Lysosomes and lysosomal disorders
|
|
|
- Godfrey Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lysosomes and lysosomal disorders
2 Eukaryotic cell Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition
3 Lysosomes Image M.H. Degradation of macromolecules Calcium store Cholesterol homeostasis Lysosomal exocytosis - plasma membrane repair Cell death
4 Late-endosomal Intralumenal vesicles are formed from domains on the endosome membrane Ubiquitylated Ubiquitylatedmembrane membraneproteins proteinsare aresorted sortedinto intoendosomal endosomalmembrane membrane domains, which sequestrate to form intralumenal vesicles domains, which sequestrate to form intralumenal vesicles Multivesicular Multivesicularbodies bodies==maturing maturingendosomes endosomeswith withintralumenal intralumenalvesicles vesicles Alberts et al. Molecular cell biology
5 Lysosomal ( storage ) diseases Deficiencies of proteins from the lysosomal system lead to storage of material in lysosomes
6 Lysosomal ( storage ) diseases Disorders of transport of enzymes into lysosome or disorders of substrate transport (e.g. due to a disruption of vesicular transport inside the cell) can also lead to lysosomal storage
7 Lysosomal disorders Hereditary disorders associated with storage of material within the lysosomes 1. Disorders of glycan degradation mucopolysaccharidoses and glycoproteinoses 2. Lipidoses 3. Proteinoses 4. Disorders of lysosomal transport of metabolites 5. Disorders of transport of proteins into lysosomes
8 Lysosomes
9 Lysosomes Lysosomes are the principal sites of intracellular degradation of macromolecules about 40 types of acid hydrolases proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, lipases, phospholipases, phosphatases, and sulfatases. acidic ph optimum protection of cytosol (neutral ph) acidic environment (ph 4.5-5) maintained by vacuolar H+ ATPase H+ gradient drives transport of small molecules across the membrane lysosomal membrane proteins are highly glycosylated protection from proteolytic attack provide interface for various lysosomal functions
10 Maturation of lysosomes Late endsosome Endolysosome Hydrolase Endolumenal vesicle Phagosome (autophagosome) Lysosome adapted from Alberts et al. Molecular cell biology
11 Lysosomes and vacuolar transport endocytosis phagocytic vacuole EE M6PR scavenger pathway chaperone mediated autophagy LE LY exocytosis M6PR NC secretory vesicle Golgi autophagic vacuole Image M.H. EE early endosome LE late endosome M6PR mannosa-6-phosphate receptor LY lysosome NC - nucleus
12 LYSOSOMES that KILL!!! and their relatives
13 Secretory lysosomes /Lysosomerelated organelles In some cells (often of haematopoietic origin) there are organelles that have properties of both lysosomes and secretory granules - acidic ph - lysosomal membrane and lumenal proteins - exocytosis in response to a stimulus Lysosome-related organelles (LRO) -lytic granules (NK cells and cytotoxic Tlymphocytes) -azurophilic granules -melanosomes - external lysosomes of osteoclasts - delta-granules in platelets
14 Lysosome-related organelles osteoclast ruffled border sealing zone H+ H + bone sealing zone H+
15 Multiple pathways deliver material to lysosomes endocytosis macropinocytosis phagocytosis EE M6PR scavenger pathway chaperone mediated autophagy LE LY exocytosis M6PR NC secretory vesicle Golgi autophagy Image M.H. EE early endosome LE late endosome M6PR mannosa-6-phosphate receptor LY lysosome NC - nucleus
16 Autophagy Macroautophagy Microautophagy Chaperone-mediated autophagy proteins containing specific signal sequence translocation of proteins driven by binding of chaperones internalization via lamp2a receptor in the lysosomal membrane Lysosomal membrane protein LAMP2 is a receptor involved in fusion of autophagic vacuoles with lysosomes
17 Autophagy is a process of self-degradation of cellular components Double-membrane autophagosomes sequester organelles or portions of cytosol and fuse with lysosomes Autophagy is upregulated in response to signals such as: starvation growth factor deprivation ER stress pathogen infection. Mizushima, Genes and Development, 2007
18 Morphology of autophagosome and autolysosome Arrows: autophagosomes Double arrows: autolysosomes/amphisomes. Arrowheads: fragments of endoplasmic reticulum inside the autophagosome Mizushima, Genes and Development, 2007
19 Import of lysosomal proteins into lysosome Soluble lysosomal proteins : mannose-6 phosphate receptor Lysosomal membrane proteins: - signals in short C-terminal tail ) - signals are recognised by adaptor proteins (AP3..) Other - glucocerebrosidase, lysosomal acid phosphatase - prosaposin - sortilin, LIMPII
20 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders
21 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders Accumulation of secondary metabolites Alterations of calcium homeostasis Free radicals and oxidative stress Neuroinflammation Abnormal autofagy
22 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders Accumulation of secondary metabolites In many lysosomal disorders are stored also metabolites unrelated to the primary defect, very often lipids or hydrophobic proteins Frequently gangliosides GM3, GM2 or cholesterol... although the protein machinery for their degradation or transport is intact Example: in some mucopolysaccharidoses (storage of polysaccharides) is in the brain present storage of glycolipids gangliosides GM2 a GM3
23 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders Alteration of calcium homeostasis Disorders of calcium homeostasis can contribute to the pathogenesis of the disease Example: Glucosylceramide: the glycolipid stored in Gaucher disease modulates the function of ryanodine receptors in neurons and leads to more prominent release of calcium from ER to cytosol In other lysosomal disorders were described different alterations of calcium homeostasis - different mechanisms
24 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders Free radicals and oxidative stress signs of increased production of free oxygen radicals and oxidative stress there is no obvious mechanism - secondary elevation of free radical production due to e.g. endoplasmic reticulum stress Oxidative stress can contribute to pathogenesis of lysosomal disorders, especially in the brain
25 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders Neuroinflammation Signs of neuroinflammation is present essentially in all lysosomal disorders with CNS involvement Activation of immune system microglia and astrocytes Similar findings are present in classic neurodegenerative disordrders Chronic glial activation in lysosomal disorders apparently contributes to neuronal damage
26 Alteration of metabolic, signalling, and transport pathways in lysosomal disorders Abnormal autophagy vacuolar mechanism for degradation of damaged organelles and long-life proteins signs of increased autophagy is present in many lysosomal disorders, can lead to cell damage and cell death the mechanism of activation of autophagy is not clerar, but may contribute to cell damage (Danon disease deficiency of LAMP2 accumulation of autophagic vacuoles)
27 Transport of soluble lysosomal proteins by mannose-6-phosphate receptors
28 Sorting of proteins containing MP6 signal The majority of soluble (luminal) lysosomal proteins is transported into lysosome via mannose-6-phosphate receptor
29 M6P signal is built on N-linked oligosaccharides of hydrolases by Glc Nac phosphotransferase in cis-golgi N-acetylglucosamine phosphotransferase (GlcNac phosphotransferase) recognises a 3-D pattern on lysosomal enzymes Hydrolase carrying M6P moiety Protective GlcNac group is enzymatically removed in transgolgi, leaving M6P exposed GlcNac GlcNac phosphotransferase GlcNac diphospho uridine Hydrolase with N-linked oligosaccharide UMP Image M.H.
30 MP6 receptors capture lysosomal enzymes by receptormediated endocytosis at plasma membrane endocytosis phagocytic vacuole EE M6PR scavenger pathway EE early endosome LE late endosome M6PR mannosa-6-phosphate receptor LY lysosome NC - nucleus chaperone mediated autophagy LE LY exocytosis M6PR NC secretory vesicle Golgi autophagic vacuole
31 Sorting of proteins containing MP6 signal protein-m6p-m6pr lysosome protein-m6p protein protein cis-golgi Secretion pathway
32 Lysosomal membrane proteins
33 Lysosomal membrane contains more than 100 proteins, majority of which have unknown function. Proteins with known function include receptors, molecules participating in vesicular transport, transporters of small molecules, vacuolar ATPase etc. Oligosaccharide chains at the inner face of lysosomal mebrane for a glycocalix protecting the membrane from the attack of hydrolases LAMP 2 (lysosomal associated membrane protein 2) is a receptor for autophagic vacuoles
34 Activators of lysosomal hydrolases
35 Exoglycosidases participating in degradation of oligosacharide moieties of glycolipids require protein activators for glycolipids with less than 3 residues
36 Activators of lysosomal hydrolases Saposins A,B,C,D deficits of saposins lead to variant forms of disorders caused by deficiencies of enzymes they activate GM2 activator activates hexosaminidase A
37
38 Overview of lysosomal disorders
39 Lysosomal enzymes 30 enzymes hereditary deficiencies of which cause human diseases lipids lipidoses, including sphingolipidoses glykosaminoglycans mucopolysaccharidoses N-glycans, oligosacharides glycoproteinoses glycogen glycogenosis type II (Pompe) proteins proteinoses
40 2006 NA c-b expanded by storage lysosomal storage disorders Ia se a MPS t e s lfa a u n=10 id a t s ase d n i f in ro osul m a u s sf. k on o n a k r u t bgl ur -glu NAc id d D i n ami c-a s o A k N u :a-gl A o fatase l C u s t a 6-sulf c A N c Gl GalNAc-6-sulfat sulfa tase GalNA c-4s u l f * atsulfatase * Nh-yaaluron * asp cetyl-aidase (hya luro ar -ga nic a ty lac cid) lg tos lu am ko ini da sa se m in id as e ase d i s o nn se a b-ma d i os n an M a NA cbgl LIPIDOSES n=9 lysosome uk os am -gl in uk id os as am e ini B -g d ase alak tosi das A ea a-neu ramin idase e ceramidas e das* i m se cera l a y s n eli acto l y a g om A g hin se p a t s lfa u yls ar mutant enzyme protein (n=30) sidase o t c la a g ylp D in I e ep th as ka tid ep id pt pr ot ein pa lm ito yl GSD IIa th ioe cid a-1 ste,4-g ra luc o si s e das e acid lip ase -glukosylceram idase * a-fukosidase pe tri NCL1,2,kong. hep a- aran LN-s id ulf ur ata on se id as e enzymopathies GLYKOPROTEINOSES n=7 hydrolases 29 transferase 1
41 N-acetyltransferase activity n=5 n=22 n=103 R412X/wt Patients Heterozygotes Controls
42
43 Fabry disease alpha-galactosidase A deficiency X-linked disease lysosomal storage of glycolipids with terminal alpha-galactose, predominantly globotriaosylceramide storage in vessel endothel, smooth muscle of the vessels, cardiomyocytes, glomerules and tubules and other cell types
44 Fabry disease clinical picture hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, arythmias chronic progressive renal disease leading to renal failure TIA, parestesias angiokeratomas, cornea verticilata X-linked disease In females the severity of phenotype depends on X-inactivation
45 Gaucher disease Lysosomal storage disorder Deficiency of glucocerebrosidase (acid beta glucosidase ) Accumulation of glucosylceramide preferentially in cells of macrophage origin (Gaucher cells) Multisystem disorder Hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, bone disease, trombocytopenia, anemia, lung infiltration In type 2 and 3 Gaucher disease: CNS disease Clinical variability, chronic progresion Type 1: chronic non-neuronopathic Type 2: acute neuronopathic Type 3: chronic neuronopathic
46 Heterozygosity or homozygosity for a mutation in the glucocerebrosidase gene is a susceptibility factor for Parkinsons disease Molecular mechanism is not clear,? tau protein transport disorder? Strong epidemiologic evidence for the association Mutant glucocerebrosidase is present in Lewy bodies in Gaucher patients with Parkinson disorder
47 Niemann-Pick type C disease Disorder of intracellular lipid trafficking, especially of cholesterol accumulation of unesterified cholesterol and glycolipids in late endosomes/lysosomes Disorder of LDL-derived cholesterolu abnormal fusion of late endosomes and lysosomes, abnormal filling of lysosomes with Ca++ Mutations in two cholesterol-transporting proteins : NPC1 and NPC2 NPC1 is more frequent (about 95% of NPC) (Note: Niemann-Pick type A and B are caused by the deficiency of acid sphingomyelinase)
48 Vanier 2010
49 Niemann-Pick disease type C Disorder of intracellular lipid traficking Neurovisceral disorder : highly variable clinical picture Prolonged neonatal jaundice of cholestasis, hepatosplenomegaly or isolated splenomegaly Later progresssive neurological disease ataxia, clumsiness, falls, spasticity, seizures, dysarthia or dysphagia tyúical signs : vertical gaze palsy, gelastic cataplexy psychiatric signs: presenile cognitive decline, dementia, paranoia (hallucinations,...)
50 Intracellular transport of LDL cholesterol
51 Function of NPC1 and NPC2 Soluble NPC2 binds LDL-derived cholesterol and transfers it to NPC1 NPC1 transfers cholesterol molecules across glycocalix at the lumenal face of the lysosome
52 Mucopolysaccharides Polysaccharides Heparan sulfate Dermatan sulfate Keratan sulfate Chondroitin sulfate
53
54
55 Mucopolysaccharidoses 11 disorders Most common : MPS I Hurler disease - deficiency of alpha-iduronidase, ARinheritance MPS II - Hunter disease - deficiency of iduronate sulfatase, Xlinked Common symptoms Progressive dementia, hepatosplenomegaly, coarse features (gargoylism), bone disease (dysostosis multiplex), corneal opacities, cardiac disease Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition
56 Mukopolysacharidosa III, MPS III Sanfilippova choroba In the first years of life normal development At 2 6 years of age prominent hyperactivity, sleep disorders, slowly progressive dementia Coarse facies, coarse hair drsné vlasy, small hepatosplenomegaly Spasticity, dementia, death usually between years of age
57
58 Activators of lysosomal hydrolases Saposins A,B,C,D deficits of saposins lead to variant forms of disorders caused by deficiencies of enzymes they activate GM2 activator activates hexosaminidase A
59
60 I-cell disease (mucolipidosis II) Disorder of transport M6P-tagged lysosomal proteins due to mutations in GlcNAC phosphotransferase increased activities of lysosomal proteins in extracellular fluid decreased activities of multiple lysosomal enzymes in lysosomes enlarged lysosomes
61 Mutations in GlcNAc transferase gene cis-golgi endoplasmické retikulum
62 Mutations in GlcNAc transferase gene lysosome protein-m6p-m6pr Proteins transported normally by M6PR are not targeted to lysosomes protein protein secretion... instead, they are secreted out of the cell. cis-golgi
63 I-cell disease Coarse facies thickening of gums small hepatomegally and splenomegally bone disease - dysostosis multiplex psychomotor delay, mental deficit elevated activities of lysosomal hydrolases in plasma, low activities in tissues Vacuolization of lymphocytes ( Inclusion cell ) = storage lysosomes
64 Figure 1 A lymphocyte with many vacuole-like inclusions (original magnification, x900). van der Meer, W et al. J Clin Pathol 2001;54: Copyright 2001 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
65 Figure 3 Electron microscopic image of lymphocytic vacuoles containing round osmiophilic structures (original magnification, x15 000). van der Meer, W et al. J Clin Pathol 2001;54: Copyright 2001 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
66
67 Danon disease LAMP2 deficiency Lamp 2 participates in fusion of lysosomes with autophagic vacuoles Cardiomyopathy - usually hypertrophic Arrythmia - typically preexcitation syndrome - WPW Intelectual disability in some patients Other symptoms X-linked disease females have usually milder phenotype Accumulation of autophagic vacuoles predominantly in cardiac and skeletal muscle
68
69 Lysosomal transporters deficiencies Cystinosis cystinosin deficiency renal disease with Fanconi syndrome renal failure renal transplantation corneal crystals, photophobia growth retardation hypothyroidism normal inteligence ocular form Sialuria sialin deficiency
70 cystine cysteamine
71 Cystinosis cystin cysteamin
72 Cystinosis
73 Disorders of lysosome-related organelle biogenesis and function A group of hereditary disorders often associated with - albinism (melanosome dysfunction) - visual impairment - bleeding tendency(platelet dysfunction) - inflammatory bowel disease - lung fibrosis - immunodeficiency - huge lysosomes in tissues Heřmanský-Pudlák,Griscelli, Chediak-Higashi syndromes heatherkirkwood.blogspot.cz
74 Diagnostics and treatment of lysosomal disorders
75 Treatment Supplementation of deficient protein Bone marrow transplantation Enzyme replacement therapy Reduction of stored substrate substrate inhibition therapy
76 Bone marrow transplantation Haematopoietic stem cell transfer Pro: In contrast to enzyme replacement therapy can influence CNS disease Con: High morbidity and mortality Lysosomal disorders Mucopolysacharidosis I Modifies natural course of the disease Early treatment can prevent neurological disease Residual disease Other MPS disorders MPS III no improvement of neurological progression Other lysosomal disorders Peroxisomal disorders X-ALD book/chapter.1.html#p13
77 Enzyme supplementation therapy Supplementation of deficient enzyme in regular infusions Gaucher disease (glucocerebrosidase) Fabry disease (alpha galactosidase A) Pompe disease (acid alpha glucosidase) MPS I (alpha iduronidase) MPS II (alpha iduronate sulfatase) MPS VI, Maroteaux-Lamy (arylsulfatase B) Niemann-Picko disease B (acid sphingomyelinase) MPS IVA, Morquio A,... Production of recombinant enzymes Genzyme, TKT, Biomarin, Shire, Inotech,...
78 Enzyme supplementation therapy in Gaucher disease Receptor-mediated endocytosis Macrophage targeted glucocerebrosidase - treatment with exoglycosidases Mannose receptor (macrophages, endothelia, liver) Regular infusions Originally glucocerebrosidase isolated from human placentas (Ceredase, Genzyme) Recombinant enzyme Cerezyme (Genzyme) Cho cells Does not cross haematoencephalic barrier High costs
79 b) Inhibition of enzymes in the metabolic pathway proximal to the metabolic block Substrate inhibition (reduction) therapy Coenzyme Apoenzyme Substrate Product
80 Substrate inhibition therapy Mutant enzymes have residual activities N-butyldeoxyjirinomycin (Zavesca) Inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase Gaucher disease, GM1 gangliosidosis
81 Diagnostics Measurement of metabolites Enzyme activity measurement Mutation analysis Morphological diagnostics
Eucaryotic cell. Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition
 Eucaryotic cell Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition Lysosomes Lysosomes Membrane-bound organelles with acidic interior Degradation of macromolecules Alberts et al : Molecular biology
Eucaryotic cell Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition Lysosomes Lysosomes Membrane-bound organelles with acidic interior Degradation of macromolecules Alberts et al : Molecular biology
Lysosomes and lysosomal disorders
 Lysosomes and lysosomal disorders Eukaryotic cell Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition Lysosomes Image M.H. Degradation of macromolecules Calcium store Cholesterol homeostasis Lysosomal
Lysosomes and lysosomal disorders Eukaryotic cell Alberts et al : Molecular biology of the cell 6th edition Lysosomes Image M.H. Degradation of macromolecules Calcium store Cholesterol homeostasis Lysosomal
Structure. Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles. Hydrolytic enzymes. Variable in size & shape need
 Lysosomes Structure Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles Hydrolytic enzymes Variable in size & shape need Degrade material taken up from outside and inside the cell Variable in size and shape Lysosomal
Lysosomes Structure Lysosomes are membrane-enclosed organelles Hydrolytic enzymes Variable in size & shape need Degrade material taken up from outside and inside the cell Variable in size and shape Lysosomal
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders
 The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
The role of the laboratory in diagnosing lysosomal disorders Dr Guy Besley, formerly Willink Biochemical Genetics Unit, Manchester Children s Hospital, Manchester M27 4HA, UK. Lysosomal disorders What
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
1. Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Disorders in Australia. 2. Comparison of Incidence/prevalence of lysosomal storage diseases in different country
 List of Tables: 1. Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Disorders in Australia 2. Comparison of Incidence/prevalence of lysosomal storage diseases in different country 3. Relative frequency of LSD in Portugal
List of Tables: 1. Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Disorders in Australia 2. Comparison of Incidence/prevalence of lysosomal storage diseases in different country 3. Relative frequency of LSD in Portugal
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases
 Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
Clinical Approach to Diagnosis of Lysosomal Storage Diseases M. Rohrbach, MD, PhD FMH Pädiatrie und FMH Medizinische Genetik Abteilung Stoffwechsel Universitätskinderklinik Zürich Lysosomal storage disorders
MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of therapeutic strategies
 Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of genetic diseases to develop preventive and therapeutic strategies G E N O T Y P E G E Researcher N 1 3 5 O T Y P E 8
Telethon Institute of Genetics and Medicine MISSION: understanding the mechanisms of genetic diseases to develop preventive and therapeutic strategies G E N O T Y P E G E Researcher N 1 3 5 O T Y P E 8
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Date of commencement: February Principal Investigator Dr. Jayesh J. Sheth CASE RECORD FORM
 ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
ICMR-FRIGE-MULTICENTRIC LSDs Project Foundation for Research in Genetics & Endocrinology [FRIGE], FRIGE House, Jodhpur Gam road, Satellite, Ahmedabad-380015 Tel no: 079-26921414, Fax no: 079-26921415 E-mail:
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Inborn Error Of Metabolism :
 Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Inborn Error Of Metabolism : Inborn Error Of Metabolism inborn error of metabolism are a large group of hereditary biochemical diseases in which specific gene mutation cause abnormal or missing proteins
Molecular Trafficking
 SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
lysosomes Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types:
 lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
lysosomes Digests Ingested materials Defective cell components Degrades macromolecules of all types: Proteins Nucleic acids Carbohydrates Lipids Single membrane bound vesicle, contains up to 50 digestive
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS
 Research Foundation, 18 month progress report THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS Ekaterina Ivanova, doctoral student Elena Levtchenko, MD, PhD, PI Antonella
Research Foundation, 18 month progress report THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS Ekaterina Ivanova, doctoral student Elena Levtchenko, MD, PhD, PI Antonella
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
Cell morphology. Cell organelles structure and function. Chapter 1: UNIT 1. Dr. Charushila Rukadikar
 UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
Glycoprotein Maturation and Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Dr. Daniel Hebert
 Glycoprotein Maturation and Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University of Massachusetts, USA 1 Intracellular protein trafficking Plasma membrane
Glycoprotein Maturation and Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University of Massachusetts, USA 1 Intracellular protein trafficking Plasma membrane
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18
 Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates. Bacterial Cell Walls
 Biochemistry 462a - Carbohydrate Function Reading - Chapter 9 Practice problems - Chapter 9: 2, 4a, 4b, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16a, 17; Carbohydrate extra problems Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates
Biochemistry 462a - Carbohydrate Function Reading - Chapter 9 Practice problems - Chapter 9: 2, 4a, 4b, 6, 9, 10, 13, 14, 15, 16a, 17; Carbohydrate extra problems Significance and Functions of Carbohydrates
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Antigen presenting cells
 Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
17/01/2017. Protein trafficking between cell compartments. Lecture 3: The cytosol. The mitochondrion - the power plant of the cell
 ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014
 Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH INTRACELLULAR PROTEIN TRANSPORT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri. Outline
 Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri Dr. Kathy Grange Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University Outline Brief overview of clinical
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Diseases in Missouri Dr. Kathy Grange Division of Genetics and Genomic Medicine Department of Pediatrics Washington University Outline Brief overview of clinical
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS. Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry
 METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport
 Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Lipids: In Born errors of Metabolism I
 Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 27 Lipids: In Born Errors of Metabolism I Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 27 Lipids: In Born Errors of Metabolism I Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al.
 Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Mucopolysaccharidoses diagnostic approaches
 Mucopolysaccharidoses diagnostic approaches George Ruijter Center for Lysosomal and Metabolic Diseases Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam, The Netherlands 1/35 / 58 2 / 58 2/35 Mucopolysaccharidoses
Mucopolysaccharidoses diagnostic approaches George Ruijter Center for Lysosomal and Metabolic Diseases Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam, The Netherlands 1/35 / 58 2 / 58 2/35 Mucopolysaccharidoses
Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids. Martina Srbová
 Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids Martina Srbová Types of glycerolipids and sphingolipids 1. Triacylglycerols function as energy reserves adipose tissue (storage of triacylglycerol), lipoproteins
Metabolism of acylglycerols and sphingolipids Martina Srbová Types of glycerolipids and sphingolipids 1. Triacylglycerols function as energy reserves adipose tissue (storage of triacylglycerol), lipoproteins
4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions
 4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University
4. Lysosomes, Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum, Mitochondria, and Inclusions Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine
 Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
-Cyclodextrin-threaded Biocleavable Polyrotaxanes Ameliorate Impaired Autophagic Flux in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease
 -Cyclodextrin-threaded Biocleavable Polyrotaxanes Ameliorate Impaired Autophagic Flux in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Atsushi Tamura and Nobuhiko Yui Department of Organic Biomaterials, Institute of Biomaterials
-Cyclodextrin-threaded Biocleavable Polyrotaxanes Ameliorate Impaired Autophagic Flux in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease Atsushi Tamura and Nobuhiko Yui Department of Organic Biomaterials, Institute of Biomaterials
Essential Cell Biology
 Alberts Bray Hopkin Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Essential Cell Biology FOURTH EDITION Chapter 15 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Copyright Garland Science 2014 CHAPTER CONTENTS MEMBRANE-ENCLOSED
Alberts Bray Hopkin Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Essential Cell Biology FOURTH EDITION Chapter 15 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Copyright Garland Science 2014 CHAPTER CONTENTS MEMBRANE-ENCLOSED
Membranous Organelles
 Membranous Organelles 1. Membrane-limited organelles 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosomes 4. Peroxisomes (microbodies) 5. Secretory vesicles (granules) 6. Coated vesicles Membrane-limited organelles Endoplasmic
Membranous Organelles 1. Membrane-limited organelles 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosomes 4. Peroxisomes (microbodies) 5. Secretory vesicles (granules) 6. Coated vesicles Membrane-limited organelles Endoplasmic
Thematic Review Series: Recent Advances in the Treatment of Lysosomal Storage Diseases. Lysosomal exocytosis and lipid storage disorders
 thematic review Thematic Review Series: Recent Advances in the Treatment of Lysosomal Storage Diseases Lysosomal exocytosis and lipid storage disorders Mohammad Ali Samie and Haoxing Xu 1 Department of
thematic review Thematic Review Series: Recent Advances in the Treatment of Lysosomal Storage Diseases Lysosomal exocytosis and lipid storage disorders Mohammad Ali Samie and Haoxing Xu 1 Department of
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Clinical Cell Biology Organelles in Health and Disease
 Department of Ophthalmology University of Kiel, University Medical Center Director: Prof. Dr. Johann Roider Clinical Cell Biology Organelles in Health and Disease Prof. Dr. Alexa Klettner Clinical cell
Department of Ophthalmology University of Kiel, University Medical Center Director: Prof. Dr. Johann Roider Clinical Cell Biology Organelles in Health and Disease Prof. Dr. Alexa Klettner Clinical cell
MCB130 Midterm. GSI s Name:
 1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
Membranous Organelles 2
 Membranous Organelles 2 1. Membrane-limited organelles 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosomes 4. Peroxisomes (microbodies) 5. Secretory vesicles (granules) 6. Coated vesicles Membrane-limited organelles Endoplasmic
Membranous Organelles 2 1. Membrane-limited organelles 2. Golgi apparatus 3. Lysosomes 4. Peroxisomes (microbodies) 5. Secretory vesicles (granules) 6. Coated vesicles Membrane-limited organelles Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
QUESTIONSHEET 1. The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows some of the cell structures involved in the secretion of an extracellular enzyme. C D A (a) Identify A,, C, and D. A:... :... C:... D:... [4] (b) Outline the role of each
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Chapter 6. Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
7 Medical Genetics. Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobinopathies. Protein and Gene Structure. and Biochemical Genetics
 SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
SESSION 7 Medical Genetics Hemoglobinopathies and Biochemical Genetics J a v a d F a s a J a m s h i d i U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 Hemoglobinopathies
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry. The cell: Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell
 Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae.
 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited disorders 1
 Disease category Disorder S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited 1 Augmented protein 2 Source of therapeutic protein / peptide Outcome References 3 Membrane transport Coagulation Cystic fibrosis
Disease category Disorder S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited 1 Augmented protein 2 Source of therapeutic protein / peptide Outcome References 3 Membrane transport Coagulation Cystic fibrosis
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester
 BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
Cell Physiology
 Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1793 (2009) 684 696 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbamcr Review Lysosomal disorders: From
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1793 (2009) 684 696 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbamcr Review Lysosomal disorders: From
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units
 Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
Glycosaminoglycans: Anionic polysaccharide chains made of repeating disaccharide units Glycosaminoglycans present on the animal cell surface and in the extracellular matrix. Glycoseaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides)
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
A Rare disease: MPS III San Filippo disease
 A Rare disease: MPS III San Filippo disease Annick Raas-Rothschild, MD Pediatrician-Medical Geneticist Director of the Rare Diseases institute Institute of Genetics Sheba Tel Hashomer Medical Center Annick.rothschild@sheba.health.gov.il
A Rare disease: MPS III San Filippo disease Annick Raas-Rothschild, MD Pediatrician-Medical Geneticist Director of the Rare Diseases institute Institute of Genetics Sheba Tel Hashomer Medical Center Annick.rothschild@sheba.health.gov.il
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis
 Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Corporate Medical Policy. Policy Effective 6/30/2017
 Corporate Medical Policy Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) for Lysosomal Storage File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: enzyme_replacement_therapy_for_lysosomal_storage_disorders
Corporate Medical Policy Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT) for Lysosomal Storage File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: enzyme_replacement_therapy_for_lysosomal_storage_disorders
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
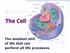 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION In format provided by Saftig and Klumperman (SEPTEMBER 2009)
 Lysosomal protein Synonyms Expression TM domai ns Lysosomal targeting sequence/ adaptor protein interaction Phenotype of knockout mice Discussed functions LAMP-1 LAMP-2 LGP-A; LGP120; LEP100; LAMP-A, CD107a
Lysosomal protein Synonyms Expression TM domai ns Lysosomal targeting sequence/ adaptor protein interaction Phenotype of knockout mice Discussed functions LAMP-1 LAMP-2 LGP-A; LGP120; LEP100; LAMP-A, CD107a
1- Which of the following statements is TRUE in regards to eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
 Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Rare metabolic diseases: the miglustat experience. Fran Platt Department of Pharmacology University of Oxford
 Rare metabolic diseases: the miglustat experience Fran Platt Department of Pharmacology University of Oxford The lysosome is an organelle involved in degrading and recycling macromolecules Christian de
Rare metabolic diseases: the miglustat experience Fran Platt Department of Pharmacology University of Oxford The lysosome is an organelle involved in degrading and recycling macromolecules Christian de
C3, C4, C5, C6 2. & C7
 Overview 1. Glucose conversion to pentoses & NADPH Precursors of nucleic acids, ATP, NAD, FAD, CoA 2. Inter-conversion of C3, C4, C5, C6 & C7 saccharides Glucose or fructose dietary input Glycogen 3. Nucleotide-linked
Overview 1. Glucose conversion to pentoses & NADPH Precursors of nucleic acids, ATP, NAD, FAD, CoA 2. Inter-conversion of C3, C4, C5, C6 & C7 saccharides Glucose or fructose dietary input Glycogen 3. Nucleotide-linked
DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History. Tuesday, April 16, 2013
 DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History Tuesday, April 16, 2013 Objectives Recognize the importance & impact of newborn screening Describe the process of newborn screening
DNA Day Illinois 2013 Webinar: Newborn Screening and Family Health History Tuesday, April 16, 2013 Objectives Recognize the importance & impact of newborn screening Describe the process of newborn screening
Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet
 Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet Website:www.tipn.org.tw Telephone:(02)85962050 Ext. 401-403 Service line:(02)85962065 Fax:(02)85962067
Newborn screening for congenital metabolic diseases Optional out-of-pocket tests Information Sheet Website:www.tipn.org.tw Telephone:(02)85962050 Ext. 401-403 Service line:(02)85962065 Fax:(02)85962067
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cell wall components:
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure.
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17
 Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17 Exocytosis and endocytosis Transport from the trans-golgi network to the cell exterior: exocytosis. All eukaryotic cells continuously
Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17 Exocytosis and endocytosis Transport from the trans-golgi network to the cell exterior: exocytosis. All eukaryotic cells continuously
2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. PROTEIN SORTING. Lecture 10 BIOL 266/ Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S.
 PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
Cells & Tissues. Chapter 3
 Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Cells & Tissues Chapter 3 Cell Theory Cell is structural and functional unit of life Activity of an organism is dependent upon its cells Principle of Complementarity functions of cells are dependent upon
Glycoproteins and Mucins. B.Sopko
 Glycoproteins and Mucins B.Sopko Content Glycoproteins: Structures and Linkages Interconversions and activation of dietary sugars Other pathways of sugar nucleotide metabolism Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides
Glycoproteins and Mucins B.Sopko Content Glycoproteins: Structures and Linkages Interconversions and activation of dietary sugars Other pathways of sugar nucleotide metabolism Biosynthesis of oligosaccharides
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Organization of ATPases
 The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
1 of 25 07/06/ :45 AM
 1 of 25 07/06/2015 11:45 AM Number: 0442 Policy I. Imiglucerase (Cerezyme), Miglustat (Zavesca), Taliglucerase alfa (Elelyso), and Velaglucerase Alfa (VPRIV) A. Aetna considers eliglustat (Cerdelga), imiglucerase
1 of 25 07/06/2015 11:45 AM Number: 0442 Policy I. Imiglucerase (Cerezyme), Miglustat (Zavesca), Taliglucerase alfa (Elelyso), and Velaglucerase Alfa (VPRIV) A. Aetna considers eliglustat (Cerdelga), imiglucerase
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Newborn Screening and Studies of Lysosomal Storage Diseases in CFOH
 Newborn Screening and Studies of Lysosomal Storage Diseases in CFOH Chinese Foundation of Health National Yang-Ming University Director: Dr. Chuan-Chi Chiang Speaker: Hsuan-Chieh Liao (Joyce) 1 Newborn
Newborn Screening and Studies of Lysosomal Storage Diseases in CFOH Chinese Foundation of Health National Yang-Ming University Director: Dr. Chuan-Chi Chiang Speaker: Hsuan-Chieh Liao (Joyce) 1 Newborn
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Cellular control of cholesterol. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cellular control of cholesterol Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Brief overview of cholesterol s biological role Regulation of cholesterol synthesis Dietary and cellular uptake of cholesterol
Cellular control of cholesterol Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Brief overview of cholesterol s biological role Regulation of cholesterol synthesis Dietary and cellular uptake of cholesterol
DRUG DELIVERY TO LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASES VISWANADHA INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
 CONTENTS DRUG DELIVERY TO LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASES VISWANADHA INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES 1. INTRODUCTION 2. LSD s 3. STRATEGIES FOR TREATMENT or DRUG DELIVERY OF LSD s 4. CARRIERS FOR TREATMENT
CONTENTS DRUG DELIVERY TO LYSOSOMAL STORAGE DISEASES VISWANADHA INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES 1. INTRODUCTION 2. LSD s 3. STRATEGIES FOR TREATMENT or DRUG DELIVERY OF LSD s 4. CARRIERS FOR TREATMENT
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, MBIM 650/720 - Fall TOPIC: Antigen Processing, MHC Restriction, & Role of Thymus Lecture 12
 COURSE: Medical Microbiology, MBIM 650/720 - Fall 2008 TOPIC: Antigen Processing, MHC Restriction, & Role of Thymus Lecture 12 FACULTY: Dr. Mayer Office: Bldg. #1, Rm B32 Phone: 733-3281 Email: MAYER@MED.SC.EDU
COURSE: Medical Microbiology, MBIM 650/720 - Fall 2008 TOPIC: Antigen Processing, MHC Restriction, & Role of Thymus Lecture 12 FACULTY: Dr. Mayer Office: Bldg. #1, Rm B32 Phone: 733-3281 Email: MAYER@MED.SC.EDU
