Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts. Reagan Leverett, MD, MS
|
|
|
- Myrtle Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS
2 Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound MRI Molecular Imaging Contrast Enhanced Mammography
3 Breast Parenchyma Fat Fibrous tissue Predominantly form the suspensory ligaments of Cooper Divide the glandular tissue into lobes Glandular tissue Consists of lobes
4 healthybeingllc.com
5 Density Classified on mammography. Fatty (<25% of glandular tissue) Scattered (25-50% of glandular tissue) Heterogeneous (50-75% of glandular tissue) Extremely (75-100% of glandular tissue)
6
7 What affects breast density? Age Weight Genetics and family history Menopausal hormone therapy use Having fewer children
8 Variability in Breast Density Classification Reported breast density can change due to multiple factors including: Quality of technique Patient differences Radiologist variability
9 Reclassification 13-19% of women were reclassified from nondense to dense or vice versa. Melnikow et al in Supplemental screening for breast Cancer in Women with Dense Breasts: A Systematic Review for the USPSTF Since breast density notification is now mandated in many states, reclassification of breast density from year to year may decrease a patient s confidence in screening. Major impetus for research on automated and computer assisted breast density determination
10 Are You Dense? 28 states now have breast density legislation which requires notification of the patient of density if heterogeneously dense or extremely dense.
11 Are You Dense? Pink: Enacted Law Blue: Working on Bill White: No action Star: Insurance coverage Law
12 Are You Dense? 28 states now have breast density legislation which requires notification of the patient of density if heterogeneously dense or extremely dense. In the state of Tennessee, Breast Density Notification Law became effective January 1, 2014
13 Breast Density Notification Your mammogram shows that your breast tissue is dense. Dense breast tissue is common and is not abnormal. However, dense breast tissue can make it harder to evaluate the results of your mammogram and may also be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. This information about the results of your mammogram is given to you to raise your awareness and to inform your conversations with your doctor. Together, you can decide which screening options are right for you. A report of your results was sent to your physician.
14 Why is Breast Density Important? Affects at least half of the population
15 Dense Breasts Approximately 40% of women have heterogeneously dense breasts. Approximately 10% of women have extremely dense breasts. Approximately 50-60% of women ages have dense breasts while approximately 20-30% of year olds do. In healthy weight women, 50-60% have dense breasts while 20-30% of obese women do.
16 Why is Breast Density Important? Affects at least half of the population Breast density impacts the sensitivity of detection of breast cancer on mammography.
17 Sensitivity Decreased sensitivity on mammogram Carney et al found sensitivity of extremely dense breast to be 62%, compared to fatty at 88%.. Women with dense breast tissue have cancers that are larger and more likely lymph node positive, and higher stage. Interval cancers are more common
18 Interval Cancer The Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium found interval cancers represented 15.7% of cancers in women with extremely dense breasts as opposed to 4.5% in women with fatty breasts. Gierach GL, Ichikawa L, Kerlikowske K, et al. Relationship between mammographic density and breast cancer death in the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 2012;104(16): Boyd et al found women with extremely dense breasts were 17x more likely to have interval cancer than women with fatty breasts.
19 Why are cancers missed on mammography? Most commonly focal asymmetries Bae et al. determined the following: 78% tumors were obscured by overlapping breast tissue 19% interpretive errors 3% not included due to difficult anatomic location or poor positioning
20 Why is Breast Density Important? Affects at least half of the population Breast density impacts the sensitivity of detection of breast cancer on mammography. Independent risk factor
21 Independent Risk Factor Previously accepted as only masking bias which attributed the higher risk of breast cancer solely to mass obscuration by dense breast parenchyma. McCormick et al. demonstrated a 4.6x increase when comparing fatty to extremely dense breasts. Risk difference between scattered and heterogeneously dense groups is less than 1.5x.
22 Risk When Standardized to Average Breast Tissue Women with heterogeneously dense breasts have 1.2x greater risk of developing breast cancer Women with extremely dense breasts have 2.0x greater risk of developing breast cancer Sickles. Radiol Clin North Am. 2010
23 Risk models Gail Clause BRCA-Pro Tyrer-Cuzick *None of these account for breast density Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC) model includes BI-RADS density added to a modified Gail model.
24 Goal: Reduce Mortality Stage at diagnosis, especially node status remains the most important prognostic factors. Across 11 randomized trials, only those methods that reduced the advanced cancer rate, increasing detection of node negative invasive cancer resulted in mortality reduction.
25 Theory of Supplemental Screening The addition of supplemental screening should allow earlier detection of cancers that would have eventually been detected as a palpable mass or larger in size on a later screening, leading to fewer interval cancers and more earlier stage cancers with reduction in mortality.
26 The Unfortunate Truth Majority of breast cancer deaths are seen in women who did not participate in screening. Too young to be screened Did not comply with screening guidelines Approximately 19 % of breast cancers detected at screening had already spread. 10% of breast cancer deaths are from interval screening. Webb ML, Cady B, Michaelson JS, et al. A failure analysis of invasive breast cancer: most deaths from disease occur in women not regularly screened. Cancer 2014;120(18):
27 Forms of Additional Screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound MRI Molecular Breast Imaging Contrast Enhanced Mammography
28 Supplemental Screening Technique Trials Advantages Disadvantages
29 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
30 Tomosynthesis Technique Acquire images through the breast at multiple angles Individual images reconstructed into a series of thin high-resolution slices Typically 1 mm thick # of slices depends on the thickness of the breast Can be displayed as individual images or in a dynamic cine mode 2 D and 3 D images acquired or with C-view 2D images are reconstructed from 3D.
31 Oslo Trial Prospective trial comparing digital mammography alone and digital mammography plus tomosynthesis Across all densities: 15% reduction in recall rate 27% increase in cancer detection rate 40% increase in detection of invasive cancer Low number of extremely dense with only 6 cancers total, 2 of which were DBT only.
32 STORM Prospective non-randomized trial which compared screening digital mammography to combined digital mammography and tomosynthesis Incremental cancer detection rate due to DBT of 2.8 per 1000 screens among 6079 women with fatty or scattered fibroglandular tissue and 2.5 among 1215 women with dense breasts.
33 Tomosynthesis and Digital Mammography in Dense and Nondense Breasts Rafferty et al used data from the previously published multicenter study (JAMA 2016). Increase in cancer detection rate and a reduction in recall rate for women with both dense and nondense breast tissue. These combined gains were largest for women with heterogeneously dense breasts but were not significant in women with extremely dense breasts.
34 Advantages of Tomosynthesis Easier to implement Positioning same for technologists as standard mammography The addition of tomosynthesis increases cancer detection across all breast densities. Average added cancer detection yield of 1.3/1000 screens. Friedewald SM, Rafferty EA, Rose SL, et al: Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography. JAMA 311: , 2014 Reduces false positive recalls due to overlapping normal tissue. There is a potential for tomosynthesis to eliminate 2Dacquisition, which significantly impacts resource utilization over ultrasound.
35 Disadvantages of Tomosynthesis Capital expenditure Physician read time Radiation dose PACS storage Calcifications Reimbursement Biopsies of tomo only findings
36 Screening Breast Ultrasound
37 Screening Breast Ultrasound Hand held ultrasound (HHUS) Physician performed verses technologist performed Standard protocol such as that used in ACRIN 6666 Average time to perform for ACRIN 6666 protocol was 19 minutes in the first year and 15 minutes in the third year Interpretation of HHUS (performed by technologist) <1 minute
38 Screening Breast Ultrasound Automated breast ultrasound system (ABUS) Uses a wide (typically 15 cm) footprint transducer and requires 3 to 5 acquisitions to cover each breast, generating coronal as well as several thousand transverse images. Skaane et al found it takes 15 minutes to acquire the AUS images for most breasts and one study found an average of 9 minutes to interpret them Recalls require targeted HHUS. Requires capital equipment Skaane P, Gullien R, Eben EB, Sandhaug M, Schulz-Wendtland R, Stoeblen F. Interpretation of automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) with and without knowledge of mammography: a reader performance study.
39 ve-heard-about/
40 ACRIN 6666 Multicenter trial that evaluated the effects of adding annual screening breast ultrasound performed by expert trained physicians to annual screening mammography women with dense breast tissue and increased risk for breast cancer participated.
41 ACRIN 6666 Screening ultrasound had a sensitivity of 76% and specificity of 84%. The addition of screening ultrasound resulted in an average of 4.3 additional cancers per thousand women screened (first round).
42 Recall rate: ACRIN % mammo alone 26.6% mammo + u/s Cancer detection rate: 7.5/100 mammo alone 12.8 mammo + u/s Biopsy rate: 2.4% mammo alone 10.2% mammo + u/s Biopsies yielding cancer: 29.2% mammo alone 11/4% mammo +u/s BIRADS 3: 3.2% mammo alone 13.8% mammo + u/s
43 Advantages to Screening Ultrasound Well tolerated Widely available Does not require IV contrast Requires no radiation No side effects No additional capital
44 Disadvantages to Screening Ultrasound Time to perform Average of 19 minutes Manpower Impractical to expect radiologists to perform Training Training for technologists is not widely available. No standardization of scanning technique
45 Disadvantages to Screening Ultrasound 76641: complete breast ultrasound, unilateral. $ ($ for bilateral) False positive results Biopsies yielding cancer: 29.2% mammo alone 11/4% mammo +u/s
46 Screening Ultrasound verses Tomosynthesis
47 ASTOUND Trial Adjunct Screening with Tomosynthesis or Ultrasound in Women with Mammography-Negative Dense Breasts. Prospective multicenter trial in which women with dense breasts and negative 2D mammogram underwent tomosynthesis and physician performed whole breast ultrasound with independent interpretation.
48 ASTOUND (Interim Results) Added cancer detection yield significantly higher for ultrasound (7.1/1000) than tomosynthesis (4/1000). Concluded: If adjunct ultrasound is performed for dense breasts, the incremental cancer detection rate from tomosynthesis is negligible.
49 ASTOUND (Interim Results) The majority of the ultrasound detected cancers missed on tomosynthesis were masses. The one cancer detected on tomosynthesis and not ultrasound was architectural distortion. If adjunct ultrasound is not routinely performed in mammography negative dense breasts, results support the use of adjunctive tomosynthesis.
50 Interval Improvement ASTOUND (preliminary): Demonstrated false positive recalls of 2.0% and false positive biopsies of 0.7%. These low rates likely reflect the fact that most were incidental screens (prior examinations available). ACRIN 6666: Incidence screens in year 2 and 3 demonstrated far fewer false positives than year 1. Philpotts et al (RSNA abstract): Compared year 5 to year 1; PPV of biopsies increased from 6.5% to 25%.
51 MRI
52 MRI MRI is recommended for supplemental screening by the American Cancer Society for the following: Known BRCA-mutation carriers First-degree relatives of a BRCA-mutation carrier but untested Those with a lifetime risk of breast cancer equal to or greater than 20% (by BRCAPRO model or other models dependent on family history) If the only risk factor is dense breast tissue, lifetime risk does not meet 20%
53 Current MRI Protocol Dedicated breast coil should be used Pulse sequences include: Axial pre-contrast T1 fat sat 3 Axial post contrast T1 fat sat, every 90 seconds Saggital post contrast (4 th ) Axial T2 Axial T1 non fat sat Subtract pre-contrast from 1 st post MIP
54 Substudy to ACRIN 6666 Berg et al. performed a sub-study to assess the rate and stage of cancers detected with a single screening MRI. To be eligible women had to have completed the third round of annual ultrasound and mammography screenings and agree to undergo MRI within 8 weeks of the 24-month mammo. Women who accepted were noted to have higher risk and were younger than those who declined. Also were less likely to have had a personal history of breast cancer.
55 Substudy to ACRIN 6666 For 612 MRI participants, sensitivity increased from 7 of 16 with mammo and ultrasound, to 16 of 16 with the addition of MRI. Specificity reduced from 0.84 to of 612 participants were biopsied only because of the MRI, 8 of whom were found to have cancer.
56 Sub-study to ACRIN % absolute increase in cancer detection seen in the MRI sub-study compared to 34% absolute increase in invasive cancer detection seen by adding annual ultrasound to mammo
57 Sensitivity is the advantage to MRI Schrading et al. found in average-risk women with all breast densities, 3.2% of MRIs showed suspicious findings and 33% of those were malignant. All additional cancers were node negative. ACRIN 6666 found that even after 3 rounds of annual screening ultrasound, 8 additional cancers (all node negative) were found on MRI.
58 Disadvantages to MRI High false positives Average acquisition time between minutes High direct and indirect costs Reduced tolerability Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with acute or chronic renal disease Limited availability in small communities May not be reimbursed for lifetime risk <20%
59 Abbreviated Protocol Kuhl et al. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014 Abbreviated protocol included the first postcontrast subtracted images and a MIP Acquisition time of 3 minutes Expert radiologist reading time of the MIP of 3 seconds sufficient to establish the absence of breast cancer with a NPV of 99.8%. Reading time for the entire abbreviated protocol was <30 seconds with a diagnostic accuracy equivalent to the full diagnostic protocol Additional cancer yield of 18.2 per 1000 in women prescreened by screening ultrasound and mammo
60 Abbreviated Protocol Harvey et al produced similar results in 2016 in JACR 568 cases reviewed with no difference in cancers detected Scan times decreased by 18.8 minutes per case Interpretation time was 1.55 minutes for the abbreviated protocol Review of the full protocol led to a significant change in final BIRADS in 12 of 568 (2.1%) of cases
61 EA1141 ECOG-ACRIN study Comparison of abbreviated breast MRI and digital breast tomosynthesis in breast cancer screening in women with dense breasts.
62 Molecular Breast Imaging
63 Molecular Breast Imaging Tc-99m Sestamibi Strong affinity to cancer cells Prescribed dose 8 mci corresponding to an effective radiation dose of 2.4 msv. Image immediately with the breast in light compression in both MLO and CC projections. Exposures between 7-10 minutes per view
64 rdpress.com/2008/09/0 3/breast-cancermolecular-breastimagingmammography/
65 Rhodes et al. Purpose was to asses the diagnostic performance of supplemental screening MBI in women with dense breasts participants: 21 were diagnosed with cancer. 2 detected by mammo only 14 by MBI only 3 by both When added to screening mammography, MBI yielded a supplemental cancer detection rate of 8.8/1000 women with dense breasts. Recall rate increased from 11.0% in mammo alone to 17.6% for the combination. The biopsy rate increased from 1.3% to 4.2%.
66 Shermis et al. Study performed on women ages with BIRADS 1 or 2 on screening mammogram within 100 days. 94% had breast density heterogeneously dense or extremely dense (6% had a lower density with complex pattern) Lifetime risk ranged from 6.1%-17.2%
67 Shermis et al. MBI had a positive finding in 8.4% which led to additional diagnostic evaluation. Of 143 women, 13 malignancies were detected (11 invasive, 2 DCIS) 7 malignancies in heterogeneously dense breasts and 6 in extremely dense breasts Recall rate 8.4% Incremental cancer detection rate 7.7% PPV1 9.1%
68 Advantages to MBI Less expensive compared to MRI (5x) Utilizes functional imaging to overcome the limitations of anatomic imaging 3x more sensitive than mammography
69 Disadvantages of MBI Radiation exposure is to the whole body, not just the breast. The effective dose of radiation to the body is 5x the dose from digital mammo (although still less than background radiation per year). The typical dose of 740 MBq has been considered excessive for screening. Studies using 300 MBq Increase in recall rate and biopsy rate.
70 Contrast-Enhanced Mammography
71 Technique A mammography unit adapted to obtain both high energy and low energy images within seconds of each other is used. Images are processed to provide an iodine image Similar in appearance to subtraction images in angiography. Requires injection of iodinated contrast similar to CT.
72
73 Advantages Patient tolerance may be better than for MRI. Sensitivity may be comparable to MRI and specificity higher than MRI. Mori et al. found contrast enhanced mammography to be superior to standard mammography in dense breasts.
74 Disadvantages Requires injection of iodinated contrast. No direct method for biopsy at this time.
75 End the Confusion
76
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations
 Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
BREAST DENSITY WHAT IS IT? WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? & What IOWA SF250 Means to Patients and Providers
 BREAST DENSITY WHAT IS IT? WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? & What IOWA SF250 Means to Patients and Providers Arnold Honick, MD Radiology Consultants of Iowa, PLC ahonick@rciowa.com BREAST DENSITY LEGISLATION Nancy
BREAST DENSITY WHAT IS IT? WHY IS IT IMPORTANT? & What IOWA SF250 Means to Patients and Providers Arnold Honick, MD Radiology Consultants of Iowa, PLC ahonick@rciowa.com BREAST DENSITY LEGISLATION Nancy
Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis. How have they changed our lives?
 Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis How have they changed our lives? Renee W. Pinsky, MD Associate Professor of Radiology University of Michigan The only thing that is constant is change Heraclitus
Breast Density and Breast Tomosynthesis How have they changed our lives? Renee W. Pinsky, MD Associate Professor of Radiology University of Michigan The only thing that is constant is change Heraclitus
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography
 Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
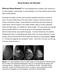 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
What s New in Breast Imaging. Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia
 What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
Screening Options in Dense Breasts. Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging
 Screening Options in Dense Breasts Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging Dense Breasted Women Decreased sensitivity of mammography
Screening Options in Dense Breasts Donna Plecha, M.D. Co-Director UHCMC Breast Centers Associate Professor of Radiology Director of Breast Imaging Dense Breasted Women Decreased sensitivity of mammography
Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD!
 Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD! ACS Estimated Cancers Statistics 2014! Breast! New Cases in Women! 232,670 (+67,570 in situ)! Deaths in Women! 40,000! Colon! 48,380! 24,040! Cervical! 12,360! 4,020!
Breast Imaging! Ravi Adhikary, MD! ACS Estimated Cancers Statistics 2014! Breast! New Cases in Women! 232,670 (+67,570 in situ)! Deaths in Women! 40,000! Colon! 48,380! 24,040! Cervical! 12,360! 4,020!
Disclosures. Breast Cancer. Breast Imaging Modalities. Breast Cancer Screening. Breast Cancer 6/4/2014
 : Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
: Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
Dense Breasts. A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge
 Dense Breasts A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge Renee Pinsky, MD University of Michigan Department of Radiology Division of Breast Imaging No Disclosures QUIZ: ARE YOU DENSE? a. Breast
Dense Breasts A Breast Cancer Risk Factor and Imaging Challenge Renee Pinsky, MD University of Michigan Department of Radiology Division of Breast Imaging No Disclosures QUIZ: ARE YOU DENSE? a. Breast
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Breast Cancer Screening and High Risk
 Breast Cancer Screening and High Risk Mary Freyvogel, DO Breast Surgeon Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery University Hospitals Case Medical Center St. John Medical Center / Elyria Medical Center
Breast Cancer Screening and High Risk Mary Freyvogel, DO Breast Surgeon Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery University Hospitals Case Medical Center St. John Medical Center / Elyria Medical Center
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document
 RSNA, 2013 Appendix E1 Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document 1. I have been getting more questions
RSNA, 2013 Appendix E1 Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk, and the Breast Density Notification Law in California: A Consensus Document 1. I have been getting more questions
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Tissue Breast Density
 Tissue Breast Density Reporting breast density within the letter to the patient is now mandated by VA law. Therefore, this website has been established by Peninsula Radiological Associates (PRA), the radiologists
Tissue Breast Density Reporting breast density within the letter to the patient is now mandated by VA law. Therefore, this website has been established by Peninsula Radiological Associates (PRA), the radiologists
The Dilemma of Breast Density in Screening
 The Dilemma of Breast Density in Screening Priscilla J. Slanetz MD, MPH, FACR, FSBI Associate Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA No financial
The Dilemma of Breast Density in Screening Priscilla J. Slanetz MD, MPH, FACR, FSBI Associate Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA No financial
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue. Public Meeting December 13, 2013
 Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Update in Breast Cancer Screening
 Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute and Grail - and - Karla Kerlikowske,
Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute and Grail - and - Karla Kerlikowske,
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue
 TITLE: AUTHORS: The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue Jeffrey A. Tice, MD Associate Professor
TITLE: AUTHORS: The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue Jeffrey A. Tice, MD Associate Professor
Henda s Law. Supplemental screening for women with dense breast tissue and increased risk
 . Henda s Law Supplemental screening for women with dense breast tissue and increased risk The 2011 Texas Legislature passed House Bill 2102 which is effective 1st September 2011. The law is informally
. Henda s Law Supplemental screening for women with dense breast tissue and increased risk The 2011 Texas Legislature passed House Bill 2102 which is effective 1st September 2011. The law is informally
The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography in Women with Dense Breast Tissue
 The New England Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council Public Meeting December 13, 2013 The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography
The New England Comparative Effectiveness Public Advisory Council Public Meeting December 13, 2013 The Comparative Clinical Effectiveness and Value of Supplemental Screening Tests Following Negative Mammography
Update in Breast Cancer Screening
 Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla Kerlikowske, MD
Disclosure information: Update in Breast Cancer Screening Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Update in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla Kerlikowske, MD
Breast Density: Significance and Notification. Carol H. Lee Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY
 Breast Density: Significance and Notification Carol H. Lee Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Significance of Breast Density Association with increased risk for breast cancer Decreased
Breast Density: Significance and Notification Carol H. Lee Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Significance of Breast Density Association with increased risk for breast cancer Decreased
Why it matters and what to do
 Breast density: Why it matters and what to do Breast density is a frequent topic on social media, in the news and within medical literature - and your patients may be asking you about it. Dense breast
Breast density: Why it matters and what to do Breast density is a frequent topic on social media, in the news and within medical literature - and your patients may be asking you about it. Dense breast
Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese
 Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis
 Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Priya Thomas, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Cancer Prevention and Breast Medical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures Dr. Thomas has
Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis Priya Thomas, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Cancer Prevention and Breast Medical Oncology University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosures Dr. Thomas has
Current Strategies in the Detection of Breast Cancer. Karla Kerlikowske, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF
 Current Strategies in the Detection of Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Outline ν Screening Film Mammography ν Film ν Digital ν Screening
Current Strategies in the Detection of Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Outline ν Screening Film Mammography ν Film ν Digital ν Screening
SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING
 SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI, FACR Professor, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging Division Chief, Breast Imaging Dec. 5, 2017 Warner, E. NEJM 2011 Screening for
SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER BREAST IMAGING Liane Philpotts, MD, FSBI, FACR Professor, Radiology and Biomedical Imaging Division Chief, Breast Imaging Dec. 5, 2017 Warner, E. NEJM 2011 Screening for
Screening with New Modalities: Breast Ultrasound
 Screening with New Modalities: Breast Ultrasound Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosures No personal financial
Screening with New Modalities: Breast Ultrasound Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosures No personal financial
Breast Imaging & You
 Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated Breast Ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
n Educational support from GE and Volpara n Reduce mortality n Healthy women will not be harmed
 Dense Breasts: What to Know and What to Do Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine wendieberg@gmail.com Disclosures
Dense Breasts: What to Know and What to Do Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Magee-Womens Hospital of UPMC University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine wendieberg@gmail.com Disclosures
Detection to Prediction: Imaging Markers of Breast Cancer Risk
 Detection to Prediction: Imaging Markers of Breast Cancer Risk Carrie B. Hruska, PhD, DABR Associate Professor of Medical Physics Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure Per agreement
Detection to Prediction: Imaging Markers of Breast Cancer Risk Carrie B. Hruska, PhD, DABR Associate Professor of Medical Physics Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure Per agreement
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? TERMS (AKA) WHAT IS TOMOSYNTHESIS? 3/3/2014. Digital breast tomosynthesis =
 #46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography
 BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
6 OBG Management August 2015 Vol. 27 No. 8 obgmanagement.com
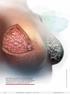 Dense breasts are composed of a lot of fibrous and glandular tissue, with less adipose tissue. Heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue (as illustrated here) make it difficult to detect
Dense breasts are composed of a lot of fibrous and glandular tissue, with less adipose tissue. Heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breast tissue (as illustrated here) make it difficult to detect
Breast Imaging & You
 Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated breast ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Breast Imaging & You What s Inside: Breast Imaging... 2 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) mammograms... 4 Breast cancer screening... 6 Dense breast tissue... 8 Automated breast ultrasound (ABUS)... 9
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR)
 Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Screening Mammography: Who, what, where, when, why and how?
 Screening Mammography: Who, what, where, when, why and how? Jillian Lloyd, MD, MPH Breast Surgical Oncologist University Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Medical Center Disclosures
Screening Mammography: Who, what, where, when, why and how? Jillian Lloyd, MD, MPH Breast Surgical Oncologist University Surgical Oncology Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Medical Center Disclosures
Outline. Abbreviated MRI and the Dense Breast. 2D Analog Screen Mammography. RCTs of Mammographic Screening
 Abbreviated MRI and the Dense Breast Christopher Comstock, MD FACR Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of mammographic screening
Abbreviated MRI and the Dense Breast Christopher Comstock, MD FACR Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of mammographic screening
MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS. Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015 No financial disclosures National Cancer Institute National Cancer Institute Increased Cancer Risk... DENSITY
MANAGEMENT OF DENSE BREASTS Nichole K Ingalls, MD, MPH NW Surgical Specialists September 25, 2015 No financial disclosures National Cancer Institute National Cancer Institute Increased Cancer Risk... DENSITY
Literature Review: California Senate Bill 1034 Health Care: Mammograms AT A GLANCE
 Literature Review: California Senate Bill 1034 Health Care: Mammograms Summary to the 2018-2019 California State Legislature, April 16, 2018 AT A GLANCE On February 26, 2018, the Senate Committee on Health
Literature Review: California Senate Bill 1034 Health Care: Mammograms Summary to the 2018-2019 California State Legislature, April 16, 2018 AT A GLANCE On February 26, 2018, the Senate Committee on Health
Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc. Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis A WHITEPAPER INTRODUCTION Numerous published studies have shown
Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc. Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis A WHITEPAPER INTRODUCTION Numerous published studies have shown
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
High Risk Screening: A Multimodality Approach
 High Risk Screening: A Multimodality Approach John Lewin, M.D., FACR, FSBI The Women s Imaging Center Denver, Colorado Disclosures Consultant to Hologic Previously received research funds from Hologic
High Risk Screening: A Multimodality Approach John Lewin, M.D., FACR, FSBI The Women s Imaging Center Denver, Colorado Disclosures Consultant to Hologic Previously received research funds from Hologic
Breast cancer screening: Does tomosynthesis augment mammography?
 REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht. Chair Dutch Expert Centre for Screening Board EUSOBI
 Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht Best practice in Breast Imaging: what s new and what women need to know and Update on the Second Implementation Report of the 2003 Council Recommendation
Ruud Pijnappel Professor of Radiology, UMC Utrecht Best practice in Breast Imaging: what s new and what women need to know and Update on the Second Implementation Report of the 2003 Council Recommendation
5/24/16. Current Issues in Breast Cancer Screening. Breast cancer screening guidelines. Outline
 Disclosure information: An Evidence based Approach to Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Current Issues in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla
Disclosure information: An Evidence based Approach to Breast Cancer Karla Kerlikowske, MDDis Current Issues in Breast Cancer Screening Grant/Research support from: National Cancer Institute - and - Karla
Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography
 2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center
 Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
Melissa Hartman, DO Women s Health Orlando VA Medical Center Most common non-skin cancer and Second deadliest cancer in women Majority are diagnosed by abnormal screening study An approach to breast cancer
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
Supplemental Screening for Breast Cancer in Women With Dense Breasts: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Service Task Force
 Evidence Synthesis Number 126 Supplemental Screening for Breast Cancer in Women With Dense Breasts: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Service Task Force Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research
Evidence Synthesis Number 126 Supplemental Screening for Breast Cancer in Women With Dense Breasts: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Service Task Force Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients
 Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Breast Cancer Imaging
 Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
the one name in cancer care.
 the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
3D Mammography. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Breast Density It's the Law
 Last year Iowa became the 30th state in the last 12 years to require that density information be added to the written mammogram report to the patient. This report is sent directly from the interpreting
Last year Iowa became the 30th state in the last 12 years to require that density information be added to the written mammogram report to the patient. This report is sent directly from the interpreting
Evaluations & CE Credits
 Evaluations & CE Credits Nursing Contact Hours, CME and CHES credits are available. Please visit www.phlive.org to fill out your evaluation and complete the post-test. 1 Breast Density and Breast Cancer
Evaluations & CE Credits Nursing Contact Hours, CME and CHES credits are available. Please visit www.phlive.org to fill out your evaluation and complete the post-test. 1 Breast Density and Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Screening
 Breast Cancer Screening Eileen Rakovitch MD MSc FRCPC Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Medical Director, Louise Temerty Breast Cancer Centre LC Campbell Chair in Breast Cancer Research Associate Professor,
Breast Cancer Screening Eileen Rakovitch MD MSc FRCPC Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre Medical Director, Louise Temerty Breast Cancer Centre LC Campbell Chair in Breast Cancer Research Associate Professor,
Ge elastography cpt codes
 Ge elastography cpt codes Aetna considers digital mammography a medically necessary acceptable alternative to film mammography. Currently, there are no guideline recommendations from leading medical professional
Ge elastography cpt codes Aetna considers digital mammography a medically necessary acceptable alternative to film mammography. Currently, there are no guideline recommendations from leading medical professional
10.2 Summary of the Votes and Considerations for Policy
 CEPAC Voting and Policy Implications Summary Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue December 13, 2013 The last CEPAC meeting addressed the comparative clinical effectiveness and value
CEPAC Voting and Policy Implications Summary Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue December 13, 2013 The last CEPAC meeting addressed the comparative clinical effectiveness and value
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view
 BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view DR CHANTEL THORNTON SPECIALIST BREAST CANCER SURGEON BMSc (hons) MBBS (hons) FRACS Epworth Hospital, Richmond- Agora Centre for Women s Health
BREAST IMAGING and NEW IMAGING MODALITIES- A Surgeons view DR CHANTEL THORNTON SPECIALIST BREAST CANCER SURGEON BMSc (hons) MBBS (hons) FRACS Epworth Hospital, Richmond- Agora Centre for Women s Health
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D Mammography Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
Breast Cancer Screening in Women at Higher-Than-Average Risk: Recommendations From the ACR
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CLINICAL PRACTICE MANAGEMENT Breast Cancer Screening in Women at Higher-Than-Average Risk: Recommendations From the ACR Debra L. Monticciolo, MD a, Mary S. Newell, MD b, Linda Moy, MD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CLINICAL PRACTICE MANAGEMENT Breast Cancer Screening in Women at Higher-Than-Average Risk: Recommendations From the ACR Debra L. Monticciolo, MD a, Mary S. Newell, MD b, Linda Moy, MD
Screening Mammography: The Controversy, Risk Assessment and Individualized Screening recommendations. Jonathan T. Sims MD, MBA
 Screening Mammography: The Controversy, Risk Assessment and Individualized Screening recommendations. Jonathan T. Sims MD, MBA I have no relevant Financial Disclosures Agenda Discuss the recent studies
Screening Mammography: The Controversy, Risk Assessment and Individualized Screening recommendations. Jonathan T. Sims MD, MBA I have no relevant Financial Disclosures Agenda Discuss the recent studies
Advances in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Heidi Memmel, MD FACS Surgical Director of Caldwell Breast Center September 26, 2015
 Advances in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Heidi Memmel, MD FACS Surgical Director of Caldwell Breast Center September 26, 2015 Advances in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Recommendations
Advances in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Heidi Memmel, MD FACS Surgical Director of Caldwell Breast Center September 26, 2015 Advances in Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment Recommendations
Low Dose Molecular Breast Imaging
 Low Dose Molecular Breast Imaging Dr. M.K. O Connor Conflict of Interest Royalties - Gamma Medica Research funding GE Healthcare Research support MTTI Michael O Connor, Ph.D Dept. of Radiology Mayo Clinic
Low Dose Molecular Breast Imaging Dr. M.K. O Connor Conflict of Interest Royalties - Gamma Medica Research funding GE Healthcare Research support MTTI Michael O Connor, Ph.D Dept. of Radiology Mayo Clinic
BREAKING THE SOUND WAVES!
 BREAKING THE SOUND WAVES! SURVEY (HAND-HELD) VERSES AUTOMATIC BREAST ULTRASOUND WHAT S THE DIFFERENCE Patricia Gaspard (RT)(M)(R)(CRA)/Marie Barnett (RT)(M)(R) March 16, 2019 Hand Held vs ABUS (Automatic
BREAKING THE SOUND WAVES! SURVEY (HAND-HELD) VERSES AUTOMATIC BREAST ULTRASOUND WHAT S THE DIFFERENCE Patricia Gaspard (RT)(M)(R)(CRA)/Marie Barnett (RT)(M)(R) March 16, 2019 Hand Held vs ABUS (Automatic
Breast Density. Update 2018: Implications for Clinical Practice
 Breast Density Update 2018: Implications for Clinical Practice Matthew A. Stein, MD Assistant professor Breast Imaging Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Disclosures
Breast Density Update 2018: Implications for Clinical Practice Matthew A. Stein, MD Assistant professor Breast Imaging Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Disclosures
Mammography limitations. Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study
 Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Breast Cancer Screening EVIDENCE TABLE. See Last Page for Key Revised 2017 Mainiero Page 1.
 1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7-0. Type Review/Other- N/A To estimate the numbers of new cancer cases and deaths that will occur in the United
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67(1):7-0. Type Review/Other- N/A To estimate the numbers of new cancer cases and deaths that will occur in the United
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening?
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
ATHENA WISDOM INITIATIVE: RISK-BASED SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER
 ATHENA WISDOM INITIATIVE: RISK-BASED SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER The Screening Debate in the US? ACS vs. USPSTF When to start, when to stop, screening intervals, modality] Little guidance around operationalizing
ATHENA WISDOM INITIATIVE: RISK-BASED SCREENING FOR BREAST CANCER The Screening Debate in the US? ACS vs. USPSTF When to start, when to stop, screening intervals, modality] Little guidance around operationalizing
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine
 International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
TOMOSYNTHESIS. Daniela Bernardi. U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy
 TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
Can Digital Breast Tomosynthesis(DBT) Perform Better than Standard Digital Mammography Workup in a Breast Cancer Assessment Clinic?
 Can Digital Breast Tomosynthesis(DBT) Perform Better than Standard Digital Mammography Workup in a Breast Cancer Assessment Clinic? Accepted for publication in European Radiology Authors: S Mall, J Noakes,
Can Digital Breast Tomosynthesis(DBT) Perform Better than Standard Digital Mammography Workup in a Breast Cancer Assessment Clinic? Accepted for publication in European Radiology Authors: S Mall, J Noakes,
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium. Sat Nov 12 th 2016
 Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Breast Density. Information for Health Professionals
 Breast Density Information for Health Professionals BreastScreen NSW provides free screening mammography to asymptomatic women aged 50-74 every two years, with the aim of diagnosing breast cancer at an
Breast Density Information for Health Professionals BreastScreen NSW provides free screening mammography to asymptomatic women aged 50-74 every two years, with the aim of diagnosing breast cancer at an
Scintimammography and Gamma Imaging of the Breast and Axilla
 Scintimammography and Gamma Imaging of the Breast and Axilla Policy Number: 6.01.18 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 9/2006 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
Scintimammography and Gamma Imaging of the Breast and Axilla Policy Number: 6.01.18 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 9/2006 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC)
The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes
 The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes Connie Lehman MD PhD Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director of Breast Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Opportunities New technology provides
The Future of Breast MRI Improving Outcomes Connie Lehman MD PhD Professor of Radiology Harvard Medical School Director of Breast Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Opportunities New technology provides
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scenarios for Clinicians
 Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk and Wisconsin Breast Density Notification Law (2017 Wisconsin Act 201) Scenarios for Clinicians Content adapted from the California Breast Density Information Group,
Breast Density, Breast Cancer Risk and Wisconsin Breast Density Notification Law (2017 Wisconsin Act 201) Scenarios for Clinicians Content adapted from the California Breast Density Information Group,
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning. Dr. med. M. Golatta
 The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
