SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER
|
|
|
- Edward Howard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide
2
3 SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Anatomy of the Lungs...2 Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)...3 Risk Factors...3 Your Care Team...4 Diagnosing SCLC...6 Imaging...6 Biopsies...7 Lymphatic System...8 Staging...9 Treatment Options...10 Chemotherapy...11 Radiation...12 Immunotherapy...13 Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI)...14 Surgery...15 Clinical Trials...15 Palliative Care (Care for Symptoms and Side Effects)...16 For More Information...17
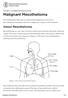
4 ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS TRACHEA (WINDPIPE) Lymph nodes Alveoli UPPER LOBE MIDDLE LOBE Bronchiole UPPER LOBE LOWER LOBE Right Lung MAIN BRONCHI Left Lung LOWER LOBE Pleura The above image shows different parts that make up the lungs. Please use this picture to help guide you through the topics discussed in this brochure. Your lungs are 2 sponge-like organs in your chest that are covered by a protective layer called the pleura. The right lung has 3 sections, called lobes and your left lung has 2 lobes. When you breathe in, air enters through your mouth and nose and goes into your lungs through the trachea (windpipe). The trachea divides into tubes called the bronchi, which enter the lungs and divide into smaller branches called bronchioles. At the end of the bronchioles are tiny air sacs known as alveoli. 2
5 SMALL CELL LUNG CANCER Cancer is a group of diseases in which normal cells change, grow and divide out of control. Cancer that begins in the lungs lung cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers in the United States. There are two main types: small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). SCLC is less common but the most aggressive (fast-growing) type making up about 15% of all lung cancer diagnoses. SCLC is named for the small, oval-shaped cancer cells seen under a microscope. It is a type of cancer that usually starts in the bronchi in the center of the chest and spreads quickly. RISK FACTORS A history of smoking is the main risk factor for developing lung cancer particularly SCLC. Cigarettes contain many carcinogens, which are substances that cause lung cancer. Other risk factors include: EXPOSURE TO RADON (an invisible, odorless, tasteless radioactive gas that occurs naturally in soil and rocks). FAMILY HISTORY of lung cancer. RADIATION THERAPY to the chest area. OTHER LUNG ILLNESSES (such as emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD] or tuberculosis). If you smoke, quitting is one of the single most important lifestyle changes you can make to improve your health. Even if you have lung cancer, quitting may help improve how you respond to treatment. If you want to quit, help is available. Ask your doctor or other healthcare provider for information. EXPOSURE TO INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS including arsenic, asbestos, beryllium uranium and Agent Orange. EXPOSURE TO SECONDHAND SMOKE (or passive smoking). 3
6 YOUR CARE TEAM WHAT S THE DIFFERENCE? A multidisciplinary team approach is when members of the healthcare team discuss your situation and work together to make treatment recommendations. It is thought that this approach improves coordination of care and communication among the team. MEDICAL ONCOLOGIST: A doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating cancer. ONCOLOGY NURSE: A nurse who specializes in helping people with cancer and who may further specialize in the surgical or medical management of a patient s care. ONCOLOGY SOCIAL WORKER OR COUNSELOR: A social worker or counselor who specializes in helping patients and loved ones cope with the emotional impact of cancer and who may help identify other needed resources. PALLIATIVE CARE SPECIALIST: A doctor, nurse or other healthcare professional who works with a patient s healthcare team to provide an extra layer of support such as relief from symptoms, pain and stress of an illness like cancer. PATHOLOGIST: A doctor who specializes in diagnosing and classifying cancer by studying tissue, fluid or blood samples. PATIENT ADVOCACY GROUP: Groups like Lung Cancer Alliance that provide additional education, support and referral services at no cost. PATIENT NAVIGATOR: A nurse, social worker or trained lay person who assists patients and loved ones on their journey through the healthcare system. PULMONARY REHABILITATION SPECIALIST: A specialist who works to reduce symptoms and side effects from diseases of the lung including lung cancer and their treatments. PULMONOLOGIST: A doctor who specializes in treating diseases and conditions involving the lungs. RADIATION ONCOLOGIST: A doctor who specializes in treating cancer using various forms of radiation by focusing it on the tumor site in the body. THORACIC SURGEON: A doctor who performs surgeries in the chest region. Some thoracic surgeons specialize in lung cancer. 4
7 5
8 DIAGNOSING SCLC IMAGING A number of tests provide information on areas of the lungs that do not appear normal. Doctors sometimes refer to these areas as tumors, spots, lesions, nodules or masses. These imaging techniques can provide information beyond what can be seen with a chest X-ray. Imaging can help doctors learn if a suspicious area is cancerous (malignant) or not cancerous (benign). Some imaging tools include the following: CT (computed tomography) or CAT scanning can show tumors that may not be visible on a normal chest X-ray. LDCT (low-dose computed tomography) scanning is used to screen those who are at high risk every year to see if they have lung cancer. PET (positron emission tomography) scanning shows how a tumor is using glucose (also known as sugar). Since tumors typically use more glucose than surrounding tissue, they appear as hot spots (bright areas) in these images. PET scans are often used to see if cancer has spread to other parts of the body. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) creates detailed images of the body and can help determine whether a tumor has spread beyond its original location. Used in SCLC to check for spread of cancer to the brain. 6
9 BIOPSIES A biopsy is a procedure in which tissue is removed from the body for testing. The tissue can help doctors diagnose cancer and provide specific information about the suspicious area. There are several types of biopsy procedures: NEEDLE BIOPSY OR NEEDLE ASPIRATION: A hollow needle is inserted through the skin to draw out tissue for testing. The procedure is usually done with the aid of imaging tests such as CT scans, fluoroscopy, ultrasound or MRI to determine where to insert the needle. There are two types of this kind of biopsy: x Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): Tissue is removed using a thin hollow needle. Depending on the location of the tumor, FNA is done during a bronchoscopy procedure (in which a camera-equipped tube is used to view the windpipe and other airways) or through skin. This procedure may be guided by an ultrasound or a CT scan. x Core Needle Biopsy: Tissue is removed using a wider needle. More tissue can be removed with this procedure than with fine needle aspiration. THORACENTESIS: Fluid is removed from the space around the lungs (also called the pleural cavity) using a hollow needle inserted into the chest. BRONCHOSCOPY: A thin, lighted tube (bronchoscope) is passed down the throat through the mouth or nose and into the center area of the lungs. A needle is then inserted down the tube and samples are removed for testing. x Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS): Uses a bronchoscope and ultrasound (high frequency sound waves) and allows for better examination of the lymph nodes and other structures in the center of the chest to see if cancer has spread. SURGICAL BIOPSY: Tissue is removed during surgery. LIQUID BIOPSY: Blood or other fluid is removed for biomarker testing to help with planning treatment. Liquid biopsy is NOT used to diagnose lung cancer. 7
10 The Lymphatic System Lymph Nodes THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The lymphatic system includes organs, vessels and nodes that are found throughout the body. The lymphatic system collects excess fluid and returns it to the blood to fight infection. Similar to blood vessels, lymph vessels help circulate lymph fluid throughout the body. Lymph fluid contains white blood cells, which help to fight infection. Lymph nodes are small, oval-shaped organs within the lymphatic system. The nodes trap and collect harmful organisms so your white blood cells can attack them. Lymph nodes are found throughout the body, but major groups can be found behind the knee and elbow joints in the groin, armpits, neck and chest. A large group that drains lymph fluid from the lungs is found in the center of the chest (mediastinum). Cancer cells can break off from the main tumor and travel to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system. Some of these cells become trapped within a lymph node and start to grow. If cancer is in the lymph nodes, your doctor can help estimate if the cancer has spread and how far. 8
11 STAGING SCLC is divided into four stages (I, II, III, IV), based on the TNM System (see explanation below). Stage is generally determined by the size and whether or not it has spread from the place it started (including to lymph nodes). T N M TNM System stands for TUMOR: Where the tumor is and how big it is. stands for LYMPH NODES: Whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes and where the affected lymph nodes are located. stands for METASTASIS: Whether the cancer has spread beyond the lung to the other lung, the pleura, brain, bones or other parts of the body. Stage I The tumor is only in one lung and is no more than 5cm with no spread to nearby lymph nodes. Stage II The tumor is only in one lung and may be larger than a stage I tumor. The cancer may have spread to nearby lymph nodes but not beyond. Stage III The tumor or tumors are only in one lung and may have grown into other structures within the chest or spread to more lymph nodes. Stage Iv The tumor may be any size and the cancer has spread to the other lung, the lining of the lung or organs outside the lungs. Your treatment team may tell you that your stage is an A, B or C, for example, IIIA or IIIB. A is a lower stage (smaller or less spread) than B. In the past, SCLC was staged as limited or extensive stage and you may still hear it described that way. It is important to know the stage of the cancer. Staging helps doctors create a treatment plan that is best for you. x Limited-stage describes SCLC that is only found in one lung or nearby lymph nodes. x Extensive-stage describes SCLC that has spread outside the lung in which it began to spread to other parts of the body. 9
12 TREATMENT OPTIONS TREATMENT FOR SCLC USUALLY INCLUDES MORE THAN ONE OF THE FOLLOWING: x Chemotherapy x Radiation x Immunotherapy x Prophylactic Cranial Irradiation (PCI) x Surgery x Clinical Trials x Palliative Care (care for symptoms and side effects) TREATMENT DEPENDS ON THE FOLLOWING: x The stage of the cancer x How well your lungs are working x Other health problems x If you can complete activities like eating, bathing and dressing on your own 10
13 chemotherapy Chemotherapy is a treatment that kills cancer s rapidly growing and dividing cells. It is given in cycles followed by a rest period to allow recovery time. It is the most common treatment for SCLC and usually given as a combination of two chemotherapy drugs. The most common combinations are: x PLATINOL (cisplatin) and VP-16 (etoposide) x PARAPLATIN (carboplatin) and VP-16 (etoposide) Other drugs used if SCLC returns include the following: x HYCAMTIN (topotecan), oral or by injection x TAXOL (paclitaxel) x TAXOTERE (docetaxel) x GEMZAR (gemcitabine) x ADRIAMYCIN (doxorubicin) x ONCOVIN (vincristine) x TEMODAR (temozolomide) SIDE EFFECTS OF CHEMOTHERAPY The goal of chemotherapy is to kill cancer cells, which are fast growing. Because the cells that make up the hair and the lining of the digestive system are also rapidly growing, chemotherapy can damage them too and cause many common side effects. Below is a list of possible side effects a person on chemotherapy may experience. Side effects can vary from person to person. It is important to know that in most cases side effects can be prevented or managed. You and your care team should discuss potential side effects you could experience. Common side effects of drug therapy may include: x Hair loss x Nausea and vomiting x Loss of appetite (anorexia) x Constipation x Diarrhea x Shortness of breath (dyspnea) x Tiredness (fatigue) x Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet (neuropathy) x Low platelets x Low red/white blood cell count (anemia) 11
14 RADIATION therapy Radiation therapy is a treatment that uses high energy beams to kill or shrink cancer cells, to manage pain or to prevent cancer from spreading to the brain, as in the case of prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI, see box on page 12-2 pages ahead). SCLC is usually treated with general external beam radiation, which uses carefully aimed doses of radiation to specific sections of the lungs or surrounding areas. COMMON SIDE EFFECTS RADIATION THERAPY TO THE CHEST: x Tiredness (fatigue) x Loss of appetite (anorexia) x Inflammation of the esophagus (esophagitis) x Inflammation of the lung (pneumonitis) x Skin irritation - Redness - Itching - Dryness Be sure to talk with your healthcare team about ways to manage any side effects you may experience. WHOLE BRAIN RADIATION THERAPY: When SCLC has spread to the brain, whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) is typically used as treatment. Tiredness and skin irritation are common. Additional side effects may include: x Hair loss x Nausea x Vomiting x Headache x Fever x Short term memory changes 12
15 immunotherapy An important part of the immune system is its ability to recognize the difference between normal cells in the body and those it sees as foreign - like cancer cells. To do this, it uses checkpoints on certain immune cells called T- cells, that need to be turned on to start an immune response. However, cancer cells can find ways to use these checkpoints to avoid being attacked by the immune system. A class of immunotherapies called checkpoint inhibitors work to fix the problem by targeting a specific protein on the surface of our T-cells such as PD-1/PD-L1. This keeps the immune system active and working against the cancer (learn more in our Immunotherapy brochure). The following are the immunotherapies currently approved for SCLC: x OPDIVO (nivolumab) Given to patients with extensive-stage, Stage 4, SCLC after two other treatments stop working. Recent research has shown that immunotherapy in combination with chemotherapy as a first treatment can result in better overall survival than chemotherapy alone in patients with late stage SCLC. The FDA may approve this combination as a first treatment soon. SIDE EFFECTS OF IMMUNOTHERAPY Side effects from immunotherapy are generally caused by the increased activity of the immune system. These may include: x Tiredness (fatigue) x Flu-like symptoms x Rashes x Diarrhea x Shortness of breath (dyspnea) x Inflammation within the lungs, liver, kidneys or hormone-producing glands such as thyroid or pituitary. Be sure to talk with your healthcare team about ways to manage any side effects you may experience. 13
16 PROPHYLACTIC CRANIAL IRRADIATION (PCI) WHAT IS PCI AND WHY SHOULD I CONSIDER IT? SCLC often spreads (metastasizes) to the brain. PCI is radiation to the brain with the goal of preventing cancer from growing in the brain by killing cells too small to see on imaging tests. WHAT CAN I EXPECT? PCI usually starts three to four weeks after chemotherapy ends. During PCI, the head must stay still so the radiation is given the same way each time. To help, a plastic mask is made before treatment starts. The doses of radiation used in PCI are smaller than those used to treat the cancer if it spreads to the brain. Anxiety or fear of being closed in can be helped by medication. Some centers have ways to help patients stay calm during PCI, such as playing music. SHORT-TERM SIDE EFFECTS Due to the low dose of radiation used, side effects are usually mild. Tiredness and hair loss are the most common. Unless tiredness is an issue or anti-anxiety medications are used, a patient may drive home after PCI. Many people are able to work while in PCI treatments. LONG-TERM EFFECTS Some people worry that PCI will affect their memory and how they think later in life. Major long-term effects are unlikely. Similar to the normal aging process, concentration and shortterm memory seem to be the most affected. The idea of radiation to the brain can be scary, especially when no cancer has been found there. Your doctor should talk with you about the risks and benefits of PCI. Be sure to ask questions and discuss any concerns you have. 14
17 surgery Surgery is not often used to treat SCLC. However, for patients with small tumors, surgery may be an option. When surgery is considered for SCLC, learning as much as possible about the size and location of the cancer is especially important. Research into immunotherapies, targeted therapies and other new treatments continue to provide promising new approaches to the treatment of SCLC and hope to patients living with the disease. clinical trials Clinical trials are also an option for people diagnosed with SCLC and should be considered every time a treatment decision is made. Clinical trials may allow patients to receive new treatments or combinations of treatment that are still being studied by doctors and researchers. Clinical trials for SCLC patients include: x New types of immunotherapy that boost the body s immune system including other checkpoint inhibitors or cancer vaccines. x Immunotherapy combinations. x Targeted therapies that target a specific gene or protein found in your cancer. Lung Match Cancer Clinical Trial Matching Service Our goal is to make finding a clinical trial as easy as possible. With information about your diagnosis, such as the stage and type of lung cancer and your treatment history, our Clinical Trial Navigators can help you understand the clinical trial process and find trials that you may be eligible for. Having that information to discuss with your treatment team can help you decide if joining a trial is right for you. MATCH Lung Lung Cancer Alliance Talk to your treatment team about whether a clinical trial is right for you. To see if you may qualify for a research study, call our HelpLine at or visit lungmatch.org 15
18 PALLIATIVE CARE Palliative Care is a supportive service that can help cancer patients find ways to address symptoms and side effects related to the cancer or treatment. Here is a list of problems that palliative care may be able to help with: x Constipation x Diarrhea x Difficulty breathing x Fatigue x Loss of appetite x Mood changes related to treatment x Nausea x Pain x Sleep problems x Weight loss Who provides Palliative Care? Usually it is provided by a healthcare professional that has special training or experience improving the quality of life for patients with cancer or a chronic disease. Palliative care teams may also include other professionals like nurses, dieticians, social workers, chaplains and therapists. Where is Palliative Care Provided? Palliative care options vary depending on location and the needs of the patient. Sometimes palliative care is offered in the hospital, outpatient office, long-term care facility or in a patient s home. What Palliative Care is not: x Palliative care is not a treatment for cancer. x Palliative care is not hospice. Hospice is a service that is only available to people who are not seeking treatment and are considered terminal (less than six months to live). Finding Palliative Care: If you are interested in finding palliative care, ask your oncologist if palliative care is right for you. 16
19 ABOUT LUNG CANCER ALLIANCE Lung Cancer Alliance serves and listens to those living with and at risk for lung cancer to reduce stigma, improve quality of life and increase survival. We empower our community by helping people navigate the paths of early detection, diagnosis and treatment. Insights allow us to improve care, amplify awareness, drive advocacy and lead research with the vision of tripling the number of survivors in the next decade. For more information about our support services, research collaborations, awareness campaigns, advocacy efforts and early detection initiatives, please contact us. HELPLINE MOLECULAR TESTING & CLINICAL TRIAL MATCHING lungmatch.org WEBSITE lungcanceralliance.org MAIL 1700 K Street NW, Suite 660 Washington, DC Saving lives. Advancing research. Empowering people.
20 This publication is supported by our sponsors. They do not influence or provide input on content. Lung Cancer Alliance is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization. Our programs are made possible by generous support from people like you. All donations are tax deductible to the fullest extent permitted by law. The content of this brochure has been reviewed by members of our Medical and Professional Advisory Board and our Patient & Caregiver Research Advocates. Copyright 2019, Lung Cancer Alliance. All rights reserved.
Small cell lung cancer
 understanding SerieS Small cell lung cancer 1-800-298-2436 lungcanceralliance.org a Guide for the patient i table of contents anatomy of the lungs The following image shows different parts that make up
understanding SerieS Small cell lung cancer 1-800-298-2436 lungcanceralliance.org a Guide for the patient i table of contents anatomy of the lungs The following image shows different parts that make up
UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER BIOPSIES LungCancerAlliance.org
 UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER BIOPSIES 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org CONTENTS What is a Biopsy?...2 Non-Surgical Biopsies...3 Surgical Biopsies...5 Biopsy Risks...6 Biopsy Results...6 Questions
UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER BIOPSIES 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org CONTENTS What is a Biopsy?...2 Non-Surgical Biopsies...3 Surgical Biopsies...5 Biopsy Risks...6 Biopsy Results...6 Questions
Small Cell Lung Cancer
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
Small Cell Lung Cancer Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) affects 15% of all lung cancer patients. SCLC is the most aggressive type of lung cancer. It may be treated with chemotherapy and radiation. SCLC has
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Lung Cancer Basics... 2 Immunotherapy... 3 FDA Approved Immunotherapies...
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Lung Cancer Basics... 2 Immunotherapy... 3 FDA Approved Immunotherapies...
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program. Patient information for. Last revised: November
 Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Thoracic Diagnostic Assessment Program Patient information for Last revised: November 2016 1 A list of your tests and appointments Diagnostic tests 2 3 4 Specialist appointments Doctor: Specialty: Notes:
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Lung Cancer: Diagnosis, Staging and Treatment Cancer starts in your cells. Cells are the building blocks of your tissues. Tissues make up the organs of your
immunotherapy a guide for the patient
 immunotherapy FOR LUNG CANCER a guide for the patient TABLE OF CONTENTS lung cancer basics... 2 immunotherapy... 5 Checkpoint Inhibitors... 6-9 Monoclonal Antibodies... 9 Vaccines... 10 Adoptive T-Cell
immunotherapy FOR LUNG CANCER a guide for the patient TABLE OF CONTENTS lung cancer basics... 2 immunotherapy... 5 Checkpoint Inhibitors... 6-9 Monoclonal Antibodies... 9 Vaccines... 10 Adoptive T-Cell
Esophageal cancer. What is esophageal cancer? Esophageal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the esophagus.
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer What is esophageal cancer? What are risk factors? Signs and symptoms Tests for esophageal cancer Stages of esophageal cancer Treatment options What is esophageal cancer?
Esophageal Cancer. Source: National Cancer Institute
 Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer forms in the tissues that line the esophagus, or the long, hollow tube that connects the mouth and stomach. Food and drink pass through the esophagus to be digested.
LUNG CANCER FINDING YOUR BEST CARE
 LUNG CANCER FINDING YOUR BEST CARE FINDING THE BEST CARE FOR YOU Do you wonder how to find the best lung cancer care? The answer to this question is unique to you. We want you to find safe, up-to-date,
LUNG CANCER FINDING YOUR BEST CARE FINDING THE BEST CARE FOR YOU Do you wonder how to find the best lung cancer care? The answer to this question is unique to you. We want you to find safe, up-to-date,
Lung Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis cancer.ca
 Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed
Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Lung Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed
TARGETED THERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER. Patient and Caregiver Guide
 TARGETED THERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TARGETED THERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Why Targeted Therapy?...2 Lung Cancer Basics...2 Changes in
TARGETED THERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TARGETED THERAPY FOR LUNG CANCER Patient and Caregiver Guide TABLE OF CONTENTS Why Targeted Therapy?...2 Lung Cancer Basics...2 Changes in
WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW
 WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW To promote personal well-being, fitness and nutrition for all TDCJ employees. November 2008 Lung cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining
WELLNESS INITIATIVE NOW To promote personal well-being, fitness and nutrition for all TDCJ employees. November 2008 Lung cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining
UNDERSTANDING SQUAMOUS CELL LUNG CANCER
 UNDERSTANDING SQUAMOUS CELL LUNG CANCER A guide for patients and caregivers FREE TO BREATHE SUPPORT LINE (844) 835-4325 A FREE resource for lung cancer patients & caregivers About this brochure This brochure
UNDERSTANDING SQUAMOUS CELL LUNG CANCER A guide for patients and caregivers FREE TO BREATHE SUPPORT LINE (844) 835-4325 A FREE resource for lung cancer patients & caregivers About this brochure This brochure
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy
 Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung.
 Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Lung Cancer Lung cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lung. The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer
 Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Thoracoscopy for Lung Cancer Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your doctor may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer. The
Lung cancer forms in tissues of the lung, usually in the cells lining air passages.
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Lung cancer usually forms in the tissue cells lining the air passages within the lungs. The two main types are small-cell lung cancer (usually found in cigarette smokers)
Guide to Understanding Lung Cancer
 Guide to Understanding Lung Cancer Lung cancer is the second most common cancer overall for men and women in the U.S., with an estimated 222,500 new cases in 2017. However, lung cancer is the most common
Guide to Understanding Lung Cancer Lung cancer is the second most common cancer overall for men and women in the U.S., with an estimated 222,500 new cases in 2017. However, lung cancer is the most common
Lung Cancer Resection
 Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Lung Cancer Resection Introduction The occurrence of lung cancer has increased dramatically over the last 50 years. Your health care provider may have recommended an operation to remove your lung cancer.
Charlton Campus Map Information Handbook
 Charlton Campus Map Information Handbook 50 Charlton Avenue East Hamilton, Ontario, L8N 4A6 S Parking Garage Public Parking W N Walkway to Hospital Fontbonne for patients and families Staff Only Parking
Charlton Campus Map Information Handbook 50 Charlton Avenue East Hamilton, Ontario, L8N 4A6 S Parking Garage Public Parking W N Walkway to Hospital Fontbonne for patients and families Staff Only Parking
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma
 Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
Understanding Pleural Mesothelioma UHN Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn about: What is pleural mesothelioma? What causes it? What are the symptoms? What tests are done to
What Is Small Cell Lung Cancer?
 About Small Cell Lung Cancer Overview If you have been diagnosed with small cell lung cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start.
About Small Cell Lung Cancer Overview If you have been diagnosed with small cell lung cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start.
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
 Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
Cancer Biology What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells. What is cancer? l Cancer is a group of several diseases caused by the abnormal growth of cells.
YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT
 UNDERSTANDING SERIES YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...2 The Basics...3 Sections of a Pathology Report...6
UNDERSTANDING SERIES YOUR LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY REPORT 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT 1 CONTENTS What is a Pathology Report?...2 The Basics...3 Sections of a Pathology Report...6
What is Thyroid Cancer?
 Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
Thyroid Cancer What is Thyroid Cancer? The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea (windpipe). It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin
General Information Key Points
 The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
The content of this booklet was adapted from content originally published by the National Cancer Institute. Male Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ ) Patient Version. Updated September 29,2017. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/patient/male-breast-treatment-pdq
LUNG CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS
 UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT THE BASICS ABOUT CLINICAL TRIALS WITH MORE INFORMATION YOU CAN MAKE BETTER CHOICES. The decision
UNDERSTANDING SERIES LUNG CANCER CLINICAL TRIALS 1-800-298-2436 LungCancerAlliance.org A GUIDE FOR THE PATIENT THE BASICS ABOUT CLINICAL TRIALS WITH MORE INFORMATION YOU CAN MAKE BETTER CHOICES. The decision
Information for. Patients with an Abnormal Lung X-ray
 Information for Patients with an Abnormal Lung X-ray Some of the materials in this resource were adapted with permission from: Understanding Lung Cancer, Juravinski Cancer Centre, Hamilton Health Sciences,
Information for Patients with an Abnormal Lung X-ray Some of the materials in this resource were adapted with permission from: Understanding Lung Cancer, Juravinski Cancer Centre, Hamilton Health Sciences,
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer
 Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
Gastric (Stomach) Cancer Gastric cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The stomach is a J-shaped organ in the upper abdomen. It is part of the digestive
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER
 IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER A guide for patients and caregivers FREE TO BREATHE SUPPORT LINE (844) 835-4325 A FREE resource for lung cancer patients & caregivers About this brochure
IMMUNOTHERAPY FOR THE TREATMENT OF LUNG CANCER A guide for patients and caregivers FREE TO BREATHE SUPPORT LINE (844) 835-4325 A FREE resource for lung cancer patients & caregivers About this brochure
Mesothelioma. Understanding your diagnosis
 Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis Mesothelioma Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be overwhelmed by the large amount of
Diagnosed with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer?
 ESSENTIALS Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Diagnosed with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer? It can be frightening to learn you or a loved one has been diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer. It is important
ESSENTIALS Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Diagnosed with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer? It can be frightening to learn you or a loved one has been diagnosed with metastatic colorectal cancer. It is important
Laryngeal Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis cancer.ca
 Laryngeal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Laryngeal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be
Laryngeal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Laryngeal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be
patient decision aid advanced lung cancer
 patient decision aid advanced lung cancer Introduction This aid is meant to supplement conversations with your care team. Patients who have used a decision aid like this said it helped them make care choices
patient decision aid advanced lung cancer Introduction This aid is meant to supplement conversations with your care team. Patients who have used a decision aid like this said it helped them make care choices
GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1
 GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1 S16-1661-01A Pre-release Article for Examination in May 2016 1661 01A001 CJ*(S16-1661-01A) 2 Information for Teachers The pre-release article is intended
GCE AS/A level 1661/01-A APPLIED SCIENCE UNIT 1 S16-1661-01A Pre-release Article for Examination in May 2016 1661 01A001 CJ*(S16-1661-01A) 2 Information for Teachers The pre-release article is intended
Glossary of terms for cancer
 Glossary of terms for cancer A Adjuvant chemotherapy Adjuvant therapy Alopecia Alveoli Anemia Anesthetic Anorexia Antibiotic Antiemetic Asymptomatic Atypical Axillary node The use of anticancer drugs after
Glossary of terms for cancer A Adjuvant chemotherapy Adjuvant therapy Alopecia Alveoli Anemia Anesthetic Anorexia Antibiotic Antiemetic Asymptomatic Atypical Axillary node The use of anticancer drugs after
Esophageal Cancer. What is esophageal cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Scan for mobile link. Esophageal Cancer Esophageal cancer occurs when cancer cells develop in the esophagus. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Esophageal cancer may not
Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. ocf80101 Last reviewed: 06/08/2016 1
 Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Cancer Introduction Cancer begins in your cells, which are the building blocks of your body. Extra cells can form a mass called a tumor. Some tumors aren t cancerous, while other ones are. Cells from cancerous
Head and Neck Cancer. What is head and neck cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Understanding surgery
 What does surgery for lung cancer involve? Surgery for lung cancer involves an operation, which aims to remove all the cancer from the lung. Who will carry out my operation? In the UK, we have cardio-thoracic
What does surgery for lung cancer involve? Surgery for lung cancer involves an operation, which aims to remove all the cancer from the lung. Who will carry out my operation? In the UK, we have cardio-thoracic
Lung Cancer. you can face it if you know it better
 Lung Cancer you can face it if you know it better Table of contents This booklet was prepared by: pag. 4 pag. 5 pag. 7 pag. 10 pag. 12 pag. 15 pag. 17 pag. 19 pag. 21 Silvia Novello Matteo Giaj Levra
Lung Cancer you can face it if you know it better Table of contents This booklet was prepared by: pag. 4 pag. 5 pag. 7 pag. 10 pag. 12 pag. 15 pag. 17 pag. 19 pag. 21 Silvia Novello Matteo Giaj Levra
Know about brain metastases and treatment
 Know about brain metastases and treatment Princess Margaret For patients and families living with brain metastases Read this resource to learn: What are brain metastases 2 How can the Brain Metastases
Know about brain metastases and treatment Princess Margaret For patients and families living with brain metastases Read this resource to learn: What are brain metastases 2 How can the Brain Metastases
Patient information from BMJ
 Patient information from BMJ Last published: Dec 02, 2016 Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important
Patient information from BMJ Last published: Dec 02, 2016 Lung cancer (non-small-cell) It can be devastating to find out that you or someone close to you has lung cancer. You will have to make some important
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy
 What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
What You Need to Know About Lung Cancer Immunotherapy Lung.org/immunotherapy What is immunotherapy? Immunotherapy for cancer, sometimes called immune-oncology, is a type of medicine that treats cancer
squamous cell lung cancer
 TYPES OF LUNG CANCER UPDATED FEBRUARY 2016 What you need to know about... squamous cell lung cancer Copyright 2018 LUNGevity Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
TYPES OF LUNG CANCER UPDATED FEBRUARY 2016 What you need to know about... squamous cell lung cancer Copyright 2018 LUNGevity Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
LIVING WITH A DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER
 LIVING WITH A DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER We are Free to Breathe. We are a partnership of lung cancer survivors, advocates, researchers, healthcare providers and industry leaders. We are united in the belief
LIVING WITH A DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER We are Free to Breathe. We are a partnership of lung cancer survivors, advocates, researchers, healthcare providers and industry leaders. We are united in the belief
Breast Cancer. Common kinds of breast cancer are
 Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Breast Cancer A breast is made up of three main parts: glands, ducts, and connective tissue. The glands produce milk. The ducts are passages that carry milk to the nipple. The connective tissue (which
Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that
What is lung cancer? Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
Cancer of the oropharynx
 Cancer of the oropharynx Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly
Cancer of the oropharynx Patient information What is cancer? The human body is made up of billions of cells. In healthy people, cells grow, divide and die. New cells constantly replace old ones in an orderly
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul. Epidemiology. Risk factors/aetiology
 Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Slide 1 Investigation and management of lung cancer Robert Rintoul Department of Thoracic Oncology Papworth Hospital Slide 2 Epidemiology Second most common cancer in the UK (after breast). 38 000 new
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
To help doctors give their patients the best possible care, the American. What to Know
 Patient Information Resources from ASCO What to Know ASCO s Guideline on Chemotherapy for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer SEPTEMBER 2011 KEY MESSAGES Chemotherapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer
Patient Information Resources from ASCO What to Know ASCO s Guideline on Chemotherapy for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer SEPTEMBER 2011 KEY MESSAGES Chemotherapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer
What is Thyroid Cancer? Here are four types of thyroid cancer:
 What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
What is Thyroid Cancer? Thyroid cancer is a group of malignant tumors that originate from the thyroid gland. The thyroid is a gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid gland absorbs iodine from the bloodstream
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
X-Plain Lung Cancer Reference Summary Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Lung cancer rates among Southeast
What is head and neck cancer? How is head and neck cancer diagnosed and evaluated? How is head and neck cancer treated?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells (lymphocytes) of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Malignant Mesothelioma
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Malignant Mesothelioma This information will help you understand malig nant (cancerous) mesothelioma, including risk factors, diag nosis, surg ery, and treatment. About Mesothelioma
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Malignant Mesothelioma This information will help you understand malig nant (cancerous) mesothelioma, including risk factors, diag nosis, surg ery, and treatment. About Mesothelioma
Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Symptoms. Types
 Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Lung Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Living With Lung Cancer. Patient Education Guide
 Living With Lung Cancer Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Your doctor has just told you that you have lung cancer. Even if you thought that you might
Living With Lung Cancer Patient Education Guide A M E R I C A N C O L L E G E O F C H E S T P H Y S I C I A N S Your doctor has just told you that you have lung cancer. Even if you thought that you might
lung adenocarcinoma What you need to know about... TYPES OF LUNG CANCER
 TYPES OF LUNG CANCER What you need to know about... lung adenocarcinoma Copyright 2018 LUNGevity Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted
TYPES OF LUNG CANCER What you need to know about... lung adenocarcinoma Copyright 2018 LUNGevity Foundation All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, distributed, or transmitted
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer:
 1 Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A Doctor s Perspective for Patients and Families Living with the Disease By Maria E. Cabanillas, M.D., F.A.C.E. Associate Professor and Faculty Director of Clinical Research
1 Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A Doctor s Perspective for Patients and Families Living with the Disease By Maria E. Cabanillas, M.D., F.A.C.E. Associate Professor and Faculty Director of Clinical Research
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
LUNG SURGERY. Treatment for Lung Problems
 LUNG SURGERY Treatment for Lung Problems When You Need Lung Surgery Your doctor is recommending surgery for your lung problem. Surgery alone may treat your problem. Or you may need other treatments as
LUNG SURGERY Treatment for Lung Problems When You Need Lung Surgery Your doctor is recommending surgery for your lung problem. Surgery alone may treat your problem. Or you may need other treatments as
ABOUT LUNG CANCER ALLIANCE
 ABOUT LUNG CANCER ALLIANCE www.lungcanceralliance.org 1-800-298-2436 WHO WE ARE Lung Cancer Alliance serves and listens to those living with and at risk for lung cancer to reduce stigma, improve quality
ABOUT LUNG CANCER ALLIANCE www.lungcanceralliance.org 1-800-298-2436 WHO WE ARE Lung Cancer Alliance serves and listens to those living with and at risk for lung cancer to reduce stigma, improve quality
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer
 Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Investigations to diagnose asbestos related conditions. Helpline
 Investigations to diagnose asbestos related conditions Helpline 0800 089 1717 www.clydesideactiononasbestos.org.uk Common investigations used to diagnose your condition Contents Introduction...3 Blood
Investigations to diagnose asbestos related conditions Helpline 0800 089 1717 www.clydesideactiononasbestos.org.uk Common investigations used to diagnose your condition Contents Introduction...3 Blood
Lung Carcinoid Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Lung Carcinoid Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Lung Carcinoid Tumor Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery
 Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Adam J. Hansen, MD UHC Thoracic Surgery Sometimes seen on Chest X-ray (CXR) Common incidental findings on computed tomography (CT) chest and abdomen done for other reasons Most lung cancers discovered
Preparing for Your Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (CPI) Treatment
 Preparing for Your Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (CPI) Treatment Overview What is the immune system? What are immune checkpoint inhibitors? What are the side effects to look out for? How are side effects
Preparing for Your Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor (CPI) Treatment Overview What is the immune system? What are immune checkpoint inhibitors? What are the side effects to look out for? How are side effects
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
GUIDE TO LUNG CANCER. Comprehensive, oncologistapproved. from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Made available through:
 GUIDE TO LUNG CANCER Comprehensive, oncologistapproved cancer information from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) www.cancer.net Made available through: ABOUT ASCO The American Society of
GUIDE TO LUNG CANCER Comprehensive, oncologistapproved cancer information from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) www.cancer.net Made available through: ABOUT ASCO The American Society of
Lung Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Screening What is lung cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease at
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Screening What is lung cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease at
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
Understand Your Disease: Brain Metastases
 Understand Your Disease: Brain Metastases Princess Margaret For patients and families coping with brain metastases Read this resource to know: What brain metastases are Common symptoms of brain metastases
Understand Your Disease: Brain Metastases Princess Margaret For patients and families coping with brain metastases Read this resource to know: What brain metastases are Common symptoms of brain metastases
BOWEL CANCER. Causes of bowel cancer
 A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
A cancer is an abnormality in an organ that grows without control. The growth is often quite slow, but will continue unabated until it is detected. It can cause symptoms by its presence in the organ or
Leukemia. There are different types of leukemia and several treatment options for each type.
 Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Total Thyroidectomy. Post-Surgery Instructions for: WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW:
 Post-Surgery Instructions for: Orlando Health Surgical Group 14 West Gore Street Orlando, FL 32806 321-843-5001 Total Thyroidectomy Michael Kahky, MD, F.A.C.S Marc Demers, MD, F.A.C.S Jeffrey R. Smith,
Post-Surgery Instructions for: Orlando Health Surgical Group 14 West Gore Street Orlando, FL 32806 321-843-5001 Total Thyroidectomy Michael Kahky, MD, F.A.C.S Marc Demers, MD, F.A.C.S Jeffrey R. Smith,
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer:
 1 Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A Doctor s Perspective for Patients and Families Living with the Disease By Maria E. Cabanillas, M.D., F.A.C.E. Associate Professor and Faculty Director of Clinical Research
1 Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: A Doctor s Perspective for Patients and Families Living with the Disease By Maria E. Cabanillas, M.D., F.A.C.E. Associate Professor and Faculty Director of Clinical Research
Esophageal Cancer. Understanding your diagnosis cancer.ca
 Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be
Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Esophageal Cancer Understanding your diagnosis When you first hear that you have cancer, you may feel alone and afraid. You may be
This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated.
 A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
A-Z of medical words This page explains some of the medical words that you may hear when you are finding out about pancreatic cancer and how it is treated. Absorption: once your food has been broken down,
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
Lung Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Screening What is lung cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease at
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Screening What is lung cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease at
Parathyroidectomy. Surgery for Parathyroid Problems
 Parathyroidectomy Surgery for Parathyroid Problems Why You Need Parathyroid Surgery Has your doctor just recommended that you have parathyroid surgery? If so, you likely have many questions. What are the
Parathyroidectomy Surgery for Parathyroid Problems Why You Need Parathyroid Surgery Has your doctor just recommended that you have parathyroid surgery? If so, you likely have many questions. What are the
What you need to know about Thyroid Cancer
 What you need to know about Thyroid Cancer This booklet has been designed to help you to learn more about your thyroid cancer. It covers the most important areas and answers some of the frequently asked
What you need to know about Thyroid Cancer This booklet has been designed to help you to learn more about your thyroid cancer. It covers the most important areas and answers some of the frequently asked
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms
Introduction. Growths in the prostate can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
 This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
