Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain and In-vitro Culture against PCR Assay for the Diagnosis of Blastocystis sp.
|
|
|
- Alvin Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 1, Jan-Mar 2018, pp Iran J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian Society of Parasitology isp.tums.ac.ir Short Communication Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain and In-vitro Culture against PCR Assay for the Diagnosis of Blastocystis sp. in Stool Samples Nabilah Amelia MOHAMMAD 1, Mohd Fahmi MASTUKI 1, Hesham M. AL-MEKHLAFI 2,3, Norhayati MOKTAR 4, *Tengku Shahrul ANUAR 1,5 1. Center of Medical Laboratory Technology, Faculty of Health Sciences, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Puncak Alam Campus, Selangor, Malaysia 2. Endemic and Tropical Diseases Unit, Medical Research Center, Jazan University, Jazan, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia 3. Dept. of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sana a University, Sana a, Yemen 4. Dept. of Pre-Clinical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman, Sungai Long Campus, Selangor, Malaysia 5. Integrative Pharmacogenomics Institute, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Puncak Alam Campus, Selangor, Malaysia Received 18 Mar 2017 Accepted 22 Aug 2017 Keywords: Trichrome stain, In-vitro culture, PCR, Blastocystis *Correspondence tsauitm@gmail.com Abstract Background: This study evaluated the performance of routine permanent stain and cultivation method in comparison with polymerase chain reaction assay as the reference technique to detect Blastocystis sp. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted among aboriginal populations that reside in Pahang, Peninsular Malaysia in Feb to Mar A total of 359 stool samples were examined using Wheatley s trichrome stain, in-vitro cultivation in Jones medium and PCR assay. Positive amplicons were subjected to sequencing and phylogenetic analysis. Results: Fifty-six (15.6%) samples were detected positive with Blastocystis sp. by Wheatley s trichrome stain and 73 (20.3%) by in-vitro culture, while PCR assay detected 71 (19.8%) positive samples. Detection rate of Blastocystis sp. was highest in combination of microscopic techniques (27.9%). The sensitivity and specificity of Wheatley s trichrome staining and in-vitro culture techniques compared to PCR assay were 49.3% (95% CI: ) and 92.7% (95% CI: ) and 39.4% (95% CI: ) and 84.4% (95% CI: ), respectively. However, the sensitivity [60.6% (95% CI: )] of the method increased when both microscopic techniques were performed together. False negative results produced by microscopic techniques were associated with subtype 3. The agreement between Wheatley s trichrome stain, in-vitro culture and combination of microscopic techniques with PCR assay were statistically significant by Kappa statistics (Wheatley s trichrome stain: K = 0.456, P<0.001; in-vitro culture: K = 0.236, P<0.001 and combination techniques: K = 0.353, P<0.001). Conclusion: The combination of microscopic technique is highly recommended to be used as a screening method for the diagnosis of Blastocystis infection either for clinical or epidemiological study to ensure better and accurate diagnosis. 127 Available at:
2 Mohammad et al.: Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain Introduction B lastocystis sp. is a unicellular enigmatic protozoan parasite commonly isolated from humans and animals stool samples with unsettled clinical significance. It possesses higher prevalence ranging from 1% to 60% in developed and developing countries (1-3). Blastocystosis is an infection caused by Blastocystis sp. characterized by symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, loss of weight and vomiting (4, 5). This parasite was suggested to be transmitted through fecal-oral route via contamination of food and water in both humans and animals (1, 6). Blastocystis sp. (STs) showed an extensive genetic diversity with currently recorded 17 distinct subtypes based on the analysis of the small subunit ribosomal RNA (SSU rrna) gene, comprising different hosts; the humans and wide array of animals (7). ST1-ST9 are found in humans with some isolates from humans has been demonstrated to be closely related to animals isolates. ST10-ST17 is exclusively found in animals. Majority of human infections are attributed to ST3 (7, 8). Detection of Blastocystis sp. largely depends on the microscopic examination with wet mount preparation or permanent stain. Being cost effective and time-consuming are the reasons why these methods still widely employed in the diagnostic laboratories (9, 10). Microscopic examination relies on the detection of four different morphologies of Blastocystis sp. including vacuolar, granular, cysts and amoeboid forms. However, this diagnostic method usually leads to misidentification as polymorphic morphologies of Blastocystis sp. possess great variation in term of size and shape (10, 11). In-vitro cultivation of viable Blastocystis sp. with non-standardized microorganisms had been widely addressed as the gold standard for its detection. Its usefulness has been demonstrated by numbers of researchers worldwide (12, 13). It is a huge advantage when observing samples from symptomatic subjects. Amoeboid form that commonly found among these subjects tends to be bigger in size thus, can be easily detected. However, the inabilities of the technician to recognize this form often lead to underreported (14). Molecular approaches involving polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay has become method of choice for diagnosing Blastocystis infection. It is astounding ability in revealing the genetic information of the parasite helps in providing further knowledge on the subtype's distribution among different hosts, its zoonotic risks, and pathogenicity of different subtypes (15, 16). However, most of the developing countries cannot afford to use PCR as a part of their diagnostic tool because it required fancy tools that are complex and expensive. It also requires specialized and highly trained technician to promote intended results (17). Hence, microscopic examination consisted permanent stain and in-vitro culture are still favorable in detecting Blastocystis sp. The main objective of this study was to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, and agreement of two methods (Wheatley s trichrome stain and in-vitro culture) in detection of Blastocystis sp. in stool samples compared with PCR assay as a reference technique. Materials and Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted among aboriginal populations that reside in Pahang, Peninsular Malaysia. Three-hundred and fifty-nine stool samples were collected from different hosts over the period of two months (Feb to Mar 2015). Of it, 253 samples were collected from the aboriginal. The remaining 106 samples were collected from domestic animals and livestock such as chickens, birds, dogs, cows, ducks, macaque, cat, geese, rabbits, sheep and deer that were reared and breed by these populations and Sungai Jin Deer Farm that located within the aboriginal settlements. Informed consent was taken from the participants and the study was approved by the Ethics committee of the university. Available at: 128
3 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 1, Jan-Mar 2018, pp Samples were processed at the designated work area located adjacent to the study site within four hours after samples collection. Samples were divided into three portions; (i) 5 g of stool were fixed in 15 ml centrifuge tube containing 3 ml polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), stored at room temperature for later Wheatley s trichrome stain; (ii) approximately 10 mg of stool were transferred into new stool container, stored at room temperature for in-vitro culture; (iii) the remaining stool were kept in the original stool container and stored at -20 C for genomic DNA extraction and PCR analysis. All stool samples were processed within 2 to 4 wk after collection. Wheatley s trichrome stain Samples fixed in PVA were filtered, centrifuged and dried prior to permanent staining. The smeared cover slips were allowed to airdry and stained with Wheatley s trichrome stain (18). Slides were mounted with Distrene, Plasticiser, and Xylene (DPX) (Sigma Aldrich) and observed microscopically under 100x magnification for the presence of Blastocystis sp. Slides were cross-checked by experienced technologist. A sample was reported as positive if any of the four morphologies (vacuolar, granular, cyst and amoeboid) of Blastocystis sp. were seen (Fig. 1). In-vitro culture Inoculation of 5 mg stool samples was carried out into 5 ml screw-capped tubes containing 3 ml Jones medium using sterile applicator stick (10, 19). The culture medium was supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated horse serum (Gibco, USA) prior to use. The culture tubes were incubated at 37 C. The presence of Blastocystis sp. was observed daily for 3 d (humans) and 7 d (animals) of cultivation by placing one drop of culture products onto PVA-coated coverslips and stained with Wheatley s trichrome. Prepared slides were examined microscopically at a magnification of 100x and cross-checked by senior technologist. Sample was reported as positive if any of the four morphologies (vacuolar, granular, cyst and amoeboid) of Blastocystis sp. were observed (Fig. 2). Fig. 1: Vacuolar form with four nucleuses found at the rim of cytoplasm along with large and round vacuole at the center. a) Nucleus. b) Vacuole. c) Cytoplasm Fig. 2: Granular form revealed large central vacuole filled with dense granules and nucleus located along the thin rim of cytoplasm. a) Nucleus. b) Vacuole. c) Cytoplasm. d) Granules Genomic DNA extraction and molecular analysis Genomic DNA was directly extracted from all unfixed stool samples using QIAamp Fast DNA Stool Mini Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer s instructions. The final DNA elution was made in 100 µl of elution buffer and stored at -20 C until required for PCR amplification. The conventional PCR was conducted on the extracted DNA using primer F1: 5 -GGA 129 Available at:
4 Mohammad et al.: Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain GGT AGT GAC AAT AAA TC-3 (20) and BHCRseq3: 5 -TAA GAC TAC GAG GGT ATC TA-3 (21) which targeted the SSU rrna of Blastocystis sp. PCR amplification was performed in a final volume of 50 μl per reaction containing 25 µl TopTaq Master Mix kit (QI- AGEN, Hilden, Germany), 17 µl nuclease-free water, 4 µl template DNA and 2 µl of each primer. Amplification was carried out in Nyx Technik thermal cycler (Nyx Technik, USA) and the following amplification profile was used: 3 min of initial denaturation at 94 C, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94 C for 30 sec, annealing at 59 C for 30 sec and extension at 72 C for 1 min. Final extension was conducted at 72 C for 10 min. Fragment of 550 to 585 basepairs of the amplified PCR products were separated on a 1.5% (w/v) agarose gel (Vivantis Technologies, USA) at 70 V for 110 min (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA), stained with GelRed (Biotium, USA), visualized under ultraviolet light and photographed using Sastec ST GD 1510 (SASTEC Instrument Inc., Canada). Positive and negative controls were included in every PCR reactions. Blastocystis ST1, ST2, and ST3 were used as positive control, whereas, nuclease-free water was used as negative control replacing template DNA. Sequencing was performed on all PCR positive samples. Sequences obtained in the present study were aligned and edited manually with reference sequences of Blastocystis sp. (ST1- ST14) using ClustalX2.1 software. Phylogenetic tree was constructed using maximum likelihood method (1000 bootstrap replicates) based on Hasegawa. Kishino. Yano+G (Gamma distribution)+ I(Invariant) model (best-fit substitution model) using MEGA 6.06 software (22). Proteromonas lacertae (U37108) was used as outgroup. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis of the data was performed using the SPSS software for Windows Ver. 20 (Inc. Chicago, IL, USA). Calculation involving sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) with exact binomial 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were used to assess the applied methods. The weighted Kappa statistic was used to assess the agreement between the methods used. The assessment of agreement was as follows: >0.81 indicate perfect agreement, substantial agreement, moderate agreement, fair agreement, slight agreement and <0.20 poor agreement (23). A P-value <0.05 was indicated as the level of significance. Results The prevalence rates of Blastocystis sp. in all examined stool samples were 15.6% (Wheatley s trichrome stain), 20.3% (in-vitro culture) and 16.2% (PCR assay). Of 71 samples that were positive by PCR (Fig. 3), only 58 readable sequences were obtained. Fifty-eight isolates could be separated into 4 subtypes contained isolates from humans and animals (Fig. 4). Fig. 3: Analysis of PCR products on a 1.5% (w/v) agarose gel. Lane 1) 100-bp DNA ladder, Lane 2) Negative control, Lane 3) Positive control, Lane 4-8) Positive Blastocystis isolates Among human isolates, ST3 (9.5%) was the predominant subtype, followed by ST1 (5.5%) and ST2 (2.8%). Results of animal positive isolates showed that ST10 was predominant among deer (11.3%), while ST2 (1.0%) was found in macaque. Available at: 130
5 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 1, Jan-Mar 2018, pp Phylogenetic analysis showed higher detection rate was observed when both microscopic methods were performed together (27.9%) as compared to individual method (Table 1). PCR assay managed to amplify SSU rrna gene sequence of Blastocystis in 28 samples initially observed as microscopy-negative. However, PCR assay was unable to amplify 50 (13.9%) stool samples initially diagnosed as positive by both methods. The performance of Wheatley s trichrome stain and in-vitro culture in term of sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV in comparison to PCR assay (reference technique) were presented in Table 2. The Wheatley s trichrome stain showed higher sensitivity [49.3% (95% CI: )] and specificity [92.7% (95% CI: )] compared to in-vitro culture technique, which only showed 39.4% sensitivity (95% CI: ) and 84.4% specificity (95% CI: ). Fig. 4: Maximum likelihood tree displaying relationship amongst SSU rrna gene sequences of Blastocystis from this study (bold line) with reference sequences (ST1-ST14) from GenBank. P. lacertae served as outgroup Table 1: Comparison of different diagnostic methods in detection of Blastocystis sp. Diagnostic tests Results 131 Available at:
6 Mohammad et al.: Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain Positive n (%) Negative n (%) Wheatley s trichrome stain 56 (15.6) 303 (84.4) In-vitro culture 73 (20.3) 286 (79.7) Combination techniques 100 (27.9) 259 (72.1) PCR assay 71 (19.8) 288 (80.2) However, when both diagnostic methods were performed together, the results showed high sensitivity [60.6% (95% CI: )] but the specificity decreased to 80.2% (95% CI: ) (Table 3). The agreement between the PCR assay and Wheatley s trichrome stain was statistically significant by Kappa (K=0.456; P<0.001). Similar results were also obtained between PCR assay and invitro culture (K = 0.236; P<0.001) and PCR assay and combination of microscopic techniques (K = 0.353; P<0.001). Table 2: Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of two microscopic diagnostic methods compared to PCR assay +ve (n = 71) PCR -ve (n = 288) Wheatley s trichrome stain In-vitro culture +ve -ve +ve -ve Total Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) 49.3 ( ) 39.4 ( ) Specificity (%) (95% CI) 92.7 ( ) 84.4 ( ) PPV (%) NPV (%) Kappa (P-value) K = (P<0.001) a K = (P<0.001) a CI; confidence interval. PPV; positive predictive value. NPV; negative predictive value. a; significant association (P<0.05) Table 3: Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV of combination microscopic techniques compared to PCR assay +ve (n = 71) PCR -ve (n = 288) Combination techniques +ve -ve Total Sensitivity (%) (95% CI) 60.6 ( ) Specificity (%) (95% CI) 80.2 ( ) PPV (%) 43.0 NPV (%) 89.2 Kappa (P-value) CI; confidence interval. PPV; positive predictive value. NPV; negative predictive value. a; significant association (P<0.05) Discussion K = (P<0.001) a Microscopic examination using wet mount, concentration technique and variety of per- Available at: 132
7 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 1, Jan-Mar 2018, pp manent stain have been widely employed to identify Blastocystis sp. Easy access to the resources and less time required to conduct these methods are the factors contributing to its frequent adoption as the routine diagnostic methods (17, 24). However, morphologybased diagnosis usually goes underreported as the vegetative stages of Blastocystis sp. often mistaken for fat globules and other contaminants (11). In this study, Wheatley s trichrome stain showed high sensitivity (49.3%) and specificity (92.7%) despite detecting slightly lower prevalence rate (15.6%). Wheatley s trichrome stain was able to correctly identify those subjects having blastocystosis. The uses of preservatives prior to staining procedure retain the morphology of protozoan parasites thus increasing the detection rate (25, 26). A very strong agreement of trichrome stain when culture was used as the reference technique (K=0.922) (27). In concordance to that, 100% specificity of Wheatley s trichrome stain in detecting Blastocystis sp. from irritable bowel syndrome/irritable bowel disease patients proved it diagnostic accuracies (28). Wintergreen oil was used to replace xylene as the clearing agent. The usage of wintergreen oil gave a high clarity of the image observed as it deeply stained the cytoplasm, peripheral chromatin, karyosome and provide better background that further ease the observation (18). In-vitro culture gave higher prevalence than Wheatley s trichrome stain which was 20.3%. However, when testing the performance and effectiveness of in-vitro culture against the reference technique, in-vitro culture resulted in the highest detection of false positive which was in 45 samples. This corresponds to lower sensitivity value of 39.4%. This finding was supported by previous studies which reported that in-vitro culture showed no significant differences with comparable detection accuracies as compared to trichrome stain. This showed that in-vitro culture does not necessarily superior and sensitive than other diagnostic methods (13, 29). In-vitro culture unable to detect Blastocystis sp., although some of the samples were positive by PCR technique (30). In-vitro culture was rather insensitive despite being a renowned gold standard for Blastocystis sp. detection (16). Apparently, there are a lot of culture media available such as Jones medium and Iscove s modified Dulbecco s medium with each of it possess different reagents, composition, and protocols in order to grow the viable Blastocystis sp. These differences contribute to a variation of sensitivity and specificity of culture technique recorded worldwide (30, 31). An optimization and standardization of various culture techniques are urgently needed in order to curb with the ineffectiveness and underperformance of this technique. Furthermore, viable Blastocystis sp. can easily degenerate and intermittent shedding regularly occur in the fresh stool samples, hence, lower the chances of the parasite to grows and detected during cultivation (21, 32). The present study showed that when both microscopic techniques (Wheatley s trichrome stain and in-vitro culture) were used together, the overall prevalence and sensitivity of the Blastocystis sp. detection was markedly improved and increased, which were 27.9% and 60.6%, respectively. It concurs with postulation made, at least two diagnostic methods should be used together to ensure accurate diagnosis whenever molecular technique cannot be adopted (16). Being solely depends on one technique could lead to underreported results. Wheatley s trichrome stain alone has proved to successfully detect the presence of Blastocystis sp. in stool samples by giving color to the cytoplasm (blue-green to purple) and nuclei (red or purple-red), thus ease the detection (18). However, this microscopy-based technique was greatly affected by the number of parasite presence in the stool samples. Hence, the employment of in-vitro is equally important as it will allow Blastocystis sp. to grow. This method will increase the number and size of the parasite and makes the identification through light microscopy much easier (31, 33). 133 Available at:
8 Mohammad et al.: Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain Nowadays, detection of Blastocystis through PCR-based method has become the most favorable diagnostic method. PCR assay was widely used as reference technique because of its high sensitivity and specificity over other microscopy methods, as well as its ability to reveal the genetic information of Blastocystis (15, 30). This corresponded to the detection of four subtypes in this study which was ST1, ST2, ST3, and ST10 that constitute both human and animal samples. The predominant of ST3 among human isolates were in concordance with other studies conducted worldwide (34, 35). Furthermore, through molecular analysis, the ability of Wheatley trichrome stain and in-vitro culture to detect Blastocystis sp. depends on the subtypes. False negative result appeared to be associated with Blastocystis subtype 3. ST3 of Blastocystis might encyst before shedding; hence the present of inconspicuous cyst was hardly recognized by these microscopy techniques (21). PCR assay also presented with many disadvantages. Unsuccessful DNA extraction and the choice of unsuitable primers could lead to no and/or over-amplification of PCR assay (12). Furthermore, PCR is a complex and costly method to be adopted by developing countries as advanced equipment and specialized personnel are needed to run this technique. Conclusion We suggest the use of combination of Wheatley s trichrome stain and in-vitro culture as screening tools for detection of Blastocystis sp. especially in community laboratories that facing financial constraints and are not equipped with molecular facilities. The high specificity shown by both microscopic techniques indicates that it can be used to identify those not infected with Blastocystis sp. with high diagnostic accuracies. However, whenever applicable, PCR assay should acts as confirmatory test as it s the only method that can recognize subtypes of Blastocystis. Acknowledgments We sincerely acknowledge Ministry of Rural and Regional Development of Malaysia for granting the permission to conduct this study. Heartfelt gratitude and thanks also deliver to all participants that providing their stool samples. We sincerely thank Mr. Mohd Akhbar Chiraghdin for granting permission to collect stool samples from deer farm. Our study was funded by LESTARI Research Grant: 600- RMI/DANA 5/3/LESTARI (44/2015) from the Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia. Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. References 1. Li LH, Zhou XN, Du ZW et al. Molecular epidemiology of human Blastocystis in a village in Yunnan province, China. Parasitol Int. 2007;56(4): Wong KH, Ng GC, Lin RT et al. Predominance of subtype 3 among Blastocystis isolates from a major hospital in Singapore. Parasitol Res. 2008;102(4): Anuar TS, Ghani MK, Azreen SN, Salleh FM, Moktar N. Blastocystis infection in Malaysia: Evidence of waterborne and human-to-human transmissions among the Proto-Malay, Negrito and Senoi tribes of Orang Asli. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6: Stensvold CR, Arendrup MC, Nielsen HV, Bada A, Thorsen S. Symptomatic infection with Blastocystis sp. subtype 8 successfully treated with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2008;102(3): Tan KS. New insights on classification, identification, and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2008;21(4): Lee LI, Chye TT, Karmacharya BM, Govind S. Blastocystis sp.: waterborne zoonotic organism, a possibility. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5: Souppart L, Moussa H, Cian A et al. Subtype analysis of Blastocystis isolates from symptomatic Available at: 134
9 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 1, Jan-Mar 2018, pp patients in Egypt. Parasitol Res. 2010;106(2): Alfellani MA, Taner-Mulla D, Jacob AS et al. Genetic diversity of Blastocystis in livestock and zoo animals. Protist. 2013;164(4): Boorom KF, Smith H, Nimri L E et al. Oh my aching gut: irritable bowel syndrome, Blastocystis, and asymptomatic infection. Parasit Vectors. 2008;1(1): Tan TC, Suresh KG, Smith HV. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Blastocystis hominis isolates implicates subtype 3 as a subtype with pathogenic potential. Parasitol Res. 2008;104(1): Eida AM, Eida MM. Identification of Blastocystis hominis in patients with irritable bowel syndrome using microscopy and culture compared to PCR. Parasitol United J. 2008; 1(2): Santos HJ, Rivera WL. Comparison of direct fecal smear microscopy, culture, and polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Blastocystis sp. in human stool samples. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013;6(10): Elghareeb AS, Younis MS, El Fakahany AF et al. Laboratory diagnosis of Blastocystis spp. in diarrheic patients. Trop Parasitol. 2015;5(1): Rajamanikam A, Govind SK. Amoebic forms of Blastocystis spp.-evidence for a pathogenic role. Parasit Vectors. 2013; 6(1): Stensvold R, Brillowska-Dabrowska A, Nielsen HV, Arendrup MC. Detection of Blastocystis hominis in unpreserved stool specimens by using polymerase chain reaction. J Parasitol. 2006;92(5): Roberts T, Barratt J, Harkness J, Ellis J, Stark D. Comparison of microscopy, culture, and conventional polymerase chain reaction for detection of Blastocystis sp. in clinical stool samples. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011;84(2): Anuar TS, Al-Mekhlafi HM, Abdul Ghani MK et al. Evaluation of formalin-ether sedimentation and trichrome staining techniques: its effectiveness in detecting Entamoeba histolytica/dispar/moshkovskii in stool samples. J Microbiol Methods. 2013;92(3): Salleh FM, Anuar TS, Yasin AM, Moktar N. Wintergreen oil: a novel method in Wheatley's trichrome staining technique. J Microbiol Methods. 2012;91(1): JONES WR. The experimental infection of rats with Entamoeba histolytica; with a method for evaluating the anti-amoebic properties of new compounds. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1946;40: Böhm Gloning B, Knobloch J, Walderich B. Five subgroups of Blastocystis hominis isolates from symptomatic and asymptomatic patients revealed by restriction site analysis of PCR amplified 16S like rdna. Trop Med Int Health 1997; 2(8): Stensvold CR, Arendrup MC, Jespersgaard C, Mølbak K, Nielsen HV. Detecting Blastocystis using parasitologic and DNA-based methods: a comparative study. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007; 59(3): Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12): Fegan DF. Evaluation of diagnostic tests: the epidemiological approach. DNA-based molecular diagnostic techniques. Research needs for standardization and validation of the detection of aquatic animal pathogens and diseases. FAO Fish Tech Pap. 2000; 395: Markell EK, Udkow MP. Association of Blastocystis hominis with human disease? J Clin Microbiol. 1990; 28(5): Tan ZN, Wong WK, Nik Zairi Z et al. Identification of Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites in fresh stool sample: comparison of three staining techniques and study on the viability period of the trophozoites. Trop Biomed. 2010; 27(1): Bart A, Wentink-Bonnema EM, Gilis H et al. Diagnosis and subtype analysis of Blastocystis sp. in 442 patients in a hospital setting in the Netherlands. BMC Infect Dis. 2013;13: Adıyaman Korkmaz G, Doğruman Al F, Mumcuoğlu İ. Investigation of the presence of Blastocystis spp. in stool samples with microscopic, culture and molecular methods. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015;49(1): Dogruman-Al F, Simsek Z, Boorom K et al. Comparison of methods for detection of Blastocystis infection in routinely submitted stool samples, and also in IBS/IBD Patients in Ankara, Turkey. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e Termmathurapoj S, Leelayoova S, Aimpun P et al. The usefulness of short-term in vitro cultiva- 135 Available at:
10 Mohammad et al.: Comparative Study of Wheatley s Trichrome Stain tion for the detection and molecular study of Blastocystis hominis in stool specimens. Parasitol Res. 2004;93(6): Parkar U, Traub RJ, Kumar S M et al. Direct characterization of Blastocystis from faeces by PCR and evidence of zoonotic potential. Parasitology. 2007;134(Pt 3): Leelayoova S, Taamasri P, Rangsin R et al. Invitro cultivation: a sensitive method for detecting Blastocystis hominis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2002;96(8): Zierdt CH, Swan JC. Generation time and growth rate of the human intestinal parasite Blastocystis hominis. J Protozool. 1981; 28(4): Suresh K, Smith H. Comparison of methods for detecting Blastocystis hominis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2004;23(6): Abu-Madi M, Aly M, Behnke JM, Clark CG, Balkhy H. The distribution of Blastocystis subtypes in isolates from Qatar. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8: Popruk S, Udonsom R, Koompapong K et al. Subtype Distribution of Blastocystis in Thai- Myanmar Border, Thailand. Korean J Parasitol. 2015;53(1):13-9. Available at: 136
A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF Blastocystis sp. ISOLATED FROM CHICKEN IN PERAK AND SELANGOR, MALAYSIA
 VOLUME 5 NO. 1 JANUARY 2014 pages 21-25 A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF Blastocystis sp. ISOLATED FROM CHICKEN IN PERAK AND SELANGOR, MALAYSIA FARAH HAZIQAH M.T. 1 *, CHANDRAWATHANI P. 2, MOHD ZAIN S.N. 1, SURESH
VOLUME 5 NO. 1 JANUARY 2014 pages 21-25 A PRELIMINARY STUDY OF Blastocystis sp. ISOLATED FROM CHICKEN IN PERAK AND SELANGOR, MALAYSIA FARAH HAZIQAH M.T. 1 *, CHANDRAWATHANI P. 2, MOHD ZAIN S.N. 1, SURESH
Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolated from humans and associated animals in an indigenous community with poor hygiene in Peninsular Malaysia
 Tropical Biomedicine 35(4): 849 860 (2018) Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolated from humans and associated animals in an indigenous community with poor hygiene in Peninsular Malaysia Mohammad,
Tropical Biomedicine 35(4): 849 860 (2018) Subtype distribution of Blastocystis isolated from humans and associated animals in an indigenous community with poor hygiene in Peninsular Malaysia Mohammad,
American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX
 Q3 2018 Parasitology American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX 77005 800-234-5315 281-436-5357 Specimen 1 Referees Extent 1 Extent 2 Total Few to 534 Giardia lamblia Many
Q3 2018 Parasitology American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX 77005 800-234-5315 281-436-5357 Specimen 1 Referees Extent 1 Extent 2 Total Few to 534 Giardia lamblia Many
MOLECULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BLASTOCYSTIS SP IN ANIMALS REARED BY THE ABORIGINES DURING WET AND DRY SEASONS IN RURAL COMMUNITIES, PAHANG, MALAYSIA
 Epidemiology of Blastocystis Subtypes in Animals MOLECULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BLASTOCYSTIS SP IN ANIMALS REARED BY THE ABORIGINES DURING WET AND DRY SEASONS IN RURAL COMMUNITIES, PAHANG, MALAYSIA Samseh Abdullah
Epidemiology of Blastocystis Subtypes in Animals MOLECULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BLASTOCYSTIS SP IN ANIMALS REARED BY THE ABORIGINES DURING WET AND DRY SEASONS IN RURAL COMMUNITIES, PAHANG, MALAYSIA Samseh Abdullah
Comparison of Conventional and Molecular Diagnostic Techniques for Detection of Blastocystis sp. in Pig Faeces
 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 4, Oct-Dec 2018, pp.594-601 Iran J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http://tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at http://ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian Society
Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 13, No. 4, Oct-Dec 2018, pp.594-601 Iran J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http://tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at http://ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian Society
Advantage of using colonic washouts for Blastocystis detection in colorectal cancer patients
 Kumarasamy et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:162 RESEARCH Open Access Advantage of using colonic washouts for Blastocystis detection in colorectal cancer patients Vinoth Kumarasamy 1, April Camilla Roslani
Kumarasamy et al. Parasites & Vectors 2014, 7:162 RESEARCH Open Access Advantage of using colonic washouts for Blastocystis detection in colorectal cancer patients Vinoth Kumarasamy 1, April Camilla Roslani
PREVALENCE OF DIENTAMOEBA FRAGILIS AMONG AN ORANG ASLI POPULATION IN RURAL MALAYSIA
 Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health PREVALENCE OF DIENTAMOEBA FRAGILIS AMONG AN ORANG ASLI POPULATION IN RURAL MALAYSIA Tengku Shahrul Anuar 1, Liyana Hasim 1, Norhayati Moktar 2, Fatmah Md Salleh
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health PREVALENCE OF DIENTAMOEBA FRAGILIS AMONG AN ORANG ASLI POPULATION IN RURAL MALAYSIA Tengku Shahrul Anuar 1, Liyana Hasim 1, Norhayati Moktar 2, Fatmah Md Salleh
RESEARCH NOTE GENETIC SUBTYPES OF BLASTOCYSTIS ISOLATED FROM THAI HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND
 RESEARCH NOTE GENETIC SUBTYPES OF BLASTOCYSTIS ISOLATED FROM THAI HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Oranuch Sanpool 1,2, Pokkamol Laoraksawong 3,4, Penchom Janwan 1,5, Pewpan M Intapan 1,3,6,
RESEARCH NOTE GENETIC SUBTYPES OF BLASTOCYSTIS ISOLATED FROM THAI HOSPITALIZED PATIENTS IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Oranuch Sanpool 1,2, Pokkamol Laoraksawong 3,4, Penchom Janwan 1,5, Pewpan M Intapan 1,3,6,
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Infection of Blastocystis hominis in primary schoolchildren from Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand
 Tropical Biomedicine 23(1): 117 122 (2006) Infection of Blastocystis hominis in primary schoolchildren from Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand Rapeeporn Yaicharoen, Warunee Ngrenngarmlert, Nuttapong Wongjindanon,
Tropical Biomedicine 23(1): 117 122 (2006) Infection of Blastocystis hominis in primary schoolchildren from Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand Rapeeporn Yaicharoen, Warunee Ngrenngarmlert, Nuttapong Wongjindanon,
Kit Components Product # EP42720 (24 preps) MDx 2X PCR Master Mix 350 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Primer Mix 70 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Positive
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
HUMAN GIARDIASIS IN MALAYSIA: CORRELATION BETWEEN THE PRESENCE OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATION AND GIARDIA INTESTINALIS ASSEMBLAGE
 HUMAN GIARDIASIS IN MALAYSIA: CORRELATION BETWEEN THE PRESENCE OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATION AND GIARDIA INTESTINALIS ASSEMBLAGE Tengku Shahrul Anuar 1, Norhayati Moktar 2, Fatmah Md Salleh 2 and Hesham M
HUMAN GIARDIASIS IN MALAYSIA: CORRELATION BETWEEN THE PRESENCE OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATION AND GIARDIA INTESTINALIS ASSEMBLAGE Tengku Shahrul Anuar 1, Norhayati Moktar 2, Fatmah Md Salleh 2 and Hesham M
Product # Kit Components
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
On the Importance of Validating Dientamoeba fragilis Real-Time PCR Assays. Dr Damien Stark Division of Microbiology St Vincent s Hospital
 On the Importance of Validating Dientamoeba fragilis Real-Time PCR Assays Dr Damien Stark Division of Microbiology St Vincent s Hospital Dientamoeba fragilis D. fragilis is a protozoan parasite worldwide
On the Importance of Validating Dientamoeba fragilis Real-Time PCR Assays Dr Damien Stark Division of Microbiology St Vincent s Hospital Dientamoeba fragilis D. fragilis is a protozoan parasite worldwide
Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran
 Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran Aliehsan Heidari, Manizheh Nourian, Hossein Keshavarz Associate Prof. Dept.
Comparison of light microscopy and nested PCR assay in detecting of malaria mixed species infections in an endemic area of Iran Aliehsan Heidari, Manizheh Nourian, Hossein Keshavarz Associate Prof. Dept.
ELISA TEST FOR DETECTION OF BLASTOCYSTIS SPP. IN HUMAN FAECES: COMPARISON OF THREE METHODS
 ELISA TEST FOR DETECTION OF BLASTOCYSTIS SPP. IN HUMAN FAECES: COMPARISON OF THREE METHODS István Kucsera, Mónika Molnár, Eszter Gályász, József Danka, Erika Orosz National Center for Epidemiology, Department
ELISA TEST FOR DETECTION OF BLASTOCYSTIS SPP. IN HUMAN FAECES: COMPARISON OF THREE METHODS István Kucsera, Mónika Molnár, Eszter Gályász, József Danka, Erika Orosz National Center for Epidemiology, Department
A Study of Blastocystis hominis Infection in Sulaimani Pediatric Teaching Hospital
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 8 (August-2015) pp. 290-299 www.ijcrar.com A Study of Blastocystis hominis Infection in Sulaimani Pediatric Teaching Hospital Rezan Mahmood Mohammed 1 and Shahnaz Abdul
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 3 Number 8 (August-2015) pp. 290-299 www.ijcrar.com A Study of Blastocystis hominis Infection in Sulaimani Pediatric Teaching Hospital Rezan Mahmood Mohammed 1 and Shahnaz Abdul
POLYPEPTIDES ASSOCIATED WITH IN VITRO CYST FORMATION OF BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS
 IN VITRO CYST FORMATION OF B. HOMINIS POLYPEPTIDES ASSOCIATED WITH IN VITRO CYST FORMATION OF BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS I Init 1, JW Mak 2, S Top 3, Z Zulhainan 4, S Prummongkol 5, V Nissapatorn 1, WS Wan-Yusoff
IN VITRO CYST FORMATION OF B. HOMINIS POLYPEPTIDES ASSOCIATED WITH IN VITRO CYST FORMATION OF BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS I Init 1, JW Mak 2, S Top 3, Z Zulhainan 4, S Prummongkol 5, V Nissapatorn 1, WS Wan-Yusoff
PARASITIC INFECTIONS AMONG ORANG ASLI (ABORIGINE) IN THE CAMERON HIGHLANDS, MALAYSIA
 PARASITIC INFECTIONS AMONG ORANG ASLI (ABORIGINE) IN THE CAMERON HIGHLANDS, MALAYSIA S Lokman Hakim 1, CC Gan 1, K Malkit 1, My Noor Azian 1, CK Chong 2, N Shaari 2, W Zainuddin 3, CN Chin 2, Y Sara 2
PARASITIC INFECTIONS AMONG ORANG ASLI (ABORIGINE) IN THE CAMERON HIGHLANDS, MALAYSIA S Lokman Hakim 1, CC Gan 1, K Malkit 1, My Noor Azian 1, CK Chong 2, N Shaari 2, W Zainuddin 3, CN Chin 2, Y Sara 2
Norgen s HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit was developed and validated to be used with the following PCR instruments: Qiagen Rotor-Gene Q BioRad T1000 Cycler
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product# 33840 Product Insert Intended
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product# 33840 Product Insert Intended
IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR
 IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR Zulhainan Hamzah 1, Songsak Petmitr 2, Mathirut Mungthin 3 and Porntip Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr 1 1 Department
IDENTIFICATION OF CRYPTOSPORIDIUM PARVUM GENOTYPE FROM HIV AND NON-HIV FECAL SAMPLES BY PCR Zulhainan Hamzah 1, Songsak Petmitr 2, Mathirut Mungthin 3 and Porntip Chavalitshewinkoon-Petmitr 1 1 Department
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 11, November ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 11, November-2015 1183 Isolation and Identification of Blastocystis hominis isolated from Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients using
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 11, November-2015 1183 Isolation and Identification of Blastocystis hominis isolated from Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients using
The Awareness of Health Professionals in Diagnostic Techniques for Intestinal Parasites in Gaza Strip, Palestine
 Original Article The Awareness of Health Professionals in Diagnostic Techniques for Intestinal Parasites in Gaza Strip, Palestine Hindi AI Department of Medical Technology Sciences, Islamic University
Original Article The Awareness of Health Professionals in Diagnostic Techniques for Intestinal Parasites in Gaza Strip, Palestine Hindi AI Department of Medical Technology Sciences, Islamic University
TRANSMISSION OF INTESTINAL BLASTOCYSTOSIS RELATED TO THE QUALITY OF DRINKING WATER
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH TRANSMISSION OF INTESTINAL BLASTOCYSTOSIS RELATED TO THE QUALITY OF DRINKING WATER Paanjit Taamasri 1, Mathirut Mungthin 1 Ram Rangsin 2, Benchamart Tongupprakarn
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH TRANSMISSION OF INTESTINAL BLASTOCYSTOSIS RELATED TO THE QUALITY OF DRINKING WATER Paanjit Taamasri 1, Mathirut Mungthin 1 Ram Rangsin 2, Benchamart Tongupprakarn
Norgen s HIV proviral DNA PCR Kit was developed and validated to be used with the following PCR instruments: Qiagen Rotor-Gene Q BioRad icycler
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product # 33840 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product # 33840 Product Insert Background Information
Sains Malaysiana 47(9)(2018):
 Sains na 47(9)(2018): 2099 2104 http://dx.doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2018-4709-18 Comparison of Direct Examination and In Vitro Culture for the Detection of Blastocystis sp. in Orang Asli Stool Samples (Perbandingan
Sains na 47(9)(2018): 2099 2104 http://dx.doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2018-4709-18 Comparison of Direct Examination and In Vitro Culture for the Detection of Blastocystis sp. in Orang Asli Stool Samples (Perbandingan
Genotyping of Blastocystis Species Revealed In Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients
 AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC AND APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN:1991-8178 EISSN: 2309-8414 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Genotyping of Blastocystis Species Revealed In Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients 1 Marwa
AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF BASIC AND APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN:1991-8178 EISSN: 2309-8414 Journal home page: www.ajbasweb.com Genotyping of Blastocystis Species Revealed In Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients 1 Marwa
A novel ELISA test for laboratory diagnosis of Blastocystis spp. in human stool specimens
 Parasitol Res (2015) 114:495 500 DOI 10.1007/s00436-014-4208-y ORIGINAL PAPER A novel ELISA test for laboratory diagnosis of Blastocystis spp. in human stool specimens Funda Dogruman-Al & Songul Turk &
Parasitol Res (2015) 114:495 500 DOI 10.1007/s00436-014-4208-y ORIGINAL PAPER A novel ELISA test for laboratory diagnosis of Blastocystis spp. in human stool specimens Funda Dogruman-Al & Songul Turk &
Outline EP1201. NEHA 2012 AEC June 2012
 Food and Water Borne Enteric Protozoa: Environmental Health Perspectives Stephanie M. Fletcher, PhD (c) NEHA AEC & Exhibition San Diego June 30, 2012 Outline Introduction Overview of the Epidemiology of
Food and Water Borne Enteric Protozoa: Environmental Health Perspectives Stephanie M. Fletcher, PhD (c) NEHA AEC & Exhibition San Diego June 30, 2012 Outline Introduction Overview of the Epidemiology of
PREVALENCE OF DIFFERENT PROTOZOAN PARASITES IN PATIENTS VISITING AT ICDDR B HOSPITAL, DHAKA
 J. Asiat. Soc. Bangladesh, Sci. 39(1): 117-123, June 213 PREVALENCE OF DIFFERENT PROTOZOAN PARASITES IN PATIENTS VISITING AT ICDDR B HOSPITAL, DHAKA SHAHELA ALAM, HAMIDA KHANUM 1, RIMI FARHANA ZAMAN AND
J. Asiat. Soc. Bangladesh, Sci. 39(1): 117-123, June 213 PREVALENCE OF DIFFERENT PROTOZOAN PARASITES IN PATIENTS VISITING AT ICDDR B HOSPITAL, DHAKA SHAHELA ALAM, HAMIDA KHANUM 1, RIMI FARHANA ZAMAN AND
Comparison of Polyvinyl Alcohol Fixative with Three Less Hazardous Fixatives for Detection and Identification of Intestinal Parasites
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2000, p. 1592 1598 Vol. 38, No. 4 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Comparison of Polyvinyl Alcohol Fixative with Three Less Hazardous Fixatives for Detection and Identification
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2000, p. 1592 1598 Vol. 38, No. 4 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Comparison of Polyvinyl Alcohol Fixative with Three Less Hazardous Fixatives for Detection and Identification
PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES
 PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES Rev.00 January 10, 2011 1. Introduction Intestinal parasitic diseases represent a serious public health issue in underdeveloped
PARATEST STABILITY STUDY, SYSTEM USED FOR DIAGNOSIS OF INTESTINAL PARASITES Rev.00 January 10, 2011 1. Introduction Intestinal parasitic diseases represent a serious public health issue in underdeveloped
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP36300
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cytomegalovirus (CMV) End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP36300 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cytomegalovirus (CMV) End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP36300 Product
Detection of Dientamoeba fragilis among diarrheal patients referred to Tabriz health care centers by nested PCR
 Tropical Biomedicine 30(1): 113 118 (2013) Detection of Dientamoeba fragilis among diarrheal patients referred to Tabriz health care centers by nested PCR Sarafraz, S. 1, Farajnia, S. 2*, Jamali, J. 3,
Tropical Biomedicine 30(1): 113 118 (2013) Detection of Dientamoeba fragilis among diarrheal patients referred to Tabriz health care centers by nested PCR Sarafraz, S. 1, Farajnia, S. 2*, Jamali, J. 3,
CURRENT SITUATION OF GIARDIA AND CRYPTOSPORIDIUM AMONG ORANG ASLI (ABORIGINAL) COMMUNITIES IN PAHANG, MALAYSIA
 CURRENT SITUATION OF GIARDIA AND CRYPTOSPORIDIUM AMONG ORANG ASLI (ABORIGINAL) COMMUNITIES IN PAHANG, MALAYSIA AK Mohammed Mahdy, Johari Surin, YAL Lim and MS Hesham AI-Mekhlafi Department of Parasitology,
CURRENT SITUATION OF GIARDIA AND CRYPTOSPORIDIUM AMONG ORANG ASLI (ABORIGINAL) COMMUNITIES IN PAHANG, MALAYSIA AK Mohammed Mahdy, Johari Surin, YAL Lim and MS Hesham AI-Mekhlafi Department of Parasitology,
Biology and Medicine
 eissn: 09748369 Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis by smear microscopy and culture in a tertiary health care facility Biology and Medicine SI Khatib, MT Williamson, R Singh, JM Joshi Accepted: 28 th Feb
eissn: 09748369 Diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis by smear microscopy and culture in a tertiary health care facility Biology and Medicine SI Khatib, MT Williamson, R Singh, JM Joshi Accepted: 28 th Feb
Classification - Protozoa. Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba. Stools for O&P Examination. Stool Specimen. What to look for.
 Classification - Protozoa Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba Phylum Phylum Sarcomastigophora Sarcomastigophora Subkingdom Subkingdom Protozoa Protozoa Phylum Phylum Ciliophora Ciliophora Phylum Phylum Apicomplexa
Classification - Protozoa Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba Phylum Phylum Sarcomastigophora Sarcomastigophora Subkingdom Subkingdom Protozoa Protozoa Phylum Phylum Ciliophora Ciliophora Phylum Phylum Apicomplexa
HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
Distribution of haematological indices among subjects with Blastocystis hominis infection compared to controls
 Original paper Distribution of haematological indices among subjects with Blastocystis hominis infection compared to controls Hazhir Javaherizadeh 1, Shahram Khademvatan 2, Shahrzad Soltani 2, Mehdi Torabizadeh
Original paper Distribution of haematological indices among subjects with Blastocystis hominis infection compared to controls Hazhir Javaherizadeh 1, Shahram Khademvatan 2, Shahrzad Soltani 2, Mehdi Torabizadeh
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases. (Amoebiasis)
 Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
Different Clinical Outcomes of Entamoeba histolytica in Malaysia: Does Genetic Diversity Exist?
 ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Korean J Parasitol Vol. 51, No. 2: 231-236, April 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2013.51.2.231 Different Clinical Outcomes of Entamoeba
ISSN (Print) 0023-4001 ISSN (Online) 1738-0006 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Korean J Parasitol Vol. 51, No. 2: 231-236, April 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2013.51.2.231 Different Clinical Outcomes of Entamoeba
Detection of intestinal protozoa in paediatric patients with gastrointestinal symptoms by multiplex real-time PCR
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE PARASITOLOGICAL Detection of intestinal protozoa in paediatric patients with gastrointestinal symptoms by multiplex real-time PCR L. Maas 1, J. W. Dorigo-Zetsma 2, C. J. de Groot 1, S.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE PARASITOLOGICAL Detection of intestinal protozoa in paediatric patients with gastrointestinal symptoms by multiplex real-time PCR L. Maas 1, J. W. Dorigo-Zetsma 2, C. J. de Groot 1, S.
Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections
 Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections By Dr. Doaa Abdel Badie Salem Lecturer of Medical Parasitology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Agenda Intestinal parasites. Traditional Diagnostic
Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections By Dr. Doaa Abdel Badie Salem Lecturer of Medical Parasitology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Agenda Intestinal parasites. Traditional Diagnostic
Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness
 World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
MORPHOLOGY AND FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION OF PROTOZOAN BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS
 MORPHOLOGY AND FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION OF PROTOZOAN BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 322 To 324 M. Naqi Zafar ( Zafar Research and Diagnostic Centre, 7/14, Riznpa Plaza,
MORPHOLOGY AND FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION OF PROTOZOAN BLASTOCYSTIS HOMINIS Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 322 To 324 M. Naqi Zafar ( Zafar Research and Diagnostic Centre, 7/14, Riznpa Plaza,
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 2 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control. 12 K (All Parasites)
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: Vol.9, No.3, pp , 2016
 International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: 0974-4304 Vol.9, No.3, pp 240-244, 2016 Polymerase chain reaction compared with wet mount for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in
International Journal of PharmTech Research CODEN (USA): IJPRIF, ISSN: 0974-4304 Vol.9, No.3, pp 240-244, 2016 Polymerase chain reaction compared with wet mount for detection of Trichomonas vaginalis in
Study of Intestinal Protozoan Parasites in Rural Inhabitants of Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran
 Original Article Study of Intestinal Protozoan Parasites in Rural Inhabitants of Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran EB Kia 1, M Hosseini 2, MR Nilforoushan 1, AR Meamar 3, *M Rezaeian 1 1 Dept. of Medical
Original Article Study of Intestinal Protozoan Parasites in Rural Inhabitants of Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran EB Kia 1, M Hosseini 2, MR Nilforoushan 1, AR Meamar 3, *M Rezaeian 1 1 Dept. of Medical
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate)
 Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture Two GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture Two GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Blastocystis Hominis Infection Pathogenic or Commensal: Short Review
 International Journal of Research Studies in Microbiology and Biotechnology Volume 3, Issue 3 2017, PP 1-5 ISSN No. (Online) 2454-9428 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-9428.0303001 www.arcjournals.org
International Journal of Research Studies in Microbiology and Biotechnology Volume 3, Issue 3 2017, PP 1-5 ISSN No. (Online) 2454-9428 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2454-9428.0303001 www.arcjournals.org
Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Pinpoint Slide RNA Isolation System II Catalog No. R1007 Highlights Allows for the isolation of total RNA from paraffin-embedded tissue sections on glass slides Simple procedure combines
E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit
 E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3193 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3193 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Validation Report: VERSA Mini PCR Workstation Reverse Transcription of Avian Flu RNA and Amplification of cdna & Detection of H5N1
 I. Objectives Validation Report: VERSA Mini PCR Workstation Reverse Transcription of Avian Flu RNA and Amplification of cdna & Detection of H5N1 1. To ensure stability of RNA (highly thermolabile and degradatively
I. Objectives Validation Report: VERSA Mini PCR Workstation Reverse Transcription of Avian Flu RNA and Amplification of cdna & Detection of H5N1 1. To ensure stability of RNA (highly thermolabile and degradatively
Amoebic forms of Blastocystis spp. - evidence for a pathogenic role
 Rajamanikam and Govind Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:295 RESEARCH Open Access Amoebic forms of Blastocystis spp. - evidence for a pathogenic role Arutchelvan Rajamanikam and Suresh Kumar Govind * Abstract
Rajamanikam and Govind Parasites & Vectors 2013, 6:295 RESEARCH Open Access Amoebic forms of Blastocystis spp. - evidence for a pathogenic role Arutchelvan Rajamanikam and Suresh Kumar Govind * Abstract
Molecular Epidemiology of Cryptosporidiosis in Iranian Children, Tehran, Iran
 Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http:// tums.ac.ir Original Article Iranian J Parasitol Open access Journal at http:// ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian Society of Parasitology http:// isp.tums.ac.ir
Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http:// tums.ac.ir Original Article Iranian J Parasitol Open access Journal at http:// ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian Society of Parasitology http:// isp.tums.ac.ir
Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans:
 The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Amoebiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
August 2011 Amoebiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
Mycoplasma Total Solution. Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Elimination Mycoplasma Prevention Cell Freezing Medium (Mycoplasma Free)
 Mycoplasma Total Solution Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Elimination Mycoplasma Prevention Cell Freezing Medium (Mycoplasma Free) Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Detection CellSafe s Mycoplasma Detection
Mycoplasma Total Solution Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Elimination Mycoplasma Prevention Cell Freezing Medium (Mycoplasma Free) Mycoplasma Detection Mycoplasma Detection CellSafe s Mycoplasma Detection
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 5 November 2013
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Beginning with the May 2013 event a separate set of 3 samples were supplied for laboratories performing antigen detection. For the
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Beginning with the May 2013 event a separate set of 3 samples were supplied for laboratories performing antigen detection. For the
More than 98 countries affected by Leishmaniasis
 More than 98 countries affected by Leishmaniasis ACL In many urban & sub urban areas (8 provinces) Tehran, Mashhad, Neishabur, Shiraz, Kerman, Bam (Sharifi et al. 2011) ZCL In 2012, totally ( ZCL & ACL)
More than 98 countries affected by Leishmaniasis ACL In many urban & sub urban areas (8 provinces) Tehran, Mashhad, Neishabur, Shiraz, Kerman, Bam (Sharifi et al. 2011) ZCL In 2012, totally ( ZCL & ACL)
Comparison of Three Collection-Preservation Methods for
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1981, p. 656-660 0095-1 137/81/120656-05$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 6 Comparison of Three Collection-Preservation Methods for Detection of Intestinal Parasites DONALD L.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1981, p. 656-660 0095-1 137/81/120656-05$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 6 Comparison of Three Collection-Preservation Methods for Detection of Intestinal Parasites DONALD L.
Parasitology. Helminthology (Helminths)
 Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA COPY NUMBER VARIATIONS OF ORANG ASLI (NEGRITO) FROM PENINSULAR MALAYSIA
 UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA COPY NUMBER VARIATIONS OF ORANG ASLI (NEGRITO) FROM PENINSULAR MALAYSIA SITI SHUHADA MOKHTAR Thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA COPY NUMBER VARIATIONS OF ORANG ASLI (NEGRITO) FROM PENINSULAR MALAYSIA SITI SHUHADA MOKHTAR Thesis submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Downloaded from:
 Stensvold, CR; Clark, CG; Rser, D (2013) Limited intra-genetic diversity in Dientamoeba fragilis housekeeping genes. Infection, genetics and evolution, 18. pp. 284-6. ISSN 1567-1348 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2013.0
Stensvold, CR; Clark, CG; Rser, D (2013) Limited intra-genetic diversity in Dientamoeba fragilis housekeeping genes. Infection, genetics and evolution, 18. pp. 284-6. ISSN 1567-1348 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2013.0
Received 8 July 2010/Returned for modification 24 August 2010/Accepted 13 December 2010
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 975 983 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01392-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Development and
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 2011, p. 975 983 Vol. 49, No. 3 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01392-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Development and
Independent Forensics 4600 West Roosevelt Road Suite 201 Hillside IL 60162, USA. Telephone: (708) Fax: (708)
 Developmental validation of SPERM HY-LITER A Specific, Sensitive and Confirmatory Microscopic Screening Method for the Detection of Human Sperm from Sexual Assault Evidence Independent Forensics 4600 West
Developmental validation of SPERM HY-LITER A Specific, Sensitive and Confirmatory Microscopic Screening Method for the Detection of Human Sperm from Sexual Assault Evidence Independent Forensics 4600 West
The role of Blastocystis sp. as an etiology of irritable bowel syndrome
 1 Polish Annals of Medicine, Article In Press, doi:10.1016/j.poamed.2015.04.001 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 The role of Blastocystis sp. as an etiology of irritable bowel syndrome
1 Polish Annals of Medicine, Article In Press, doi:10.1016/j.poamed.2015.04.001 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 The role of Blastocystis sp. as an etiology of irritable bowel syndrome
Hepatitis B Virus Genemer
 Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Product Manual Hepatitis B Virus Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HBV Viral Specific Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2007-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures
Spotting Malaria reliably
 Spotting Malaria reliably Track down infections easily with highly sensitive Malaria-LAMP even in low-prevalent settings Molecular DX Microscopy and RDT s are not able to track down parasites in low-transmission
Spotting Malaria reliably Track down infections easily with highly sensitive Malaria-LAMP even in low-prevalent settings Molecular DX Microscopy and RDT s are not able to track down parasites in low-transmission
Origination Date: 25 Mar 2004 Total Pages: Effective Date: 18 Sep 2012 SOP Number LTC-SOP-17 v2.0. Network Name, Title Signature Date
 Title: Stool Processing and Cryptosporidium/Giardia Origination Date: 25 Mar 2004 Total Pages: Effective Date: 18 Sep 2012 SOP Number LTC-SOP-17 v2.0 Prepared By: Bill Kabat and Nancy Isham of the Supersedes
Title: Stool Processing and Cryptosporidium/Giardia Origination Date: 25 Mar 2004 Total Pages: Effective Date: 18 Sep 2012 SOP Number LTC-SOP-17 v2.0 Prepared By: Bill Kabat and Nancy Isham of the Supersedes
Prevalence and Risk Factors of Human Intestinal Parasites in Roudehen, Tehran Province, Iran
 Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 12, No. 3, Jul-Sep 2017, pp. 364-373 Iran J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http:// tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at http:// ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian
Iran J Parasitol: Vol. 12, No. 3, Jul-Sep 2017, pp. 364-373 Iran J Parasitol Tehran University of Medical Sciences Publication http:// tums.ac.ir Open access Journal at http:// ijpa.tums.ac.ir Iranian
Detection and Identification of Entamoeba Species in Stool Samples by a Reverse Line Hybridization Assay
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2003, p. 5041 5045 Vol. 41, No. 11 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.5041 5045.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2003, p. 5041 5045 Vol. 41, No. 11 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.5041 5045.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
RealLine Mycoplasma genitalium Str-Format
 Instructions for use ASSAY KIT FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM DNA BY REAL-TIME PCR METHOD In vitro Diagnostics () VBD4396 96 Tests valid from December 2018 Rev06_1218_EN Page 1
Instructions for use ASSAY KIT FOR THE QUALITATIVE DETECTION OF MYCOPLASMA GENITALIUM DNA BY REAL-TIME PCR METHOD In vitro Diagnostics () VBD4396 96 Tests valid from December 2018 Rev06_1218_EN Page 1
MICROBIOLOGY ECOLOGY. The microbial eukaryote Blastocystis is a prevalent and diverse member of the healthy human gut microbiota SHORT COMMUNICATION
 MICROBIOLOGY ECOLOGY SHORT COMMUNICATION The microbial eukaryote Blastocystis is a prevalent and diverse member of the healthy human gut microbiota Pauline D. Scanlan 1, Christen R. Stensvold 2, Mirjana
MICROBIOLOGY ECOLOGY SHORT COMMUNICATION The microbial eukaryote Blastocystis is a prevalent and diverse member of the healthy human gut microbiota Pauline D. Scanlan 1, Christen R. Stensvold 2, Mirjana
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
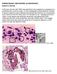 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum in chickensbn from industrial farms in Kerman province
 Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014: 100-104 Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum
Available online at http://www.ijabbr.com International journal of Advanced Biological and Biomedical Research Volume 2, Issue 1, 2014: 100-104 Isolation and identification of Mycoplasma gallisepticum
A New Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay For Detection Of Intestinal Parasites
 A New Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay For Detection Of Intestinal Parasites Dr. Andreas Simons Worldwide provider of diagnostic assay solutions Offers a variety of test kit methodologies R-Biopharm Headquarters
A New Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay For Detection Of Intestinal Parasites Dr. Andreas Simons Worldwide provider of diagnostic assay solutions Offers a variety of test kit methodologies R-Biopharm Headquarters
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Novel Coronavirus 2012
 Novel Coronavirus 2012 Susan I. Gerber, MD Respiratory Virus Program Division of Viral Diseases National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Jan.
Novel Coronavirus 2012 Susan I. Gerber, MD Respiratory Virus Program Division of Viral Diseases National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Jan.
PARA-TECT Cryptosporidium/Giardia Direct Fluorescent Assay Directions For Use For In Vitro Diagnostic Use
 Medical Chemical Corp., 19430 Van Ness Avenue, Torrance, California 90501 (310)787-6800, Fax (310)787-4464 Catalog # MCC-C/G - DFA, 75 Test PARA-TECT Cryptosporidium/Giardia Direct Fluorescent Assay Directions
Medical Chemical Corp., 19430 Van Ness Avenue, Torrance, California 90501 (310)787-6800, Fax (310)787-4464 Catalog # MCC-C/G - DFA, 75 Test PARA-TECT Cryptosporidium/Giardia Direct Fluorescent Assay Directions
Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar. A. Haghighi,
 Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar A. Haghighi, Wednesday, February 14, 2018 Classification of Protozoa? The protozoa are generally unicellular and may be divided for convenience, into four distinct groups
Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar A. Haghighi, Wednesday, February 14, 2018 Classification of Protozoa? The protozoa are generally unicellular and may be divided for convenience, into four distinct groups
Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis
 PARA 317331 Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Microspora A group of organisms: small single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites belonging to Phylum Microspora Early-
PARA 317331 Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Microspora A group of organisms: small single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites belonging to Phylum Microspora Early-
Detect TB. Accurately. Easily.
 Detect TB. Accurately. Easily. Fast and robust test results with TB-LAMP Molecular DX Smear microscopy misses nearly every second positive TB case We need new tests to rapidly diagnose people with TB;
Detect TB. Accurately. Easily. Fast and robust test results with TB-LAMP Molecular DX Smear microscopy misses nearly every second positive TB case We need new tests to rapidly diagnose people with TB;
in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares
 Influence of Probiotics on Microflora in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares Katie Barnhart Research Advisors: Dr. Kimberly Cole and Dr. John Mark Reddish Department of
Influence of Probiotics on Microflora in the Gastrointestinal and Reproductive Tracts of Quarter Horse Mares Katie Barnhart Research Advisors: Dr. Kimberly Cole and Dr. John Mark Reddish Department of
3-Mutualism: It is a relationship between two. organisms; one called. or harmless. 2-Commensalism: It is a relationship in which one
 Host-Parasite relationships Symbiosis: It is the permanent relationship between two dissimilar organisms which depending each others. They are three types 1- Parasitism : It is a relationship between two
Host-Parasite relationships Symbiosis: It is the permanent relationship between two dissimilar organisms which depending each others. They are three types 1- Parasitism : It is a relationship between two
Giardiasis. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Description of Dientamoeba fragilis cyst and precystic forms from
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 May 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00813-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Description of Dientamoeba
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 May 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00813-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Description of Dientamoeba
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer. Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment
 Product Manual Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2002-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in
Product Manual Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) Genemer Primer Pair for amplification of HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Catalog No.: 60-2002-10 Store at 20 o C For research use only. Not for use in
ENDEMIC MALARIA IN FOUR VILLAGES IN ATTAPEU PROVINCE, LAO PDR
 ENDEMIC MALARIA IN FOUR VILLAGES IN ATTAPEU PROVINCE, LAO PDR R Phetsouvanh 1, I Vythilingam 2, B Sivadong 1, S Lokman Hakim 2, ST Chan 2 and S Phompida 1 1 Center for Malaria, Parasitology and Entomology,
ENDEMIC MALARIA IN FOUR VILLAGES IN ATTAPEU PROVINCE, LAO PDR R Phetsouvanh 1, I Vythilingam 2, B Sivadong 1, S Lokman Hakim 2, ST Chan 2 and S Phompida 1 1 Center for Malaria, Parasitology and Entomology,
Epidemiology of Gray Leaf Spot of Perennial Ryegrass Philip Harmon and Richard Latin. Objective
 Epidemiology of Gray Leaf Spot of Perennial Ryegrass Philip Harmon and Richard Latin Objective Rationale The continuing objective of this research is to investigate the environmental factors that influence
Epidemiology of Gray Leaf Spot of Perennial Ryegrass Philip Harmon and Richard Latin Objective Rationale The continuing objective of this research is to investigate the environmental factors that influence
1 Trophozoite stage : The typical characteristics of this stage are :
 Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 2 - Genus : Entamoeba coli It is considered to be a nonpathogenic with world wide distribution. That frequently exists as a commensal parasite
Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 2 - Genus : Entamoeba coli It is considered to be a nonpathogenic with world wide distribution. That frequently exists as a commensal parasite
The diagnostic value of gyrb RFLP PCR. Mycobacteria in patients with clinical. in Mazandaran
 Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences The diagnostic value of gyrb RFLP PCR test t in differentiation between pathogenic Mycobacteria in patients with clinical suspicions spicions of tuberculosis in
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences The diagnostic value of gyrb RFLP PCR test t in differentiation between pathogenic Mycobacteria in patients with clinical suspicions spicions of tuberculosis in
Original Article. Amira B. Mokhtar 1 and Ahmed I. Youssef 2
 Original Article Subtype analysis of Blastocystis spp. isolated from domestic mammals and poultry and its relation to transmission to their incontact humans in Ismailia governorate, Egypt. Amira B. Mokhtar
Original Article Subtype analysis of Blastocystis spp. isolated from domestic mammals and poultry and its relation to transmission to their incontact humans in Ismailia governorate, Egypt. Amira B. Mokhtar
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates
 Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT. Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx
 WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx 0226-032-00 Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect with product codes 270110050, 270110010 and 270300001,
WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx 0226-032-00 Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect with product codes 270110050, 270110010 and 270300001,
Usefulness of Modified Centrifuged Blood Smear in Diagnosis of Malaria
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 3(2016) pp. 764-769 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.503.088
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 5 Number 3(2016) pp. 764-769 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2016.503.088
Dako IT S ABOUT TIME. Interpretation Guide. Agilent Pathology Solutions. ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis)
 INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 08 Page August 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i8.57 Controversial Pathogen: Blastocystis hominis
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i8.57 Controversial Pathogen: Blastocystis hominis
HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis
 Product Manual HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures for clinical purposes Catalog
Product Manual HIV-1 Genemer Detection Kit Ready to Use Amplification Kit for HIV-1 Specific DNA Fragment Analysis For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures for clinical purposes Catalog
