Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
|
|
|
- Kathlyn Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
2 ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers To understand the role of host cells in carcinogenesis In depth understanding of the first hallmark: self sufficiency in growth signals.
3 Intro Cancer occurs due to successful breach of anticancer mechanisms, i:e of regulatory mechanisms in our cells and tissues that prevent uncontrolled proliferation. Each cancer cell needs to acquire certain phenotypic characteristics to become malignant. Of course these phenotypic characteristics reflect genetic mutations ( or alterations) The phenotypic characteristics needed for cancer cells to survive are called : the hallmarks of cancer.
4 Hallmarks of Cancer Hallmarks of cancer: changes in cell physiology resulting from genetic changes that result in cancer.
5 HALLMARKS OF CANCER: the original scientific work: Douglas Hanahan and Robert A. Weinberg published in 2000 a review article about the expanding knowledge of tumorigenesis. They suggested that ALL tumor cells need to acquire SIX traits in order for the cells to be transformed to malignant cells. These six traits were called: hallmarks of cancer The original work was revisited and another article was published in See next
6 The 2013 article described the 6 characteristics (hallmarks) and emphasized the importance of genomic instability and tumor promoting inflammation as two enablers of malignancy ( they enable and help the development of the 6 hallmarks. Also two new, emerging hallmarks were discussed: evasion of the immune system and reprogramming of metabolism Moreover, the stromal, host derived cells are thought to play a major role in carcinogenesis as they provide a suitable microenvironment of the tumor to evolve.
7 The hallmarks of cancer You can read this article from: I encourage you to at least take a look. This is a fantastic paper. Some of your colleagues ( school of medicine, University of Jordan) have translated the paper to Arabic: tuw_dcdppwezi9bq3px1iok/view?usp=driv esdk
8 SO: FOR CANCER TO DEVELOP: we need the 8 characteristics (hallmarks) plus the 2 enabling characteristics and the correct microenvironment. All the above are acquired as mutations or epigenetic alterations accumulating overtime So: no single mutation is enough to cause cancer.
9 Carcinogenesis is a multistep process. Each step results from a genetic change Each genetic change results in acquiring a certain phenotype ( one of the hallmarks) There is no specific sequence of acquiring these phenotypes the main issue is to acquire them all
10 Hallmarks of cancer Eight hallmarks 1. self sufficiency in growth signals 2. insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. evasion of cell death 4. limitless replicative potential 5. sustained angiogenesis 6. ability to invade and metastasize 7. reprogramming of metabolism 8. evasion of the immune system
11 Two enablers Enablers ( help in the tumorigenesis process and set the right conditions for genetic changes to develop) 1. genomic instability 2. inflammation
12 Tumor microenvironment Tumors need a suitable environment to flourish. This is obtained from the host cells: Stromal cells, mainly fibroblasts and pericytes
13
14 1. Self sufficiency in growth signals Tumors proliferate regardless of the normal regulatory mechanisms. This is achieved by mutations in proto-oncogenes Oncogenes cause increased growth by increasing oncoproteins which act as growth factors, growth factor receptors, transcription factors..etc
15 Physiologic cell proliferation 1. growth factor binds to its receptor 2. this causes transient limited activation of the receptor 3. the activated receptor activates signal transducing proteins on the inner leaflet of plasma membrane and the transduced signal is transmitted through cytosol to the nucleus 4.activation of nuclear regulatory factors that regulate DNA transcription 5. entry into cell cycle
16 Increased growth can happen if there is interference with any of the 5 steps in the previous slide.
17 1. Increased growth facors 2. Increased receptors or increase in their func 3. Increased signal transduction 4. Increased transcription factors 5. Cell cycle entry
18 Growth factors Some tumors produce their own growth factors, ie factors they respond to. This creates an autocrine loop Eg glioblastomas produce PDGF and express its receptor
19 Growth factors Tumor cells can interact with their stroma to produce growth factors. This is an example of how microenvironment ( interaction with host cells including stromal cells) can help tumors to grow.
20 GF receptors GF receptors can increase cell proliferation in two situations: 1. Overexpression of the receptor.. So, Receptor is hyper responsive to GF even in levels that don t normally trigger proliferation. 2. Mutant receptor proteins. So the receptor itself is mutated and acquires a configuration that is always stimulated. This causes continuous mitogenic signal even in the absence of GF. Remember that when a GF ( or indeed any ligand) binds to its receptor, this causes conformational changes in the receptor proteins, so its shape changes and this change is what activates the receptor. If there is a mutation that causes conformational change resulting in the receptor s shape being in the active state, then we don t need any stimulator for the receptor to function! It s in the alert, functioning state continuously.
21 Notice the shape change and dimerization of this receptor when attached to its ligand.
22 Amplification of GF receptor/ example Gene encoding her2/neu is amplified in 25-30% of breast cancers and adenocarcinoma of lung, ovary and salivary gland High level of HER2/Neu protein in breast cancer worsens prognosis ( results in more proliferation) If her 2 receptor blocked.. By anti her2 antibodies.. Treatment used ( refer to details in previous lecture: the case study)
23 Signal transducing proteins Main signal transducing proteins involved: RAS and ABL
24 RAS RAS is the most commonly mutated oncogene in humans 30% of human cancers contain RAS mutation Even higher incidence in colon and pancreatic carcinomas
25 How does RAS function normally? RAS is a small protein that binds GDP and GTP ( it s a G protein) It is inactive with GDP binding. If a growth factor binds to a receptor.. GDP is phosphorylated to GTP.. This Actives RAS Activation is short lived as GTPase hydrolyses GTP to GDP GTPase activating proteins (GAPs ) prevent over activation of RAS, so they act as brakes of RAS activation.
26 G coupled proteins, which RAS is one of them. Seven transmembrane alpha helices, coupled with G protein (GTP binding protein). Ligand binding: GDP in the G protein changes to GTP receptor activated.
27
28 Activated RAS.. Sends messengers to the nucleus by two pathways ( see next slide) 1. RAF.. MAPK 2. PI3K..AKT..mTOR If 1 or 2 mutated.. Can mimic RAS effect Eg RAF mutated in 60% of melanomas
29
30 RAS RAS is stimulated when a growth factor binds to its receptor. This binding causes phosphorylation of GDP to GTP. GTP activated RAS Activated RAS acts via two pathways to send signals to the nucleus 1. mtor pathway. 2. RAF- MAPK pathway These two pathways send messages to the nucleus to express transcription factors that allow cells to enter cell cycle and proliferate.
31 How RAS is activated ( mutated) Point mutation in an amino acid residues within the GTP binding pocket or in the enzymatic region of GTP hydrolysis Both result in defective hydrolysis.. Leading to trapped RAS in active phosphorylated GTP bound RAS
32 ABL Proto-oncogene with tyrosine kinase activity regulated by internal negative regulatory domain ABL-BCR translocation.. Results in a hybrid gene The hybrid gene produces novel tyrosine kinase which is always active and stimulating proliferation This is the Philadelphia chromosome we talked about previously. ABL-BCR pathway activates all the downstream signals of ras
33 Philadelphia chromosome
34 CML =chronic myelogenous leukemia : t(9;22)= Philadelphia chromosome. ABL-BCR fusion gene.tyrosine kinase which is always turned on. Kinase inhibitors can be used to treat CML Imatinab/gleevec.. Inhibits the kinase and treats the leukemia = targeted therapy
35
36 Nuclear transcription factors Most commonly involved in human cancers: MYC
37 myc Can activate or repress expression of other genes Activates cyclins and cyclin dependent kinases CDK ( so cells enter cell cycle and divide) Myc also inhibits cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKI) These cyclins, CDK, CDKI play a role in entry to cell cycle, which we will discuss in detail in this lecture.
38 MYC amplified in breast, colon, lung and other carcinomas T(8; 14) in Burkitt dysregulates myc activate
39 Entry into cell cycle All the stimuli mentioned till now aim for quiescent cells to enter the cell cycle. Each phase in the cell cycle depends on successful completion of the previous one Cycle stops when essential gene function is lost
40 cyclins Progression through cell cycle, especially G1-S is regulated by proteins called cyclins Cyclins activate kinases CDK (cyclin dependent kinases) Cyclin and CDK form complexes that phosphorylate target proteins that drive the cell through the cell cycle. Cyclins : D, E, A, B (they appear in this sequence)
41
42
43 The DEAB sequence of cyclins!
44 SO: cyclin/cdk complexes cause proliferation. Theses are inhibited by cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKI) CDKI important for enforcing the checkpoints and delaying cell cycle.
45 Mutations causing increased cyclins or CDK cause self sufficiency in growth signals. Mutations inhibiting CDKI will cause increased growth. Examples: cyclin D is activated in several tumors mainly lymphomas.
46 Summary 1/3 Transformed cells acquire several mutations resulting in several phenotypes. There are 8 phenotypes needed in each transformed cell and these are called the hall marks of cancer. All these hallmarks must be gained through mutations, but there is no specific sequence for acquiring them. We don t need 8 mutations for the 8 phenotypes as one mutation might cause more than phenotype. these 8 are: self sufficiency of growth factors, insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals, evasion of cell death and the immune system, changes in metabolism, immortality, ustained angiogenesis and ability to invade and metastasize. Genomic instability and inflammation act as enablers of malignancy; they set the proper environment for mutations to occur. Tumors also need a proper microenvironment provided by host stromal cells.
47 Summary 2/3 Self sufficiency in growth signals can occur through increased growth factors, growth factor receptors, signal transduction proteins, transcription factors or cell cycle stimulators. GF can be synthesized by tumor cells or host stromal cells. GF receptors can be activated via overexpression ( HER 2) or changes in their architecture that makes them active even without binding to GF. Signal transduction can increase via increase in any protein involved in second messengers that convey growth signals to the nucleus. These include RAS and ABL plus their downstream protein pathways ( BRAF- MAP kinase and MTOR pathways) RAS is the most commonly mutated oncogene in humans. RAS is a G protein that is stimulated upon phosphorylation of GDP to GTP. Point mutations that cause entrapment of RAS in the activated state cause cell transformation.
48 Summary 3/3 ABL is a protooncogene that can be stimulated via translocation ( 9;22) with formation of ABL-BCR fusion gene that encodes a kinase which is active and causes cell proliferation. This causes a leukemia that be treated by blocking the kinase. Cell cycle is stimulated by cyclins/ Cyclin dependent kinase(cdk) complexes. Increase in Cyclins or CDK can transform cells. Cyclin/CDK complexes are normally regulated by CDK inhibitors.. A decrease in the inhibitors can also transform cells.
49 Test yourself The questions to follow are from webpath website, it s a very good source of pathology MCQ questions: - My aim here is to show you how long, seemingly difficult questions are actually very easy. Just know your concepts and practice how to deal with these questions: let s try
50 A 73-year-old man has an episode of hematemesis. Upper GI endoscopy reveals an irregular 4 cm gastric antral ulceration. Biopsies are performed and microscopically reveal adenocarcinoma. Molecular analysis shows DNA hypermethylation of the CDKN2 complex. Through which of the following mechanisms has this abnormal gene expression most likely occurred? A Amplification B Epigenetic alteration C Growth factor binding D Point mutation E Reduced mirna expression
51 answer A 73-year-old man has an episode of hematemesis. Upper GI endoscopy reveals an irregular 4 cm gastric antral ulceration. Biopsies are performed and microscopically reveal adenocarcinoma. Molecular analysis shows DNA hypermethylation of the CDKN2 complex ( this is the only relevant piece of information. If you know that hypermwthylation is an epigenetic change then you solved the whole issue.. Through which of the following mechanisms has this abnormal gene expression most likely occurred? A Amplification B Epigenetic alteration C Growth factor binding D Point mutation E Reduced mirna expression
52 Columnar epithelial cells from the colonic mucosa are studied to identify abnormalities in cell signaling pathways. Abnormal epithelial cells from colonic adenocarcinoma are shown to have a mutation that blocks hydrolysis of GTPbound active RAS. Normal columnar cells have active RAS protein that undergoes hydrolysis to the inactive GDP-bound form. Which of the following signaling pathways is most likely abnormally stimulated in the carcinoma cells? A ADP B BCR-ABL C Cyclic AMP D Cyclin D1 E MAP kinase F p53
53 Columnar epithelial cells from the colonic mucosa are studied to identify abnormalities in cell signaling pathways. Abnormal epithelial cells from colonic adenocarcinoma are shown to have a mutation that blocks hydrolysis of GTPbound active RAS. Normal columnar cells have active RAS protein that undergoes hydrolysis to the inactive GDP-bound form. Which of the following signaling pathways is most likely abnormally stimulated in the carcinoma cells? A ADP B BCR-ABL C Cyclic AMP D Cyclin D1 E MAP kinase. All what you need to know here is the signaling pathways of ras: RAF- MAPK and MTOR F p53
54 A 50-year-old woman notes a lump in her breast. Her physician's assistant palpates a 2 cm firm mass in her left breast. A fine needle aspiration biopsy is performed, and on microscopic examination a carcinoma is present. Molecular analysis shows HER2 positivity but estrogen receptor negativity in these malignant cells. Through which of the following mechanisms has this abnormal expression most likely occurred? A Amplification B Epigenetic alteration C Growth factor binding D Point mutation E Reduced mirna expression
55 A 50-year-old woman notes a lump in her breast. Her physician's assistant palpates a 2 cm firm mass in her left breast. A fine needle aspiration biopsy is performed, and on microscopic examination a carcinoma is present. Molecular analysis shows HER2 positivity but estrogen receptor negativity in these malignant cells. Through which of the following mechanisms has this abnormal expression most likely occurred? A Amplification.. All the information is irrelevant.. They are just asking about how HER 2 is activated, and you should know by now it s through amplification B Epigenetic alteration C Growth factor binding D Point mutation E Reduced mirna expression
56 A 66-year-old man has noted darker urine for the past 2 weeks. A urine alysis shows hematuria. Cystoscopy is performed and there is a 3 cm mass in the dome of the bladder. Biopsies of the mass are taken and on microscopic examination show a urothelial carcinoma. Cells of this neoplasm demonstrate a single mutation causing cellular inability to hydrolyze GTP, thus resulting in cellular transformation. Which of the following oncogenes is most likely implicated in this case? A ABL B ERBB2 C SIS D RAS E N-MYC
57 A 66-year-old man has noted darker urine for the past 2 weeks. A urine alysis shows hematuria. Cystoscopy is performed and there is a 3 cm mass in the dome of the bladder. Biopsies of the mass are taken and on microscopic examination show a urothelial carcinoma. Cells of this neoplasm demonstrate a single mutation causing cellular inability to hydrolyze GTP, thus resulting in cellular transformation. Which of the following oncogenes is most likely implicated in this case? A ABL B ERBB2 C SIS D RAS. You only need to know that RAS is a G protein and its function is related to GDP/GTP. You should be able to answer the question even if you have no idea what the rest of the choices are. E N-MYC
58 A 52-year-old man has had increasing fatigue for the past 6 months. On physical examination he has a palpable spleen tip. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 189,000/microliter. The peripheral blood smear shows many mature and immature myeloid cells present. Cytogenetic analysis of cells obtained via bone marrow aspiration reveals a t(9:22) translocation. This translocation leads to formation of a hybrid gene that greatly increases tyrosine kinase activity. Which of the following genes is most likely translocated to cause these findings? A p53 B RB C ABL D NF-1 E RAS
59 A 52-year-old man has had increasing fatigue for the past 6 months. On physical examination he has a palpable spleen tip. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 189,000/microliter. The peripheral blood smear shows many mature and immature myeloid cells present. Cytogenetic analysis of cells obtained via bone marrow aspiration reveals a t(9:22) translocation. This translocation leads to formation of a hybrid gene that greatly increases tyrosine kinase activity. Which of the following genes is most likely translocated to cause these findings? A p53 B RB C ABL.. This is very easy, you only need to practice to pick the relevant information in these questions D NF-1 E RAS
60 THANK YOU AND PLEASEDO NOT HESITATE TO ASK IF YOU NEED HELP WITH THE QUESTIONS.
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Activation of cellular proto-oncogenes to oncogenes. How was active Ras identified?
 Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Major Principles (cont d) 4. Principle targets of genetic damage: 4 classes
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Major Principles (cont d) 4. Principle targets of genetic damage: 4 classes
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II. Prof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department
 Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer
 Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
An Overview of Molecular Cancer Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Diagnosis
 1 An Overview of Molecular Cancer Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Diagnosis John M. Cullen and Matthew Breen North Carolina State University, USA Fundamentals of cancer biology Cancer is a disease of the
1 An Overview of Molecular Cancer Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Diagnosis John M. Cullen and Matthew Breen North Carolina State University, USA Fundamentals of cancer biology Cancer is a disease of the
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Signal Transduction: Information Metabolism. Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire
 Signal Transduction: Information Metabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire Introduction Information Metabolism How cells receive, process and respond
Signal Transduction: Information Metabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire Introduction Information Metabolism How cells receive, process and respond
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CANCER.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Plasma membranes. Plasmodesmata between plant cells. Gap junctions between animal cells Cell junctions. Cell-cell recognition
 Cell Communication Cell Signaling Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Communicate by chemical messengers Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Communicate by chemical messengers Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the. ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP
 Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the following equation: 2 ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP ATP represents adenosine trisphosphate, ADP
Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the following equation: 2 ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP ATP represents adenosine trisphosphate, ADP
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor. supressors
 Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 29, 2015 Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct 29, 2015 Signal Transduction Pathways in Human Diseases Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Mohammed El-Khateeb. Tumor Genetics. MGL-12 May 13 th Chapter 22 slide 1 台大農藝系遺傳學
 Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 May 13 th 2014 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cancer Genetics Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer Multistage Model
Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 May 13 th 2014 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cancer Genetics Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer Multistage Model
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Cellular Signaling Pathways. Signaling Overview
 Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Signal Transduction Pathways. Part 2
 Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th Edition by Kumar
 Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-bykumar-abbas-and-aster Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-robbins-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-bykumar-abbas-and-aster Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease
Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
Cancer and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition
 Cancer and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition 1 Motivation (1) In first world countries cancer is the second most common cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. For most tumors, treatment is limited to surgery,
Cancer and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition 1 Motivation (1) In first world countries cancer is the second most common cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. For most tumors, treatment is limited to surgery,
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors
 Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Chapter 11. Cell Communication. Signal Transduction Pathways
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication Signal Transduction Pathways Signal-Transduction Pathway Signal on a cell s surface is converted into a specific cellular response Local signaling (short distance) - Paracrine
Chapter 11 Cell Communication Signal Transduction Pathways Signal-Transduction Pathway Signal on a cell s surface is converted into a specific cellular response Local signaling (short distance) - Paracrine
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11. Dr H Awad FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
 Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Life Science 1A Final Exam. January 19, 2006
 ame: TF: Section Time Life Science 1A Final Exam January 19, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use non-erasable
ame: TF: Section Time Life Science 1A Final Exam January 19, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use non-erasable
Contents. Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX
 Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th Edition by Kumar
 Link full download:https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-robbinsand-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-by-kumar Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th
Link full download:https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-robbinsand-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-by-kumar Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th
Chapter 9. Cellular Signaling
 Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
34 Cancer. Lecture Outline, 11/30/05. Cancer is caused by mutant genes. Changes in growth properties of cancer cells
 34 Cancer Lecture Outline, 11/30/05 Review the Cell cycle Cancer is a genetic disease Oncogenes and roto-oncogenes Normally romote cell growth. Become oncogenic after oint mutations, dulications, deletion
34 Cancer Lecture Outline, 11/30/05 Review the Cell cycle Cancer is a genetic disease Oncogenes and roto-oncogenes Normally romote cell growth. Become oncogenic after oint mutations, dulications, deletion
General Pathology VPM 152. Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
Lecture 15. Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction
 Lecture 15 Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis Regulation of gene expression by signals
Lecture 15 Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis Regulation of gene expression by signals
Regulation of Cell Division
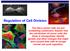 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Functional Limitations
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Cell Communication. Local and Long Distance Signaling
 Cell Communication Cell to cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation providing more evidence for the evolutionary relatedness of all life
Cell Communication Cell to cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation providing more evidence for the evolutionary relatedness of all life
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test
 Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Molecular Oncology, oncology parameters see each test DPD deficiency Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase deficiency (DPD deficiency) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder in which there is absent or
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers
 Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS
 TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS AZIZA SHAD, MD AMEY DISTINGUISHED PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY, BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION LOMBARDI CANCER CENTER GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS AZIZA SHAD, MD AMEY DISTINGUISHED PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY, BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION LOMBARDI CANCER CENTER GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
Section D. Genes whose Mutation can lead to Initiation
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 6 - CELL COMMUNICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-TO-CELL CONNECTIONS AND SIGNALING Gap and Tight Junctions: Adjacent cells communicate and hold on to each other via junctions. Two important kinds: Gap Junctions are
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-TO-CELL CONNECTIONS AND SIGNALING Gap and Tight Junctions: Adjacent cells communicate and hold on to each other via junctions. Two important kinds: Gap Junctions are
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION
 AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION CELL CYCLE 2 crucial factors for normal growth: Timing and rate of cell division Cell division frequency depends on cell type: skin cells: frequently Liver cells: can divide when
AP: CELL CYCLE REGULATION CELL CYCLE 2 crucial factors for normal growth: Timing and rate of cell division Cell division frequency depends on cell type: skin cells: frequently Liver cells: can divide when
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
