The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis What is the cell membrane? A quick review A. Cell Membrane and Cell Transport. Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport
|
|
|
- Calvin Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport Cell Membrane and Cell Transport Name: Directions: Go to and on the Biology page, find the document labelled Cell Membrane and Cell Transport and use the information it has to fill out this paper. Warm-Up Stations: Station 1 Which object or materials are made up of cells or were once made of cells? Station 2 Each function below is performed by plants, animals, or both. Write each example into the correct column. Plant 1) Animal 1) Both Station 3 Which things are typically larger than a normal plant or animal cell? Station 4 Write down the best answer here: The Cell Membrane and Homeostasis What is the cell membrane? A quick review A. B. C. Cell membrane is made mostly of 2 main organic molecules:. The cell membrane to pass through while others from passing through. Other names for the cell membrane: - -Phospholipid bilayer = Phospholipid= Bilayer= -Semi-permeable= -Semi= -Permeable=
2 Cell Membrane Composition Phospholipid Bilayer (lipid bilayer) 2 layers of Proteins are in the bilayer chains are attached to the proteins So many kinds of molecules = The Membrane is very flexible because of the fatty acid chains and the membrane has all of the structures listed inside of it so we call it a Fluid Mosaic Model Fluid because Mosaic because Cell Membrane Properties and Functions Selectively permeable = only certain molecules can free pass across the membrane Only small, uncharged, polar molecules can pass freely E.g. Large molecules and ions are impermeable = Protein Function in Cell Membrane 1. Surface Proteins receptors that provide 2. Transport Proteins help transport Carbohydrate Function in Cell Membrane Serves as identifiers allowing individual cells to Homeostasis: Maintaining a constant internal. Plants and animals regulate things like:, water,, glucose,, etc. The cell controls what goes and = maintaining homeostasis! Concentration gradient: the in the of across the. Cellular Transport: Maintains in the.
3 Match the cell organelle with its function! 1. Cell membrane A. Controls what goes in and out of the cell 2. Cell wall B. Storage 3. Nucleus C. Makes ATP 4. Ribosome D. Offers support and protection Unit 2: Cells and Cell Transport 5. Mitochondria E. Makes Glucose 6. Chloroplast F. Contains DNA, controls all functions 7. Vacuole G. Makes proteins Cell Transport -Material moves in/out through the. -The cell membrane is. Types of Cell Transport Passive Cell Transport Active Cell Transport -Diffusion is the movement of molecules from. -An example of diffusion is:. -Osmosis is the movement of from. -An example of osmosis is:. Quick Review 1. Diffusion moves substances from to concentration. 2. Diffusion moves a concentration gradient. 3. The U-shaped tube in the figure is divided by a membrane that is impermeable to starch but permeable to water. In what direction will water move? -Facilitated diffusion is the movement of through a. -Active transport: uses (energy). -Movement of particles the concentration gradient ( ) Quick Review: Which cell process will move substances against a concentration gradient? Passive Type Diffusion What does it move? What direction does it move? Does it use energy? Does it use a protein? Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Active Transport
4 Fill in the table below to compare and contrast PASSIVE and ACTIVE transport. Place an X in the boxes that apply. Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Active Transport Diffusion Moves from HIGH to LOW Moves from LOW to HIGH Needs a protein Needs energy Moves particles Moves water Fill out the flow chart below. You may use the following words or phrases more than once: Simple diffusion, dynamic equilibrium, energy, no energy, high concentration, low concentration, osmosis, passive, active, facilitated diffusion, transport protein Movement across membranes can Can be which requires which requires and a The three types are In order to move particles from a region of They move particles from a region of to a region of to a region of Which results in
5 FLIP Homeostasis is one of the 8 characteristics of living things. Homeostasis is the maintenance of the internal environment within certain limits. Cells must maintain a number of limits. These include properties like temperature, salinity, ph, blood glucose level, the concentrations of other nutrients and wastes, and water balance. Temperature Enzymes have a small part called the active site where substrates bind and the chemical reaction takes place. Only molecules with the correct shape can fit with the enzyme. The shape of the active site is changed by heating the enzyme above a certain temperature. Then the molecules can no longer fit and the reaction cannot happen. ph A measure of the degree of the acidity or the alkalinity of a solution as measured on the ph scale of 0 to 14. Parts of the cells work best at specific phs. Glucose Concentration in the Blood Cells want to maintain the same glucose balance in and out of cells. When there is excess glucose that the cells do not want inside, it is stored in special cells in the liver or turned into lipids. Insulin, a hormone, helps regulate the amount of glucose in our blood. Water Balance The body s cells are bathed in water, and the correct water balance is crucial to life. Water crosses easily across most membranes. Cell membranes are what regulate things like ph, glucose, and water balance. Cells have semi-permeable membranes which allow some things to pass through but prevent other things from passing through. Cell membranes will allow small molecules like oxygen, water, carbon dioxide and glucose to pass through. Cell membranes will not allow larger molecules like starch and proteins to pass through. FLOP Name the properties that cells work to maintain through homeostasis: What would happen if your body did not maintain homeostasis? What is the term used to describe enzymes that no longer work due to temperature changes? Why does a cell need to maintain temperature and ph? What happens to excess glucose in the bloodstream? What molecules does the cell membrane let through? What molecules does the cell membrane prevent from passing through?
6 What structures do you see embedded in the cell (plasma) membrane? The cell membrane controls what goes in and what goes out of the cell. The movement of molecules across the membrane is called transport. There are different types of transport, but all molecules are moving in relation to a concentration gradient, a measure of how the concentration of particles changes from one area to another There are two main types of transport: Active and Passive. Active transport involves the use of energy. Substances are moved AGAINST the concentration gradient, from an area of LOW concentration to HIGH concentration. Active transport generally requires the use of protein pumps to move molecules. Passive Transport does not require energy. Substances are moved WITH the concentration gradient, from areas of HIGH concentration to LOW concentration. There are 3 types of passive transport: 1) Diffusion: Passive transport from high to low concentration 2) Osmosis: Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane 3) Facilitated Diffusion: Passive transport of specific molecules (like glucose) across the membrane with the help of protein channels Sample Problem Label the area of HIGH and LOW concentrations. What is the major difference between active transport and passive transport? What is the relationship between diffusion and osmosis?(hint: what is the only substance that carries out osmosis?) Which of the following is NOT an example of active transport? I. Facilitated diffusion II. Osmosis III. Diffusion A. I only B. III only C. I and II only D. I, II, and III Where is there the highest concentration of water? water cell Cup of Which way will the water move? What will happen to the cell if it gains water? What will happen to the cell if it loses water?
7
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes
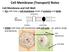 Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Cell Membrane (Transport) Notes Cell Membrane and Cell Wall: ALL cells have a cell membrane made of proteins and lipids protein channel Cell Membrane Layer 1 Layer 2 lipid bilayer protein pump SOME cells
Written Response #1: True/False
 Written Response #1: True/False 1. Osmosis means to absorb something. 2. Cells are able to excrete waste. 3. Cells obtain energy by gaining nutrition from food. 4. Plants use sunlight for food. 5. Plants
Written Response #1: True/False 1. Osmosis means to absorb something. 2. Cells are able to excrete waste. 3. Cells obtain energy by gaining nutrition from food. 4. Plants use sunlight for food. 5. Plants
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1: Cell Membrane KEY IDEAS > How does the cell membrane help a cell maintain homeostasis? > How does the cell membrane restrict the exchange
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8. Cell Membrane Section 1
 Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Cells and Their Environment Chapter 8 Cell Membrane Section 1 Homeostasis Key Idea: One way that a cell maintains homeostasis is by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane. Homeostasis
Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems. Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells
 IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
IN: Unit 2: More on Matter & Energy in Ecosystems Macromolecules to Organelles to Cells Where are cells on the biological scale? Sub-Atomic Particles Atoms Molecules Macromolecules (proteins, lipids, nucleic
Cell Boundaries. Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h
 Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Cell Boundaries Chapter 7.3 Strand: B2.5h Review: Cell Membrane What is the role of the cell membrane within a cell? The cell membrane regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides protection
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Biology 2201 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life 2.2 Cell Membrane Structure Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different conditions
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 3 : Homeostasis and Cell Transport
 Unit 3 : Homeostasis and Cell Transport A. Maintaining Homeostasis 1. Homeostasis process of regulating and maintaining a constant internal env. 2. Need to maintain homeostasis of water levels, glucose
Unit 3 : Homeostasis and Cell Transport A. Maintaining Homeostasis 1. Homeostasis process of regulating and maintaining a constant internal env. 2. Need to maintain homeostasis of water levels, glucose
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Biology 12 Name: Cell Structure and Function Practice Exam - KEY Cell parts and Function 1. Identify each part of the cell indicated and give one role for each structure in the secretion and/or synthesis
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment. Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane
 Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Chapter 3: Exchanging Materials with the Environment Cellular Transport Transport across the Membrane Transport? Cells need things water, oxygen, balance of ions, nutrients (amino acids, sugars..building
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Passive and Active transport across a cell membrane REVIEW MEMBRANE TRANSPORT Cell (plasma) membrane Thin, flexible barrier Membranes also organize the interior of a cell. Cell organelles are defined by
Plasma Membrane Function
 Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Plasma Membrane Function Cells have to maintain homeostasis, they do this by controlling what moves across their membranes Structure Double Layer of phospholipids Head (polar) hydrophiliclikes water -
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Sept. 2011 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Gateway to the Cell 11/1/2012. The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
 Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Gateway to the Cell The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move Isolates the cell, yet allows communication with its surroundings fluid mosaics = proteins (and everything else)
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structures Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Section 2.2 Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE. SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion).
 CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
CELL TRANSPORT and THE PLASMA MEMBRANE SB1d. Explain the impact of water on life processes (i.e., osmosis, diffusion). What if What would happen if an organism could not get energy or get rid of wastes?
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell
 The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell 1 Photograph of a Cell Membrane 2 Cell Membrane The cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular organism to move 3 Homeostasis Balanced internal condition
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Chapter 1 Plasma membranes
 1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
1 of 5 TEXTBOOK ANSWERS Chapter 1 Plasma membranes Recap 1.1 1 The plasma membrane: keeps internal contents of the cell confined to one area keeps out foreign molecules that damage or destroy the cell
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7
 Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
Cell Structure and Function C H A P T E R 7 EQ: What Scientists and inventions helped aid in creating Cell Theory? 7.1 Cell Theory (Cells and Living Things) Cells are the basic building block of all life
3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes
 alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes SPECIFICATION The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes,
alevelbiology.co.uk 3.2.3 Transport across cell membranes SPECIFICATION The basic structure of all cell membranes, including cell-surface membranes and the membranes around the cell organelles of eukaryotes,
Cells & Transport. Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4
 Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cell Transport. Movement of molecules
 Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Cell Transport Movement of molecules TEKS Students will investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis and transport of molecules Homeostasis The maintaining of a stable body system
Biology. Membranes.
 1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
1 Biology Membranes 2015 10 28 www.njctl.org 2 Vocabulary active transport carrier protein channel protein concentration gradient diffusion enzymatic activity facilitated diffusion fluid mosaic hypertonic
The Cell Membrane. Why cells must control materials. Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival.
 The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
The Cell Membrane Why cells must control materials Living cells must maintain homeostasis for survival. The cell membrane is the boundary between the cell and its environment. It is the cell membrane s
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Equilibrium when two areas have the same concentration or are filled evenly
 Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Aim: How does the cell membrane function to maintain homeostasis? Do Now: Describe what homeostasis is. Homework: Vocab: Homeostasis, equilibrium, concentration gradient, diffusion, carrier protein, osmosis,
Cellular Transport Notes
 Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a cell membrane a.controls what enters and exits the cell to maintain an internal balance called homeostasis b.provides protection and support
7.3 Cell Boundaries. Regents Biology. Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham
 7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
7.3 Cell Boundaries Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Don t look at your reading guide/textbook or talk with each other yet! Write down one thing you know/remember
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life
 Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Unit 1 Matter & Energy for Life Chapter 2 Interaction of Cell Structure Biology 2201 Primary Membrane Function: Homeostasis Conditions in the cell must remain more or less constant under many different
Homeostasis and The Plasma Membrane
 Mosaic Homeostasis and The Plasma Membrane phospholipid cholesterol PLASMA MEMBRANE (FLUID MOSAIC MODEL) membrane protein filaments of cytoskeleton phospholipid cytoplasm (inside of cell) PHOSPHOLIPID
Mosaic Homeostasis and The Plasma Membrane phospholipid cholesterol PLASMA MEMBRANE (FLUID MOSAIC MODEL) membrane protein filaments of cytoskeleton phospholipid cytoplasm (inside of cell) PHOSPHOLIPID
Constant Motion of Molecules. Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers
 CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
CELL TRANSPORT Constant Motion of Molecules Kinetic Theory of Matter Molecules move randomly and bump into each other and other barriers Solution homogenous liquid throughout which two or more substances
Movement Through the Cell Membrane
 Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
Movement Through the Cell Membrane Cellular Movement All living organisms rely on diffusion Get oxygen for respiration Removing waste products Transpiration in plants Cellular Movement The cell membrane
Chapter 7 Cellular Structure and Function
 Section 1: Cell Discovery and Theory Section 2: The Plasma Membrane Section 3: Structures and Organelles Section 4: Cellular Transport Click on a lesson name to select. 7.2 The Plasma/Cell Membrane Thin,
Section 1: Cell Discovery and Theory Section 2: The Plasma Membrane Section 3: Structures and Organelles Section 4: Cellular Transport Click on a lesson name to select. 7.2 The Plasma/Cell Membrane Thin,
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
UNIT 1: WELLNESS AND HOMEOSTASIS
 UNIT 1: WELLNESS AND HOMEOSTASIS WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HEALTH AND WELLNESS? 5 FACTORS OF WELL-BEING PHYSICAL EMOTIONAL SPIRITUAL INTELLECTUAL SOCIAL WHAT IS BIOLOGY? BIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF
UNIT 1: WELLNESS AND HOMEOSTASIS WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HEALTH AND WELLNESS? 5 FACTORS OF WELL-BEING PHYSICAL EMOTIONAL SPIRITUAL INTELLECTUAL SOCIAL WHAT IS BIOLOGY? BIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF
[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution
![[S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution [S] [S] Hypertonic [H O] [H 2 O] g. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through membranes! 15. Osmosis. Concentrated sugar solution](/thumbs/88/115710711.jpg) Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
Concentrated sugar solution Sugar molecules (Water molecules not shown) 100ml 100ml Hypertonic [S] g [H2 Hypotonic [H O] 2 O] [H 2 O] g Semipermeable Dilute sugar solution (100ml) Time 125ml Osmosis 75ml
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology
 CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
CH 7.2 & 7.4 Biology LABEL THE MEMBRANE Phospholipids Cholesterol Peripheral proteins Integral proteins Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Extracellular fluid Most of the membrane A phospholipid bi-layer makes up
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Think About it. Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells. The Discovery of the Cell. The cell theory states: Exploring the Cell 10/10/2016
 Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Think About it What s the smallest part of any living thing that still counts as being alive? Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Can we just keep dividing living things into smaller and smaller parts, or
Biology Unit 3 Review. Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids
 Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
Biology Unit 3 Review Name Objective 1. Describe the important functions of organic molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids 1. What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules?
The Cell Membrane. Also known as the Plasma Membrane
 Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Student Objectives Know the different parts of the cell membrane Understand the role of the cell membrane in cellular transport Understand diffusion and osmosis Determine what will happen to plant and
Transport. Slide 1 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 & Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
& Transport 1 of 47 Learning Targets TN Standard CLE 3216.1.3 Explain how materials move into and out of cells. CLE 3216.1.5 Investigate how proteins regulate the internal environment of a cell through
Cell membrane & Transport. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Membrane Function. How does the cell membrane control movement of materials? Type 1 Ions Type 2 Molecules Type 3 Molecules Type 4 Molecules H O H
 Why? Membrane Function ow does the cell membrane control movement of materials? The membrane is critical to the maintenance of homeostasis in living organisms. The cell membrane separates the cell from
Why? Membrane Function ow does the cell membrane control movement of materials? The membrane is critical to the maintenance of homeostasis in living organisms. The cell membrane separates the cell from
1.14. Passive Transport
 Passive Transport 1.14 Simple Diffusion Cell s are selectively permeable only certain substances are able to pass through them. As mentioned in section 1.2, cell s are largely composed of a phospholipid
Passive Transport 1.14 Simple Diffusion Cell s are selectively permeable only certain substances are able to pass through them. As mentioned in section 1.2, cell s are largely composed of a phospholipid
Explain how the structure of the plasma membrane allows material to move through. Explain the processes of Passive Transport and Active Transport.
 Objectives: Explain how the structure of the plasma membrane allows material to move through. Explain the processes of Passive Transport and Active Transport. Predict whether active or passive transport
Objectives: Explain how the structure of the plasma membrane allows material to move through. Explain the processes of Passive Transport and Active Transport. Predict whether active or passive transport
UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT. Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018
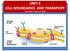 UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018 Cell Wall CELL BOUNDARIES support protect & the cell cell membrane Lies outside of the Is made of & carbohydrates proteins Plant cell
UNIT 4 CELL BOUNDARIES AND TRANSPORT Unit 4 test: October 16, 2018 Cell Wall CELL BOUNDARIES support protect & the cell cell membrane Lies outside of the Is made of & carbohydrates proteins Plant cell
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
Membrane structure & function
 Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Membrane structure & function Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The phospholipid bilayer describes a structure with. a. polar layers on the
Slide 2 of 47. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. End Show
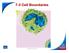 2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
2 of 47 7-3 Cell Boundaries All cells are surrounded by a thin, flexible barrier known as the cell membrane. Many cells also produce a strong supporting layer around the membrane known as a cell wall.
Name Date Class. Cellular Structure
 Concept Mapping Cellular Structure Complete the network tree about cellular structure. These terms may be used more than once: animals, bacteria, chloroplasts, eukaryotes, a large central vacuole, plants,
Concept Mapping Cellular Structure Complete the network tree about cellular structure. These terms may be used more than once: animals, bacteria, chloroplasts, eukaryotes, a large central vacuole, plants,
Cell Membrane Diagram
 Cell Membrane Diagram Draw a diagram of the cell membrane. Please include (and label): - Phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) Protein channel An ion pump Cholesterol Gylcoproteins* Define
Cell Membrane Diagram Draw a diagram of the cell membrane. Please include (and label): - Phospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) Protein channel An ion pump Cholesterol Gylcoproteins* Define
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane. Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5
 Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Homeostasis, Transport & The Cell Membrane Chapter 4-2 (pg 73 75) Chapter 5 Unit 5: Lecture 1 Topic: The Cell Membrane Covers: Chapter 5, pages 95-96 Chapter 4, pages 73-75 The Cell Membrane The chemistry
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function
 Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Ch7: Membrane Structure & Function History 1915 RBC membranes studied found proteins and lipids 1935 membrane mostly phospholipids 2 layers 1950 electron microscopes supported bilayer idea (Sandwich model)
Transport Movement across the Cell Membrane
 Transport Movement across the Cell Membrane Lipids of cell membrane Membrane consists primarily of phosphos phospho bilayer inside cell phosphate hydrophilic outside cell hydrophobic S1 The Fluidity of
Transport Movement across the Cell Membrane Lipids of cell membrane Membrane consists primarily of phosphos phospho bilayer inside cell phosphate hydrophilic outside cell hydrophobic S1 The Fluidity of
1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome
 Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function
 Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
Chapter 4 Skeleton Notes: Membrane Structure & Function Overview/Objectives 4.1 Plasma Membrane Structure & Function o Structure and Function of the PM o Major functions of proteins 4.2- Permeability of
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY
 Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Ch3: Cellular Transport Review KEY OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic means there is a GREATER concentration of
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport
 Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport Assessment Anchors: to describe how the structure of the plasma allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for
Keystone Biology Remediation A4: Homeostasis and Transport Assessment Anchors: to describe how the structure of the plasma allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function
 Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
Plasma Membrane Structure and Function The plasma membrane separates the internal environment of the cell from its surroundings. The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The
CP Biology Semester 1 FINAL Study Guide
 Name: KEY CP Biology Semester 1 FINAL Study Guide Unit 1- Introduction to Biology Define each of the following: 1. Match the following vocabulary words on the left with their definition on the right. b
Name: KEY CP Biology Semester 1 FINAL Study Guide Unit 1- Introduction to Biology Define each of the following: 1. Match the following vocabulary words on the left with their definition on the right. b
A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life
 AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Membrane. Lecture 3a. Overview: Membranes. What is a membrane? Structure of the cell membrane. Fluid Mosaic Model. Membranes and Transport
 Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Lecture 3a. The Cell Membrane Membranes and Transport Overview: Membranes Structure of cell membranes Functions of cell membranes How things get in and out of cells What is a membrane? Basically, a covering
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers
 Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Structure and Function
 Structure and Function Cell Membrane Functions Cell membrane surrounds the cell, regulating the transport of materials into and out of the cell Cell Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer: a double layer of
Structure and Function Cell Membrane Functions Cell membrane surrounds the cell, regulating the transport of materials into and out of the cell Cell Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer: a double layer of
Cell Transport & the Cell Membrane
 Cell Transport & the Cell Membrane I. Cell Membrane A. Structure Structure of the cell membrane is referred to as the Fluid Mosaic Model. It is made up of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. The membrane
Cell Transport & the Cell Membrane I. Cell Membrane A. Structure Structure of the cell membrane is referred to as the Fluid Mosaic Model. It is made up of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. The membrane
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
WEDNESDAY 10/18/17. Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes.
 WEDNESDAY 10/18/17 Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE - 2 Gateway to Cell HOMEOSTASIS Balanced
WEDNESDAY 10/18/17 Why is the cell/plasma membrane important? What is the cell/plasma membrane made of? Label the cell membrane on your notes. THE PLASMA MEMBRANE - 2 Gateway to Cell HOMEOSTASIS Balanced
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Review: Cellular Transport
 Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
Review: Cellular Transport OSMOSIS 1. Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic). The dots represent solutes. A. B. C. 2. means there is a GREATER concentration of solute molecules
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head
 CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELLS and TRANSPORT Student Packet SUMMARY CELL MEMBRANES ARE SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE DUE TO THEIR STRUCTURE Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tail Hydrophobic regions of protein Hydrophilic regions of protein
CELL BOUNDARIES. Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants
 CELL BOUNDARIES CELL BOUNDARIES Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants TYPES OF MEMBRANES Some substances = too large or
CELL BOUNDARIES CELL BOUNDARIES Cells create boundaries through: Cell Membranes made of the phospholipid bilayer Cell Walls made of cellulose in plants TYPES OF MEMBRANES Some substances = too large or
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Cell Theory. Eukaryote Cells. Prokaryote Cells 8/18/16
 Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
Cell Theory http://www.beatricebiologist.com www.beatricebiologist.com 1) All living things are made up of cells 2) All cells come from pre-existing cells 3) The cell is the fundamental unit of structure
DistanceLearningCentre.com
 DistanceLearningCentre.com Course: Essential reading: Tortora, G.J., and Grabowski, S.R., 2002. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 10 th ed. London: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN: 9780471224723 Recommended
DistanceLearningCentre.com Course: Essential reading: Tortora, G.J., and Grabowski, S.R., 2002. Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. 10 th ed. London: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN: 9780471224723 Recommended
Contents. Module A Cells and Cell Processes. Module B Continuity and Unity Of Life. Introduction to Keystone Finish Line Biology...
 Contents Introduction to Keystone Finish Line Biology...5 Module A Cells and Cell Processes Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles...7 Lesson 1 Unifying Characteristics of Life BIO.A.1.1.1, BIO.A.1.2.1...8
Contents Introduction to Keystone Finish Line Biology...5 Module A Cells and Cell Processes Unit 1 Basic Biological Principles...7 Lesson 1 Unifying Characteristics of Life BIO.A.1.1.1, BIO.A.1.2.1...8
Cell Processes. Chapter 3. Learning Target 3/15/16. l I can. l 1)Explain the difference between diffusion and osmosis.
 Chapter 3 Cell Processes Learning Target l I can. l 1)Explain the difference between diffusion and osmosis. l 2)Predict the movement of particles into and out of a cell. 1 Section 3.2 MOVING CELLULAR MATERIAL
Chapter 3 Cell Processes Learning Target l I can. l 1)Explain the difference between diffusion and osmosis. l 2)Predict the movement of particles into and out of a cell. 1 Section 3.2 MOVING CELLULAR MATERIAL
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3
 Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cell Boundaries Section 7-3 The most important parts of a cell are its borders, which separate the cell from its surroundings. The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells. The
Cell (plasma) membrane
 Cell Membranes & Movement Across Them 2006-2007 Cell (plasma) membrane Cells need an inside & an outside separate cell from its environment cell membrane is the boundary IN food - s - proteins - s salts
Cell Membranes & Movement Across Them 2006-2007 Cell (plasma) membrane Cells need an inside & an outside separate cell from its environment cell membrane is the boundary IN food - s - proteins - s salts
Plasma Membranes. Plasma Membranes WJEC GCE BIOLOGY 4.6
 4.6 Repeat Fig 3.20A here Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane Carbohydrate chain Glycoprotein Intrinsic Protein Non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid Phospholipids Appearance of the Cell Membrane Seen
4.6 Repeat Fig 3.20A here Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane Carbohydrate chain Glycoprotein Intrinsic Protein Non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid Phospholipids Appearance of the Cell Membrane Seen
1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy.
 1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy. ATP is the primary energy molecule for the cell. It is produced in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which breaks down
1. I can explain the structure of ATP and how it is used to store energy. ATP is the primary energy molecule for the cell. It is produced in the mitochondria during cellular respiration, which breaks down
Biology Study Guide Answers. Cells/Cell Transport
 Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 1.) All living things are made of cells. 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.) Cells come from pre-existing
Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 1.) All living things are made of cells. 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.) Cells come from pre-existing
9/20/2016 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES. Section Objectives. Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions.
 CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
CHAPTER 7 LECTURE NOTES Kennedy biol. 1ab Section Objectives Explain how a cell s plasma membrane functions. Relate the function of the plasma membrane to the fluid mosaic model. All living cells must
Cell Membrane Structure and Function. What is the importance of having a cell membrane?
 Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
Cell Membrane Structure and Function What is the importance of having a cell membrane? I. Membrane Structure a. Membranes contain proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates (which are all types of macromolecules)
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
The Discovery of the Cell
 The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
The Discovery of the Cell 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review the cell in relation to: - Its definition - The origin of life - The characteristics of life - The hierarchy of biological organization - The science
Warm Up 12/06/2018. In a Solution of Salt Water, which substance acts as the Solvent and which substance acts as the Solute?
 Warm Up 12/06/2018 In a Solution of Salt Water, which substance acts as the Solvent and which substance acts as the Solute? Cell Membrane and Cell Transport How Nutrients move in and Wastes Move Out of
Warm Up 12/06/2018 In a Solution of Salt Water, which substance acts as the Solvent and which substance acts as the Solute? Cell Membrane and Cell Transport How Nutrients move in and Wastes Move Out of
d. When the salt concentration outside the cell is very low, diffusion causes water to
 4B EOC Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water movement into and out of cells is of prime importance to all living things. A single
4B EOC Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Water movement into and out of cells is of prime importance to all living things. A single
1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
