrease of somatic intrachromosomal recombination produced by etoposide. Mutat Res 500: Institution of Physics and Engineering in Medicine and Biology The IPEMB code of practice for the determination of absorbed dose for X-rays below 300 kv generating potential (0.035 mm A1 4 mm Cu HVL; kv generating potential). Phys Med Biol 41: Kohler SW, Provost GS, Fieck A, Kretz PL, Bullock WO, Putman DL, Sorge JA and Short JM Analysis of spontaneous and induced mutations in transgenic mice using a lambda ZAP/lacI shuttle vector. Environ Mol Mutagen 18: Lieber MR. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis Award Lecture Pathological and physiological double-strand-breaks: roles in cancer, aging and the immune system. Am J Path 153: Matsuoka M, Nagawa F, Okazaki K, Kingsbury L, Yoshida K, Muller U, Larue DT, Winer JA and Sakano H Detection of somatic DNA recombination in the transgenic mouse brain. Science 254: Pollycove M and Feinendegen LE Radiation-induced versus endogenous DNA damage: possible effect of inducible protective responses in mitigating endogenous damage. Hum Exp Toxicol 22: Schiestl RH, Khogali F and Carls N Reversion of the mouse pink-eyed unstable mutation induced by low doses of X-rays. Science 266: Sykes PJ, Hooker AM, Harrington CS, Jacobs AK. Kingsbury L and Morley AA Induction of somatic intrachromosomal inversion events by cyclophosphamide in a transgenic mouse model. Mutat Res 397: Valerie K and Povkirk LF Regulation and mechanisms of mammalian double-strand break repair. Oncogene 22: Published by ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst,
10 Dose-Response: An International Journal, Vol. 4 [2014], Iss. 4, Art. 8 P. J. Sykes and others West CM, Elyan SA, Berry P, Cowan R and Scott D A comparison of the radiosensitivity of lymphocytes from normal donors, cancer patients and individuals with ataxia telangiectasia (A-T) and A-T heterozygotes. Int J Radiat Biol 68: Winegar RA, Lutze LH, Hamer JD, O Loughlin KG and Mirsalis JC Radiation-induced point mutations, deletions and micronuclei in laci transgenic mice. Mutat Res 307: Wolff S Aspects of the adaptive response to very low doses of radiation and other agents. Mutat Res 358: Wolff S The adaptive response in radiobiology: evolving insights and implications. Environ Health Perspect 106: Suppl. 1: Worgul BV, Smilenov L, Brenner DJ, Junk A, Zhou W and Hall EJ Atm heterozygous mice are more sensitive to radiation-induced cataracts than are their wild-type counterparts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:
THE PKZ1 RECOMBINATION MUTATION ASSAY: A SENSITIVE ASSAY FOR LOW DOSE STUDIES
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 4 Issue 2 Article 4 6-2006 THE PKZ1 RECOMBINATION MUTATION ASSAY: A SENSITIVE ASSAY FOR LOW DOSE STUDIES PJ Sykes Flinders University and Flinders Medical
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 4 Issue 2 Article 4 6-2006 THE PKZ1 RECOMBINATION MUTATION ASSAY: A SENSITIVE ASSAY FOR LOW DOSE STUDIES PJ Sykes Flinders University and Flinders Medical
LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 1 ADAPTIVE BIOLOGICAL RESPONSES FOLLOWING EXPOSURES TO IONIZING RADIATION Article 4 3-2007 LOW DOSES OF RADIATION REDUCE RISK IN VIVO REJ Mitchel
Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach. R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham
 Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch, AECL, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River
Radiation Protection in the World of Modern Radiobiology: Time for A New Approach R. E. J. Mitchel and D. R Boreham Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch, AECL, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY
 LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
LYMHOCYTE CHROMOSOMAL ABERRATION ASSAY IN RADIATION BIODOSIMETRY Dr. Birutė Gricienė 1,2 1 Radiation Protection Centre 2 Vilnius University Introduction Ionising radiation is a well-known mutagenic and
RADIATION-INDUCED NEOPLASTIC TRANSFORMATION IN VITRO, HORMESIS AND RISK ASSESSMENT
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 6 6-2007 RADIATION-INDUCED NEOPLASTIC TRANSFORMATION IN VITRO, HORMESIS AND RISK ASSESSMENT J Leslie Redpath University of California Irvine,
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 6 6-2007 RADIATION-INDUCED NEOPLASTIC TRANSFORMATION IN VITRO, HORMESIS AND RISK ASSESSMENT J Leslie Redpath University of California Irvine,
CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
 CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION Ron Mitchel Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River,
CANCER AND LOW DOSE RESPONSES IN VIVO: IMPLICATIONS FOR RADIATION PROTECTION Ron Mitchel Radiation Biology and Health Physics Branch Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, Chalk River Laboratories, Chalk River,
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting
 BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
BEIR VIII Planning Meeting Recent reviews and novel data - low dose radiobiology Simon Bouffler 17 November 2014 Outline Advisory Group on Ionising Radiation activities human radiosensitivity, transgenerational
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program
 U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program Update November 2010 ISCORS NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research The Department of Energy Office of
María José Mesa López
 María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
Standardization of dosimetry practices for small and large animal irradiation in radiobiological studies
 Standardization of dosimetry practices for small and large animal irradiation in radiobiological studies Abdul Kazi, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology University of Maryland
Standardization of dosimetry practices for small and large animal irradiation in radiobiological studies Abdul Kazi, Ph.D., DABR Assistant Professor, Department of Radiation Oncology University of Maryland
Radiation Carcinogenesis
 Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Radiation Carcinogenesis November 11, 2014 Dhyan Chandra, Ph.D. Pharmacology and Therapeutics Roswell Park Cancer Institute Email: dhyan.chandra@roswellpark.org Overview - History of radiation and radiation-induced
Mutagenesis. David M. DeMarini, Ph.D. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
 Mutagenesis David M. DeMarini, Ph.D. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ddemarini@nc.rr.com 1. DNA as the Target Mutagenesis Overview 2. DNA Damage (The Mutagenesis Paradigm) A. Types of Damage
Mutagenesis David M. DeMarini, Ph.D. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ddemarini@nc.rr.com 1. DNA as the Target Mutagenesis Overview 2. DNA Damage (The Mutagenesis Paradigm) A. Types of Damage
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
Genomic Instability Induced by Ionizing Radiation Christian Streffer Universitätsklinikum Essen, 45122 Essen, Germany INTRODUCTION In contrast to general assumptions it has frequently been shown that DNA
The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity
 International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity Simon Bouffler December 2009 Indicators of radiosenitivity In Patients
International Conference on Modern Radiotherapy The range of radiosensitivity in the human population: hyper- and hypo-sensitivity Simon Bouffler December 2009 Indicators of radiosenitivity In Patients
Radiation-Induced. Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro, Hormesis and Risk Assessment. Les Redpath Department of Radiation Oncology UC Irvine
 Radiation-Induced Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro, Hormesis and Risk Assessment Les Redpath Department of Radiation Oncology UC Irvine Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro Clear cancer-related related
Radiation-Induced Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro, Hormesis and Risk Assessment Les Redpath Department of Radiation Oncology UC Irvine Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro Clear cancer-related related
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1
 RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
RADIATION RESEARCH 18, 96-105 (1963) Early Repair Processes in Marrow Cells Irradiated and Proliferating in Vivo1 J. E. TILL AND E. A. McCULLOCH Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto,
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
mouse, which show a combination of unusual properties. The
 EFFECT OF X-RAYS ON THE MUTATION OF t-alleles IN THE MOUSE MARY F. LYON M.R.C. Radiobio!ogica! Research Unit, Harwell, Berkshire Received 18.ix.59 1.!NTRODUCTtON THE t-alleles are a long series of recessive
EFFECT OF X-RAYS ON THE MUTATION OF t-alleles IN THE MOUSE MARY F. LYON M.R.C. Radiobio!ogica! Research Unit, Harwell, Berkshire Received 18.ix.59 1.!NTRODUCTtON THE t-alleles are a long series of recessive
Chapter 2. Aims & Objectives
 2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
2.1. Statement of the problem: Earlier reports have shown ambiguous alteration of histone marks in response to DNA damage in asynchronized population of cells. These histone marks not only undergo dynamic
HUMAN LUNG CANCER RISKS FROM RADON PART II INFLUENCE FROM COMBINED ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER EFFECTS A MICRODOSE ANALYSIS
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 9 Issue 4 Article 8 12-2011 HUMAN LUNG CANCER RISKS FROM RADON PART II INFLUENCE FROM COMBINED ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER EFFECTS A MICRODOSE ANALYSIS
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 9 Issue 4 Article 8 12-2011 HUMAN LUNG CANCER RISKS FROM RADON PART II INFLUENCE FROM COMBINED ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER EFFECTS A MICRODOSE ANALYSIS
COMMENTARY ON USING LNT FOR RADIATION PROTECTION AND RISK ASSESSMENT
 Dose-Response, X:xxx xxx, 2010 Formerly Nonlinearity in Biology, Toxicology, and Medicine Copyright 2010 University of Massachusetts ISSN: 1559-3258 DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.10-003.Cuttler COMMENTARY
Dose-Response, X:xxx xxx, 2010 Formerly Nonlinearity in Biology, Toxicology, and Medicine Copyright 2010 University of Massachusetts ISSN: 1559-3258 DOI: 10.2203/dose-response.10-003.Cuttler COMMENTARY
Advances in biological dosimetry
 Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Advances in biological dosimetry A Ivashkevich 1,2, T Ohnesorg 3, C E Sparbier 1, H Elsaleh 1,4 1 Radiation Oncology, Canberra Hospital, Garran, ACT, 2605, Australia 2 Australian National University, Canberra
Genome Stability Department of Physiology
 Cytogenetic biomarkers of ionising radiation exposure: a multiparametric approach M. Prakash HANDE, Ph.D., M.P.H. Genome Stability Laboratory Department of Physiology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National
Cytogenetic biomarkers of ionising radiation exposure: a multiparametric approach M. Prakash HANDE, Ph.D., M.P.H. Genome Stability Laboratory Department of Physiology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine National
Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo. Günter Speit
 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo Günter Speit Universität Ulm Institut für Humangenetik D-89069 Ulm (Germany) guenter.speit@uni-ulm.de CEFIC-2012 Günter Speit 1 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde
Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in vitro and in vivo Günter Speit Universität Ulm Institut für Humangenetik D-89069 Ulm (Germany) guenter.speit@uni-ulm.de CEFIC-2012 Günter Speit 1 Genotoxicity of formaldehyde
DSB. Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci
 DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci METODI DDR foci formation in irradiated (2 Gy) cells fixed 2 h later IRIF IRradiation Induced Focus Laser micro-irradiation DDR
DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci METODI DDR foci formation in irradiated (2 Gy) cells fixed 2 h later IRIF IRradiation Induced Focus Laser micro-irradiation DDR
STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V.
 STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V. Sotnik, T. V. Azizova, and S. V. Osovets Southern Urals Biophysics Institute, Ozyorskoe shosse 19, Ozyorsk, 456780, Russia ABSTRACT The research objective
STRUCTURAL GENOMIC DAMAGE IN PLUTONIUM WORKERS N. V. Sotnik, T. V. Azizova, and S. V. Osovets Southern Urals Biophysics Institute, Ozyorskoe shosse 19, Ozyorsk, 456780, Russia ABSTRACT The research objective
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1
 J. Radiat. Res., 47: Suppl., B19 B24 (2006) Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1 Christian STREFFER* Genomic instability/malformation/transgenerational
J. Radiat. Res., 47: Suppl., B19 B24 (2006) Transgenerational Transmission of Radiation Damage: Genomic Instability and Congenital Malformation 1 Christian STREFFER* Genomic instability/malformation/transgenerational
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure
 Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
Chronic cell death may play a crucial role in mutagenesis and carcinogenesis due to radon exposure Balázs G. Madas, Imre Balásházy MTA Centre for Energy Research,, Hungary balazs.madas@energia.mta.hu Low
CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS
 10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Modelling of Biological Processes
 Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Modelling of Biological Processes WHAT HAPPENS AFTER EARLY MOLECULAR DAMAGE? Stephen McMahon Queen s University, Belfast, Northern Ireland 3 rd August 2016 1 Do we need biology? The Linear-quadratic relationship
Introduction. Introduction. Lymphocyte development (maturation)
 Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
Introduction Abbas Chapter 8: Lymphocyte Development and the Rearrangement and Expression of Antigen Receptor Genes Christina Ciaccio, MD Children s Mercy Hospital January 5, 2009 Lymphocyte development
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program
 U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager EFCOG Radiation Protection Subgroup 13-15 March 2012 Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research DOE s Low
U.S. Low Dose Radiation Research Program NF Metting, ScD, Program Manager EFCOG Radiation Protection Subgroup 13-15 March 2012 Office of Science Office of Biological and Environmental Research DOE s Low
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
TITLE: Reduction of Radiation- or Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity by Specific Expression of Anti-Apoptotic Molecules in Normal Cells
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0304 TITLE: Reduction of Radiation- or Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity by Specific Expression of Anti-Apoptotic Molecules in Normal Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Naoto T. Ueno,
AD Award Number: DAMD17-01-1-0304 TITLE: Reduction of Radiation- or Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity by Specific Expression of Anti-Apoptotic Molecules in Normal Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Naoto T. Ueno,
Application of chromosomal radiosensitivity assays to temporary nuclear power plant workers
 Application of chromosomal radiosensitivity assays to temporary nuclear power plant workers Research group University Ghent in collaboration with Dr. M. Barbé and the Occupational Medicine Service Nuclear
Application of chromosomal radiosensitivity assays to temporary nuclear power plant workers Research group University Ghent in collaboration with Dr. M. Barbé and the Occupational Medicine Service Nuclear
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology The role of intercellular communication and DNA double-strand breaks in the induction of bystander effects (INTERSTANDER) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00218
Estimates of Risks LONG-TERM LOW DOSE EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION
 Estimates of Risks LONG-TERM LOW DOSE EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION Low Level Radiation Exposure Single exposure of 10 rad or less Larger exposures delivered over periods of days or longer (low dose
Estimates of Risks LONG-TERM LOW DOSE EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION Low Level Radiation Exposure Single exposure of 10 rad or less Larger exposures delivered over periods of days or longer (low dose
Determination of Radon Concentration in Some Types of Cigarettes
 Determination of Radon Concentration in Some Types of Cigarettes Tarfa.H.Alsheddi 1, Amal Mohamed 2 and Shaffa.Al.Mansour 3 1 Department of physics, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia. 2 Department of
Determination of Radon Concentration in Some Types of Cigarettes Tarfa.H.Alsheddi 1, Amal Mohamed 2 and Shaffa.Al.Mansour 3 1 Department of physics, King Faisal University, Saudi Arabia. 2 Department of
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam
 Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Peak temperature ratio of TLD glow curves to investigate the spatial variation of LET in a clinical proton beam University of Chicago CDH Proton Center LET study C. Reft 1, H. Ramirez 2 and M. Pankuch
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
A REVIEW: DEVELOPMENT OF A MICRODOSE MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER DOSE RESPONSE BEHAVIOR
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 6 Issue 2 Article 3 6-2008 A REVIEW: DEVELOPMENT OF A MICRODOSE MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER DOSE RESPONSE BEHAVIOR Bobby E Leonard
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 6 Issue 2 Article 3 6-2008 A REVIEW: DEVELOPMENT OF A MICRODOSE MODEL FOR ANALYSIS OF ADAPTIVE RESPONSE AND BYSTANDER DOSE RESPONSE BEHAVIOR Bobby E Leonard
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation Module 8 - AAPM/RSNA Curriculum. Basic Radiation Biology
 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation Module 8 - AAPM/RSNA Curriculum Basic Radiation Biology Kalpana M. Kanal, PhD, DABR Associate Professor, Radiology Director, Resident Physics Education a copy of
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation Module 8 - AAPM/RSNA Curriculum Basic Radiation Biology Kalpana M. Kanal, PhD, DABR Associate Professor, Radiology Director, Resident Physics Education a copy of
Ernest Rutherford:
 November 1895: Roentgen discovers x rays February 1896: Becquerel discovers radioactivity Ernest Rutherford 1898-99 Ernest Rutherford: 1898-99 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Interaction of Charged Particles
November 1895: Roentgen discovers x rays February 1896: Becquerel discovers radioactivity Ernest Rutherford 1898-99 Ernest Rutherford: 1898-99 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Interaction of Charged Particles
Cataract following low dose ionising radiation exposures: Mechanistic understanding and current research
 Cataract following low dose ionising radiation exposures: Mechanistic understanding and current research Liz Ainsbury, PHE CNSC/CRPA Webinar: Lens of the eye 21 st March 2018 Human Lens Diameter ~9-10
Cataract following low dose ionising radiation exposures: Mechanistic understanding and current research Liz Ainsbury, PHE CNSC/CRPA Webinar: Lens of the eye 21 st March 2018 Human Lens Diameter ~9-10
Evidence for variation in human radiosensitivity: potential impact on radiological protection
 Evidence for variation in human radiosensitivity: potential impact on radiological protection Simon Bouffler 22 October 2015 ICRP Symposium 2015, Seoul, South Korea Current system of protection Avoid tissue
Evidence for variation in human radiosensitivity: potential impact on radiological protection Simon Bouffler 22 October 2015 ICRP Symposium 2015, Seoul, South Korea Current system of protection Avoid tissue
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
$QH[DPLQDWLRQRIDGDSWLYHFHOOXODUSURWHFWLYHPHFKDQLVPV XVLQJDPXOWLVWDJHFDUFLQRJHQHVLVPRGHO
 $Q[PQQIGSYXSYPKQVPV XVQJPXVJQJQVVPG +6K QEJ 5'6Z E 5(-0K QG:+IPQQ G a National Institute for Public ealth and the Environment (IVM), P Box 1, 3720 BA Bilthoven, The Netherlands, helmut.schollnberger@rivm.nl,
$Q[PQQIGSYXSYPKQVPV XVQJPXVJQJQVVPG +6K QEJ 5'6Z E 5(-0K QG:+IPQQ G a National Institute for Public ealth and the Environment (IVM), P Box 1, 3720 BA Bilthoven, The Netherlands, helmut.schollnberger@rivm.nl,
Patterns of Inheritance
 Patterns of Inheritance Mendel the monk studied inheritance keys to his success: he picked pea plants he focused on easily categorized traits he used true-breeding populations parents always produced offspring
Patterns of Inheritance Mendel the monk studied inheritance keys to his success: he picked pea plants he focused on easily categorized traits he used true-breeding populations parents always produced offspring
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology
 Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
Accelerated heavy ions as a tool for solving problems in fundamental and space radiobiology E. Krasavin Round Table 2 Italy-Russia@Dubna on SPACE PHISICS and BIOLOGY On Earth - accelerators of heavy charged
William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc.
 Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Biological Responses at Low Radiation Doses: Advances in Radiation Biology and Potential ti Implications for Radiation Exposure Regulations. William F. Morgan. Ph.D., D.Sc. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned. Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago
 The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
The Linear No-Threshold Model (LNT): Made to Be Tested, Made to Be Questioned Richard C. Miller, PhD Associate Professor The University of Chicago Regulatory Organizations NCRP (Nat l Council on Radiation
Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation
 J. RADIAT. RES., 40: SUPPL., 53 59 (1999) Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation RICHARD C. MILLER 1 *, STEPHEN A. MARINO 1, STEWART G. MARTlN 2, KENSHI KOMATSU 3, CHARLES
J. RADIAT. RES., 40: SUPPL., 53 59 (1999) Neutron-Energy-Dependent Cell Survival and Oncogenic Transformation RICHARD C. MILLER 1 *, STEPHEN A. MARINO 1, STEWART G. MARTlN 2, KENSHI KOMATSU 3, CHARLES
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function. Ch. 8
 Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Spring 2015 Module 2 System Engineering and Protein Founda<ons
 20.109 Spring 2015 Module 2 System Engineering and Protein Founda
20.109 Spring 2015 Module 2 System Engineering and Protein Founda
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
Acquisition of Radiation Resistant Ability in Non- Irradiated Cells by Secreted Factors from Low Dose Irradiated Cells
 Nagoya University Acquisition of Radiation Resistant Ability in Non- Irradiated Cells by Secreted Factors from Low Dose Irradiated Cells Jun Kumagai a *, Akane Oohashi b and Genro Kashino c a Institute
Nagoya University Acquisition of Radiation Resistant Ability in Non- Irradiated Cells by Secreted Factors from Low Dose Irradiated Cells Jun Kumagai a *, Akane Oohashi b and Genro Kashino c a Institute
The mutagenic and carcinogenic effects of sparsely ionizing
 Radiation dose-rate effects, endogenous DNA damage, and signaling resonance Michael M. Vilenchik* and Alfred G. Knudson *The Sally Balin Medical Center, 110 Chesley Drive, Media, PA 19063; and Division
Radiation dose-rate effects, endogenous DNA damage, and signaling resonance Michael M. Vilenchik* and Alfred G. Knudson *The Sally Balin Medical Center, 110 Chesley Drive, Media, PA 19063; and Division
1/31/2014. Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public
 Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Gene Expression and Mutation
 Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Gene Expression and Mutation GENE EXPRESSION: There are hormonal and environmental factors that may cause the expression of some genetic information. Some examples are: 1. The two- colour pattern of some
Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Dose-Response Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University
 Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University Outline Bystander effects and genomic instability In vivo relevance and evidence The fish model
Radiation induced bystander effects What? Why? And How? Carmel Mothersill Colin Seymour McMaster University Outline Bystander effects and genomic instability In vivo relevance and evidence The fish model
Survey of Radiation Dose Levels in Patients in X-Ray Units of Some Selected Hospitals in Jos Metropolis
 International Journal of Innovative Scientific & Engineering Technologies Research 6(4):1-9, Oct.-.Dec., 2018 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2018 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2360-896X Survey of Radiation Dose Levels in
International Journal of Innovative Scientific & Engineering Technologies Research 6(4):1-9, Oct.-.Dec., 2018 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2018 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2360-896X Survey of Radiation Dose Levels in
Analysis of individual differences in radiosensitivity using genome editing
 3 rd International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection ICRP2015 Analysis of individual differences in radiosensitivity using genome editing Shinya Matsuura Department of Genetics and Cell
3 rd International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection ICRP2015 Analysis of individual differences in radiosensitivity using genome editing Shinya Matsuura Department of Genetics and Cell
SPECIAL ISSUE INTRODUCTION
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 10 Issue 4 Special Issue in Honor of Zbigniew Jaworowski Article 4 12-2012 SPECIAL ISSUE INTRODUCTION Bobby R Scott Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 10 Issue 4 Special Issue in Honor of Zbigniew Jaworowski Article 4 12-2012 SPECIAL ISSUE INTRODUCTION Bobby R Scott Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute
6.3 DNA Mutations. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 6.3 DNA Mutations SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau DNA Mutations Gene expression can be affected by errors that occur during DNA replication. Some errors are repaired, but others can become mutations (changes in the nucleotide
6.3 DNA Mutations SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau DNA Mutations Gene expression can be affected by errors that occur during DNA replication. Some errors are repaired, but others can become mutations (changes in the nucleotide
Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research
 Mutation Research 659 (2008) 211 220 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/reviewsmr Community address: www.elsevier.com/locate/mutres
Mutation Research 659 (2008) 211 220 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/reviewsmr Community address: www.elsevier.com/locate/mutres
RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW
 RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW PILLALAMARRI ILA Earth Atmospheric & Planetary Sciences Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 IAP
RADON RESEARCH IN MULTI DISCIPLINES: A REVIEW PILLALAMARRI ILA Earth Atmospheric & Planetary Sciences Neutron Activation Analysis Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 IAP
LDR and its potential application in clinics
 LDR and its potential application in clinics Lu Cai Departments of Medicine & Radiation Oncology University it of Louisville School of Medicine LDR effects Hormesis Adaptive response Bystander effects
LDR and its potential application in clinics Lu Cai Departments of Medicine & Radiation Oncology University it of Louisville School of Medicine LDR effects Hormesis Adaptive response Bystander effects
LOW-DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED PROTECTIVE PROCESS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR RISK ASSESSMENT, CANCER PREVENTION, AND CANCER THERAPY
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 7 6-2007 LOW-DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED PROTECTIVE PROCESS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR RISK ASSESSMENT, CANCER PREVENTION, AND CANCER THERAPY BR Scott
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 5 Issue 2 Article 7 6-2007 LOW-DOSE RADIATION-INDUCED PROTECTIVE PROCESS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR RISK ASSESSMENT, CANCER PREVENTION, AND CANCER THERAPY BR Scott
Original Article Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in patient with glioma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(8):9463-9467 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0011215 Original Article Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(8):9463-9467 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0011215 Original Article Blood-based DNA methylation of DNA repair genes in the non-homologous end-joining (NEHJ) pathway in
Is a Linear Extrapolation of Cancer Risks to Very Low Doses Justified?
 Is a Linear Extrapolation of Cancer Risks to Very Low Doses Justified? May 3, 2000 Radiation Research Society Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Daniel J. Strom Risk Analysis & Health Protection Richland, Washington
Is a Linear Extrapolation of Cancer Risks to Very Low Doses Justified? May 3, 2000 Radiation Research Society Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA Daniel J. Strom Risk Analysis & Health Protection Richland, Washington
Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Medical students awareness of radiation exposure related to radiological imaging procedures
 ORIGINAL PAPER Medical students awareness of radiation exposure related to radiological imaging procedures Katarzyna Jończyk-Potoczna 1, Lidia Strzelczuk-Judka 1, Ewa Szłyk 1, 2, Łucja Stefaniak 1, 2 1
ORIGINAL PAPER Medical students awareness of radiation exposure related to radiological imaging procedures Katarzyna Jończyk-Potoczna 1, Lidia Strzelczuk-Judka 1, Ewa Szłyk 1, 2, Łucja Stefaniak 1, 2 1
APPENDIX AVAILABLE ON THE HEI WEB SITE
 APPENDIX AVAILABLE ON THE HEI WEB SITE Research Report 166 Advanced Collaborative Emissions Study (ACES) Subchronic Exposure Results: Biologic Responses in Rats and Mice and Assessment of Genotoxicity
APPENDIX AVAILABLE ON THE HEI WEB SITE Research Report 166 Advanced Collaborative Emissions Study (ACES) Subchronic Exposure Results: Biologic Responses in Rats and Mice and Assessment of Genotoxicity
Factors determining DNA double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase.
 Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
Supplementary Data Factors determining DN double strand break repair pathway choice in G2 phase. tsushi Shibata 1, Sandro Conrad 2, Julie irraux 1, Verena Geuting 2, Olivia arton 2, mani Ismail 1, ndreas
The Role of ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis
 The Role of ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis Background Ataxia-Telangiectasia Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) is a primary immunodeficiency disorder that occurs
The Role of ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis Background Ataxia-Telangiectasia Ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) is a primary immunodeficiency disorder that occurs
INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR ADAPTIVE RESPONSES AND SPLIT DOSE RECOVERY INDUCED BY IONIZING RADIATION IN THREE HUMAN EPITHELIAL DERIVED CELL LINES
 Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 7 Issue 4 Article 2 12-2009 INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR ADAPTIVE RESPONSES AND SPLIT DOSE RECOVERY INDUCED BY IONIZING RADIATION IN THREE HUMAN EPITHELIAL
Dose-Response: An International Journal Volume 7 Issue 4 Article 2 12-2009 INVESTIGATION OF NON-LINEAR ADAPTIVE RESPONSES AND SPLIT DOSE RECOVERY INDUCED BY IONIZING RADIATION IN THREE HUMAN EPITHELIAL
Mutations. A2 Biology For WJEC
 12. Mutation is a change in the amount, arrangement or structure in the DNA of an organism. 13. There are two types of mutations, chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Mutations A2 Biology For WJEC
12. Mutation is a change in the amount, arrangement or structure in the DNA of an organism. 13. There are two types of mutations, chromosome mutations and gene mutations. Mutations A2 Biology For WJEC
Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation. Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic
 Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) 2007 National Academy of Science National Research
Sources of Data of Stochastic Effects of Radiation Michael K O Connor, Ph.D. Dept. of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) 2007 National Academy of Science National Research
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay
 The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
The Need for a PARP in vivo Pharmacodynamic Assay Jay George, Ph.D. Chief Scientific Officer Trevigen, Inc. Gaithersburg, MD Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases are promising therapeutic targets. In response
Lecture -2- Environmental Biotechnology
 Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Lecture -2-1-General Bioassay in pollution Monitoring 1 1 Genotoxicity test At the early testing stages, the genotoxicity assays for predicting potential heritable germ cell damage are the same as used
Biochemistry 201: DNA repair January 24, 26, 2000 Gilbert Chu
 1) Why study DNA repair? Biochemistry 201: DNA repair January 24, 26, 2000 Gilbert Chu The genome is assaulted by a myriad of different agents that cause DNA damage. Sources of damage can be both exogenous
1) Why study DNA repair? Biochemistry 201: DNA repair January 24, 26, 2000 Gilbert Chu The genome is assaulted by a myriad of different agents that cause DNA damage. Sources of damage can be both exogenous
Cellular Stress Response Induced by Low Dose Gamma Radiation
 Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (2): 139 144 (2014) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Research Article Cellular
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences 51 (2): 139 144 (2014) Pakistan Academy of Sciences Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 0377-2969 (print), 2306-1448 (online) Research Article Cellular
Leukemia: Lessons from the Japanese Experience
 Leukemia: Lessons from the Japanese Experience STUART C. FINCH Cooper Hospital, Camden, New Jersey, USA Key Words. Leukemia. Japan Life Span Study Atomic bomb. Radiation ABSTRACT Probably more has been
Leukemia: Lessons from the Japanese Experience STUART C. FINCH Cooper Hospital, Camden, New Jersey, USA Key Words. Leukemia. Japan Life Span Study Atomic bomb. Radiation ABSTRACT Probably more has been
Cell Damage. Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence
 Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence Patents: CN 2702421, EP 2208068, TR 201308237, 200880115751 The Platform Motorized, inverse fluorescence microscope
Standardized and automatic determination of DNA double strand breaks using immunofluorescence Patents: CN 2702421, EP 2208068, TR 201308237, 200880115751 The Platform Motorized, inverse fluorescence microscope
What is the Appropriate Radiation Level for Evacuations? J. M. Cuttler Cuttler & Associates Inc., Mississauga, Ontario, Canada
 What is the Appropriate Radiation Level for Evacuations? J. M. Cuttler jerrycuttler@rogers.com Cuttler & Associates Inc., Mississauga, Ontario, Canada Abstract This commentary reviews the international
What is the Appropriate Radiation Level for Evacuations? J. M. Cuttler jerrycuttler@rogers.com Cuttler & Associates Inc., Mississauga, Ontario, Canada Abstract This commentary reviews the international
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes
 A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells
 The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
The impact of different radiation qualities on cancer cells Marjan Moreels, PhD Radiobiology Unit,, Belgium XXth Colloque GANIL Session 10, Amboise, France Oct 19, 2017 1 The Belgian Nuclear Research Center
Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to. Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority
 Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to ionizing radiation Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Objectives: Identify clastogenic factors in blood
Clastogenic factors in blood plasma obtained from subjects exposed to ionizing radiation Carita Lindholm STUK - Radiation and Nuclear Safety Authority Objectives: Identify clastogenic factors in blood
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Mutant SOD1 Transgenic Rodents as Models of FALS
 Mutant SOD1 Transgenic Rodents as Models of FALS Transgenic mice and rats expressing mutant forms of SOD1 develop motor neuron pathology and clinical symptoms similar to those seen in patients with ALS.
Mutant SOD1 Transgenic Rodents as Models of FALS Transgenic mice and rats expressing mutant forms of SOD1 develop motor neuron pathology and clinical symptoms similar to those seen in patients with ALS.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Measurement of Absorbed Doses in Anatomical Phantoms
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Physics. ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 8, Number 1 (2012), pp. 53-58 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijpap.htm Measurement of Absorbed Doses in
International Journal of Pure and Applied Physics. ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 8, Number 1 (2012), pp. 53-58 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijpap.htm Measurement of Absorbed Doses in
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT
 RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
