Name: Date: Class: Construction of the Cell Membrane
|
|
|
- Anabel Cobb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Construction of the Cell Membrane Today we will be working on looking at the cell membrane on the web. Go to the following website: Be sure to type it exactly. You should see the title in blue. A small, green next button is in the right-hand corner. Read and follow along. I will periodically have questions for you to answer. 1. What is the cell membrane composed of? A. Lipds B. Proteins 2. What are the two major types of proteins? A. fibrous B. integral and peripheral 3. What types of molecules CAN go through the membrane? Lipid-soluble substances 4. What types of molecules CANNOT go through the membrane? Water-soluble substances 5. Draw a picture of the phospholipid bilayer: 6.What do you think hydrophobic means? Water insoluble (water-hating) 7. What do you think hydrophilic means? Water soluble (water-loving)
2 Serve as receptors 8. What do the fibrous proteins do? 9. What is the difference between pore proteins and channel proteins? Pores allows lipid insoluble things through, channels allow ions through. 10.What does peripheral mean? Associated with the surface 11.What are glycoproteins? Proteins with carbohydrate associations 12.Have you seen glycoproteins somewhere else? Where? Cell-surface markers, in class 13.What does cholesterol do for the cell membrane? Helps make the membrane impermeable to water, stabilizes the membrane Pore protein, phospholipid, fibrous proteins, glycoprotein, channel protein 14.Complete Question 1 of 10. Write your answers down from left to right. 15.Question 2 of 10: Which part forms the basic frame of the cell membrane? Phospholipid OR #2, OR B OR second from left OR 16.Question 3 of 10: Where are the hydrophilic heads located on the membrane below?
3 17. Question 4 of 10: Where are the hydrophobic tails located on the membrane below? 18.Question 5 of 10: Which one was the fibrous receptor protein? Third from the left OR #3 OR C OR 19.Question 6 of 10: Which one was the pore protein? First from the left, OR #1 OR A OR 20.Question 7 of 10: Which one was the channel protein? Fifth or last from the left, OR #5, OR E, OR 21.Question 8 of 10: Which one was the glycoprotein?
4 Fourth from the left, OR #4, OR D, OR 22.Question 9 of 10: What is the function of the glycoprotein? c) identification and recognition 23.Question 10 of 10: What molecules are found in the animal cell membranes, but not in plant cell membranes? a) cholesterol When you are finished go to the following websites: Click on 5.1 The Fluid Mosaic Model. Identify components of a cell membrane. Some things may be new to you. Write the new things in the space below. New words should be accompanied by definitions. Cholesterol: Increases the fluidity of the membrane Extracellular Region: Outside the cell, shown by oligosaccharide components of glycolipids and glycoproteins Hydrophobic Area of the Membrane: fatty acid tails of phosphor lipids Non-Transmembrane Integral Protein: protein that penetrates the lipid bilayer but does not go all the way through Oligosaccharide: carbohydrate (15-units) that is attached to a protein (glycoprotein) or lipid (glycolipid) Peripheral Protein: proteins not attached to lipid bilayer, usually attached to integral proteins Transmembrane Integral Protein: protein that extens all the way through the lipid bilayer THEN Write down in the space below how this animation illustrates why they call it the fluid mosaic model.
5 The 'Fluid' part represents how some parts of the membrane can move around freely, if they are not attached to other parts of the cell. The 'mosaic' part illustrates the 'patchwork' of proteins that is found in the Phospholipid Bilayer. (
Main Functions maintain homeostasis
 The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
The Cell Membrane Main Functions The main goal is to maintain homeostasis. Regulates materials moving in and out of the cell. Provides a large surface area on which specific chemical reactions can occur.
The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7)
 The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7) Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water Aaaah, one of those structure
The Cell Membrane (Ch. 7) Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water Aaaah, one of those structure
Cell Boundaries. Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h
 Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Bell Work The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and strong acids to aid in the
 Bell Work The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and strong acids to aid in the digestion of food, playing a very important role in
Bell Work The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. The stomach secretes digestive enzymes and strong acids to aid in the digestion of food, playing a very important role in
What do you remember about the cell membrane?
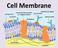 Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cell Membrane What do you remember about the cell membrane? Cell (Plasma) Membrane Separates the internal environment of the cell from the external environment All cells have a cell membrane Selectively
Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins.
 Study Guide e Plasma Membrane You should be able to write out the definitions to each of the following terms in your own words: plasma membrane fluid mosaic integral proteins peripheral proteins receptor
Study Guide e Plasma Membrane You should be able to write out the definitions to each of the following terms in your own words: plasma membrane fluid mosaic integral proteins peripheral proteins receptor
Name: Period: Date: Cell Transport Tutorials CELL MEMBRANE
 Cell Transport Tutorials CELL MEMBRANE http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index.asp?objid=ap1101 Click through the animation. As you do, answer the following questions: 1. What is the fundamental unit
Cell Transport Tutorials CELL MEMBRANE http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index.asp?objid=ap1101 Click through the animation. As you do, answer the following questions: 1. What is the fundamental unit
Cell Membranes. Q: What components of the cell membrane are in a mosaic pattern?
 Cell Membranes The cell / plasma membrane is. Selective in that it allows things in and some things out of the cell. Recall that phospholipids have hydrophobic and hydrophilic. The term to describe this
Cell Membranes The cell / plasma membrane is. Selective in that it allows things in and some things out of the cell. Recall that phospholipids have hydrophobic and hydrophilic. The term to describe this
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 7 Objectives Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion Distinguish between the following pairs or sets of terms: peripheral and integral
(03) WMP/Jun13/BIOL1
 3 Do not write outside the box Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagram shows the structure of the cell-surface membrane of a cell. C B A 1 (a) Name A and B. A... B... (2 marks) 1 (b)
3 Do not write outside the box Answer all questions in the spaces provided. 1 The diagram shows the structure of the cell-surface membrane of a cell. C B A 1 (a) Name A and B. A... B... (2 marks) 1 (b)
1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment
 Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
The Cell Membrane. Lecture 3a. Overview: Membranes. What is a membrane? Structure of the cell membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model. Membranes and Transport
 Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 2.4.2 Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells Membranes provide structural order for metabolism Form most of the cell's organelles Compartmentalize chemical
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules. Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine
 Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Membrane Structure and Membrane Transport of Small Molecules Assist. Prof. Pinar Tulay Faculty of Medicine Introduction Cell membranes define compartments of different compositions. Membranes are composed
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment. Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane
 Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Build-A-Membrane. Print-and-Go. Name Date
 Name Date Print-and-Go http://learn.genetics.utah.edu Build-A-Membrane Cell membranes are made of phospholipid molecules that arrange themselves into two rows called a bilayer. s are embedded in the phospholipid
Name Date Print-and-Go http://learn.genetics.utah.edu Build-A-Membrane Cell membranes are made of phospholipid molecules that arrange themselves into two rows called a bilayer. s are embedded in the phospholipid
Lipids are macromolecules, but NOT polymers. They are amphipathic composed of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol
 d 1 2 Lipids are macromolecules, but NOT polymers. They are amphipathic composed of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol backbone. The phosphate head group is hydrophilic water
d 1 2 Lipids are macromolecules, but NOT polymers. They are amphipathic composed of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails attached to a glycerol backbone. The phosphate head group is hydrophilic water
3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes SPECIFICATION The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes,
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes SPECIFICATION The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes,
Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer. Membrane Structure and Function. Fluid Mosaic Model. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Cell Membrane: a Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Hydrophilic Head Hydrophobic Tail Lipid Bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model Mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty
Membrane transport. Pharmacy Dr. Szilvia Barkó
 Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Membrane transport Pharmacy 04.10.2017 Dr. Szilvia Barkó Cell Membranes Cell Membrane Functions Protection Communication Import and and export of molecules Movement of the cell General Structure A lipid
Phospholipids. Extracellular fluid. Polar hydrophilic heads. Nonpolar hydrophobic tails. Polar hydrophilic heads. Intracellular fluid (cytosol)
 Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Module 2C Membranes and Cell Transport All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Eukaryotic cells also contain internal membranes and membrane- bound organelles. In this module, we will examine the
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function
 Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
Cell Membrane-Structure and Function BIO 250 Living things are composed of cells and cell products (extracellular) Cells are the basic unit of structure They are the basic unit of function They vary in
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC. Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC Cell Membrane Structure and Function 4.1 How Is the Structure of a Membrane Related to Its Function? 4.1.1 The Plasma Membrane Isolates the Cell While Allowing Communication
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND TRAFFIC Cell Membrane Structure and Function 4.1 How Is the Structure of a Membrane Related to Its Function? 4.1.1 The Plasma Membrane Isolates the Cell While Allowing Communication
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Membrane Structure and Function. Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function
 Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Membrane Structure and Function Selectively permeable membranes are key to the cell's ability to function Amphipathic Molecules Have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipids have hydrophilic
Cell Membranes and Signaling
 5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
5 Cell Membranes and Signaling Concept 5.1 Biological Membranes Have a Common Structure and Are Fluid A membrane s structure and functions are determined by its constituents: lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Classification of Lipids
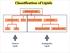 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222
 Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
Ch. 7 Cell Membrane BIOL 222 Overview: Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings Selec4ve permeability Allowance of some substances to cross more easily
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transportation Oct 20 7:07 PM Cell Membrane Forms a barrier between the cell and the external environment. Has three main functions: 1) helps the cell retain the molecules
Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 4 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
Cell Transport. Movement of molecules
 Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
1. Double bilayer of with imbedded, dispersed 2. Bilayer consists of, cholesterol, and glycolipids
 Bio Chapter 7.3 Cellular Movement Notes I. Background Information A. - a mixture in which the (molecules being ) never settle out in the (water). B. In a 25% Koolaid solution, how much water is there?
Bio Chapter 7.3 Cellular Movement Notes I. Background Information A. - a mixture in which the (molecules being ) never settle out in the (water). B. In a 25% Koolaid solution, how much water is there?
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function. Key Terms:
 Key Terms: Selectively permeable Fluid mosaic model Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phosphate head Fatty acid tail Davson-Danielli Singer-Nicolson Freeze-Fracture EM Unsaturated
Key Terms: Selectively permeable Fluid mosaic model Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Phosphate head Fatty acid tail Davson-Danielli Singer-Nicolson Freeze-Fracture EM Unsaturated
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: 1) Isolate cell s contents from outside environment
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
DistanceLearningCentre.com
 DistanceLearningCentre.com Course: Essential reading: Tortora, G.J., and Grabowski, S.R., 2002. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 10 th ed. London: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN: 9780471224723 Recommended
DistanceLearningCentre.com Course: Essential reading: Tortora, G.J., and Grabowski, S.R., 2002. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 10 th ed. London: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN: 9780471224723 Recommended
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Membrane Structure and Function - 1
 Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Membrane Structure and Function - 1 The Cell Membrane and Interactions with the Environment Cells interact with their environment in a number of ways. Each cell needs to obtain oxygen and other nutrients
Cell membranes. Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102
 Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
Cell membranes Stef Elorriaga 4/11/2016 BIO102 Announcements Lab report 2 is due now Quiz 2 is on Wednesday on cells, part of the cells, plasma membrane, and enzymes Outline of the day Activity on the
The Cell Membrane: How the cell maintains homeostasis
 The Cell Membrane: How the cell maintains homeostasis Cell Homeostasis Cats hate and are afraid of water. What do you hate or fear? Think of one or two things that you hate. What do you love and what are
The Cell Membrane: How the cell maintains homeostasis Cell Homeostasis Cats hate and are afraid of water. What do you hate or fear? Think of one or two things that you hate. What do you love and what are
CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT (PASSIVE and ACTIVE) Webquest
 Name: Period: CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT (PASSIVE and ACTIVE) Webquest PART I: CELL MEMBRANES WEBSITE #1: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap1101 1. What is the BASIC UNIT of LIFE?
Name: Period: CELL MEMBRANE & CELL TRANSPORT (PASSIVE and ACTIVE) Webquest PART I: CELL MEMBRANES WEBSITE #1: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap1101 1. What is the BASIC UNIT of LIFE?
Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes
 2.4 Membranes 2.4.1 - Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes Phospholipid Bilayer - This is arranged with the hydrophilic phosphate heads facing outwards, and the hydrophobic fatty
2.4 Membranes 2.4.1 - Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of membranes Phospholipid Bilayer - This is arranged with the hydrophilic phosphate heads facing outwards, and the hydrophobic fatty
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Cell Membrane Diagram
 Cell Membrane Diagram Draw a diagram of the cell membrane. Please include (and label): - Phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) Protein channel An ion pump Cholesterol Gylcoproteins* Define
Cell Membrane Diagram Draw a diagram of the cell membrane. Please include (and label): - Phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) Protein channel An ion pump Cholesterol Gylcoproteins* Define
Structure and Function
 Structure and Function Cell Membrane Functions Cell membrane surrounds the cell, regulating the transport of materials into and out of the cell Cell Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer: a double layer of
Structure and Function Cell Membrane Functions Cell membrane surrounds the cell, regulating the transport of materials into and out of the cell Cell Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer: a double layer of
The Plasma Membrane. 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane. Phospholipid Bilayer. The Plasma Membrane
 5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
5.1 The Nature of the Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane Four principal components in animals Phospholipid bilayer Molecules of cholesterol interspersed within the bilayer. Membrane proteins embedded
Movement of substances across the cell membrane
 Ch 4 Movement of substances across the cell membrane Think about (Ch 4, p.2) 1. The structure of the cell membrane can be explained by the fluid mosaic model. It describes that the cell membrane is mainly
Ch 4 Movement of substances across the cell membrane Think about (Ch 4, p.2) 1. The structure of the cell membrane can be explained by the fluid mosaic model. It describes that the cell membrane is mainly
Cell Membrane and Transport
 Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
Cell Membrane and Transport 29/06/2015 11:08 AM Describe the Characteristics of the phospholipid Bilayer. The Phospholipid bilayer is made up of a double layer of membrane lipids that have a hydrophobic
1.4 Page 1 Cell Membranes S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport Page 1 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport from your syllabus l. Cell Membrane Structure 1. Read and
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport Page 1 1.3 Cell Membranes and Transport from your syllabus l. Cell Membrane Structure 1. Read and
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins
 1 Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins 2 Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Amphipathic Phosphate attracted to
1 Boundary Lipid bilayer Selectively Permeable Fluid mosaic of lipids and proteins Contains embedded proteins 2 Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Amphipathic Phosphate attracted to
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis What is the cell membrane? A quick review A. Cell Membrane and Cell Transport. Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport
 Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to https://shimkoscience.weebly.com/ and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport
Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to https://shimkoscience.weebly.com/ and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Name Period Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes.
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Name Period Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes.
Phospholipids. Phosphate head. Fatty acid tails. Arranged as a bilayer. hydrophilic. hydrophobic. Phosphate. Fatty acid. attracted to water
 The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water I want you to remember: Structure
The Cell Membrane Phospholipids Phosphate head hydrophilic Fatty acid tails hydrophobic Arranged as a bilayer Phosphate attracted to water Fatty acid repelled by water I want you to remember: Structure
BELLRINGER DAY In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane?
 BELLRINGER DAY 01 1. In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane? THE CELL MEMBRANE S T R U C T U R E A N D F U N C T I O N CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS Cell
BELLRINGER DAY 01 1. In which types of cell is a cell membrane located? 2. What is the function of the cell membrane? THE CELL MEMBRANE S T R U C T U R E A N D F U N C T I O N CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS Cell
The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on C number 3 of a triacylglycerol molecule O O CH 2 O C R CH 2 O P O X OH.
 Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Phosphoacylglycerols (Phospholipids) Phosphoacylglycerols are fatty acid esters of glycerol which also contain a phosphate group and other specific groups The phosphate group replaces the fatty acid on
Cell Membrane Structure and Function. What is the importance of having a cell membrane?
 Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Cell Membrane & Transport SBI4U 2016/10/18
 Cell Membrane & Transport SBI4U 2016/10/18 Cell membrane All cells exist in an aqueous environment, separated by their membrane; The membrane regulates which substances pass into or out of the cell; It
Cell Membrane & Transport SBI4U 2016/10/18 Cell membrane All cells exist in an aqueous environment, separated by their membrane; The membrane regulates which substances pass into or out of the cell; It
PLASMA MEMBRANE. Submitted by:- DR.Madhurima Sharma PGGCG-II,Chandigarh
 PLASMA MEMBRANE Submitted by:- DR.Madhurima Sharma PGGCG-II,Chandigarh LIPID COMPONENTS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE The outer leaflet consists predominantly of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and glycolipids,
PLASMA MEMBRANE Submitted by:- DR.Madhurima Sharma PGGCG-II,Chandigarh LIPID COMPONENTS OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE The outer leaflet consists predominantly of phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, and glycolipids,
Diffusion across cell membrane
 The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
The Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport Diffusion across cell membrane Cell membrane is the boundary between inside & outside separates cell from its environment Can it be an impenetrable boundary? NO!
Biology. Membranes.
 1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
The Cell Membrane. Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings. Controls traffic in & out of the cell
 The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
The Cell Membrane 1 Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings thin barrier = 8nm thick Controls traffic in & out of the cell selectively permeable allows some substances
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Biological membranes are composed of lipid bilayers
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 100-119. There are many great figures in this chapter. Make sure you study all
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 5 Membrane Transport and Cell Signaling BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 100-119. There are many great figures in this chapter. Make sure you study all
Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure. Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure. Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure. Functions of cell membrane. Functions of cell membrane
 Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure Functions of cell membrane 1 Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure Functions of cell membrane As a container/ barrier to movement of small molecules. Figure 11 2 Chapt. 11, Membrane
Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure Functions of cell membrane 1 Chapt. 11, Membrane Structure Functions of cell membrane As a container/ barrier to movement of small molecules. Figure 11 2 Chapt. 11, Membrane
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
The Cell Membrane AP Biology
 The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
The Cell Membrane AP Biology! 2007-2008 Overview! Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings " thin barrier = 8nm thick! Controls traffic in & out of the cell " selectively permeable
Cell Membrane Structure (1.3) IB Diploma Biology
 Cell Membrane Structure (1.3) IB Diploma Biology Essential idea: The structure of biological membranes makes them fluid and dynamic http://www.flickr.com/photos/edsweeney/6346198056/ 1.3.1 Phospholipids
Cell Membrane Structure (1.3) IB Diploma Biology Essential idea: The structure of biological membranes makes them fluid and dynamic http://www.flickr.com/photos/edsweeney/6346198056/ 1.3.1 Phospholipids
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 4.1 What is a Cell? Each cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells) or a nucleoid (in prokaryotic cells) 1 Nucleoid concentrated DNA
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 4.1 What is a Cell? Each cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells) or a nucleoid (in prokaryotic cells) 1 Nucleoid concentrated DNA
The Cell Membrane. Why cells must control materials. Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival.
 The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
7.3 Cell Boundaries. Regents Biology. Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham
 7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 20: Cell Membrane
 Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 20: Cell Membrane Date Objective: Students will be able to prove why a simple defect in a cell membrane protein can make a life or- death difference.
Name Unit 2: Characteristics of Living Things Lesson 20: Cell Membrane Date Objective: Students will be able to prove why a simple defect in a cell membrane protein can make a life or- death difference.
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function What You Must Know: Why membranes are selectively permeable. The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. How water will move if a cell is placed
Membrane Structure and Function What You Must Know: Why membranes are selectively permeable. The role of phospholipids, proteins, and carbohydrates in membranes. How water will move if a cell is placed
In & Out of the Cell (cell transport) Web Quest.
 In & Out of the Cell (cell transport) Web Quest All website links can be found on the THS library home page. Objectives: Understand the structure and function of the cell membrane. Understand how cells
In & Out of the Cell (cell transport) Web Quest All website links can be found on the THS library home page. Objectives: Understand the structure and function of the cell membrane. Understand how cells
The Cell Membrane. Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit. Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia
 The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
The Cell Membrane Usman Sumo Friend Tambunan Arli Aditya Parikesit Bioinformatics Group Faculty of Mathematics and Science University of Indonesia Overview Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving
The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11
 1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
1 February 26, The Cell Membrane & Movement of Materials In & Out of Cells PACKET #11 Introduction I 2 Biological membranes are phospholipid bilayers with associated proteins. Current data support a fluid
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
CHAPTER 8 MEMBRANE STUCTURE AND FUNCTION Plasma Membrane Plasma membrane is selectively permeable, (allowing some substances to cross more easily than others) PM is flexible bends and changes shape
10/28/2013. Double bilayer of lipids with imbedded, dispersed proteins Bilayer consists of phospholipids, cholesterol, and glycolipids
 Structure of a Generalized Cell MEMBRANES Figure 3.1 Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Glycocalyx is
Structure of a Generalized Cell MEMBRANES Figure 3.1 Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Separates intracellular fluids from extracellular fluids Plays a dynamic role in cellular activity Glycocalyx is
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE. Lecture 8. Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S. Azam BIOL 266/
 1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Lecture 8 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Plasma Membrane 2 Plasma membrane: The outer boundary of the cell that separates it from the world
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Membrane Structure and Function
 Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Membrane Structure and Function Check Your Gummy Bears Ø Take Day One measurements l Same measurements you took yesterday Ø What type solution was the gummy bear in? Hyper, Hypo, or Isotonic? Ø Put your
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function 1. Membrane Structure 2. Transport Across Membranes 1. Membrane Structure Chapter Reading pp. 125-129 What are Biological Membranes? Hydrophilic head WATER They
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure & Function 1. Membrane Structure 2. Transport Across Membranes 1. Membrane Structure Chapter Reading pp. 125-129 What are Biological Membranes? Hydrophilic head WATER They
