Evaluation of Functional Gene for Classification of Pathogenic Bacteria
|
|
|
- Maximillian Wade
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of Functional Gene for Classification of Pathogenic Bacteria Department of Microbiology Regeneration and Advanced Medical Science, Gifu University, Graduate school of Medicine Yanagido 1-1, Gifu, Japan
2 MLST (multilocus sequence typing) analysis information is rapidly accumulated, but we need more conveincing data to satisfy medical community and veterinarian to change BSL3 classification. It is no doubt that DNA based identification and detection of pathogens have a powerful potential to control infectious diseases because of the rapiness and sensitiveness. However, current taxonomy of BSL3 pathogens have many problems to use genetic identification and detection methods.
3 Problems of classification of BSL3 Pathogens Examples: 1. Bacillus cereus group:b.anthracis,b.cereus, B thuringiensis, and B.mycoides carry identical 16S rrna sequences. They were classified different organisms because of their pathogenic factors. 2. Escherichia coli and Shigella species shares identical 16S rrna. They were classified different organisms because of their pathogenic factors. 3. Clostridium botulinum species is clusters of phylogenetically different organisms. They only shares common feature to produce botulinum toxins.
4 Historical Errors Strain which does not produce gas from glucose, lactose negative and nonmotile and etc. No Biochemically identified as Escherichia group Yes Classied as Shigella species and serologically identified as Shigella species c c Later, none motile, lactose negative, were found and described as Pathogenic E.coli E.coli O antigen: O1 to O180 E.coliO7 =S.boydii 12 E.coli 28a,c=S.boydii13 E.coli O112a,c=S.dysenteriae 2 E.coli O124=S.dysenteriae 3 E.coli O143=S.boydii 8 E.coli O144=S.dysenteriae 10 E.coli O152=S.dysenteriae12
5 Average 16S rrna SNP within a species is less than 1.3%(Constantinidis and Tiedje 2005) Species cut off 16S rdna cannot differentiate BSL3 pathogens and Plant pathogens from their closely related species because their sequence are related more than 99.5%.
6 Need complete protein sequence analysis to use housekeeping genes as a taxonomic tool Whole genome sequenced strains(1230str.) (Million species>7000species>1400gensus>280family) 1. Only 500 dollar to determine whole genome of one strain. 2. Shot gun sequencing produced many full sequenced genes and protein information. Strain level information is bursting. In medical micobiology, pathogenic species are well defined and their differentiation methods from nonpathogenics are well established in detail through 100 year history of pathogenic bacterial history.
7 Cannot reach to Common ancester Higher taxon Species level :pick up only specific genes, pathogenic factors among species Higher taxon Common ancester Species level: compare commonly conserved hose keeping genes
8 Commonly Conserved Genes among whole genome sequenced strains [J] COG0048 Ribosomal protein S [J] COG0049 Ribosomal protein S7 32 [J] COG0051 Ribosomal protein S [J] COG0052 Ribosomal protein S2 241 [J] COG0088 Ribosomal protein L4 201 [J] COG0089 Ribosomal protein L [J] COG0090 Ribosomal protein L2 273 [J] COG0091 Ribosomal protein L [J] COG0100 Ribosomal protein S [J] COG0102 Ribosomal protein L [J] COG0103 Ribosomal protein S9 130 [J] COG0244 Ribosomal protein L [J] COG0255 Ribosomal protein L29 63 [J] COG0256 Ribosomal protein L [J] COG0231 Translation elongation factor P (EF-P)/translation initiation factor 5A (eif-5a) 188 [J] COG0361 Translation initiation factor 1 (IF-1) 72 [J] COG0532 Translation initiation factor 2 (IF-2; GTPase) 890 [L] COG0550 Topoisomerase IA 653 [J] COG0124 Histidyl-tRNA synthetase 414 [J] COG0143 Methionyl-tRNA synthetase 677 [J] COG0162 Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase 424 [J] COG0441 Threonyl-tRNA synthetase 642 [J] COG0442 Prolyl-tRNA synthetase 572 [J] COG0495 Leucyl-tRNA synthetase 891 [J] COG0522 Ribosomal protein S4 206 [J] COG0525 Valyl-tRNA synthetase 951 [E] COG0006 Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase1 361 [E] COG0006 Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase2 441 [O] COG0492 Thioredoxin reductase 321 [E] COG0112 Glycine/serine hydroxymethyltransferase 417 [F] COG0504 CTP synthase (UTP-ammonia lyase) 545 [G] COG phosphoglycerate kinase 387 [G] COG0148 Enolase 432 [G] COG0149 Triosephosphate isomerase 255 [G] COG1109 Phosphomannomutase 456 [J] COG0030 Dimethyladenosine transferase (rrna methylation) 273 glycine trna synthetase, alpha subunit 303 glycine trna synthetase, beta subunit 689 [J] COG0008 Glutaminyl-tRNA synthetases 471 [J] COG0013 Alanyl-tRNA synthetase 876 [J] COG0016 Phenylalanine trna synthetase, alpha subunit 327 [J] COG0072 Phenylalanine trna synthetase, beta subunit 795 [J] COG0018 Arginyl-tRNA synthetase 577 [J] COG0024 Methionine aminopeptidase 264 Ribosome Proteins, Replication Modification, Protein maturation T-RNA Synthesis [J] COG0060 Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase 938
9 House keeping Protein SAP in Escherichia (N=44strains) coli 0,000% 0,500% 1,000% 1,500% 2,000% 2,500% 3,000% 3,500% Ribosome Proteins T-RNA synthesis DNA replica tion Extension, Modificatio n,
10 Ribosome protein SAP in E.coli(N=44 strains) Ribosome protein Amino Averag e Range SD Ribosomal protein L % 0.000% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0.000% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0-0.8% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0-0.3% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0-0.3% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0-1.0% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0-0.5% 0.000% Ribosomal protein S % 0.000% 0.000% Ribosomal protein S % 0.000% 0.000% Ribosome Proteins Ribosomal protein S % 0.000% 0.000% Ribosomal protein S % 0.000% 0.000% Ribosomal protein S % 0-0.8% 0.000% Ribosomal protein L % 0-1.6% 0.000% Ribosomal protein S % 0-0.8% 0.219% Ribosomal protein S % 0-0.4% 0.198% Ribosome protein SNP within a species was less than 1.6%
11 T-RNA and Replication associated Protein SNP Escherichia coli 44 株 (COG genes) Amino Average Range SD Translation elongation factor P (EF-P)/translation initiation factor 5A (eif-5a) % 0-0.5% 0.000% Translation initiation factor 1 (IF-1) % 0.000% 0.000% Triosephosphate isomerase % 0-0.4% 0.000% Translation initiation factor 2 (IF-2; GTPase) % 0-0.1% 0.000% Phosphoglycerate kinase % 0-0.3% 0.153% Thioredoxin reductase % 0-1.2% 0.321% CTP synthase (UTP-ammonia lyase) % 0-0.6% 0.148% Topoisomerase IA % 0-4.6% 1.243% Phosphomannomutase % % 3.502% Glycine/serine hydroxymethyltransferase % 0-0.2% 0.098% Glycine trna synthetase % 0-0.4% 0.182% Dimethyladenosine transferase (rrna methylation) % 0-0.7% 0.280% Threonyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-1.1% 0.084% Valyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-0.7% 0.124% Phenylalanine trna synthetase, beta subunit % 0-1.0% 0.272% Alanyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-2.7% 0.185% Methionine aminopeptidase % 0-1.5% 0.276% Methionyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-1.5% 0.182% Phenylalanine trna synthetase, alpha subunit % 0-0.9% 0.209% Arginyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-1.9% 0.179% Glutaminyl-tRNA synthetases % 0-1.1% 0.262% Isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-1.0% 0.227% Leucyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-1.0% 0.172% Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-4.7% 0.282% Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase % 0-1.8% 0.806% Prolyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-1.2% 0.203% Histidyl-tRNA synthetase % 0-6.8% 0.409% Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase % 0-6.1% 1.634% DNA T-RNA
12 t-rna Str.K-12 Str.K-12 Str.K-12 W3110 DH10B MG1655 Ile-tRNA Ala-tRNA Asp-tRNA Thr-tRNA Arg-tRNA Gln-tRNA Leu-tRNA Met-tRNA Lys-tRNA Val-tRNA Ser-tRNA Tyr-tRNA Val-tRNA Cys-tRNA Gly-tRNA Asn-tRNA Pro-tRNA Glu-tRNA Phe-tRNA His-tRNA Trp-tRNA 1 1 Sec-tRNA 1 1 Xaa-tRNA 3 Copy Numbers of T-RNA gene within E.coli K-12 strains Different among strain level: Not suitable for classification
13 House keeping genes (dnaj, rpob, gyrb) are usually exit only one on their chromosome only exit one copy on their chromosome
14 Genus Escherichia E. coli E. furgsonii E. arbertii Shigella spp. E. vulneri E. hurmanii E. blattae 16S rrna phylogeny
15 dnaj sequence E.ictaruliT E-hosinae E-hosinae T E-tarda E- tardat E-ictaluri - E dwardsiella Citrobacter (Animal source) C_lapgei 1132 C_neteri 1133 E. hermannii GTC347 C_koseri 1138 C_rodentium 1139 C_sedlakiiGTC 1322 C_amalonaticus 1135 C_werkmanii C_wermanii 1141 C_youngae Ci.fr Citrobacter (Human source) C_braakii 1136 Ci.fr9517 C.fr9635 Ci.frDNA Ci.fr9502 C.fr1 612 E.vulneris1164 Leclercia L.adecarboxylata L.adecarboxylata E. blattae1161 E. albertii TW E.coli E.coliDNA E.coli Sh.boy Sh.dys Sh.dys E.coli E.coli Sh.dys E_fergusonii Sh.flex 1057 Sh.son E.coli E.furgsonii Shigella spp. 0.1
16 E.coli serovars (O1 to 180) and Shigella sp. DnaJ sequence
17 DnaJ Protein SAP( E.coli ) E. coli-shigella spp.(<0.53%) Other Escherichia (2.1%) Citrobacter (3.2%-3.7%) Salmonella(4.3%)
18 RpoB Protein SAP E. coli- Shigella(<0.005%) Other Escherichia Citrobacter Salmonella
19 GryB Protein SAP E. coli-shigella (0-0.25%) Other Escherichia ( o%) Citrobacter ( %) Salmonell a (3.2%)
20 House keeping Protein SAP Escherichia Citorbacter Salmonella 5,00% 376 AA 4,00% 3,00% 2,00% DnaJ<0.53% 1,00% 0,00% ,00% 1342 AA 4,00% 3,00% 2,00% 1,00% 0,00% RopB<0.005% 804 AA 5,00% 4,00% 3,00% 2,00% 1,00% 0,00% GryB<0.25 % E. vulneri, E. hurmanii, E. blattae should be reclassified as different genera
21 Genus level DnaJ Amino acid diversities
22 Reclassification of Shigella and E.coli Escherichia coli Enterohaemorrhagic Engeroinvasive Enterotoxigenic Enteoaggregative Enteropathogenic E. furgsonii-> nonpathogenic E.coli Shigella dysenteiae Serovar O1 Serovar all others Shigella flexneri Shigella sonnei Shigella boydii E. arbartii-> independent species in the genus Escherichia E. vulneris E. blattae E. hurmanii Citrobacter or new genera * E.blattae is already proposed to transfer to a new genus
23 Bacillus cereus group B.anthracis B.cereus B.thuringiensis B.mycoides B.pseudomycoides B.weihenstephanensis These shares more than 99.5% 16S rrna similarities with B.anthracis 99.3%-95% similarities to B.anthracis
24 DnaJ sequence of Out break strains of B.cereus was more than 99% related to B.anthracis (DnaJ variation within B.cereus (9.6%) is bigger than E.coli(1.5%)
25 dnaj sequence Diversities among B.cereus isolated from Blood culture B.cereus divided into 4major groups. DnaJ sequence isolated from severe pneumoniae was closely related to B.anthracis
26 Pathogenic factors to diffeentiate B.cereus group
27 DnaJ sequence SNP B.pseudomycoides GTC 02831T B.cereus group3 (n=21 ) B.cereus group1 (n= 4 ) B.mycoides- B.weihenstephanensis Group(n=18) B.cereus thuringiensis Group2 (n= 39 ) Cereus (n=22), Thuringiensis(n=17) Outbreak strains of B.cereus (n=4) Anthracis group (n=38 strains) 0.1
28 Outbreak strains make typical B.cereus colonies Suspect B.cereus, B.thuringiensis Suspect B.subtilis, B.anthracis Suspect B.mycoides
29 When does a strain spin out from a species? House keeping Protein variation (SAP) Use complete amino acid sequence to discuss Species border or genus border. Until amino acid of a protein changes, the function is same among strains with different coden usage. House keeping Gene Sequence variation (SNP) Analyze strain evolution within a species. Different coden usage among strains in a species is useful to analyze whether a strain is ready to spin out from a species.
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 4 Protein Sequence
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ARTICLE NUMBER: 16198 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.198 Genome reduction in an abundant and ubiquitous soil bacterium, Candidatus Udaeobacter copiosus Tess E Brewer 1, 2, Kim M Handley 3, Paul Carini 1,
ARTICLE NUMBER: 16198 DOI: 10.1038/NMICROBIOL.2016.198 Genome reduction in an abundant and ubiquitous soil bacterium, Candidatus Udaeobacter copiosus Tess E Brewer 1, 2, Kim M Handley 3, Paul Carini 1,
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Cells N5 Homework book
 1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Biochemistry 423 Final Examination NAME:
 Biochemistry 423 Final Examination NAME: 1 Circle the single BEST answer (3 points each) 1. At equilibrium the free energy of a reaction G A. depends only on the temperature B. is positive C. is 0 D. is
Biochemistry 423 Final Examination NAME: 1 Circle the single BEST answer (3 points each) 1. At equilibrium the free energy of a reaction G A. depends only on the temperature B. is positive C. is 0 D. is
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Protein Synthesis and Mutation Review
 Protein Synthesis and Mutation Review 1. Using the diagram of RNA below, identify at least three things different from a DNA molecule. Additionally, circle a nucleotide. 1) RNA is single stranded; DNA
Protein Synthesis and Mutation Review 1. Using the diagram of RNA below, identify at least three things different from a DNA molecule. Additionally, circle a nucleotide. 1) RNA is single stranded; DNA
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
TRANSLATION: 3 Stages to translation, can you guess what they are?
 TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
Point total. Page # Exam Total (out of 90) The number next to each intermediate represents the total # of C-C and C-H bonds in that molecule.
 This exam is worth 90 points. Pages 2- have questions. Page 1 is for your reference only. Honor Code Agreement - Signature: Date: (You agree to not accept or provide assistance to anyone else during this
This exam is worth 90 points. Pages 2- have questions. Page 1 is for your reference only. Honor Code Agreement - Signature: Date: (You agree to not accept or provide assistance to anyone else during this
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism
 Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology:
 The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM
 SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
Midterm 2 Results. Standard Deviation:
 Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
endopeptidases aminopeptidases carboxypeptidases hydrolyzes a peptide bond somewhere in the middle of the polypeptide
 1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
New genomic typing method MLST
 New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
7.012 F 04 Problem Set 1 September 10 th 2004
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. laudette Gardel ame Question 1 TA Section 7.012 F 04 Problem Set 1 September
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. laudette Gardel ame Question 1 TA Section 7.012 F 04 Problem Set 1 September
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Nitrogen Metabolism. Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Algal Biofuels Research: Using basic science to maximize fuel output. Jacob Dums, PhD candidate, Heike Sederoff Lab March 9, 2015
 Algal Biofuels Research: Using basic science to maximize fuel output Jacob Dums, PhD candidate, jtdums@ncsu.edu Heike Sederoff Lab March 9, 2015 Outline Research Approach Dunaliella Increase Oil Content
Algal Biofuels Research: Using basic science to maximize fuel output Jacob Dums, PhD candidate, jtdums@ncsu.edu Heike Sederoff Lab March 9, 2015 Outline Research Approach Dunaliella Increase Oil Content
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. Cell 7.5
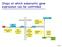 Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
TRANSLATION. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand.
 TRANSLATION Dr. Mahesha H B, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand. Or The process in the ribosomes of a
TRANSLATION Dr. Mahesha H B, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand. Or The process in the ribosomes of a
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
What is most limiting?
 The Amino Acid Content of Rumen Microbes, Feed, Milk and Tissue after Multiple Hydrolysis Times and Implications for the CNCPS M. E. Van Amburgh, A. F. Ortega, S. W. Fessenden, D. A. Ross, and P. A. LaPierre
The Amino Acid Content of Rumen Microbes, Feed, Milk and Tissue after Multiple Hydrolysis Times and Implications for the CNCPS M. E. Van Amburgh, A. F. Ortega, S. W. Fessenden, D. A. Ross, and P. A. LaPierre
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels. Supplementary Information
 Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Arginine side chain interactions and the role of arginine as a mobile charge carrier in voltage sensitive ion channels Craig T. Armstrong, Philip E. Mason, J. L. Ross Anderson and Christopher E. Dempsey
Welcome to Class 14! Class 14: Outline and Objectives. Overview of amino acid catabolism! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Welcome to Class 14 Introductory Biochemistry Class 14: Outline and Objectives Amino Acid Catabolism Fates of amino groups transamination urea cycle Fates of carbon skeletons important cofactors metabolic
Welcome to Class 14 Introductory Biochemistry Class 14: Outline and Objectives Amino Acid Catabolism Fates of amino groups transamination urea cycle Fates of carbon skeletons important cofactors metabolic
The composition of macromolecular cellular composition of mouse cell lines can be found
 Supplementary 2: Cell biomass composition The composition of macromolecular cellular composition of mouse cell lines can be found elsewhere. 1-5 Following table shows the percentage composition of important
Supplementary 2: Cell biomass composition The composition of macromolecular cellular composition of mouse cell lines can be found elsewhere. 1-5 Following table shows the percentage composition of important
paper and beads don t fall off. Then, place the beads in the following order on the pipe cleaner:
 Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
BIO th September, 1997
 BIO 451 26th September, 1997 EXAM I This exam will be taken apart for grading. Please PRINT your name on each page. If you do not have sufficient room for your answer in the space provided, please continue
BIO 451 26th September, 1997 EXAM I This exam will be taken apart for grading. Please PRINT your name on each page. If you do not have sufficient room for your answer in the space provided, please continue
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Structure of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Phenylketonuria (PKU) Structure of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Biol 405 Molecular Medicine 1998 Crystal structure of phenylalanine hydroxylase solved. The polypeptide consists of three regions: Regulatory
Phenylketonuria (PKU) Structure of Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Biol 405 Molecular Medicine 1998 Crystal structure of phenylalanine hydroxylase solved. The polypeptide consists of three regions: Regulatory
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Case Study. Malaria and the human genome STUDENT S GUIDE. Steve Cross, Bronwyn Terrill and colleagues. Version 1.1
 STUDENT S GUIDE Case Study Malaria and the human genome Version 1.1 Steve Cross, Bronwyn Terrill and colleagues Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Hinxton Malaria and the human genome Each year, the malaria
STUDENT S GUIDE Case Study Malaria and the human genome Version 1.1 Steve Cross, Bronwyn Terrill and colleagues Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Hinxton Malaria and the human genome Each year, the malaria
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Discovery of linear low-cationic peptides to target methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vivo Yuan Liu, Meirong Song, Shuangyang Ding,, Kui Zhu*,,, Beijing Advanced Innovation
Supporting Information Discovery of linear low-cationic peptides to target methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in vivo Yuan Liu, Meirong Song, Shuangyang Ding,, Kui Zhu*,,, Beijing Advanced Innovation
Third Exam Practice Test
 Third Exam Practice Test 1. A mixture of aspartic acid, methionine and arginine can be separated by electrophoresis. Explain how this would be done and what exactly happens during the separation. What
Third Exam Practice Test 1. A mixture of aspartic acid, methionine and arginine can be separated by electrophoresis. Explain how this would be done and what exactly happens during the separation. What
Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves
 Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Food Microbiology 101
 Food Microbiology 101 Nina G. Parkinson NGP Consulting November 6, 2018 Food Safety and Sanitation Conference Summary Microbiological contamination of food Routes of contamination by pathogens Overview
Food Microbiology 101 Nina G. Parkinson NGP Consulting November 6, 2018 Food Safety and Sanitation Conference Summary Microbiological contamination of food Routes of contamination by pathogens Overview
LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a Novel Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Katrine G. Joensen. Whole genome sequencing (WGS) surveillance of VTEC and Shigella
 Whole genome sequencing (WGS) surveillance of VTEC and Shigella Katrine G. Joensen & Flemming Scheutz WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Escherichia and Klebsiella Foodborne Infections
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) surveillance of VTEC and Shigella Katrine G. Joensen & Flemming Scheutz WHO Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Escherichia and Klebsiella Foodborne Infections
Central Dogma. Central Dogma. Translation (mrna -> protein)
 Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS
 Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 2. The fate of the carbon sceleton 3 N + C R Active C 1 intermediers The folate derivatives structure s Folate (F) - vitamin Folate, 2 F, 4 F Dihydrofolate ( 2
Dr. M. Sasvari METABOLISM OF AMINO ACIDS 2. The fate of the carbon sceleton 3 N + C R Active C 1 intermediers The folate derivatives structure s Folate (F) - vitamin Folate, 2 F, 4 F Dihydrofolate ( 2
Study of Amino Acids in DDGS
 Study of Amino Acids in DDGS Y. Zhang, J. V. Simpson and B. A. Wrenn National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center Edwardsville, IL 62025 Hans Stein University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Gerald C. Shurson
Study of Amino Acids in DDGS Y. Zhang, J. V. Simpson and B. A. Wrenn National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center Edwardsville, IL 62025 Hans Stein University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Gerald C. Shurson
Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin
 Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin This chapter will calculate the information and molecular knowledge in a real protein. The techniques discussed in this chapter to calculate
Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin This chapter will calculate the information and molecular knowledge in a real protein. The techniques discussed in this chapter to calculate
Four melanocyte-stimulating hormones have the following amino acid sequences:
 Assignment 14: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone belongs to a group called the melanocortins. This group includes ACTH, alpha-msh, beta-msh and gamma-msh; these peptides are all cleavage products of a large
Assignment 14: Melanocyte-stimulating hormone belongs to a group called the melanocortins. This group includes ACTH, alpha-msh, beta-msh and gamma-msh; these peptides are all cleavage products of a large
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression II TRANSLATION RIBOSOMES: protein synthesizing machines Translation takes place on defined
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression II TRANSLATION RIBOSOMES: protein synthesizing machines Translation takes place on defined
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Regulation. 1. Short term control 8-1
 Regulation Several aspects of regulation have been alluded to or described in detail as we have progressed through the various sections of the course. These include: (a) compartmentation: This was not
Regulation Several aspects of regulation have been alluded to or described in detail as we have progressed through the various sections of the course. These include: (a) compartmentation: This was not
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Bio Factsheet. Proteins and Proteomics. Number 340
 Number 340 Proteins and Proteomics Every living thing on the planet is composed of cells, and cells in turn are made of many types of molecules, including the biological molecules carbohydrates, lipids,
Number 340 Proteins and Proteomics Every living thing on the planet is composed of cells, and cells in turn are made of many types of molecules, including the biological molecules carbohydrates, lipids,
Lecture 4. Grouping Amino Acid 7/1/10. Proteins. Amino Acids. Where Are Proteins Located. Nonpolar Amino Acids
 Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Surveillance and outbreak investigation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli using whole genome sequencing- time for a change!
 Surveillance and outbreak investigation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli using whole genome sequencing- time for a change! Dr Marie Anne Chattaway Deputy Head STEC Laboratory Gastrointestinal
Surveillance and outbreak investigation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli using whole genome sequencing- time for a change! Dr Marie Anne Chattaway Deputy Head STEC Laboratory Gastrointestinal
Lezione 10. Sommario. Bioinformatica. Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins Central dogma: DNA makes RNA makes proteins Genetic code
 Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza
Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza
PROTEINS. Building blocks, structure and function. Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties
 PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences V1(2)2010 IN SILICO PHARMACOGENOMIC ANALYSIS OF ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE INVOLVED IN ALCOHOLISM
 SINGH SATENDRA, MECARTY S. D., JAIN P.A., GAUTAM B., FARMER R., YADAV P.K. AND RAM G.D. 1 Department of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics, JSBBE, SHIATS, Allahabad-211007,India 1 Department of Tissue
SINGH SATENDRA, MECARTY S. D., JAIN P.A., GAUTAM B., FARMER R., YADAV P.K. AND RAM G.D. 1 Department of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics, JSBBE, SHIATS, Allahabad-211007,India 1 Department of Tissue
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Genetic information flows from mrna to protein through the process of translation
 Genetic information flows from mrn to protein through the process of translation TYPES OF RN (RIBONUCLEIC CID) RN s job - protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Three main types: 1.
Genetic information flows from mrn to protein through the process of translation TYPES OF RN (RIBONUCLEIC CID) RN s job - protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Three main types: 1.
Comparative genomics of E. coli and Shigella:
 Comparative genomics of E. coli and Shigella: Identification and characterization of pathogenic variants based on whole genome sequence analysis David A. Rasko PhD. University of Maryland School of Medicine
Comparative genomics of E. coli and Shigella: Identification and characterization of pathogenic variants based on whole genome sequence analysis David A. Rasko PhD. University of Maryland School of Medicine
The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R
 The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R Nuclear envelope Transcription DNA RNA Processing Pre-mRNA Translation mrna Nuclear pores Ribosome Polypeptide Transcription RNA is synthesized from DNA in
The Cell T H E C E L L C Y C L E C A N C E R Nuclear envelope Transcription DNA RNA Processing Pre-mRNA Translation mrna Nuclear pores Ribosome Polypeptide Transcription RNA is synthesized from DNA in
