Zaloge metaboličnih goriv
|
|
|
- Laura Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Osnovne naloge metabolizma Integracija metabolizma 1. Zagotavljanje metaboličnih goriv vsem celicam 2. Odstranjevanje odpadnih produktov 3. Zaščita 4. Integracija prof.dr.m.žakelj-mavrič Zagotavljanje metaboličnih goriv vsem celicam Funkcijo opravljajo: maščevje, jetra, mišice, tanko črevo, pankreas Pomembna metabolična goriva: glukoza, maščobne kisline, ketonske spojine, AK Poleg tega potrebujemo še vitamine, ione (Na +, K +, Ca 2+, Mg 2+, Zn 2+...), vodo Zaloge metaboličnih goriv Metabolična goriva pridobimo s hrano, iz endogenih zalog ali pa jih sintetiziramo sami iz drugih goriv (ketonske spojine) 400 1
2 Stopnje katabolizma Pridobivanje energije iz metaboličnih goriv je razdeljeno na tri stopnje. V prisotnosti kisika in funkcionalnih mitohondrijev poteka oksidacija metaboličnih goriv SH 2 + NAD + S + NADH + H + (FAD) (FADH 2 ) NADH + H + + 1/2 O 2 NAD + + H 2 0 (FADH 2 ) (FAD) Oksidativna fosforilacija Pridobivanje ATP iz metaboličnih goriv NADH + H + + 3ADP + 3 P i +1/2 O 2 > NAD + + H 2 O + 3 ATP + 3H 2 O 1 MK, Glc,(AK), ketonska telesa AcCoA Kaj pa če ni kisika ali funkcionalnih mitohondrijev? 2NAD + glukoza 2NAD + 2NADH + 2H + 2piruvat V tem slučaju celice pridobivajo energijo z anaerobno glikolizo 2laktat Anaerobna glikoliza lahko predstavlja izhod v sili!!! 2
3 Prekurzorji za biosinteze Metabolične poti Glikoliza in citratni ciklus dajeta prekurzorje za sintezo številnih biomolekul JETRA pentoza-p pentoze glukoza-6-p glikogen acetil-coa piruvat laktat maščobe FAT CO 2 Poiščite razlike med jetri, mišicami in maščevjem! MOŽGANI ERITROCIT glukoza pentoza-p pentoze glukoza-6-p pentoza-p pentoze glukoza-6p acetil-coa piruvat piruvat CO 2 Kateri procesi omogočajo pridobivanje energije iz Glc v možganih? laktat laktat 3
4 Katere skupne intermediate še poznamo? fosfatidat Kaj pa HMG-CoA in karbamoilfosfat? Od česa zavisi, po kateri poti se usmeri metabolit????? Odstranjevanje odpadnih produktov Zaščita Funkcijo opravljajo: jetra, ledvica.. Odpadni produkti: npr. sečnina, sečna kislina, bilirubin, ksenobiotiki, CO 2... Pri tej vlogi sodelujejo: mišice, kri (sistem za strjevanje krvi), koža in sluznice, imunski sistem... jetra in ledvica (detoksifikacija in izločanje npr. NH 3, ksenobiotikov) Integracija Integracija ob stresu-os hipotalamus-hipofiza-adrenalka Povezava centralnega živčevja z deli telesa preko živčevja in s pomočjo hormonov. Pri tej nalogi sodelujejo centralno živčevje, kri, pankreas... 4
5 Integracija ob stresu-os hipotalamus-hipofiza-adrenalka Osnovne naloge metabolizma 1. Zagotavljanje metaboličnih goriv vsem celicam 2. Odstranjevanje odpadnih produktov 3. Zaščita 4. Integracija Odziv metabolizma na različna prehrambena in hormonska stanja Metabolični procesi v stanju dobre prehranjenosti Metabolične povezave v stanju dobre prehranjenosti Odziv metabolizma na različna prehrambena in hormonska stanja 5
6 Spremembe v koncentracijah metaboličnih goriv med stradanjem Metabolične povezave ob podaljšanem stradanju Metabolični procesi ob stradanju Po cca 60 dneh se začno porabljati pomembni proteini, npr. proteini srčne mišice in nastopi smrt. Primerjava metabolizma Metabolična goriva in telesna aktivnost A)v času dobre hranjenosti B) ob podaljšanem stradanju 6
7 Metabolična goriva in telesna aktivnost Hitrost sinteze ATP v primerjavi s sposobnostjo vzdrževanja maksimalne mišične aktivnosti sprint Miokinaza!!!! Uravnavanje metabolizma glukoze med telesno aktivnostjo Med aktivnostjo se poveča izločanje glukagona, ki v jetrih omogoči proces glikogenolize Adrenalin in noradrenalin dodatno stimulirata glikogenolizo Raven kortizola se med vadbo tudi poveča, sproščene AK iz procesa proteolize služijo kot substrati za glukoneogenezo Kortizol, adrenalin in NE stimulirajo metabolizem MK Spremembe v konc. hormonov so odvisne od vrste in trajanja aktivnosti, treniranosti... Sproščeni hormoni omogočijo uravnavanje metaboličnih procesov na ravni organizma - omogočajo integracijo metaboličnih procesov med celicami in organi (npr. hormoni v jetrih stimulirajo sintezo glukoze,ki jo porabijo mišice). Na ravni celice poteka prilagoditev glede na razmere v celici- npr. uravnavanje celičnega metabolizma glede na energijsko stanje v celici - nastanek ATP v skladu s potrebami po ATP 7
8 vezava z regulatornim proteinom prisotnost encima v določenem celičnem razdelku Smo si podobni ali se razlikujemo???? Kako je z našimi metaboličnimi potmi?????? sinteza ENCIM razgradnja uravnavanje z alosteričnimi modulatorji uravnavanje s kovalentno modifikacijo Izražanje individualnosti Metabolomika Geni Individualnost Okolje sprememba poškodba... metaboliti filtracija resorpcija redčenje koncentracija prstni odtis metabolitov Porast koncentracije celičnih encimov (še( e posebej značilnih izoencimov) v krvi ima diagnostičen pomen (AST) (ALT) Številne bolezni so posledica sprememb v strukturi biomolekul (npr. DNA), množini biomolekul ali motenj v pomembnih biokemijskih reakcijah ali procesih. Poznavanje vzrokov bolezni lahko omogoči diagnostiko bolezni in pravilen tretma bolnika ( npr. diagnostika na osnovi metabolitov fenilalanina in pravilna dieta pri fenilketonuriji) 8
9 Uporaba inhibitorjev 1. Nekateri inhibitorji procesov pri človeku so hudi strupi, uporaba smrtno nevarna (npr. CO) (?) 2. Druge inhibitorje človeških encimov uporabljamo kot zdravila (npr. statini inhibirajo HMG-CoA-reduktazo, aspirin inhibira COX) 3. Inhibitorji lahko selektivno inhibirajo proces pri bakterijah (najprimernejše mesto delovanja proces, ki pri človeku ne poteka, kot npr. biosinteza celične stene bakterij oz. proces, ki se pri človeku razlikuje od bakterijskega) Sept. 30, 2004: Merck pulls popular pain drug due to risks of heart attacks COX-1 konstitutivna Cox-1 / Cox-2 Stališče izpred nekaj let arahidonska k. COX-2 inducibilna dobri prostaglandini slabi prostaglandini zaščita GI akt. trombocitov funkcija ledvic vnetje bolečina vročina COX-1 konstitutivna (izjeme!) Cox-1 / Cox-2 Ugotovitve danes arahidonska k. COX-2 inducibilna (izjeme!) Hvala za pozornost! prostaglandini zaščita GI akt. trombocitov funkcija ledvic prostaglandini patološki vnetje bolečina vročina fiziološki funkcija ledvic žilni popravilo tkiv Vprašanja naslovite na: Marija.Zakelj-Mavric@mf.uni-lj.si ali Marijo Žakelj-Mavrič (osebno!) 9
Fiksacija dušika nitrogenaza
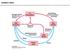 Dušikov ciklus Fiksacija dušika Ključna stopnja kroženja dušika je fiksacija N 2 iz atmosfere, ki jo katalizirajo nekatere bakterije, npr. talne bakterije iz rodov Rhizobia in Franka, ki živijo v simbiozi
Dušikov ciklus Fiksacija dušika Ključna stopnja kroženja dušika je fiksacija N 2 iz atmosfere, ki jo katalizirajo nekatere bakterije, npr. talne bakterije iz rodov Rhizobia in Franka, ki živijo v simbiozi
Kortikosteroidi. glukokortikoidi C21 (OH ali O skupina na C11, OH na C17) kortizol, kortizon. mineralokortikoidi C21 (CHO na C18) aldosteron
 regulirajo reabsorbcijo Na + ionov v ledvicah, zadrževanje vode v organizmu, vplivajo na krvni tlak Kortikosteroidi glukokortikoidi C21 (OH ali O skupina na C11, OH na C17) kortizol, kortizon H 2 COH H
regulirajo reabsorbcijo Na + ionov v ledvicah, zadrževanje vode v organizmu, vplivajo na krvni tlak Kortikosteroidi glukokortikoidi C21 (OH ali O skupina na C11, OH na C17) kortizol, kortizon H 2 COH H
Medcelična signalizacija. Lodish 4:
 Medcelična signalizacija Lodish 4: 20.1-20.4 Šest stopenj zunajceličnega signaliziranja Sinteza signalne molekule v signalizacijski celici Sproščanje signalne molekule iz signalizacijske celice Transport
Medcelična signalizacija Lodish 4: 20.1-20.4 Šest stopenj zunajceličnega signaliziranja Sinteza signalne molekule v signalizacijski celici Sproščanje signalne molekule iz signalizacijske celice Transport
Celični razdelki in transport proteinov
 Celični razdelki in transport proteinov Kompartmentalizacija celic Kompartmentalizacija celic Kompartmentalizacija celic Celične membrane Glavni celični organeli Evolucijski izvor topologije celic Topology
Celični razdelki in transport proteinov Kompartmentalizacija celic Kompartmentalizacija celic Kompartmentalizacija celic Celične membrane Glavni celični organeli Evolucijski izvor topologije celic Topology
NUTRIENT INTAKE VARIABILITY INDUCED BY PROCESSING OF FOOD DIARY DATA: A PILOT STUDY
 COBISS: 1.01 Agris category code: S40, Q04 NUTRIENT INTAKE VARIABILITY INDUCED BY PROCESSING OF FOOD DIARY DATA: A PILOT STUDY Tamara PUŠ 1, Ksenija PODGRAJŠEK 2, Marjan SIMČIČ 3 Received October 10, 2012;
COBISS: 1.01 Agris category code: S40, Q04 NUTRIENT INTAKE VARIABILITY INDUCED BY PROCESSING OF FOOD DIARY DATA: A PILOT STUDY Tamara PUŠ 1, Ksenija PODGRAJŠEK 2, Marjan SIMČIČ 3 Received October 10, 2012;
UČNI NAČRT PREDMETA / COURSE SYLLABUS. Študijska smer Study field. General Medicine-EMŠP General Medicine 1 2. Lab. vaje Laboratory work
 Predmet: Course title: UČNI NAČRT PREDMETA / COURSE SYLLABUS Biokemija Biochemistry Študijski program in stopnja Study programme and level Splošna medicina Študijska smer Study field Letnik Academic year
Predmet: Course title: UČNI NAČRT PREDMETA / COURSE SYLLABUS Biokemija Biochemistry Študijski program in stopnja Study programme and level Splošna medicina Študijska smer Study field Letnik Academic year
GINKGO BILOBA IN MISELNE SPOSOBNOSTI. Avtorji: Jelena Raković, Božica Ljušanin Grbavac 18. modularna skupina April 2015
 GINKGO BILOBA IN MISELNE SPOSOBNOSTI Avtorji: Jelena Raković, Božica Ljušanin Grbavac 18. modularna skupina April 2015 KLINIČNO VPRAŠANJE Ali uporaba standardiziranih pripravkov Ginkgo bilobe izboljšuje
GINKGO BILOBA IN MISELNE SPOSOBNOSTI Avtorji: Jelena Raković, Božica Ljušanin Grbavac 18. modularna skupina April 2015 KLINIČNO VPRAŠANJE Ali uporaba standardiziranih pripravkov Ginkgo bilobe izboljšuje
MOLEKULARNI MEHANIZMI NASTANKA DEBELOSTI S POUDARKOM NA VLOGI SISTEMA RENIN-ANGIOTENZIN- ALDOSTERON
 MOLEKULARNI MEHANIZMI NASTANKA DEBELOSTI S POUDARKOM NA VLOGI SISTEMA RENIN-ANGIOTENZIN- ALDOSTERON MOLECULAR MECHANISMS Of OBESITY WITH EMPHASIS ON THE ROLE Of THE RENIN- ANGIOTENSIN- ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
MOLEKULARNI MEHANIZMI NASTANKA DEBELOSTI S POUDARKOM NA VLOGI SISTEMA RENIN-ANGIOTENZIN- ALDOSTERON MOLECULAR MECHANISMS Of OBESITY WITH EMPHASIS ON THE ROLE Of THE RENIN- ANGIOTENSIN- ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
HIV/AIDS UPDATE Janez Tomažič Klinika za infekcijske bolezni in vročinska stanja Katedra za infekcijske bolezni in epidemiologijo
 HIV/AIDS UPDATE 2017 Janez Tomažič Klinika za infekcijske bolezni in vročinska stanja Katedra za infekcijske bolezni in epidemiologijo Patogeneza okužbe s HIV 1. Sesutje imunskega sistema KLINIČNE OPREDELITVE
HIV/AIDS UPDATE 2017 Janez Tomažič Klinika za infekcijske bolezni in vročinska stanja Katedra za infekcijske bolezni in epidemiologijo Patogeneza okužbe s HIV 1. Sesutje imunskega sistema KLINIČNE OPREDELITVE
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen In biology and chemistry, energy is referred to
Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration is the process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen In biology and chemistry, energy is referred to
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Chapter 27 Bioenergetics; How the Body Converts Food to Energy
 Chapter 27 Bioenergetics; How the Body Converts Food to Energy 1 Metabolism Metabolism: The sum of all chemical reactions involved in maintaining the dynamic state of a cell or organism. Pathway: A series
Chapter 27 Bioenergetics; How the Body Converts Food to Energy 1 Metabolism Metabolism: The sum of all chemical reactions involved in maintaining the dynamic state of a cell or organism. Pathway: A series
ZDRAVILA, KI VPLIVAJO NA METABOLIZEM LIPIDOV
 ZDRAVILA, KI VPLIVAJO NA METABOLIZEM LIPIDOV Prof. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Kratek povzetek zgodbe Pregled
ZDRAVILA, KI VPLIVAJO NA METABOLIZEM LIPIDOV Prof. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Kratek povzetek zgodbe Pregled
ZDRAVILA, KI VPLIVAJO NA METABOLIZEM LIPIDOV
 ZDRAVILA, KI VPLIVAJO NA METABOLIZEM LIPIDOV Prof. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Pregled Nastanek aterosklerotičnega
ZDRAVILA, KI VPLIVAJO NA METABOLIZEM LIPIDOV Prof. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Pregled Nastanek aterosklerotičnega
How Cells Release Chemical Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 7 7.1 Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways All organisms (including photoautotrophs) convert chemical energy of organic compounds to chemical energy of
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 7 7.1 Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways All organisms (including photoautotrophs) convert chemical energy of organic compounds to chemical energy of
Zdravljenje pridobljene hemofilije. Irena Preložnik Zupan
 Zdravljenje pridobljene hemofilije Irena Preložnik Zupan CILJI 1. Definicija, klinična slika, diagnoza 2. Zdravljenje zdravljenje akutnih krvavitev odstranjevanje inhibitorjev Pridobljeni inhibitorji koagulacije
Zdravljenje pridobljene hemofilije Irena Preložnik Zupan CILJI 1. Definicija, klinična slika, diagnoza 2. Zdravljenje zdravljenje akutnih krvavitev odstranjevanje inhibitorjev Pridobljeni inhibitorji koagulacije
Energy Metabolism. Topics
 Energy Metabolism Nur Hidayat Topics TOPIC 1: OXIDATION, REDUCTION, AND NADH TOPIC 2: GLYCOLYSIS TOPIC 3: KREBS (CITRIC ACID) CYCLE TOPIC 4: ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION TOPIC
Energy Metabolism Nur Hidayat Topics TOPIC 1: OXIDATION, REDUCTION, AND NADH TOPIC 2: GLYCOLYSIS TOPIC 3: KREBS (CITRIC ACID) CYCLE TOPIC 4: ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION TOPIC
Cells extract energy from their environment and use the energy for a host of biological activities including biosynthesis.
 ATP=cellular energy Cells extract energy from their environment and use the energy for a host of biological activities including biosynthesis. The reactions of energy extraction and energy use are called
ATP=cellular energy Cells extract energy from their environment and use the energy for a host of biological activities including biosynthesis. The reactions of energy extraction and energy use are called
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Biological Science 101 General Biology
 Lecture Seven: Cellular Respiration Ch. 9, Pgs. 163-181 Figs. 9.2-9.20 Biological Science 101 General Biology Cellular Respiration: - A series of processes that is involved in converting food to energy
Lecture Seven: Cellular Respiration Ch. 9, Pgs. 163-181 Figs. 9.2-9.20 Biological Science 101 General Biology Cellular Respiration: - A series of processes that is involved in converting food to energy
Principi PET-CT preiskave. Marko Grmek
 Principi PET-CT preiskave Marko Grmek PET-CT PET pozitronska emisijska tomografija CT računalniška tomografija Fuzijska slika Detektor sevanja - PET skener - CT naprava PET-CT preiskava Radiofarmak - 18
Principi PET-CT preiskave Marko Grmek PET-CT PET pozitronska emisijska tomografija CT računalniška tomografija Fuzijska slika Detektor sevanja - PET skener - CT naprava PET-CT preiskava Radiofarmak - 18
Chapter 12 Nutrition
 Chapter 12 Nutrition Nutrients macronutrients: large required daily quantities carbohydrates, lipids, proteins micronutrients: small required daily quantities vitamins, minerals Also required: water and
Chapter 12 Nutrition Nutrients macronutrients: large required daily quantities carbohydrates, lipids, proteins micronutrients: small required daily quantities vitamins, minerals Also required: water and
Releasing Chemical Energy
 Releasing Chemical Energy Ø Energy From Carbohydrates Ø Aerobic Respiration/ Stages Ø Fermentation Ø Food as a Source of Energy How Do Cells Access the Chemical Energy in Carbohydrayes? Aerobic Respiration
Releasing Chemical Energy Ø Energy From Carbohydrates Ø Aerobic Respiration/ Stages Ø Fermentation Ø Food as a Source of Energy How Do Cells Access the Chemical Energy in Carbohydrayes? Aerobic Respiration
Section 9 2 The Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport (pages )
 Section 9 2 The Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport (pages 226 232) This section describes what happens during the second stage of cellular respiration, called the Krebs cycle. It also explains how high-energy
Section 9 2 The Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport (pages 226 232) This section describes what happens during the second stage of cellular respiration, called the Krebs cycle. It also explains how high-energy
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI FAKULTETA ZA FARMACIJO UROŠ MESEC
 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI FAKULTETA ZA FARMACIJO UROŠ MESEC ISKANJE NOVIH POTENCIALNIH ZAVIRALCEV N-ACETILGLUKOZAMIN ENOLPIRUVIL TRANSFERAZE Z REŠETANJEM KNJIŽNICE SPOJIN FAKULTETE ZA FARMACIJO SEARCHING FOR
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI FAKULTETA ZA FARMACIJO UROŠ MESEC ISKANJE NOVIH POTENCIALNIH ZAVIRALCEV N-ACETILGLUKOZAMIN ENOLPIRUVIL TRANSFERAZE Z REŠETANJEM KNJIŽNICE SPOJIN FAKULTETE ZA FARMACIJO SEARCHING FOR
Metabolism. Chapter 5. Catabolism Drives Anabolism 8/29/11. Complete Catabolism of Glucose
 8/29/11 Metabolism Chapter 5 All of the reactions in the body that require energy transfer. Can be divided into: Cell Respiration and Metabolism Anabolism: requires the input of energy to synthesize large
8/29/11 Metabolism Chapter 5 All of the reactions in the body that require energy transfer. Can be divided into: Cell Respiration and Metabolism Anabolism: requires the input of energy to synthesize large
TEMPERATURNA ODVISNOST METABOLIZMA GLUKOZE V PODGANJIH ASTROCITIH
 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA Viktorija RADOTIĆ TEMPERATURNA ODVISNOST METABOLIZMA GLUKOZE V PODGANJIH ASTROCITIH MAGISTRSKO DELO (Magistrski študij 2. stopnja) Ljubljana, 2014 UNIVERZA V
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA Viktorija RADOTIĆ TEMPERATURNA ODVISNOST METABOLIZMA GLUKOZE V PODGANJIH ASTROCITIH MAGISTRSKO DELO (Magistrski študij 2. stopnja) Ljubljana, 2014 UNIVERZA V
3.7 CELLULAR RESPIRATION. How are these two images related?
 3.7 CELLULAR RESPIRATION How are these two images related? CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is the process whereby the body converts the energy that we get from food (glucose) into an energy form
3.7 CELLULAR RESPIRATION How are these two images related? CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is the process whereby the body converts the energy that we get from food (glucose) into an energy form
Case Study: Carbohydrate Metabolism. eating an early dinner the night before and skipping breakfast that morning, Sid goes to the
 Student Name Biochemistry 4320 Case Study Part I 4 November 2013 Case Study: Carbohydrate Metabolism Sid is a high school student who has decided to start exercising before school. After eating an early
Student Name Biochemistry 4320 Case Study Part I 4 November 2013 Case Study: Carbohydrate Metabolism Sid is a high school student who has decided to start exercising before school. After eating an early
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Breaking down glucose a little at a time.. It s like turning a five pound bag of sugar into several tiny sugar packets worth of energy in the form of ATP. Remember the carbon
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Breaking down glucose a little at a time.. It s like turning a five pound bag of sugar into several tiny sugar packets worth of energy in the form of ATP. Remember the carbon
What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP
 2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There s got to be a better way!
2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Glycolysis 2 ATP Kreb s cycle 2 ATP Life takes a lot of energy to run, need to extract more energy than 4 ATP! There s got to be a better way!
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Producers Producers get their energy from the sun. Producers convert this light energy into stored chemical energy (glucose). This process is called photosynthesis. Consumers Consumers
Cellular Respiration Producers Producers get their energy from the sun. Producers convert this light energy into stored chemical energy (glucose). This process is called photosynthesis. Consumers Consumers
VPLIV METFORMINA NA RAKAVE CELICE V KULTURI V ODVISNOSTI OD RAZPOLOŽLJIVIH HRANIL
 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA Maruša BIZJAK VPLIV METFORMINA NA RAKAVE CELICE V KULTURI V ODVISNOSTI OD RAZPOLOŽLJIVIH HRANIL DOKTORSKA DISERTACIJA Ljubljana, 2018 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA Maruša BIZJAK VPLIV METFORMINA NA RAKAVE CELICE V KULTURI V ODVISNOSTI OD RAZPOLOŽLJIVIH HRANIL DOKTORSKA DISERTACIJA Ljubljana, 2018 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA
Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
Cellular Respiration. Objectives
 Lecture 07 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures, you should be able to: Define terms. Compare the processes and locations of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Explain how breathing and
Lecture 07 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures, you should be able to: Define terms. Compare the processes and locations of cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Explain how breathing and
Sladkorna bolezen in kirurški poseg
 Sladkorna bolezen in kirurški poseg Doc.dr.Vilma Urbančič, dr.med. UKC Ljubljana KO EDBP, Diabetološki oddelek 1.12.2010 10. Podiplomski tečaj iz hospitalne diabetologije Ljubljana, 24.11. -2.12.2010 Noordzij
Sladkorna bolezen in kirurški poseg Doc.dr.Vilma Urbančič, dr.med. UKC Ljubljana KO EDBP, Diabetološki oddelek 1.12.2010 10. Podiplomski tečaj iz hospitalne diabetologije Ljubljana, 24.11. -2.12.2010 Noordzij
9.2 The Process of Cellular Respiration
 9.2 The Process of Cellular Respiration Oxygen Carbon 2 2 Dioxide 34 Water Glycolysis Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of
9.2 The Process of Cellular Respiration Oxygen Carbon 2 2 Dioxide 34 Water Glycolysis Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration. During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of
Ch 07. Microbial Metabolism
 Ch 07 Microbial Metabolism SLOs Differentiate between metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. Fully describe the structure and function of enzymes. Differentiate between constitutive and regulated enzymes.
Ch 07 Microbial Metabolism SLOs Differentiate between metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. Fully describe the structure and function of enzymes. Differentiate between constitutive and regulated enzymes.
2/4/17. Cellular Metabolism. Metabolism. Cellular Metabolism. Consists of all of the chemical reactions that take place in a cell.
 Metabolism Cellular Metabolism Consists of all of the chemical reactions that take place in a cell. Can be reactions that break things down. (Catabolism) Or reactions that build things up. (Anabolism)
Metabolism Cellular Metabolism Consists of all of the chemical reactions that take place in a cell. Can be reactions that break things down. (Catabolism) Or reactions that build things up. (Anabolism)
Cellular Respiration. Unit 5: Plants, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration Unit 5: Plants, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration Overview! Organisms obtain energy (ATP) by breaking down (catabolic pathway, exergonic reaction) organic molecules (glucose)
Cellular Respiration Unit 5: Plants, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration Overview! Organisms obtain energy (ATP) by breaking down (catabolic pathway, exergonic reaction) organic molecules (glucose)
Microbial Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism The sum total of chemical reactions that take place within cells (of an organism) Metabolic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism The sum total of chemical reactions that take place within cells (of an organism) Metabolic
(A) Urea cycle (B) TCA cycle (C) Glycolysis (D) Pyruvate oxidation (E) Respiratory chain
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Cellular Respiration. How our body makes ATP, ENERGY!!
 Cellular Respiration How our body makes ATP, ENERGY!! Useable Energy Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) Adenosine Ribose Sugar 3 Phosphates November 27, 2017 November 27, 2017 Where do our cells get energy?
Cellular Respiration How our body makes ATP, ENERGY!! Useable Energy Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP) Adenosine Ribose Sugar 3 Phosphates November 27, 2017 November 27, 2017 Where do our cells get energy?
DELOVANJE KETOGENE DIETE NA MOŽGANE
 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA ODDELEK ZA ŽIVILSTVO Ema OGRIZEK DELOVANJE KETOGENE DIETE NA MOŽGANE DIPLOMSKO DELO Univerzitetni študij - 1. stopnja Živilstvo in prehrana Ljubljana, 2018 UNIVERZA
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA ODDELEK ZA ŽIVILSTVO Ema OGRIZEK DELOVANJE KETOGENE DIETE NA MOŽGANE DIPLOMSKO DELO Univerzitetni študij - 1. stopnja Živilstvo in prehrana Ljubljana, 2018 UNIVERZA
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy ATP
 Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy ATP 2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP 2006-2007 Harvesting stored energy Energy is stored in organic molecules carbohydrates, fats,
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy ATP 2006-2007 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP 2006-2007 Harvesting stored energy Energy is stored in organic molecules carbohydrates, fats,
1 Which pathway for aerobic cellular respiration is located in the cytoplasm of the cell?
 1 Which pathway for aerobic cellular respiration is located in the cytoplasm of the cell? glycolysis citric cycle 2 Which of the following statements is NOT correct regarding aerobic cellular respiration?
1 Which pathway for aerobic cellular respiration is located in the cytoplasm of the cell? glycolysis citric cycle 2 Which of the following statements is NOT correct regarding aerobic cellular respiration?
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function
 Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Lesson Overview. Cellular Respiration: An Overview. 9.2 process of cell respiration
 9.2 process of cell respiration Glycolysis During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is a reactant in the Krebs cycle. ATP and NADH
9.2 process of cell respiration Glycolysis During glycolysis, glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of the 3-carbon molecule pyruvic acid. Pyruvic acid is a reactant in the Krebs cycle. ATP and NADH
Name: Block: Date: PACKET #8 Unit 3: Energy Transfer, Part II: Cellular Respiration
 Name: Block: Date: PACKET #8 Unit 3: Energy Transfer, Part II: Cellular Respiration Reading: BSCS Text chapters 4, 5, and 2.8. Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit the student will be able to: Topic
Name: Block: Date: PACKET #8 Unit 3: Energy Transfer, Part II: Cellular Respiration Reading: BSCS Text chapters 4, 5, and 2.8. Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit the student will be able to: Topic
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK. Metabolism: Glucose is the middleman for ATP
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Homeostasis The tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium that is maintained by physiological processes. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Homeostasis The tendency toward a relatively stable equilibrium that is maintained by physiological processes. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 2.2 WORKBOOK
AEROBIC RESPIRATION. Chapter 8
 AEROBIC RESPIRATION Chapter 8 AEROBIC RESPIRATION Aerobic respiration is the next step after Glycolysis if the cell can obtain oxygen. We won t need it until the last step but we still need it. Remember
AEROBIC RESPIRATION Chapter 8 AEROBIC RESPIRATION Aerobic respiration is the next step after Glycolysis if the cell can obtain oxygen. We won t need it until the last step but we still need it. Remember
NAJVAŽNEJŠE HORMONSKE ŽLEZE
 KAJ SO HORMONI? So naravne telesne snovi, ki jih izločajo endokrine žleze in se prenašajo po krvi ter nadzorujejo mnoge procese, kot so rast, izraba energije, ravnotežje tekočin v telesu in tvorba urina.
KAJ SO HORMONI? So naravne telesne snovi, ki jih izločajo endokrine žleze in se prenašajo po krvi ter nadzorujejo mnoge procese, kot so rast, izraba energije, ravnotežje tekočin v telesu in tvorba urina.
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Page by: OpenStax Summary The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Page by: OpenStax Summary The Citric Acid Cycle In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria,
ANALIZA VNOSA MAKRO IN MIKRO HRANIL PRI PROFESIONALNIH IGRALKAH ROKOMETA Z RAČUNALNIŠKIM PROGRAMOM Prodi 5.0
 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA ODDELEK ZA ŽIVILSTVO Špela CERAR ANALIZA VNOSA MAKRO IN MIKRO HRANIL PRI PROFESIONALNIH IGRALKAH ROKOMETA Z RAČUNALNIŠKIM PROGRAMOM Prodi 5.0 DIPLOMSKO DELO Univerzitetni
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI BIOTEHNIŠKA FAKULTETA ODDELEK ZA ŽIVILSTVO Špela CERAR ANALIZA VNOSA MAKRO IN MIKRO HRANIL PRI PROFESIONALNIH IGRALKAH ROKOMETA Z RAČUNALNIŠKIM PROGRAMOM Prodi 5.0 DIPLOMSKO DELO Univerzitetni
Osnove prehrane športnikov
 Osnove prehrane športnikov povzeto po: Fred Brouns, Essentials of sports nutrition John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 2002 (1993) Andrej N. September 2010 1 1 UVOD 6 1.1 Metabolizem 7 1.1.1 Prebava 7 1.1.2 Energija
Osnove prehrane športnikov povzeto po: Fred Brouns, Essentials of sports nutrition John Wiley & Sons Ltd. 2002 (1993) Andrej N. September 2010 1 1 UVOD 6 1.1 Metabolizem 7 1.1.1 Prebava 7 1.1.2 Energija
VPLIV SOČASNE UPORABE MELOKSIKAMA IN DEKSAMETAZONA Z MIZOPROSTOLOM NA VSEBNOST PROSTAGLANDINOV, LEVKOTRIENOV IN TROMBOKSANOV V SERUMU PRI PSIH
 UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI VETERINARSKA FAKULTETA Podiplomski študij biomedicine TINA ROŠKAR VPLIV SOČASNE UPORABE MELOKSIKAMA IN DEKSAMETAZONA Z MIZOPROSTOLOM NA VSEBNOST PROSTAGLANDINOV, LEVKOTRIENOV IN TROMBOKSANOV
UNIVERZA V LJUBLJANI VETERINARSKA FAKULTETA Podiplomski študij biomedicine TINA ROŠKAR VPLIV SOČASNE UPORABE MELOKSIKAMA IN DEKSAMETAZONA Z MIZOPROSTOLOM NA VSEBNOST PROSTAGLANDINOV, LEVKOTRIENOV IN TROMBOKSANOV
Osnove farmakokinetike
 Osnove farmakokinetike prof. dr. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Farmakologija Vedo o delovanju zdravilih in drugih
Osnove farmakokinetike prof. dr. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Farmakologija Vedo o delovanju zdravilih in drugih
NEGATIVNA POVRATNA SPREGA RECEPTOR (SENZOR) Fiziološki refleks ULAZNI PUT IZLAZNI SIGNAL/PUT. Homeostatski refleks EFEKTOR ODGOVOR
 HORMONI PANKREASA NEGATIVNA POVRATNA SPREGA RECEPTOR (SENZOR) ULAZNI PUT Fiziološki refleks IZLAZNI SIGNAL/PUT EFEKTOR Homeostatski refleks ODGOVOR POVRATNA SPREGA RECEPTOR (SENZOR) ULAZNI SPUT IZLAZNI
HORMONI PANKREASA NEGATIVNA POVRATNA SPREGA RECEPTOR (SENZOR) ULAZNI PUT Fiziološki refleks IZLAZNI SIGNAL/PUT EFEKTOR Homeostatski refleks ODGOVOR POVRATNA SPREGA RECEPTOR (SENZOR) ULAZNI SPUT IZLAZNI
Cellular Metabolism 6/20/2015. Metabolism. Summary of Cellular Respiration. Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell!
 Cellular Metabolism Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61) Metabolism Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell! Cellular metabolism: Aerobic cellular respiration requires
Cellular Metabolism Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61) Metabolism Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell! Cellular metabolism: Aerobic cellular respiration requires
Chapter 13 - TCA Cycle
 Chapter 13 TCA Cycle The third fate of glucose/pyruvate is complete oxidation to C 2 + H 2 in the matrix of the mitochondrion. The 1 st step is the oxidation and decarboxylation of pyruvate to AcetylCoA,
Chapter 13 TCA Cycle The third fate of glucose/pyruvate is complete oxidation to C 2 + H 2 in the matrix of the mitochondrion. The 1 st step is the oxidation and decarboxylation of pyruvate to AcetylCoA,
Cellular Metabolism 9/24/2013. Metabolism. Cellular Metabolism. Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell!
 Cellular Metabolism Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61) Metabolism Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell! Cellular Metabolism Aerobic cellular respiration requires
Cellular Metabolism Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61) Metabolism Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell! Cellular Metabolism Aerobic cellular respiration requires
Cellular Metabolism. Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61)
 Cellular Metabolism Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61) Metabolism Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell! Cellular Metabolism Aerobic cellular respiration requires
Cellular Metabolism Biology 105 Lecture 6 Chapter 3 (pages 56-61) Metabolism Consists of all the chemical reactions that take place in a cell! Cellular Metabolism Aerobic cellular respiration requires
Respiration. Energy is everything!
 Respiration Energy is everything! Tesla was incredible Everyone was intrigued by Tesla Tesla showed that energy does not need to be feared So what does this have to do with twinkies? Everything! Cellular
Respiration Energy is everything! Tesla was incredible Everyone was intrigued by Tesla Tesla showed that energy does not need to be feared So what does this have to do with twinkies? Everything! Cellular
Cellular Metabolism. Biol 105 Lecture 6 Read Chapter 3 (pages 63 69)
 Cellular Metabolism Biol 105 Lecture 6 Read Chapter 3 (pages 63 69) Metabolism Consists of all of the chemical reactions that take place in a cell Metabolism Animation Breaking Down Glucose For Energy
Cellular Metabolism Biol 105 Lecture 6 Read Chapter 3 (pages 63 69) Metabolism Consists of all of the chemical reactions that take place in a cell Metabolism Animation Breaking Down Glucose For Energy
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration
 ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration What Is ATP? Energy used by all Cells Adenosine Triphosphate Organic molecule containing highenergy Phosphate bonds Chemical Structure of ATP Adenine Base 3 Phosphates
ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration What Is ATP? Energy used by all Cells Adenosine Triphosphate Organic molecule containing highenergy Phosphate bonds Chemical Structure of ATP Adenine Base 3 Phosphates
Energy storage in cells
 Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Energy storage in cells Josef Fontana EC - 58 Overview of the lecture Introduction to the storage substances of human body Overview of storage compounds in the body Glycogen metabolism Structure of glycogen
Name Class Date. 1. Cellular respiration is the process by which the of "food"
 Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
Biology Chapter-7 Cellular Respiration
 Biology-1406 Chapter-7 Cellular Respiration Energy is stored in Chemicals Catabolism- the breaking down of complex molecules, such as glucose, to release their stored energy. Catabolism may or may not
Biology-1406 Chapter-7 Cellular Respiration Energy is stored in Chemicals Catabolism- the breaking down of complex molecules, such as glucose, to release their stored energy. Catabolism may or may not
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular
 III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
Farmakokinetika Osnovni principi, absorpcija zdravil
 Farmakokinetika Osnovni principi, absorpcija zdravil Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Osnovna farmakokinetska dogajanja
Farmakokinetika Osnovni principi, absorpcija zdravil Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Osnovna farmakokinetska dogajanja
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3: Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle
 Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3: Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle 2006-2007 Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip off (to
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3: Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle 2006-2007 Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip off (to
Respiration. Energy is everything!
 Respiration Energy is everything! Tesla was incredible Everyone was intrigued by Tesla Tesla showed that energy does not need to be feared So what does this have to do with twinkies? Everything! Cellular
Respiration Energy is everything! Tesla was incredible Everyone was intrigued by Tesla Tesla showed that energy does not need to be feared So what does this have to do with twinkies? Everything! Cellular
HEMATURIJA PRI OTROCIH HAEMATURIA IN CHILDREN
 HEMATURIJA PRI OTROCIH HAEMATURIA IN CHILDREN - ABSTRACT - - UVOD IN OPREDELITEV POJMOV Hematurija je prisotnost krvi v urinu. - - - mesecev. Lahko je - - Hematurija je sicer lahko pomemben znak bolezni
HEMATURIJA PRI OTROCIH HAEMATURIA IN CHILDREN - ABSTRACT - - UVOD IN OPREDELITEV POJMOV Hematurija je prisotnost krvi v urinu. - - - mesecev. Lahko je - - Hematurija je sicer lahko pomemben znak bolezni
A cell has enough ATP to last for about three seconds.
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Ch 9: Cellular Respiration
 Ch 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration An overview Exergonic reactions and catabolic pathway Energy stored in bonds of food molecules is transferred to ATP Cellular respiration provides the energy
Ch 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration An overview Exergonic reactions and catabolic pathway Energy stored in bonds of food molecules is transferred to ATP Cellular respiration provides the energy
Farmakologija noradrenergičnega sistema
 Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Farmakologija noradrenergičnega sistema Prof. dr. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno
Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno toksikologijo, Medicinska fakulteta, Univerza v Ljubljani Farmakologija noradrenergičnega sistema Prof. dr. Lovro Stanovnik Inštitut za farmakologijo in eksperimentalno
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Task Cards. Respiration 1. Cellular. Respiration. Cellular Respiration. Cellular. List two reasons why food is important to living organisms.
 Task Cards Direc(ons: Complete the ques(on or task found on each of the cards. Record your answers on the answer sheet or on your notebook paper as directed by your teacher. 1 List two reasons why food
Task Cards Direc(ons: Complete the ques(on or task found on each of the cards. Record your answers on the answer sheet or on your notebook paper as directed by your teacher. 1 List two reasons why food
Growth. Principles of Metabolism. Principles of Metabolism 1/18/2011. The role of ATP energy currency. Adenosine triphosphate
 Metabolism: Fueling Cell Growth Principles of Metabolism Cells (including your own) must: Synthesize new components (anabolism/biosynthesis) Harvest energy and convert it to a usable form (catabolism)
Metabolism: Fueling Cell Growth Principles of Metabolism Cells (including your own) must: Synthesize new components (anabolism/biosynthesis) Harvest energy and convert it to a usable form (catabolism)
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION. C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15
 Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular I can describe cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways releasing energy from a foodstuff e.g. glucose. This yields energy in the form of ATP adenosine P i P
Cellular I can describe cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways releasing energy from a foodstuff e.g. glucose. This yields energy in the form of ATP adenosine P i P
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical Energy
 Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical Energy 7.1 Mighty Mitochondria More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many of those afflicted die young
Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical Energy 7.1 Mighty Mitochondria More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many of those afflicted die young
Chem 109 C. Fall Armen Zakarian Office: Chemistry Bldn 2217
 Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian ffice: Chemistry Bldn 2217 Chapter 25 o Glycolysis : fates of pyruvate NADH, H + H + C 2 NADH, H + H - (S)-lactic acid lactate dehydrogenase; anaerobic conditions -
Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian ffice: Chemistry Bldn 2217 Chapter 25 o Glycolysis : fates of pyruvate NADH, H + H + C 2 NADH, H + H - (S)-lactic acid lactate dehydrogenase; anaerobic conditions -
Metabolism. Metabolism. Energy. Metabolism. Energy. Energy 5/22/2016
 5//016 Metabolism Metabolism All the biochemical reactions occurring in the body Generating, storing and expending energy ATP Supports body activities Assists in constructing new tissue Metabolism Two
5//016 Metabolism Metabolism All the biochemical reactions occurring in the body Generating, storing and expending energy ATP Supports body activities Assists in constructing new tissue Metabolism Two
Cellular Respiration. Cellular Respiration. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O > 6CO 2 + 6H energy. Heat + ATP. You need to know this!
 Cellular Respiration LISA Biology Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 - - - - - > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy You need to know this! Heat + ATP 1 Did that equation look familiar? * The equation for cellular
Cellular Respiration LISA Biology Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 - - - - - > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy You need to know this! Heat + ATP 1 Did that equation look familiar? * The equation for cellular
STEROIDI KOT ZDRAVILA
 STEROIDI KOT ZDRAVILA Holesterol (ni zdravilo, običajno z zdravili znižujemo njegovo koncentracijo; najbilj znana zdravila so statini) Vitamin D kot zdravilo Žolčne kisline Steroidni hormoni Selektivni
STEROIDI KOT ZDRAVILA Holesterol (ni zdravilo, običajno z zdravili znižujemo njegovo koncentracijo; najbilj znana zdravila so statini) Vitamin D kot zdravilo Žolčne kisline Steroidni hormoni Selektivni
4. Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules? a. 2. d. 5
 1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
g) Cellular Respiration Higher Human Biology
 g) Cellular Respiration Higher Human Biology What can you remember about respiration? 1. What is respiration? 2. What are the raw materials? 3. What are the products? 4. Where does it occur? 5. Why does
g) Cellular Respiration Higher Human Biology What can you remember about respiration? 1. What is respiration? 2. What are the raw materials? 3. What are the products? 4. Where does it occur? 5. Why does
Respiration. Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
An organic catalysts that enhances the speed or likelihood of a bio-chemical reaction by lowering the energy of activation.
 Micro 260 Fall 2009 Name: Allan Keys Tools: You may use your notes and or book for this assignment 1) What is an enzyme? (4 pts) An organic catalysts that enhances the speed or likelihood of a bio-chemical
Micro 260 Fall 2009 Name: Allan Keys Tools: You may use your notes and or book for this assignment 1) What is an enzyme? (4 pts) An organic catalysts that enhances the speed or likelihood of a bio-chemical
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
Intracellular Localization and Some Properties of Cytochrome P450 of Rhizopus nigricans*
 CROATICA CHEMICA ACTA CCACAA 49 (2) 207-212 (1977) CCA-992 YU ISSN 0011-1643 577.15.08 Conference Paper Intracellular Localization and Some Properties of Cytochrome P450 of Rhizopus nigricans* K. Breskvar
CROATICA CHEMICA ACTA CCACAA 49 (2) 207-212 (1977) CCA-992 YU ISSN 0011-1643 577.15.08 Conference Paper Intracellular Localization and Some Properties of Cytochrome P450 of Rhizopus nigricans* K. Breskvar
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Priporočila za zdravljenje primarne imunske trombocitopenije. Barbara Skopec
 Priporočila za zdravljenje primarne imunske trombocitopenije Barbara Skopec ITP = Idiopatična trombocitopenična purpura ITP = primarna imunska trombocitopenija Rodeghiero F, et al. Blood 2009;113:2386
Priporočila za zdravljenje primarne imunske trombocitopenije Barbara Skopec ITP = Idiopatična trombocitopenična purpura ITP = primarna imunska trombocitopenija Rodeghiero F, et al. Blood 2009;113:2386
How Cells Release Chemical Energy. Chapter 8
 How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 8 Impacts, Issues: When Mitochondria Spin Their Wheels More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 8 Impacts, Issues: When Mitochondria Spin Their Wheels More than forty disorders related to defective mitochondria are known (such as Friedreich s ataxia); many
What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP
 ATP Chapter 8 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Energy is stored in organic compounds Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Heterotrophs eat
ATP Chapter 8 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Energy is stored in organic compounds Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Heterotrophs eat
