Antibiotics for Research
|
|
|
- Clifton Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Antibiotics for Research Natural antibiotics have existed for centuries prior to scientists identifying and isolating active moieties responsible for antibacterial activity. Today antibiotics are widely used in the Life Sciences not only to eliminate contamination, but also to identify bacterial mechanisms of resistance, protein modification and DNA/RNA manipulation to develop new antineoplastic compounds. Antibiotics are frequently interchangeably called antibacterials, yet the term antibiotic today often includes antifungal and antineoplastic reagents. Antibacterials are generally divided into two major groups based on their biological mode of action on microorganisms: Bactericidal compounds actually kill bacteria, while bacteriostatic compounds inhibit or interfere with protein synthesis and cell wall biosynthesis. Additionally, antibacterial antibiotics may target certain specific types of bacteria, such as gram-positive or gram-negative organisms, while others are more broad-spectrum and attack a range of bacteria. Specific antibacterials may inhibit the synthesis of cell walls, preventing further bacterial growth. Ampicillin and bacitracin are examples of antibiotics that inhibit enzymes associated with cell wall synthesis, preventing bacterial growth. Ciprofloxacin and Actinomycin D interfere with DNA and RNA synthesis respectively, and are often studied as antitumor compounds which can attack quickly growing malignant cells. Doxycycline, streptomycin and kanamycin are examples of antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis by interfering with formation processes at the 30S or 50S subunits of the 70S bacterial ribosome. Finally, antibiotics like monensin and valinomycin act as ionophores and form cationic (Na +, K +, H + ) channels in bacterial cell walls and membranes, which in turn detrimentally change the intracellular cationic environment of the bacterial cells, typically causing lysis and cell death. Alfa Aesar is pleased to present a sampling of our diverse antibiotic showcase. These antibiotics are widely used in both mammalian and plant cell culture, cancer research, as antineoplastic agents, and in proteomics research. Our extensive line of antibiotics includes more than 240 high purity compounds for all of your antibacterial research needs. For additional antibiotics not listed in this brochure, please visit our website, /bio, call Alfa Aesar Customer Service, or consult our Bio Catalog. Product application The materials and products featured in this publication are for research use only. They are not intended for animal or human diagnostic or therapeutic use.
2 Antibiotics for Mammalian Cell Culture In Mammalian cell culture there are typically two types of contamination of concern: contamination of one cell line with another and the contamination of cultures with microbiological organisms like bacteria, mycoplasma, fungi, yeast, and endotoxin. The detrimental impact of microbiological contamination should not be underestimated. Fortunately, judicious use of selected antibiotics in cell culture media may control and eliminate contamination from bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma, and yeasts. Alfa Aesar offers a wide range of antibiotics to control bacterial contamination in cell culture media, and a selected sampling is listed below. Be sure to consult our website, /bio, for a complete list of all our antibiotics. J61491 Amphotericin B From Streptomyces nodosus. Antifungal agent useful in cell culture to prevent contamination by fungi. Binds with ergosterol to form monovalent (Na +, K +, Cl ) transmembrane channels causing ion leakage, which leads to fungal cell death. J60977 Ampicillin A beta-lactam antibiotic effective against gram-positive bacteria and some gramnegative bacteria. Inhibits transpeptidase, which is necessary for bacterial cell wall formation. J63807 Ampicillin Sodium Salt Broad spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic widely used in cell culture. Inhibits the final stage of bacterial cell wall formation, resulting in lysis. J65274 Cefazolin sodium salt (Cefamedin). A broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic effective against grampositive bacteria. It inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase and vitamin K epoxide reductase. J61317 Ciprofloxacin, 98% A fluoroquinone antibiotic with broad-spectrum activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Inhibits DNA gyrase, thus interfering with bacterial cell division J61970 Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride An antibacterial agent effective against anaerobic bacteria. Widely used in cell culture research for its broad-spectrum activity against bacterial contamination of the media. J60495 Dihydrostreptomycin sulfate An aminoglycoside bactericidal antibiotic available as the sesquisulfate salt. It destroys bacteria by inhibiting protein synthesis of the 30S bacterial ribosome. J62834 Gentamycin sulfate, 600 IU/mg Bactericidal antibiotic in the aminoglycoside class. Predominantly effective against gram-negative bacteria. Its mode of action is to disrupt protein synthesis of the 30S ribosome. J61669 Monensin sodium salt A polyether antibiotic that functions as an ionophore with monovalent cations (Na+, K+, Li + ), transporting them across lipid membranes. Blocks intracellular protein transport. J61499 Neomycin sulfate An aminoglycoside antibiotic effective against gram-negative bacteria. It can inhibit protein synthesis. Useful in tissue culture studies. J62486 Nystatin A polyene antifungal useful in mammalian cell culture against molds, fungi and yeast contamination. Similar to Amphotericin B, it binds to ergosterol and leads to K + leakage resulting in fungal cell death. J63032 Penicillin G sodium salt (Benzylpenicillin). A penicillin antibiotic effective against gram-positive bacteria. It inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by disrupting peptidoglycan cross-linking. 100mg, 100g 25g, 100g 5g, 10g, 100g J61763 Polymixin B sulfate, Antibiotic for gram-negative bacteria. It binds to cell walls, making them more permeable, and the resulting increased water uptake destroys the bacterial cells. Also used in cell culture to clear endotoxin contamination. J62633 Tylosin tartrate, 98% A macrolide antibiotic mainly effective against gram-positive bacteria. Its bacteriostatic effect is caused by binding to the 50S ribosome thus inhibiting protein synthesis.
3 Antibiotics for Plant Cell Culture For plant cell culture, antibiotics are typically used to maintain sterility of the media. Bacteria, fungi and mycoplasma which contaminate the media can rapidly deplete essential nutrients necessary for plant cell growth. It is best to use the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics that are effective for controlling bacteria, because the antibiotics themselves may be phytotoxic, and may restrict rooting, general growth and multiplication in some plant cultures. We are pleased to offer a large range of antibiotic for cell culture research. Don t see what you re looking for here? Please visit our website, /bio, or refer to our Bio Catalog for a complete list of all the antibiotics we offer. J62432 Bacitracin A cyclic polypeptide antibiotic effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It interferes with peptidoglycan bacterial cell wall formation by inhibiting the dephosphorylation of isoprenyl pyrophosphate. J61949 Carbenicillin disodium salt A water-soluble bacteriolytic antibiotic of the carboxypenicillin subgroup. Effective against gram-negative bacteria. J62690 Cefotaxime sodium salt A broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It inhibits transpeptidation of peptidoglycan synthesis disrupting cell wall formation. Useful in plant cell culture because it has no effect on the plastids of developed vascular plants. J62671 G418 disulfate, (Geneticin). An aminoglycoside antibiotic similar to gentamicin. It blocks polypeptide synthesis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Useful for selection of genetically engineered eukaryotic cells in culture. J63871 G418 disulfate, 50mg/ml solution An aminoglycoside antibiotic that is toxic to bacteria, yeast, and protozoans. Useful for selecting genetically engineered cells. J62834 Gentamycin sulfate, 600 IU/mg Bactericidal antibiotic in the aminoglycoside class. Predominantly effective against gram-negative bacteria. Its mode of action is to disrupt protein synthesis of the 30S ribosome. J60681 Hygromycin B An aminoglycoside antibiotic that kills bacteria, fungi and higher eukaryotic cells by disrupting protein synthesis. It s mode of action is to stabilize trna-ribosomal acceptor sites, which inhibits translocation. Useful for selection and maintenance of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells with the Hygromycin B resistance gene. 10ml, 50ml 100mg, 250mg, 1g J60668 Kanamycin monosulfate, An aminoglycoside bacteriocidal antibiotic effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It induces mistranslation of the 30S ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis. Useful in plant cell culture for selecting plasmids that have the kanamycin resistance gene. J61274 Paromomycin sulfate An aminoglycoside antibiotic especially effective against gram-negative bacteria and to a lesser degree some gram-positive bacteria. Like neomycin, it inhibits protein synthesis by binding to 16S ribosomal RNA. J60836 Rifampin, Molecular Biology Grade (Rifampicin). A bactericidal antibiotic that inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase. Especially effective against mycobacteria. J61299 Streptomycin sulfate, An aminoglycoside antimycobacterial effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 12S rrna of the 30S ribosome, causing misreading of the codon. 50g, 100g J62790 Vancomycin hydrochloride, Molecular Biology Grade A glycopeptide antibiotic effective against gram-positive bacteria. It inhibits cell wall formation by interfering with bacterial mucopeptide synthesis at the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus.
4 Antibiotics for Nucleic Acid and Protein Modification Numerous antibiotics have been shown to be involved in modifying nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Their predominant mode of action appears to be interference and inhibition of DNA and RNA synthesis by inhibiting cellular enzymes like topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase), and RNA polymerase. During protein synthesis most antibiotics that interfere involve processes at the 30S or 50S subunits of the 70S bacterial ribosome. Some antibiotics prevent binding of the aminoacyl site of the 30S ribosome, while others block formation of the larger 70S complex. Still other antibiotics disrupt cell wall synthesis and cause premature chain termination. Below are several of our many antibiotics useful for proteomics research due to their effects on nucleic acid and protein synthesis. For a more complete listing of all our antibiotics please visit our website, /bio, consult our Bio catalog, or simply call out customer service group. J60148 Actinomycin D A polypeptide antibiotic with anti-cancer activity. It inhibits DNA/nucleic acid synthesis and potently induces apoptosis by binding to DNA complexes and inhibiting RNA polymerase. J60849 Amikacin An aminoglycoside antibiotic derived from Kanamycin A. It binds to bacterial 30S ribosomes and causes misreading of the mrna which interferes with protein synthesis. J60727 Bleomycin sulfate A glycopeptide antibiotic with anti-cancer properties. Inhibits DNA synthesis by causing breaks in DNA strands. J62927 Chromomycin A3, 98% An anthraquinone glycosidic antibiotic useful as a fluorescent DNA stain. It inhibits DNA and RNA polymerases, disrupting protein synthesis. J60422 Doxycycline hydrochloride A tetracycline antibiotic effective against bacteria, fungi, and protozoans. It inhibits angiogenesis and reduces lung metastases by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinases. J62279 Erythromycin, A macrolide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. It binds to the 50S subunit of the bacterial 70S rrna complex, preventing aminoacyl translocation, blocking trna transfer. 5mg 25mg, 100mg 10mg 10g, 25g J60668 Kanamycin monosulfate, An aminoglycoside bacteriocidal antibiotic effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It induces mistranslation of the 30S ribosome and inhibits protein synthesis. Useful in plant cell culture for selecting plasmids that have the kanamycin resistance gene. J61251 Lincomycin hydrochloride A lincosamide antibiotic active against gram-positive bacteria. It is a bacteriostat that inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. J63193 Mitomycin C Antineoplastic agent which inhibits DNA synthesis and induces apoptosis. It is a potent DNA linker, which makes it an effective destroyer of bacteria. J61669 Monensin sodium salt A polyether antibiotic that functions as a sodium ionophore. As a Na + /H + antiporter, it blocks intracellular protein transport. It induces apoptosis in HL-60 cells. J60928 Novobiocin sodium salt An aminocoumarin antibiotic that acts as a bacterial topoisomerase (DNA gyrase) inhibitor. It is effective against gram-positive bacteria, and is widely used in cell culture research. 1mg, 5mg, 10mg J61278 Puromycin dihydrochloride, 99+% An aminonucleoside antibiotic that causes premature chain termination in protein synthesis. It inhibits serine peptidases (proteases) and metallopeptidases, and is widely used in cell culture as a selective agent. It is toxic to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 25mg, 100mg, 250mg J62473 Rapamycin, 99+% (Sirolimus). A macrolide immunosuppressant agent that blocks cytokine-mediated signal transduction pathways. It inhibits the response to Interleukin 2, thus suppressing T and B cell activation. 50mg, 100mg, 200mg J61820 Spectinomycin dihcl, An aminocyclitol antibiotic that binds to the 30S ribosomal subunit of bacteria and interrupts protein synthesis. It is effective against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. J61299 Streptomycin sulfate, An aminoglycoside antimycobacterial effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 12S rrna of the 30S ribosome, causing misreading of the codon. 50g, 100g J61714 Tetracycline Antibiotic effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. A potent protein synthesis inhibitor that binds to the 30S subunit of bacterial ribosomes, thus blocking the attachment of aminoacyl-trna, which in turn prevents attachment of new amino acids to the peptide chain. Also shown to induce apoptosis in osteoblasts. J62312 Valinomycin A cyclodepsipeptide antibiotic that inhibits mitochondrial action. Highly selective potassium ionophore that facilitates movement of K + ions through cellular membranes., 100g 100mg
5 Antibiotic Selection Chart Item # Name Antibiotic type Grampositive bacteria Gramnegative bacteria J60148 Actinomycin D Polypeptide + + Fungi Yeasts Myco-plasma J60849 Amikacin Aminoglycoside J61491 Amphotericin B Polyene + + J60977 Ampicillin β-lactam penicillin + + J62432 Bacitracin Polypeptide + + J60727 Bleomycin sulfate Aminoglycoside + + J61949 Carbenicillin disodium salt Carboxypenicillin + J65274 Cefazolin sodium salt Cephalosporin + J62690 Cefotaxime sodium salt Cephalosporin + + J61317 Ciprofloxacin, 98% Fluoroquinone + + J62927 Chromomycin A3, 98% Glycoside J60495 Dihydrostreptomycin sulfate Aminoglycoside + + J60422 Doxycycline hydrochloride Tetracycline J62279 Erythromycin Macrolide J62671 G418 disulfate Aminoglycoside J62834 Gentamycin sulfate Aminoglycoside + + J60681 Hygromycin B Aminoglycoside J60668 Kanamycin monosulfate Aminoglycoside J61251 Lincomycin hydrochloride Lincosamide + J63193 Mitomycin C Antineoplastic + + J61669 Monensin sodium salt Polyether J61499 Neomycin sulfate Aminoglycoside + + J60928 Novobiocin sodium salt Aminocoumarin + J62486 Nystatin Polyene + + J61274 Paromomycin sulfate Aminoglycoside + + J63032 Penicillin G sodium salt Penicillin + J61763 Polymixin B sulfate Polypeptide + J61278 Puromycin dihcl, 99+% Aminonucleoside + + J62473 Rapamycin, 99+% Macrolide + + J60836 Rifampin Rifamycin + J61820 Spectinomycin dihcl Aminocyclitol + + J61299 Streptomycin sulfate Aminoglycoside J61714 Tetracycline Tetracycline J62633 Tylosin tartrate, 98% Macrolide + + J62312 Valinomycin Polypeptide J62790 Vancomycin hydrochloride Glycopeptide +
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics. Question No. 1 of 10. Question. Feedback. Question
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
Microbiology - Problem Drill 16: Antibiotics No. 1 of 10 1. An effective chemotherapeutic drug should have. (A) Low therapeutic index (B) More toxicity (C) Selective toxicity (D) Mutation inducing properties
B. Incorrect! Peginterferon α-2a is used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B and may be preferable to interferon- α.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 24: Antibiotics, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs Question No. 1 of 10 1. reduces the replication of influenza A and B viruses by inhibiting viral neuraminidase. Question #01
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 24: Antibiotics, Antifungal and Antiviral Drugs Question No. 1 of 10 1. reduces the replication of influenza A and B viruses by inhibiting viral neuraminidase. Question #01
Antibiotic and Antimycotic Products
 Antibiotic and Antimycotic Products Corning products include antibiotics and antimycotics for microbiological/mammalian cell culture selection or prophylactic control of contamination due to bacteria,
Antibiotic and Antimycotic Products Corning products include antibiotics and antimycotics for microbiological/mammalian cell culture selection or prophylactic control of contamination due to bacteria,
gram neg.(semisynthetic) Bacteria Drugs that inhibit cell wall synthesis Drug Action Organisms Comments Spectrum of Action Mycobacterium
 Mickey Dufilho s Drugs and Bugs Revised 10/10/15 Bacteria Drugs that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis Drug Action Spectrum of Action Comments Spectrum of Action Bacitracin Beta-Lactam antibiotics Penicillin
Mickey Dufilho s Drugs and Bugs Revised 10/10/15 Bacteria Drugs that Inhibit Cell Wall Synthesis Drug Action Spectrum of Action Comments Spectrum of Action Bacitracin Beta-Lactam antibiotics Penicillin
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets
 Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Antibiotics and Ribosomes as Drug Targets www.biochemj.org/bj/330/0581/bj3300581.htm Professor Vassie Ware Bioscience in the 21 st Century November 5, 2012 PERSPECTIVE Widespread use of antibiotics after
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Objectives: Prof.Dr. H.D.El-Yassin
 Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Protein Synthesis and drugs that inhibit protein synthesis Objectives: 1. To understand the steps involved in the translation process that leads to protein synthesis 2. To understand and know about all
Antibiotics acting on Protein Synthesis E. Westhof
 Antibiotics acting on Protein Synthesis E. Westhof 1. Considérations générales et introductives 1 Facts about Antibiotics Alexander Fleming (1928) discovered penicillin Ignored until early 1940s with extensive
Antibiotics acting on Protein Synthesis E. Westhof 1. Considérations générales et introductives 1 Facts about Antibiotics Alexander Fleming (1928) discovered penicillin Ignored until early 1940s with extensive
Medicinal Chemistry 410 Exam #1 February 20, 2009 Name: Med. Chem. #
 Medicinal Chemistry 410 Exam #1 February 20, 2009 ame: Med. Chem. # 1 Part. (75 Points) There are 50 multiple choice questions worth 1.5 points each (75 Points). Please use the cantron heet provided. f
Medicinal Chemistry 410 Exam #1 February 20, 2009 ame: Med. Chem. # 1 Part. (75 Points) There are 50 multiple choice questions worth 1.5 points each (75 Points). Please use the cantron heet provided. f
Aminoglycosides. Not orally absorbed. Interact with negatively charged lipopolysaccharide on Gram- cell wall. Aminoglycoside properties
 Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
Aminoglycosides Tobramycin Kanamycin H2N Gentamicin Amikacin NHCOCHCH2CH2NH2 OH Aminoglycosides made of linked sugars. Decorated with many OH and NH2 groups, which render these compounds positively charged
life-threatening infections
 Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
Vancomycin Vancomycin has become increasingly important in the treatment of life-threatening infections. MRSA infections. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections Enterococcal
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi
 number 8 Done by م ها أبو عجمي ة Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi The last page includes definitions for the underlined asterisked words *, You can skip Extra notes, Enjoy! A Brief Introduction
number 8 Done by م ها أبو عجمي ة Corrected by Mamoon Alqtamin Doctor Hamed Al Zoubi The last page includes definitions for the underlined asterisked words *, You can skip Extra notes, Enjoy! A Brief Introduction
Vancomycin. A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci.
 Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Vancomycin A bactericidal drug which acts by inhibiting cell wall synthesis. Active only against gram-positive bacteria, particularly staphylococci. Used IV in treating endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins
 Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
Macrolides, Clindamycin & Ketolides Polymyxins Kwan Soo Ko Macrolides - Erythromycin - Azithromycin - Clarithromycin Lincosamides - Lincomycin - Clindamycin Unrelated chemically But, many similar biological
HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 9 (Written Synoptic)
 Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2003 Advanced Level Examination HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 9 (Written
Surname Other Names Leave blank Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Signature General Certificate of Education June 2003 Advanced Level Examination HUMAN BIOLOGY (SPECIFICATION A) Unit 9 (Written
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
 Frank Lowy Protein Synthesis Inhibitors This lecture discusses a diverse group of antibiotics that are grouped together because they all have a common mechanism of action they are protein synthesis inhibitors.
Frank Lowy Protein Synthesis Inhibitors This lecture discusses a diverse group of antibiotics that are grouped together because they all have a common mechanism of action they are protein synthesis inhibitors.
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology 19.03.2018 Helmut Pospiech Microbiology from Greek mīkros, - "small bios, "life -logia) the study of small, single-celled organisms Bacteria (Prokaryotes) Viruses Unicellular Eukaryotes What
Microbiology 19.03.2018 Helmut Pospiech Microbiology from Greek mīkros, - "small bios, "life -logia) the study of small, single-celled organisms Bacteria (Prokaryotes) Viruses Unicellular Eukaryotes What
Bacterial Structures. Capsule or Glycocalyx TYPES OF FLAGELLA FLAGELLA. Average size: µm 2-8 µm Basic shapes:
 PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
I is a cascading prodrug. II is used to treat hepatitis B infection III ultimately inhibits viral reverse transcriptase.
 Medicinal Chemistry 410 Exam #1 February 19, 2010 ame: Med. Chem. # 1 Part. (75 Points) There are 50 multiple choice questions worth 1.5 points each (75 Points). Please use the cantron heet provided. f
Medicinal Chemistry 410 Exam #1 February 19, 2010 ame: Med. Chem. # 1 Part. (75 Points) There are 50 multiple choice questions worth 1.5 points each (75 Points). Please use the cantron heet provided. f
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Continuation of Antibiotics
 Continuation of Antibiotics CLASSIFICATIN F ANTIBITICS According to their mechanism of action Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome
Continuation of Antibiotics CLASSIFICATIN F ANTIBITICS According to their mechanism of action Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Ass Prof. Dr. Naza M. Ali 15 Nov 2018 Lec 8 These drugs selectively inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. The selectivity is due to the differences between bacterial and human
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 1: Membranes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Introduction Cells and Organelles have membranes Membranes contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides
Chapter 10. 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation)
 Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Aminoglycosides Macrolides
 Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Protein synthesis inhibitors Antimicrobial protein synthesis inhibitors Joseph K. Ritter, PhD Assoc. Prof Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology MSB Room 536 jritter@mail2.vcu.edu 828-1022 Tetracyclines
Signal Transduction. & Mechanisms of Drug Action
 Signal Transduction & Mechanisms of Drug Action Why do some drugs produce effects that persist for long after the drug is no longer present? Why do response to other drugs diminish rapidly with repeated
Signal Transduction & Mechanisms of Drug Action Why do some drugs produce effects that persist for long after the drug is no longer present? Why do response to other drugs diminish rapidly with repeated
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
 RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP)
 NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) NEOSPORIN SOLUTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) NEOSPORIN SOLUTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B
Antibiotics.. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol
 Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Antibiotics. Tetracyclines. Aminoglycoside. Macrolides. Chloramphenicol Antibiotics as disturber with the biosynthesis of protein These antibiotics all target the bacterial ribosome and interfere in the
Other β-lactam. A. Carbapenems:
 A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
A. Carbapenems: Other β-lactam Carbapenems are synthetic β-lactam antibiotics Differ in structure from the penicillins in that the sulfur atom of the thiazolidine ring. Imipenem, meropenem, doripenem,
Protein Synthesis
 Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
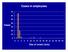 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Chemotherapy. SELECTIVITY: exploiting qualitative and quantitative differences between the host and pathogen, can be structural or biochemical.
 Chemotherapy SELECTIVITY: exploiting qualitative and quantitative differences between the host and pathogen, can be structural or biochemical. Antibacterial chemotherapy Several targets: cell wall synthesis,
Chemotherapy SELECTIVITY: exploiting qualitative and quantitative differences between the host and pathogen, can be structural or biochemical. Antibacterial chemotherapy Several targets: cell wall synthesis,
BUGS and DRUGS Part 2 March 13, 2013 Marieke Kruidering- Hall
 BUGS and DRUGS Part March, 0 Marieke Kruidering- Hall BIOGRAPHY: Marieke Kruidering- Hall is Associate Professor in the Department of Cellular & Molecular Pharmacology. She was born in the Netherlands.
BUGS and DRUGS Part March, 0 Marieke Kruidering- Hall BIOGRAPHY: Marieke Kruidering- Hall is Associate Professor in the Department of Cellular & Molecular Pharmacology. She was born in the Netherlands.
Medical Microbiology. Microscopic Techniques :
 ! Lecture 2 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Microscopic Techniques : Several types of microscopes are used in study of microbiology one of the most important tools for studying microorganisms
! Lecture 2 Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology Microscopic Techniques : Several types of microscopes are used in study of microbiology one of the most important tools for studying microorganisms
Lahore University of Management Sciences. BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015)
 BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
Tamer Barakat ABDUL AZIZ AL-SHAMALI ABDUL AZIZ AL-SHAMALI
 6 Tamer Barakat ABDUL AZIZ AL-SHAMALI ABDUL AZIZ AL-SHAMALI Anas Abu Humaidan Revision in form of questions: 1- Which of the following is the true order of ATP production from highest to lowest? (R stands
6 Tamer Barakat ABDUL AZIZ AL-SHAMALI ABDUL AZIZ AL-SHAMALI Anas Abu Humaidan Revision in form of questions: 1- Which of the following is the true order of ATP production from highest to lowest? (R stands
Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences
 Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Adding a 5 cap Lecture 4 mrna splicing and protein synthesis Another day in the life of a gene. Pre-mRNA has introns The splicing complex recognizes semiconserved sequences Introns are removed by a process
Chapter 14. Bugs that Resist Drugs
 Chapter 14 Bugs that Resist Drugs See website Learning Objectives Important Terminology Power point- posted after chapter is completed What happened to Carlos Don, Rebecca Lohsen, Ricky Lannetti? Carlos
Chapter 14 Bugs that Resist Drugs See website Learning Objectives Important Terminology Power point- posted after chapter is completed What happened to Carlos Don, Rebecca Lohsen, Ricky Lannetti? Carlos
1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY).
 Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
Problem Set 11 (Due Nov 25 th ) 1. Investigate the structure of the trna Synthase in complex with a trna molecule. (pdb ID 1ASY). a. Why don t trna molecules contain a 5 triphosphate like other RNA molecules
IN VIVO AND IN VITRO CROSS-RESISTANCE OF KANAMYCIN-RESISTANT MUTANTS OF E. COLI TO OTHER
 1527 IN VIVO AND IN VITRO CROSS-RESISTANCE OF KANAMYCIN-RESISTANT MUTANTS OF E. COLI TO OTHER AMINOGLYCOSIDE ANTIBIOTICS EUNG CHIL CHOI, TOSHIO NISHIMURA, YOKO TANAKA and NOBUO TANAKA Institute of Applied
1527 IN VIVO AND IN VITRO CROSS-RESISTANCE OF KANAMYCIN-RESISTANT MUTANTS OF E. COLI TO OTHER AMINOGLYCOSIDE ANTIBIOTICS EUNG CHIL CHOI, TOSHIO NISHIMURA, YOKO TANAKA and NOBUO TANAKA Institute of Applied
Report on the Japanese Veterinary Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System
 Report on the Japanese Veterinary Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System 2014 2015 National Veterinary Assay Laboratory Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries 2018 Contents Introduction...
Report on the Japanese Veterinary Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System 2014 2015 National Veterinary Assay Laboratory Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries 2018 Contents Introduction...
Annex to the Guidance for Completing the OIE template for the collection of data on Antimicrobial Agents intended for use in Animals:
 Annex to the Guidance for Completing the OIE template for the collection of data on Antimicrobial Agents intended for use in Animals: Considerations on converting content of antimicrobial active ingredients
Annex to the Guidance for Completing the OIE template for the collection of data on Antimicrobial Agents intended for use in Animals: Considerations on converting content of antimicrobial active ingredients
For some diseases, this is all that can be done. The common cold, for instance.
 Disease treatments: I. treat symptoms: For some diseases, this is all that can be done. The common cold, for instance. - Some evidence that for rabies this may eventually lead to a treatment/cure (coma
Disease treatments: I. treat symptoms: For some diseases, this is all that can be done. The common cold, for instance. - Some evidence that for rabies this may eventually lead to a treatment/cure (coma
Metabolism of Extremophiles
 1 Microbial Metabolism Metabolism of Extremophiles Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy Building, Room 111 Tel: (02) 33664454 E-mail: cthuang@ntu.edu.tw Extremophiles 2 Definition Inhabit some of
1 Microbial Metabolism Metabolism of Extremophiles Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy Building, Room 111 Tel: (02) 33664454 E-mail: cthuang@ntu.edu.tw Extremophiles 2 Definition Inhabit some of
Overview of Translation (2) Protein Synthesis Inhibitors. Overview of Translation (3) Lecture Outline. Overview of Translation (1)
 Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptogramins Oxazolidinones Overview of Translation (2) Initiation trna + AA binds translation elongation
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors Macrolides - Lincosamides Aminoglycosides Tetracyclines Chloramphenicol Streptogramins Oxazolidinones Overview of Translation (2) Initiation trna + AA binds translation elongation
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn Series
 ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
ICU Volume 11 - Issue 3 - Autumn 2011 - Series Impact of Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in ICU Clinical Practice Introduction The efficacy of a drug is mainly dependent on its ability to achieve an effective
Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 7- Biological Membranes
 Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 7- Biological Membranes Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction The cell membrane separates the cell the
Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Chapter 7- Biological Membranes Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Introduction The cell membrane separates the cell the
ii. cellular organization: prokaryotes have no membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotes have membranebound organelles, including a nucleus.
 Bacteriology Exam 1 Name 1/31/06 1. (3 pts) What are 3 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Explain each difference. i. size: prokaryotes are typically from 1 to 10 μm in diameter, whereas eukaryotes
Bacteriology Exam 1 Name 1/31/06 1. (3 pts) What are 3 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Explain each difference. i. size: prokaryotes are typically from 1 to 10 μm in diameter, whereas eukaryotes
Control of mycoplasma infection of poultry by antibiotics
 Control of mycoplasma diseases of poultry, swine and cattle Control of mycoplasma infection of poultry by antibiotics László Stipkovits and Susan Szathmáry RT-Europe Research Center, Mosonmagyaróvár, Hungary
Control of mycoplasma diseases of poultry, swine and cattle Control of mycoplasma infection of poultry by antibiotics László Stipkovits and Susan Szathmáry RT-Europe Research Center, Mosonmagyaróvár, Hungary
Levels of organization
 The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Principles of Biotechnology INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY WEEKS 8+9
 Principles of Biotechnology INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY WEEKS 8+9 Industrial Microbiology Industrial Microorganisms and Product formation involved: 1- Use microorganisms to produce valuable commercial product
Principles of Biotechnology INDUSTRIAL BIOTECHNOLOGY WEEKS 8+9 Industrial Microbiology Industrial Microorganisms and Product formation involved: 1- Use microorganisms to produce valuable commercial product
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
7. Reverse transcription ID nucleophile and electrophile. Substitution reaction.
 Spring 2018 Chem 12B Possible Bio or Industrial Reactions: 1. Naproxen synthesis from 2-naphthol (see ROH and epoxides slides) 2. aspirin synthesis from benzene 3. benzo[a]pyrene in cigarette smoke how
Spring 2018 Chem 12B Possible Bio or Industrial Reactions: 1. Naproxen synthesis from 2-naphthol (see ROH and epoxides slides) 2. aspirin synthesis from benzene 3. benzo[a]pyrene in cigarette smoke how
Central Dogma. Central Dogma. Translation (mrna -> protein)
 Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
Central Dogma Central Dogma Translation (mrna -> protein) mrna code for amino acids 1. Codons as Triplet code 2. Redundancy 3. Open reading frames 4. Start and stop codons 5. Mistakes in translation 6.
2017/18 PRODUCT CATALOGUE ANTIBIOTICS, BIOCHEMICALS AND LIQUID BUFFERS
 2017/18 PRODUCT CATALOGUE ANTIBIOTICS, BIOCHEMICALS AND LIQUID BUFFERS CONTENTS 2 3 3-Amino-1,2,4-Triazole, 3-AT 4 5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride 4 5-Fluoro Orotic Acid Monohydrate 5 Ampicillin Sodium
2017/18 PRODUCT CATALOGUE ANTIBIOTICS, BIOCHEMICALS AND LIQUID BUFFERS CONTENTS 2 3 3-Amino-1,2,4-Triazole, 3-AT 4 5-Aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride 4 5-Fluoro Orotic Acid Monohydrate 5 Ampicillin Sodium
Point total. Page # Exam Total (out of 90) The number next to each intermediate represents the total # of C-C and C-H bonds in that molecule.
 This exam is worth 90 points. Pages 2- have questions. Page 1 is for your reference only. Honor Code Agreement - Signature: Date: (You agree to not accept or provide assistance to anyone else during this
This exam is worth 90 points. Pages 2- have questions. Page 1 is for your reference only. Honor Code Agreement - Signature: Date: (You agree to not accept or provide assistance to anyone else during this
A Novel Lantibiotic Acting on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Produced by the Uncommon FLAVIA MARINELLI. DBSM, University of Insubria, Varese Italy
 A Novel Lantibiotic Acting on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Produced by the Uncommon Actinomycete Planomonospora sp. FLAVIA MARINELLI DBSM, University of Insubria, Varese Italy Vicuron Pharmaceuticals,
A Novel Lantibiotic Acting on Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis Produced by the Uncommon Actinomycete Planomonospora sp. FLAVIA MARINELLI DBSM, University of Insubria, Varese Italy Vicuron Pharmaceuticals,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMATIN*CAP
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMATIN*CAP (Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules MANUFACTURER STANDARD) 250 mg Capsules ANTIBIOTIC DATE OF PREPARATION January 08, 2001 8250 Décarie Blvd, suite 110 Montréal,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION PRODUCT MONOGRAPH HUMATIN*CAP (Paromomycin Sulfate Capsules MANUFACTURER STANDARD) 250 mg Capsules ANTIBIOTIC DATE OF PREPARATION January 08, 2001 8250 Décarie Blvd, suite 110 Montréal,
3. When he discovered enzymes in 1897, Eduard Buchner was investigating the causes of. disease antisepsis spontaneous generation fermentation
 Chapter 2 1. Which of the following elements forms the backbone of organic molecules? carbon fluorine chlorine sodium carbon 2. The smallest chemical unit of matter is the. neutron element atom proton
Chapter 2 1. Which of the following elements forms the backbone of organic molecules? carbon fluorine chlorine sodium carbon 2. The smallest chemical unit of matter is the. neutron element atom proton
Cell Structure. Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell. Cytoplasmic Membrane 4/6/2011. Chapter 3. Cytoplasmic membrane
 Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Levels of organization
 The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
TRANSLATION. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand.
 TRANSLATION Dr. Mahesha H B, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand. Or The process in the ribosomes of a
TRANSLATION Dr. Mahesha H B, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Mysuru. Translation is a process where proteins are made by the ribosomes on the mrna strand. Or The process in the ribosomes of a
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Adenium Biotech. Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes
 Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Adenium Biotech Management: - Peter Nordkild, MD, CEO, ex Novo Nordisk, Ferring, Egalet - Søren Neve, PhD, project director, ex Lundbeck, Novozymes Board of Directors: - Stephan Christgau, PhD, chairman,
Antibiotics derived from the acetate metabolism
 Antibiotics derived from the acetate metabolism 1- Antibiotics with fused ring system: -Griseofulvin -Tetracyclines -[Fusidic acid] 2-Macrolide antibiotics 3-Polyene antibiotics Griseofulvin: Produced
Antibiotics derived from the acetate metabolism 1- Antibiotics with fused ring system: -Griseofulvin -Tetracyclines -[Fusidic acid] 2-Macrolide antibiotics 3-Polyene antibiotics Griseofulvin: Produced
(A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids. A. Incorrect! Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have cell membranes.
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
High School Biology - Problem Drill 03: The Cell No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following is NOT found in prokaryotic cells? #01 (A) Cell membrane (B) Ribosome (C) DNA (D) Nucleus (E) Plasmids Both prokaryotic
Drugs, Microbes, Host The Elements of Chemotherapy
 Chapter 12 Drugs, Microbes, Host The Elements of Chemotherapy Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 12.1 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Administer
Chapter 12 Drugs, Microbes, Host The Elements of Chemotherapy Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 12.1 Principles of Antimicrobial Therapy Administer
EFFECT OF ANTIMICROBIAL DRUGS ON THE INTESTINAL MICROFLORA: IMPORTANCE OF PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES OF ANTIBACTERIAL AGENTS TOM BERGAN
 Old Herborn University Seminar Monograph 3: Consequences of antimicrobial therapy for the composition of the microflora of the digestive tract. Editors: Carl Erik Nord, Peter J. Heidt, Volker Rusch, and
Old Herborn University Seminar Monograph 3: Consequences of antimicrobial therapy for the composition of the microflora of the digestive tract. Editors: Carl Erik Nord, Peter J. Heidt, Volker Rusch, and
Antimycobacterial drugs. Dr.Naza M.Ali lec Dec 2018
 Antimycobacterial drugs Dr.Naza M.Ali lec 14-15 6 Dec 2018 About one-third of the world s population is infected with M. tuberculosis With 30 million people having active disease. Worldwide, 9 million
Antimycobacterial drugs Dr.Naza M.Ali lec 14-15 6 Dec 2018 About one-third of the world s population is infected with M. tuberculosis With 30 million people having active disease. Worldwide, 9 million
Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry
 Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry Dr Sanmarié Schlebusch Director of Microbiology Mater Pathology Brisbane Outline Introduction Plug and play Pre-prep and
Rapid identification and resistance assessment: The future is mass spectrometry Dr Sanmarié Schlebusch Director of Microbiology Mater Pathology Brisbane Outline Introduction Plug and play Pre-prep and
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD)
 Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Mohammed Nooraldeen Al-Qattan (PhD) Macrolides are macro lactone rings made up of 12 or more atoms, and usually contain one or more sugars. They are bacteriostatic agents that inhibit protein synthesis
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
A look at macromolecules (Text pages 38-54) What is the typical chemical composition of a cell? (Source of figures to right: Madigan et al.
 A look at macromolecules (Text pages 38-54) What is the typical chemical composition of a cell? (Source of figures to right: Madigan et al. 2002 Chemical Bonds Ionic Electron-negativity differences cause
A look at macromolecules (Text pages 38-54) What is the typical chemical composition of a cell? (Source of figures to right: Madigan et al. 2002 Chemical Bonds Ionic Electron-negativity differences cause
Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products
 Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products Presented by Akram Najafi Marine actinobacteria Actinobacteria are a group of Gram positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial (soil)
Marine actinobacteria: an important source of bioactive natural products Presented by Akram Najafi Marine actinobacteria Actinobacteria are a group of Gram positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial (soil)
Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics
 Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2012 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part IV: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis Introduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2012 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part IV: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis Introduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Anti-Microbial Drugs
 Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
Name: Date: Monday March 7 th 2011 Class: I "Pharmacology Anti-Microbial Drugs Lecture 5 د. حيدر الشكرجي Macrolides: Anti-Microbial Drugs Erythromycin was the 1 st of macrolides to find clinical application,
DRUG RESISTANCE IN TUBERCULOSIS
 DRUG RESISTANCE IN TUBERCULOSIS INTRODUCTION Up to 50 million people may be infected with drug-resistant resistant TB.* Hot zones of MDR-TB such as Russia, Latvia, Estonia, Argentina and the Dominican
DRUG RESISTANCE IN TUBERCULOSIS INTRODUCTION Up to 50 million people may be infected with drug-resistant resistant TB.* Hot zones of MDR-TB such as Russia, Latvia, Estonia, Argentina and the Dominican
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM
 CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
Ch 4. Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
 Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Ch 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Objectives Compare and contrast the overall cell structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Identify the three basic shapes of bacteria. Describe
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics
 Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2008 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part V: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis ntroduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chemistry 259 Medicinal Chemistry of Modern Antibiotics Spring 2008 Lecture 9: Antibiotics Classes & Targets Part V: Drugs Targeting Protein Biosynthesis ntroduction & 30S Subunit Target Thomas ermann
Chapter 32: Translation
 Chapter 32: Translation Voet & Voet: Pages 1343-1385 (Parts of sections 1-3) Slide 1 Genetic code Translates the genetic information into functional proteins mrna is read in 5 to 3 direction Codons are
Chapter 32: Translation Voet & Voet: Pages 1343-1385 (Parts of sections 1-3) Slide 1 Genetic code Translates the genetic information into functional proteins mrna is read in 5 to 3 direction Codons are
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
ILOs. 10/10/2016 Maha Fathy 2
 ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP)
 NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) DESCRIPTION Neosporin Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) DESCRIPTION Neosporin Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin
Antibiotic Inhibitors of the Bacterial Ribosome
 BACTERIOLOGICAL REVIEWS, Dec., 1968, p. 493-528 Vol. 32, No. 4, Pt. 2 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Antibiotic Inhibitors of the Bacterial Ribosome BERNARD WEISBLUM
BACTERIOLOGICAL REVIEWS, Dec., 1968, p. 493-528 Vol. 32, No. 4, Pt. 2 Copyright 1968 American Society for Microbiology Printed in U.S.A. Antibiotic Inhibitors of the Bacterial Ribosome BERNARD WEISBLUM
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O
 BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
BIOCHEMISTRY LECTURES BY RASAQ, N.O LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION POLYSACCHARIDES STRUCTURAL POLYSACCHARIDES: CELLULOSE AND CHITIN BACTERIA CELL WALLS PEPTIDOGLYCAN PENICILLIN AND β-lactam ANTIBIOTICS AND
Antituberculous Agents
 Antituberculous Agents Primary or First Line Drugs: Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin Rifadin or Rimactane Ethambutal Streptomycin Pyrazinamide Isoniazid(INH) Most active. Small molecule, water soluble, Structurally
Antituberculous Agents Primary or First Line Drugs: Isoniazid (INH) Rifampin Rifadin or Rimactane Ethambutal Streptomycin Pyrazinamide Isoniazid(INH) Most active. Small molecule, water soluble, Structurally
Amy-Jo Hooley Specialist Clinical Pharmacist
 Gut Decontamination Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for the Safe Administration
Gut Decontamination Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Contact Name and Job Title (author) Directorate & Speciality Guideline for the Safe Administration
BACTERIAL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND GROWTH
 Dr. Ronald E. Gill Wednesday, February 15, 2017 10:00 11:50 AM BACTERIAL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND GROWTH I. Introduction Bacteria are unicellular organisms with a relatively simple structure. Unlike the
Dr. Ronald E. Gill Wednesday, February 15, 2017 10:00 11:50 AM BACTERIAL STRUCTURE, FUNCTION AND GROWTH I. Introduction Bacteria are unicellular organisms with a relatively simple structure. Unlike the
Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2. November 13, 2006
 Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
Name: TF: Section Time Life Sciences 1A Midterm Exam 2 November 13, 2006 Please write legibly in the space provided below each question. You may not use calculators on this exam. We prefer that you use
KEY NAME (printed very legibly) UT-EID
 BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2007 KEY NAME (printed very legibly) UT-EID EXAMINATION II Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
BIOLOGY 311C - Brand Spring 2007 KEY NAME (printed very legibly) UT-EID EXAMINATION II Before beginning, check to be sure that this exam contains 7 pages (including front and back) numbered consecutively,
