Editorial Process: Submission:12/15/2017 Acceptance:02/19/2018
|
|
|
- Melinda Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /APJCP Evaluation of Collagen in Potentially Malignant Disorders Using Polarizing Microscopy and Immunohistochemistry RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:12/15/2017 Acceptance:02/19/2018 Evaluation of Collagen in Leukoplakia, Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Using Polarizing Microscopy and Immunohistochemistry Krishna Singh Arora 1, Amit Nayyar 2, Prabhpreet Kaur 3, Karandeep Singh Arora 4 *, Ankur Goel 5, Simarjeev Singh 6 Abstract Objectives: Picrosirius red and MMP are capable of degrading extracellular matrix proteins, expressed in lesions such as squamous cell carcinomas. The present study was undertaken with an aim to analyze and compare changes in collagen using Picrosirius red staining under polarizing microscopy and immunohistochemical staining using anti MMP-13 in samples of oral leukoplakia, oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Materials and Methods: A total of 70 slides were prepared and divided into 3 groups. Group I comprised 10 slides of normal gingival tissue, Group II 40 slides of potentially malignant disorders and Group III 20 slides of well differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma. Half the slides for each group were stained with Picrosirius red stain and the remainder with antibodies to MMP-13. Rerults: In Group II, MMP-13 connective tissue expression was greater in OSMF as compared to leukoplakia. Group III showed elevated expression among 70% of cases. Picrosirius red staining in Group II cases, showed higher staining Yellow-Orange andgreen-yellow mature fibers in OSMF than leukoplakia cases while in Group III, 50% OSCC cases showed Green-yellow stained immature thin fibers. Conclusion: In future, therapeutic measures targeted against MMP-13 may inhibit collagenolysis to some extent and delay spread of tumors. An easy and reliable method to determine the state of the stroma in such cases may be Picrosirius red staining with polarizing microscopy. Keywords: Immunohistochemistry-MMP-13- picrosirius red stain- polarizing microscopy- oral squamous cell carcinoma Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 19 (4), Introduction The use of tobacco in different forms is highly prevalent in the Asian subcontinent. Tobacco contains many carcinogens like nicotine, N-nitrosamines, and many others which induce generation of free radicals and reactive oxygen species, that affect the essential constituents of cell membrane and might be involved in carcinogenesis. The oral cavity witnesses the development of a variety of Red and White lesions associated with tobacco use. These lesions often precede the development of frank cancerous lesions (Lodi et al., 2006). Oral potentially malignant lesions comprises of a multitude of histologically diverse lesions with variable but overall increased risk for development of invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or potentially malignant lesion of the oral mucosa. The reported prevalence ranges from 0.2 to 5%, with remarkable regional differences: India ( %), Sweden (3.6%), Germany (1.6%), and Holland (1.4%) (Marrija, 2000). Oral Submucous fibrosis (OSMF) is a chronic, progressive, scarring disease that predominantly affects the people of South East Asian origin. The disease was first described by Schwartz (1952) and he ascribed the term atrophica idiopathica (tropica) mucosae oris. Later, in 1953, Joshi from Bombay redesignated the condition as oral submucous fibrosis, implying predominantly its histological nature (Rajendran, 1994). Despite the attainments already achieved concerning OSCC diagnosis and therapy, mortality and morbidity rates are still exceedingly high, challenging the available methods of prognosis assessment and encouraging the search for new and better markers. Recent advancements in Cancer Genetics and the role of molecular markers in pathogenesis of cancer are particularly notable. One of the major aspects of tumor cell invasion and metastasis is the interaction between cancer cells and the 1 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Desh Bhagat Dental College and Hospital, Mandigobindgarh, 3 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, BJS Dental College Hospital and Research Institute, Ludhiana, 6 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Sri Sukhmani Dental College and Hospital, Derabassi, Punjab, 2 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Swami Devi Dyal Hospital and Dental College, 5 Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, BRS Dental College and General Hospital, Barwala, Haryana, 4 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Bhojia Dental College and Hospital, Bhud, Baddi, Himachal Pradesh, India. *For Correspondence: drkaranarora@yahoo.com Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
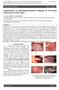
2 Krishna Singh Arora et al surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM).This interaction involves all the components of the extracellular matrix, of which type I collagen is the most abundant and is synthesized predominantly by fibroblasts. Collagen is involved in tumor progression in two very different ways. The desmoplastic response to a tumor results in excess deposition of collagen around the tumor. Conversely, collagen degradation and decreased synthesis allow invasion of tumor cells through the stroma. Degradation of the extracellular matrix is dependent on specific interactions between tumor and host cells (Fenhalls et al., 1998). Traditionally, stains like Van Gieson and other trichome stains were used to demonstrate collagen fibers in tissue sections. But they lacked the precise selectivity and failed to reveal very thin collagen fibers. Sirius Red is an elongated dye molecule which reacts with collagen with high specificity and promotes an enhancement of the normal birefringence of collagen under polarizing microscopy (Constantine and Mowry, 1968). Matrix metalloproteinase s (MMPs) are zinc dependent endopeptidases that are capable of degrading extracellular matrix proteins. The activity of MMPs is seen not only during normal organogenesis and wound healing but also in pathological conditions like inflammatory diseases and tumor invasion (Mehanna et al., 2009). Myofibroblasts (MF) has been reported and plays a key role in ECM synthesis, re-organization and tissue contractions during both physiologic and pathologic processes like wound healing and tumourigenesis (Desmoulier et al., 2004). It may be postulated that an excess of MF in malignancies may secrete excess MMP, which breakup ECM thus allowing for easier and faster dissemination of epithelial cells into the matrix. Moreover, the MF, also secrete numerous growth factors and cytokines that stimulate epithelial cell proliferation (Desmoulier et al., 2004). Hence MMPs appear to be essential for tumor invasion and metastatic spread, and it may be hypothesized that positive identification andquantifictorial of MMP may be useful in the prognosis of malignancies. Therefore the present study was undertaken with an aim to analyze and compare the changes in collagen using Picrosirius red staining under polarizing microscope and immune histochemical staining using Anti MMP-13 in oral leukoplakia, oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Materials and Methods The present study was conducted in the Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology after the clearance from the ethical committee of the institute. Formalin fixed paraffin embedded blocks of previously diagnosed cases as leukoplakia, oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma were taken from the archives of the department. Normal blocks of oral gingival tissues were taken as control. A total of 70 slides were prepared from these blocks taken from the archives of the department and were divided in to 3 groups. Group I consisted of 10 slides 1076 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19 which were prepared from normal gingival tissue which was excised during implant exposure (Stage II), and these served as negative control. Group II consisted of 40 slides out of which 20 were clinical and histopathologically diagnosed as oral leukoplakia and epithelial dysplasia respectively and 20 were clinically and histopathologically diagnosed as oral submucous fibrosis. Group III consisted of 20 slides were histopathologically diagnosed as well differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma. Further, half the slides for each group were stained with Picrosirius Red Stain. The remaining halves from each group were stained with immune histochemical stains for Antibody to MMP-13. Further they were observed under Polarizing microscope, where 10 fields from each sample were observed under oil immersion for different polarizing colors. The slides that were prepared were evaluated by one senior oral pathologist and one resident oral pathologist of the department. Each slide was observed under polarizing microscope and was evaluated for the degree of the staining for MMP 13 and scores were given as follow (Culhaci et al., 2004): 0 : No staining of the tumor cells or stromal cells 1+: Weak (<50%) positive staining of the tumor cells or weak staining of stromal cells 2+ : Moderate (>50%) positive staining of the tumor cells and or moderate staining of stromal cells 3+ : Extreme staining of the tumor cells and or strong straining of stromal cells The data collected was archived and tabulated and statistical evaluation was done using SPSS (v16) software. Results Table 1 shows the comparison of MMP-13 immuno-histochemical expression in epithelium among all the three groups. Table 2 exhibits the comparison of MMP-13 immuno-histochemical expression in connective tissue among all the three groups. Figure 1 depicts photomicrograph of epithelial/collagen tissue fibres with Anti- MMP-13 expression in Leukoplakia, OSMF and OSCC. Table 3 shows the comparison of Polarizing colors of picrosirius red staining among all the three groups. Figure 2 depicts photomicrograph of collagen tissue fibres stained with Picrosirius red stain seen under Polarizing microscope in Leukoplakia and OSCC. Table 4, Table5, Table 6 materializes the co-relation between immune-histochemical expression of MMP-13 Table 1. Comparison of MMP-13 Immuno-histochemical Expression In Epithelium Among All Three Scores I II III Normal Leukoplakia OSMF OSCC 0 Negative 4 (80%) 0 (0%) 2 (20%) 0 (0%) 1+ 1 (20%) 1 (10%) 4 (40%) 2 (20%) 2+ Moderate 0 (0%) 6 (60%) 2 (20%) 3 (30%) 3+ Extensive 0 (0%) 3 (30%) 2 (20%) 5 (50%)
3 DOI: /APJCP Evaluation of Collagen in Potentially Malignant Disorders Using Polarizing Microscopy and Immunohistochemistry Figure 2. Photomicrograph Showing Collagen Fibres (Stained with Picro-Sirius Red Stain) in Under Polarizing Microscope a) Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma b) Leukoplakia Figure 1. Photomicrograph of Epithelium/Collagen Fibres (Anti MMP-13 Expression) a) Leukoplakia b) Oral Submucous Fibrosis c) Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and picrosirius polarizing staining. Discussion Oral cancer is a significant health problem in the world. Most oral cancer patients are diagnosed at a late stage, when treatment is less successful and treatment associated morbidity is more severe. A number of new diagnostic aids to conventional oral examination have Table 2. Comparison of MMP-13 Immuno-histochemical Expression in Connective Tissue Among All Three Scores I II III Normal Leukoplakia OSMF OSCC 0 Negative 5 (100%) 1 (10%) 0 (0%) 1 (10%) 1+ 0 (0%) 6 (60%) 4 (40%) 2 (20%) 2+ Moderate 0 (0%) 2 (20%) 4 (40%) 3 (30%) 3+ Extensive 0 (0%) 1 (10%) 2 (20%) 4 (40%) recently been introduced to assist in the early detection of oral neoplasia. A Workshop coordinated by WHO collaborating centre for oral cancer and pre-cancer at London in May 2005 did not favor subdividing precancer into lesions and conditions and the consensus view was to refer to all clinical presentations that carry risk of cancer under the term potentially malignant disorders to reflect their widespread anatomic distribution (Warnakulasuriya et al., 2007). Numerous studies have stressed on the importance of the stroma in the spread of Oral cancer. Of the many steps of invasion and metastasis, the breakdown of matrix components and the migration of cells through the degraded matrix are important determinants. The increase in collagen fiber bundles in Oral Submucous Fibrosis results in diminished vascularity which causes atrophy of the overlying epithelium, making it more susceptible to carcinogenic agents. Stains for collagen are useful in when they are highly selective. An ideal collagen stain should not stain anything besides collagen, with the remainder of the tissue visualized by the counter stain. It is well known that collagen viewed by polarized light is birefringent. Staining with Picrosirius red F3BA Table 3. Comparison of Polarizing Colors of Picrosirius Red Staining Among All Three Staining Colors Observed I II III Normal Leukoplakia OSMF OSCC Red-Yellow 1 (20%) 3 (30%) 4 (40%) 3 (30%) Yellow-Orange 4 (80%) 6 (60%) 4 (40%) 2 (20%) Green-Yellow 0 (0 %) 1 (10%) 2 (20%) 5 (50%) Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
4 Krishna Singh Arora et al Table 4. Co-relation Between Immuno- Histochemical Expression of MMP-13 and Picrosirius Polarizing Staining in Group I Picro-Sirius Staining Data MMP-13 S No Red Yellow Yellow Orange Green Yellow Normal 1 P P Total Table 5. Co-relation Between Immuno- Histochemical Expression of MMP-13 and Picrosirius Polarizing Staining in Group II Picro-Sirius Staining Data MMP-13 S No Red Yellow Yellow Orange Green Yellow OSMF 1 P P 6 P P 7 P P 8 P P 9 P P 10 P P Total Leukoplakia 1 P P 6 P P 7 P P 8 P P 9 P P 10 P P Total produces a remarkable degree of birefringence of all the collagen fibers which appear bright yellow when viewed by polarized light. This property permits even very small fibers to be seen easily. This intensity of the birefringence after Sirius red exceeds greatly that seen either in unstained sections or after any of the other procedures tested here (Constantine et al., 1968). Sirius red does not impart birefringence to structures that lack it normally. This helps distinguish collagen from other substances that are also stained by Sirius red. Moreover, it also helps to differentiate between thick fibers and thin fibers, which is otherwise very difficult under the light microscope (Venigella and Charu, 2010). The use of Picrosirius stain along with Polarizing microscopy has been especially helpful in these studies. Usually, normal thin collagen fibers show green to greenish yellow polarization, whereas thick fibers show yellowish-orange through orange to red polarization. It has also been stated that in both thin and thick fibers, green to greenish yellow colors suggest that the collagen is poorly packed and orange red color originates from tightly packed fibers. It was suggested by the authors that change in polarization colors of collagen fibers may be indicative of neoplastic transformation (Gangana et al., 2012). It has been reported that in well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma and moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma, distinct deposits of collagen showed reddish orange to yellowish orange birefringence, which was mainly concentrated around the tumor islands. Whereas, moderately differentiated and poorly 1078 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19
5 DOI: /APJCP Evaluation of Collagen in Potentially Malignant Disorders Using Polarizing Microscopy and Immunohistochemistry Table 6. Co-relation Between Immuno-histochemical Expression of MMP-13 and Picrosirius Polarizing Staining in Group III Picro-Sirius Staining Data MMP-13 S No Red Yellow Yellow Orange Green Yellow OSCC 1 P P 6 P P 7 P P 8 P P 9 P P 10 P P Total differentiated squamous cell carcinoma in the same study showed a gradual change in the polarizing color from yellowish orange to greenish yellow, particularly in the immediate vicinity of the invading tumor islands (Venigella and Charu, 2010). The transformation of lesions from a pre-neoplastic to cancerous state is associated with an increase in collagenolytic activity. Cancer cells produce collagenases as collagen type I and III are the most abundant component in the extracellular matrix of dermal and oral submucous connective tissue. By increased formation of collagenases, the invading tumor cells are capable of dissolving collagen in connective tissue obstructing its course, and migrate through the degraded matrix (Gangana et al., 2012). MMPs are a family of zinc-dependent neutral endopeptidases collectively capable of degrading all components of the extracellular matrix. The MMP family contains at least 24 structurally related members, which are divided into collagenases, gelatinases and stromelysin like MMPs. Members of the collagenase subgroup of MMPs i.e. collagenase 1 (MMP-1), collagenase 2 (MMP-8), and collagenase 3 (MMP-13), are the principal neutral proteinases capable of degrading native fibrillar collagens in the extracellular space. They all cleave type I, II and III collagens at a specific site, generating ¾ N-terminal and ¼ C-terminal fragments, which then denature in physiological temperature and are degraded by the other MMPs, e.g., gelatinases [2,3 of nina Johansson]. MMP-13 is a member of the collagenase family, which degrades fibrillar collagens of types I, II, III, IV, X and XIV, tenasin, fibronectin, aggrecan, vesicant, and fibrillin-i. MMP-13 also cleaves native type I collagen in the N-terminal non-helical telopeptide [4 of nina Johansson]. It also plays a key role in the activation cascade, both activating and being activated by several MMPs. Elevated MMP-13 levels have been reported in a number of malignancies, and has also been associated with tumor behavior and prognosis (Johansson, 1999). In our study, we attempted to study the expression of MMP-13 in different Oral potentially malignant disorders, and compare the findings with those seen in Oral Squamous cell carcinoma. Moreover, we also studied the stroma in the same study group by Picrosirius staining, as this has been reported to describe the stroma better than routine H ande staining. Further, we attempted to see whether there was any co-relation between the levels of expression of MMP-13 and the color of collagen seen under polarizing microscopy. Our study showed a significantly increased expression of MMP-13 in the connective tissue of Oral Squamous cell carcinoma cases as compared to the expression in potentially malignant disorders (Leukoplakia and Oral submucous fibrosis). Further, an increased expression was also noted in the pre-neoplastic group when compared with normal tissue, which did not show any expression at all. An intra-group comparison of the distribution of MMP-13 between Leukoplakia and Oral submucous fibrosis showed increased expression in Submucous fibrosis. Our findings are contrary to the widespread view that a reduction in collagenolytic activity is responsible for the pathogenesis of Oral Submucous Fibrosis. It is possible that the cases studied by us were in an advanced stage, or that there may be other unknown factors acting. Moreover, our study showed half of the cases of Oral Squamous cell carcinoma showing extensive expression of MMP-13 in the epithelium which was significantly more than that in the premalignant group. While most cases (60%) of Leukoplakia showed moderate expression of MMP-13 in the epithelium, most of the cases of Oral Submucous Fibrosis (60%) showed negative/minimal expression, correlating well with the fact that oral epithelium undergoes atrophy in this lesion. Picrosirius staining under fluorescent microscopy showed predominance of red-yellow and yellow-orange staining (40% each) in Oral submucous fibrosis while more than half of the cases of Leukoplakia and 80% of normal tissue showed yellow-orange staining. However, a significant finding was that half of the cases of Oral squamous cell carcinoma showed Green-yellow birefringence. This finding suggests that Oral malignancy is indeed associated with a breakdown of matrix. There have been numerous studies in literature which have studied the collagen fibers in submucous fibrosis and Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol
6 Krishna Singh Arora et al in Oral squamous cell carcinomas. These studies were based on the supposition that tightly packed collagen fiber bundles would act to inhibit the progression of cancer cells. Numerous other studies have focused on the expression of MMP-13 in these lesions as it is a principal agent in degradation of Type I collagen. These studies were based on the supposition that a breakdown in the extracellular matrix would allow for easy spread of the neoplastic cells. An analysis of studies of these natures suggested to us that MMP-13 expression, which is known to be an indicator of progression of neoplastic lesions, should also have a correlation to the type of collagen present n the connective tissue stroma of the lesions. It would only be logical to assume that an increased expression of MMP-13 should be associated with thin or loosely packed collagen fibers (Johansson, 1999). In our study, an increased expression of MMP-13 in the connective tissue stroma of oral Squamous cell carcinoma correlated well with the demonstration of greenish-yellow birefringence with picrosirius red stain. Also, the predominance of yellow-orange birefringence in the connective tissue of pre-malignancies correlated with minimal / no expression of MMP-13. This stands to logic as the connective tissue in normal tissue (80%) also showed yellow-orange birefringence. The findings of our study seem to suggest that the connective tissue undergoes significant alterations as lesions progress from pre-malignancy to malignancy. Furthermore, our study also shows that the use of Picrosirius stain with polarizing microscopy may be a more economical, rapid and easy to perform procedure to evaluate the connective tissue changes in lesions, as compared to immune-histochemical study of MMP-13 which is more technique sensitive, takes more time and more expensive (Veli-Matti, 2003). In conclusion, the findings of our study seem to suggest that the connective tissue undergoes significant alterations as lesions progress from pre-malignancy to malignancy. Furthermore, our study also shows that the use of Picrosirius stain with polarizing microscopy may be a more economical, rapid and easy to perform procedure to evaluate the connective tissue changes in lesions, as compared to immune-histochemical study of MMP-13 which is more technique sensitive, takes more time and more expensive. Thus Picrosirius stain can be used independently or as an adjunct with MMP-13 for evaluation of connective tissue. While cancer therapy is directed on one end towards the malignant cells per se, numerous studies are directed towards associated developments. It is probable to assume that in future, therapeutic measures targeted against MMP-13 may inhibit collagenolysis to an extent and delay the spread of tumor. An easy method to determine the state of the stoma in these cases may be the use of Picrosirius Red stain with Polarizing microscopy. Constantine VS, Mowry RW (1968). Selective staining of human dermal collagen. J Invest Dermato, 50, Desmoulier A, Guyot C, Gabbiani G (2004). The stromal reaction myofibroblast: a key player in the control of tumor cell behavior. Int J Dev Biol, 48, Fenhalls G, Geyp M, Dent DM, Parker MI (1998). Breast tumour cell-induced down-regulation of type I collagen mrna in fibroblasts. Br J Cancer, 81, Gangana K, Shetty P, Shroff SE (2012). Collagen in histologic stages of Oral submucous fibrosis a polarizing microscopic study. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol, 16, Johansson N (1999). Collagenase-3 (MMP-13) is expressed by tumor cells in invasive vulvar squamous cell carcinomas. Am J Pathol, 154, Lodi G, Sardella A, Bez C, Demarosi F, Carrassi A (2006). Interventions for treating oral leukoplakia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 18, CD Marrija BB (2000). The prevalence of precancerous oral lesions. Oral leukoplakia. Arch Oncol, 8, Mehanna HM, Rattay T, Smith J, McConkey CC (2009). Treatment and follow up of oral dysplasia- a systemic review and meta analysis. Head Neck, 31, Rajendran R (1994). Oral submucous fibrosis: etiology, pathogenesis, and future research. Bull WHO, 72, Veli-Matti K, Ala-Aho R, Ahonen M (2003). Novel ribozyme and its use. U.S. Patent applications US A1. Venigella A, Charu S (2010). Evaluation of collagen in various grades of oral squamous cell carcinoma by using Picrosirius red: A histochemical study. J Clin Diag Res, 23, Warnakulasuriya S, Johnson NW, VandeWaal I (2007). Nomenclature and classification of potentially malignant disorders of the oral mucosa. J Oral Path Med, 36, This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- Non Commercial 4.0 International License. References Culhaci N, Metin K, Copcu E, Dikicioglu E (2004). Elevated expression of MMP-13 and TIMP-1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas may reflect increased tumor invasiveness. BMC Cancer, 4, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 19
Role Of Collagen Fibres In The Expansion Of Odontogenic Cysts A Histochemical Study.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 11 Number 2 Role Of Collagen Fibres In The Expansion Of Odontogenic Cysts A Histochemical Study. S Viswanathan, R Venkatapathy, B Danasekaran Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 11 Number 2 Role Of Collagen Fibres In The Expansion Of Odontogenic Cysts A Histochemical Study. S Viswanathan, R Venkatapathy, B Danasekaran Citation
Figure 1: Juxtaepithelial Hyalinisation. Figure 2: Dense Collagen Fibres around Blood Vessels
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF COLLAGEN WITH PICROSIRIUS RED STAIN IN ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS UNDER POLARISING MICROSCOPE S. Swetha* & Dr. S. Gheena** * BDS (Third Year), Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF COLLAGEN WITH PICROSIRIUS RED STAIN IN ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS UNDER POLARISING MICROSCOPE S. Swetha* & Dr. S. Gheena** * BDS (Third Year), Saveetha Dental College and Hospitals,
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
ROLE OF HISTOLOGICAL STAINS IN EVALUATION OF COLLAGEN IN ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL : A REVIEW.
 ROLE OF HISTOLOGICAL STAINS IN EVALUATION OF COLLAGEN IN ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL : A REVIEW 1 2 3 4 Shahla Khan, Hitesh Vij, Vineeta Gupta, Nutan Tyagi 1 2 3 4 Post Graduate Student,
ROLE OF HISTOLOGICAL STAINS IN EVALUATION OF COLLAGEN IN ORAL SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA AS A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL : A REVIEW 1 2 3 4 Shahla Khan, Hitesh Vij, Vineeta Gupta, Nutan Tyagi 1 2 3 4 Post Graduate Student,
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice
 Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
DR.SHERIN.A.KHALAM,MSc(PSY),MDS,FICOI Associate Professor, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Kerala University of Health Sciences; Consultant
 DR.SHERIN.A.KHALAM,MSc(PSY),MDS,FICOI Associate Professor, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Kerala University of Health Sciences; Consultant Maxillofacial Surgeon & Surgical Head, SUT Royal Hospitals,
DR.SHERIN.A.KHALAM,MSc(PSY),MDS,FICOI Associate Professor, PMS College of Dental Science & Research, Kerala University of Health Sciences; Consultant Maxillofacial Surgeon & Surgical Head, SUT Royal Hospitals,
Association of Histological Grading of Oral Submucous Fibrosis to Cytokeratin 19 Immunohistochemical Staining
 Association of Histological Grading of Oral Submucous Fibrosis to Cytokeratin 19 Immunohistochemical Staining DR SHAN NAWAZ MALIK 1, DR ZANKANA VYAS 2, DR HEMANTH KOTARI 3, DR. VISHNUDAS DINESH PRABHU
Association of Histological Grading of Oral Submucous Fibrosis to Cytokeratin 19 Immunohistochemical Staining DR SHAN NAWAZ MALIK 1, DR ZANKANA VYAS 2, DR HEMANTH KOTARI 3, DR. VISHNUDAS DINESH PRABHU
Original Research. Received: 12th July 2013 Accepted: 15th December 2013 Conflict of Interest: None. Contributors:
 Received: 12th July 2013 Accepted: 15th December 2013 Conflict of Interest: None Original Research Histochemical analysis of polarizing colors of collagen using Picrosirius Red staining in oral submucous
Received: 12th July 2013 Accepted: 15th December 2013 Conflict of Interest: None Original Research Histochemical analysis of polarizing colors of collagen using Picrosirius Red staining in oral submucous
Case Report ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS: A CASE REPORT. Jindal DG, 1Joshi S, 2Bhardwaj A.
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.06 Case Report ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS: A CASE REPORT Jindal DG, 1Joshi S, 2Bhardwaj A. Reader, 1Senior lecturer, 2Post Graduate student, Department of Oral Pathology and
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.06 Case Report ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS: A CASE REPORT Jindal DG, 1Joshi S, 2Bhardwaj A. Reader, 1Senior lecturer, 2Post Graduate student, Department of Oral Pathology and
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Epidemiology Clinical presentation
 LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
LEUKOPLAKIA Definition Leukoplakia is the most common premalignant or "potentially malignant" lesion of the oral mucosa. Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa than cannot be clinicopathologically
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Nitu S S Mishra 1, Sangeeta P Wanjari 2, Rajkumar N Parwani 3, Panjab V Wanjari 4, Sumedha P Kaothalker 5. Original Research
 Original Research Assessment of collagen and elastic fibres in various stages of oral submucous fibrosis using Masson's trichrome, Verhoeff vangieson and picrosirius staining under light and polarizing
Original Research Assessment of collagen and elastic fibres in various stages of oral submucous fibrosis using Masson's trichrome, Verhoeff vangieson and picrosirius staining under light and polarizing
Original Research. Serum lipid profile in oral precancer and cancer...garg D et al
 Journal of International Oral Health 14; 6(2):33-39 Received: 1th August 13 Accepted: 15th December 13 Conflict of Interest: one Source of Support: il Original Research Serum lipid profile in oral precancer
Journal of International Oral Health 14; 6(2):33-39 Received: 1th August 13 Accepted: 15th December 13 Conflict of Interest: one Source of Support: il Original Research Serum lipid profile in oral precancer
الطلاوة = Leukoplakia LEUKOPLAKIA
 LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
LEUKOPLAKIA Leukoplakia is a clinical term that refers to a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be rubbed off or characterized by any other definable lesion or known disease. 130
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen. Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang
 Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(7):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 586-591 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.065
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 586-591 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.065
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
Evaluation of Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Betel Quid Associated Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
 Original Article Evaluation of Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Betel Quid Associated Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients Su Mon Than*, Sein Shwe**, Zaw Moe Thein**, Swe Swe
Original Article Evaluation of Serum Copper and Zinc Levels in Betel Quid Associated Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients Su Mon Than*, Sein Shwe**, Zaw Moe Thein**, Swe Swe
ONCOLOGY. Csaba Bödör. Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research november 19., ÁOK, III.
 ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
Topical nanocrystalline silver cream inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in animal models of allergic contact dermatitis.
 Topical nanocrystalline silver cream inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in animal models of allergic contact dermatitis. K C Bhol, P J Schechter NUCRYST Pharmaceuticals Inc, Wakefield, MA
Topical nanocrystalline silver cream inhibits expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in animal models of allergic contact dermatitis. K C Bhol, P J Schechter NUCRYST Pharmaceuticals Inc, Wakefield, MA
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek
 ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek Oral diagnostics Definition of the discipline That area of dentistry, the which deals with gathering, recording
ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS IS THE ONLY TRUE CORNERSTONE ON WHICH RATIONAL TREATMENT CAN BE BUILT. C Noyek Oral diagnostics Definition of the discipline That area of dentistry, the which deals with gathering, recording
Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1294 Manjula A Hebbale et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study Manjula
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1294 Manjula A Hebbale et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Mirror Image Biopsy for Incidence of Multiple Premalignant and Malignant Lesions in Oral Cancer: A Clinical Study Manjula
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Anam Ali 1 *, Muhammad Asif 2, Bismah Ahmad 2, Shahid Jamal 3, Iram Ali 4, Muhammad Tahir Khadim 1. Abstract.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:08/20/2018 Acceptance:12/30/2018 Stromal Expression of CD10 by Immunohistochemistry in Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Dentigerous and Radicular Cysts and Its
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:08/20/2018 Acceptance:12/30/2018 Stromal Expression of CD10 by Immunohistochemistry in Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC), Dentigerous and Radicular Cysts and Its
Salivary MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3 and MMP-13 Levels in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus and Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Salivary MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3 and MMP-13 Levels in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus and Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tahereh Nosratzehi 1 *, Ebrahim Alijani 2, Marziyeh Moodi 3 Abstract The
RESEARCH ARTICLE Salivary MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3 and MMP-13 Levels in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus and Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tahereh Nosratzehi 1 *, Ebrahim Alijani 2, Marziyeh Moodi 3 Abstract The
The role of interventional surgery in oral potentially malignant disorders by Peter Thomson
 84 Peter Thomson DOI 10.1308/204268514X13939420839142 The role of interventional surgery in oral potentially malignant disorders by Peter Thomson Oral potentially malignant disorders are mucosal diseases
84 Peter Thomson DOI 10.1308/204268514X13939420839142 The role of interventional surgery in oral potentially malignant disorders by Peter Thomson Oral potentially malignant disorders are mucosal diseases
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Assessment of Tumor Cell Morphology and Peri-Tumoral Stromal Changes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Assessment of Tumor Cell Morphology and Peri-Tumoral Stromal Changes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Authors Dr Mahima Rakheja 1, Dr Jasleen
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Assessment of Tumor Cell Morphology and Peri-Tumoral Stromal Changes in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Authors Dr Mahima Rakheja 1, Dr Jasleen
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF
 ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF A GUIDE TO UTILISATION. The following guidelines have been agreed by consensus of Anatomical Pathologists who are members of the Anatomical Pathologist s Group, or the National
ANATOMICAL PATHOLOGY TARIFF A GUIDE TO UTILISATION. The following guidelines have been agreed by consensus of Anatomical Pathologists who are members of the Anatomical Pathologist s Group, or the National
Comparison of CD10 expression in stroma of epithelial and mesenchymal tumors of the breast
 Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Dermatoglyphic patterns in subjects with potentially malignant disorders and oral carcinoma
 Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2015), 2, 7 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dermatoglyphic patterns in subjects with potentially malignant disorders and oral carcinoma Maria Priscilla David 1, Pooja
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2015), 2, 7 11 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dermatoglyphic patterns in subjects with potentially malignant disorders and oral carcinoma Maria Priscilla David 1, Pooja
Healing & Repair. Tissue Regeneration
 Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for
 INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(2):155 159 HPV and p53 expression in dysplastic lesions and squamous carcinomas of the oral mucosa CRISTIANA SIMIONESCU 1), CL. MĂRGĂRITESCU 1), CLAUDIA
Original Research Article
 ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
ASSESSMENT OF HUMAN PAPILLOMA VIRUS SUBTYPES BY POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DEGREE OF DYSPLASIA IN ORAL LEUKOPLAKIA Submitted on: XXXX Dr. N. Kannan, Dr Teja Srinivas, Dr. Rakesh
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Healing and Repair. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Healing and Repair Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD 1 ILOs Know the classification of human cells according to their ability for proliferation. Understand the mechanism of cellular regeneration. Identify the types
Healing and Repair Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD 1 ILOs Know the classification of human cells according to their ability for proliferation. Understand the mechanism of cellular regeneration. Identify the types
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy. Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI
 A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS
 MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
MAST CELLS IN ORAL LICHEN PLANUS Mahija Janardhanan* V.Ramesh. ** *Reader, Department of Oral Pathology & Microbiology, Amrita school of Dentistry, Kochi. **Professor & HOD, Department of Oral Pathology
Trends of prevalence and pathological spectrum of head and neck cancers in North India
 Original Article Trends of prevalence and pathological spectrum of head and neck cancers in North India Mehrotra Ravi, Singh Mamata, Gupta Raj Kishore, Singh Manish, Kapoor Anil K* Department of Pathology
Original Article Trends of prevalence and pathological spectrum of head and neck cancers in North India Mehrotra Ravi, Singh Mamata, Gupta Raj Kishore, Singh Manish, Kapoor Anil K* Department of Pathology
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Department of Pathology, Jawaharlal Nehru Medical College, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, India 2
 original article Oman Medical Journal [2016], Vol. 31, No. 3:165 169 Transition of Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Vimentin from Premalignant to Malignant Lesions of Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
original article Oman Medical Journal [2016], Vol. 31, No. 3:165 169 Transition of Immunohistochemical Expression of E-Cadherin and Vimentin from Premalignant to Malignant Lesions of Oral Cavity and Oropharynx
Using Histoindex Genesis 200 imaging technology to analyse the Pattern of ECM Deposition in Human Breast Cancer Tissue
 Using Histoindex Genesis 200 imaging technology to analyse the Pattern of ECM Deposition in Human Breast Cancer Tissue Introduction to technology High Resolution Detects fine collagen fibers up to 0.1µm
Using Histoindex Genesis 200 imaging technology to analyse the Pattern of ECM Deposition in Human Breast Cancer Tissue Introduction to technology High Resolution Detects fine collagen fibers up to 0.1µm
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Saudi Journal of Pathology and Microbiology. DOI: /sjpm ISSN (Print)
 DOI:10.21276/sjpm.2016.1.3.1 Saudi Journal of Pathology and Microbiology Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3362 (Print) ISSN 2518-3370
DOI:10.21276/sjpm.2016.1.3.1 Saudi Journal of Pathology and Microbiology Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3362 (Print) ISSN 2518-3370
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY)
 Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
SUBMUCOSA PRECEDES LAMINA PROPRIA IN INITIATING FIBROSIS IN ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS - EVIDENCE BASED ON COLLAGEN HISTOCHEMISTRY.
 SUBMUCOSA PRECEDES LAMINA PROPRIA IN INITIATING FIBROSIS IN ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS - EVIDENCE BASED ON COLLAGEN HISTOCHEMISTRY. *Anna P. Joseph ** R. Rajendran Abstract Oral submucous fibrosis is a chronic
SUBMUCOSA PRECEDES LAMINA PROPRIA IN INITIATING FIBROSIS IN ORAL SUBMUCOUS FIBROSIS - EVIDENCE BASED ON COLLAGEN HISTOCHEMISTRY. *Anna P. Joseph ** R. Rajendran Abstract Oral submucous fibrosis is a chronic
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Lecturer, Department of Oral Medicine, University of Dental Medicine, Mandalay.
 Original Article Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44 and ALDH1 in Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Khin Soe 1, Moe Thida Htwe 2 and Zaw Moe Thein 3 1 Lecturer, Department of
Original Article Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44 and ALDH1 in Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Khin Soe 1, Moe Thida Htwe 2 and Zaw Moe Thein 3 1 Lecturer, Department of
Clinicopathological and Histological Features of Ovarian Tumour- A Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 9 Ver. IX (September. 2017), PP 56-60 www.iosrjournals.org Clinicopathological and Histological
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 9 Ver. IX (September. 2017), PP 56-60 www.iosrjournals.org Clinicopathological and Histological
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
TITLE: Breast Tumor-Generated Type 1 Collagen Breakdown Fragments Act as Matrikines to Drive Osteolysis
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0639 TITLE: Breast Tumor-Generated Type 1 Collagen Breakdown Fragments Act as Matrikines to Drive Osteolysis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ching Hua William Wu PhD. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0639 TITLE: Breast Tumor-Generated Type 1 Collagen Breakdown Fragments Act as Matrikines to Drive Osteolysis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ching Hua William Wu PhD. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test
 753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
Characteristics of Collagen to Differentiate Fibrous Hyperplasia from Mesenchymal and Mixed Odontogenic Tumors: A Polarized Microscopic Study
 Original Article Original Article Characteristics of Collagen to Differentiate Fibrous Hyperplasia from Mesenchymal and Mixed Odontogenic Tumors: A Polarized Microscopic Study Mohamed Nassar M 1 *, Nirmal
Original Article Original Article Characteristics of Collagen to Differentiate Fibrous Hyperplasia from Mesenchymal and Mixed Odontogenic Tumors: A Polarized Microscopic Study Mohamed Nassar M 1 *, Nirmal
Table 1 Classification of oral biopsied lesions
 Original Article A Review of Biopsied Oral Lesions in Department of Oral Medicine, University of Dental Medicine, Mandalay Mu Mu Win**, Thiri Su Myat Chel*, Su Mon Than*, Aye Mya Mya*, Aye Aye Thet*, Nandar
Original Article A Review of Biopsied Oral Lesions in Department of Oral Medicine, University of Dental Medicine, Mandalay Mu Mu Win**, Thiri Su Myat Chel*, Su Mon Than*, Aye Mya Mya*, Aye Aye Thet*, Nandar
Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 12 (December-2014) pp. 91-96 www.ijcrar.com Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma M.N.Divyarani*, M.L.Harendra Kumar, B.V.Swaroop raj, and U.D.Manoranjan
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 12 (December-2014) pp. 91-96 www.ijcrar.com Quantitative analysis of mast cells in invasive ductal carcinoma M.N.Divyarani*, M.L.Harendra Kumar, B.V.Swaroop raj, and U.D.Manoranjan
Toluidine blue staining as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of dysplastic changes in the oral mucosa
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51121 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51121 Toluidine blue staining as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51121 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51121 Toluidine blue staining as an adjunctive tool for early diagnosis of
Pap Smear and Histopathological Study of Cervical Lesions
 Global Journal of Medical research: c Microbiology and Pathology Volume 14 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Global Journal of Medical research: c Microbiology and Pathology Volume 14 Issue 4 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc.
Segmentation of Immunohistochemical Staining Of B-Catenin Expression of Oral Cancer
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Segmentation of Immunohistochemical Staining Of B-Catenin Expression of Oral Cancer V. Jeya Sutha 1, K.Srividhya 2 (PG Student [Applied Electronics], Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Segmentation of Immunohistochemical Staining Of B-Catenin Expression of Oral Cancer V. Jeya Sutha 1, K.Srividhya 2 (PG Student [Applied Electronics], Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara
MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES AND THEIR ROLE IN ORAL DISEASES: A REVIEW
 MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES AND THEIR ROLE IN ORAL DISEASES: A REVIEW 1 2 3 Varun BR Bindu J Nair Sivakumar TT Anna P Joseph 1 2 3 Senior Lecturer, Professor & HOD, Professor, Reader, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial
MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES AND THEIR ROLE IN ORAL DISEASES: A REVIEW 1 2 3 Varun BR Bindu J Nair Sivakumar TT Anna P Joseph 1 2 3 Senior Lecturer, Professor & HOD, Professor, Reader, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial
ALAEZI CM 1 *, ADISA JO 2, OKOROCHI EC 3 and OKECHI OO 4
 Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2016) 5(7):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 558-564 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.061
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 7 (2016) pp. 558-564 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.507.061
Cells and Tissues 3PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART D Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body Includes the most abundant
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART D Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body Includes the most abundant
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
NEOPLASIA. 3. Which of the following tumour is benign a. Chondrosarcoma b. Osteochondroma c. Chondroblastoma d. Ewing s tumour e.
 NEOPLASIA 1. malignant neoplasms a. are independent of hormonal influence b. are always composed of homogenous cell lines c. arise from differentiated cells by a process of anaplasia d. display abnormal
NEOPLASIA 1. malignant neoplasms a. are independent of hormonal influence b. are always composed of homogenous cell lines c. arise from differentiated cells by a process of anaplasia d. display abnormal
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS.
 NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel
 12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
12th symposium of the Association of Korean Dermatologists (2009) 1 Evaluation of the wound healing response post deep dermal heating by fractional RF: INTRAcel Un-Cheol.Yeo, M.D. S&U Dermatologic Clinic,
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Fluorescence Spectroscopy: A New Approach in Cervical Cancer
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0298-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE : A New Approach in Cervical Cancer Pandey Kiran Pradhan Asima Agarwal Asha Bhagoliwal Ajay Agarwal Nidhi Received: 2 June 2008 / Accepted: 7 August 2012
DOI 10.1007/s13224-012-0298-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE : A New Approach in Cervical Cancer Pandey Kiran Pradhan Asima Agarwal Asha Bhagoliwal Ajay Agarwal Nidhi Received: 2 June 2008 / Accepted: 7 August 2012
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
MR imaging of FIGO stage I uterine cervical cancer: The diagnostic impact of 3T-MRI
 MR imaging of FIGO stage I uterine cervical cancer: The diagnostic impact of 3T-MRI Poster No.: C-1191 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: M. Takeuchi, K. Matsuzaki,
MR imaging of FIGO stage I uterine cervical cancer: The diagnostic impact of 3T-MRI Poster No.: C-1191 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: M. Takeuchi, K. Matsuzaki,
PREVENTION OF ORAL CANCER
 PREVENTION OF ORAL CANCER Oral cancer is increasing in incidence worldwide. Throughout the world, malignant neoplasms of the mouth and pharynx rate as the fifth most common cancer in men and the seventh
PREVENTION OF ORAL CANCER Oral cancer is increasing in incidence worldwide. Throughout the world, malignant neoplasms of the mouth and pharynx rate as the fifth most common cancer in men and the seventh
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
-1- Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks).
 -1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
-1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
DUSTURBANCES OF GROWTH. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L8 Uz: Musa
 DUSTURBANCES OF GROWTH MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L8 Uz: Musa Agnesia: means complete absence of an organ (Kidney). Aplasia: s defined in general as "defective development
DUSTURBANCES OF GROWTH MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L8 Uz: Musa Agnesia: means complete absence of an organ (Kidney). Aplasia: s defined in general as "defective development
Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
 Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Christopher L. Winters, DPM American Health Network Indianapolis,
Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Christopher L. Winters, DPM American Health Network Indianapolis,
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS
 A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
A QUANTITATIVE EVALUATION OF EPITHELIUM AND INFLAMMATORY INFILTRATE OF LICHEN PLANUS AND LICHENOID REACTIONS 1 2 Usha Balan Nitin Gonsalves Maji Jose 1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology, KMCT
The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center
 The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center Ramona Vlad, DMD Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy
The Prevalence of Oral Leukoplakia: Results From a Romanian Medical Center Ramona Vlad, DMD Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and Pharmacy
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Mesothelioma: diagnostic challenges from a pathological perspective. Naseema Vorajee August 2016
 Mesothelioma: diagnostic challenges from a pathological perspective Naseema Vorajee August 2016 Naseema.vorajee@nhls.ac.za Pleural diseases (whether neoplastic, reactive or infective) may have similar
Mesothelioma: diagnostic challenges from a pathological perspective Naseema Vorajee August 2016 Naseema.vorajee@nhls.ac.za Pleural diseases (whether neoplastic, reactive or infective) may have similar
MDJ The Role of K-Ras and PI3Kcb Expression in Oral Vol.:10 No.:2 2013
 MDJ The Role of K-Ras and PI3Kcb Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Dr. Asseel Mohammed ghazi. B.D.S Dr.Muna S. Merza. B.D.S, M.Sc. Ph.D Abstract Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma is an
MDJ The Role of K-Ras and PI3Kcb Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Dr. Asseel Mohammed ghazi. B.D.S Dr.Muna S. Merza. B.D.S, M.Sc. Ph.D Abstract Background: Oral squamous cell carcinoma is an
The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 17 Number 1 The Utility Of Congo Red Stain And Cytokeratin Immunostain In The Detection Of Primary Cutaneous A,A Citation A, A.. The Internet Journal
Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting. factor & may be induced to undergo malignant. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of
 بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
Advanced Diagnostic Aids in Detection of Oral Cancer
 Advanced Diagnostic Aids in Detection of Oral Cancer Roopam Chaudhary 1, Anshul Shah 2, Dishani M Shah 3, Sandeep Singh 4, Pooja Thakkar 5, Sandeep Goyal 6 1,6- Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology,
Advanced Diagnostic Aids in Detection of Oral Cancer Roopam Chaudhary 1, Anshul Shah 2, Dishani M Shah 3, Sandeep Singh 4, Pooja Thakkar 5, Sandeep Goyal 6 1,6- Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology,
Feasibility of recruitment to an oral dysplasia trial in the United Kingdom
 Nankivell et al. Head & Neck Oncology 2012, 4:40 RESEARCH Open Access Feasibility of recruitment to an oral dysplasia trial in the United Kingdom Paul Nankivell 1,2, Janet Dunn 3, Michael Langman 4 and
Nankivell et al. Head & Neck Oncology 2012, 4:40 RESEARCH Open Access Feasibility of recruitment to an oral dysplasia trial in the United Kingdom Paul Nankivell 1,2, Janet Dunn 3, Michael Langman 4 and
Tissues organs system organism. pg151
 Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
