COURSE DESCRIPTION. Page 1 of 18. Rev 3.0 February 2016
|
|
|
- Baldwin Shaw
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COURSE DESCRIPTION Proper CPT wound repair coding is often a challenging process. The coder must first understand the various classifications of wound repair coding as well as the CPT manual s guidelines in coding these procedures. This continuing education course describes the different types of wounds and gives instructions on how to code these wound repair procedures accurately. Rev 3.0 February 2016 Page 1 of 18
2 COURSE TITLE: 2007 Update: A Guide to Wound Repair Coding Author: Virginia Escobedo, CPC, NCICS Program Director, Medical Billing & Coding Virginia Austin Number of Clock Hours Credit: 3.0 Course # P.A.C.E. Approved: Yes X No Upon completion of this continuing education module, the professional should be able to: 1. Name and describe five types of wounds. 2. Describe simple, intermediate, and complex repair of wounds as discussed in the CPT manual. 3. Identify CPT codes used for simple, intermediate, and complex repair of wounds. 4. Identify factors to take into account when coding for wound repair. 5. Identify when multiple wound repairs may be treated as one repair. 6. Identify when modifier 51 is attached to a CPT code for wound repair. 7. Given case studies, identify the CPT code(s) for wound repairs. Disclaimer The writers for NCCT continuing education courses attempt to provide factual information based on literature review and current professional practice. However, NCCT does not guarantee that the information contained in the continuing education courses is free from all errors and omissions. Page 2 of 18
3 INTRODUCTION The goal of all healthcare providers is to receive the maximum legal reimbursement for services provided while efficiently utilizing proper coding. Wound repair (closure) coding can sometimes be a challenge. There are several types of wounds in which the skin or tissue may be in need of repair: abrasions, lacerations, amputations, incisions, punctures and avulsions. A wound may include only one of these types or may include a combination of them. The definition of these wound types are: Abrasion the skin is rubbed or scraped off. Rope burns or rug burns are a few examples of an abrasion. This type of wound can become easily infected as dirt can be embedded into the wound. Laceration a ragged skin tear often made by a blunt object or machinery accidents. Lacerations sometimes have the added complication of the tissues being crushed due from the nature of the injury. These types of wounds are also prone to infection. Amputation nonsurgical removal of a limb. Bleeding is heavy and shock is common. In certain situations, the limb may be reattached surgically. Incision a wound from a sharp object; a cut. These types of wounds are least likely to become infected. Puncture a wound caused by a penetrating object that usually causes less surface damage than other wounds. Wounds made by nails and bullets are usually puncture wounds. If the nail or penetrating object has bacteria on it, infections may be common. Avulsion a tearing away of tissue from a body part. Bleeding may be heavy. It is possible that the torn tissue may be surgically reattached. The wound repair codes found in the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT*), surgery section, integumentary system subsection, are to be used only when the physician uses sutures, staples and/or tissue adhesives to close a wound. If the physician only uses adhesive strips to close the wound, the CPT directs the physician to use the appropriate evaluation and management code ( ). The more simple procedure would be billed an evaluation code rather than a procedure code. The physician may use adhesive strips in addition to these procedures, but he may not bill for a wound repair code that is found in the surgery section if adhesive strips are the only method utilized to close the wound. Page 3 of 18
4 It should be noted that Medicare is the only payer that uses a HCPCS code to report a simple repair using tissue adhesives (G0168). This is sometimes used in lieu of sutures. A good coder will always reference the CPT manual for notes and/or directions. The three types of classifications for the wound repair (closure) codes found in the surgery section of the CPT are simple, intermediate, or complex. Following are the CPT definitions of these classifications. *CPT is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association. CPT WOUND REPAIR CLASSIFICATION DEFINITIONS The CPT manual defines simple repair ( ) when the wound is superficial; eg, involving primarily epidermis or dermis, or subcutaneous tissues without significant involvement of deeper structures, and requires simple one layer closure. This includes local anesthesia and chemical or electrocauterization of wounds not closed. In other words, this code is utilized for the simplest type of surgical wound repair on the integumentary system. Normal debridement (cleaning the skin tissue until normal tissue is viewed) and single-layered closure are included in a simple repair. In the documentation, the physician may bill for a simple repair by indicating in the medical record that the patient had a superficial wound that was repaired using sutures. Intermediate repair ( ) includes, in addition to the requirements of a simple repair, layered closure of one or more of the deeper layers of subcutaneous tissue and superficial (non-muscle) fascia, in addition to the skin (epidermal and dermal) closure. Single-layer closure of heavily contaminated wounds that have required extensive cleaning or removal of particulate matter also constitutes intermediate repair. In other words, an intermediate repair may be coded if the physician performed a layered closure or a single-layered closure that required extensive debridement. If the documentation shows that the physician performed a deep layered closure on the patient s wound using staples for the method of repair, then the physician would be able to use an intermediate repair code from the surgery section. Or, if the documentation reveals that the physician performed a single-layered closure only but he had to perform extensive debridement in addition to the single-layered closure, therefore going above and beyond normal debridement, the physician may bill for the intermediate repair code. Also, note that the physician does not need to specifically use the word intermediate in the documentation to bill for an intermediate repair. A layered closure constitutes an intermediate repair, therefore he may simply document that a layered closure was performed. Page 4 of 18
5 Complex repair ( ) includes the repair of wounds requiring more than layered closure, viz., scar revision, debridement (eg, traumatic lacerations or avulsions), extensive undermining, stents, or retention sutures. Necessary preparation includes creation of a defect for repairs (eg, excision of a scar requiring a complex repair) or the debridement of complicated lacerations or avulsions. Complex repair does not include excision of benign ( ) or malignant ( ) lesions. A complex repair code is the most complicated surgical repair that a physician will perform on the integumentary system. The physician would have to perform more than layered closure in order to bill for a complex repair. In addition, if the physician removed a benign lesion before he performed a wound repair procedure, then at least two surgical codes would be billed: one for the excision and one for the repair. INSTRUCTIONS All insurance companies go by the rule: If it is not documented, then it was not done. What this means is that even if a physician provided a high level of service to a patient, the physician does not get to bill for this level of service if the service is not documented appropriately. To obtain optimal reimbursement, detailed procedure information MUST be documented in the medical record. Sometimes, physicians forget to dictate seemingly insignificant information into the dictated letter that causes them to lose reimbursement. The physician knows what level of service he provided, but the documentation sometimes does not reflect this. When this occurs, optimal reimbursement is not being obtained. The first step in being a good coder is to educate the office staff and physicians that the more detailed information that is listed in the medical record usually results in greater reimbursement. One recommendation would be to have monthly meetings in which you go into detail about specific cases or examples in which you thought you could have billed for a higher level code if the required documentation was in the medical record. This method is usually quite effective and does not have to be time consuming for the busy physician. The factors that the coder needs to take into account when coding for wound repair ( ) are the anatomic site, the length of the wound and the type of repair. The CPT manual precisely states that wound repairs should be recorded in centimeters. When multiple wounds are repaired, it is possible to sometimes treat multiple repairs as one repair. You may add up the lengths of wounds from the same classification (simple, intermediate or complex) if the anatomic sites are grouped together in the CPT manual. This allows you to bill for multiple wound repairs using one CPT code. Page 5 of 18
6 Reference the CPT code below for the following scenario. You can observe that the CPT code groups together the scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk, and/or extremities (including the hands and feet). The CPT groups these anatomic sites together because the techniques used to perform these repairs are similar. In other words, the procedures used to repair these anatomic sites are treated, according to the CPT manual, as the same procedure as long as the classification for the repair is simple. CPT Code Simple repair of superficial wounds of scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk and/or extremities (including hands and feet); 2.6 cm to 7.5 cm If the documentation states that the physician performed a simple repair of a 2.5 cm abrasion on the neck and a simple repair of a 3.4 cm laceration on the back, then the length of these wounds may be added up and billed as one simple repair. The two items to look at in this scenario: Is the wound repair classification the same? Yes, the physician performed a simple repair on both anatomic sites. Does the CPT manual group the anatomic sites together? Notice that code pertains to the scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk and/or extremities (including hands and feet). Therefore, yes, the neck and trunk (back is part of the trunk) are grouped together. The CPT now directs you to add up the lengths of the simple repairs and code these two wound repairs as one: 3.4 cm cm = 5.9 cm. Because is a simple repair between 2.6 cm and 7.5 cm, then this is the correct code for this scenario. For the next scenario, some of the information will be the same as the previous scenario. The documentation in this scenario states that the physician performed a simple repair of a 2.5 cm abrasion on the lip and a simple repair of a 3.4 cm laceration on the back. Notice, the size of the wounds has not changed, but one of the anatomic sites has. What difference do you think this will make in the answer? Factors to look at before coding this case: Is the wound repair classification the same? Yes, the physician performed a simple repair on both anatomic sites. This is step one to allowing us to add up our wounds and code the repair as one CPT code. Does the CPT manual group the anatomic sites together? There is an abrasion on the lip and laceration on the back. Reference the following codes: Page 6 of 18
7 CPT Code CPT Code CPT Code CPT Code CPT Code Simple repair of superficial wounds of scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk and/or extremities (including hands and feet); 2.5 cm or less Simple repair of superficial wounds of scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk and/or extremities (including hands and feet); 2.6 cm to 7.5 cm Simple repair of superficial wounds of face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips and/or mucous membranes; 2.5 cm or less Simple repair of superficial wounds of face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips and/or mucous membranes; 2.6 cm to 5.0 cm Simple repair of superficial wounds of face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips and/or mucous membranes; 5.1 cm to 7.5 cm Lips and back are not grouped together. CPT code is the stand-alone code for scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk, and/or extremities (including hands and feet). CPT code is the stand-alone code for the face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips, and/or mucous membranes. Therefore, you are not allowed to add up the sum of these simple repairs. You are instructed to code them separately and (with modifier 51 added to this second code) are the correct codes for this case study. You may never add together the lengths of different classifications. In other words, you can not add together a 3.2 cm complex repair of the hand with a 7.2 cm simple of the hand. Even though they are the same anatomic sites, different classifications are always coded separately. When more than one classification of wounds is repaired, always list the more complicated procedure first. This stems from the rule to always code the most resource intensive reason for the visit first. A complicated wound is more serious, and therefore more in need of a repair, than a simple wound. It is also more time consuming. Page 7 of 18
8 Add modifier 51 to the secondary procedure to indicate that multiple procedures were performed. These rules will be demonstrated with the following example. The documentation states that the physician performed a 2.5 cm complex repair of the forearm and a much larger 10.7 cm intermediate repair to the forearm. The CPT directs you always to list the most complicated procedure first, and then the biggest repair would go next, and so on. Reference the following codes for this case study. CPT Code Repair, complex, scalp, arms, and/or legs; 1.1 cm to 2.5 cm CPT Code Layer closure of wounds of scalp, axillae, trunk and/or extremities (excluding hands and feet); 7.6 cm to 12.5 cm The factors to consider when coding: Are the classifications that the physician performed similar? No, the physician performed a 2.5 cm complex repair of the forearm and a 10.7 cm intermediate repair of the forearm. Even though the physician operated on the same anatomic sites, the classifications are different. Therefore, the coder is not able to add up the length of the repairs. Which procedure should be listed first? The most complicated procedure that the physician performed was the 2.5 cm complex repair of the forearm. The CPT directs the coder to list the most complex repair first. Code is a complex repair of the arm; therefore, this code is listed first is an intermediate repair of the extremities between 7.6 cm and 12.5 cm; therefore, this code is listed second. Is modifier 51 needed? Yes. You are directed to add modifier 51 to the secondary procedure to indicate that multiple procedures were performed. o ANSWER: 13120, Page 8 of 18
9 CONCLUSION Debridement is not considered a separate procedure unless prolonged cleansing is required to remove the contaminated tissue, or if debridement is performed separately from the repair. In other words, debridement is usually considered part of the repair procedure. However, if a physician performs debridement on a day other than the wound closure procedure, then he may bill for the debridement. The CPT manual also states, For extensive debridement of soft tissue and/or bone, not associated with open fracture(s) and/or dislocation(s) resulting from penetrating and/or blunt trauma, see ( ) For extensive debridement of subcutaneous tissue, muscle fascia, muscle, and/or bone associated with open fracture(s) and/or dislocation(s), the coder is directed to reference codes ( ) The CPT manual differentiates between debridement procedures that are associated with fractures and/or dislocations and other debridement procedures that are not. The debridement codes are listed at the end of this course. In this next case study, the physician performed a 7.4 cm complex repair of a laceration to the chest that was grossly contaminated. The documentation revealed that the wound required prolonged cleansing in order to remove the contaminated tissue. The physician spent extra time cleaning the wound. Partial thickness debridement was performed. Reference the codes below. CPT Code Repair, complex, trunk; 2.6 cm to 7.5 cm CPT Code Debridement; skin, partial thickness In this case, due to the prolonged cleaning of the grossly contaminated wound, the physician is able to bill for the debridement in addition to the wound repair code. The physician would list the complex repair code first and the debridement code second with modifier 51 attached. o ANSWER: 13101, Page 9 of 18
10 A few more things to consider when coding for wound repair (closure) procedures: If the wound that is repaired involves nerves, blood vessels and tendons, the CPT manual directs the coder to report these procedures under the appropriate body system. For example, if a physician repairs a blood vessel in the heart, then the CPT manual directs the coder to go to the surgery section, cardiovascular subsection to find the correct code. The coder would not bill for this procedure in the integumentary system subsection. Simple ligation of vessels and simple exploration of nerves, blood vessels, or tendons is included in the wound repair procedure. Simple repair (closure) is bundled into the excision codes. If the physician excised a malignant lesion and performed a simple repair during the same operative session, the physician would only report the excision code. The simple repair is included in the excision procedure. Intermediate or complex repair is not included in the excision procedure and therefore may be billed separately. Use the following list of codes to answer the test questions. Page 10 of 18
11 Repair (Closure) 2007 CPT Codes 2007 CPT CODES DESCRIPTION SURGERY/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Repair-Simple Sum of lengths of repairs for each group of anatomic sites Simple repair of superficial wounds of scalp, neck, axillae, external genitalia, trunk and/or extremities (including hands and feet); 2.5 cm or less cm to 7.5 cm cm to 12.5 cm cm to 20.0 cm cm to 30.0 cm over 30.0 cm Simple repair of superficial wounds of face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips and/or mucous membranes; 2.5 cm or less cm to 5.0 cm cm to 7.5 cm cm to 12.5 cm cm to 20.0 cm cm to 30.0 cm over 30.0 cm Treatment of superficial wound dehiscence; simple closure with packing SURGERY/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Repair-Intermediate Sum of lengths of repairs for each group of anatomic sites Layer closure of wounds of scalp, axillae, trunk and/or extremities (excluding hands and feet); 2.5 cm or less cm to 7.5 cm cm to 12.5 cm cm to 20.0 cm cm to 30.0 cm over 30.0 cm Layer closure of wounds of neck, hands, feet and/or external genitalia; 2.5 cm or less cm to 7.5 cm cm to 12.5 cm cm to 20.0 cm cm to 30.0 cm over 30.0 cm Layer closure of wounds of face, ears, eyelids, nose, lips and/or mucous membranes; 2.5 cm or less cm to 5.0 cm cm to 7.5 cm Page 11 of 18
12 Repair (Closure) 2007 CPT Codes-continued 2007 CPT CODES DESCRIPTION SURGERY/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM cont. Repair-Intermediate cont. Sum of lengths of repairs for each group of anatomic sites cm to 12.5 cm cm to 20.0 cm cm to 30.0 cm over 30.0 cm SURGERY/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Repair-Complex Reconstructive procedures, complicated wound closure. Sum of lengths of repairs for each group of anatomic sites. (For full thickness repair of lip or eyelid, see respective anatomical subsections) Repair, complex, trunk; 1.1 cm to 2.5 cm (for 1.0 cm or less, see simple or intermediate repairs) cm to 7.5 cm each additional 5 cm or less (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use in conjunction with 13101) Repair, complex, scalp, arms, and/or legs; 1.1 cm to 2.5 cm (For 1.0 cm or less, see simple or intermediate repairs) cm to 7.5 cm Each additional 5 cm or less (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use in conjunction with 13121) Repair, complex, forehead, cheeks, chin, mouth, neck, axillae, genitalia, hands and/or feet; 1.1 cm to 2.5 cm (for 1.0 cm or less, see simple or intermediate repairs) cm to 7.5 cm each additional 5 cm or less (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use in conjunction with 13132) Repair, complex, eyelids, nose, ears and/or lips; 1.0 cm or less cm to 2.5 cm cm to 7.5 cm each additional 5 cm or less (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use in conjunction with 13152) Secondary closure of surgical wound or dehiscence, extensive or complicated (For packing or simple secondary wound closure, see 12020, 12021) Page 12 of 18
13 Excision--Debridement 2007 CPT Codes 2007 CPT CODES DESCRIPTION SURGERY/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Skin, Subcutaneous and Accessory Structures Debridement including removal of foreign material associated with open fracture(s) and/or dislocation(s); skin and subcutaneous tissues skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle fascia, and muscle skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle fascia, muscle and bone Debridement; skin, partial thickness skin, full thickness skin, and subcutaneous tissue skin, subcutaneous tissue, and muscle skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle and bone Page 13 of 18
14 References (National Library of Medicine pictures) American Medical Association Current Procedural Terminology Standard Edition. Chicago, IL., page (wound repair definitions) pg&imgrefurl= nid=j1wvlnpkt6mnom:&tbnh=115&tbnw=93&prev=/images%3fq%3dabrasion%2bpi cture&start=2&sa=x&oi=images&ct=image&cd=2 (abrasion picture) Page 14 of 18
15 TEST QUESTIONS A Guide to Wound Repair Coding Course # Directions: Before taking this test, read the instructions on how to correctly complete the answer sheet. Select the response that best completes each sentence or answers each question from the information presented in the module. If you are having great difficulty answering a question, go to and select CE/Renewals, then select CE Update to see if course content and/or a test question have been revised. Code ONLY the wound repair codes. Modifier 51 is the only modifier that will be utilized for this test. 1. A four-year-old patient came into the emergency department after she fell off a swing and scraped her arm. The physician examined the abrasion and documented that she required a 4.3 cm simple repair on her left arm. a b c d A 52-year-old male patient slipped on a wet floor in a local restaurant. The patient collided with a bus boy, landed on a dirty fork, and cut himself on a broken plate. The restaurant manager recommended that the fork stay where it was to prevent heavy bleeding. The puncture wound measured 2.8 cm on his index finger. The patient also had a 3.4 cm laceration on his index finger from the broken plate. The physician performed a 2.8 cm intermediate repair on the patient s index finger and a 3.4 cm simple repair of the laceration on his index finger. Normal debridement was performed. a , b , c d Page 15 of 18
16 3. The patient got his finger caught in the car door when his brother accidentally shut the door on him. Part of the patient s right middle finger was hanging to the side. The patient s mother rushed him to the hospital after wrapping his finger in a tee shirt to help stop the bleeding. Patient was very distressed and in pain. The surgeon performed an immediate 7.5 cm complex repair to the patient s right middle finger to reattach the finger. a b , c , d A police officer suffered a series of knife wounds to the chest while on duty. The physician performed a 2.6 cm intermediate repair, a 5.2 cm intermediate repair, a 3.7 cm complex repair and an 8.4 cm simple repair. a , , , b , , c ,12034,12004 d , , A 6-year-old girl fell on a nail while her father was repairing a shelf in the garage. The nail is stuck in her right hand with minimal bleeding. The patient had a tetanus shot about 18 months ago. The physician performed a 1.2 cm intermediate repair to heal the puncture wound and applied an adhesive strip to a small abrasion on her forearm. a b c RT, d A 55-year-old woman came into the Emergency Department at 7:52 am with several lacerations on her chest and scalp. She was standing on a chair in the kitchen trying to reach the jelly jar at the top of the storage cabinet. The jelly jar broke and several pieces of glass were embedded in her wounds. The doctor irrigated the wound to remove all the debris before performing an 8.5 cm complex repair on the side of her chest and a 2.5 cm complex repair on her scalp. a , b , 13102, c , d x 2 Page 16 of 18
17 7. A 25-year-old female patient was injured in a motor vehicle accident when she lost control of her car and ran into a tree. The physician performed a 3.7 cm complex repair to her upper lip, a 10.5 cm complex repair to her cheek and a 4.2 cm intermediate repair to her thigh. a , ,12031 b , , c , 13133, , d , , , A construction worker fell 1½ floors while building a house. He landed on a bed of nails, plywood and other debris. He had several lacerations to his arms, chest and face. The physician repaired a 5.9 cm complex repair to his chest, an 8.2 cm complex repair to his arm, a 4.9 cm intermediate repair to his cheek and a 2.5 cm intermediate repair to his lip. Because of the gross contamination of the wounds, the physician performed a prolonged cleansing using partial thickness debridement. a , 13101, , b , , 11041, c , 13122, , , d , , , A 28-year-old woman was plucking her eyebrows while at a stop light on the highway. A car going about 30 miles per hour hit her from behind. She suffered a 4.2 cm laceration to her forehead. The physician performed an intermediate repair. The physician is uncertain if the patient will sustain a scar so a referral was made to a plastic surgeon. a b c , d , A young boy was skateboarding down the long stone stairs at the Capital Building, and wounded himself when his board flipped to the side. The patient was going quite fast and suffered a serious abrasion to his nose and his arm. The physician performed a 7.6 cm complex repair to his nose and a 7.4 cm intermediate repair to his knee. a , b , 13153, c , d , 12046, Page 17 of 18
18 11. A 43-year-old woman was hurt at work while using a box cutter to open a package. Patient was ordered by her work to go to the Emergency Department to have her incision evaluated. The physician performed a 1.7 cm one-layer closure on her left hand. a b c d A 14-year-old male patient was dared by his friends to jump from his home s room to his neighbor s roof. He was knocked unconscious and received several lacerations and abrasions to his chest, face, head, and legs. He was rushed to the Emergency Department where he was evaluated by a physician. The physician performed a 9.5 cm complex repair to his scalp, a 7.5 cm complex repair on his chest, a 3.4 cm intermediate repair on his lip, an 8.4 cm intermediate repair on his left leg, and a 5.5 cm intermediate repair on his right leg. a , 13122, , , b , , , c , , , d , 13133, , , *End of Test* Page 18 of 18
2017 Physician Coding Survival Guide
 2017 Physician Coding Survival Guide Chapter 3: Dermatology Melanoma: Stop Melanoma Coding Errors Before They Spread If the dermatologist gets down to the fascia, would you still stick with an integumentary
2017 Physician Coding Survival Guide Chapter 3: Dermatology Melanoma: Stop Melanoma Coding Errors Before They Spread If the dermatologist gets down to the fascia, would you still stick with an integumentary
Chapter 11 Worksheet Code It
 Class: Date: Chapter 11 Worksheet 3 2 1 Code It True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Surgical destruction is considered part of the surgical procedure description. 2. Prepping
Class: Date: Chapter 11 Worksheet 3 2 1 Code It True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Surgical destruction is considered part of the surgical procedure description. 2. Prepping
Dynamic Tissue Systems. Reimbursement & Coding Guide
 Dynamic Tissue Systems Reimbursement & Coding Guide Dynamic Tissue Systems Reimbursement and Coding Guide The following information is shared for educational purposes only to help answer common coding
Dynamic Tissue Systems Reimbursement & Coding Guide Dynamic Tissue Systems Reimbursement and Coding Guide The following information is shared for educational purposes only to help answer common coding
Skin Deep. Agenda. Burns Wounds Debridement Evaluation and Management Services. Presented by: Mike Strong, SFM The Work Comp Experts.
 Presented by: Mike Strong, SFM The Work Comp Experts Agenda Wounds Debridement Evaluation and Management Services 2 1 Types of First Degree Second Degree Third Degree Rule of 9 Adults Infants Burn Coding
Presented by: Mike Strong, SFM The Work Comp Experts Agenda Wounds Debridement Evaluation and Management Services 2 1 Types of First Degree Second Degree Third Degree Rule of 9 Adults Infants Burn Coding
Breast debridement and closure cpt
 Breast debridement and closure cpt Close Breast debridement cpt code Medicare Billing Guidelines, Medicare payment and reimbursment, Medicare codes. Here is a list of CPT codes and Diagnoses that are.
Breast debridement and closure cpt Close Breast debridement cpt code Medicare Billing Guidelines, Medicare payment and reimbursment, Medicare codes. Here is a list of CPT codes and Diagnoses that are.
Appendix C Podiatriac Services
 Appendix C Podiatriac Services CPT/ HCPCS Codes Description Auth required Y or N Mod Service Limits Age Limits Notes 10021-10022 Fine Needle Aspiration w/ or w/o imaging guidance 10060-10061 10120-10121
Appendix C Podiatriac Services CPT/ HCPCS Codes Description Auth required Y or N Mod Service Limits Age Limits Notes 10021-10022 Fine Needle Aspiration w/ or w/o imaging guidance 10060-10061 10120-10121
Surgical Preparation Codes for Skin Replacement Surgery** Hospital Outpatient/Ambulatory Surgical Center Setting
 2018 National Medicare Reimbursement Rate Summary* for Integra Dermal Regeneration Template, & Office Settings Integra LifeSciences Corporation compiles this summary of Medicare payment rates to provide
2018 National Medicare Reimbursement Rate Summary* for Integra Dermal Regeneration Template, & Office Settings Integra LifeSciences Corporation compiles this summary of Medicare payment rates to provide
Wound Management in Urgent Care
 Wound Management in Urgent Care Brittany Busse Wound Management in Urgent Care Brittany Busse, MD Med 7 Urgent Care Folsom, CA, USA ISBN 978-3-319-27426-3 DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-27428-7 ISBN 978-3-319-27428-7
Wound Management in Urgent Care Brittany Busse Wound Management in Urgent Care Brittany Busse, MD Med 7 Urgent Care Folsom, CA, USA ISBN 978-3-319-27426-3 DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-27428-7 ISBN 978-3-319-27428-7
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents ANESTHESIA SECTION------------------------------------------------------------------------2 GENERAL INFORMATION
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents ANESTHESIA SECTION------------------------------------------------------------------------2 GENERAL INFORMATION
Coding for Wound Care
 Coding for Wound Care ****IMPORTANT*** Disclaimer ***Information provided is to the best of our knowledge and as current as possible. ***Please verify all policy and reimbursement information with your
Coding for Wound Care ****IMPORTANT*** Disclaimer ***Information provided is to the best of our knowledge and as current as possible. ***Please verify all policy and reimbursement information with your
Skin Anatomy and Physiology
 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
SAMPLE. Relative Values for Dentists Relative values based on survey data from Relative Value Studies, Inc. ICD-10
 www.optumcoding.com Relative Values for Dentists Relative values based on survey data from Relative Value Studies, Inc. 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products,
www.optumcoding.com Relative Values for Dentists Relative values based on survey data from Relative Value Studies, Inc. 2017 a ICD-10 A full suite of resources including the latest code set, mapping products,
Procedures in the ED. MCEP Straight Talk Most $$$ ED CPT Codes (not including E&M codes) EKGs X-rays Ultrasounds.
 Procedures in the ED Most $$$ ED CPT Codes (not including E&M codes) 93010 Electrocardiogram report 31500 Insert emergency airway 36556 Insert non-tunnel CV cath 92950 Heart/lung resuscitation CPR 12001
Procedures in the ED Most $$$ ED CPT Codes (not including E&M codes) 93010 Electrocardiogram report 31500 Insert emergency airway 36556 Insert non-tunnel CV cath 92950 Heart/lung resuscitation CPR 12001
Working Smarter. Coding For Orthopaedic Trauma; Receiving Correct Reimbursement for Complex Cases
 Coding For Orthopaedic Trauma; Receiving Correct Reimbursement for Complex Cases 1 Presenting the claims for appropriate payment Unless the documentation is clear Coders cannot properly code No basis of
Coding For Orthopaedic Trauma; Receiving Correct Reimbursement for Complex Cases 1 Presenting the claims for appropriate payment Unless the documentation is clear Coders cannot properly code No basis of
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-6 PGY-7 PGY-8
 PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
Telehealth Billing. April 19, 2018
 Telehealth Billing April 19, 2018 We want to offer telehealth in our office as an added service line to our patients. How do we indicate to the insurance company that the visit was a telehealth visit?
Telehealth Billing April 19, 2018 We want to offer telehealth in our office as an added service line to our patients. How do we indicate to the insurance company that the visit was a telehealth visit?
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Documentation Tips Job Aid
 Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2 GENERAL INFORMATION
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2 GENERAL INFORMATION
2013 MCT CPC-H Quiz #8 Chapters 13 and 14
 2013 MCT CPC-H Quiz #8 Chapters 13 and 14 Name: Date: Instructor: Score: 1. A female patient presents to the outpatient clinic for excision of a 4.8 cm malignant melanoma of the left inner thigh. A 6 cm
2013 MCT CPC-H Quiz #8 Chapters 13 and 14 Name: Date: Instructor: Score: 1. A female patient presents to the outpatient clinic for excision of a 4.8 cm malignant melanoma of the left inner thigh. A 6 cm
FM 3.0.MH.1 Medical Handbook
 FM 3.0.MH.1 Medical Handbook DISTRIBUTION RESTRICITON: Distribution authorized to 3 rd Battalion, 75th Ranger Regiment Senior Leadership and Instructors to protect operational information that is of use.
FM 3.0.MH.1 Medical Handbook DISTRIBUTION RESTRICITON: Distribution authorized to 3 rd Battalion, 75th Ranger Regiment Senior Leadership and Instructors to protect operational information that is of use.
Dermatology Procedure Coding
 Dermatology Procedure Coding Anatomy Two layers that make up human skin Epidermis most superficial layer Composed of four to five layers called stratum Anyone remember the mnemonic? Thickness varies based
Dermatology Procedure Coding Anatomy Two layers that make up human skin Epidermis most superficial layer Composed of four to five layers called stratum Anyone remember the mnemonic? Thickness varies based
Coding Wars: The Coding and Documentation Weapons to Win the Battle
 Coding Wars: The Coding and Documentation Weapons to Win the Battle Howard W. Rogers M.D., Ph.D. Advanced Dermatology Norwich, CT rogershoward@sbcglobal.net Conflict of Interest Statement I have no relevant
Coding Wars: The Coding and Documentation Weapons to Win the Battle Howard W. Rogers M.D., Ph.D. Advanced Dermatology Norwich, CT rogershoward@sbcglobal.net Conflict of Interest Statement I have no relevant
Property Latmedical, LLC.
 Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description)
 New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION... 3 GENERAL INFORMATION AND RULES... 3 SURGERY SERVICES... 8 GENERAL... 8 INTERGUMENTARY
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION... 3 GENERAL INFORMATION AND RULES... 3 SURGERY SERVICES... 8 GENERAL... 8 INTERGUMENTARY
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION... 3 GENERAL INFORMATION AND RULES... 3 SURGERY SERVICES... 9 GENERAL... 9 INTERGUMENTARY
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION... 3 GENERAL INFORMATION AND RULES... 3 SURGERY SERVICES... 9 GENERAL... 9 INTERGUMENTARY
CYGNUS REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE
 CYGNUS REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE The CYGNUS amnion patch is an immune-privileged tissue containing the natural regenerative factors responsible for creating a wound healing environment conducive to tissue regeneration.
CYGNUS REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE The CYGNUS amnion patch is an immune-privileged tissue containing the natural regenerative factors responsible for creating a wound healing environment conducive to tissue regeneration.
Surgery/Integumentary System ( )
 10030 The provider inserts a catheter through the skin using imaging to view the fluid. He then drains the fluid from the soft tissue in cases such as abscess, hematoma, seroma, lymphocele, or cyst. Imaging
10030 The provider inserts a catheter through the skin using imaging to view the fluid. He then drains the fluid from the soft tissue in cases such as abscess, hematoma, seroma, lymphocele, or cyst. Imaging
Primary Care Dermatology Coding. Webinar Subscription Access Expires December 31.
 Primary Care Dermatology Coding Questions Answers Webinar Subscription Access Expires December 31. How long can I access the on demand version? You will find that in the same instructions box you utilized
Primary Care Dermatology Coding Questions Answers Webinar Subscription Access Expires December 31. How long can I access the on demand version? You will find that in the same instructions box you utilized
Pinni Meedha Mojutho Ammanu Dengina Koduku Part 1 Kama Kathalu
 Search for: Search Search Cpt code for punch biopsy of skin Pinni Meedha Mojutho Ammanu Dengina Koduku Part 1 Kama Kathalu Code this! Answers: CPT curetting, and using a skin punch. Biopsy codes are arranged
Search for: Search Search Cpt code for punch biopsy of skin Pinni Meedha Mojutho Ammanu Dengina Koduku Part 1 Kama Kathalu Code this! Answers: CPT curetting, and using a skin punch. Biopsy codes are arranged
2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide
 2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide Chapter 8: General Surgery Integumentary Procedures: 4 Questions Focus Your Skin Substitute Graft Coding Hint: Graft size doesn t matter. If your surgeon treats
2017 Coding and Reimbursement Survival Guide Chapter 8: General Surgery Integumentary Procedures: 4 Questions Focus Your Skin Substitute Graft Coding Hint: Graft size doesn t matter. If your surgeon treats
QI. Read the following questions and choose the most correct answer (20 Marks):
 Question One: QI. Read the following questions and choose the most correct answer (20 Marks): 1- Some people are very allergic to some drugs like penicillin. This condition is called: a) Septic shock.
Question One: QI. Read the following questions and choose the most correct answer (20 Marks): 1- Some people are very allergic to some drugs like penicillin. This condition is called: a) Septic shock.
Complex Limb Injury. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Medical Coding Exam System - Week 1 Day 2 Practice Exam Questions 1-25
 1 Medical Coding Exam System - Week 1 Day 2 Practice Exam Questions 1-25 1. A man suffered a severe crushing injury to his left upper leg. Two days after surgery, the doctor completed a dressing change
1 Medical Coding Exam System - Week 1 Day 2 Practice Exam Questions 1-25 1. A man suffered a severe crushing injury to his left upper leg. Two days after surgery, the doctor completed a dressing change
Wound & Burn. Reimbursement & Coding Guide
 Wound & Burn Reimbursement & Coding Guide Wound & Burn Reimbursement and Coding Guide MicroMatrix and Cytal devices facilitate the remodeling of functional, site-appropriate tissue. Comprised of ACell
Wound & Burn Reimbursement & Coding Guide Wound & Burn Reimbursement and Coding Guide MicroMatrix and Cytal devices facilitate the remodeling of functional, site-appropriate tissue. Comprised of ACell
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY
 NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2 GENERAL INFORMATION
NEW YORK STATE MEDICAID PROGRAM PHYSICIAN PROCEDURE CODES SECTION 5 - SURGERY Table of Contents SURGERY SECTION -----------------------------------------------------------------------------2 GENERAL INFORMATION
First Responders to Orthopaedic Emergencies
 First Responders to Orthopaedic Emergencies Tom McPartland MD FABOS, FAAP Assistant Clinical Professor Rutgers-RWJMS October 17,2018 Goals Review Epidemiology of School Injuries Review Definitions of Different
First Responders to Orthopaedic Emergencies Tom McPartland MD FABOS, FAAP Assistant Clinical Professor Rutgers-RWJMS October 17,2018 Goals Review Epidemiology of School Injuries Review Definitions of Different
WPS Medicare Policy Primer
 WPS Medicare Policy Primer Medicare Jurisdiction (J5 & J8) NE, KS, IA, MO, IN, & MI Retired skin substitute LCD 3/2016 Indications Apligraf Non-infected partial and full-thickness skin ulcers due to VSU
WPS Medicare Policy Primer Medicare Jurisdiction (J5 & J8) NE, KS, IA, MO, IN, & MI Retired skin substitute LCD 3/2016 Indications Apligraf Non-infected partial and full-thickness skin ulcers due to VSU
Summary of Package Insert 1 for PuraPly Wound Matrix
 Summary of Package Insert 1 for PuraPly Wound Matrix For NGS Indications Indicated for the management of wounds including: Partial and full-thickness wounds Venous ulcers Diabetic ulcers Drainage wounds
Summary of Package Insert 1 for PuraPly Wound Matrix For NGS Indications Indicated for the management of wounds including: Partial and full-thickness wounds Venous ulcers Diabetic ulcers Drainage wounds
INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT
 INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT An injury is damage to the body caused by external forces, which may be physical or chemical. 1) Incisions 2) Types of wounds and their closure
INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT An injury is damage to the body caused by external forces, which may be physical or chemical. 1) Incisions 2) Types of wounds and their closure
Summary of Package Insert 1 for PuraPly Antimicrobial Wound Matrix
 Summary of Package Insert 1 for PuraPly Antimicrobial Wound Matrix For States with Non-Published Policies-Novitas Indications Indicated for the management of wounds as an effective barrier to resist microbial
Summary of Package Insert 1 for PuraPly Antimicrobial Wound Matrix For States with Non-Published Policies-Novitas Indications Indicated for the management of wounds as an effective barrier to resist microbial
First Aid in Agriculture
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
Appendix D: Authorization Guidelines for Dermatology Services
 Appendix D: Authorization Guidelines for Dermatology Services Revised June 2011 1 Appendix D: Authorization Guidelines for Dermatology Dermatologists are limited to the CPT codes referenced in this Section.
Appendix D: Authorization Guidelines for Dermatology Services Revised June 2011 1 Appendix D: Authorization Guidelines for Dermatology Dermatologists are limited to the CPT codes referenced in this Section.
Coding Hot Topics. Lawrence A. Santi, DPM, FASPS Member, APMA Coding Committee
 Coding Hot Topics Lawrence A. Santi, DPM, FASPS Member, APMA Coding Committee 1 Disclaimer Participants in the APMA Coding Webinar are reminded that CPT code descriptors and coding policies do not reflect
Coding Hot Topics Lawrence A. Santi, DPM, FASPS Member, APMA Coding Committee 1 Disclaimer Participants in the APMA Coding Webinar are reminded that CPT code descriptors and coding policies do not reflect
The ABCs of Coding Pediatric Clinic Procedures
 The ABCs of Coding Pediatric Clinic Procedures Facilitated by JoAnne M. Wolf, RHIT, CPC Objectives and Agenda To network with colleagues To understand the coding and required documentation of common ped
The ABCs of Coding Pediatric Clinic Procedures Facilitated by JoAnne M. Wolf, RHIT, CPC Objectives and Agenda To network with colleagues To understand the coding and required documentation of common ped
by Dr. Steve G. Jones Statbrook Associates
 Radiant Health by Dr. Steve G. Jones Radiant Health Hypnosis Script By Dr. Steve G. Jones And as you continue relaxing deeper and deeper and more deeply relaxed, I would like you to imagine your body to
Radiant Health by Dr. Steve G. Jones Radiant Health Hypnosis Script By Dr. Steve G. Jones And as you continue relaxing deeper and deeper and more deeply relaxed, I would like you to imagine your body to
APPLY FIRST AID ONLINE WORKBOOK
 APPLY FIRST AID ONLINE WORKBOOK STUDENT NAME: ADDRESS: PHONE CONTACT: DATE OF COURSE: Welcome to CYNERGEX GROUP pre-learning package for the APPLY FIRST AID course. This workbook is to be completed in
APPLY FIRST AID ONLINE WORKBOOK STUDENT NAME: ADDRESS: PHONE CONTACT: DATE OF COURSE: Welcome to CYNERGEX GROUP pre-learning package for the APPLY FIRST AID course. This workbook is to be completed in
NOTE TO CEU APPLICANT
 NOTE TO CEU APPLICANT In order to receive CEU credit for taking this exam, the following criteria must be met: You must be certified by AAPC prior to purchasing this textbook and prior to submitting this
NOTE TO CEU APPLICANT In order to receive CEU credit for taking this exam, the following criteria must be met: You must be certified by AAPC prior to purchasing this textbook and prior to submitting this
 55-year-old male with 2nd and 3rd degree burns to face, chest, and arms on 25% of the body Respirations: 34 Pulse: 120 Mental Status: moans to painful stimulus Mucous membranes charred Stridor 10 cm scalp
55-year-old male with 2nd and 3rd degree burns to face, chest, and arms on 25% of the body Respirations: 34 Pulse: 120 Mental Status: moans to painful stimulus Mucous membranes charred Stridor 10 cm scalp
External Cause Coding. Corrie Alvarez, CPC, CPMA, CEDC, CPC-I
 External Cause Coding Corrie Alvarez, CPC, CPMA, CEDC, CPC-I Agenda Quick Review of ICD-10 Injury Coding Guidelines for Coding External Causes Overview External Cause Coding Five Coding Scenarios Chapter
External Cause Coding Corrie Alvarez, CPC, CPMA, CEDC, CPC-I Agenda Quick Review of ICD-10 Injury Coding Guidelines for Coding External Causes Overview External Cause Coding Five Coding Scenarios Chapter
DermACELL AWM Comprehensive Reimbursement Resource Guide. Prepared by Musculoskeletal Clinical Regulatory Advisers, LLC. Version 01/2018.
 2018 Comprehensive Reimbursement Resource Guide Prepared by Musculoskeletal Clinical Regulatory Advisers, LLC. Version 01/2018. DermACELL AWM Disclaimer: This information is for educational/informational
2018 Comprehensive Reimbursement Resource Guide Prepared by Musculoskeletal Clinical Regulatory Advisers, LLC. Version 01/2018. DermACELL AWM Disclaimer: This information is for educational/informational
Minor Surgery. Using the Limbs & Things skin pads and jig. Skin Pad Jig Mk 3. Skin Pad Jig Strap. 44 Minor Surgery
 Using the Limbs & Things skin pads and jig The Skin Pad Jig can be used initially on a work surface for ease of learning, and can then be attached to the body of a fellow trainee to practise these skills,
Using the Limbs & Things skin pads and jig The Skin Pad Jig can be used initially on a work surface for ease of learning, and can then be attached to the body of a fellow trainee to practise these skills,
Anesthesia Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes
 Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2015 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Resequenced
Anesthesia Cross Coder Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-9-CM and HCPCS codes 2015 Contents Introduction... i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Crosswalk...i Format...i Icon Key...ii CPT Codes...ii Resequenced
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Key Words. clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma. Linked Core Abilities
 Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
CM01 Facelift. Copyright 2007 Page 1 of 6
 CM01 Facelift What is a facelift? A facelift is an operation to tighten and lift the soft tissues of your face and neck. Your surgeon will assess you and let you know if a facelift is suitable for you.
CM01 Facelift What is a facelift? A facelift is an operation to tighten and lift the soft tissues of your face and neck. Your surgeon will assess you and let you know if a facelift is suitable for you.
You Are the Emergency Medical Responder
 Lesson 32: Injuries to the Chest, Abdomen and Genitalia You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your police unit responds to a call in a part of town plagued by violence. When you arrive, you find the
Lesson 32: Injuries to the Chest, Abdomen and Genitalia You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your police unit responds to a call in a part of town plagued by violence. When you arrive, you find the
Ears. Mouth. Jowls 6 Major Bones of the Face Nasal bone Two
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
CROSS CODER. Sample page. Anesthesia. codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS. Essential links from CPT. Power up your coding optum360coding.
 CROSS CODER 2019 Anesthesia Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Introduction...i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Code Crosswalk... i Format...
CROSS CODER 2019 Anesthesia Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Introduction...i CPT Anesthesia to Procedure Code Crosswalk... i Format...
SKIN SERVICES REVIEW Changes to Medicare Benefits Schedule for 1 November 2016
 Attachment A SKIN SERVICES REVIEW Changes to Medicare Benefits Schedule for 1 November 2016 Deleted items 31200-31215, 31230-31240 31255-31335 Colour Coding for new / updated items: MUCOSAL BIOPSY AND
Attachment A SKIN SERVICES REVIEW Changes to Medicare Benefits Schedule for 1 November 2016 Deleted items 31200-31215, 31230-31240 31255-31335 Colour Coding for new / updated items: MUCOSAL BIOPSY AND
Management of Penetrating Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department
 Management of Penetrating Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department Ioannis E. Bitzos, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, New Jersey Medical School, University of Medicine and Dentistry
Management of Penetrating Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department Ioannis E. Bitzos, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, New Jersey Medical School, University of Medicine and Dentistry
Top Missed Coding Concepts
 Top Missed Coding Concepts Open vs Closed Fracture Care Open fracture care is reported when the provider creates an opening to expose the bone to treat a fracture. Not performed in the ED Patient is taken
Top Missed Coding Concepts Open vs Closed Fracture Care Open fracture care is reported when the provider creates an opening to expose the bone to treat a fracture. Not performed in the ED Patient is taken
2012 Head and Neck Reconstruction/ENT Repair Coding Observations
 Health Policy, Economics & Reimbursement Reimbursement Hotline Tel: 888.543.3656 Fax: 866.262.6977 reimbursement@lifecell.com www.lifecell.com 2012 Head and Neck Reconstruction/ENT Repair Coding Observations
Health Policy, Economics & Reimbursement Reimbursement Hotline Tel: 888.543.3656 Fax: 866.262.6977 reimbursement@lifecell.com www.lifecell.com 2012 Head and Neck Reconstruction/ENT Repair Coding Observations
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Integumentary System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Reconstructive and Cosmetic Services
 Reconstructive and Cosmetic Services Policy Number: 10.01.09 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 2/2006 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Determination of whether a proposed therapy would be considered reconstructive
Reconstructive and Cosmetic Services Policy Number: 10.01.09 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 2/2006 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Determination of whether a proposed therapy would be considered reconstructive
Core Strengthening After Lower Limb Amputation
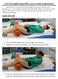 After the loss of a leg, the muscles in the middle of your body will become very important to you. You can think of strength in the core or the middle of your body as a stable platform which makes it easier
After the loss of a leg, the muscles in the middle of your body will become very important to you. You can think of strength in the core or the middle of your body as a stable platform which makes it easier
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department
 Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Coding Companion for Orthopaedics Lower: Hips & Below. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Orthopaedics Lower: Hips & Below comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2015 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin...1 Nails...12 Repair...21
Coding Companion for Orthopaedics Lower: Hips & Below comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2015 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin...1 Nails...12 Repair...21
Destruction or Excision: What's Happening in Your Dermatology Office?
 Questions Destruction or Excision: What's Happening in Your Dermatology Office? Answers Webinar Subscription Access Expires December 31. Doc excises a "pendunculated gluteal mass" with a fullthickness
Questions Destruction or Excision: What's Happening in Your Dermatology Office? Answers Webinar Subscription Access Expires December 31. Doc excises a "pendunculated gluteal mass" with a fullthickness
Surgery, integumentary system
 Surgery, integumentary system 1. James suffered a severe crushing injury to his left upper leg. Two days after surgery, Dr. Barnes completed a dressing change under general anesthesia. How would you report
Surgery, integumentary system 1. James suffered a severe crushing injury to his left upper leg. Two days after surgery, Dr. Barnes completed a dressing change under general anesthesia. How would you report
Shoulder Instability Latarjet Procedure
 Explanation of Procedure and/or Diagnosis Anatomy The shoulder is a ball and socket joint and is the most mobile joint of the body. Its plays a major role in positioning your arm and hand in space. Because
Explanation of Procedure and/or Diagnosis Anatomy The shoulder is a ball and socket joint and is the most mobile joint of the body. Its plays a major role in positioning your arm and hand in space. Because
Difficulty breathing Altered level of consciousness Amputated arm
 Difficulty breathing 22-year-old male, severe difficulty breathing, chest sinks in on inspiration, respirations over 30/min, radial pulse present, responds to instructions. Altered level of consciousness
Difficulty breathing 22-year-old male, severe difficulty breathing, chest sinks in on inspiration, respirations over 30/min, radial pulse present, responds to instructions. Altered level of consciousness
Review. A. abrasion B. contusion C. hematoma D. avulsion
 Chapter 24 Review Review 1. A young male was struck in the forearm with a baseball and complains of pain to the area. Slight swelling and ecchymosis are present, but no external bleeding. What type of
Chapter 24 Review Review 1. A young male was struck in the forearm with a baseball and complains of pain to the area. Slight swelling and ecchymosis are present, but no external bleeding. What type of
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Training. Module 12
 Evaluation and Management (E/M) Training Module 12 AMA Disclaimer CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related
Evaluation and Management (E/M) Training Module 12 AMA Disclaimer CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related
MRI masterfile Part 5 WM Heme Strokes.ppt 2
 Imaging of Orbital Trauma Corneal Abrasion CT scan is preferable to MRI Bone, Rapid, Easy to monitor patient Foreign bodies, air, hemorrhage Fractures Cost Needed for an MRI MRI Globe and intraocular injuries
Imaging of Orbital Trauma Corneal Abrasion CT scan is preferable to MRI Bone, Rapid, Easy to monitor patient Foreign bodies, air, hemorrhage Fractures Cost Needed for an MRI MRI Globe and intraocular injuries
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Miami J Collar. General Guidelines. How to Put On Your. Miami J Collar. Safe Exercises to Do While in The Collar.
 Miami J Collar General Guidelines How to Put On Your Miami J Collar Safe Exercises to Do While in The Collar www.neurosurgery.med.miami.edu General Guidelines Wear the Miami J Collar at all times. Do not
Miami J Collar General Guidelines How to Put On Your Miami J Collar Safe Exercises to Do While in The Collar www.neurosurgery.med.miami.edu General Guidelines Wear the Miami J Collar at all times. Do not
A Patient s Guide. ACL Injury: Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, Ø Preoperative and postoperative. surgery and recovery.
 ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
ACL Injury: A Patient s Guide Ø Frequently asked questions on injury, surgery and recovery Ø Preoperative and postoperative guidelines Mia S. Hagen, M.D. Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedics
Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture
 19 Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture S. Ghosh, P. Laing, and Nicola Maffulli Introduction Fascial turn-down flaps can be used for an anatomic repair of chronic Achilles tendon
19 Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture S. Ghosh, P. Laing, and Nicola Maffulli Introduction Fascial turn-down flaps can be used for an anatomic repair of chronic Achilles tendon
Eyelid Reconstruction An Oculoplastic Surgical Coding Minicourse. Riva Lee Asbell Philadelphia, PA. Part II
 INTRODUCTION Eyelid Reconstruction An Oculoplastic Surgical Coding Minicourse Riva Lee Asbell Philadelphia, PA Part II In this second part of the Minicourse on Surgical Coding for Eyelid Reconstruction
INTRODUCTION Eyelid Reconstruction An Oculoplastic Surgical Coding Minicourse Riva Lee Asbell Philadelphia, PA Part II In this second part of the Minicourse on Surgical Coding for Eyelid Reconstruction
NovoSorb BTM. A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold. Regenerating tissue. Changing lives.
 NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
NovoSorb BTM A unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold Regenerating tissue. Changing lives. Overview NovoSorb BTM is a unique synthetic biodegradable wound scaffold that delivers good cosmetic and
Schedule of Benefits for General Practitioners
 Schedule of Benefits for General Practitioners Aviva Health Insurance Ireland Limited SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS FOR GENERAL PRACTITIONERS FROM AVIVA HEALTH INSURANCE IRELAND LIMITED Welcome to Aviva s schedule
Schedule of Benefits for General Practitioners Aviva Health Insurance Ireland Limited SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS FOR GENERAL PRACTITIONERS FROM AVIVA HEALTH INSURANCE IRELAND LIMITED Welcome to Aviva s schedule
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE
 SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
SKIN INTEGRITY & WOUND CARE Chapter 34 1 skin integrity: intact skin refers to the presence of normal skin layer uninterrupted by wound 2 WOUNDS DISRUPTION IN THE INTEGRITY OF BODY TISSUE CLASSIFIED AS:
u A 14 year old female with no significant past medical history presents to the ED for evaluation of a finger laceration. While playing a card game
 Finger Lacerations u A 14 year old female with no significant past medical history presents to the ED for evaluation of a finger laceration. While playing a card game with her family, she lost her balance
Finger Lacerations u A 14 year old female with no significant past medical history presents to the ED for evaluation of a finger laceration. While playing a card game with her family, she lost her balance
The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patien
 The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
The Cryo/Cuff provides two functions: 1. Compression - to keep swelling down. 2. Ice Therapy - to keep swelling down and to help minimize pain. Patients, for the most part, experience less pain and/or
injury poisoning and certain other (s00-t98)
 1 of 13 1 injury poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes (s00-t98) ICD S T P10-P15 ( ) O70-O71 ( ) S T injuries to the head (s00-s09) injuries to the neck (s10-s19) injuries to the
1 of 13 1 injury poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes (s00-t98) ICD S T P10-P15 ( ) O70-O71 ( ) S T injuries to the head (s00-s09) injuries to the neck (s10-s19) injuries to the
HULC (ORTHOPEDICS/PLASTIC SURGERY)
 Rotation Specific Learning Objectives CCFP(EM) Residency Program Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry HULC (ORTHOPEDICS/PLASTIC SURGERY) To utilize the relevant competencies contained within the CanMEDS-FM
Rotation Specific Learning Objectives CCFP(EM) Residency Program Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry HULC (ORTHOPEDICS/PLASTIC SURGERY) To utilize the relevant competencies contained within the CanMEDS-FM
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
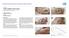 CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
Icd 10 dx code skin lesion of back
 Icd 10 dx code skin lesion of back The Borg System is 100 % Icd 10 dx code skin lesion of back ICD-10-CM Codes; ; L00-L99 Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue; ; L80-L99 Other disorders of the
Icd 10 dx code skin lesion of back The Borg System is 100 % Icd 10 dx code skin lesion of back ICD-10-CM Codes; ; L00-L99 Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue; ; L80-L99 Other disorders of the
2015 Procedure Billing Codes Update
 2015 Procedure Billing Codes Update COURSE DESCRIPTION Important Update! This learning activity consists of questions about new, deleted, and revised 2015 CPT procedure billing codes. The lists of new,
2015 Procedure Billing Codes Update COURSE DESCRIPTION Important Update! This learning activity consists of questions about new, deleted, and revised 2015 CPT procedure billing codes. The lists of new,
The etiology of the trauma was defined as the mechanism by which the traumatic event occurred and
 APPENDIX 2: Additional Methodological Details The etiology of the trauma was defined as the mechanism by which the traumatic event occurred and consisted of the following fifteen categories: motor vehicle
APPENDIX 2: Additional Methodological Details The etiology of the trauma was defined as the mechanism by which the traumatic event occurred and consisted of the following fifteen categories: motor vehicle
Sample page. OMS An essential coding, billing and reimbursement resource for oral and maxillofacial surgery CODING & PAYMENT GUIDE
 CODING & PAYMENT GUIDE 2019 OMS An essential coding, billing and reimbursement resource for oral and maxillofacial surgery Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Getting Started with Coding Guide...1
CODING & PAYMENT GUIDE 2019 OMS An essential coding, billing and reimbursement resource for oral and maxillofacial surgery Power up your coding optum360coding.com Contents Getting Started with Coding Guide...1
Coding Companion for Emergency Medicine. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Emergency Medicine A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin/Incision...1 Debridement...7 Excision...14
Coding Companion for Emergency Medicine A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2013 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Skin/Incision...1 Debridement...7 Excision...14
FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY
 FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY Austin Trauma and Critical Care Conference 2018 May 31-June 1, 2018 Outline 1. Scope
FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY Austin Trauma and Critical Care Conference 2018 May 31-June 1, 2018 Outline 1. Scope
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma. Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center
 Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
