Excision of painful dorsal wrist ganglion by open or arthroscopic approach : a compariso n study
|
|
|
- Dana Byrd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 83, ORIGINAL STUDY Excision of painful dorsal wrist ganglion by open or arthroscopic approach : a compariso n study Hyun l.l. Lee, Keun Ho Lee, Kyoung Hwan Koh, Hee Jae Won, Hyung Kwon Cho, Min Jong Park From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea Dorsal wrist ganglion can be removed through open or arthroscopic excision. The better method for relieving pain remains unknown. In this study, we addressed the following questions: (1) does open excision provide better pain relief than arthroscopic? (2) is there any difference in patient satisfaction, functional outcome, and re-operation rate? Forty-five patients with painful dorsal wrist ganglions underwent open or arthroscopic excision. Posterior interosseous neurectomy was performed during open excision. Clinical outcomes were assessed with a focus on pain relief. Patient satisfaction, recurrence, and reoperation due to residual pain were also assessed. The average pain scores improved significantly after both, open and arthroscopic excision. However, five patients who underwent arthroscopic excision reported the same or worse pain, whereas all patients who underwent open excision reported postoperative alleviation of pain. The recurrence rate was comparable. Patient satisfaction was better in those who underwent open excision. Reoperation was performed in four patients who had residual pain after arthroscopic excision. Both, open and arthroscopic methods can alleviate pain in patients with painful dorsal wrist ganglion. However, 20% of the patients who underwent arthroscopic excision reported residual or persistent pain. Keywords : ganglion, wrist, arthroscopy, posterior interosseous nerve Level of evidence : III INTRODUCTION Ganglion is a common cystic mass in the wrist. The dorsal wrist is the most prevalent location for the occurrence of wrist ganglion (17). This ganglion usually originates from the dorsal side of the scapholunate interosseous ligament (1). Most cases are asymptomatic; therefore, patients with dorsal wrist ganglion generally seek medical advice due to a cosmetic issue or concern about the possibility of a tumor (21). However, some patients may complain of wrist pain and discomfort that limits their daily activities. The cause of this pain has not been established. A mass effect on nearby n Hyun ll Lee 1, n Keun Ho Lee 2, n Kyoung Hwan Koh 1, n Hee Jae Won 3, n Hyung Kwon Cho 3, n Min Jong Park 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea 2 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, SungKyunKwan University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 3 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea Correspondence: Min Jong Park, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, SungKyunKwan University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea lhi76@icloud.com 2017, Acta Orthopædica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study. The authors report no conflict of interests. Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
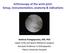
2 316 h.l.l. lee, k.h. lee, k.h. koh, h.j. won, h.k. cho, m.j. park structures or an inflammatory reaction to ganglion may be the cause. Compression or irritation of the terminal branch of the posterior interosseous nerve (PIN), located on the base of the fourth extensor compartment, has been identified as a potential source of pain (Figure 1) (6,11,15). Other concomitant pathologies of the wrist joint such as intercarpal ligament tears and subclinical instability of the scaphoid can also cause pain (14). to pain (1,4,10,12). In one prospective randomized study, a comparison of open and arthroscopic excision showed a similar rate of ganglion recurrence and residual pain after both procedures; however, the presence of preoperative pain and the intensity of residual pain were not considered (12). Although open excision is more invasive than the arthroscopic approach, this method can offer an additional advantage over the arthroscopic approach by removing the PIN terminal branch, which may be the source of the pain (20). The purposes of the present study were to assess the clinical outcome after surgical excision in patients with painful dorsal wrist ganglion and to determine whether there is a difference between open and arthroscopic excision in terms of pain relief. Unlike previous studies, we only included patients who had considerable dorsal wrist pain with ganglion. PATIENTS AND METHODS Fig. 1. Schematic illustrations of dorsal wrist ganglion and its association with neighboring posterior interosseous nerve. EPL: extensor policis longus, ECRB: extensor carpi radialis brevis, EIP: extensor indicis proprius, EDC II: extensor digiti communis of index finger Various treatment modalities have been proposed, including observation, needle aspiration, controlled rupture, and surgery (11). Nonsurgical methods can be considered initially in most instances. Surgery can be offered when patients have persistent pain, weakness, and limited function or when they desire removal of the ganglion for cosmesis. Open or arthroscopic excision is the current mainstay of surgical treatment with an acceptable recurrence rate. The open procedure, which does not require complex equipment, is regarded as the standard method. Arthroscopic excision has gained wide acceptance among hand surgeons as a minimally invasive procedure. Advantages include fewer scars, less postoperative pain, and faster recovery (2,8,10,12,13,18,19). Although many favorable outcomes regarding recurrence and symptom improvement have been reported for both surgical procedures, there are few reports comparing the clinical outcome with respect This was a retrospective, case-control, comparative study performed from 2005 to During this period, 107 adult patients with dorsal wrist ganglion underwent surgical excision by a single surgeon. The diagnosis of dorsal wrist ganglion was based on patients history and physical examination. Ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging was used in suspicious cases. Surgery was offered to select patients who wished to remove ganglion because of pain, weakness, and concern with its progressive increase in size, or a cosmetic issue. After reviewing the electronic medical records, 66 patients who had painful dorsal wrist ganglion were included in this study. Painful ganglion was defined as dorsally located ganglion eliciting dorsal wrist pain with a pain visual analog scale (pvas) score 3 points during daily activity or exercise. All the patients had tenderness over the ganglion or dorsal wrist pain at the terminal range of dorsiflexion. Patients were excluded if they had wrist pain in a location other than the dorsal wrist, such as the ulnar side or far radial side, that suggested other pathologies (n = 6); any bony abnormality or carpal instability on physical examination or radiological examination (n = 2); Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
3 excision of painful dorsal wrist ganglion 317 recurrence after previous surgery (n = 4); or obvious traumatic history to the wrist (n = 2). The remaining 52 patients underwent either open excision (n = 24) or arthroscopic excision (n = 28). The choice of surgical treatment was made through a shared decision-making process after discussing the risks and benefits of each procedure. Patient preference was the basis for selection in most instances. Seven patients were lost to follow-up. Finally, 45 patients (20 open procedures, follow-up rate 83%; 25 arthroscopic procedures, follow-up rate 89%) were enrolled in this study. The average follow-up duration was 32 months (range, months). The dominant arm was involved in 26 patients (58%). Each group had similar demographic characteristics (Table 1). Our institutional review board approved this study (IRB number ). Care was taken to protect the dorsal portion of the scapholunate interosseous ligament. A standard arthroscopic technique was used for arthroscopic excision. The 4-5 portal was first established as a visualization portal. The 3-4 portal was carefully created adjacent to the ganglion to avoid uncontrolled decompression of the cyst. We thoroughly examined the wrist joint to identify any intraarticular pathology. Then we localized the dorsal scapholunate ligament and traced it dorsally to the capsular reflection to visualize the stalk of the ganglion or intraarticular ganglion. A 2.9-mm shaver was introduced into the 3-4 portal to debride the ganglion with a portion of the dorsal capsule until the extensor tendon was exposed. Care was taken to avoid injuring the dorsal scapholunate ligament and extensor tendons. We routinely used Table I. Patients preoperative demographic data Variable Open group Arthroscopy group P-value Number of patients Age at surgery, years (range) 34.4 (18 60) 34.6 (19 56) Sex, number of males (%) 8 (40%) 10 (40%) Affected number of right wrists (%) 11 (55%) 15 (60%) Dominant arm operated, number (%) 10 (60%) 16 (64%) Ganglion size, cm (range) 1.5 ( ) 1.3 ( ) Symptom duration, months (range) 21.8 (3 60) 27.2 (4 60) Preoperative pain VAS (range) 4.8 (3 8) 4.8 (3 8) Follow-up duration, months (range) 31.9 (18 47) 30.4 (19 49) VAS, visual analog scale Patients had arm block with hemostatic control by pneumatic tourniquet. Open excision consisted of a transverse skin incision approximately 2 cm in length. Care was taken to avoid injuring the superficial vein and cutaneous nerve. We freed the cyst from the surrounding tissue and traced down the stalk to the capsular attachment at the scapholunate ligament. We identified the posterior interosseous nerve lying on the floor of the fourth extensor compartment adjacent to the stalk. The nerve was sufficiently exposed and transected at the most proximal point. The ganglion was excised with a portion of the capsule, leaving the joint open. the direct ganglion portal (i.e., the intrafocal portal) as a working portal to excise the remnant of cystic wall with the arthroscope in the 3-4 portal (3). Postoperatively, the wrist was immobilized in a compressive dressing and volar splint for 5 days. Thereafter, patients were allowed to mobilize the wrist and were advised to avoid strenuous work for approximately 4 weeks. Regular follow-up at the outpatient clinic was arranged at 3- or 6-month intervals. The clinical outcome was assessed by a trained observer (H.I.L.) not involved in the primary care of patients. Clinical data obtained at endpoint Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
4 318 h.l.l. lee, k.h. lee, k.h. koh, h.j. won, h.k. cho, m.j. park was used for comparison. Wrist pain during daily activity was assessed using the VAS from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst pain ever felt). The raw change in the pvas postoperatively was calculated by subtracting the baseline from the endpoint. The percent change was computed (raw change in the pvas baseline pvas 100). The change in pain postoperatively was also measured with the patient global impression change (PGIC) score. The PGIC is a one-item questionnaire that asks patients to describe the change in pain after surgery. Patients answered the PGIC using a 7-point scale as follows: (1) very much improved, (2) much improved, (3) minimally improved, (4) no change, (5) minimally worse, (6) much worse, or (7) very much worse. This scale is validated in a study of chronic neuropathic or non-neuropathic pain (9). A score of 1 and 2 ( very much and much improved, respectively) on the PGIC indicates a clinically important difference. Patient-rated wrist evaluation (PRWE) was used to measure self-reported pain and disability. The recurrence of ganglion was checked grossly. In suspicious cases with pain, sonography was performed to confirm occult ganglion. Subjective satisfaction of the results of surgery was measured with a numeric rating scale: 0, not satisfied and 10, entirely satisfied. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 14.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The paired t and Fisher exact tests were used to assess differences in the pre- and postoperative results of each group. The Student s t test, Mann- Whitney test, or Fisher exact test were used to assess differences between the open and arthroscopy groups. A P value <0.05 indicated significance. RESULTS The mean pvas improved significantly postoperatively in both groups (both, P < 0.001, Table 2). The average raw and percentage change in the pvas postoperatively was greater for open excision compared with arthroscopic excision. However, it did not reach a statistically significant level (P = and 0.229, respectively; Table 2). The average PGIC score was not significantly different between groups (Figure 2, Table 3). Evaluation of the PGIC demonstrated that no patients in the open group reported that their wrist pain was the same postoperatively compared with their preoperative pain (i.e., no change postoperatively), and only 5 (20%) in the arthroscopy group reported no change postoperatively (P = 0.056). Eighty five percent and 72% of patients in the open and arthroscopic groups, respectively, reported that their pain was much improved or very much improved (P = 0.473). No patients pain became worse postoperatively. Satisfaction VAS postoperatively was better in the open group (9.3 vs. 7.8, P = 0.042; Table 4). The mean postoperative PRWE score was similar between groups (Table 4). After a mean follow-up of 32 months, ganglion had grossly recurred in 3 patients (15%) who had open excision and in 4 (16%) who had arthroscopic excision. The average duration of recurrence postoperatively was 15.2 months (range, 5-30 months). No complications were noted after both surgeries. We did not observe any obvious intra-articular lesions during arthroscopic examination. Among 5 patients who had residual pain after arthroscopic excision, 4 underwent reoperation using the open method due to persistent pain. Among these patients, 2 had gross recurrence and another 2 showed an occult lesion, which was only detectable on ultrasonography. During reoperation, thick fibrous tissue and mucoid degeneration was found over the dorsal scapholunate ligament. The posterior interosseous nerve had been transected; however, it was not retracted and adhered to the scar tissue. In 1 patient, neuroma formed at the end of the proximal stump. We dissected the PIN and excised it at the most proximal end as much as possible. All patients who underwent reoperation achieved satisfactory pain relief. DISCUSSION Few studies have compared changes in preoperative pain after surgical removal of painful dorsal wrist ganglion. In this comparison study, we found the following: (1) pain was resolved postoperatively in both approaches, and (2) reoperation was performed in four patients who had residual pain after arthroscopic excision. Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
5 excision of painful dorsal wrist ganglion 319 Table II. Comparison of postoperative clinical outcomes regarding pain between the two groups * Open Arthroscopy P-value Postoperative pvas 0.8 (1.2) 1.9 (2.3) Raw change in pvas 4.1 (2.2) 2.9 (2.1) % change in pvas 81.0 (30.5) 65.2 (39.4) * Values are presented as mean (standard deviation). pvas, pain visual analog scale Table IV. Comparison of function, satisfaction, and recurrence between the two procedures Open Arthroscopy P-value PRWE 2.8 (3.7) 12.6 (17.9) Satisfaction NRS 9.3 (1.3) 7.8 (2.3) Reoperation (n) Gross recurrence (%) 3 (15%) 4 (16%) PRWE, patient-rated wrist evaluation. NRS, numeric rating scale Fig. 2. Number of patients according to the patient global impression change (PGIC) score. AS, arthroscopic Table III. Comparison of patient global impression change (PGIC) scores between the two procedures Open Arthroscopy P-value Average PGIC (mean 1.8 (0.7) 2.1 (1.1) [standard deviation]) Clinically meaningful improvement in PGIC (1 and 2) n (%) 17 (85%) 18 (72%) No change and worse PGIC n (%) 0 (0%) 5 (20%) We acknowledge several limitations in this study. First, our case series was retrospective, and selection bias likely influenced our analysis. Since the type of surgery was not randomized or blinded, there may be selection biases. Second, our study population was small. This is because we only included patients with sufficient pain that impaired daily activity. A properly powered prospective study might be beneficial. In the current study, a favorable improvement in pain was noted after both procedures. Numerous case series have reported favorable clinical results regarding pain, which were similar to our results. In one report on open excision with 103 patients, pain was initially reported by 78%, but this deceased to 28% at follow-up, although the intensity of pain was not described (7). In another series, pain relief was observed in 79% patient with radical open excision of 51 patients (4). Preoperatively, 87% of patients had pain and in 19%, this was of a sufficient severity to interfere with daily activities. Good relief of preoperative pain was also reported after arthroscopic excision of 38 patients with an initial pvas 3, only four reported that their pain was a 3-4 on the pvas at follow-up (10). Except for seven patients, 41 reported improvement in pain (19). A recent study reported that 24 of 78 wrists with preoperative pain had postoperative residual pain (13). However, the severity of residual pain was not described. In another report, among 37 patients, 35 with preoperative pain reported that their pain completely disappeared postoperatively (2). However, there was few report, which directly compared the post-operative pain between open and arthroscopic excision. Five patients who had arthroscopic excision reported the same or worse pain, whereas all patients who had open excision reported improvement in preoperative pain. The discrepancy between our results and other reports might partly originate from different patient selection. We specifically selected patients with only remarkable pain. Many patients with dorsal wrist ganglion do not experience pain in their wrist (2,16,21). Heterogeneous patient populations in previous reports failed to evaluate Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
6 320 h.l.l. lee, k.h. lee, k.h. koh, h.j. won, h.k. cho, m.j. park whether preoperative pain was properly relieved postoperatively. Moreover, the severity of pain was not mentioned in detail. Our results indicate that arthroscopic excision seems less effective in terms of pain relief. A possible reason for residual pain after arthroscopic excision may be that the extraarticular structures and PIN are inadequately addressed. It is noteworthy that there was no other intraarticular pathology during arthroscopic examination, which might be a cause of pain. Open excision is more amenable to extensive debridement of extracapsular pathology, including possible separated cyst, mucinous degeneration, or extensor tenosynovitis. PIN has been previously indicated as a possible source of wrist pain (6,11,15). There is a basic difference in performing PIN neurectomy between open and arthroscopic method: direct transection versus blind avulsion. In open excision, we dissected the nerve to a sufficient length followed by transection, allowing the proximal nerve stump to be retracted proximally. When we used arthroscopy, we routinely excised a portion of the dorsal wrist capsule. Because the PIN lies on the fourth compartment floor adjacent to the ganglion base, we assumed that the nerve could be ruptured during blinded debridement of the joint capsule, but it was consistently located in scar tissue, which might have caused the residual pain. Findings observed during revision open excision indicate that the avulsed nerve stump may become adhered to the fibrous scar instead of being retracted proximally. A previous report stated that an injured PIN during arthroscopy might be the cause of dorsal pain (5). Since we did not experience any newly developed wrist pain in patients who had not complained about pain preoperatively before arthroscopic excision, it seems that blind avulsion of the PIN itself was not a sole reason for residual pain. A local inflammatory environment, which is specific to patients with pain, might cause pain by irritating the avulsed PIN. Among patients who showed gross recurrence, no patients reported residual pain after open excision, and two of four patients complained of pain after arthroscopic excision, highlighting that recurrence does not necessarily induce pain. We presumed that PIN resection may contribute to pain relief despite recurrence after open excision, whereas no pain relief after arthroscopic excision may be attributed to the nerve stump adhering to the scarred capsule. According to the results of the current study, we recommend both treatment modalities as primary treatment for painful dorsal wrist ganglion. However, the open technique is potentially more valuable to surgeons seeking to ensure that the source of pain is completely addressed. The possibilities of residual pain should be discussed with patients who will undergo arthroscopic excision in advance. REFERENCES 1. Angelides AC, Wallace PF. The dorsal ganglion of the wrist: its pathogenesis, gross and microscopic anatomy, and surgical treatment. J Hand Surg Am ; 1 : Aslani H, Najafi A, Zaaferani Z. Prospective outcomes of arthroscopic treatment of dorsal wrist ganglia. Orthopedics ; 35 : e Chen AC-Y, Lee W-C, Hsu K-Y, Chan Y-S, Yuan L-J, Chang C-H. Arthroscopic ganglionectomy through an intrafocal cystic portal for wrist ganglia. Arthroscopy ; 26 : Clay NR, Clement DA. The treatment of dorsal wrist ganglia by radical excision. J Hand Surg Br ; 13 : del Pinal F, Herrero F, Cruz-Camara A, San Jose J. Complete avulsion of the distal posterior interosseous nerve during wrist arthroscopy: a possible cause of persistent pain after arthroscopy. J Hand Surg Am ; 24 : Dellon AL, Seif SS. Anatomic dissections relating the posterior interosseous nerve to the carpus, and the etiology of dorsal wrist ganglion pain. J Hand Surg Am ; 3 : Dias JJ, Dhukaram V, Kumar P. The natural history of untreated dorsal wrist ganglia and patient reported outcome 6 years after intervention. J Hand Surg Eur Vol ; 32 : Edwards SG, Johansen JA. Prospective outcomes and associations of wrist ganglion cysts resected arthroscopically. J Hand Surg Am ; 34 : Farrar JT, Young JP, Jr., LaMoreaux L, Werth JL, Poole RM. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain ; 94 : Gallego S, Mathoulin C. Arthroscopic resection of dorsal wrist ganglia: 114 cases with minimum follow-up of 2 years. Arthroscopy ; 26 : Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
7 excision of painful dorsal wrist ganglion Ho PC, Griffiths J, Lo WN, Yen CH, Hung LK. Current treatment of ganglion of the wrist. Hand Surg ; 6 : Kang L, Akelman E, Weiss AP. Arthroscopic versus open dorsal ganglion excision: a prospective, randomized comparison of rates of recurrence and of residual pain. J Hand Surg Am ; 33 : Kim JP, Seo JB, Park HG, Park YH. Arthroscopic excision of dorsal wrist ganglion: factors related to recurrence and postoperative residual pain. Arthroscopy ; 29 : Langner I, Krueger PC, Merk HR, Ekkernkamp A, Zach A. Ganglions of the wrist and associated triangular fibrocartilage lesions: a prospective study in arthroscopically-treated patients. J Hand Surg Am ; 37 : Loh YC, Stanley JK, Jari S, Trail IA. Neuroma of the distal posterior interosseous nerve. A cause of iatrogenic wrist pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br ; 80 : Mathoulin C, Hoyos A, Pelaez J. Arthroscopic resection of wrist ganglia. Hand Surg ; 9 : Nahra ME, Bucchieri JS. Ganglion cysts and other tumor related conditions of the hand and wrist. Hand Clin ; 20 : Osterman AL, Raphael J. Arthroscopic resection of dorsal ganglion of the wrist. Hand Clin ; 11 : Rizzo M, Berger RA, Steinmann SP, Bishop AT. Arthroscopic resection in the management of dorsal wrist ganglions: results with a minimum 2-year follow-up period. J Hand Surg Am ; 29 : Steinberg BD, Kleinman WB. Occult scapholunate ganglion: a cause of dorsal radial wrist pain. J Hand Surg Am ; 24 : Westbrook AP, Stephen AB, Oni J, Davis TR. Ganglia: the patient s perception. J Hand Surg Br ; 25 : Lee.indd /10/17 17:39
Arthroscopic resection of dorsal wrist ganglion
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Patel MR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Sep;2(3):127-131 http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162871
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Patel MR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Sep;2(3):127-131 http://www.ijoro.org Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20162871
A Patient's Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist
 Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Volar Wrist Ganglion: A Report of an Unusual Case. Eyad Alqasim, MD* Rashid Kameshki, MBBS** Maged Mostafa, MD***
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 3, September 2012 Volar Wrist Ganglion: A Report of an Unusual Case Eyad Alqasim, MD* Rashid Kameshki, MBBS** Maged Mostafa, MD*** A patient presented with wrist
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 34, No. 3, September 2012 Volar Wrist Ganglion: A Report of an Unusual Case Eyad Alqasim, MD* Rashid Kameshki, MBBS** Maged Mostafa, MD*** A patient presented with wrist
A new method in the management of wrist ganglion (Silk thread passed through the ganglion); in comparison with other traditional methods
 A new method in the management of wrist ganglion (Silk thread passed through the ganglion); in comparison with other traditional methods Abdulqadir M. Zangana (1) Kawa F. Dizaye (2) (1) Professor of Surgery,
A new method in the management of wrist ganglion (Silk thread passed through the ganglion); in comparison with other traditional methods Abdulqadir M. Zangana (1) Kawa F. Dizaye (2) (1) Professor of Surgery,
Endoscopic surgery has gained much popularity
 Sonography-Assisted Arthroscopic Resection of Volar Wrist Ganglia: A New Technique Michiro Yamamoto, M.D., Ph.D., Shigeru Kurimoto, M.D., Nobuyuki Okui, M.D., Ph.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Ph.D., Takaaki
Sonography-Assisted Arthroscopic Resection of Volar Wrist Ganglia: A New Technique Michiro Yamamoto, M.D., Ph.D., Shigeru Kurimoto, M.D., Nobuyuki Okui, M.D., Ph.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Ph.D., Takaaki
A Patient s Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist
 A Patient s Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Safety and Efficacy of Arthroscopic Volar Carpal Ganglion Excision: An Anatomic and Clinical Study
 DOJ Safety and Efficacy of Arthroscopic Volar Carpal Ganglion Excision: 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1046 An Anatomic and Clinical Study Retrospective review Safety and Efficacy of Arthroscopic Volar Carpal
DOJ Safety and Efficacy of Arthroscopic Volar Carpal Ganglion Excision: 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1046 An Anatomic and Clinical Study Retrospective review Safety and Efficacy of Arthroscopic Volar Carpal
Interesting Case Series. Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female
 Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
Interesting Case Series Radial Tunnel Syndrome Complicated by Lateral Epicondylitis in a Middle-Aged Female Sumesh Kaswan, MD, a Olivier Deigni, MD, MPH, a Kashyap K. Tadisina, BS, b Michael Totten, BS,
2013/10/18 GANGLION CYSTS ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY ARTHROSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OPEN GANGLIONECTOMY COMPARED TO FOOT AND ANKLE
 GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
Intratendinous Ganglion of the Extensor Digitorum Tendon
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2014;19(4):195-199 http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.4.195 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Intratendinous
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2014;19(4):195-199 http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2014.19.4.195 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Intratendinous
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Mini-open Muscle Resection Procedure under Local Anesthesia for Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:123-127 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.123 Mini-open Muscle Resection Procedure under Local Anesthesia for Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis Byung-Ki Cho,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:123-127 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.3.123 Mini-open Muscle Resection Procedure under Local Anesthesia for Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis Byung-Ki Cho,
Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure)
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 306-310 ORIGINAL STUDIES Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure) Bart VINGERHOEDS, Ilse DEGREEF, Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 306-310 ORIGINAL STUDIES Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure) Bart VINGERHOEDS, Ilse DEGREEF, Luc DE SMET From the University
Failed Extensor Indicis Proprius Tendon Transfer for Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture after Distal Radial Fracture
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
PROXIMAL AVULSION of RADIOCARPAL CAPSULE Parc Lesion: a new entity
 PROXIMAL AVULSION of RADIOCARPAL CAPSULE Parc Lesion: a new entity Ch. Mathoulin PARC LESION Parc lesion is a large capsular tear of the dorsal wrist capsule, from TFCC to DCSS, often neglected in wrist
PROXIMAL AVULSION of RADIOCARPAL CAPSULE Parc Lesion: a new entity Ch. Mathoulin PARC LESION Parc lesion is a large capsular tear of the dorsal wrist capsule, from TFCC to DCSS, often neglected in wrist
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings
 Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
SURGERY OF THE HAND INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT. Hee-June Kim 1, Hyun-Joo Lee 1, Dong-Hyun Kim 1, Joon-Woo Kim 1, Ji Won Oh 2
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2017;22(3):202-207. http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.3.202 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Extensor Pollicis
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2017;22(3):202-207. http://doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2017.22.3.202 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Extensor Pollicis
Interesting Case Series. Ulnolunate Impaction Syndrome
 Interesting Case Series Ulnolunate Impaction Syndrome Saptarshi Biswas, MD, FRCS Westchester University Medical Center, Valhalla, NY Keywords: ulnar impaction, ulnar impaction syndrome, ulnar wrist pain,
Interesting Case Series Ulnolunate Impaction Syndrome Saptarshi Biswas, MD, FRCS Westchester University Medical Center, Valhalla, NY Keywords: ulnar impaction, ulnar impaction syndrome, ulnar wrist pain,
Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 451-455 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach Eline A. VAN AMERONGEN, Arnold H. SCHUURMAN From the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 451-455 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach Eline A. VAN AMERONGEN, Arnold H. SCHUURMAN From the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Chapter 24. Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty. Introduction. Operative Technique. Patient Preparation and Positioning
 Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Case Report Solitary Bone Cyst of the Lunate: A Case Report MihirDesai* and Shivanand Bandekar Department of Orthopedics, Goa Medical College, Goa, India *Corresponding
Extensor Tendon Repair Zones II, III, IV
 Zones II, III, IV D. WATTS, MD Indications Lacerations to the central slip, lateral bends and/or triangular ligament Rupture of the central slip in association with a PIP joint volar dislocation Avulsion
Zones II, III, IV D. WATTS, MD Indications Lacerations to the central slip, lateral bends and/or triangular ligament Rupture of the central slip in association with a PIP joint volar dislocation Avulsion
Arhtroscopy of the wrist joint: Setup, instrumentation, anatomy & indications
 Arhtroscopy of the wrist joint: Setup, instrumentation, anatomy & indications Andreas Panagopoulos, MD, PhD Upper Limb and Sports Medicine Surgeon Assistant Professor in Orthopaedics Patras University
Arhtroscopy of the wrist joint: Setup, instrumentation, anatomy & indications Andreas Panagopoulos, MD, PhD Upper Limb and Sports Medicine Surgeon Assistant Professor in Orthopaedics Patras University
Chapter 19. Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion. Introduction. Operative Technique. Radiocarpal and Midcarpal Exploration
 Chapter 19 Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion Introduction Scaphoid fractures are often initially missed and then diagnosed only once nonunion manifests. Because the natural history of these
Chapter 19 Arthroscopic Bone Grafting for Scaphoid Nonunion Introduction Scaphoid fractures are often initially missed and then diagnosed only once nonunion manifests. Because the natural history of these
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Interesting Case Series. Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus
 Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Chapter 13. Arthroscopic Lunotriquetral Arthrodesis and Head of the Hamate Resection. Introduction. Operative Technique (Fontes) Midcarpal Exploration
 Chapter 13 Arthroscopic Lunotriquetral Arthrodesis and Head of the Hamate Resection Introduction Lunotriquetral arthrodesis is a controversial procedure but is sometimes proposed as a last resort for lunotriquetral
Chapter 13 Arthroscopic Lunotriquetral Arthrodesis and Head of the Hamate Resection Introduction Lunotriquetral arthrodesis is a controversial procedure but is sometimes proposed as a last resort for lunotriquetral
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity. Mark Tait MD
 Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Repair. The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the main stabilizers of the
 Michelle Brandt and Megan Passarelle Surgical Assignment Due: 11/9/14 Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Repair Abstract The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the main stabilizers of the
Michelle Brandt and Megan Passarelle Surgical Assignment Due: 11/9/14 Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Repair Abstract The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the main stabilizers of the
H.P. Teng, Y.J. Chou, L.C. Lin, and C.Y. Wong Under general or spinal anesthesia, the knee was flexed gently. In the cases of limited ROM, gentle and
 THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
Index. Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2016 J.N. Lawton (ed.), Distal Radius Fractures, DOI /
 Index A AAOS. See American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Abductor pollicis longus (APL) tendon, 34, 73 Acute carpal tunnel syndrome, 93 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), 66, 238
Index A AAOS. See American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Abductor pollicis longus (APL) tendon, 34, 73 Acute carpal tunnel syndrome, 93 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS), 66, 238
Seroma formation as a rare complication of lateral epicondylitis release: A case report
 Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine and Therapy Case Report ISSN 2573-1726 Seroma formation as a rare complication of lateral epicondylitis release: A case report Parth B Patel 1, Allison L Boden 2
Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine and Therapy Case Report ISSN 2573-1726 Seroma formation as a rare complication of lateral epicondylitis release: A case report Parth B Patel 1, Allison L Boden 2
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION?
 WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
Vascular Pedicle Pisiform Bone Grafting for Kienbocks Disease : A Case Report
 Case Report Vascular Pedicle Pisiform Bone Grafting for Kienbocks Disease : A Case Report Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Valya B 2, Vishnu Vardhan M 3 1 Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics Osmania Medical
Case Report Vascular Pedicle Pisiform Bone Grafting for Kienbocks Disease : A Case Report Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Valya B 2, Vishnu Vardhan M 3 1 Associate Professor Department of Orthopaedics Osmania Medical
Stress radiographs under anesthesia for painful chronic lateral ankle instability
 Stress radiographs under anesthesia for painful chronic lateral ankle instability Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea *W Institute
Stress radiographs under anesthesia for painful chronic lateral ankle instability Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea *W Institute
Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments. Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center
 Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center Outline Hand Anatomy and Function Workplace injuries & Case
Workplace Hand Injuries & Disorders: Evaluation and Treatments Hervey L. Kimball MD, MS Hand Surgical Associates Occupational Medicine Center Outline Hand Anatomy and Function Workplace injuries & Case
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
엄지의수근중수관절염에의한장무지신건의특발성파열 : 증례보고
 Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(2):93-98. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.2.93 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 엄지의수근중수관절염에의한장무지신건의특발성파열 : 증례보고 이상기ㆍ김수민ㆍ최원식
Archives of Hand and Microsurgery Arch Hand Microsurg 2018;23(2):93-98. https://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.2018.23.2.93 pissn 2586-3290 eissn 2586-3533 Case Report 엄지의수근중수관절염에의한장무지신건의특발성파열 : 증례보고 이상기ㆍ김수민ㆍ최원식
PATIENTS, METHODS AND RESULTS
 WRIST GANGLION Pages with reference to book, From 123 To 124 Ijaz Ahmad ( Department of Surgery, King Edward Medical College, Lahore. ) Ganglia account for about two third of all hand tumours 1. They occur
WRIST GANGLION Pages with reference to book, From 123 To 124 Ijaz Ahmad ( Department of Surgery, King Edward Medical College, Lahore. ) Ganglia account for about two third of all hand tumours 1. They occur
Wrist Arthroscopy. Outline. This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 Wrist Arthroscopy Background: Why Do Wrist Arthroscopy? Ramesh C. Srinivasan Hand & Upper Extremity Surgeon Director of Research The Hand Center of San Antonio Associate Master Instructor, AANA Wrist and
Wrist Arthroscopy Background: Why Do Wrist Arthroscopy? Ramesh C. Srinivasan Hand & Upper Extremity Surgeon Director of Research The Hand Center of San Antonio Associate Master Instructor, AANA Wrist and
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Radiographic observation of the scaphoid shift test
 Radiographic observation of the scaphoid shift test Min Jong Park From Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea T he movements of the carpal bones during the scaphoid shift test were evaluated
Radiographic observation of the scaphoid shift test Min Jong Park From Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea T he movements of the carpal bones during the scaphoid shift test were evaluated
Fracture and Dislocation of the Carpus ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Early Arthroscopic Management of Heterotopic Ossification of the Elbow
 25 Early Arthroscopic Management of Heterotopic Ossification of the Elbow Felix H. Savoie III, MD; Michael J. O Brien, MD; and Matthew Wert Introduction The formation of heterotopic ossification (HO) about
25 Early Arthroscopic Management of Heterotopic Ossification of the Elbow Felix H. Savoie III, MD; Michael J. O Brien, MD; and Matthew Wert Introduction The formation of heterotopic ossification (HO) about
Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
 60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Origin of Satellite Ganglion Cysts with Effusion in the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Sheath around the Hallux
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:94-98 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.94 Origin of Satellite Ganglion Cysts with Effusion in the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Sheath around
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:94-98 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.1.94 Origin of Satellite Ganglion Cysts with Effusion in the Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendon Sheath around
Long-term Outcomes of Arthroscopic Debridement and Thermal Shrinkage for Isolated Partial Intercarpal Ligament Tears
 n Feature Article Long-term Outcomes of Arthroscopic Debridement and Thermal Shrinkage for Isolated Partial Intercarpal Ligament Tears Jung Il Lee, MD; Kyung Wook Nha, MD, PhD; Guen Young Lee, MD; Baek
n Feature Article Long-term Outcomes of Arthroscopic Debridement and Thermal Shrinkage for Isolated Partial Intercarpal Ligament Tears Jung Il Lee, MD; Kyung Wook Nha, MD, PhD; Guen Young Lee, MD; Baek
Index. orthopedic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Acute Wrist Injuries OUCH!
 Acute Wrist Injuries OUCH! Case the athlete FOOSH from sporting event 2 days ago C/O wrist swelling, pain, worse with movement Hmmm Wrist pain Exam of the wrist - basics Appearance Swelling, bruising,
Acute Wrist Injuries OUCH! Case the athlete FOOSH from sporting event 2 days ago C/O wrist swelling, pain, worse with movement Hmmm Wrist pain Exam of the wrist - basics Appearance Swelling, bruising,
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Modified anconeus muscle transfer as treatment of failed surgical release of lateral epicondylitis of the elbow
 310 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, t. luyckx, 83, 310-314 a. decramer, l. luyckx, j. noyez ORIGINAL STUDY Modified anconeus muscle transfer as treatment of failed surgical release of lateral epicondylitis of
310 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, t. luyckx, 83, 310-314 a. decramer, l. luyckx, j. noyez ORIGINAL STUDY Modified anconeus muscle transfer as treatment of failed surgical release of lateral epicondylitis of
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW?
 ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW? Christian Veillette M.D., M.Sc., FRCSC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Shoulder & Elbow Reconstructive Surgery Toronto Western Hospital @ University Health
ELBOW ARTHROSCOPY WHERE ARE WE NOW? Christian Veillette M.D., M.Sc., FRCSC Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Shoulder & Elbow Reconstructive Surgery Toronto Western Hospital @ University Health
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article. College, Hospital & Research Institute, Budhera, Gurgaon , Haryana, India
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(4D):1366-1370 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(4D):1366-1370 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Lateral Elbow Pathology
 Lateral Elbow Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of adiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal adiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE, Philips
Lateral Elbow Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of adiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal adiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE, Philips
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First Carpometacarpal Arthritis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:372-376 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.372 Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:372-376 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.372 Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First
Chapter 12 Distal Ulnar Resection
 Chapter 12 Distal Ulnar Resection Introduction Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common but often unrecognized cause of pain on the ulnar side of the wrist. Although it can be congenital (due to a long ulna),
Chapter 12 Distal Ulnar Resection Introduction Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common but often unrecognized cause of pain on the ulnar side of the wrist. Although it can be congenital (due to a long ulna),
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial Radial Nerve and Cephalic Vein Ki Hoon Kim, MD, Eun Jin Byun, MD, Eun Hyun Oh, MD
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(1):52-56 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.52 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(1):52-56 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.52 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial
Clinical Workshop and Symposium on Chronic Wrist Pain Management
 Clinical Workshop and Symposium on Chronic Wrist Pain Management Date: 1 st November 2011 Venue: Kai Chong Tong, PEC Moderator: CH Yen Clinical Approach to Ulnar Wrist Pain: 08:15 08:30 Registration 08:30
Clinical Workshop and Symposium on Chronic Wrist Pain Management Date: 1 st November 2011 Venue: Kai Chong Tong, PEC Moderator: CH Yen Clinical Approach to Ulnar Wrist Pain: 08:15 08:30 Registration 08:30
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE. The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus.
 TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE Introduction The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus. It is also known as the triquetral bone, (and in the past the pyramidal or triangular bone) Triquetrum
TRIQUETRUM FRACTURE Introduction The triquetrum bone is one of the small bones that make up the carpus. It is also known as the triquetral bone, (and in the past the pyramidal or triangular bone) Triquetrum
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
Identification of Double Compression Lesion of Ulnar Nerve after Cubital Tunnel Release
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):148-152. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.148 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Identification
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):148-152. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.148 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Identification
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
Proximal row carpectomy : a motion-preserving procedure in the treatment of advanced Kienbock s disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 530-534 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : a motion-preserving procedure in the treatment of advanced Kienbock s disease Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mahmoud EL-HADIDI, Esam EL-KAREF
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 530-534 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : a motion-preserving procedure in the treatment of advanced Kienbock s disease Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mahmoud EL-HADIDI, Esam EL-KAREF
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE RADIAL TUNNEL BY CADAVERIC DISSECTION, FOR POSSIBLE SITES OF THE POSTERIOR INTEROSSEOUS NERVE ENTRAPMENT
 Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Bhavana Sunil Junagade and Aruna Mukherjee, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved ANATOMICAL STUDY
Int. J. Pharm. Med. & Bio. Sc. 2014 Bhavana Sunil Junagade and Aruna Mukherjee, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2278 5221 www.ijpmbs.com Vol. 3, No. 2, April 2014 2014 IJPMBS. All Rights Reserved ANATOMICAL STUDY
Chapter 7. Anatomy of the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex: Current Concepts. Introduction. Anatomy. Histology
 Chapter 7 Anatomy of the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex: Current Concepts Introduction The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the intrinsic ligaments of the wrist. It is often injured
Chapter 7 Anatomy of the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex: Current Concepts Introduction The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is one of the intrinsic ligaments of the wrist. It is often injured
Vascularized pedicle dorsal distal radius graft in management of scaphoid nonunion Osama M Essawy MD, Mohamed S Singer MD, Ahmed Shawkat Rizk MD
 Vascularized pedicle dorsal distal radius graft in management of scaphoid nonunion Osama M Essawy MD, Mohamed S Singer MD, Ahmed Shawkat Rizk MD Orthopaedic Department, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University,
Vascularized pedicle dorsal distal radius graft in management of scaphoid nonunion Osama M Essawy MD, Mohamed S Singer MD, Ahmed Shawkat Rizk MD Orthopaedic Department, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University,
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
What Treatment Works, What Does Not, When Is ENOUGH Enough?
 What Treatment Works, What Does Not, When Is ENOUGH Enough? Hand And Elbow Injuries Dori Cage, M.D. Goals of Talk Provide cases to stimulate discussion Present an approach when considering further surgery
What Treatment Works, What Does Not, When Is ENOUGH Enough? Hand And Elbow Injuries Dori Cage, M.D. Goals of Talk Provide cases to stimulate discussion Present an approach when considering further surgery
Disclosures. Distal Radius Fractures 5/16/2017. Distal Radius Fractures: Complications & Limitations of the Volar Approach
 Distal Radius Fractures: Complications & Limitations of the Volar Approach Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures
Distal Radius Fractures: Complications & Limitations of the Volar Approach Frank R. Avilucea, MD Assistant Professor Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Medical Center Disclosures
VOLAR PERILUNATE CARPAL FRACTURE DISLOCATION: A CASE REPORT OF UNCOMMON INJURY PATTERN
 Basrah Journal Case Report Of Surgery VOLAR PERILUNATE CARPAL FRACTURE DISLOCATION: A CASE REPORT OF UNCOMMON INJURY PATTERN Mohammed A Akrawi * & Avadis A Muradian @ * MB,ChB, FDSOT, Senior Consultant
Basrah Journal Case Report Of Surgery VOLAR PERILUNATE CARPAL FRACTURE DISLOCATION: A CASE REPORT OF UNCOMMON INJURY PATTERN Mohammed A Akrawi * & Avadis A Muradian @ * MB,ChB, FDSOT, Senior Consultant
AJO needle, and compartment pressures were measured
 An Original Study Extensor Pollicis Longus Ruptures in Distal Radius Fractures: Clinical and Cadaveric Studies With a New Therapeutic Intervention Gary M. Lourie, MD, Andrew Putman, MD, Taylor Cates, MD,
An Original Study Extensor Pollicis Longus Ruptures in Distal Radius Fractures: Clinical and Cadaveric Studies With a New Therapeutic Intervention Gary M. Lourie, MD, Andrew Putman, MD, Taylor Cates, MD,
Mayo Clinic Disorders of the Wrist
 Mayo Clinic Disorders of the Wrist Thursday, May 19, 2016 Pre-Conference Laboratory Workshop Anatomy of the Wrist & Wrist Arthroscopy 6:30 a.m. Registration and Breakfast 7:30 a.m. Welcome and Introduction
Mayo Clinic Disorders of the Wrist Thursday, May 19, 2016 Pre-Conference Laboratory Workshop Anatomy of the Wrist & Wrist Arthroscopy 6:30 a.m. Registration and Breakfast 7:30 a.m. Welcome and Introduction
Title. Author(s)Iwasaki, Norimasa; Minami, Akio. CitationThe Journal of Hand Surgery, 34(7): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title Arthroscopically Assisted Reattachment of Avulsed Tr Author(s)Iwasaki, Norimasa; Minami, Akio CitationThe Journal of Hand Surgery, 34(7): 1323-1326 Issue Date 2009-09 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39285
Title Arthroscopically Assisted Reattachment of Avulsed Tr Author(s)Iwasaki, Norimasa; Minami, Akio CitationThe Journal of Hand Surgery, 34(7): 1323-1326 Issue Date 2009-09 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/39285
A Patient s Guide to Mucous Cysts of the Fingers
 A Patient s Guide to Mucous Cysts of the Fingers Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can better
A Patient s Guide to Mucous Cysts of the Fingers Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can better
Anatomic Landmarks for the Radial Tunnel
 Anatomic Landmarks for the Radial Tunnel Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Arian Mowlavi, MD, Michael Neumeister, MD, W.P. Andrew Lee, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Anatomic Landmarks for the Radial Tunnel Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Arian Mowlavi, MD, Michael Neumeister, MD, W.P. Andrew Lee, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
