Constipation in children: diagnosis and management
|
|
|
- Abel Morgan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Practice Constipation in children: diagnosis and management Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2009; 38: (Key words: Constipation, Rome III criteria, child) Constipation is a common gastrointestinal disorder in children and adolescents accounting for a significant healthcare burden. Clinical spectrum ranges from mild constipation that resolves spontaneously to chronic treatment resistant constipation with devastating physical and psychosocial consequences. This article provides clinicians with a current concise review of diagnostic and management strategies of constipation. Definitions Constipation had been a difficult condition to diagnose due to a lack of uniform diagnostic criteria. It was often perceived as a symptom rather than a disorder. Therefore many researchers and clinicians have defined constipation using a single symptom, such as infrequent passage of stools, hard stools or difficulty in passing stools 1. Formulating uniform diagnostic criteria acceptable to both clinicians and researchers was the main aim of the experts in paediatric gastroenterology who developed the Rome II criteria for defaecation disorders in However, these criteria were found to be too restrictive in diagnosis of constipation as they excluded a significant percentage of affected children 3. This led to revision of Rome II criteria and the new Rome III criteria for childhood constipation were released in These criteria use multiple symptoms and signs and are therefore useful in diagnosis of constipation in both clinical and research fields (Box 1). They concentrate on characteristics of stool (frequency, consistency, and volume), pain during defaecation, faecal incontinence, withholding behaviour and presence of faecal mass during examination. Box 1 - Rome III diagnostic criteria for functional constipation in children Must include 2 or more of the following in a child with a developmental age of at least 4 years with insufficient criteria to diagnose irritable bowel syndrome: 1. Two or fewer defaecations in the toilet per week 2. At least one episode of faecal incontinence per week 3. History of retentive posturing or excessive volitional stool retention 4. History of painful or hard bowel movements 5. Presence of a large faecal mass in the rectum 6. History of large diameter stools that may obstruct the toilet * Criteria fulfilled at least once per week for at least 2 months before diagnosis Epidemiology There is a wide variation in prevalence (0.7% %) of constipation around the world 5 mostly due to variations in definitions used and age groups of study participants recruited. Due to lack of epidemiological data from third world countries, constipation was perceived to be a disorder of the 1 Senior Lecturer in Paediatrics, 2 Senior Lecturer in Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Kelaniya, Ragama, Sri Lanka Western hemisphere. However, a recent epidemiological study from Sri Lanka reported constipation in 10.4% children and adolescents 6. This implies that it had been an overlooked problem in developing countries. Furthermore, longitudinal data from the USA demonstrated nearly 4 fold rise in rates of constipation during the last decade and the majority of ambulatory care visits for constipation were in children under 15 years 7. Therefore constipation is a growing public health problem among the paediatric population.
2 Pathophysiology The human colon is a complex organ which serves a multitude of functions including absorption of water and electrolytes from the ileal effluent to storing faecal material in the rectosigmoid area before elimination. These functions of the colon are strictly controlled by the enteric nervous system. Constipation can stem from organic disorders such as structural abnormalities of the colon, metabolic and endocrine problems and functional abnormalities (Box 2). Over 90% of children with constipation have no identifiable organic cause for their symptoms and are suffering from functional constipation 8. Box 2 Common organic causes for paediatric constipation Hirschsprung disease Anorectal malformations Coeliac disease Neuronal intestinal dysplasia Anorexia nervosa Sexual abuse Drugs opiates anticholinergics antidepressants Hypothyroidism Hypercalcaemia Diabetes mellitus Renal tubular acidosis Scleroderma Amyloidosis Cystic fibrosis The exact mechanism of symptoms is unclear in those with functional constipation. Previous studies have demonstrated a close relationship between constipation and psychological factors including emotional stress 9,10,11. Furthermore, there was a significant negative correlation between mean bowel frequency and number of stressful life events faced by affected children 9. It is possible that psychological distress, via brain gut axis, impair colonic motility and anorectal function leading to slow colonic transit and stool withholding 12,13. Stool withholding leads to formation of large faecal masses which are difficult and painful to eliminate, further aggravating the withholding behaviour. This vicious cycle of stool retention ultimately ends up in developing constipation. Differential diagnosis Constipation predominant irritable bowel syndrome is the commonest differential diagnosis for constipation. In those with irritable bowel syndrome, abdominal pain or discomfort is the predominant symptom and they are likely to have pain relief after defaecation and changing stool consistency and frequency Evaluation of a child with constipation History Clinical history should start from the neonatal period to assess the timing of passage of meconium. Meconium is passed within 48 hours after birth in a normal neonate and delayed passage is often associated with Hirschsprung disease which is an important organic cause for constipation. Two retrospective cohort studies have shown newborns with Hirschsprung disease had significant delay in passing meconium compared to children with functional constipation 14,15. Time of onset of symptoms is another cardinal point to elicit in the history. The majority develop functional constipation around 2-4 years of age 16 and development of significant symptoms before the age of 1 year is highly suggestive of organic pathology. Some report exposure to stressful life events (e.g. birth of a sibling, death of a close family member, sexual abuse) just before the onset of constipation 8. Symptoms included in the current Rome III diagnostic criteria for constipation are concentrating on characteristic of stool (frequency, consistency and volume), painful defaecation, faecal incontinence and withholding behaviour (Box 1). However there are other clinical features that are not included in the diagnostic criteria, but often seen in clinical practice. Straining on passing stools is a common symptom and its prevalence among children with constipation ranges from 35%-75% 6,8. Other symptoms often seen in affected children include abdominal pain and distension, anorexia, vomiting, blood stained stools and urinary symptoms 1,6,8,17,18. Some of these problems are incapacitating and associate with poor quality of life and therefore need to be recognized early in the evaluation. General medical history, social details and the developmental and psychological history are also integral components in assessing the constipated child. During history, it is important to inquire about stool withholding behaviour which is identified as one of the commonest causes for constipation in older children and adolescents. The poor condition of school toilets has been identified as the commonest reason for withholding behaviour 19 and some children resist using toilets other than ones at home. Furthermore, a careful dietary history is useful to assess the amount of fibre intake. Box 3 lists the possible risk factors for constipation.
3 Box 3 Common risk factors for development of constipation in children Low fibre diet Psychological factors emotional stress anxiety depression Cows milk protein allergy History of constipation in first degree relatives Prematurity Painful defaecation Living in urban area Physical examination Physical examination should be meticulous and should include assessment of growth and nutritional status. Poor growth (faltering of height and weight) is a good indicator of the presence of an organic disease. Thyroid swelling, though not common, raises the possibility of underlying hypothyroidism. During physical examination of a child with constipation, abdominal and perianal examination should not be overlooked. Presence of palpable faecal masses in the abdominal and rectal examination is an important clinical feature indicating faecal impaction. In addition, thorough examination of the perianal region may show abnormally placed anus, fistulae and perianal fissures. It has been noted that the rate of digital examination of rectum is unacceptably low in children with constipation 20. Neurological assessment is also an integral part in the evaluation of a child with constipation. Delayed milestones, spasticity, or hypotonia may indicate underlying cerebral palsy. Spinal dysraphism will be obvious if there are features such as repaired myelomeningocele, tuft of hair or haemangioma. Asymmetry of buttocks, patulous anus and abnormal neurological signs of lower limb neurological examination also indicate the possibility of associated organic disorder for the constipation. Investigations Constipation is a symptom based diagnosis and there are no biological markers to confirm it. Even so, when faced with a child suffering from constipation, some clinicians tend to order a battery of investigations in order to find an organic cause. However, it is important to realize that without clinical evidence suggestive of an organic disease (history and physical examination) such tests would rarely give abnormal results of clinical importance. However, chronic treatment resistant constipation warrants investigations to find a possible aetiology. Common investigations performed in children with constipation are discussed below. Plain x-ray of abdomen Plain abdominal x-ray has been frequently used to assess the degree of faecal impaction, but is reported to have lower sensitivity and specificity 21. Furthermore, a recent systematic review failed to reveal a definite association between clinical and radiological diagnosis 22. Therefore it is difficult to justify a plain abdominal radiograph in routine assessment of constipation. Colonic transit studies Colonic transit is assessed by scintigraphy and radio-opaque marker techniques. Colonic transit is reported to be slow in the majority of children with constipation Those with slow transit constipation have significantly more faecal soiling and palpable abdominal and rectal masses, which indicate severe and long-term constipation 23. Furthermore, patients with slow transit constipation often do not respond to standard medical management. Therefore, colonic transit studies are beneficial for identifying and managing children with chronic treatment resistant constipation. Ano-rectal manometry Anorectal manometry assesses the pressure changes, anorectal sensation and myoelectrical activity of external anal sphincter and puborectalis muscle during defaecation. Traditionally, manometry was used to rule out Hirschsprung disease in infants, and has shown very high sensitivity and specificity 27,28. In addition, anorectal manometry has reported several physiological abnormalities of defaecation in children with functional constipation. Children with constipation have increased threshold for rectal sensation 29,30 and abnormally high resting anal tones 31,32 compared to normal children. Furthermore, balloon expulsion test combined with surface electromyography has demonstrated abnormal contraction of the puborectalis muscle during defaecation, leading to pelvic flow dyssynergia in functional constipation Other investigations Colonic manometry is used to identify abnormal colonic motor activity and elicit the presence of gastro-colic response. Research using colonic manometry has shown that children with intractable constipation had varying percentages of neuromuscular impairment of the colon 36,37. Faeco-flowmetry evaluates pressure changes in rectum and the anal canal while infusing saline and
4 evacuation rates of saline by using an uroflow meter. Recent study has shown abnormalities in pressure curves and faecoflowmetry curves in children with chronic constipation 38. Management Management of chronic constipation needs good rapport between the patient, parents and clinician. It is important to build a trustworthy relationship at the first consultation without downplaying the difficulty that patient and family are experiencing. As mentioned earlier, a thorough history and physical examination would help to rule out organic pathologies and to direct the pathway of management. The key steps in management include education and demystification, treatment of faecal impaction, maintenance therapy and close follow up. Education and demystification The first step in management is educating parents and the child regarding constipation. Some parents tend to accuse the child for withholding stools purposely. This derailed family relationship often interferes with compliance of medical management. Some parents have certain beliefs that often stem from cultural roots which may hamper management decisions and it is of paramount importance to educate them thoroughly on risk factors for constipation, management and follow up. Some children with chronic constipation simply improve with non accusatory education and toilet training 39. Behavioural modifications Mass movements of colon move faeces towards the rectum and increase rectal pressure stimulating the defaecation reflex. Mass movements are maximal after waking up and after a meal 40,41. Therefore, children need to be trained to evacuate their bowel in relationship to these physiological phenomena 42. Behavioural protocols with emphasis on toilet training, reward systems for positive reinforcement, maintenance of a stool diary, avoidance of punitive behaviour and play therapy had been used with variable success 43,44. Aims of these protocols are to regularise the toilet habits to minimize faecal withholding. According to randomized controlled trials, enhanced toilet training plus medical management are more effective than both intensive medical treatment and biofeedback training 45. Regular exercise in healthy adults has been shown to increase colonic high amplitude propagatory contractions 46 but its therapeutic value in childhood constipation has not been established. Dietary interventions Increasing water and dietary fibre intake is probably the commonest advice given by clinicians regarding childhood constipation. Low consumption of dietary fibre had been identified as a risk factor to chronic constipation 47-49, but exact therapeutic value of high fibre diet in childhood constipation has not been established. Several previous randomized controlled trials in children with constipation failed to show a significant resolution of symptoms following high fibre diet 50,51. Another recent trial failed to demonstrate any significant advantage of fibre supplement over conventional lactulose therapy 52. Therefore, further trials are clearly needed before recommending dietary supplements as a treatment modality for constipation in children. Similarly, two studies performed to assess the value of water intake in constipation failed to demonstrate a significant effect on stool output or consistency 53,54. Disimpaction Traditionally rectal faecal impaction is treated with enemas and suppositories. However, there is a growing body of evidence that oral drugs can be used effectively in faecal disimpaction. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) 3350 given orally was proven to be the best pharmacological agent in disimpaction of faeces in children 55. In a multicentre retrospective study, PEG 3350 plus electrolytes given for 5 day were reported to be more successful in disimpaction in children with intractable constipation than enemas, suppositories or manual evacuation under anaesthesia 56. Similarly, another study involving children with intractable constipation showed successful clearance of impacted faeces in 92% following treatment with PEG plus electrolytes 57. Phosphate enemas are still useful in children who do not respond to oral medications. It is necessary to use a sedative before administrating enemas to minimize discomfort and psychological effects. Phosphate enemas should be administered under medical supervision in a hospital because if phosphate is retained without passing stools there is a risk of hyperphosphataemia and hypocalcaemia which need emergency medical care. Maintenance therapy Laxatives Several groups of laxative are being used in maintenance therapy (e.g. osmotic laxatives, stimulant laxatives and faecal softeners). Research evidences are scanty for most of the laxatives. However some laxatives are extensively studied in randomized controlled trials. Osmotic laxatives Polyethylene glycol (PEG) acts as a powerful, nondigestible osmotic laxative, in addition to faecal disimpactant. According to randomized controlled
5 trials PEG (PEG Electrolytes) was more effective than lactulose as maintenance therapy and in addition, children on lactulose had significantly more re-impaction and needed stimulant laxatives 57. In contrast, another trial found no significant difference between PEG and lactulose with regards to the stool frequency at 42 and 84 days, but similar to previous study, more hard stools and faecal impaction were noted in the children receiving lactuolse 58. A recent systematic review has shown that PEG is as good as or better than lactulose or milk of magnesia for maintenance therapy over a wide range of ages 59. Lactulose is another common osmotic laxative used in paediatric constipation, but its long term efficacy has not been tested properly. One randomized, controlled, cross over trial reported lactulose to be as equally effective as senna 60 while another study reported lactulose to be less effective than liquid paraffin 61. However it is a drug that is commonly used in the initial maintenance therapy. Stimulant laxatives Except senna, the therapeutic value of other stimulant laxatives (e.g. bisacodyl) has not been studied. One open label trial had shown that senna was as effective as lactulose in increasing the number of stools a week 60. Another single blind study comparing senna with mineral oil found that mineral oil was more effective than senna in increasing bowel frequency 62. Stimulant laxatives are important in the maintenance phase when osmotic laxatives alone are not sufficient to sustain regular bowel motions. Other treatments Rectal enemas According to a recent therapeutic trial, rectal enemas are successful in normalizing stool frequency in the initial period of management, but the final outcome was not different indicating that rectal enemas have no added benefit in long-term maintenance therapy 63. Biofeedback therapy During biofeedback, patients receive visual and auditory feedback on the functioning of their anal sphincter and pelvic floor muscles. Biofeedback is used to train patients to relax their pelvic floor muscles during straining and to coordinate this relaxation with abdominal manoeuvres to enhance the entry of stools into the rectum 64. Adult studies had shown that biofeedback improves clinical outcome of patients with pelvic floor dyssynergia 65,66. One randomized controlled study has assessed the therapeutic value of biofeedback in the management of constipation in children and this study failed to show significant clinical improvement over the conventional therapy 33. Exact valued of biofeedback in management of childhood constipations has to be established later. New therapeutic agents New therapeutic options like Tegaserod, (a serotonin receptor agonist), Lubiprostone (a bicyclic fatty acid), and Alvimopan (a µ-opioid receptor antagonist) need further research involving children before they are used in paediatric practice. Probiotics are live bacterial preparations used in many gastrointestinal diseases. One randomized controlled trial on effectiveness of Lactobacillus GG as an adjunct to lactulose for children with constipation failed to show an additional therapeutic benefit 67. Surgery Surgical options are reserved for children suffering from intractable constipation which does not respond to intense medical management. Sigmoid colectomy was a suggested option in severe cases. Caecostomy with antegrade colonic enemas are becoming popular. Botulinum toxin injection to anal sphincter in cases of pelvic floor dyssynergia is another therapeutic procedure employed by surgeons. Long term prognosis Van Ginkel et al followed up 418 children with chronic constipation and noted that 30% of these children continued to have constipation beyond puberty with several complications associated with it 68. Furthermore, Chitkara et al noted that children who have an early (<5 years) medical visit due to constipation were approximately three times more likely to have subsequent medical visits due to the same condition and to have symptoms throughout early adulthood compared with children who present later in life 69. Therefore contrary to popular belief that children outgrow their constipation, in some children it may become chronic treatment resistant constipation. Summary Constipation is a common paediatric problem affecting children and adolescents worldwide. The majority have functional constipation. Exact cause of symptoms is unclear in most patients, but emotional stress leading to alteration of the brain gut axis seems to play an important role. It is predominantly a symptom based diagnosis and investigations including anorectal manometry and colonic transit studies are reserved for treatment resistant constipation. Multifaceted management approach including education, toilet training, judicial use of laxatives both in disimpaction and
6 maintenance are the key steps in management. Since most treatment options are not evidence based, good quality randomized controlled trials are required to assess their efficacy in paediatric constipation. A significant percentage of children with constipation continue to have symptoms during adulthood in contrast to the common misconception that children outgrow constipation and therefore long term follow up is mandatory in management of this condition. References 1. de Araujo Sant Anna AM, Calcado AC. Constipation in school-aged children at public schools in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999; 29: Rasquin-Weber A, Hymes PE, Cucchiara S, Fleisher DR, Hyams JS, Milla PJ, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gut 1999; 45 (Suppl 2): II Voskuijl WP, Heijmans J, Heimans HAS, Taminiau JAJM, Benninga MA. Use of Rome II criteria in childhood defaecation disorders: applicability in clinical and research practice. J Pediatr 2004; 145: Rasquin A, Di Lorenzo C, Forber D, Guiraldes E, Hyams JS, Saiano AM, et al. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: child / adolescent. Gastroenterology 2006; 130: van den Berg MM, Benninga MA, Di Lorenzo C. Epidemiology of childhood constipation: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 2006; 101: Rajindrajith S, Devanarayana NM, Mettananda S, Perera P, Jasmin S, Karunarathna U et al. Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka. Sri Lanka J Child Health 2009; 38: Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States Part II.: Lower gastrointestinal disease. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: Benninga MA, Voskuijl WP, Taminiau JAJM. Childhood constipation: is there new light in the tunnel? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2004; 39: Devanarayana NM, Rajindrajith S. Association between constipation and stressful life events in a cohort of Sri Lankan children and adolescents. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics Advance Access published online on August 20, Inan M, Aydiner CY, Tokuc B, Aksu B, Ayvaz S, Ayhan S, et al. Factors associated with childhood constipation. J Pediatr Child Health 2007; 43: Lisboa VCA, Felizola MCM, Martins LAN, Tahan S, Neto UF, de Morais MB. Aggressiveness and hostility in the family environment and chronic constipation in children. Dig Dis Sci 2008; 53: Towers AL, Burgio KL, Locher JL, Merkel IS, Safaeian M, Wald A. Constipation in the elderly. Influence of dietary, psychological, and physiological factors. J Am Geriatr Soc 1994; 42: Merkel IS, Locher J, Burgio K, Towers A, Wald A. Physiologic and psychologic characteristics of an elderly population with chronic constipation. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88: Lewis NA, Levitt MA, Zallen GS, Zafar MS, Iacono KL, Rossman JE, et al. Diagnosing Hirschsprung's disease: increasing the odds of a positive rectal biopsy result. J Pediatr Surg 2003; 38: Pini-Prato A, Avanzini S, Gentilino V, Martucciello G, Mattioli G, Coccia C, et al. Rectal suction biopsy in workup of childhood chronic constipation: indications and diagnostic value. Pediatr Surg Int 2007; 23: Plunkett A, Phillips CP, Beattie M. Management of chronic functional constipation in childhood. Pediatr Drugs 2007; 9: Croffie JM, Fitzgerald J. Idiopathic constipation. In: Walker WA, Goulet O, Kleinman RE, editors. Pediatric gastrointestinal disease. Ontario: BC Decker; p Loening-Baucke V. Prevalence rates for constipation and faecal and urinary incontinence. Arch Dis Child 2007; 92: Barnes PM, Maddocks A. Standards in school toilets- a questionnaire survey. J Publ Helath Med 2002; 24: Gold DM, Levine J, Weinstein TA, Kessler BH, Pettei MJ. Frequency of digital rectal examination in children with chronic constipation. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153:377-9.
7 21. de Lorijn F, van Rijn RR, Heijmans J, Reitsma JB, Voskuijl, WP, Henneman ODF, et al. The Leech method for diagnosing constipation: intra-and-inter observer variability and accuracy. Pediatr Radiol 2006; 36: Reuchlin-Vroklage LM, Bidrma-Zeinstra S, Benninga MA, Berger MY. Diagnostic value of abdominal radiography in constipated children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2005; 159: Benninga MA, Buller HA, Tytgat GNJ, Akkermans LM, Bossuyt PM, Taminiau JA. Colonic transit time in constipated children: does pediatric slow-transit constipation exist? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1996; 23: Gutierrea C, Marco A, Nogales A, Tebar R.Total and segmental colonic transit time and anorectal manometry in children with chronic idiopathic constipation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2002; 35: Zaslavsky C, da Silveria R, Maguilnik I. Total and segmental colonic transit time with radioopaque markers in adolescents with functional constipation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1998; 27: Cook BJ, Lim E, Cook D, Hughes J, Chow CW, Stanton MP, et al. Radionuclear transit to assess sites of delay in large bowel transit in children with chronic idiopathic constipation. J Pedatr Surg 2005; 40: Jarvi K, Koivusalo A, Rintala RJ, Pakarinen MP. Anorectal manometry with reference to operative rectal biopsy for diagnosis/ exclusion of Hirschprung disease in children under 1 year of age. Int J Colorec Dis 2009; 24: Low PS, Quak SH, Prabhakaran K, Joseph VT, Chiang GS, Aiyathurai EJ. Accuracy of anorectal manometry in the diagnosis of Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutrition 1989; 9: Benninga MA, Buller HA, Taminiau JAJM. Biofeedback training in chronic constipation. Arch Dis Child 1993; 68: van der Plus RN, Benninga MA, Staalman CR, Akkermans LMA, Redkop WK, Taminiau JAJM, et al. Megarectum in constipation. Arch Dis Child 2000; 83: Leoning-Baucke V, Younoszai MK. Abnormal anal sphincter response in chronically constipated children. J Pediatr 1982; 100: Loening-Baucke V. Abnormal rectoanal function in children recovered from chronic constipation and encopresis. Gastroentorology 1984; 87: van der Plus RN, Benninga MA, Buller HA, Bossuyt PM, Akkermans LMA, Redekop et al. Biofeedback training in treatment of childhood constipation: a randomized controlled study. Lancet 1996; 348: van Ginkel R, Buller HA, Boeckxstaens GE, van Der Plas RN, Taminiau JA, Benninga MA. The effect of anorectal manometry on the outcome of treatment in severe childhood constipation: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2001;108:E9 35. Loening-Bucke V. Biofeedback treatment for chronic constipation and encopresis in childhood: long term outcome. Pediatrics 1995; 96: Villarreal J, Sood M, Zangen T, Flores A, Michel R, Reddy N, et al. Colonic diversion for intractable constipation in children: Colonic manometry helps guide clinical decisions. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2001; 33: Gertken JT, Cocjin J, Pehlivanov N, Danda C, Hyman PE. Co morbidities associated with constipation in children referred for colon manometry may mask functional diagnosis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005; 41: Kayaba H, Hebiguchi T, Yoshino H, Mizuno M, Saitoh N, Kobayashi Y et al. Fecoflowmetric evaluation of anorectal function and ability to defecate in children with idiopathic chronic constipation. Pedatr Surg Int 2003; 19: van der Plus RN, Benninga MA, Taminiau JAJM, Buller HA. Treatment of defecation problems in children: the role of education, demystification and toilet training. Eur J Pediatr 1997; 156: Rao SSC, Kavelock R, Beaty J, Ackerson K, Stumbo P. Effects of fat and carbohydrate meals on colonic motor response. Gut 2000; 46: Rao SSC, Sadeghi P, Beaty J, R Kavlock. Ambulatory 24 hour colonic manometry in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Gastroint Liver Physiol 2001; 280:G
8 42. Rao SSC. Dyssynergic defaecation. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 2001; 30: Felt B, Wise CG, Olson A, Kochhar P, Marcus S, Coran A. Guideline for the management of pediatric idiopathic constipation and soiling. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: van Dijk M, Benninga MA, Grootenhuis MA, Nieuwenhuizen AM, Last BF. Chronic childhood constipation: A review of the literature and the introduction of a protocolized behavioral intervention program. Patient Educ Couns 2007; 67: Borowitz SM, Cox DJ, Sutphan JL, Kovatchev B. Treatment of childhood encopresis: A randomized trail comparing three treatment protocols. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr2002; 34: Rao SSC, Beaty J, Chamberlain M, Lambert PG, Gisolfi C. Effects of acute graded exercise on human colonic motility. Am J Physiol 1999; 276:G Lee WTK, Ip KS, Chan JSH, Lui NWM, Young BWY. Increased prevalence of constipation in pre-school children is attributable to under consumption of plant foods: a community based study. J Pediatr Child Health 2008; 44: Roma E, Adamidis D, Nikolara R Constantopoulos A, Messatitakis J. Diet and chronic constipation in children: role of fiber. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999; 28: Morais MB, Vitolo MR, Aguirre ANC, Fagundes-Neto U. Measurement of low dietory fiber intake as a risk factor for chronic constipation in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999; 29: Loening-Baucke V, Miele E, Staiano A. Fiber (Glucomannan) is beneficial in the treatment of childhood constipation. Pedatrics 2004; 113: e259-e Castillejo G, Bullo M, Anguera A, Escribano J, Salas-Salvado J. A controlled, randomized double blind trial to evaluate the effect of a supplement of cocoa husk that is rich in dietary fiber on colonic transit in constipated pediatric patients. Pediatrics 2006; 118:e641-e Kokke FTM, Scholtens PAMJ, Alles MS, Decates TS, Fiselier TJW, Tolboom JLL, et al. A dietary fiber mixture versus lactulose in the treatment of childhood constipation: a double blind randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009; 47: Ziegenhagen DJ, Tewinkel G, Kruis W, Herrman F. Adding more fluid to wheat bran has no significant effect on intestinal function of healthy subjects. J Clin Gastroenterol 1991; 13: Chung BD, Parekh U, Sellin JH. Effect of increased fluid intake on stool output in normal healthy volunteers. J Clin Gastroenterol 1999; 28: Youssef NN, Peters JM, Henderson W, Shultz- Peters S, Lockhart DK, Di Lorenzo C. Dose response of PEG 3350for the treatment of childhood fecal impaction. J Pediatr 2002; 141: Guest JF, Candy DC, Clegg JP, Edwards D, Helter MT, Dale AK, et al. Clinical and economic impact of using macrogol 3350 plus electrolytes in an outpatient setting compared to enemas and suppositories and manual evacuation to treat paediatric faecal impaction based on actual clinical practice in England and Wales. Curr Med Res Opinion 2007; 23: Candy DC, Edwards D, Geraint M. Treatment of faecal impaction with polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes (PEG+E) followed by a double blind comparison of PEG+E versus lactulose as maintenance therapy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006; 43: Dupont C, Leluyer B, Maamri N, Morali A, Joye JP, Fiorini JM, et al. Double-blind randomized evaluation of clinical and biological tolerance of polyethylene glycol 4000 versus lactulose in constipated children J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005; 41: Candy Da, Belsey J. Macrogol (Polyethylene glycol) laxatives in children with functional constipation and faecal impaction: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child 2009; 94: Perkin JM. Constipation in childhood: a controlled comparison between lactulose and standardized senna. Curr Med Res Opin 1977; 4:540-3.
9 61. Urganci N, Akyildiz B, Polat TB. A comparative study: the efficacy of liquid paraffin and lactulose in management of chronic functional constipation. Pedaitr Int 2005; 47: Sondheimer JM, Gervaise EP. Lubricant versus laxatives in the treatment of chronic functional constipation of children. J Pediatr Gastroenterool Nutr 1982; 1: Bongers MEJ, van den Berg MM, Reitsma JB, Voskuijl WP, Benninga MA. A randomized controlled trial of enemas in combination with oral laxatives therapy for children with chronic constipation. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 7: Lembo A, Camilleri M. Chronic constipation. N Eng J Med 2003; 349: Chiarioni G, Whitehead WE, Pezza V, Morelli A, Bassotti G. Bioifeedback is superior to laxatives for normal transit constipation due to pelvic floor dyssynergia. Gastroenterology 2006; 130: Chiarioni G, Salandini L, Whitehead WE. Biofeedback benefits only patients with outlet dysfunction, not patients with isolated slow transit constipation. Gastroenterology 2005; 129: Banaszkiewicz A, Szajewska H. Ineffectiveness of Lactobacillus GG as an adjunct to lactulose for the treatment of constipation in children: a double blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. J Pediatr 2005; 146: van Ginkel R, Reitsma, JB, Buller HA, van Wijk MP, Taminiau JA, Benninga MA. Childhood constipation: Longitudinal followup beyond puberty. Gastroenterology 2003; 125: Chitkara DK, Talley NJ, Locke III GR, Weaver AL, Katusic SK, de Schepper H et al. Medical presentation of constipation from childhood to early adulthood; a population based study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 5:
10
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka
 Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation and functional faecal retention in a group of school children in a district in Sri Lanka Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2, Sachith Mettananda 3, Priyantha Perera 1, Sanofer
Constipation in childhood is characterized by a low defecation frequency in combination with either involuntary loss of
 USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
USE OF ROME II CRITERIA IN CHILDHOOD DEFECATION DISORDERS: APPLICABILITY IN CLINICAL AND RESEARCH PRACTICE WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL, MD, JAROM HEIJMANS, HUGO S. A. HEIJMANS, MD, PHD, JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,MD,PHD,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: management of idiopathic constipation in children in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title Constipation
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Constipation in children
 Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
Search date August 2003 Gregory Rubin QUESTIONS Effects of treatments...397 395 INTERVENTIONS CONSTIPATION Trade off between benefits and harms Cisapride with or without magnesium oxide*...397 Unknown
TREATMENT SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION
 SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
SOCIETY GUIDELINES FOR CONSTIPATION: WHAT IS NEW? Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders FUNCTIONAL CONSTIPATION One of the most common functional GI disorders
Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol. glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide, lactulose. treatment of functional constipation in children
 Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
Original article Comparing the efficacy of polyethylene glycol (PEG), magnesium hydroxide and lactulosein treatment of functional constipation in children Hossein Saneian 1, Neda Mostofizadeh 2 1 Assistant
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014
 Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
Treatment of functional constipation in children: Evidence-based recommendations from ESPGHAN and NASPGHAN 2014 BS. Nguyễn Thị Kim Ngân Khoa Tiêu Hóa BV Nhi Đồng 2 Introduction Constipation is a common
CONSTIPATION. Atan Baas Sinuhaji
 CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
CONSTIPATION Atan Baas Sinuhaji Sub Division of Pediatrics Gastroentero-Hepatolgy Department of ChildHealth,School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara MEDAN DEFECATION REGULAR PATTERN CONSTIPATION
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 ㅋ JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 1 January, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.1.35 Review Constipation in Children: Novel Insight Into Epidemiology,
ㅋ JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 1 January, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.1.35 Review Constipation in Children: Novel Insight Into Epidemiology,
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands
 Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Childhood constipation, a real problem..? Marc Benninga, Emma Children s Hospital, AMC, Amsterdam, the Netherlands Constipation 0-10% >10-20% >20-30% >30-40% Mugie SM, et al. Best Pract & Res Clin Gastroenterol
Constipation in Children. Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG*
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 Education-Family Physician Corner Constipation in Children Amani Al Hajeri, MD, CABFM, IBFM, MSc MG* Constipation in pediatrics age group is frequently
The involuntary loss of feces in the underwear after. Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 26;4:67 72 Longitudinal Follow-up of Children With Functional Nonretentive Fecal Incontinence WIEGER P. VOSKUIJL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, RIJK VAN GINKEL,* HANS A.
Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Etiology and Clinical Spectrum of Constipation in Indian Children VIKRANT KHANNA*, UJJAL PODDAR AND SURENDER KUMAR YACHHA From the Departments of Pediatric Gastroenterology and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Constipation: the diagnosis and management of idiopathic childhood constipation in primary and secondary care 1.1 Short title
Chronic constipation, often accompanied by encopresis. Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty. Patients and Methods
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2003;125:357 363 Childhood Constipation: Longitudinal Follow-up Beyond Puberty RIJK VAN GINKEL,* JOHANNES B. REITSMA, HANS A. BÜLLER, MICHIEL P. VAN WIJK,* JAN A. J. M. TAMINIAU,* and
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction. Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Management of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction Fiona Paul, DNP, RN, CPNP Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders DEFECATION Delivery of colon contents to the rectum Rectal compliance
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation
 Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Elderly Man With Chronic Constipation Linda Nguyen, MD Director, Neurogastroenterology and Motility Clinical Assistant Professor Stanford University Overview Normal bowel function Defining Constipation:
Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence
 The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
The UNC Center for Functional GI & Motility Disorders www.med.unc.edu/ibs Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Disorders and Incontinence Olafur S. Palsson, Psy.D. Associate Professor of Medicine UNC Center for
C onstipation is a common problem in children, accounting
 723 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of constipation: clinical factors and colonic transit time F de Lorijn, M P van Wijk, J B Reitsma, R van Ginkel, J A J M Taminiau, M A Benninga... See end of article for
723 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of constipation: clinical factors and colonic transit time F de Lorijn, M P van Wijk, J B Reitsma, R van Ginkel, J A J M Taminiau, M A Benninga... See end of article for
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children
 Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Prescribing Guidance for the Treatment of Constipation in Children Effective Date: July 2007 Reviewed: September 2009 & December 2011 Review Date: December 2013 Gateshead Medicines Management Approved
Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation
 Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Pediatr Radiol (2010) 40:1789 1793 DOI 10.1007/s00247-010-1725-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Starreveld scoring method in diagnosing childhood constipation Fredericus T. Kokke & Judith S. Sittig & Annemiek de Bruijn
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone. Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club
 Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Efficacy and Safety of Lubiprostone Laura Wozniak February 23, 2010 K30 Monthly Journal Club Objectives Brief overview of constipation Review of article Discussion Constipation in Children 3-5% of all
Human Anatomy rectum
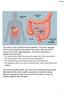 rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
rectum The colon is also called the large intestine. The ileum (last part of the small intestine) connects to the cecum (first part of the colon) in the lower right abdomen. The rest of the colon is divided
Constipation an Old Friend. Presented by Dr. Keith Harris
 Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Constipation an Old Friend Presented by Dr. Keith Harris Irregularity and the Tricks of the Trade." CONSTIPATION What is constipation? INFREQUENT BOWEL MOVEMENTS DIFFICULTY DURING DEFECATION SENSATION
Current Treatment of Childhood Constipation
 Ann Nestlé [Engl] 2007;65:73 79 DOI: 10.1159/000101716 O livia Liem a, b Carlo Di Lorenzo b Jan A.J.M. Taminiau a Hayat M. Mousa b Marc A. Benninga a a Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition,
Ann Nestlé [Engl] 2007;65:73 79 DOI: 10.1159/000101716 O livia Liem a, b Carlo Di Lorenzo b Jan A.J.M. Taminiau a Hayat M. Mousa b Marc A. Benninga a a Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition,
Constipation is a common disorder in children,
 The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
The Effect of Anorectal Manometry on the Outcome of Treatment in Severe Childhood Constipation: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Rijk van Ginkel, MD*; Hans A. Büller, PhD ; Guy E. Boeckxstaens, PhD ; Roos
Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Sep 2009; Vol 19 (No 3), Pp:255-261 Polyethylene Glycol versus Paraffin for the Treatment of Childhood Functional Constipation Hasan Karami* 1, MD; Mohammad Khademloo 2,
Paediatric constipation
 EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS constipation Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Best practice Paediatric constipation Diagnosis and treatment Dr Tim De Maayer Paediatric Gastroenterologist
EARN 3 FREE CPD POINTS constipation Leader in digital CPD for Southern African healthcare professionals Best practice Paediatric constipation Diagnosis and treatment Dr Tim De Maayer Paediatric Gastroenterologist
IPS Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki. Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.
 Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.H Dubai 22-24 Feb. 2018 Objectives: Why constipation?!!! Is it a burden
Childhood Constipation when we refer to Ped.Gastroenterologist? Dr.Muath Al Turaiki Consultant of Pediatric Gastroenterology, K.S.H Dubai 22-24 Feb. 2018 Objectives: Why constipation?!!! Is it a burden
Constipation An Overview. Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment
 CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
CONSTIPATION Constipation An Overview Definition Physiology of GI tract Etiology Assessment Treatment Definition Constipation = the infrequent passage of hard feces Definition of Infrequent The meaning
Constipation. What is constipation? What is the criteria for having constipation? What are the different types of constipation?
 What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
What is constipation? is defined as having a bowel movement less than 3 times per week. It is usually associated with hard stools or difficulty passing stools. You may have pain while passing stools or
Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate.
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
NAME OF THE MEDICINE KLYX Enema Active ingredients per ml: Docusate sodium 1 mg/sorbitol solution (70%) (crystallising) 357 mg Structural formula: Docusate Sorbitol C20H37NaO7S MW: 444.56 CAS no: 577-11-7
Approaching Childhood Constipation Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology. Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Epidemiology.
 Approaching Childhood Constipation p Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Disclosure Anees Siddiqui, MD, has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Specially for Children Dell
Approaching Childhood Constipation p Anees Siddiqui, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Disclosure Anees Siddiqui, MD, has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Specially for Children Dell
Authors and Disclosures
 Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Role of Carbon Dioxide-Releasing Suppositories in the Treatment of Chronic Functional Constipation A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial M. Lazzaroni; V. Casini; G. Bianchi Porro Authors
Clinical guideline Published: 26 May 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg99
 Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 26 May 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg99 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management Clinical guideline Published: 26 May 2010 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg99 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Constipation Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Constipation Constipation is a symptom that can mean different things to different people but the usual
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Surveillance programme
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Surveillance programme Surveillance proposal consultation document Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Surveillance programme Surveillance proposal consultation document Constipation in children and young people: diagnosis and management. NICE guideline
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin
 Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Children s Hospital Of Wisconsin Co-Management Guidelines To support collaborative care, we have developed guidelines for our community providers to utilize when referring to, and managing patients with,
Managing functional constipation in children
 PRACTICE POINT Managing functional constipation in children A Rowan-Legg; Canadian Paediatric Society Community Paediatrics Committee Paediatr Child Health 2011;16(10):661-5 Posted: Dec 1 2011 Reaffirmed:
PRACTICE POINT Managing functional constipation in children A Rowan-Legg; Canadian Paediatric Society Community Paediatrics Committee Paediatr Child Health 2011;16(10):661-5 Posted: Dec 1 2011 Reaffirmed:
Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2016;21:74-78 Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, KKW LIU, TW FAN Abstract Key words Objective:
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2016;21:74-78 Suspected Hirschsprung's Disease in Infants: The Diagnostic Accuracy of Contrast Enema PMY TANG, MWY LEUNG, NSY CHAO, KKW LIU, TW FAN Abstract Key words Objective:
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 February ; 25(1): 159 166. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2011.01.004. BIOFEEDBACK THERAPY FOR CONSTIPATION
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 February ; 25(1): 159 166. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2011.01.004. BIOFEEDBACK THERAPY FOR CONSTIPATION
OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA
 OMED 17 OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA 29.5 Category 1-A CME credits anticipated ACOFP / AOA s 122 nd Annual Osteopathic Medical Conference & Exposition Joint Session with ACOFP and Cleveland
OMED 17 OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA 29.5 Category 1-A CME credits anticipated ACOFP / AOA s 122 nd Annual Osteopathic Medical Conference & Exposition Joint Session with ACOFP and Cleveland
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Constipation. (Medical Aspects)
 Constipation (Medical Aspects) By Dr. Ehab Abdel Khalik MD. Anatomy of the anorectum The rectum is 12-15 15 cm. long. It connects with the sigmoid colon by the rectosigmoid junction which is believed to
Constipation (Medical Aspects) By Dr. Ehab Abdel Khalik MD. Anatomy of the anorectum The rectum is 12-15 15 cm. long. It connects with the sigmoid colon by the rectosigmoid junction which is believed to
Megarectum in constipation
 Author Keyword(s) HOME HELP FEEDBACK SUBSCRIPTIONS ARCHIVE SEARCH TABLE OF CONTENTS Vol [Advanced] Page Go Arch Dis Child 2000; 83: 2-8 ( July ) This Article Megarectum in constipation a a b R N van der
Author Keyword(s) HOME HELP FEEDBACK SUBSCRIPTIONS ARCHIVE SEARCH TABLE OF CONTENTS Vol [Advanced] Page Go Arch Dis Child 2000; 83: 2-8 ( July ) This Article Megarectum in constipation a a b R N van der
Review article: faecal incontinence in children: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation and management
 Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Review article: faecal incontinence in children: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation and management S. Rajindrajith*, N. M. Devanarayana & M. A.
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Review article: faecal incontinence in children: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical evaluation and management S. Rajindrajith*, N. M. Devanarayana & M. A.
Chronic constipation in the elderly
 Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Chronic constipation in the elderly 1 Dec,2011 R 2 Natta Asanaleykha Epidemiology Definition Scope The impact of chronic constipation in the elderly Pathophysiology Evaluation the elderly patient with
Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?'
 Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 77 July 1984 559 Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?' M R B Keighley MS FRCS P Shouler FRCS Department of Surgery, General Hospital, Birmingham
Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Volume 77 July 1984 559 Outlet syndrome: is there a surgical option?' M R B Keighley MS FRCS P Shouler FRCS Department of Surgery, General Hospital, Birmingham
Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up
 1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
1400 Gut 1993; 34:1400-1404 Constipation in early childhood: patient characteristics, treatment, and longterm follow up Department of Pediatrics, University of Iowa, USA V Loening-Baucke Correspondence
Constipation. H. David Vargas, MD. Overview
 Constipation H. David Vargas, MD Overview Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation usually is simple to avoid and easy to treat when
Constipation H. David Vargas, MD Overview Constipation is a very common complaint affecting upwards of 15% of all Americans. Fortunately, constipation usually is simple to avoid and easy to treat when
Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Paediatric constipation and functional non-retentive faecal soiling Voskuijl, W.P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Voskuijl, W. P. (2005).
Hirschsprung Disease and Contrast Enema: Diagnostic Value of Simplified Contrast Enema and Twenty-Four-Hour-Delayed Abdominal Radiographs
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 159-164 Hirschsprung Disease and Contrast Enema: Diagnostic Value of Simplified Contrast Enema and Twenty-Four-Hour-Delayed Abdominal Radiographs Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Shin-Lin Shih
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 159-164 Hirschsprung Disease and Contrast Enema: Diagnostic Value of Simplified Contrast Enema and Twenty-Four-Hour-Delayed Abdominal Radiographs Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Shin-Lin Shih
Controlled randomised trial of visual biofeedback
 Gut 1995; 37: 95-99 Service de Medecine C, CHG de F6camp, 764 F6camp, France D Koutsomanis St Mark's Hospital, London EC1V 2PS J E Lennard-Jones A J Roy M A Kamm Correspondence to: Professor J E Lennard-Jones,
Gut 1995; 37: 95-99 Service de Medecine C, CHG de F6camp, 764 F6camp, France D Koutsomanis St Mark's Hospital, London EC1V 2PS J E Lennard-Jones A J Roy M A Kamm Correspondence to: Professor J E Lennard-Jones,
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications
 15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
15. Prevention of UTI and lifestyle modifications Key questions: Does improving poor voiding habits help prevent UTI recurrence? Does improving constipation help prevent UTI recurrence? Does increasing
Childhood constipation
 Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Childhood constipation Marcus K H Auth, Rakesh Vora, Paul Farrelly, Colin Baillie Departments
Follow the link from the online version of this article to obtain certified continuing medical education credits Childhood constipation Marcus K H Auth, Rakesh Vora, Paul Farrelly, Colin Baillie Departments
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction. Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield
 GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
GI Physiology - Investigating and treating patients with pelvic floor dysfunction Lynne Smith Department of GI Physiology NGH Sheffield Aims o o o To give an overview of lower GI investigations To demonstrate
Constipation. Disease Review
 bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
bowel. 1 Constipation is a symptom, not a disease. Almost everyone experiences Disease Review Constipation Introduction: Constipation is exceedingly common and is rarely associated with mortality in developed
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines. Version 1 November 2016
 Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
Primary Care Constipation Guidelines Version 1 November 2016 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1 November 2016 New guideline Contents 1. Management of constipation in adults: acute and
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management
 UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
UNDERSTANDING IBS AND CC Implications for diagnosis and management J. TACK, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Gastroenterology University Hospitals, K.U. Leuven Leuven, Belgium TYPES OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly
 Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Common Gastrointestinal Problems in the Elderly Brian Viviano, D.O. Objectives Understand the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of GI diseases of the elderly. Differentiate
Biofeedback provides long term benefit for patients with intractable, slow and normal transit constipation
 Gut 1998;42:517 521 517 St Mark s Hospital, London, UK E Chiotakakou-Faliakou M A Kamm AJRoy J B Storrie I C Turner Correspondence to: Dr M A Kamm, St Mark s Hospital, Northwick Park, Watford Road, Harrow,
Gut 1998;42:517 521 517 St Mark s Hospital, London, UK E Chiotakakou-Faliakou M A Kamm AJRoy J B Storrie I C Turner Correspondence to: Dr M A Kamm, St Mark s Hospital, Northwick Park, Watford Road, Harrow,
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination
 Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Chapter 31 Bowel Elimination Defecation Defecation: the act of expelling feces from the body Peristalsis: rhythmic contractions of intestinal smooth muscle to facilitate defecation Gastrocolic reflex:
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation. Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class
 Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Understanding & Alleviating Constipation Living (Well!) with Gastroparesis Program Warm-Up Class Please Remember The information presented is for educational purposes only and is in no way intended as
Biofeedback pelvic floor exercise therapy for pelvic floor dyssynergia: an observational study
 International Surgery Journal Porwal A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Oct;4(10):3461-3465 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20174516
International Surgery Journal Porwal A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Oct;4(10):3461-3465 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20174516
Clinical Characteristics and Management of Benign Transient Non-Organic Ileus of Neonates: A Single-Center Experience
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.157 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(1):157-161, 2014 Clinical Characteristics and Management of Benign Transient Non-Organic
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.157 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(1):157-161, 2014 Clinical Characteristics and Management of Benign Transient Non-Organic
Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 4 August 2010; 595-601 Original article Anterior displacement of anus: a common association with constipation in infancy Sanguansak Rerksuppaphol a, Lakkana Rerksuppaphol b
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES
 OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
OPIOID-INDUCED CONSTIPATION DR ANDREW DAVIES Introduction Introduction Mean faecal weight 128 g / cap / day Mean range 51-796 g Absolute range 15-1505 g Main factors affecting mass are caloric intake,
The efficacy of a multidisciplinary approach to the management of constipation: a case series
 Journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Women s Health, Spring 2008, 102, 36 44 CLINICAL PAPER The efficacy of a multidisciplinary approach to the management of constipation: a case
Journal of the Association of Chartered Physiotherapists in Women s Health, Spring 2008, 102, 36 44 CLINICAL PAPER The efficacy of a multidisciplinary approach to the management of constipation: a case
Constipation. Information for adults. GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1
 Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
Constipation Information for adults GI Motility Clinic (UMCCC University Medical Clinics of Campbelltown and Camden) Page 1 Contents Role of the large intestine..3 Mass movements in the large intestine..4
1. What evidence exists that prevention of constipation in the first year of life improves outcome of bowel management in later childhood?
 BOWEL FUNCTION AND CARE Overall Outcomes Primary Outcomes o Maintenance of social continence as appropriate for age level Secondary Outcomes o Maximization of independence with managing bowel program o
BOWEL FUNCTION AND CARE Overall Outcomes Primary Outcomes o Maintenance of social continence as appropriate for age level Secondary Outcomes o Maximization of independence with managing bowel program o
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With fecal incontinence
 Protocol Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation (20164) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/13 Next Review Date: 03/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09,
Protocol Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation (20164) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/13 Next Review Date: 03/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09,
Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mustafa Giaffer March 2017
 Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Irritable Bowel Syndrome Mustafa Giaffer March 2017 Introduction First described in 1771. 50% of patients present
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report
 Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Functional constipation in children: which treatment is effective and safe? An evidence-based case report 1. Private practice, Quebec, Canada. Email: nathaelle@chirostmartin.com By Nathaëlle Martin-Marcotte,
Effect of biofeedback therapy on anorectal physiological parameters among patients with fecal evacuation disorder
 DOI 10.1007/s12664-017-0731-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of biofeedback therapy on anorectal physiological parameters among patients with fecal evacuation disorder Abhai Verma 1 & Asha Misra 1 & Uday C Ghoshal
DOI 10.1007/s12664-017-0731-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of biofeedback therapy on anorectal physiological parameters among patients with fecal evacuation disorder Abhai Verma 1 & Asha Misra 1 & Uday C Ghoshal
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview
 Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Anorectal Diagnostic Overview 11-25-09 3.11.2010 2009 2010 Anorectal Manometry Overview Measurement of pressures and the annotation of rectal sensation throughout the rectum and anal canal to determine:
Paediatric constipation
 Paediatric constipation An approach and evidence-based treatment regimen Harveen Singh, Frances Connor This article is the second in a series on paediatric health. Articles in this series aim to provide
Paediatric constipation An approach and evidence-based treatment regimen Harveen Singh, Frances Connor This article is the second in a series on paediatric health. Articles in this series aim to provide
Is one of the most common chronic disorders. causing patients to seek medical treatment.
 ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
ILOs After this lecture you should be able to : Define IBS Identify causes and risk factors of IBS Determine the appropriate therapeutic options for IBS Is one of the most common chronic disorders causing
Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
 HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
HIRSCHSPRUNG'S DISEASE Samuel Nurko MD MPH Center for Motility and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Children s Hospital Medical Center, Boston Ma Long-Term Bowel Symptoms Following Corrective Surgery
A 27-Year-Old Woman With Constipation: Diagnosis and Treatment
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:838 842 EDUCATION PRACTICE A 27-Year-Old Woman With Constipation: Diagnosis and Treatment ARNOLD WALD Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:838 842 EDUCATION PRACTICE A 27-Year-Old Woman With Constipation: Diagnosis and Treatment ARNOLD WALD Section of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Associated with
 Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Table1: Rome III and Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS, functional constipation and functional dyspepsia. Rome III diagnostic criteria 1,2 Rome IV diagnostic criteria 3,4 Diagnostic criteria for IBS
Case Report Postoperative Megarectum in an Adult Patient with Imperforate Anus and Rectourethral Fistula
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 613926, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/613926 Case Report Postoperative Megarectum in an Adult Patient with Imperforate Anus and
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 613926, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/613926 Case Report Postoperative Megarectum in an Adult Patient with Imperforate Anus and
Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation
 Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation Policy Number: 2.01.64 Last Review: 7/2018 Origination: 7/2008 Next Review: 7/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation Policy Number: 2.01.64 Last Review: 7/2018 Origination: 7/2008 Next Review: 7/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Functional gastrointestinal diseases in children: Stepping out of the box
 Leading Article Functional gastrointestinal diseases in children: Stepping out of the box Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2013; 42: 65-69 (Key words:
Leading Article Functional gastrointestinal diseases in children: Stepping out of the box Shaman Rajindrajith 1, Niranga Manjuri Devanarayana 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2013; 42: 65-69 (Key words:
Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests
 Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Defecatory Dysfunction Diagnosis of Impaired Defecatory Function with Special Reference to Physiological Tests JMAJ 46(9): 373 377, 2003 Masatoshi OYA, Masashi UENO, and Tetsuichiro MUTO Department of
Medical Presentation of Constipation From Childhood to Early Adulthood: A Population-Based Cohort Study
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1059 1064 Medical Presentation of Constipation From Childhood to Early Adulthood: A Population-Based Cohort Study DENESH K. CHITKARA,* NICHOLAS J. TALLEY,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1059 1064 Medical Presentation of Constipation From Childhood to Early Adulthood: A Population-Based Cohort Study DENESH K. CHITKARA,* NICHOLAS J. TALLEY,
Bowel Function and Care. Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold
 Bowel Function and Care Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold Outcomes Primary Outcomes Maintenance of social continence as appropriate
Bowel Function and Care Pat Beierwaltes, Chair Paige Church Lusine Ambartsumyan Sharon Braille Julie Dicker Tiffany Gordon Sue Liebold Outcomes Primary Outcomes Maintenance of social continence as appropriate
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus.
 The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
The Digestive System or tract extends from the mouth to the anus. FUNCTION The Digestive System breaks down and absorbs food materials e.g. amino acids, glucose DEFINITIONS: Ingestion: Ingestion is the
Colon Transit Time Test in Korean Children with Chronic Functional Constipation
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.1.38 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016 March 19(1):38-43 Original Article PGHN Colon Transit Time Test in Korean Children
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2016.19.1.38 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2016 March 19(1):38-43 Original Article PGHN Colon Transit Time Test in Korean Children
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS
 BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: ENCOPRESIS BI-PED PROJECT (BRIEF INTERVENTIONS: PEDIATRICS) Emotional Health Committee Maryland Chapter American Academy of Pediatrics David Bromberg M.D. Overview: Encopresis is diagnosed
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 ... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
Randomised controlled trial of biofeedback training in persistent encopresis with anismus
 Arch Dis Child 1998;79:131 135 131 Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Unit, Melbourne University Department of Paediatrics, Royal Children s Hospital, Parkville Victoria, Australia 3052 T Nolan Department
Arch Dis Child 1998;79:131 135 131 Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics Unit, Melbourne University Department of Paediatrics, Royal Children s Hospital, Parkville Victoria, Australia 3052 T Nolan Department
Research Article Efficacy of Adaptive Biofeedback Training in Treating Constipation-Related Symptoms
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 959734, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/959734 Research Article Efficacy of Adaptive Biofeedback Training in Treating
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 959734, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/959734 Research Article Efficacy of Adaptive Biofeedback Training in Treating
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Behavioral therapy for functional constipation in childhood: health-related quality of life, emotional and behavior problems & parental child-rearing attitudes van
Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation in childhood
 Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Russo et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2017) 43:24 DOI 10.1186/s13052-017-0334-3 RESEARCH Open Access Efficacy of a mixture of probiotic agents as complementary therapy for chronic functional constipation
Diagnostic dilemmas and results of treatment for
 36 Department of Paediatrics, Free University Hospital, PO Box 757, 17 MB Amsterdam, The Netherlands CW Keuzenkamp-Jansen CJ Fijnvandraat CMF Kneepkens AC Douwes Correspondence and reprint requests to:
36 Department of Paediatrics, Free University Hospital, PO Box 757, 17 MB Amsterdam, The Netherlands CW Keuzenkamp-Jansen CJ Fijnvandraat CMF Kneepkens AC Douwes Correspondence and reprint requests to:
What Is Constipation?
 CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
CONSTIPATION What Is Constipation? Constipation is when you have infrequent or hard-to-pass bowel movements (meaning they are painful or you have to strain), have hard stools or feel like your bowel movements
Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation
 Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation Policy Number: 2.01.64 Last Review: 7/2014 Origination: 7/2008 Next Review: 7/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Biofeedback as a Treatment of Fecal Incontinence or Constipation Policy Number: 2.01.64 Last Review: 7/2014 Origination: 7/2008 Next Review: 7/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
