Contents. Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX
|
|
|
- Shon Fox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy General Principles of Signal Transduction Biological Signals have to be Processed What is a Signal Transduction Pathway? Mechanisms of Direct Signal Transduction The Interactome Gives Insight into the Signaling Network Protein Domains for Protein-Protein Interaction and Signal Transduction Functions of Mutated Proteins in Tumor Cells Drugs against Cancer Terms and Definitions The Steps from a Normal Cell to a Tumor Interference Levels of Therapeutic Drugs Drugs Attacking the Whole Cell DNA Alkylating Drugs Process-Blocking Drugs Drugs Blocking Synthesis of DNA and RNA Drugs Blocking the Synthesis of DNA and RNA Precursor Molecules Drugs Blocking Dynamics of Microtubules Innovative Molecule-Interfering Drugs Fast-Dividing Normal Cells and Slowly Dividing Tumor Cells: Side Effects and Relapse Drug Resistance Drugs Circumventing Resistance Outlook 20 References 21
2 Tumor Cell Heterogeneity and Resistance to Targeted Therapy 23 The Genetic Basis of Tumorigenesis 24 Clonal Heterogeneity 24 Clonal Origin of Tumors 24 Clonal Evolution 26 The Time Course of Clonal Evolution 30 Clonal Evolution and Resistance to Therapy 32 Targeting Essential Drivers (Driver Addiction) 34 Resistance by Alternative Pathway Activation 36 Overcoming Resistance by Combinatorial Therapies 36 Tumor Stem Cells and Tumor Cell Hierarchies 37 Epigenetics and Phenotypic Plasticity 40 Microenvironment 42 Outlook 43 References 44 Cell Cycle of Tumor Cells 47 Properties of Tumor Cells 48 Differences between Tumor Cells and Normal Cells In vitro 49 Regulation of Cell Number 49 The Cell Cycle 50 Checkpoints 51 Cyclins 52 Cyclin-Dependent Kinases (CDKs) 53 The Retinoblastoma-Associated Protein Rb as Regulator of the Cell Cycle 54 Inhibitors of CDKs 54 Checkpoints and DNA Integrity 55 The Repair Mechanism Depends on the Cell Cycle Phase 57 Tumor-Relevant Proteins in the Cell Cycle 57 The Cell Cycle as Therapeutic Target 58 Small Compounds Inhibiting Cell-Cycle-Dependent Kinases as Anticancer Drugs 59 Outlook 60 References 61 Cell Aging and Cell Death 63 A Cells Journey through Life 64 Cellular Aging and Senescence 64 Replicative Senescence 65 Shortening of Chromosomal Telomeres during Replication 67 Chromosomal Telomeres 67 Telomerase 69 Animal Models 72
3 4.2.6 Overcoming Replicative Senescence in Tumor Cells Nonreplicative Senescence Cell Death Morphologies of Dying Cells Morphology of Necrotic Cells Morphologies of Apoptotic and Necroptotic Cells Morphology of Autophagy Necroptosis Apoptosis in the Healthy Organism The Four Phases of Apoptosis Extrinsic Initiation TNF Pathway TNF Receptor Downstream Signaling Caspases Intrinsic Initiation Execution Phase Phagocytosis and Degradation Apoptosis of Tumor Cells Autophagy Autophagy in Tumor Development Regulation of Autophagy Cell Death and Cell Aging as Therapeutic Targets in Cancer Treatment Induction of Apoptosis by Radiation Induction of Apoptosis by Conventional Anticancer Drugs Innovative Drugs Targeting Aging and Death Pathways Targeting TRAIL (TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand) Targeting Bcl Simulating the Effects of ciap Inhibitors Targeting Autophagy Pathways Senescence in Anticancer Therapy Outlook 94 References 95 5 Growth Factors and Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Growth Factors Protein Kinases Receptor Protein Tyrosine Kinases Receptor Protein Tyrosine Kinase Activation The Family of EGF Receptors The Family of PDGF Receptors The Insulin Receptor Family and its Ligands Prostate-Specific Antigen Signaling from Receptor Protein Tyrosine Kinases 108
4 5.2.7 Association of PDGF and EGF Receptors with Cytoplasmic Proteins Signaling from PDGF and EGF Receptors Constitutive Activation of RTKs in Tumor Cells Therapy of Tumors with Deregulated Growth Factors and their Receptors Targeting Growth Factors Targeting EGF Receptors by Antibodies Targeting EGF Receptors by Kinase Inhibitors Outlook 117 References The Philadelphia Chromosome and BCR-ABL Analysis of Chromosomes Aberrant Chromosomes in Tumor Cells The Philadelphia Chromosome Molecular Diagnosis of the BCR-ABL1 Fusion Gene The BCR-ABL1 Kinase Protein Structural Aspects of BCR-ABL1 Kinase Substrates and Effects of BCR-ABL1 Kinase The BCR-ABL1 Kinase Inhibitor Imatinib Imatinib in Treatment of Tumors Other than CML Mechanism of Imatinib Action Resistance against Imatinib BCR-ABL1 Kinase Inhibitors of the Second and the Third Generation Allosteric Inhibitors of BCR-ABL Outlook 133 References MARK Signaling The RAS Gene The Ras Protein The Ras Protein as a Molecular Switch The GTPase Reaction in Wild-Type and Mutant Ras Proteins Neurofibromin: The Second RasGAP Downstream Signaling of Ras The BRaf Protein The BRAF Gene The MAPK Signaling Pathway Mutations in Genes of the MAPK Pathway Therapy of Tumors with Constitutively Active MAPK Pathway Ras as a Therapeutic Target Inhibiting Posttranslational Modification and Membrane Anchoring of Ras 150
5 Direct Targeting Mutant Ras Preventing Ras/Raf Interaction BRaf Inhibitors Consequences of BRaf Inhibition by Vemurafenib S.2.2 Resistance against BRaf Inhibitors Based on BRaf Dependent Mechanisms Z Resistance against BRaf Inhibitors Based on BRaf Independent Mechanisms Treatment of Vemurafenib-Resistant Tumors Outlook 156 References PI3K-AKT-mTOR Signaling Discovery of the PI3I<-AI<T-mTOR Pathway Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase (PI3K) Inositol Trisphosphate, Diacylglycerol, and Protein Kinase C (PKC) Protein Kinase C (PKC) Activation and Functions of PKC AKT (Protein Kinase B) mtor mtorcl: Inputs mtorc2: Inputs mtorcl: Outputs mtorc2: Outputs Feedback Controls PTEN Activation of the PI3K/AI<T/mTOR Pathway in Cancer Sporadic Carcinomas Hamartoma Syndromes PKC in Cancer Therapy Outlook 178 References Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) Responses of HIF to Hypoxia and Oncogenic Pathways HIF Functional Domains Regulation of HIF Regulation of HIF under Normoxic Conditions Regulation of HIF under Hypoxic Conditions Oxygen-Independent Regulation of HIF Context-Dependence of HIF Regulation Regulation of HIF in Malignant Disease Expression of HIF in Human Tumors 191
6 9.4.2 von Hippel-Lindau Disease HIF Targets in Cancer Target Genes of HIFI«and HIF2ct HIF Target Genes Affecting Tumor Growth HIF Target Genes Affecting Metabolism i Glucose Uptake and Metabolism HIFloc and the Warburg Effect The Warburg Paradox TCA Cycle Intermediates and Tumor Syndromes Drugs Targeting HIFs Outlook 202 References NF-kB Pathways NF-kB Signaling in Inflammation, Growth Control, and Cancer The Core of NF-kB Signaling Family of IkB Proteins Canonical NF-kB Signaling from TNF Receptor B-Cell Receptor Signaling Other Receptors Activating the Canonical Pathway Alternative NF-kB Pathway Terminating the NF-kB Response Ubiquitinylation in NF-kB Signaling Transcriptional Regulation Physiological Role of NF-kB Transcription Factors Mutational Activation of NF-kB Pathways in Malignant Disease B-Cell Lymphomas Multiple Myeloma Activation of NF-kB Pathways by Polycomb-Mediated Loss of microrna-31 in Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Carcinomas Cross Talk between Mutant KRas and NF-kB Inflammation, NF-kB, and Cancer Activation of Osteoclasts in Multiple Myeloma and Breast Cancer Metastases Targeting NF-kB Pathways B-Cell Malignancies Carcinomas Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Outlook 233 References 234
7 11 Wnt Signaling The History of Wnt The Canonical Wnt Pathway The Nonactivated Wnt Pathway The Physiologically Activated Wnt Pathway The Nonphysiologically Activated Wnt Pathway in the Absence of the Wnt Signal The Wnt Network Proteins of the Wnt Pathway with Diverse Functions APC (Adenomatous Polyposis Coli Protein) ß-Catenin Axin The Wnt Targe tome The Three Levels of the Wnt Targetome Biological Effects of Wnt Target Genes The Wnt Pathway as Therapeutic Target Strategies to Identify Anti-Wnt Drugs Molecules Interfering with the Wnt Pathway Outlook 254 References Notch Signaling Introduction Determination of Cell Fate Decisions Notch Proteins and Notch Ligands Notch Signaling The Notch Signaling Pathway Regulation of Notch Signaling by Posttranslational Modification Ubiquitinylation Glycosylation of Notch Notch Signaling in Malignant Disease Acute T-Cell Leukemia (T-ALL) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia (CMML) Breast Cancer Cholangiocellular Carcinoma (CCC) Squamous Cell Carcinomas (SCCs) Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) Angiogenesis Drugs Targeting the Notch Pathway Outlook 275 References 275
8 13 Hedgehog Signaling Overview of Hedgehog Signaling Hedgehog Ligands The Primary Cilium Patched (Ptch) and Smoothened (Smo) Gli Transcription Factors Signaling in the Absence of Hedgehog Signaling after Binding of Hedgehog to Patched Activation of the Canonical Hedgehog Pathway in Basal Cell Carcinoma and Medulloblastoma Noncanonical Activation of Hedgehog-Responsive Genes KRas Atypical Protein Kinase-Lambda/Iota (apkci) PI3-Kinase-AKT (PI3K-AKT) mtor Paracrine Activation of Hedgehog Signaling Pharmacological Inhibition of the Hedgehog Pathway Inhibition of Hh Binding to Ptch Inhibitors of Smoothened Inhibition of Cilial Trafficking Inhibition of Gli Resistance against Direct Inhibitors of Smoothened Outlook 296 References TGFß Signaling The TGFß Superfamily Structure and Processing of TGFß Superfamily Members The TGFß Signaling Pathway Transcriptional Regulation by TGFß Superfamily Members Regulation of Stem Cells by TGFß Superfamily Members TGFß Superfamily Members as Tumor Suppressors in Human Cancer Active role of TGFß in Tumor Progression Drugs Interfering with TGFß Signaling TGFß Superfamily Members in Tumor Cachexia Outlook 315 Nomenclature 316 References 317 Index 319
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San
 Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits)
 Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Basic tumor nomenclature
 Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Cancer as a Metabolic Disease
 Cancer as a Metabolic Disease On the Origin, Management and Prevention of Cancer Thomas N. Seyfried @WILEY "" Forword Preface xiii xv 1. Images of Cancer 1 How Cancer is Viewed 2 References 13 2. Confusion
Cancer as a Metabolic Disease On the Origin, Management and Prevention of Cancer Thomas N. Seyfried @WILEY "" Forword Preface xiii xv 1. Images of Cancer 1 How Cancer is Viewed 2 References 13 2. Confusion
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Oncogenes and Tumor. supressors
 Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS
 TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS AZIZA SHAD, MD AMEY DISTINGUISHED PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY, BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION LOMBARDI CANCER CENTER GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
TARGETED THERAPY FOR CHILDHOOD CANCERS AZIZA SHAD, MD AMEY DISTINGUISHED PROFESSOR OF PEDIATRIC HEMATOLOGY ONCOLOGY, BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION LOMBARDI CANCER CENTER GEORGETOWN UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID
 Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Pathway Map Reference Guide
 Pathway Map Reference Guide Focus Attention-grabber Your Pathway The most popular cell signaling pathways Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents AKT Signaling 4 camp Signaling 5 Cellular Apoptosis
Pathway Map Reference Guide Focus Attention-grabber Your Pathway The most popular cell signaling pathways Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents AKT Signaling 4 camp Signaling 5 Cellular Apoptosis
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer This illustration encompasses the six hallmark capabilities originally proposed in our 2000 perspective. The past decade has witnessed remarkable progress toward understanding the
The Hallmarks of Cancer This illustration encompasses the six hallmark capabilities originally proposed in our 2000 perspective. The past decade has witnessed remarkable progress toward understanding the
Activation of cellular proto-oncogenes to oncogenes. How was active Ras identified?
 Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CANCER.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis. Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval
 Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Chapter 6: Cancer Pathways. Other Pathways. Cancer Pathways
 Chapter 6: Cancer Pathways Limited number of pathways control proliferation and differentiation Transmit signals from growth factors, hormones, cell-to-cell communications/interactions Pathways turn into
Chapter 6: Cancer Pathways Limited number of pathways control proliferation and differentiation Transmit signals from growth factors, hormones, cell-to-cell communications/interactions Pathways turn into
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA
 PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes.
 What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer
 Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer Mariana S. De Lorenzo, PhD Department of Cell Biology & Molecular Medicine delorems@umdnj.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. To identify convergent and divergent
Convergent and Divergent Mechanisms in Aging and Cancer Mariana S. De Lorenzo, PhD Department of Cell Biology & Molecular Medicine delorems@umdnj.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. To identify convergent and divergent
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Evolution at Its Worst: Cancer. SHP-Neurobiology of Development and Disease
 Evolution at Its Worst: Cancer SHP-Neurobiology of Development and Disease Introduction to Cancer Cancer is currently the second leading cause of death in the US (22.8%) behind heart disease. Yearly 0.5%
Evolution at Its Worst: Cancer SHP-Neurobiology of Development and Disease Introduction to Cancer Cancer is currently the second leading cause of death in the US (22.8%) behind heart disease. Yearly 0.5%
Molecular pathogenesis of lung cancer
 Molecular pathogenesis of lung cancer Pr. Elisabeth Brambilla INSERM U823 Department of Pathology CHU Grenoble France Lung epithelial cells Carcinogen exposure genetic predisposition Auto- and paracrine
Molecular pathogenesis of lung cancer Pr. Elisabeth Brambilla INSERM U823 Department of Pathology CHU Grenoble France Lung epithelial cells Carcinogen exposure genetic predisposition Auto- and paracrine
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
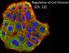
Regulation of Cell Division
 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Post-translational modifications of proteins in gene regulation under hypoxic conditions
 203 Review Article Post-translational modifications of proteins in gene regulation under hypoxic conditions 1, 2) Olga S. Safronova 1) Department of Cellular Physiological Chemistry, Tokyo Medical and
203 Review Article Post-translational modifications of proteins in gene regulation under hypoxic conditions 1, 2) Olga S. Safronova 1) Department of Cellular Physiological Chemistry, Tokyo Medical and
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES. Molecular Oncology Michael Lea
 TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. - Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday 3-4 pm, Natural Sciences Building, Room 5316
 BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2014 Lectures: WLH 2204 Tuesdays/Thursdays, April 1 June 5 8:00 9:20 AM Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. email - e1bennett@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday
BIMM134 The Biology of Cancer SPRING 2014 Lectures: WLH 2204 Tuesdays/Thursdays, April 1 June 5 8:00 9:20 AM Instructor: Eric Bennett, Ph.D. email - e1bennett@ucsd.edu Office Hours: Tuesday and Thursday
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS To understand the concept of the hallmarks of cancer and that they are phenotypic changes needed in all cancer cells. To list the tumor enablers
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4
 Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4 Johan Lennartsson Molecular Cell Biology (1BG320), 2014 Johan.Lennartsson@licr.uu.se 1 Receptor tyrosine kinase-induced signal transduction Erk MAP kinase pathway
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4 Johan Lennartsson Molecular Cell Biology (1BG320), 2014 Johan.Lennartsson@licr.uu.se 1 Receptor tyrosine kinase-induced signal transduction Erk MAP kinase pathway
Signal transduction networks in cancer. Prof. Dr. Thomas Wirth Institute of Physiological Chemistry Ulm University
 Signal transduction networks in cancer Prof. Dr. Thomas Wirth Institute of Physiological Chemistry Ulm University How is a cancer cell characterized? Hanahan/Weinberg: The new hallmarks of cancer (Altered)
Signal transduction networks in cancer Prof. Dr. Thomas Wirth Institute of Physiological Chemistry Ulm University How is a cancer cell characterized? Hanahan/Weinberg: The new hallmarks of cancer (Altered)
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Mechanisms of Chemotherapeutic Drug Resistance An Overview
 Human Journals Review Article May 2018 Vol.:12, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by R. Vimalavathini et al. Mechanisms of Chemotherapeutic Drug Resistance An Overview Keywords: Cancer, mechanism, drug resistance,
Human Journals Review Article May 2018 Vol.:12, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by R. Vimalavathini et al. Mechanisms of Chemotherapeutic Drug Resistance An Overview Keywords: Cancer, mechanism, drug resistance,
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
7/6/2015. Cancer Related Deaths: United States. Management of NSCLC TODAY. Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview
 Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death
 02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes
 Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes Gisela Keller Institute of Pathology Technische Universität München gisela.keller@lrz.tum.de Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes epidemiology models
Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes Gisela Keller Institute of Pathology Technische Universität München gisela.keller@lrz.tum.de Colon Cancer and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes epidemiology models
Regulation of Enzymatic Activity. Lesson 4
 Regulation of Enzymatic Activity Lesson 4 Regulation of Enzymatic Activity no real regulation: - regulation of enzyme expression and turnover - control of enzyme trafficking - supply of cofactors real
Regulation of Enzymatic Activity Lesson 4 Regulation of Enzymatic Activity no real regulation: - regulation of enzyme expression and turnover - control of enzyme trafficking - supply of cofactors real
Overview of Cancer. Mylene Freires Advanced Nurse Practitioner, Haematology
 Overview of Cancer Mylene Freires Advanced Nurse Practitioner, Haematology Aim of the Presentation Review basic concepts of cancer Gain some understanding of the socio-economic impact of cancer Order of
Overview of Cancer Mylene Freires Advanced Nurse Practitioner, Haematology Aim of the Presentation Review basic concepts of cancer Gain some understanding of the socio-economic impact of cancer Order of
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Mohammed El-Khateeb. Tumor Genetics. MGL-12 May 13 th Chapter 22 slide 1 台大農藝系遺傳學
 Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 May 13 th 2014 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cancer Genetics Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer Multistage Model
Mohammed El-Khateeb Tumor Genetics MGL-12 May 13 th 2014 台大農藝系遺傳學 601 20000 Chapter 22 slide 1 Cancer Genetics Types of Genetic Alterations in Cancer Evidence that Mutations Cause Cancer Multistage Model
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer
 Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Chapter 18- Oncogenes, tumor suppressors & Cancer - Previously we have talked about cancer which is an uncontrolled cell proliferation and we have discussed about the definition of benign, malignant, metastasis
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Chapter 9. Cells Grow and Reproduce
 Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit
 The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
Signal Transduction Pathways. Part 2
 Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia!
 Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
CARCINOGENESIS: THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF CANCER
 CARCINOGENESIS: THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF CANCER Nonlethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis. Mutation may be acquired by the action of environmental agents, such as chemicals, radiation,
CARCINOGENESIS: THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF CANCER Nonlethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis. Mutation may be acquired by the action of environmental agents, such as chemicals, radiation,
Section D. Genes whose Mutation can lead to Initiation
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Glioblastoma pathophysiology: or a
 Glioblastoma pathophysiology: A or a? M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Pathophysiology: pathophysiology seeks to explain the physiological
Glioblastoma pathophysiology: A or a? M.J. van den Bent The Brain Tumor Center at Erasmus MC Cancer Center Rotterdam, the Netherlands Pathophysiology: pathophysiology seeks to explain the physiological
