Been Diagnosed with Ovarian Cancer, Now What?
|
|
|
- Audra Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Been Diagnosed with Ovarian Cancer, Now What? Teresa P. Díaz-Montes, MD, MPH, FACOG Associate Director, Lya Segall Ovarian Cancer Institute Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, MD
2 Ovarian Cancer Statistics: 2018 US 22,240 new ovarian cancer diagnosis. 14,070 ovarian cancer related deaths. 5 th cause of cancer related death among women. 1 st cause of gynecologic cancer related deaths. 1:78 woman's risk of developing ovarian cancer during lifetime. 1:108 lifetime chance of dying from ovarian cancer. Median age of diagnosis is about 63 years old. More common in white women than African-American women. Rate of diagnosis has slowly been falling over the past 20 years. American Cancer Society
3 Factors: Increase Risk Age Nulligravid or having children after age 35 Early menarche, late menopause Infertility Caucasian High socioeconomic status North American/European origin Hormone replacement therapy after menopause (estrogen therapy alone) Family history of ovarian cancer, breast cancer, or colorectal cancer (first degree relative) Personal history of breast cancer
4 Factors: Increase Risk Family cancer syndrome (About 5 to 10% of ovarian cancers): Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome Inherited mutations in the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Related to most inherited ovarian cancers. About 10 times more common in those who are Ashkenazi Jewish. Lifetime ovarian cancer risk BRCA1 mutation is estimated to be between 35% and 70% and for BRCA2 mutation is estimated to be between 10% and 30% by age 70. PTEN tumor hamartoma syndrome Cowden disease: primarily affected with thyroid problems, thyroid cancer, and breast cancer. There is also an increased risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer. Caused by inherited mutations in the PTEN gene. Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (Lynch Syndrome) High risk of colon cancer as well as increased risk of developing uterine and ovarian cancer. Genes involved include MLH1, MLH3, MSH2, MSH6, TGFBR2, PMS1, and PMS2. The lifetime risk of ovarian cancer in women with hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) is about 10%.
5 Factors: Increase Risk Family cancer syndrome: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome Rare genetic syndrome with increased risk for development of polyps in the stomach and intestine during teenage years. High risk of cancer, particularly cancers of the digestive tract (esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon). Increased risk of ovarian cancer, including both epithelial ovarian cancer and a type of stromal tumor called sex cord tumor with annular tubules (SCTAT). Caused by mutations in the gene STK11. MUTYH-associated polyposis Increased risk of development of polyps in the colon and small intestine and have a high risk of colon cancer. More likely to develop other cancers, including cancers of the ovary and bladder. Caused by mutations in the gene MUTYH.
6 Factor: Lower Risk Pregnancy Breastfeeding Birth Control OCP s Tubal ligation IUD s. Hysterectomy Removal of the Ovaries and Fallopian Tubes
7 Factors: Unclear Risk Androgens There appears to be a link between certain androgens and specific types of ovarian cancer, but further studies of the role of androgens in ovarian cancer are needed. Talcum powder Studies had looked at the possible link between talcum powder use and ovarian cancer. Findings have been mixed. Research in this area continues. Diet Studies have shown a reduced rate of ovarian cancer in women who ate a diet high in vegetables or a low fat diet, but other studies disagree. Research in this area continues.
8 Prevention?
9 Risk Reduction Surgery Removal of both tubes and ovaries (BSO) is recommended for genetic mutation carriers or high risk individuals by age 35 to 40 or when childbearing is completed, or Individualized based on age of onset of ovarian cancer in the family BSO decreases the risk of both breast cancer and ovarian cancer among genetic mutation carriers
10 Risk Reducing Surgery: Why not in the General Population? Estimated approximately 300 prophylactic oophorectomies would have to be performed to prevent a single case of ovarian cancer. Averette et al., Gynecol Oncol. 1994
11 Ovarian Cancer Origins
12 Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
13 Fallopian Tube Origin
14 Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis Symptom Assessment Physical Exam CA-125 serum levels Transvaginal Ultrasound Abdominopelvic CT or MRI
15 Signs and Symptoms Symptoms are non-specific - Bloating, fullness, pressure (70-80%) - Gastrointestinal (70%) - Constitutional (50%) - Urinary (34%) Symptomatic: Stage I/II 89% Stage III/IV 97% Olson et al. Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:212. Goff et al. Cancer 2000; 89:
16 Ovarian Cancer Staging
17 Ovarian Cancer: Patterns of Spread 1. Direct Extension - pelvic organs - simultaneous with other metastases 2. Intraperitoneal Dissemination - exfoliation of tumor cells - peritoneal flow pattern 3. Lymphatic Metastases 4. Hematogenous Spread
18 Surgical Management Pelvis TAH+BSO Pelvic lymph node dissection Ablation or resection of peritoneal nodules Abdomen Infracolic omentectomy Appendectomy Para-aortic lymph node dissection Ablation or resection of peritoneal nodules
19 Radical Surgical Management Pelvis Radical oophorectomy Rectosigmoid colectomy Debulking of pelvic lymph nodes Resection of bladder / ureter Resection of ileac vessels Abdomen Total omentectomy Partical gastrectomy Splenectomy Distal pancreatectomy Diaphragmatic peritonectomy Diaphragmatic resection Liver resection Debulking of para-aortic lymph nodes Nephrectomy
20 Cytoreductive Surgery Theoretical Benefits Improved vascularity / oxygenation - delivery of chemotherapy Removal of chemotherapy resistant cells Tumor growth kinetics - increased growth fraction of remaining tumor cells
21 Cytoreductive Surgery Quality of Life Clinical Benefits comfort level relief of potential bowel obstruction reduce adverse metabolic effects Residual Disease
22 Cytoreductive Surgery: Survival GOG 97
23 Cytoreductive Surgery: Survival GOG 52/97 Summary
24 Cytoreductive Surgery - Survival GOG 52 / 97 Summary Cytoreduction ¹ tumor biology Survival determinants - multifactorial Three distinct groups Survival (5yr) no gross residual 60% optimal ( 2cm) 35% suboptimal (> 2cm) 20% Microscopic residual should be the goal
25
26 Cytoreduction Factors limiting the ability to achieve optimal cytoreduction may be technical or related to poor performance status: Presence of extraabdominal or retroperitoneal disease, or large tumor bulk Bowel involvement Parenchymal liver involvement Presence of ascites Poor nutritional state Comorbid conditions
27 Cytoreduction Can we predict who can be cytoreduced? Tumor markers or molecular factors Imaging studies Patient characteristics Diagnostic laparoscopy
28 Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Treatment of tumor with chemotherapy drugs prior to surgery to decrease the bulk of the tumor Standard chemo with carboplatin and paclitaxel Reassessment after 3 treatments with imaging studies and physical exam If adequate response proceed with interval cytoreductive surgery
29 Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy No difference in progression-free survival (PFS, 12 months in both groups). Similar overall survival (neoadjuvant: 29 and initial surgery: 30 months). Improved proportion of patients who achieved an optimal cytoreduction (81 vs. 42 %). No improvement on the five-year overall survival rates. Lower rate of complications. Vergote I, et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(10):943.
30 Progression-free survival 18.3 mos 23.8 mos Overall survival 49.5 mos 66.9 mos Armstrong et.al. 2002
31 Van Driel et al, NEJM 2018; 378:230-40
32 What Happens When You Are Diagnosed With a Ovarian Cancer?
33 What To Do Next?
34 Keep Calm & Breath
35 What To Do Next? Find a partner. spouse/partner, family member or close friend, someone you can talk to openly about serious issues. Get organized. Start a notebook or binder to coordinate appointments, doctors phone numbers, and the information you collect along the way. Take it with you to each medical appointment, and keep notes of your test results and treatment options. Start a running list of questions to ask your doctor on your next visit. Get informed. Take steps to learn more about your cancer diagnosis and treatment options -- but do so at a pace that is comfortable for you. Be sure to consult only unbiased, trustworthy sources when you do your research. Consider a second opinion. Cancer treatment is complicated. A second opinion can also help you feel more confident in your treatment plan.
36 What To Do Next? Try to keep life as normal as possible. Stay positive. However, expressing your feelings -- even ones that seem negative -- is even more important. Learn to rely on others. Consider speaking with a mental health professional, particularly if you are depressed or anxious. Therapy can help relieve the stress of a cancer diagnosis, and give you a safe place to express your fears and hopes for the future.
37 Team Based Care Team-based care is defined by the National Academy of Medicine (formerly known as the Institute of Medicine) as "...the provision of health services to individuals, families, and/or their communities by at least two health providers who work collaboratively with patients and their caregivers to the extent preferred by each patient - to accomplish shared goals within and across settings to achieve coordinated, high-quality care." National Academy of Medicine
38 Team Based Care Potential to improve the: Comprehensiveness Coordination Efficiency Effectiveness Value of care Satisfaction of patients and providers
39 Team Based Care Members: Primary Care Provider (Family Physician, Internist, Nurse Practitioner) Gynecologic Oncologist Surgical Oncologist Medical Oncologist Social Worker Nutritionist Physical therapist Psychologist/Psychiatrist Palliative Care Provider
40 Building Your Team There is no formula to make the best selection. Choose a doctor you feel comfortable with: Languages spoken Gender Ethnicity Educational background Personality Bedside manner Experience (Volume of care managed as well as personal statistics and reports)
41 Be a Self Advocate Keep a personal medical record It should include: Diagnosis (Cancer type and stage) Date of diagnosis and treatment Copy of diagnostic test and pathology results Complete treatment information (chemotherapy drug names and doses or site and doses of radiation therapy) Treatment results, including complication and side effects Information about supportive care Complete contact information for doctors and treatment centers
42 Be a Self Advocate: What to Ask General information What type of cancer do I have? Where exactly is it located? What are the risk factors for this disease? Is this type of cancer caused by genetic factors? Are other members of my family at risk? How many people are diagnosed with this type of cancer each year? What lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, rest) do you recommend I make to stay as healthy as possible before, during, and after treatment? Where can I find more information about my cancer?
43 Be a Self Advocate: What to Ask Symptoms What are some common symptoms or side effects of this type of cancer? How can I avoid these and/or manage them with my daily activities? Is there anything that can be done to make my symptoms or side effects better? Are there activities that may make them worse? If new symptoms or side effects arise or existing ones worsen, what should I do? Diagnosis What diagnostic test / procedures are necessary? How often? What information will these tests tell us? How can I prepare myself for each test or procedure? Where do I need to go to have this test? When will I get the results? How will I get the results (over the phone, at the next appointment, etc.)? Can you explain my pathology report (laboratory test results) to me? If I seek a second opinion, will I have to repeat any tests or procedures? How much information about my diagnosis should I share, and at what time, with my friends and loved ones?
44 Be a Self Advocate: What to Ask Staging What is the stage of my cancer? What does this mean? Has cancer spread to my lymph nodes or anywhere else? How is staging used to find out cancer treatment? What is my prognosis (chance of recovery)? Treatment What are my treatment options? Which treatments, or combination of treatments, do you recommend? Why? What is the goal of the treatment you are recommending? What clinical trials (research studies involving people) are open to me? Who will be part of my treatment team, and what does each member do? How much experience do you (or the treatment team) have treating this type of cancer? Will I need to be hospitalized for treatment, or is this treatment done in an outpatient clinic? What is the expected timeline for my treatment plan? Do I need to be treated right away? How will this treatment affect my daily life? Will I be able to work, exercise, and perform my usual activities? What are the short-term side effects of this treatment? What long-term side effects may be associated with this cancer treatment? Will this treatment affect my fertility (ability to become pregnant or father children)? Besides treating cancer, what can be done to treat my symptoms? How can I keep myself as healthy as possible during treatment?
45 Be a Self Advocate: What to Ask Clinical trials What are clinical trials? How do clinical trials help people with cancer? Is this a treatment option for me? What happens during a clinical trial? What are the benefits and risks of participating in a clinical trial? How will I be monitored while participating in a clinical trial? What are my responsibilities during the clinical trial? Are there any costs associated with my participation in a clinical trial? Where can I learn more about clinical trials? Support What support services are available to me? To my family? Whom should I call with questions or concerns during non-business hours? May I contact you or the nurse to talk about additional information I find? Can you recommend a social worker to help locate support services? Where can I find resources for children? For teenagers? For young adults? For older adults? If I'm worried about managing the costs related to my cancer care, who can help me with these concerns? Who handles health insurance concerns in your office? Follow-up care What follow-up tests do I need, and how often will I need them? Is there anything else I should be asking?
46 Wellness Plan: How to Develop one after completion of therapy? A wellness plan is a plan of action geared toward the achievement of personal wellness. Personal wellness implies a state of multidimensional health and satisfaction. There are many aspects, or dimensions, to personal wellness, and they must each be developed and maintained for optimal overall well being. Wellness plans take all of those aspects into consideration, and are tailored to the individual.
47 Wellness Plan Development Assess your wellness: Emotional wellness Social wellness Intellectual wellness Spiritual wellness Mental wellness Financial wellness Physical wellness Occupational wellness Environmental wellness Medical wellness
48 Wellness Plan Development Identify areas that could use improvement. Be honest with yourself about how satisfied you feel in each aspect of wellness so that you can create a wellness plan tailored to your needs.
49 Wellness Plan Development Set goals related to improvements you want to make. Once you identify the areas that you feel you need to work on, write down specific goals to accomplish in each area that will move you toward greater overall well being.
50 Wellness Plan Development Record your progress. Keep a chart or a journal outlining each aspect of personal wellness and the goals you set to improve on those aspects. Mark important dates and checkpoints in a calendar designated specifically for the purpose of your personal wellness plan so that you can see your progress.
51 Wellness Plan Development Update the goals of your wellness plan as needed. As you develop greater personal wellness, you may find that it is taking a longer or shorter time than you'd planned to reach certain goals, or that some goals are no longer inside the scope of what you want to accomplish. Monitor your progress and reassess your needs frequently so as to keep your wellness plan as tailored to your growth as possible.
52 Life is a Journey
53 Is up to us to decide the road to follow
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer
 What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer
 GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer KRISTEN STARBUCK, MD ROSWELL PARK CANCER INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY APRIL 19 TH, 2018 Objectives Basic Cancer Statistics Discuss
GYNECOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES: Ovarian Cancer KRISTEN STARBUCK, MD ROSWELL PARK CANCER INSTITUTE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY APRIL 19 TH, 2018 Objectives Basic Cancer Statistics Discuss
What is ovarian cancer?
 What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that forms in tissues of the ovary. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface
What is ovarian cancer? Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that forms in tissues of the ovary. Most ovarian cancers are either ovarian epithelial cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Optimizing First Line Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Optimizing First Line Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer Ira R. Horowitz, MD, SM, FACOG, FACS John D. Thompson Professor and Chairman Department of Gynecology
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Optimizing First Line Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer Ira R. Horowitz, MD, SM, FACOG, FACS John D. Thompson Professor and Chairman Department of Gynecology
Tumori eredofamiliari: sorveglianza di donne ad alto rischio
 Tumori eredofamiliari: sorveglianza di donne ad alto rischio 14/01/2018 Dott Matteo Generali AUSL Modena Carpi U.O. Ostetricia e Ginecologia Screening for gynaecologic cancer in genetically predisposed
Tumori eredofamiliari: sorveglianza di donne ad alto rischio 14/01/2018 Dott Matteo Generali AUSL Modena Carpi U.O. Ostetricia e Ginecologia Screening for gynaecologic cancer in genetically predisposed
Understanding and Managing Lynch Syndrome
 Understanding and Managing Lynch Syndrome Princess Margaret For women who may have Lynch syndrome and their family members Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca
Understanding and Managing Lynch Syndrome Princess Margaret For women who may have Lynch syndrome and their family members Please visit the UHN Patient Education website for more health information: www.uhnpatienteducation.ca
Practice of Medicine-1 Ovarian Cancer Clinical Correlation
 Practice of Medicine-1 Ovarian Cancer Clinical Correlation Amir A. Jazaeri, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Gynecologic Oncology American Cancer Society Female Cancers 2000 Statistics Reprinted by
Practice of Medicine-1 Ovarian Cancer Clinical Correlation Amir A. Jazaeri, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Gynecologic Oncology American Cancer Society Female Cancers 2000 Statistics Reprinted by
Ovarian Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
What is cancer? Ovarian Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide to make new cells, and die in an orderly way. During the early years of a person's life,
After Ovarian Cancer Treatment
 After Ovarian Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. What Will Happen After Treatment for Ovarian Cancer?
After Ovarian Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. What Will Happen After Treatment for Ovarian Cancer?
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know
 Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
Ovarian Cancer What you need to know www.ovarian.org.uk Contents Your body and your ovaries What is ovarian cancer? Your body and your ovaries 3 What is ovarian cancer? 3 Not one disease, but many 4 The
Cancer Genomics 101. BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting
 Cancer Genomics 101 BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting Objectives Identify red flags in a person s personal and family medical history that indicate a potential inherited susceptibility to cancer Develop a systematic
Cancer Genomics 101 BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting Objectives Identify red flags in a person s personal and family medical history that indicate a potential inherited susceptibility to cancer Develop a systematic
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer. Information for Women at Increased Risk
 Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
4:00 into mp3 file Huang_342831_5_v1.mp3
 Support for Yale Cancer Answers comes from AstraZeneca, providing important treatment options for women living with advanced ovarian cancer. Learn more at astrazeneca-us.com. Welcome to Yale Cancer Answers
Support for Yale Cancer Answers comes from AstraZeneca, providing important treatment options for women living with advanced ovarian cancer. Learn more at astrazeneca-us.com. Welcome to Yale Cancer Answers
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes
 Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Welcome! Here s our agenda for today:
 Welcome! Here s our agenda for today: What is ovarian cancer? What causes it? When does genetic testing come in? When are families at risk for ovarian cancer? What are the treatments? 3 things to remember
Welcome! Here s our agenda for today: What is ovarian cancer? What causes it? When does genetic testing come in? When are families at risk for ovarian cancer? What are the treatments? 3 things to remember
Hitting the High Points Gynecologic Oncology Review
 Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
Hitting the High Points is designed to cover exam-based material, from preinvasive neoplasms of the female genital tract to the presentation, diagnosis and treatment, including surgery, chemotherapy, and
Ovarian Cancer. What you should know. making cancer less frightening by enlightening
 Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
Ovarian Cancer What you should know making cancer less frightening by enlightening ovarian cancer the facts Over 360 cases are diagnosed in Ireland annually It is the 6th most common cancer in women 4
OVARIAN CANCER Updates in Screening, Early Detection and Prevention
 UW MEDICINE SUSAN PATRICIA TECK MEMORIAL LECTURE October 2017 OVARIAN CANCER Updates in Screening, Early Detection and Prevention BARBARA GOFF, MD Seattle Gynecologic Society March 2018 OVARIAN CANCER
UW MEDICINE SUSAN PATRICIA TECK MEMORIAL LECTURE October 2017 OVARIAN CANCER Updates in Screening, Early Detection and Prevention BARBARA GOFF, MD Seattle Gynecologic Society March 2018 OVARIAN CANCER
WHAT IS OVARIAN CANCER?
 WHAT IS OVARIAN CANCER? The ovaries are small female reproductive organs that reside in the pelvis. There are two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus, or womb. The ovaries produce the female hormones,
WHAT IS OVARIAN CANCER? The ovaries are small female reproductive organs that reside in the pelvis. There are two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus, or womb. The ovaries produce the female hormones,
Genetic Determinants, Risk Assessment and Management
 Genetic Determinants, Risk Assessment and Management Rachel Rando, MS, CGC Genetic Counselor Hunterdon Regional Cancer Center Flemington, NJ I have no disclosures. Acknowledgements: Staff of Hunterdon
Genetic Determinants, Risk Assessment and Management Rachel Rando, MS, CGC Genetic Counselor Hunterdon Regional Cancer Center Flemington, NJ I have no disclosures. Acknowledgements: Staff of Hunterdon
Partners: Introductions: Dr. Carolyn Johnston Deanna Cosens & Ann Garvin. Ovarian Cancer and Primary Care July 16, :00 9:00am EST 7/16/2014
 Welcome To The Webinar Technical Support Ovarian Cancer and Primary Care July 16, 2014 8:00 9:00am EST In order to hear the presentation please call 1 (626) 544-0058, access code 167-314-644, followed
Welcome To The Webinar Technical Support Ovarian Cancer and Primary Care July 16, 2014 8:00 9:00am EST In order to hear the presentation please call 1 (626) 544-0058, access code 167-314-644, followed
Beyond Cancer Moving On
 Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Clinical guideline Published: 27 April 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg122
 Ovarian cancer: recognition and initial management Clinical guideline Published: 27 April 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg122 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Ovarian cancer: recognition and initial management Clinical guideline Published: 27 April 2011 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg122 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers
 Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Passport to Health Preventing and Recognizing Gynecologic Cancers Presented by: Obstetrician/Gynecologist Leigh Bauer, M.D. They can sneak up on you. 2 Gynecologic cancers, that is. Knowing the facts can
Ovarian Cancer. Georgia McCann, MD. Division of Gynecologic Oncology
 Ovarian Cancer Georgia McCann, MD Division of Gynecologic Oncology Myth: Ovarian cancer is a silent killer Non-specific Abdominal pain, discomfort Bloating, back pain Urinary urgency Constipation Tiredness
Ovarian Cancer Georgia McCann, MD Division of Gynecologic Oncology Myth: Ovarian cancer is a silent killer Non-specific Abdominal pain, discomfort Bloating, back pain Urinary urgency Constipation Tiredness
BRCA genes and inherited breast and ovarian cancer. Information for patients
 BRCA genes and inherited breast and ovarian cancer Information for patients This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could be
BRCA genes and inherited breast and ovarian cancer Information for patients This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could be
Key Recommendations. Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer. HBOC related genes. I have nothing to disclose
 Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program I have nothing to disclose Key Recommendations
Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program I have nothing to disclose Key Recommendations
Endometrial Cancer. Incidence. Types 3/25/2019
 Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Cancer Institute. cancer institute Program overview Report 2013
 Cancer Institute cancer institute Program overview Report 2013 Saint Francis Medical Center in Cape Girardeau, Mo., is a regional leader in the battle against cancer, bringing new techniques, ideas and
Cancer Institute cancer institute Program overview Report 2013 Saint Francis Medical Center in Cape Girardeau, Mo., is a regional leader in the battle against cancer, bringing new techniques, ideas and
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers
 Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers Jubilee Brown MD and Pamela T. Soliman MD, MPH Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gynecologic Cancers Jubilee Brown MD and Pamela T. Soliman MD, MPH Department of Gynecologic Oncology and Reproductive Medicine University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer
GHUK BowelGene_2017.qxp_Layout 1 22/02/ :22 Page 3 BowelGene
 GHUK BowelGene_2017.qxp_Layout 1 22/02/2017 10:22 Page 3 BowelGene BowelGene What is hereditary bowel cancer? Bowel cancer (also known as colorectal cancer) is the fourth most common cancer in the UK.
GHUK BowelGene_2017.qxp_Layout 1 22/02/2017 10:22 Page 3 BowelGene BowelGene What is hereditary bowel cancer? Bowel cancer (also known as colorectal cancer) is the fourth most common cancer in the UK.
Gynecologic Oncologist. Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Hormonal Therapy Immunotherapy. Cervical cancer
 Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
LAPAROSCOPY and OVARIAN CANCER
 LAPAROSCOPY and OVARIAN CANCER J. DAUPLAT Clermont-Ferrand France UNIVERSITÉ D'AUVERGNE CLERMONT 1 1 - PROPHYLACTIC OOPHORECTOMY 2 - DIAGNOSIS 3 - EARLY STAGES : STAGING 4 - ADVANCED STAGES - ASSESSMENT
LAPAROSCOPY and OVARIAN CANCER J. DAUPLAT Clermont-Ferrand France UNIVERSITÉ D'AUVERGNE CLERMONT 1 1 - PROPHYLACTIC OOPHORECTOMY 2 - DIAGNOSIS 3 - EARLY STAGES : STAGING 4 - ADVANCED STAGES - ASSESSMENT
Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN
 Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN Adenocarcinomas of the endometrium Most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries Second most common in developing countries. Adenocarcinomas, grade 1 and 2 endometrioid
Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN Adenocarcinomas of the endometrium Most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries Second most common in developing countries. Adenocarcinomas, grade 1 and 2 endometrioid
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
Ovarian cancer: clinical practice the Arabic perspective
 Lead Group Log Ovarian cancer: clinical practice the Arabic perspective Experience of Hôtel-Dieu de France University Hospital (Beirut, LEBANON) in supraradical surgery for ovarian cancer David ATALLAH
Lead Group Log Ovarian cancer: clinical practice the Arabic perspective Experience of Hôtel-Dieu de France University Hospital (Beirut, LEBANON) in supraradical surgery for ovarian cancer David ATALLAH
OVARIAN CANCER STATISTICS
 bioprognos OncoOVARIAN Dx Non-invasive blood test useful to suggest a possible diagnosis in patients with suspected malignancy in the ovarians, reduce inappropriate diagnostic tests, days of hospitalization,
bioprognos OncoOVARIAN Dx Non-invasive blood test useful to suggest a possible diagnosis in patients with suspected malignancy in the ovarians, reduce inappropriate diagnostic tests, days of hospitalization,
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors
 Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Ovarian Cancer Includes Epithelial, Fallopian Tube, Primary Peritoneal Cancer, and Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Overview Ovarian epithelial cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and primary peritoneal cancer are
Advice about familial aspects of breast cancer and epithelial ovarian cancer
 Advice about familial aspects of breast cancer and epithelial ovarian cancer a guide for health professionals FEBRUARY 2006 These guidelines contain three parts: 1. Information for health professionals
Advice about familial aspects of breast cancer and epithelial ovarian cancer a guide for health professionals FEBRUARY 2006 These guidelines contain three parts: 1. Information for health professionals
Cancer Facts for Women
 Cancer Facts for Women Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to
Cancer Facts for Women Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancers. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine. Speaker Disclosure:
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Advances in Internal Medicine Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Hereditary Cancer Syndromes and the Obstetrician/Gynecologist
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hereditary-cancer-syndromes-and-theobstetriciangynecologist/6990/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/clinicians-roundtable/hereditary-cancer-syndromes-and-theobstetriciangynecologist/6990/
Gynecologic Cancers are many diseases. Speaker Disclosure: Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine. Controversies in Women s Health
 Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
Gynecologic Cancer Care in the Age of Precision Medicine Gynecologic Cancers in the Age of Precision Medicine Controversies in Women s Health Lee-may Chen, MD Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive
is time consuming and expensive. An intra-operative assessment is not going to be helpful if there is no more tissue that can be taken to improve the
 My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
My name is Barry Feig. I am a Professor of Surgical Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas. I am going to talk to you today about the role for surgery in the treatment
So, now, that we have reviewed some basics of cancer genetics I will provide an overview of some common syndromes.
 Hello. My name is Maureen Mork and I m a Certified Genetic Counselor in the Clinical Cancer Genetics Program at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I ll be lecturing today on the Cancer
Hello. My name is Maureen Mork and I m a Certified Genetic Counselor in the Clinical Cancer Genetics Program at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I ll be lecturing today on the Cancer
Surgical management and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage III-IV ovarian cancer
 Ovarian cancer Surgical management and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage III-IV ovarian cancer JM. Classe, R. Rouzier, O.Glehen, P.Meeus, L.Gladieff, JM. Bereder, F Lécuru Suitable candidates for neo-adjuvant
Ovarian cancer Surgical management and neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage III-IV ovarian cancer JM. Classe, R. Rouzier, O.Glehen, P.Meeus, L.Gladieff, JM. Bereder, F Lécuru Suitable candidates for neo-adjuvant
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
6 Week Course Agenda. Today s Agenda. Ovarian Cancer: Risk Factors. Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention
 6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
6 Week Course Agenda Winning the War 11/30/2016 on Women s Cancer Gynecologic Cancer Prevention Lee-may Chen, MD Director, Division of Gynecologic Oncology Professor Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology
Familial Cancer Clinic Information Sheet. Surgery to prevent endometrial and ovarian cancer. in women with Lynch Syndrome
 Familial Cancer Clinic Institute for Women s Health 1 st Floor, Maple House 124 Tottenham Court Road W1T 7DN Telephone: 020 7380 6912 Fax: 020 7380 6929 Email: michelle.johnson@ucl.ac.uk Familial Cancer
Familial Cancer Clinic Institute for Women s Health 1 st Floor, Maple House 124 Tottenham Court Road W1T 7DN Telephone: 020 7380 6912 Fax: 020 7380 6929 Email: michelle.johnson@ucl.ac.uk Familial Cancer
BowelGene. How do I know if I am at risk? Families with hereditary bowel cancer generally show one or more of the following clues:
 BowelGene BowelGene What is hereditary bowel cancer? Bowel cancer (also known as colorectal cancer) is the fourth most common cancer in the UK. Unfortunately 1 in 19 women and 1 in 14 men will develop
BowelGene BowelGene What is hereditary bowel cancer? Bowel cancer (also known as colorectal cancer) is the fourth most common cancer in the UK. Unfortunately 1 in 19 women and 1 in 14 men will develop
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG
 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2015 Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG Among a consecutive series of 11,159 women requesting BRCA testing over one year, 3874 responded to a mailed survey. Most respondents
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2015 Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG Among a consecutive series of 11,159 women requesting BRCA testing over one year, 3874 responded to a mailed survey. Most respondents
Gynaecological Oncology Cases
 Gynaecological Oncology Cases 1. Tamoxifen and the endometrium 2. Cancer and the older woman Dr Julie M Lamont Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Epworth Freemasons Hospital 21 st April 2015 Mrs FS 66
Gynaecological Oncology Cases 1. Tamoxifen and the endometrium 2. Cancer and the older woman Dr Julie M Lamont Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Epworth Freemasons Hospital 21 st April 2015 Mrs FS 66
See the latest estimates for new cases of ovarian cancer and deaths in the US and what research is currently being done.
 About Ovarian Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What Is
About Ovarian Cancer Overview and Types If you have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or are worried about it, you likely have a lot of questions. Learning some basics is a good place to start. What Is
AllinaHealthSystems 1
 Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Hysterectomy. What is a hysterectomy? Why is hysterectomy done? Are there alternatives to hysterectomy?
 301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
301.681.3400 OBGYNCWC.COM What is a hysterectomy? Hysterectomy Hysterectomy is surgery to remove the uterus. It is a very common type of surgery for women in the United States. Removing your uterus means
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125. Learning Outcomes
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CA 125 Learning Outcomes Upon completion of this exercise, participants will be able to: discuss the use of CA 125 levels in monitoring patients undergoing treatment for ovarian
--- or not, and do we need to come up with newer strategies for ovarian cancer screening.
 My name is Dr. Karen Lu and I am a Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I also serve as Co-Medical Director for Clinical Cancer Genetics. I m going to
My name is Dr. Karen Lu and I am a Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I also serve as Co-Medical Director for Clinical Cancer Genetics. I m going to
FACT SHEET 49. What is meant by a family history of bowel cancer? What is bowel cancer? What causes bowel cancer?
 Important points The most important factors that can influence an individual s chance of developing bowel cancer are getting older and having a family history of bowel cancer A family history of bowel
Important points The most important factors that can influence an individual s chance of developing bowel cancer are getting older and having a family history of bowel cancer A family history of bowel
Lynch Syndrome (HNPCC) and MYH-Associated Polyposis (MAP)
 Lynch Syndrome (HNPCC) and MYH-Associated Polyposis (MAP) A Patient s Guide to risk assessment Hereditary Cancer Testing: Is it Right for You? This workbook is designed to help you decide if hereditary
Lynch Syndrome (HNPCC) and MYH-Associated Polyposis (MAP) A Patient s Guide to risk assessment Hereditary Cancer Testing: Is it Right for You? This workbook is designed to help you decide if hereditary
Talking about Cancer in Your Family Can Keep You and Your Family Healthy. Do you know your Kin Facts? A guide for and your family
 Talking about Cancer in Your Family Can Keep You and Your Family Healthy Do you know your Kin Facts? A guide for and your family Did you know? Breast and colon cancers are leading cancer killers for women
Talking about Cancer in Your Family Can Keep You and Your Family Healthy Do you know your Kin Facts? A guide for and your family Did you know? Breast and colon cancers are leading cancer killers for women
Screening tests. When you need them and when you don t
 Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Screening tests When you need them and when you don t S creening tests help doctors look for diseases when you don t have symptoms. The tests can Screenings find problems early, when they are easier to
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect
 Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Vaginal cancer: Know what to expect For women with vaginal cancer What is the vagina? The vagina is a hollow canal that connects the cervix and the uterus to the outside. of the body. When a woman gives
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
 Helpful Information for People With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Their Families What you should know about Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Learning the basics of metastatic colorectal cancer If you or
Helpful Information for People With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Their Families What you should know about Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Learning the basics of metastatic colorectal cancer If you or
Ovarian, Peritoneal, and Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cancer (OPT)
 Ovarian, Peritoneal, and Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cancer (OPT) ACOG District II 2 Learning Objectives At the end of this clinical presentation, obstetrician gynecologists and other women s health care
Ovarian, Peritoneal, and Fallopian Tube Epithelial Cancer (OPT) ACOG District II 2 Learning Objectives At the end of this clinical presentation, obstetrician gynecologists and other women s health care
GYNplus: A Genetic Test for Hereditary Ovarian and/or Uterine Cancer
 GYNplus: A Genetic Test for Hereditary Ovarian and/or Uterine Cancer Causes of Hereditary Ovarian and Uterine Cancer uterine cancer ovarian cancer Sporadic 75-90% Sporadic 70-80% Hereditary, 5% Lynch syndrome
GYNplus: A Genetic Test for Hereditary Ovarian and/or Uterine Cancer Causes of Hereditary Ovarian and Uterine Cancer uterine cancer ovarian cancer Sporadic 75-90% Sporadic 70-80% Hereditary, 5% Lynch syndrome
Information for You and Your Family
 Information for You and Your Family What is Prevention? Cancer prevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. In 2017, more than 1.6 million people will be diagnosed with cancer in the
Information for You and Your Family What is Prevention? Cancer prevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. In 2017, more than 1.6 million people will be diagnosed with cancer in the
GeneHealth BreastGene_New qxp_Layout 1 21/02/ :42 Page 3 BreastGene GeneHealth UK
 GeneHealth BreastGene_New 8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:42 Page 3 BreastGene GeneHealth UK BreastGene What is hereditary breast cancer? Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Unfortunately
GeneHealth BreastGene_New 8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:42 Page 3 BreastGene GeneHealth UK BreastGene What is hereditary breast cancer? Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Unfortunately
Risk of Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Hereditary Syndromes in GI Cancer GENETIC MALPRACTICE
 Identifying the Patient at Risk for an Inherited Syndrome Sapna Syngal, MD, MPH, FACG Director, Gastroenterology Director, Familial GI Program Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women s Cancer Center Associate Professor
Identifying the Patient at Risk for an Inherited Syndrome Sapna Syngal, MD, MPH, FACG Director, Gastroenterology Director, Familial GI Program Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women s Cancer Center Associate Professor
Screening for Genes for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Jewish Women
 Screening for Genes for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Jewish Women Background About 5% of women in Canada with breast cancer and about 12% of women with ovarian cancer, are born with an inherited
Screening for Genes for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Jewish Women Background About 5% of women in Canada with breast cancer and about 12% of women with ovarian cancer, are born with an inherited
This information explains the advice about familial breast cancer (breast cancer in the family) that is set out in NICE guideline CG164.
 Familial breast cancer (breast cancer in the family) Information for the public Published: 1 June 2013 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should
Familial breast cancer (breast cancer in the family) Information for the public Published: 1 June 2013 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should
Jill Stopfer, MS, CGC Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania
 Jill Stopfer, MS, CGC Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Aging Family history Early menarche Late menopause Nulliparity Estrogen / Progesterone use after menopause More than two alcoholic
Jill Stopfer, MS, CGC Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Aging Family history Early menarche Late menopause Nulliparity Estrogen / Progesterone use after menopause More than two alcoholic
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
 Helpful Information for People With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Their Families WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Learning the basics of metastatic colorectal cancer If you or
Helpful Information for People With Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Their Families WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Learning the basics of metastatic colorectal cancer If you or
What s In Your Genes: How changes in the BRCA1/BRCA2 genes
 ESSENTIALS BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutations What s In Your Genes: How changes in the BRCA1/BRCA2 genes might affect you and your family Our genes contain the codes for producing the proteins that are the building
ESSENTIALS BRCA1/BRCA2 Mutations What s In Your Genes: How changes in the BRCA1/BRCA2 genes might affect you and your family Our genes contain the codes for producing the proteins that are the building
Genetic testing for Lynch Syndrome Information for people who have had a cancer and are eligible for genetic testing for Lynch Syndrome.
 Genetic testing for Lynch Syndrome Information for people who have had a cancer and are eligible for genetic testing for Lynch Syndrome. Introduction Cancer is common in the general population with 1 in
Genetic testing for Lynch Syndrome Information for people who have had a cancer and are eligible for genetic testing for Lynch Syndrome. Introduction Cancer is common in the general population with 1 in
Lynch Syndrome. A Patient s Guide to Genetic Testing for Lynch Syndrome
 Lynch Syndrome A Patient s Guide to Genetic Testing for Lynch Syndrome What is Lynch Syndrome? Lynch syndrome is an inherited condition that increases your risk of developing colon cancer and other cancers
Lynch Syndrome A Patient s Guide to Genetic Testing for Lynch Syndrome What is Lynch Syndrome? Lynch syndrome is an inherited condition that increases your risk of developing colon cancer and other cancers
After Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment
 After Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. What Happens After Treatment for Soft Tissue Sarcomas?
After Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. What Happens After Treatment for Soft Tissue Sarcomas?
Objectives. Case Study #1 1/28/14. A Collaborative Practice Approach to Genetic Testing in Cancer: Translating Science Into Clinical Practice
 A Collaborative Practice Approach to Genetic Testing in Cancer: Translating Science Into Clinical Practice Heather Hampel, MS, CGC Associate Director, Division of Human Genetics Professor, Department of
A Collaborative Practice Approach to Genetic Testing in Cancer: Translating Science Into Clinical Practice Heather Hampel, MS, CGC Associate Director, Division of Human Genetics Professor, Department of
Cervical Cancer. Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year.
 Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
Cervical Cancer Introduction Cervical cancer is a very common cancer. Nearly one half million cases are diagnosed worldwide each year. Most cases of cervical cancer can be prevented by getting regular
From Research to Practice: What s New in Gynecologic Cancers?
 From Research to Practice: What s New in Gynecologic Cancers? David Warshal, M.D. Head, Division of Gynecologic Oncology MD Anderson Cooper Cancer Institute Associate Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
From Research to Practice: What s New in Gynecologic Cancers? David Warshal, M.D. Head, Division of Gynecologic Oncology MD Anderson Cooper Cancer Institute Associate Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
A Patient s Guide to risk assessment. Hereditary Colorectal Cancer
 A Patient s Guide to risk assessment Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Hereditary Cancer Testing: Is it Right for You? Overview of Syndromes This workbook is designed to help you decide if hereditary cancer
A Patient s Guide to risk assessment Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Hereditary Cancer Testing: Is it Right for You? Overview of Syndromes This workbook is designed to help you decide if hereditary cancer
GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR. cancer that affects the digestive system
 Understanding GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR cancer that affects the digestive system GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR About This Guide This guide will: Help you understand gastrointestinal stromal tumor
Understanding GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR cancer that affects the digestive system GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR About This Guide This guide will: Help you understand gastrointestinal stromal tumor
CANCER GENETICS PROVIDER SURVEY
 Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Surgery to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer
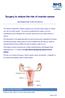 Surgery to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS This leaflet is designed to answer questions you may have about surgery to reduce your risk of ovarian cancer. You may be considering
Surgery to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS This leaflet is designed to answer questions you may have about surgery to reduce your risk of ovarian cancer. You may be considering
Key Recommendations. Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer
 Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program Lead, Kaiser Permanente Northern California
Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program Lead, Kaiser Permanente Northern California
Carol Christianson, MS, CGC Genetic Counselor West Michigan Cancer Center
 Carol Christianson, MS, CGC Genetic Counselor West Michigan Cancer Center Following this presentation you will be able to: Identify cancer survivors in your practice who might benefit from genetic counseling
Carol Christianson, MS, CGC Genetic Counselor West Michigan Cancer Center Following this presentation you will be able to: Identify cancer survivors in your practice who might benefit from genetic counseling
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: MSH6
 Result Navigator Positive Test Result: MSH6 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
Result Navigator Positive Test Result: MSH6 Positive test results identify a change, or misspelling, of DNA that is known or predicted to cause an increased risk for cancer. DNA is the blueprint of life
What a history of cancer may mean for you and your family and the steps you can take to reduce the risk
 What a history of cancer may mean for you and your family and the steps you can take to reduce the risk www.myriadtests.com 1-800-469-7423 Family Ties and Colon Cancer In every family, certain traits are
What a history of cancer may mean for you and your family and the steps you can take to reduce the risk www.myriadtests.com 1-800-469-7423 Family Ties and Colon Cancer In every family, certain traits are
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment
 After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
How is primary breast cancer treated?
 How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
How is primary breast cancer treated? The treatment team This information is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. It is written by Breast Cancer Care,
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated.
 How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
How is primary breast cancer treated? This booklet is for anyone who has primary breast cancer and wants to know more about how it is treated. How is primary breast cancer treated? Part 1 the treatment
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Index. B Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO), 69
 A Advanced stage endometrial cancer diagnosis, 92 lymph node metastasis, 92 multivariate analysis, 92 myometrial invasion, 92 prognostic factors FIGO stage, 94 histological grade, 94, 95 histologic cell
A Advanced stage endometrial cancer diagnosis, 92 lymph node metastasis, 92 multivariate analysis, 92 myometrial invasion, 92 prognostic factors FIGO stage, 94 histological grade, 94, 95 histologic cell
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer
 Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
