(From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) Materials and Methods
|
|
|
- Anabel Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XI. THF. DISTRIBUTION OF /~-GLucURONIDASE* BY WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. (From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) PLATES 117 To 118 (Received for publication, November 30, 1956) INTRODUCTION Beta-glucuronidase has been demonstrated histochemically in the skin of the rat (8) and in that of man (2). This paper confirms the observations made by other authors, and gives a more detailed account than is available on the distribution of ~-glucuronidase in the skin of man. All of the cutaneous appendages studied contain/~-glucuronidase; the apocrine sweat glands and the sebaceous glands contain the most. All of the cells in the dermis contain some fl-glucuronidase, but the mast cells seem to have a greater concentration than the others. Materials and Methods Biopsy specimens of skin from the axilla, the back, and the scalp were fixed for 4 hours in neutral, unbuffered 10 per cent formalin. Frozen sections about 30/z in thickness were washed thoroughly in distilled water and then incubated in the buffered substrate mixture of Seligman, et al. (8). In preparing the substrate mixture, 30 mg. ot 6-bromo-2-naphthyl-~-D-glucuronide was dissolved in 5 cc. of absolute alcohol, to which was then added 20 cc. of phospho-citrate buffer (ph 4.9) and 75 cc. of distilled water. Mter enzyme hydrolysis of the ester for 8 hours at 37 C., the product, 6 bromo-2-naphthol, was coupled with tetrazotized diorthoanisidine (diazo blue B), buffered to ph 7.5 with phosphate buffer. Control sections exposed to hot steam and then incubated together with the others showed no enzyme activity. The sections were mounted in glycerin jelly. The azo dye at the place of enzyme reaction is soluble in fat, and preparations deteriorate after a few days if fats are present. The observations, therefore, were made soon after the tissues were prepared. OBSERVATIONS The cytoplasm of all the epidermal cells, from the basal layer to the stratum granulosum, stains a medium blue, an indication of moderate enzyme reaction (Figs. 1 and 2). The staining is never strong and does not occur in tissues that are incubated in the substrate for less than 8 hours. The cytoplasm of the cells of the stratum granulosum and the keratohyalin granules stain an * This work was supported in part by a grant from the United States Public Health Service, RG 2125 C J. BIOPHYslc. AND BIOCHE~. CYTOL., 1957, VoL 3, No. 3
2 344 ~-GLUCUNONIDASE IN HUM.AN SKIN intense blue. These cells and those just above them form a strongly colored band which is easily distinguished from the rest of the epidermis (Fig. 2). A similar band has also been observed by others in the skin of the rat and of man (2, 8). The stratum corneum is almost unreactive. At the junction of the epidermis and the ducts of the eccrine sweat glands, in the lower coil of the intraepidermal portion of the duct, there is an abrupt transition from the moderately reactive epidermis to the strongly reactive epithelium of the duct (Fig. 3). The reaction in the duct becomes increasingly intense and is strongest in the coiled, dermal portion (Fig. 4). Both layers of cells of the duct, and even the cuticle, are colored a deep blue. The basal cells are slightly more strongly reactive than the superficial cells. A strong reaction of variable intensity is also always encountered in the secretory cells of the eccrine sweat glands. The lack of delicate resolution in these preparations does not permit one to discern precisely whether or not there is a difference in the distribution of the enzyme in the dark and light cells. The reaction, however, seems to be stronger in the light cells (Fig. 5). The cytoplasm and some coarse granules above the nucleus become colored a deep blue. The nuclei remain unstained. The myoepithelial cells have a very slight reaction. The cells in the duct of apocrine glands are stained a moderately deep blue, like the cells of the outer root sheath of hair follicles. The secretory cells of the aprocrine glands, however, have the strongest concentration of enzyme reaction in the skin (Fig. 6). The base of each secretory cell is colored a homogeneous dark blue. The cytoplasm which bulges into the lumen is full of coarse, very strongly positive granules. In all cells, regardless of their sizes or shapes, the reaction is very strong all the way to the luminal edge. The myoepithelial cells are very lightly colored. The wall of the pilary canal, in contrast with the surface epidermis, with which it is contiguous, is stained a moderately strong blue. The ducts of sebaceous glands are stained dark blue. The sebaceous glands are very strongly reactive (Fig. 8). The peripheral, undifferentiated cells are a homogeneous dark blue; the cells undergoing early differentiation and the mature sebaceous cells contain many intensely reactive granules of different sizes. The sebum shows no reaction. The outer root sheath in the upper half of active hair follicles shows moderate enzyme reaction, particularly in the cells toward the periphery; the reaction diminishes centripetally. The inner border of the outer root sheath, and the inner root sheath, show no reaction. From about midway in the follicle to the bulb, the reaction in the outer root sheath becomes increasingly stronger. The cells of the outer root sheath around the level of the keratogenous zone of the cortex are full of very intensely staining granules. All of the cells of the lower part of the bulb, or matrix, are strongly reactive (Fig. 7).
3 WILLIAM[ MONTAGNA 345 All of the layers of cells which move upward from the matrix also stain an intense, homogeneous blue color (Fig. 7). The layers of the inner root sheath and those of the cortex lose their reactivity when they begin to undergo keratinization. The cortex loses its reaction first, immediately above the constriction of the follicle, but the cells of the two layers of cuticle and the cells of Huxley's layer show some reaction up to about the middle of the follicle (Fig. 7). In Henle's layer the reaction fades at the constriction of the follicle. The dermal papilla of active hair follicles shows a very strong reaction in all of its cells. In quiescent hair follicles enzyme reaction is concentrated in the entire outer root sheath, or epithelial sac. The reaction is not particularly strong, and resembles that in the pilary canal of active follicles. The cells of the dermal papilla are very small and show practically no reaction. In the dermis, large amounts of ~-glucuronidase are concentrated in the myelinated nerve fibers. Perhaps all nerve fibers contain some enzyme activity. The fibroblasts are usually unreactive, or they show at most a faint blue tint. The endothelial cells and the smooth muscle fibers of the arteries and of the arrectores pilorum are moderately reactive. The cells of the blood vessels around active hair follicles and sebaceous glands and those in the papillary layer show some enzyme activity. The recognizable mature mast cells in the papillary layer contain intensely reactive coarse granules; those in the adipose layer and those in the areolar tissue around sweat glands are intensely stained (Fig. 9). The young fat cells in the adipose layer contain dark blue staining granules in the cytoplasm. Similar granules are also found in the cytoplasm in the periphery of mature fat cells (8). The fibroblasts in the fatty layer are more strongly reactive than those elsewhere. DISCUSSION It has been demonstrated previously that human skin contains a great deal of ~-glucuronidase (3). When the dermis and epidermis were separated, the epidermis yielded considerably more enzyme activity than the dermis. Histochemical studies, however, only partially support this observation, and the cutaneous appendages found in the dermis are much richer in/3-glucuronidase than is the epidermis. An explanation for this may be that the specimens of human skin used for biochemical analysis were from the female breast, an area of skin that contains relatively few appendages. If skin containing numerous sweat glands, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands had been used, the figures would have been different. The histochemical findings in this investigation are in agreement with those of Braun-Falco (2). The secretory coil of both eccrine and apocrine sweat glands has heavy concentrations of fl-glucuronidase, but the enzyme is much
4 346 ~-GLUCURONIDASE IN HUMAN SKIN more abundant in the apocrine glands. In this respect, the distribution of /~-glucuronidase in sweat glands is like that of short-chain esterases (1). No other structure in the skin contains so much/3-glucuronidase as the apocrine glands. The distribution of the enzyme in hair follicles is similar to that of succinic dehydrogenase (7). The strongest concentration of fl-glucuronidase is in the outer root sheath around the level of the keratogenous zone. The cells in this level of the root sheath are laden with glycogen and with substances which stain metachromatically (5, 6). The keratogenous zone of the cortex is a region of high protein synthesis, and requires ready access to sources of energy. Being removed from the blood supply, its closest path of exchange is by way of the outer root sheath. The outer root sheath, at this level, must be a very active metabolic entity, and through it a great deal of exchange must take place. The dermal papilla, another site of high metabolic, and possibly also inductive activity, also has strong concentrations of/~-glucuronidase. In quiescent follicles the reaction for fl-glucuronidase is much reduced in the outer root sheath, and there is practically no reaction in the dermal papilla. In active hair follicles, /3-glucuronidase is most concentrated in the same places where there are substances which stain metachromatically with toluidine blue, and which are probably mucopolysaccharides. The dermal papilla and the outer root sheath of quiescent hair follicles do not contain metachromatically staining substances, and they also show a dramatic reduction in /3-glucuronidase. /3-glucuronidase is abundant as well in adipose tissues, sebaceous glands, and in myelinated nerve fibers but there is no intention to infer from this that fl-glucuronidase should be equated with lipide synthesis. In the epidermis a band with strong enzyme activity corresponds to a band also rich in esterase (4, 1). This band of the epidermis seems to be associated with lipide synthesis or liberation. The presence of ~-glucuronidase in mast cells may prove to be significant if these cells really secrete glucuronides. The mast cells of the mouse, the rat, and the cat also contain the enzyme, and this is a characteristic feature of these cells. SUMMARY 1. Various amounts of/3-glucuronidase activity may be found in all of the cutaneous appendages. 2. In the epidermis, the basal layer and the Malpighian layer contain a moderate amount of it, but a band of cells, including the stratum granulosum and the cells immediately above it, is rich in/3-glucuronidase. 3. The cells of the duct of eccrine sweat glands have moderately strong enzyme activity, but those in the secretory coil are strongly reactive; small and large reactive granules are crowded in the reactive cytoplasm.
5 WILLIAM: MONTAGNA The cells of the secretory coil of the apocrine glands contain more ~-glucuronidase than any other cutaneous appendage. 5. In the sebaceous glands, a very strong concentration of enzyme activity is found in the undifferentiated peripheral cells, a smaller amount of it is found in the differentiating cells. 6. In active hair follicles, the largest amount of ~-glucuronidase is found in the outer root sheath and in the bulb. In the outer sheath, the strongest concentration is found around the level of the keratogenous zone of the cortex. The dermal papilla is strongly reactive. In quiescent hair follicles, the outer root sheath has a moderate amount of enzyme concentration, but the dermal papilla is unreactive. 7. in the dermis, the fibroblasts in the papillary layer, the smooth muscle cells of the arrectores pilorum and the tunica media of arteries, and the fat cells all exhibit enzyme activity. Mast cells show a great concentration of /~-glucuronidase. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. Braun-Falco, O., Arch. klin. u. exp. Dermatol., 1956, 202, Braun-Falco, O., Arch. klin. u. exp. Dermatol., 1956, 203, Mesirow, S. M., and Stoughton, R. B., J. Inv. Dermatol., 1954, 23, Montagna, W., J. Biophysic. and Biochem. Cytol., 1955, 1, Montagna, W., Chase, H. B., and Lobitz, W. C., Jr., Anat. Rec., 1952, 114, Montagna, W., Chase, H. B., and Melaragno, H. P., J. Nat. Cancer Inst., 1951, 12, Montagna, W., and Formisano, V., Anat. Rec., 1955, 122, Seligrnan, A. M., Tsou, K. C., Rutenburg, S. H., and Cohen, R. B., J. Histochem. and Cytochem., 1954, 2, 209.
6 348 ~-GLUCURONIDASE IN HUMAN SKIN EXPLANATION OF PLATES Pr_~TE 117 FIG. 1. The epidermis from the back, with a moderate amount of enzyme activity in the Malpighian layer. The stratum granulosum and the cells just above it form a strongly reactive band. This is seen better in Fig FIG. 2. Enlarged detail of Fig. 1. The band rich in/3-glucuronidase is clearly visible. X 250. FIG. 3. Enzyme activity in the intraepidermal portion of the duct of an eccrine sweat gland. Contrast the strength of the reaction in the duct, in the lower part of the figure, with that of the epidermis, in the upper part of the figure. X 65. FIo. 4. Segments of a coiled part of an eccrine sweat gland. The arrow points to a secretory segment. Both duct and secretory segment are strongly reactive. X 65. FIo. 5. Transverse section through the secretory coil of an eccrine sweat gland. The clear cells seem to have a stronger concentration of the enzyme than the dark cells. 750.
7 THE JOURNAL OF BIOPHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL CYTOLOGY PLATE 117 VOL. 3 (Montagna: ~-Glucuronidase in human skin)
8 PLATE 118 FIG. 6. Intense reaction in the secretory cells of an apocrine sweat gland from the axilla. The luminal border is on the right of the figure FIG. 7. Beta-glucuronidase reaction in an active hair follicle from the axilla. The arrow points to the lower level of the keratogenous zone. The black center of the bulb is melanin and does not indicate enzyme activity. The reaction is very strong in the cells of the cuticle of the cortex and of the inner root sheath. 75. Fro. 8. Very strong enzyme reaction in sebaceous glands. 75. FIG. 9. Strong, granular reaction in the mast cells (arrows). This is an enlarged derail of Fig. 4, in which mast cells are very numerous. 750.
9 THE JOURNAL OF BIOPHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL CYTOLOGY PLATE 118 VOL. 3 (Montagna: fl-glucuronidase in human skln)
(From Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, ProVence) P~s 3 To 5. Materials and Methods
 Published Online: 25 January, 1955 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.1.1.13 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 21, 2018 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN IX. THE Dm~mUT~ON Ot NoN-SP~.c~Ic
Published Online: 25 January, 1955 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.1.1.13 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on June 21, 2018 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN IX. THE Dm~mUT~ON Ot NoN-SP~.c~Ic
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN*
 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN* VI. THE DIsTruBuTIoN OF SULFHYDEYL AND DISULFIDE GEOIJPStt WILLIAM MONTAGNA, Pu.D., ARTHUR Z. EISEN, M.S., ANN H. RADEMACHER, BA., AND HERMAN B. CHASE, Pn.D.
HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN* VI. THE DIsTruBuTIoN OF SULFHYDEYL AND DISULFIDE GEOIJPStt WILLIAM MONTAGNA, Pu.D., ARTHUR Z. EISEN, M.S., ANN H. RADEMACHER, BA., AND HERMAN B. CHASE, Pn.D.
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
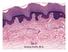 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
21 Skin and it s Accessories
 21 Skin and it s Accessories 21-001 Skin 1 2 Sweat glands Adipose tissue 3 Retinaculum cutis 21-01. Skin of the palm 1. General view. Human, H-E stain, x 3.3. Opening of sweat gland duct Stratum corneum
21 Skin and it s Accessories 21-001 Skin 1 2 Sweat glands Adipose tissue 3 Retinaculum cutis 21-01. Skin of the palm 1. General view. Human, H-E stain, x 3.3. Opening of sweat gland duct Stratum corneum
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
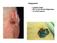 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4
 Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4 CHAPTER 3: Cells and Tissues 1. The smallest unit of living tissue is called a. All living organisms are composed of these basic units where all life processes
Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4 CHAPTER 3: Cells and Tissues 1. The smallest unit of living tissue is called a. All living organisms are composed of these basic units where all life processes
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Figure 6.1 Transparency Master 37
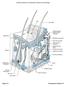 Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Cell Types in Epidermis
 Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Appendages hair follicles nails sweat glands sebaceous glands mammary glands Dermis Dense, irregular connective tissue Hypodermis Superficial fascia
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands
 Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN
 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XII. CHOLINESTERASES IN THE HAIR FOLLICLES OF THE SCALP* WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. AND RICHARD A. ELLIS, PH.D. Hair follicles are surrounded by a network of interlocking
HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XII. CHOLINESTERASES IN THE HAIR FOLLICLES OF THE SCALP* WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. AND RICHARD A. ELLIS, PH.D. Hair follicles are surrounded by a network of interlocking
IN the skin of the mouse we find that the dermal papilla of growing hair
 (240 Cyclic Changes in Polysaccharides of the Papilla of the Hair Follicle By WILLIAM MONTAGNA, HERMAN B. CHASE, JANET D. MALONE, AND HELEN P. MELARAGNO (From Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island,
(240 Cyclic Changes in Polysaccharides of the Papilla of the Hair Follicle By WILLIAM MONTAGNA, HERMAN B. CHASE, JANET D. MALONE, AND HELEN P. MELARAGNO (From Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island,
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
BI 121 LAB. WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System
 BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
BI 121 LAB 2-1 WEEK 2: Tissues (continued); Integumentary System This week you will 1) Review the four major tissue types 2) Review the characteristics of epithelial tissues. 3) Learn the major characteristics
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Histology of Integumentary System
 Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
3. Dense connective tissue is found in skin, & surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs.
 Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel,
 Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems
 Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems Welcome to Lesson 3 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. I
Basic Human Anatomy Lesson 3: The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems Welcome to Lesson 3 of the Basic Human Anatomy Course. Today, we ll be studying the Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. I
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Skin Homework. (Skin is the largest organ in the body)
 Skin Homework (Skin is the largest organ in the body) This homework is following the information in the Louise Tucker book so the answers should be easy to find. 1 Label the Cross Section of Skin below:
Skin Homework (Skin is the largest organ in the body) This homework is following the information in the Louise Tucker book so the answers should be easy to find. 1 Label the Cross Section of Skin below:
Chapter 6: Skin & the. 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing of Wounds
 Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Experiment Note the locations of the epidermis, dermis, dermal papillae, and the sweat glands. Note that fat cells that comprise the
 Experiment 1 Examining Skin, Bones and Muscle Histology Experiment Inventory Skin Digital Slide Images Cortical (Compact) Bone Digital Slide Image Trabecular (Spongy) Bone Digital Slide Image Cardiac Muscle
Experiment 1 Examining Skin, Bones and Muscle Histology Experiment Inventory Skin Digital Slide Images Cortical (Compact) Bone Digital Slide Image Trabecular (Spongy) Bone Digital Slide Image Cardiac Muscle
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
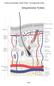 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Figure 4.1. Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 115
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Chapter 4. Skin and Body Membranes. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Mitosis Models 3-5. Chromosome. #1 Prophase. #2 Prophase. 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids. 2n = 4
 MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
Student Objectives. 7. Describe the structure of nails.
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Histology of Skin. dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008
 Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Skin Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
(From The Rockefeller Institute) Materials and Methods. Observations with the Electron Microscope
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE PAPILLOMA VIRUS IN THE SKIN OF THE RABBIT* BY ROBERT S. STONE,~ M.D., RICHARD E. SHOPE, M.D., DAN H. MOORE, P,~.D. (From The Rockefeller Institute) PLATES
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
