Hyperlipidemia as a risk factor for ischaemic stroke Khan MRK
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Turner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hyperlipidemia as a risk factor for ischaemic stroke Khan MRK The ORION Medical Journal 2004 Sep;19: Introduction Stroke is the third commonest cause of death after ischaemic heart disease cancer in developed countries is responsible for a large proportion of physical disability l. WHO defined stroke as rapidly developing clinical signs of focal (at times global) disturbance of cerebral function, lasting more than 24 hrs, or leading to death with no apparent cause other than that of vascular origin 2. The main types of stroke their relative occurrences are: Ischaemic stroke- 85% & Haemorrhagic stroke- 15% The ischaemic stroke is the resultant effect of the occlusion of the cerebral blood vessels by thrombus or embolus, non-atheromatous diseases of the vessel wall, e.g. collagen diseases vasculitis, diseases of the blood e.g. coagulopathies haemoglobinopathies, decreased cerebral perfusion due to shock of any cause cardiac dysrhythmias which leads to infarction of brain. Haemorrhagic stroke results from rupture of blood vessels as rupture of Charcoat-Bowchard aneurysm in hypertension, congenital aneurysm or artereriovenous malformation (AVM) 3. Stroke ischaemic heart disease share important risk factors such as age, hypertension, diabetes cigarette smoking 4. Although serum cholesterol is a strong consistent risk factors for coronary heart disease, its importance in stroke remains controversial as serum cholesterol concentration is strongly related to death from ischaemic stroke but not from intracerebral or subarachnoid haemorrhage rather men in the lowest category of serum cholesterol (4.14 mmol/l= 160 mg/dl) had higher death rates from both intracerebral subarachnoid heamorrhage than other men Dr. Md Rezaul Karim Khan, MBBS, FCPS (Med), MD (Neurology) Associate Professor, Dept. of Neurology, BSMMU The higher the LDL level or, LDL cholesterol level, the higher the coronary heart disease risk HDL cholesterol is inversely related 6-7. Rossner et al in a study emphasized that the importance of a low HDL concentration as an important independent risk factor for ischaemic stroke in the young adult 8. Based on six years of follow up evaluations of the Framingham, Mass, men women aged 49 to 82 years, it was found that a low density lipoprotein (LDL). cholesterol concentration with a statistically significant excess of stroke in women of deaths from non-coronary heart diseases in both sexes 7. Iso et al in a study concluded that there is an inverse relationship between the serum cholesterol level the risk of death from haemorrhagic stroke in middle aged American men, but that its public health impacts is overwhelmed by the positive association of higher cholesterol level with death from nonhaemorrhagic stroke total cardiovascular disease 9, Quizibash et al in a study of TIA ischaemic stroke concluded that fibrinogen lipids are important risk factors for ischaemic stroke. The pattern of changes mirrors that found in ischaemic heart disease l0. linderstrom et al in a study found total cholesterol as positively associated with ischaemic stroke but only for levels > 8 mmol/l, corresponding to the upper 5% of the distribution in the study population. For lower plasma cholesterol values the relative risk remained nearly constant. Plasma triglyceride concentration was significantly associated with a risk of ischaemic events, there was a negative log linear association between HDL cholesterol ischaemic stroke. There was no indication that the effects of plasma lipids were different in women men 11. Tell et al in a review of more than 20 publications a relation was sought between plasma lipid lipoprotein concentrations cerebrovascular
2 atheroscleros leads to the general conclusion that such a relation exists that is stronger in older than in younger individuals 12. There is no doubt that increasing levels of total plasma cholesterol LDL-cholesterol to, a lesser extent, decreasing levels of HDL - cholesterol, are strong risk factors for coronary heart disease The relationship between cholesterol or, lipid fractions stroke is less clear-cut but there is almost certainly some association 15. There is a study which show hyperlipidaemia as risk factor for Ischemic stroke 16 presence of hypercholesterolaemia in higher higher middle class Bangladeshi population 17. Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis global in distribution, the principal cause of the heart attack, stroke gangrene of the extremities is responsible for 50% of all mortality in the USA, Europe Japan 18. Atherosclerosis is a disease primarily of the elastic arteries (e.g. aorta, carotid, iliac arteries) large medium sized muscular arteries (e.g. coronary popliteal arteries) although any artery may be affected, which is a progressive disease that starts in childhood 19. The basic lesion- The atheroma, or fibrofatty plaque-consists of a raised focal plaque within the intima, having a core of lipid (mainly cholesterol cholesterol esters) a covering fibrous cap. Atheromas are sparsely distributed at first, but as the disease advances, they become more more numerous, sometimes covering the entire circumference of severely affected arteries. As the plaque increase in size, they progressively encroach on the lumen of the artery as well as the subjacent media. Consequently, in small arteries, thrombus are occlusive compromising blood flow to distal organs, causing ischaemic injury, but in large arteries they are destructive weakening the affected vessel wall, causing aneurysm or rupture or favouring thrombosis. Moreover, extensive atheromas are friable often yields emboli of their grumous contents into the distal circulation (atheroemboli). Epidemiological studies indicate that there are several risk factors of atherosclerosis e.g. age, sex, diet, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolaemia, cigarette smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, type A personality high carbohydrate intake 19. Among the risk factors, hypercholesterolaemia hypertriglyceridemia are important. The biologically important lipids are the fatty acids their derivatives, the neutral fats (triglycerides), the phospholipids related compounds the sterols (cholesterol its derivatives). The lipids are hydrophobic substances cannot circulate in the plasma in free form. The free fatty acids are bounded to albumin whereas, cholesterol, phospholipids, triglycerides are transported in the form of lipoprotien complexes. There are six families of lipoprotein, e.g. chylomicrons, chylolmicron remnants, very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate density lipoprotein (IDL), low density lipoprotein (LDL) high density lipoprotein (HDL) 20. A subject of great interest is the role of the cholesterol in the aetiology course of atherosclerosis. It is characterized by infiltration of cholesterol appearance of foam cells in the intima growth factors that produces proliferative lesions. The normal range for plasma cholesterol is said to be mg/dl, but it is now clear that there is a tight, positive correlation between the death rate from ischaemic heart disease plasma cholesterol levels above 180 mg/dl. Furthermore, it is now clear that lowering plasma cholesterol by diet drugs slows may even reverse the progression of atherosclerotic lesions the complications they cause 21. Plasma cholesterol levels are elevated by diet rich in cholesterol saturated fats, such as egg yolk, animal fats, butter.
3 Hyperlipidaemia Hyperlipidaemia is a major public health issue in the developed world. It is increasingly being recognized as a health problem in developing countries including Bangladesh. Hyperlipidaemia is such a disorder which require life-long monitoring, dietary manipulation, often drug therapy. Effective strategies for assessment lipid control are being established 22. The term hyperlipidaemia refers to conditions with raised levels of plasma cholesterol, triglyceride low HDL. Hyperlipidaemia may be primary due to a number of inherited conditions or secondary. The cause may vary but the result is often an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Lipid metabolism can be influenced by both genetic environment factors in majority of cases of hyperlipidaemia reflect interplay between the two. A definition of the condition The desirable upper limit for total plasma cholesterol varies in different countries. A WHO report a multidisciplinary workshop have considered population means of mmol/l respectively. The incentive of seeking a lipid lowering regimen of increased effectiveness is the acceptance by many investigators that desirable cholesterol levels are considerably lower than those traditionally assumed. It has been observed in our population that the serum cholesterol level in higher higher middle social classes are within the range when intervention to reduce is essential 17. A practical approach to treating those at increased risk of cardiovascular disease for people who have a plasma cholesterol level more than 6.7 mmol/l or fasting triglyceride greater than 2 mmol/l. Plan of investigation Hyperlipidaemia is often classified by the clinical signs as corneal arcus, xanthelesma, tendon xanthomata, indicating raised LDL with or without raised VLDL Tg, family history, total cholesterol TG levels, observation of stored plasma for opalescence. Visual inspection of the stored serum involves subjective judgment but it is highly informative. Clear serum most often indicated a normal lipid pattern or hypercholesterolemia (IIa). Uniform lactescence indicates the presence of endogenous hypertriglyceridemia (Type IV/IIB). A creamy layer at the meniscus, with lactescent subnatant indicates endogenous hypertriglyceridemia with chylomicra (Type V/III), A lactescent or creamy later floating at the meniscus with a clear subnatant, Chylomicronaemia (Type V). Table 1: Classification of hyperlipidaemia The redrikson/ WHO classification of hyperlipoproteinaemia 23 Type Lipoprotein increased Lipids increased I Chylomicrons IIa LDL Cholesterol IIb III LDL VLDL beta-vldl (=IDL+chylomicron remnants) Cholesterol Cholesterol IV VLDL V Chylomicrons VLDL Cholesterol Secondary hyperlipidaemia Some of the common causes are diabetes mellitus, alcohol excess, nephrotic syndrome, hypothyroidism, renal failure, obesity. Correction of the underlying causes normalize lipid levels. Plan for diagnosis Hyperlipidaemia is usually asymptomatic but it may be revealed through a history of premature vascular disease in patients or their families. Physical signs Corneal arcus, xanthelesma, tendon xanthoma, planar xanthomas usually indicate raised LDL with or without VLDL TG. Eruptive xanthomas: Marked increased in VLDL TG Chylo (Type IV/V), yellowish
4 discoloration of palmar creases tuboeruptive xanthoma on knees or elbow: Type III hyperlipidaemia. Screening Screening for hyperlipidaemia should begin no later than age 35 for men age 45 for women. Individuals with additional risk factors should be screened earlier. If total cholesterol is less than 5.2 mmol/l no further analysis unless there is patient with coronary heart disease or bad family history. If the value is more than that other abnormalities are suspected, then a fasting sample for cholesterol, triglyceride HDL cholesterol may be done. Goals for therapy The strategy for treatment depend on desirable level lipids. A guideline has been forwarded by National Cholesterol Education Programme (1997) American Diabetic Association (1998). Table-2: Desired levels of cholesterol Total Cholesterol LDL HDL TG Management Overall assessment plan Step1 Step2 Step3 Step4 Step5 Step6 <5.2 mmol/l (200mg/dl) <2.6 mmol/l (100 mg/dl) if there is IHD <3.35 mmol/l (130 mg/dl) for all male>0.9 mmol/l (35 mg/dl) female 1.1 mmol/l (45 mg/dl) <1.7 mmol/l (150 mg/dl) desirable >2.3 mmol/l (200 mg/dl) acceptable Define the lipid abnormality Assess other atherosclerotic risk factors. Investigate treat secondary causes of hyperlipidaemia Family screening Repeat blood lipid levels Establish goals for therapy Initial diet therapy- Iow in saturated fats energy with high in vegetables fibres should continue for at least 12 weeks when lipid values are repeated. Drug therapy is indicated when total cholesterol level is 6.5 mmol/l or more after the diet therapy (at least 12 weeks). Drug therapy is life long. There are four classes of lipid altering agents in wide use: bile acid binding agents (resins), niacin, fibrates HMG CoA reductase inhibitors 24,25. In conclusion, hyperlipidemia is a major risk factor for coronary artery disease ischaemic stroke as well. So awareness should be created among the general population regarding its dietary control, physical exercise if needed drug therapy to reduce the morbidity mortality from atherosclerotic vascular disease. References 1. Allen CMC, lueck C]. Diseases of the nervous system. In: Haslette C, Chilvers ER, Hunter JM, Boon NA, editors. Davidson's principles practice of medicine. Churchillliving stone 1999; Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre stroke register -a preliminary report Bull world Health Organ 1976;54: lindsay KW, Bone I, Call cutter R. Neurology 3rd ed. Churchilllivingstone 1976; Dyken Ml, wolf PA, Barnett H, Berganj, Hasswk, Kanel W B et al. Risk factors in stroke. A statement for physicians by subcommittee on risk factors for stroke of the stroke council. Stroke 1984;15: Marmot MG, Poulter NR. Primary prevention of stroke. lancet 1992; 339: Miller NE. Forde OH, Thelle DS, Mjos OD. High density lipoprotein coronary heart disease: A prospective case- control study. lancet 1977;1: Gordon T. Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Dawber TR. lipoproteins, Cardiovascular disease death: The Framingham study. Arch Intern Med 1981;141:
5 8. Rossner S, Kjellin KG, Mettinger Kl. Normal serum cholesterol but low HDl cholesterol concentration in young patients with ischaemic cerebrovascular disease. lancet 1978; 1: Iso H, Jacobs jr. DR, Wentworth D, Neaton jd, Cohen jd. Serum cholesterol. levels six years mortality from stroke in 350,977 men screened for the multiple risk factor intervention trial. N Engl J Med. 1989; 320: Quizibash N, jones L, Warlow C, Mann ]. Fibrinogen lipid concentrations as risk factors of transient ischaemic attacks minor ischaemic stroke. BMI 1991;303: Lindenstrom E, Boysen G, Nyboe I. Influence of total cholesterol, High density lipoprotein cholesterol triglycerides on risk of cerebrovascular disease: Copenhagen city heart study. BMI 1994; 309: Tell GS, Philos Dr, Crouse IR, Furberg CD. Relation between blood lipids, lipoprotein Cerebrovascular disease -a review. Stroke 1988;19: Martin M], Hulley SB, Browner WS, Kuller LH, Wentworth D. Serum cholesterol, Blood pressure mortality: Implications from a cohort of men. Lancet 1986;2: Pocock SJ, Sharper AG, Phillips AN. Concentrations of High density lipoprotein cholesterol triglyceride total cholesterol in ischaemic heart disease.bmj 1989;298: Quizibash N, Dully SW, Warlow C, Mann I. Lipids are risk factors for ischaemic stroke: Over view review. Cerebrovasc Dis 1992; 2: Khan MRK. Relationship between blood lipids, lipoproteins ischaemic stroke. MD (Neurology thesis), Dhaka University, Chowdhury S, Huda AMS. Study on serum cholesterol level in apparently healthy persons of different socio-economic groups in Dhaka. Bangladesh Medical lournal1979;7: Ross R. The Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990's. Nature 1993; 362: Schoen FI. Blood vessels. In: Cotran RS, Kumar V, Robbins SL, Schoen FJ. editor.robbins Pathologic basis of disease. WB saunders company, 1994; Ganong WF. Review of Medical Physiology. 19th ed. Prentice -Hall International, Inc 1999: Peto R, Yusuf S, Collins R.Cholesterol level trials in their epidemiological context.circulation 1985;72(Suppl.111): Man I, Ball M. Hyperlipidaemia. Medicine International 1985; 6: Durrington PN. Lipid lipoprotein disorders. In: Weatheral DL, Ledingham ]GG, Warrel DA editors. Oxford University press. UK, 1996: Expert panel on cholesterol education program of National heart, Lung Blood Institute, Bethesda. Cholesterol -adult treatment panel report. Arch Intern Med.1988;148: Chowdhury S. Hyperlipidaema. Continuing medical education lecture notes, BCPS 1999.
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Hyperlipidemia. Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi
 Hyperlipidemia Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi Outline The story of lipids Definition of hyperlipidemia Classification of hyperlipidemia Causes of hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia Prepared by : Muhannad Mohammed Supervisor professor : Dr. Ahmed Yahya Dallalbashi Outline The story of lipids Definition of hyperlipidemia Classification of hyperlipidemia Causes of hyperlipidemia
Smoking and Ischemic Stroke
 Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience 2008; Vol. 24 (1) : 50-54 Smoking and Ischemic Stroke MD JALAL UDDIN 1, BADRUL ALAM MONDOL 2, SHAHRUKH AHMED 3, AKM ANWAR ULLAH 4, MA JABBAR 5, QUAZI DEEN MOHAMMAD 6
Bangladesh Journal of Neuroscience 2008; Vol. 24 (1) : 50-54 Smoking and Ischemic Stroke MD JALAL UDDIN 1, BADRUL ALAM MONDOL 2, SHAHRUKH AHMED 3, AKM ANWAR ULLAH 4, MA JABBAR 5, QUAZI DEEN MOHAMMAD 6
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPID DISORDERS
 THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPID DISORDERS Hormonal regulation INSULIN lipid synthesis, lipolysis CORTISOL lipolysis GLUCAGON lipolysis GROWTH HORMONE lipolysis CATECHOLAMINES lipolysis LEPTIN catabolism
THE CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY OF LIPID DISORDERS Hormonal regulation INSULIN lipid synthesis, lipolysis CORTISOL lipolysis GLUCAGON lipolysis GROWTH HORMONE lipolysis CATECHOLAMINES lipolysis LEPTIN catabolism
The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India
 eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
MMBS, MMED (Path),MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM
 Dr Mere Kende MMBS, MMED (Path),MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM Lecturer- SMSH Brief Overview of Lipids What is dyslipidemia? Classification of hyperlipidemia Primary vs secondary hyperlipidemia Hypercholesterolaemia
Dr Mere Kende MMBS, MMED (Path),MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM Lecturer- SMSH Brief Overview of Lipids What is dyslipidemia? Classification of hyperlipidemia Primary vs secondary hyperlipidemia Hypercholesterolaemia
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
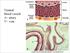 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Lipids Testing
 Previously Listed as Edit 12 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol
Previously Listed as Edit 12 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
THE BLOOD VESSELS. Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department.
 THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
THE BLOOD VESSELS Manar hajeer, MD University of Jordan Faculty of medicine, pathology department. Vascular pathology: 1- Narrowing or complete obstruction of vessel lumina, either progressively (e.g.,
ATP III (Adult Treatment Panel III) CLASSIFICATION C IN ADULTS
 LABORATORY AND RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS S R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty RISK FACTORS FOR CHD Clinical Risk Factors Laboratory Risk Factors MAJOR CLINICAL RISK
LABORATORY AND RISK FACTORS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS S R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty RISK FACTORS FOR CHD Clinical Risk Factors Laboratory Risk Factors MAJOR CLINICAL RISK
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
JMSCR Vol 3 Issue 12 Page December 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i12.07 Study of Lipid Profile in Ischemic Cerebrovascular
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i12.07 Study of Lipid Profile in Ischemic Cerebrovascular
Understanding Cholesterol
 Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke. Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital
 Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital Outline Why are we interested in cholesterol What is a heart attack and how does it
Cholesterol, Heart Attack and Stroke Dr Tai E Shyong Consultant Department of Endocrinology Singapore General Hospital Outline Why are we interested in cholesterol What is a heart attack and how does it
Role of dyslipidaemia in cardiovascular diseases and the therapeutic benefits by the appropriate drugs Banoo H
 Role of dyslipidaemia in cardiovascular diseases and the therapeutic benefits by the appropriate drugs Banoo H Introduction Coronary artery disease is an important cause of mortality and mor- bidity in
Role of dyslipidaemia in cardiovascular diseases and the therapeutic benefits by the appropriate drugs Banoo H Introduction Coronary artery disease is an important cause of mortality and mor- bidity in
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension.
 2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
Guidelines on cardiovascular risk assessment and management
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement L), L5 L10 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui079 Guidelines on cardiovascular risk assessment and management David A. Wood 1,2 * 1 Cardiovascular Medicine
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement L), L5 L10 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui079 Guidelines on cardiovascular risk assessment and management David A. Wood 1,2 * 1 Cardiovascular Medicine
CONTRIBUTING FACTORS FOR STROKE:
 CONTRIBUTING FACTORS FOR STROKE: HYPERTENSION AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA Melissa R. Stephens, MD, FAAFP Associate Professor of Clinical Sciences William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine LEARNING
CONTRIBUTING FACTORS FOR STROKE: HYPERTENSION AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA Melissa R. Stephens, MD, FAAFP Associate Professor of Clinical Sciences William Carey University College of Osteopathic Medicine LEARNING
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Dyslipidaemia
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Dyslipidaemia This guideline applies to patients with significantly abnormal lipid profiles, which may be primary (genetic), secondary to other diseases
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Dyslipidaemia This guideline applies to patients with significantly abnormal lipid profiles, which may be primary (genetic), secondary to other diseases
Introduction. Risk factors of PVD 5/8/2017
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE Dr. Muhamad Zabidi Ahmad Radiologist and Section Chief, Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine Section, Advanced Medical and Dental
Hypertriglyceridemia. Ara Metjian, M.D. Resident s Report 20 December 2002
 Hypertriglyceridemia Ara Metjian, M.D. Resident s Report 20 December 2002 Review of Lipids Chylomicrons (CM): Dietary lipids absorbed through the GI tract are assembled intracellularly into CM. Very Low
Hypertriglyceridemia Ara Metjian, M.D. Resident s Report 20 December 2002 Review of Lipids Chylomicrons (CM): Dietary lipids absorbed through the GI tract are assembled intracellularly into CM. Very Low
Total risk management of Cardiovascular diseases Nobuhiro Yamada
 Nobuhiro Yamada The worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases (WHO) To prevent cardiovascular diseases Beyond LDL Multiple risk factors With common molecular basis The Current Burden of CVD CVD is responsible
Nobuhiro Yamada The worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases (WHO) To prevent cardiovascular diseases Beyond LDL Multiple risk factors With common molecular basis The Current Burden of CVD CVD is responsible
Dyslipidemia. Team Members: Laila Mathkour, Khalid Aleedan, Bayan Al-Mugheerha, Fatima AlTassan
 Dyslipidemia Objectives: Not given. Team Members: Laila Mathkour, Khalid Aleedan, Bayan Al-Mugheerha, Fatima AlTassan Team Leader: Amal Alshaibi Revised By: Yara Aldigi and Basel almeflh Resources: 435
Dyslipidemia Objectives: Not given. Team Members: Laila Mathkour, Khalid Aleedan, Bayan Al-Mugheerha, Fatima AlTassan Team Leader: Amal Alshaibi Revised By: Yara Aldigi and Basel almeflh Resources: 435
Learning Objectives. Cholesterol and Lipids in Kids: It s a Matter of the Heart. Is Atherosclerosis a Pediatric Disease?
 Scott J. Soifer, MD Professor and Vice Chair Department of Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Cholesterol and Lipids in Kids: It s a Matter of the Heart
Scott J. Soifer, MD Professor and Vice Chair Department of Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Cholesterol and Lipids in Kids: It s a Matter of the Heart
Lipids Testing
 190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol esters and free cholesterol,
190.23 - Lipids Testing Lipoproteins are a class of heterogeneous particles of varying sizes and densities containing lipid and protein. These lipoproteins include cholesterol esters and free cholesterol,
1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver)
 I. TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF CHOLESTEROL Choose the correct answer. 1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver) 2. Only
I. TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE OF CHOLESTEROL Choose the correct answer. 1. Most of your blood cholesterol is produced by: a. your kidneys b. your liver c. your pancreas d. food consumption (Your liver) 2. Only
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA
 MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA HIGH BLOOD CHOLESTEROL IN ADULTS GUIDELINE Molina Healthcare of California has adopted the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel
MOLINA HEALTHCARE OF CALIFORNIA HIGH BLOOD CHOLESTEROL IN ADULTS GUIDELINE Molina Healthcare of California has adopted the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel
Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies
 Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society
Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic and clinical studies A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society
Chapter 18. Diet and Health
 Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
An educational booklet for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia DR. LEIV OSE
 An educational booklet for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia DR. LEIV OSE CONTENTS WHAT WILL YOU LEARN FROM THIS BOOKLET? You will learn about Familial Hypercholesterolemia, its cause, and the
An educational booklet for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia DR. LEIV OSE CONTENTS WHAT WILL YOU LEARN FROM THIS BOOKLET? You will learn about Familial Hypercholesterolemia, its cause, and the
There are many ways to lower triglycerides in humans: Which are the most relevant for pancreatitis and for CV risk?
 There are many ways to lower triglycerides in humans: Which are the most relevant for pancreatitis and for CV risk? Michael Davidson M.D. FACC, Diplomate of the American Board of Lipidology Professor,
There are many ways to lower triglycerides in humans: Which are the most relevant for pancreatitis and for CV risk? Michael Davidson M.D. FACC, Diplomate of the American Board of Lipidology Professor,
13/09/2012. Dietary fatty acids. Triglyceride. Phospholipids:
 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES (CVD) and NUTRITION Major cause of morbidity & mortality in Canada & other developed countries e.g., majority of approved health claims on food labels relate to lowering CVD Relation
Hypertriglyceridemia: Why, When, and How to Treat. Gregory Cohn, MD, FNLA, FASPC
 Hypertriglyceridemia: Why, When, and How to Treat Gregory Cohn, MD, FNLA, FASPC DISCLOSURES Consultant to Akcea Therapeutics (in the past 12 months). OUTLINE I. Lipoproteins II. Non-HDL-C III. Causes and
Hypertriglyceridemia: Why, When, and How to Treat Gregory Cohn, MD, FNLA, FASPC DISCLOSURES Consultant to Akcea Therapeutics (in the past 12 months). OUTLINE I. Lipoproteins II. Non-HDL-C III. Causes and
Section Editor Mason W Freeman, MD
 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2015 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2015 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek
1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia:
 Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Questions: 1. Which one of the following patients does not need to be screened for hyperlipidemia: a) Diabetes mellitus b) Hypertension c) Family history of premature coronary disease (first degree relatives:
Nearly 62 million people in the. ... REPORTS... New Therapeutic Options in the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III
 ... REPORTS... New Therapeutic Options in the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Robert L. Talbert, PharmD Abstract Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a common, costly, and undertreated
... REPORTS... New Therapeutic Options in the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Robert L. Talbert, PharmD Abstract Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a common, costly, and undertreated
2016 EUROPEAN GUIDELINES ON CVD PREVENTION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
 2016 EUROPEAN GUIDELINES ON CVD PREVENTION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Massimo F Piepoli, MD, PhD, FESC, Piacenza, Italy on behalf of the 6 th Joint Task Force 2 3 Guidelines still based upon the principles of
2016 EUROPEAN GUIDELINES ON CVD PREVENTION IN CLINICAL PRACTICE Massimo F Piepoli, MD, PhD, FESC, Piacenza, Italy on behalf of the 6 th Joint Task Force 2 3 Guidelines still based upon the principles of
Blood Vessels. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Blood Vessels Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the structure and function of blood vessels. Discuss the different mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. Compare and contrast the following types
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Guidelines for Screening and Management of Dyslipidemia
 PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Policy Number: 01-09-021 SUBJECT: Guidelines for Screening and Management of Dyslipidemia EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/2008 REVIEWED/REVISED: 04/12/10, 03/17/2011, 4/10/2012,
PIEDMONT ACCESS TO HEALTH SERVICES, INC. Policy Number: 01-09-021 SUBJECT: Guidelines for Screening and Management of Dyslipidemia EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/2008 REVIEWED/REVISED: 04/12/10, 03/17/2011, 4/10/2012,
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
New Features of the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Lipid-Lowering Guidelines
 Clin. Cardiol. Vol. 26 (Suppl. III), III-19 III-24 (2003) New Features of the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Lipid-Lowering Guidelines H. BRYAN BREWER, JR, M.D. Molecular
Clin. Cardiol. Vol. 26 (Suppl. III), III-19 III-24 (2003) New Features of the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Lipid-Lowering Guidelines H. BRYAN BREWER, JR, M.D. Molecular
 Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Dyslipidemia. (Med-341)
 Dyslipidemia (Med-341) Anwar A Jammah, MD, FRCPC, FACP, CCD, ECNU. Associate Professor of Medicine Consultant Medicine, Endocrinology, Thyroid Oncology Department of Medicine, King Saud University The
Dyslipidemia (Med-341) Anwar A Jammah, MD, FRCPC, FACP, CCD, ECNU. Associate Professor of Medicine Consultant Medicine, Endocrinology, Thyroid Oncology Department of Medicine, King Saud University The
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
PREVENTION OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE IN WOMEN
 1980 to 2000: Death rate fell from: 542.9 to 266.8 per 100K men 263.3 to 134.4 per 100K women 341,745 fewer deaths from CHD in 2000 Ford ES, NEJM, 2007 47% from CHD treatments, 44% from risk factor modification
1980 to 2000: Death rate fell from: 542.9 to 266.8 per 100K men 263.3 to 134.4 per 100K women 341,745 fewer deaths from CHD in 2000 Ford ES, NEJM, 2007 47% from CHD treatments, 44% from risk factor modification
Strokes , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. hp Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Strokes Introduction A stroke or a brain attack is a very serious condition that can result in death and significant disability. This disease is ranked as the third leading cause of death in the United
Strokes Introduction A stroke or a brain attack is a very serious condition that can result in death and significant disability. This disease is ranked as the third leading cause of death in the United
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions
 Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
 Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Lipid disorders: Disorders of lipid metabolism are manifest by elevation of the plasma concentrations of the various lipid and lipoprotein fractions (total and LDL cholesterol,
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs Lipid disorders: Disorders of lipid metabolism are manifest by elevation of the plasma concentrations of the various lipid and lipoprotein fractions (total and LDL cholesterol,
Case Discussions: Treatment Strategies for High Risk Populations. Most Common Reasons for Referral to the Baylor Lipid Clinic
 Case Discussions: Treatment Strategies for High Risk Populations Peter H. Jones MD, FNLA Associate Professor Methodist DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center Baylor College of Medicine Most Common Reasons for
Case Discussions: Treatment Strategies for High Risk Populations Peter H. Jones MD, FNLA Associate Professor Methodist DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center Baylor College of Medicine Most Common Reasons for
Threshold Level or Not for Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol
 ... SYMPOSIA PROCEEDINGS... Threshold Level or Not for Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Based on a debate between Philip J. Barter, MD, PhD, FRACP, and Frank M. Sacks, MD Debate Summary As drugs, such
... SYMPOSIA PROCEEDINGS... Threshold Level or Not for Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Based on a debate between Philip J. Barter, MD, PhD, FRACP, and Frank M. Sacks, MD Debate Summary As drugs, such
OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENT
 1 This chapter outlines the main arterial and venous diseases that are likely to be seen within a vascular outpatient setting. It also highlights the role of the vascular nurse specialist wherever appropriate.
1 This chapter outlines the main arterial and venous diseases that are likely to be seen within a vascular outpatient setting. It also highlights the role of the vascular nurse specialist wherever appropriate.
 Five chapters 1. What is CVD prevention 2. Why is CVD prevention needed 3. Who needs CVD prevention 4. How is CVD prevention applied 5. Where should CVD prevention be offered Shorter, more adapted to clinical
Five chapters 1. What is CVD prevention 2. Why is CVD prevention needed 3. Who needs CVD prevention 4. How is CVD prevention applied 5. Where should CVD prevention be offered Shorter, more adapted to clinical
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Dr G R Letchuman. Clogged by Cholesterol
 Dr G R Letchuman Clogged by Cholesterol Main message Cholesterol management is all about reducing risk of CV events vs the side effects, hassle and cost of drugs News that it is no longer important to
Dr G R Letchuman Clogged by Cholesterol Main message Cholesterol management is all about reducing risk of CV events vs the side effects, hassle and cost of drugs News that it is no longer important to
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
KEY COMPONENTS. Metabolic Risk Cardiovascular Risk Vascular Inflammation Markers
 CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Cholesterol (blood, plasma, serum)
 1 Cholesterol (blood, plasma, serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cholesterol (plasma; also blood, serum) 1.2 Alternative names 2,15-dimethyl-14-(1,5-dimethylhexyl)tetracyclo[8.7.0.0
1 Cholesterol (blood, plasma, serum) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Cholesterol (plasma; also blood, serum) 1.2 Alternative names 2,15-dimethyl-14-(1,5-dimethylhexyl)tetracyclo[8.7.0.0
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy
 Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
Hypertriglyceridemia, Inflammation, & Pregnancy Richard L. Nemiroff, MD, FACOG, NLA Professor, Clinical Gynecology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Philadelphia, PA Disclosure of
10/1/2008. Therapy? Disclosure Statement
 What s New in Lipid Therapy? Brooke Hudspeth, PharmD Diabetes Care Kroger Pharmacy Disclosure Statement In accordance with policies set forth by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education
What s New in Lipid Therapy? Brooke Hudspeth, PharmD Diabetes Care Kroger Pharmacy Disclosure Statement In accordance with policies set forth by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education
JUSTUS WARREN TASK FORCE MEETING DECEMBER 05, 2012
 SAMUEL TCHWENKO, MD, MPH Epidemiologist, Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section; Division of Public Health NC Department of Health & Human Services JUSTUS WARREN TASK
SAMUEL TCHWENKO, MD, MPH Epidemiologist, Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section; Division of Public Health NC Department of Health & Human Services JUSTUS WARREN TASK
Pediatric Dyslipidemia: Angela Gooden MSN, RN, CPNP- AC/PC, Texas Children s Hospital, Pediatric Cardiology
 Pediatric Dyslipidemia: Angela Gooden MSN, RN, CPNPAC/PC, Texas Children s Hospital, Pediatric Cardiology Objectives Define pediatric dyslipidemia Describe the association between pediatric dyslipidemia
Pediatric Dyslipidemia: Angela Gooden MSN, RN, CPNPAC/PC, Texas Children s Hospital, Pediatric Cardiology Objectives Define pediatric dyslipidemia Describe the association between pediatric dyslipidemia
Dyslipidaemia. Dr NM Oosthuizen Dept of Chemical Pathology SA
 Dyslipidaemia Dr NM Oosthuizen Dept of Chemical Pathology SA13 2014 Endogenous and exogenous pathways Endogenous Exogenous Reverse cholesterol transport Dyslipidaemias Causes can be primary or secondary
Dyslipidaemia Dr NM Oosthuizen Dept of Chemical Pathology SA13 2014 Endogenous and exogenous pathways Endogenous Exogenous Reverse cholesterol transport Dyslipidaemias Causes can be primary or secondary
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Maintain Cholesterol
 Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
Maintain Cholesterol What is Cholesterol? Cholesterol is a Lipid Molecule that has a waxy appearance and is found in every cell of the body and has some important natural functions. It is manufactured
!!! Aggregate Report Fasting Biometric Screening CLIENT!XXXX. May 2, ,000 participants
 Aggregate Report Fasting Biometric Screening CLIENTXXXX May 2, 2014 21,000 participants Contact:404.636.9437~Website:www.atlantahealthsys.com RISK FACTOR QUESTIONNAIRE Participants Percent Do not exercise
Aggregate Report Fasting Biometric Screening CLIENTXXXX May 2, 2014 21,000 participants Contact:404.636.9437~Website:www.atlantahealthsys.com RISK FACTOR QUESTIONNAIRE Participants Percent Do not exercise
Normal ldl cholesterol levels for men over 50
 Normal ldl cholesterol levels for men over 50 Aug 14, 2017. Thus, the healthy bad cholesterol numbers for younger people are significantly lower because the risk charts figure their numbers will rise.
Normal ldl cholesterol levels for men over 50 Aug 14, 2017. Thus, the healthy bad cholesterol numbers for younger people are significantly lower because the risk charts figure their numbers will rise.
Topic 11. Coronary Artery Disease
 Topic 11 Coronary Artery Disease Lipid metabolism http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7372495.stm Sterol Metabolism and Coronary Artery Disease Big Picture: Exogenous Cholesterol and Fat Metabolism Fats-Triglycerides
Topic 11 Coronary Artery Disease Lipid metabolism http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/7372495.stm Sterol Metabolism and Coronary Artery Disease Big Picture: Exogenous Cholesterol and Fat Metabolism Fats-Triglycerides
Classification. Etiology
 Dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia is the elevation of plasma cholesterol, triglycerides (TGs), or both, or a low high-density lipoprotein level that contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. Causes may
Dyslipidemia Dyslipidemia is the elevation of plasma cholesterol, triglycerides (TGs), or both, or a low high-density lipoprotein level that contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. Causes may
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) Term-End Examination June, 2015
 No. of Printed Pages : 20 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL 0 CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) Term-End Examination June, 2015 MCC-006 : CARDIO VASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note :
No. of Printed Pages : 20 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL 0 CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) Term-End Examination June, 2015 MCC-006 : CARDIO VASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note :
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention
 CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA. Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD
 ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
DYSLIPIDEMIA PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 DYSLIPIDEMIA PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Know normal cholesterol levels Understand what the role
DYSLIPIDEMIA PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Know normal cholesterol levels Understand what the role
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Arterial Diseases Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology Disease Spectrum Arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
EFFECT OF NICARDIPINE ON FASTING PLASMA LIPIDS AND APOLIPOPROTEINS IN MALE NEW ZEALAND WHITE RABBITS. Kamsiah Jaarin, Nafeeza MI*
 REVIEW ARTICLE Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 2, July 1999 (5-11) EFFECT OF NICARDIPINE ON FASTING PLASMA LIPIDS AND APOLIPOPROTEINS IN MALE NEW ZEALAND WHITE RABBITS Kamsiah Jaarin,
REVIEW ARTICLE Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 2, July 1999 (5-11) EFFECT OF NICARDIPINE ON FASTING PLASMA LIPIDS AND APOLIPOPROTEINS IN MALE NEW ZEALAND WHITE RABBITS Kamsiah Jaarin,
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes
 Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Disease- The Challenge in patients with diabetes Ashok Handa Reader in Surgery and Consultant Surgeon Nuffield Department of Surgery University of Oxford Introduction Vascular
ARE YOU AT RISK OF A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE? Understand How Controlling Your Cholesterol Reduces Your Risk
 ARE YOU AT RISK OF A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE? Understand How Controlling Your Cholesterol Reduces Your Risk CONSIDER YOUR HEART HEALTH: REDUCE YOUR CHOLESTEROL Uncontrolled or continuous high cholesterol
ARE YOU AT RISK OF A HEART ATTACK OR STROKE? Understand How Controlling Your Cholesterol Reduces Your Risk CONSIDER YOUR HEART HEALTH: REDUCE YOUR CHOLESTEROL Uncontrolled or continuous high cholesterol
Heart Disease Genesis
 Heart Disease Genesis The Ultimate Lecture on CAD origins Petr Polasek MD FRCPC FACC Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
Heart Disease Genesis The Ultimate Lecture on CAD origins Petr Polasek MD FRCPC FACC Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
A N A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T. Understanding and Managing Your. Triglycerides
 A N A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Understanding and Managing Your Triglycerides What are Triglycerides? Triglycerides are one of several types of fat in your body, and the most common of them all. Along
A N A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Understanding and Managing Your Triglycerides What are Triglycerides? Triglycerides are one of several types of fat in your body, and the most common of them all. Along
The health benefits of shellfish: What should we be promoting? Professor Bruce Griffin Nutrition Division Faculty of Health & Medical Sciences
 The health benefits of shellfish: What should we be promoting? Professor Bruce Griffin Nutrition Division Faculty of Health & Medical Sciences What should we be promoting? Define health benefits in terms
The health benefits of shellfish: What should we be promoting? Professor Bruce Griffin Nutrition Division Faculty of Health & Medical Sciences What should we be promoting? Define health benefits in terms
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
