Nutrition Flashcards
|
|
|
- Lester Samuel Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. Is the bloodstream water based or lipid based? Water based 2. How are lipids transported in the bloodstream? By water-soluble carriers that have a lipophilic region 3. What are lipid carriers called? Lipoproteins 4. What are the four major groups of lipoproteins, in order of size, from largest to smallest? Chylomicrons VLDL (very low density lipoproteins) LDL (low density lipoproteins) HDL (high density lipoproteins) 5. How are LDL particles formed? when lipoprotein lipase breaks a triglyceride molecule off VLDL 6. Why are LDL called bad cholesterol? higher levels of LDL particles promote health problems and cardiovascular disease 7. What is cholesterol? a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines 8. What is cholesterol used for? 1) to produce hormones A) steroid hormones (including cortisol and aldosterone) B) Sex hormones (progesterone, estrogens, testosterone) 2) To establish proper cell membranes membrane permeability and fluidity 3) To make bile 4) To make one vitamin (vitamin D) 9. How is cholesterol recycled? In the liver, cholesterol is converted to bile, which is then stored in the gallbladder. It is the excreted into the digestive tract, and about 50% of it is reabsorbed back into the bloodstream. 10. What is the function of bile? Bile contains bile salts, which emulsify fats in the digestive tract to aid in the intestinal absorption of fat molecules as well as the fat-soluble vitamins, A, D, E, and K. 11. How does a cell obtain cholesterol? it synthesizes the necessary LDL receptors, and inserts them into the plasma membrane. LDL particles which are carrying cholesterol in the blood stream bind to these extracellular LDL receptors and the cholesterol is brought into the cell and either used or stored. The LDL receptors are then removed from the plasma membrane. 12. Why is LDL called bad cholesterol? It can transport cholesterol into artery walls. 13. What happens when the cholesterol in the arterial wall becomes oxidized by a free radical (a circulating H + ion)? it hardens and forms a plaque (atherosclerosis). 14. What can happen to a plaque? It can break off and travel in the bloodstream as a fat embolism, lodge in a smaller blood vessel, and block blood flow distal to that point. 15. What happens if this occurs in the brain? Stroke 16. What happens if this occurs in the coronary arteries? Heart attack
2 17. What predicts whether or not cholesterol is High levels of LDL transported into artery walls? 18. What popular medicine group is prescribed for Statins (such as vasostatin). people with high LDL levels? 19. How do these medicines work? By inhibiting cholesterol synthesis 20. If cholesterol synthesis is inhibited, what levels Triglycerides will go up; seen in a blood test. will become elevated in the blood if the person does not cut back on their fat consumption? 21. What are triglycerides? They are the main constituents of saturated and unsaturated fat. 22. What is the function of triglycerides? They are a mechanism for storing unused calories 23. What are triglycerides correlated with? The consumption of starch and fatty foods 24. How are triglycerides useful? They transport dietary fat to cells that need it 25. What happens to triglycerides in the small They are converted to chylomicrons, which are intestine? absorbed by lacteals (lymph vessels) 26. What is the enzyme that breaks down Lipase triglycerides so they can be absorbed in the small intestine? 27. What is the most effective dietary approach to Minimizing fat stores in the greater omentum (reduce minimize LDL s in the blood? fat in the waistline) in addition to minimizing total 28. What are two reasons why is it worse to have a fat belly than to have fat in the rear end, regarding LDL levels? 29. Why is it worse to have a fat belly than to have fat in the rear end, regarding diabetes? 30. What obvious appearance is an indicator of how high your LDL and triglyceride levels are, and therefore, is an indicator of cardiovascular health? 31. What other lipid can be lowered which will reduce LDL levels? How to you lower that lipid? 32. Are LDL particles harmless until they are within the blood vessel walls and oxidized by free radicals? 33. Will ingesting antioxidants, thereby minimizing free radical exposure reduce LDL's contribution to atherosclerosis? 34. Why are HDL particles called "good cholesterol"? body fat. 1) Fat stored in the greater omentum is mobilized before subcutaneous fat (deep to the dermis). Fat stored in the rear end is subcutaneous fat. Therefore, fat stored in the omentum will be made into LDL first. 2) Greater omentum fat also produces an enzyme called resistin, which lowers circulating VLDL concentrations (which increases LDL levels). Resistin also increases insulin resistance (causing Diabetes Mellitus) Having a large waist line Triglycerides. Lower them by consuming less fat. Yes Possibly...clinical studies are inconclusive. HDL particles are able to remove cholesterol from within arterial plaques and transport it back to the liver for excretion or re-utilization
3 35. Will increasing one's HDL beyond normal No limits make you healthier than normal? 36. Where does HDL transport cholesterol? Mostly to the liver or organs that use cholesterol such as adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. 37. What happens to the cholesterol delivered to It is combined with broken-down hemoglobin and the liver? converted into the bile, which is then used to break down intestinal fats into small enough particles for digestive enzymes to work. 38. What happens to the cholesterol delivered to It is used for the synthesis of steroid hormones. adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes? 39. What three properties of HDL contribute to its inhibits oxidation, inflammation, and coagulation by ability to protect from atherosclerosis? platelets 40. Can you increase HDL by exercise? No, your levels are hereditary 41. What three things may increase HDL levels? Niacin (vit B3) and magnesium, Apo-A1. Note: Vitamin C does not raise HDL levels. 42. What are the two categories of triglycerides? Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids 43. What are examples of each? Vegetable oil (typically unsaturated) Animal fats (typically saturated) 44. What is the function of triglycerides? They are a mechanism for storing unused calories 45. What causes high levels of triglycerides in the consumption of starchy and fatty foods blood? 46. Are triglycerides directly absorbed in the small No, they are too large. intestine? 47. How are triglycerides absorbed? The pancreatic enzyme lipase acts releases the fatty acids so they can be absorbed (lipolysis). 48. How are triglycerides broken down? They are broken down to fatty acids and then the fatty acids are absorbed by the small intestine. 49. How much energy to they contain, compared to More than twice as much carbohydrates and proteins? 50. Triglycerides are an important component of VLDL and chylomicrons. which two lipid transporter proteins? 51. What happens after fatty acids from triglycerides are absorbed in the intestine? They enter the cells that make up the intestinal lining, where they are rebuilt and packaged with cholesterol and proteins to form chylomicrons. 52. Where do the chlyomicrons go? They are collected by the lymph system (lacteals in the intestinal villi), which transport them to the thoracic lymph duct, and are dumped into the subclavian vein to be mixed into the blood. 53. Once chlyomicrons are in the blood, where do they go? 54. What two cells can synthesize and store triglycerides? 55. When glucose levels are low, what does the body require as an energy source? Various tissues can capture the chylomicrons, releasing the triglycerides to be used as a source of energy when glucose is not available. Fat and liver cells fatty acids
4 56. What hormone signals the liver to break glycogen down into glucose and if that is not enough glucose, it will start gluconeogenesis? 57. What enzymes are involved in gluconeogenesis? glucagon 1) Lipase, which breaks down triglycerides to release free fatty acids, and 2) proteases to break down proteins into amino acids. The fatty acids and amino acids are then combined to make new glucose. 58. What hormone signals the production of lipase? glucagon 59. When glucose levels are low, can the brain No. The brain can only use glucose utilize fatty acids as an energy source? 60. How can the brain get more glucose when there the glycerol component of triglycerides can be is not enough? converted into glucose by way of glycogenolysis. 61. Do triglycerides cause heart disease? Probably not, but high levels are present in people with heart disease. 62. What percentage of your diet being from 60% carbohydrates will increase your blood triglyceride levels, especially if you have diabetes or are overweight? 63. When a high carbohydrate diet causes high levels of triglycerides in the blood, what is the condition is called? 64. What does carbohydrate-induced hypertriglyceridemia do to a person s glycemic index? What does that do to insulin levels? 65. What is the function of insulin? 66. What happens when cells are resistant to insulin? 67. What is the best food to reduce triglyceride levels? 68. What does it mean that Omega 3 fatty acids are essential? 69. What are some good things about Omega 3 fatty acids? carbohydrate-induced hypertriglyceridemia Elevates it, causing an overproduction of insulin 70. What is the best source of Omega 3 fatty acids? Flax (linseed) and its oil 71. Why should you avoid Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil, even though they are heavily advertised? It pulls glucose into the cells. If a cell is insulin resistant, the glucose will stay in the blood and spill into the urine. High levels of blood sugar will damage the brain and blood vessel lining. Up to 3 grams a day of omega-3 fatty acids from flax seed oil (linseed oil). They are not made in our body, so they are needed in our diet. They are essential to normal growth in young children. In adults, they may improve rheumatoid arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Because fish oils are too high in vitamin A, which is toxic in high levels. 72. What is the glycemic index? a measure of the effects of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels. 73. What makes a particular carbohydrate have a high glycemic index? What is an example of one? Carbohydrates that break down quickly during digestion and release glucose rapidly into the bloodstream. Simple sugar like glucose is an example.
5 74. What is an example of a carbohydrate with a Starch low glycemic index? 75. What carbohydrates have slower rates of Foods with a lower glycemic index digestion and absorption, causing a lower insulin demand, and are thus better for a diabetic? 76. What is the Body Mass Index (BMI)? An estimate of body fat 77. What two things are used to calculate BMI? Weight and height 78. Does BMI actually measure the percentage of No you would have to weigh yourself in a body fat? swimming pool to calculate that. 79. What is the quickest, most readily available Glucose source of energy for the body? 80. What are carbohydrates broken down into? Glucose 81. What is broken down if there is not enough blood glucose between meals? Triglycerides are broken down into fatty acids and proteins (including heart muscle) are broken down to amino acids, which combined and made into new glucose 82. What are simple carbohydrates? sugars 83. What are examples of simple carbohydrates? ice cream, cakes, and cookies. Plain white sugar from a box (called refined sugar) 84. Why are sugars called empty calories? because they contribute to energy needs and weight gain without supplying any other nutritional requirements. 85. What are examples of complex carbohydrates? whole grain pasta, rice, bread, and cereal. Less desirable complex carbohydrates (not good for overweight people) are potatoes and corn 86. Name some foods rich in protein red meat, fish, poultry, dairy products, legumes (i.e., peas and beans), nuts, and cereals 87. What happens to proteins that you eat? They are broken down into amino acids and turned into tissues like muscles, skin, hair, and nails. It s also used to make proteins such as hemoglobin, plasma proteins, enzymes, and hormones. 88. How many amino acids are used to make all the 23 proteins in our body? 89. What are essential amino acids? 90. How many are there? There are 9 amino acids which are called essential required from the diet in adults because the body is unable to produce them. Meat 91. What food contains all 23 types of amino acids? 92. What happens if one amino acid is missing The other 22 might not work right. from the diet? 93. What combination of food provides all the Cereal with milk and rice with beans or peas essential amino acids? 94. Are amino acids stored in the body? No, a daily supply is needed. 95. How much meat does a person need per day? Two servings (the size of a deck of cards)
6 96. Which meats are high in protein but also high Red meat (can be 42% fat) in fat? 97. What protein sources are low in fat? protein from plant origins (whole-grain cereals, dark breads, and legumes) 98. Why are protein and amino acid supplements They are not digested as well not good? They can cause you to have an excess of one amino 99. What happens if you have an excess of just one amino acid? 100. What type of fats raise LDL (bad) cholesterol? Name 2 examples 101. What type of fats lower LDL (bad) cholesterol? Name 2 examples acid or another It competes for receptor sites in the small intestine, causing a deficiency in absorption of the other amino acids. Saturated fats; they are solid at room temperature and have an animal origin. Butter and margarine polyunsaturated fats; they are liquid at room temperature and have a plant origin. olive oil, canola oil, corn oil, and safflower oil What are two plant oils that are NOT good, partially hydrogenated palm and coconut oil because they contain saturated fats? 103. Which meats are lower in saturated fats? Turkey, fish, and chicken How many calories are in one pound of fat? 3, How many days will it take to lose one pound 7 days of fat if you eat 500 calories less per day? 106. What is the reason why some people lose more Water loss. It will come back. than that? 107. What are the two general function of vitamins? They are needed for metabolism They make a lot of the body s enzymes What is an enzyme? It breaks a larger molecule down into smaller ones How many vitamins are there, and what are 13 vitamins; fat soluble and water soluble their 2 categories? 110. What are the 4 fat-soluble vitamins? A, D, E, K 111. What happens to excess fat-soluble vitamins? They are stored in fat and liver, and can accumulate to a toxic level 112. What happens to excess water-soluble vitamins? 113. Where is the fat on a fetus? What happens if the mother takes too much vitamin A, D, E, or K? They are excreted in the urine. That is okay as long as you are well hydrated. If not, they can cause kidney damage. In the myelin sheaths (white matter). Excess vitamins can lodge there and disrupt action potentials. The corpus callosum is a large area of white matter in the brain. Dysfunction causes autism Where is vitamin C found? Citrus fruits (oranges, tangerines, lemons) 115. Where is vitamin D made? In the skin after UV light exposure What does vitamin D do? Helps the intestines absorb ingested calcium 117. Lack of vitamin D leads to what disorder in Rickets children? 118. What is a free radical? As a cell is functioning, it generates molecules that have an extra electron, which is called a free radical.
7 119. What is the damage caused by free radicals? free radicals want to run around and get rid of their extra electron (that is called oxidizing the recipient molecule), but none of the other molecules want one, either. The parts of a cell that usually get stuck with a free radical include DNA, proteins, enzymes, and cell membranes. This leads to damage there, and can even lead to cancer What substances deactivate free radicals? What Anti-oxidants are examples? Vitamin C. E, and A, found in fruits and vegetables 121. How many servings of fruits and vegetables 5 servings (2 fruit, 3 vegetables). A serving is about should you eat per day? 122. Is it just as good to take a vitamin pill instead of eating fruits and vegetables? one cup No, you don t get the fiber, which is needed to prevent colon cancer. Also, excess vitamins A, D, E, K are toxic 123. What are some minerals? Calcium, phosphorous, iodine, sodium, chloride, magnesium, potassium, zinc, copper, iron 124. What is calcium used for? bones, teeth, nerve conduction, and muscle contraction. It helps prevent osteoporosis if you have enough calcium and you also exercise What foods are high in calcium? Dairy products and green leafy vegetables 126. What is phosphorus used for? It is used as an energy molecule. It is part of ATP 127. What is iodine used for? Thyroid hormone 128. What are sodium and chloride used for? Regulating water balance 129. How much sodium is needed per day? What 500 mg/day. Excess causes water retention, causing happens if you have too much? high blood pressure 130. What is potassium and sodium used for? Muscle contraction and nerve conduction 131. What are some foods high in potassium? Cantaloupe, avocados, potatoes, beans, bananas, fish, raisins, apricots, dates, and cocoa powder (think chocolate) What is magnesium used for? Helps muscles relax 133. What are some foods high in magnesium? seeds, brans (wheat, rice, and oat), spinach, and cocoa. Any leafy greens have a high amount of magnesium because the center of the chlorophyll molecule is magnesium What is magnesium, zinc, and copper used for? They are critical for most enzymes 135. What is iron used for? To make hemoglobin to transport oxygen in red blood cells 136. How do males and females differ in their iron Females need more, due to loss during menstruation. requirements? If you ingest too much, it makes you constipated What is glucosamine? Where in the body is it an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the found? synthesis of certain proteins and lipids. It is an important component of joint cartilage 138. How are glucosamine supplements made? Usually from the shells of crustaceans
8 139. Will ingesting glucosamine restore damaged cartilage? No; eating cartilage does not mean you will grow new cartilage. It just breaks down into the same components that are found in cartilage. It may or may not be used to restore cartilage (controversial; no evidence to support it yet). It might prevent cartilage erosion (also controversial) Name three common eating disorders Obesity, bulimia, anorexia nervosa 141. What is obesity? Being about 50 pounds overweight 142. What is moderate obesity? Being about 75 pounds overweight 143. What is morbid obesity? Being 200+ pounds overweight 144. Why is it especially important not to let children become obese? 145. What surgery is for people more than 100 pounds overweight? Their stem cells have not all differentiated yet. If they gain weight, these stem cells will become fat cells, and it will be hard for them to lose weight their whole life. Stomach stapling What are the problems with this surgery? They have to watch their diet to get enough nutrients, they need vitamin B12 shots monthly, and they must not force extra food in, or the stomach will stretch out again What is bulimia? eating to excess (called binge eating) and then purging themselves by some artificial means, such as selfinduced vomiting or use of a laxative What are the dangers of bulimia? causes an abnormal heart rhythm, and damage to the kidneys can even result in death. Vomiting up the food causes the stomach acids to eat away at the pharynx, esophagus, and teeth. Vomiting also causes loss of electrolytes, which can be deadly 149. What is anorexia? 150. What is anorexia nervosa? Anorexia is just not eating. The person might just be sick or recovering from surgery. Anorexia nervosa is a refusal to eat because they think they are too fat. It is often a control issue. The person feels like they do not have control in their life, so they control the food Who is especially at danger for anorexia Athletes such as distance runners, wrestlers, and nervosa? dancers 152. What are some symptoms of starvation? low blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, constipation, being cold, and they tend to get stress fractures. Menstruation ceases in females
Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages
 Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages 190-201 What are the 3 classes of nutrients that supply your body with energy and how does the body obtain the energy from foods? Describe the roles that carbohydrates,
Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages 190-201 What are the 3 classes of nutrients that supply your body with energy and how does the body obtain the energy from foods? Describe the roles that carbohydrates,
Six Nutrients. Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy. Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water
 Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Lecture 3. Nutrition
 Lecture 3 Nutrition, Part 1 1 Nutrition 1.Macronutrients a. Water b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Fats 2.Micronutrients a. Minerals b. Vitamins 2 1 Why is Nutrition Important? Your food choices each day
Lecture 3 Nutrition, Part 1 1 Nutrition 1.Macronutrients a. Water b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Fats 2.Micronutrients a. Minerals b. Vitamins 2 1 Why is Nutrition Important? Your food choices each day
Nutrients. The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning.
 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Be a Food Label Detective!
 Be a Food Label Detective! Elyse Kontra Kara Kelly Total Fat Type of fat is more important than total fat Limit total fat intake to 25-35% of your total calories Fat-free Caloriefree http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-ieat/taking-a-closer-look-at-labels.html
Be a Food Label Detective! Elyse Kontra Kara Kelly Total Fat Type of fat is more important than total fat Limit total fat intake to 25-35% of your total calories Fat-free Caloriefree http://www.diabetes.org/food-and-fitness/food/what-can-ieat/taking-a-closer-look-at-labels.html
Nutrition Basics. Health, Wellness & Fitness. Brenda Brown
 Nutrition Basics Health, Wellness & Fitness Brenda Brown bbrown9@asu.edu Why do we eat? Building blocks to fuel our bodies Hunger Don t want to starve Socialization Emotional eating or not eating when
Nutrition Basics Health, Wellness & Fitness Brenda Brown bbrown9@asu.edu Why do we eat? Building blocks to fuel our bodies Hunger Don t want to starve Socialization Emotional eating or not eating when
Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins. minerals vitamins fiber
 Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins minerals vitamins fiber WATER Essential nutrient 55-65% body weight Body loses water through evaporation, excretion, and respiration The only nutrient
Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins minerals vitamins fiber WATER Essential nutrient 55-65% body weight Body loses water through evaporation, excretion, and respiration The only nutrient
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT
 NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT NUTRIENT: a chemical found in food that is needed for life and growth, & the building blocks to make your body function correctly! WHAT DO
NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT NUTRIENT: a chemical found in food that is needed for life and growth, & the building blocks to make your body function correctly! WHAT DO
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
JIGSAW READING CARBOHYDRATES
 Date: CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates provide an important source of energy for our bodies. There are two types of carbohydrates: Sugars are found in foods which taste sweet like candies, jams and desserts.
Date: CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates provide an important source of energy for our bodies. There are two types of carbohydrates: Sugars are found in foods which taste sweet like candies, jams and desserts.
When people don t eat enough complex carbohydrates they don t have enough energy and feel tired and less alert. They also may not get enough fiber.
 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are compounds that come from plants and contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. These nutrients supply energy, which all living things need. Carbohydrates are the body s most
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are compounds that come from plants and contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. These nutrients supply energy, which all living things need. Carbohydrates are the body s most
Section 4: Exercise Physiology. Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance
 Section 4: Exercise Physiology Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance Learning Objectives 1. Identify the seven classes of food as: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins,
Section 4: Exercise Physiology Diet and nutrition and their effect on physical activity and performance Learning Objectives 1. Identify the seven classes of food as: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins,
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: THE BIG PICTURE WHY WE EAT FUNCTIONS FATS FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN
 ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
Facts that you need to know
 NUTRITION This article explores the basic concepts of nutrition and provides useful tips on healthy diet My neighbor walks up to me asking whether I am aware of the nutritional value of a new food product
NUTRITION This article explores the basic concepts of nutrition and provides useful tips on healthy diet My neighbor walks up to me asking whether I am aware of the nutritional value of a new food product
2002 Learning Zone Express
 1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
Foundations of Personal Fitness. Chapter 4 Nutrition and Your Personal Fitness
 Foundations of Personal Fitness Chapter 4 Nutrition and Your Personal Fitness Lesson 1: The Importance of Nutrition Healthful Eating Taking in the proper amount of nutrients each day Nutrients substances
Foundations of Personal Fitness Chapter 4 Nutrition and Your Personal Fitness Lesson 1: The Importance of Nutrition Healthful Eating Taking in the proper amount of nutrients each day Nutrients substances
Chewing the fat about fat!
 Chewing the fat about fat! When we talk about fat, most people think of fatty foods, like fries and fatty meats. But fat is an essential nutrient. It plays an important role in the many functions that
Chewing the fat about fat! When we talk about fat, most people think of fatty foods, like fries and fatty meats. But fat is an essential nutrient. It plays an important role in the many functions that
WHAT S INSIDE. Nutrient Institute LLC. All Rights Reserved
 WHAT S INSIDE Nutrient Institute LLC. All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Macronutrients PAGE 3-4 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Other Ingredients PAGE 5-6 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Bad Stuff PAGE 6-8 By Nutrients
WHAT S INSIDE Nutrient Institute LLC. All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Macronutrients PAGE 3-4 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Other Ingredients PAGE 5-6 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Bad Stuff PAGE 6-8 By Nutrients
ABLE TO READ THE LABEL?
 ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups:
 The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
Importance of Nutrition
 The EAT WELL Plate Canada s food guide Food pyramid Importance of Nutrition Energy for body metabolism (nerve impulses, contraction of muscles, repair and replacement of cells Raw materials for building
The EAT WELL Plate Canada s food guide Food pyramid Importance of Nutrition Energy for body metabolism (nerve impulses, contraction of muscles, repair and replacement of cells Raw materials for building
Choosing Healthful Foods
 LESSON 25 Choosing Healthful Foods Before You Read List some of the healthful foods you eat. What makes these foods healthful choices? What You ll Learn the functions and sources of proteins, carbohydrates,
LESSON 25 Choosing Healthful Foods Before You Read List some of the healthful foods you eat. What makes these foods healthful choices? What You ll Learn the functions and sources of proteins, carbohydrates,
Tiny structures that carry out cellular functions (cell parts) Ex: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes
 ALL living things are Building from smallest to LARGEST: Organelles- Cells- Tiny structures that carry out cellular functions (cell parts) Ex: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes The basic unit of structure
ALL living things are Building from smallest to LARGEST: Organelles- Cells- Tiny structures that carry out cellular functions (cell parts) Ex: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes The basic unit of structure
Chapter Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients
 Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
Chapter 4: Nutrition. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 4: Nutrition ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction SCAN group of dieticians who practice in sports and cardiovascular nutrition [SCAN]; locate local SCAN dieticians by contacting
Chapter 4: Nutrition ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction SCAN group of dieticians who practice in sports and cardiovascular nutrition [SCAN]; locate local SCAN dieticians by contacting
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins
 Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
A Closer Look at The Components Of a Balanced Diet
 A Closer Look at The Components Of a Balanced Diet The essential nutrients are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibre and water. These nutrients will ensure that the systems and
A Closer Look at The Components Of a Balanced Diet The essential nutrients are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, dietary fibre and water. These nutrients will ensure that the systems and
Nutrients in foods replace those used by the body
 Fundamentals of Nutrition Nutrition: those processes that allow the body to use food for energy, maintenance of health, and growth. Nutritional status: the state of one s nutrition Wellness: state of good
Fundamentals of Nutrition Nutrition: those processes that allow the body to use food for energy, maintenance of health, and growth. Nutritional status: the state of one s nutrition Wellness: state of good
OBJECTIVE. that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins play in your body.
 OBJECTIVE Describe the roles that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins play in your body. JOurnall How was your weekend? What did you do? Did you practice any of the lessons you have learned thus far? What
OBJECTIVE Describe the roles that carbohydrates, fats, and proteins play in your body. JOurnall How was your weekend? What did you do? Did you practice any of the lessons you have learned thus far? What
in the form of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals
 BCS_G8_U1C02_J15 5/23/06 11:45 AM Page 64 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems A healthy body requires nutrients from five groups: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. There are four
BCS_G8_U1C02_J15 5/23/06 11:45 AM Page 64 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems A healthy body requires nutrients from five groups: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. There are four
Fiber: What Is It and What Does It Do? By James L. Holly, MD. Your Life Your Health. The Examiner. May 5, 2005
 Fiber: What Is It and What Does It Do? By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner May 5, 2005 I don t know about you, but fiber has always been a mystery to me. Soluble fiber, insoluble fiber?
Fiber: What Is It and What Does It Do? By James L. Holly, MD Your Life Your Health The Examiner May 5, 2005 I don t know about you, but fiber has always been a mystery to me. Soluble fiber, insoluble fiber?
Nutrients. Nutrition. Carbohydrates. - ex. Carbs, Fats, Protein, Water. - ex. vitamins, minerals
 Nutrients Nutrition Introduction elements and compounds an organism needs but can not manufacture itself 6 Basic Nutrients carbohydrates fats proteins water vitamins minerals Macronutrients supply energy
Nutrients Nutrition Introduction elements and compounds an organism needs but can not manufacture itself 6 Basic Nutrients carbohydrates fats proteins water vitamins minerals Macronutrients supply energy
OM s Health Corner Cholesterol & Heart Disease!!
 Cholesterol & Heart Disease!! We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces 75% of the cholesterol that circulates in our blood.
Cholesterol & Heart Disease!! We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces 75% of the cholesterol that circulates in our blood.
How does your body use nutrients?
 How does your body use nutrients? As an energy source To heal, build and repair tissue To sustain growth To help transport oxygen to cells To regulate body functions What are carbohydrates? Starches and
How does your body use nutrients? As an energy source To heal, build and repair tissue To sustain growth To help transport oxygen to cells To regulate body functions What are carbohydrates? Starches and
Managing Cholesterol
 Managing Cholesterol Introduction Cholesterol is one of the most familiar medical words today. Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is very important for our body but could also be very dangerous if there
Managing Cholesterol Introduction Cholesterol is one of the most familiar medical words today. Cholesterol is a waxy substance that is very important for our body but could also be very dangerous if there
Macros and Micros. of a Healthy Diet. Macronutrients. Proteins
 Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Notes: A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or
 A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or strain a muscle Cooling down allows your heartbeat, breathing
A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or strain a muscle Cooling down allows your heartbeat, breathing
CONCEPTS: OBJECTIVES: MATERIALS:
 CONCEPTS: Adolescence is considered to be the period of maximum growth both in terms of height and weight. Nutrition plays an important role in providing fuel and nutrients to support this rapid growth.
CONCEPTS: Adolescence is considered to be the period of maximum growth both in terms of height and weight. Nutrition plays an important role in providing fuel and nutrients to support this rapid growth.
F. To provide energy, to spare body protein, to prevent ketosis. G. Food sources include breads, vegetables, fruit, and milk.
 Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
Maintain Cholesterol
 Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Hockey Nutrition Tips
 Hockey Nutrition Tips 6 Classes of Nutrients Essential for Top Performance 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fat 3. Protein 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Water Carbohydrates: are a source of energy that can be either simple
Hockey Nutrition Tips 6 Classes of Nutrients Essential for Top Performance 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fat 3. Protein 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Water Carbohydrates: are a source of energy that can be either simple
The food that we eat provides us with the energy we need to get us through the day. Our bodies also use that energy to perform necessary functions.
 The food that we eat provides us with the energy we need to get us through the day. Our bodies also use that energy to perform necessary functions. Breathe Maintain body temperature Heart rate Digestion
The food that we eat provides us with the energy we need to get us through the day. Our bodies also use that energy to perform necessary functions. Breathe Maintain body temperature Heart rate Digestion
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies
 Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Fats = Lipids Organic compounds- mostly carbon Found in animals & plants Don t dissolve well in H20 Dissolve in organic solvents: ether, chloroform,
 FATS Fats = Lipids Organic compounds- mostly carbon Found in animals & plants Don t dissolve well in H20 Dissolve in organic solvents: ether, chloroform, toluene, methanol Assignment Oil and Water Fats
FATS Fats = Lipids Organic compounds- mostly carbon Found in animals & plants Don t dissolve well in H20 Dissolve in organic solvents: ether, chloroform, toluene, methanol Assignment Oil and Water Fats
Cholesterol Levels -- What They Mean, Diet and Treatment
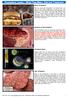 Cholesterol Levels -- What They Mean, Diet and Treatment What Is Cholesterol? We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces
Cholesterol Levels -- What They Mean, Diet and Treatment What Is Cholesterol? We may associate cholesterol with fatty foods, but most of the waxy substance is made by our own bodies. The liver produces
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health. By Dr. Isaac Eliaz
 6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
Fats and Other Lipids
 Fats and Other Lipids Chapter 6 Chapter 6: Fats and other Lipids 1 6.1 Understanding Lipids Lipids include: 1. Fatty acids 2. Triglycerides 3. Phospholipids 4. Cholesterol Oil and Water Don t Mix Because
Fats and Other Lipids Chapter 6 Chapter 6: Fats and other Lipids 1 6.1 Understanding Lipids Lipids include: 1. Fatty acids 2. Triglycerides 3. Phospholipids 4. Cholesterol Oil and Water Don t Mix Because
Lipid & Fat: Overview
 Lipid & Fat: Overview What is a lipid? Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Triglycerides = Fat Saturated & unsaturated Essential fatty acids ü Omega 3 & Omega 6 Trans fat Why do you need fat? How
Lipid & Fat: Overview What is a lipid? Triglycerides, Phospholipids and Sterols Triglycerides = Fat Saturated & unsaturated Essential fatty acids ü Omega 3 & Omega 6 Trans fat Why do you need fat? How
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Name Hour. Nutrition Notes
 Calorie: Measure of Name Hour Nutrition Notes = 9 calories per gram Carbohydrates and Protein = calories per gram. If you consume more calories than you use up, it will be stored as. Carbohydrates (CHO)
Calorie: Measure of Name Hour Nutrition Notes = 9 calories per gram Carbohydrates and Protein = calories per gram. If you consume more calories than you use up, it will be stored as. Carbohydrates (CHO)
Session 21: Heart Health
 Session 21: Heart Health Heart disease and stroke are the leading causes of death in the world for both men and women. People with pre-diabetes, diabetes, and/or the metabolic syndrome are at higher risk
Session 21: Heart Health Heart disease and stroke are the leading causes of death in the world for both men and women. People with pre-diabetes, diabetes, and/or the metabolic syndrome are at higher risk
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals
 Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015
 Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015 Introduction Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Understand basic functions of each nutrient Identify food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins Create balanced
Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015 Introduction Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Understand basic functions of each nutrient Identify food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins Create balanced
Nutrition. Metabolism. The study of how your body uses the food you eat.
 1 Nutrition The study of how your body uses the food you eat. Metabolism The speed at which your body uses energy to maintain its processes; vary by individual Nutrition Food- an edible, organic substance
1 Nutrition The study of how your body uses the food you eat. Metabolism The speed at which your body uses energy to maintain its processes; vary by individual Nutrition Food- an edible, organic substance
MY PLATE is the food guide we use in planning our nutritional needs each day. It was adopted for use in 2011 by the United States Department of
 MY PLATE is the food guide we use in planning our nutritional needs each day. It was adopted for use in 2011 by the United States Department of Agriculture. It has 5 food group sections. Meeting your daily
MY PLATE is the food guide we use in planning our nutritional needs each day. It was adopted for use in 2011 by the United States Department of Agriculture. It has 5 food group sections. Meeting your daily
25* or higher Underweight. 240 mg/dl and above High (More than twice the risk as desirable level.) OK, but higher is better
 Biometrics Screening Biometric Health Indicators The charts below provide a summary of the ranges for each of the biometric screening tests. Be sure to check with your doctor if your results are outside
Biometrics Screening Biometric Health Indicators The charts below provide a summary of the ranges for each of the biometric screening tests. Be sure to check with your doctor if your results are outside
Nutrition Notes website.notebook October 19, Nutrition
 Nutrition Nutrition Notes website.notebook October 19, 2016 Food is any substance that is ingested ("eaten") and helps sustain life. Food categories: Meats and Alternative Dairy Products Fruits and Vegetables
Nutrition Nutrition Notes website.notebook October 19, 2016 Food is any substance that is ingested ("eaten") and helps sustain life. Food categories: Meats and Alternative Dairy Products Fruits and Vegetables
PDF created with pdffactory trial version
 General Nutrition Concepts Importance of Nutrition Health Appearance Behavior Mood Role of Nutrients in Diet Growth and development Provide energy Regulate metabolism 2 Calories in Food Carbohydrates Protein
General Nutrition Concepts Importance of Nutrition Health Appearance Behavior Mood Role of Nutrients in Diet Growth and development Provide energy Regulate metabolism 2 Calories in Food Carbohydrates Protein
From Food to the Bloodstream
 FATS The total amount of fat you eat, whether high or low, isn't really linked with disease. What really matters is the type of fat you eat. The "bad" fats saturated and trans fats increase the risk for
FATS The total amount of fat you eat, whether high or low, isn't really linked with disease. What really matters is the type of fat you eat. The "bad" fats saturated and trans fats increase the risk for
Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test
 Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test 1. List the ten dietary guidelines recommended for Americans. (10) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Multiple
Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test 1. List the ten dietary guidelines recommended for Americans. (10) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Multiple
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET
 WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET Food gives us the energy required for chemical reaction to keep us alive Energy also required for many activities and to maintain body temperature Food also gives us
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET Food gives us the energy required for chemical reaction to keep us alive Energy also required for many activities and to maintain body temperature Food also gives us
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID: GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment
 TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
CHOLESTEROL CONTENT CREATED BY. Learn more at
 CHOLESTEROL CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents what is cholesterol? 4 Whether this is your first visit or a follow-up, asking your doctor these
CHOLESTEROL CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents what is cholesterol? 4 Whether this is your first visit or a follow-up, asking your doctor these
you are what you eat leader s guide Kansas State University Agricultural Experiment Station and Cooperative Extension Service
 you are what you eat leader s guide Learning Objectives for Students Understand how different nutrients affect their cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, and musculoskeletal systems. Gain a better
you are what you eat leader s guide Learning Objectives for Students Understand how different nutrients affect their cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, and musculoskeletal systems. Gain a better
The 6 Essential Nutrients for Proper Nutrition. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Protein 4. Vitamins 5. Minerals 6. Water
 Activity Level Inactive (little to no regular exercise) Moderately Active (20-30 minutes of exercise3-4 times per week Very Active (30-40 minutes of vigorous, sustained exercise 5-7 times weekly How Active
Activity Level Inactive (little to no regular exercise) Moderately Active (20-30 minutes of exercise3-4 times per week Very Active (30-40 minutes of vigorous, sustained exercise 5-7 times weekly How Active
HEALTHY EATING to reduce your risk of heart disease
 HEALTHY EATING to reduce your risk of heart disease Choose these more often: Fruits, vegetables and whole grains Enjoy a variety of fruit and vegetables every day and whole grains more often.* Small portions
HEALTHY EATING to reduce your risk of heart disease Choose these more often: Fruits, vegetables and whole grains Enjoy a variety of fruit and vegetables every day and whole grains more often.* Small portions
EXSC- STANDARD 14. Nutrients
 SPORTS NUTRITION EXSC- STANDARD 14 Nutrients Standard 14 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources related to the importance of a balanced diet in the achievement
SPORTS NUTRITION EXSC- STANDARD 14 Nutrients Standard 14 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources related to the importance of a balanced diet in the achievement
Materials Photo copied food labels and worksheet available Understanding Food Labels & Claims (take home handout)
 Reading Food Labels Grade Level: Grades 4-8 Objectives: Student will learn the key components of the food label Students will identify which nutrient values should be low and which values should be high
Reading Food Labels Grade Level: Grades 4-8 Objectives: Student will learn the key components of the food label Students will identify which nutrient values should be low and which values should be high
An overview of the digestive system. Chp. 8 DIGESTIVE S. & NUTRITION What are the steps in the digestive process?
 8.1 Overview of digestion Chp. 8 DIGESTIVE S. & NUTRITION What are the steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the mouth Digestion mechanically or chemically breaking down food into
8.1 Overview of digestion Chp. 8 DIGESTIVE S. & NUTRITION What are the steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the mouth Digestion mechanically or chemically breaking down food into
Lifelong Nutrition. Jemma O Hanlon BHlthSc(Nutr & Diet) APD AN Accredited Practising Dietitian Accredited Nutritionist
 Lifelong Nutrition Jemma O Hanlon BHlthSc(Nutr & Diet) APD AN Accredited Practising Dietitian Accredited Nutritionist Outline a Macronutrients a Micronutrients a Glycaemic Index a NHPAs The Australian
Lifelong Nutrition Jemma O Hanlon BHlthSc(Nutr & Diet) APD AN Accredited Practising Dietitian Accredited Nutritionist Outline a Macronutrients a Micronutrients a Glycaemic Index a NHPAs The Australian
Classes of Nutrients A Diet
 Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Food for Thought January 26, 2012
 Food for Thought January 26, 2012 Why is nutrition important? The foods you eat provide the energy your body and mind need to function. The foods you eat build and support your immune system, hormones,
Food for Thought January 26, 2012 Why is nutrition important? The foods you eat provide the energy your body and mind need to function. The foods you eat build and support your immune system, hormones,
The Nutritional Information Panel is a pretty technical looking piece of artwork and the main question people ask about it WHAT DOES IT ALL MEAN?
 The Nutritional Information Panel is a pretty technical looking piece of artwork and the main question people ask about it is WHAT DOES IT ALL MEAN? Well, we want you to understand it as well as we do.
The Nutritional Information Panel is a pretty technical looking piece of artwork and the main question people ask about it is WHAT DOES IT ALL MEAN? Well, we want you to understand it as well as we do.
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Organization of the Body The levels of organization in the body include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. At each level of organization, these parts of the
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Organization of the Body The levels of organization in the body include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. At each level of organization, these parts of the
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013
 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
Nutrition - What Should We Eat?
 Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
UNIT 2 DIABETES REVIEW
 UNIT 2 DIABETES REVIEW Pancreas is unable to make insulin. Therefore, glucose cannot get into the cells for energy. Insulin is made, but cell receptors do not work at getting recognizing that insulin.
UNIT 2 DIABETES REVIEW Pancreas is unable to make insulin. Therefore, glucose cannot get into the cells for energy. Insulin is made, but cell receptors do not work at getting recognizing that insulin.
Nutrition for the heart. Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist
 Nutrition for the heart Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist The Food Pyramid Dairy 2-3 servings Vegetables 3-5 servings Breads/Grains 6-11 servings Fats & Oils Use Sparingly Proteins 2-3 servings Fruits 2-4 servings
Nutrition for the heart Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist The Food Pyramid Dairy 2-3 servings Vegetables 3-5 servings Breads/Grains 6-11 servings Fats & Oils Use Sparingly Proteins 2-3 servings Fruits 2-4 servings
HEALTHY EATING. What you need to know for a long and healthy life. March National Nutrition Month
 HEALTHY EATING What you need to know for a long and healthy life March National Nutrition Month 890246 This presentation is for informational purposes only. Material within this presentation should not
HEALTHY EATING What you need to know for a long and healthy life March National Nutrition Month 890246 This presentation is for informational purposes only. Material within this presentation should not
How to Prevent Heart Disease
 How to Prevent Heart Disease Introduction Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. You can reduce your risk of heart disease with healthy habits. This reference summary explains heart disease
How to Prevent Heart Disease Introduction Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. You can reduce your risk of heart disease with healthy habits. This reference summary explains heart disease
3. A diet high in saturated fats can be linked to which of the following? A: kidney failure B: bulimia C: anorexia D: cardiovascular disease
 Nutrition and Health 1. A substance needed by the body for growth, energy, repair and maintenance is called a. A: nutrient B: carbohydrate C: calorie D: fatty acid 2. All of the following are nutrients
Nutrition and Health 1. A substance needed by the body for growth, energy, repair and maintenance is called a. A: nutrient B: carbohydrate C: calorie D: fatty acid 2. All of the following are nutrients
Lipids. PBHL 211 Darine Hachem, MS, LD
 Lipids PBHL 211 Darine Hachem, MS, LD Outline Functions of lipids in our body Types of lipids Sources of lipids Recommendation of fat intake Fat association with heart diseases Provide energy (9Kcal/g
Lipids PBHL 211 Darine Hachem, MS, LD Outline Functions of lipids in our body Types of lipids Sources of lipids Recommendation of fat intake Fat association with heart diseases Provide energy (9Kcal/g
Nutrient Presentations
 Nutrient Presentations Carbs The main function of carbohydrates is to provide energy for the body. Food 3 main food sources for Carbs are: Sugars (fruit, milk, etc.) Pasta, Cereals and Breads Most carbohydrates
Nutrient Presentations Carbs The main function of carbohydrates is to provide energy for the body. Food 3 main food sources for Carbs are: Sugars (fruit, milk, etc.) Pasta, Cereals and Breads Most carbohydrates
Preventing Diabetes. prevent or delay type 2 diabetes from
 Preventing Diabetes Introduction Diabetes is a common condition. If not controlled, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as blindness, amputations, and even death. Before people develop diabetes,
Preventing Diabetes Introduction Diabetes is a common condition. If not controlled, diabetes can lead to serious complications such as blindness, amputations, and even death. Before people develop diabetes,
Lecture Exam 1. Fever: a homeostatic imbalance. How body temperature works. Homeostasis of blood glucose concentration. Metabolic adaptations
 Lecture Exam 1 Covers Ch 24 and 25 digestion and metabolism Multiple choice and short answer 100 pts Bring scantron and #2 pencil 2 Review sheets on my website Body Temperature Homeostasis We maintain
Lecture Exam 1 Covers Ch 24 and 25 digestion and metabolism Multiple choice and short answer 100 pts Bring scantron and #2 pencil 2 Review sheets on my website Body Temperature Homeostasis We maintain
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
Nutrition for Athletic Performance in Cross-Country. By:Carly Wells, RD, LDN
 Nutrition for Athletic Performance in Cross-Country By:Carly Wells, RD, LDN Why is it important to focus on eating right? It affects performance Provides appropriate fuel Aids in recovery Facilitates strength
Nutrition for Athletic Performance in Cross-Country By:Carly Wells, RD, LDN Why is it important to focus on eating right? It affects performance Provides appropriate fuel Aids in recovery Facilitates strength
NUTRITION Unit I Food Choices & Nutritional Needs
 NUTRITION 2102 Unit I Food Choices & Nutritional Needs FOOD CHOICES What is your relationship with food? What are your favorite foods? Why? Why do you eat? Do you eat only because you are hungry? Where
NUTRITION 2102 Unit I Food Choices & Nutritional Needs FOOD CHOICES What is your relationship with food? What are your favorite foods? Why? Why do you eat? Do you eat only because you are hungry? Where
Making Responsible Food Choices. Chapter 5
 Making Responsible Food Choices Chapter 5 Bell Work Why is food and nutrition important to our physical health? How can your culture affect your health? How can your environment affect your health? How
Making Responsible Food Choices Chapter 5 Bell Work Why is food and nutrition important to our physical health? How can your culture affect your health? How can your environment affect your health? How
Module 1 An Overview of Nutrition. Module 2. Basics of Nutrition. Main Topics
 Module 1 An Overview of Nutrition Module 2 What is Nutrition? What Are Nutrients? Units of Energy Why we need energy? Maintaining energy balance Daily energy requirements Calorie Requirements for Different
Module 1 An Overview of Nutrition Module 2 What is Nutrition? What Are Nutrients? Units of Energy Why we need energy? Maintaining energy balance Daily energy requirements Calorie Requirements for Different
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Part 2: The Carbohydrates
 Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Part 2: The Carbohydrates I Types of Carbohydrates If someone told you "My carbohydrate intake is too high", what would you assume about what they're eating? A. SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATES:
Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Part 2: The Carbohydrates I Types of Carbohydrates If someone told you "My carbohydrate intake is too high", what would you assume about what they're eating? A. SIMPLE CARBOHYDRATES:
a. This is the same as for the general public, but people with diabetes, like the rest of the public, often eat more salt than they need.
 a. This is the same as for the general public, but people with diabetes, like the rest of the public, often eat more salt than they need. b. Putting this all together - cake, rice, bread, and fried chicken
a. This is the same as for the general public, but people with diabetes, like the rest of the public, often eat more salt than they need. b. Putting this all together - cake, rice, bread, and fried chicken
NUTRITION. What determines a diet? What does our body need? Sources of Carbohydrates. Carbohydrates 10/01/2012
 Movie: Nutrition and Digestive Health Eating for your future! NUTRITION Questions to Answer: What eating habits can affect the way our digestive system works? Give THREE examples and explain each example
Movie: Nutrition and Digestive Health Eating for your future! NUTRITION Questions to Answer: What eating habits can affect the way our digestive system works? Give THREE examples and explain each example
Lipids, pt. 1. Feb. 3, Bio 28: Nutrition Instructor: Paul Nagami Laney College
 Lipids, pt. 1 Feb. 3, 2014 Bio 28: Nutrition Instructor: Paul Nagami Laney College Today s Agenda Reminders + Administrative Details What Are Lipids? Chemistry and Types of Lipids Fatty Acids Saturated
Lipids, pt. 1 Feb. 3, 2014 Bio 28: Nutrition Instructor: Paul Nagami Laney College Today s Agenda Reminders + Administrative Details What Are Lipids? Chemistry and Types of Lipids Fatty Acids Saturated
Diabetes and Heart Disease
 Diabetes and Heart Disease People with diabetes are at a higher risk for developing heart attacks and stroke than people who do not have diabetes. Adults with diabetes are 2 to 4 times more likely to have
Diabetes and Heart Disease People with diabetes are at a higher risk for developing heart attacks and stroke than people who do not have diabetes. Adults with diabetes are 2 to 4 times more likely to have
Answering the question- Why Should You Care What You Are Eating???
 Answering the question- Why Should You Care What You Are Eating??? Never eat more than you can lift. - Miss Piggy Portion Distortion 6 Main Nutrients Vitamins Minerals Water Carbohydrates Protein Fat Keep
Answering the question- Why Should You Care What You Are Eating??? Never eat more than you can lift. - Miss Piggy Portion Distortion 6 Main Nutrients Vitamins Minerals Water Carbohydrates Protein Fat Keep
